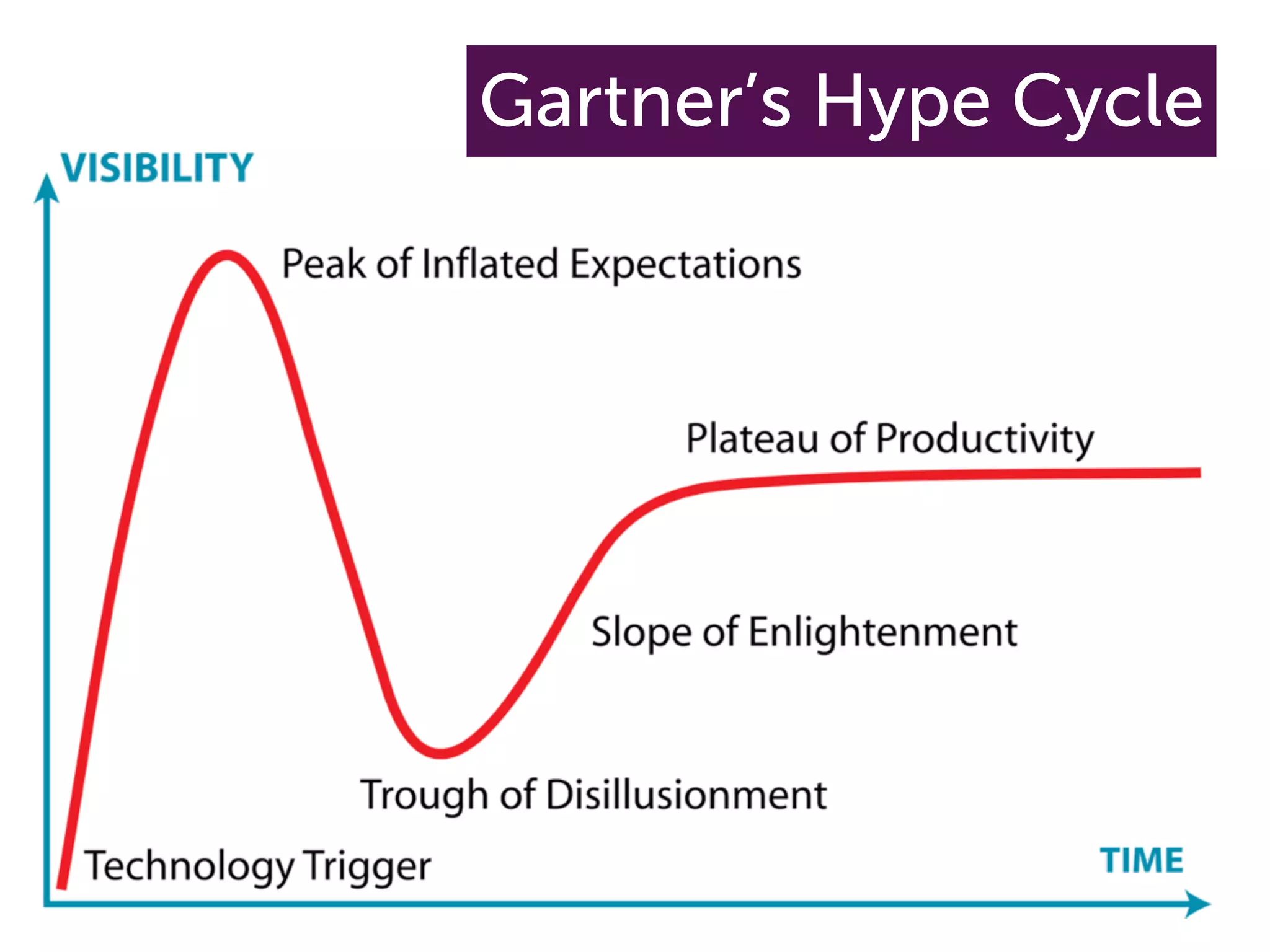
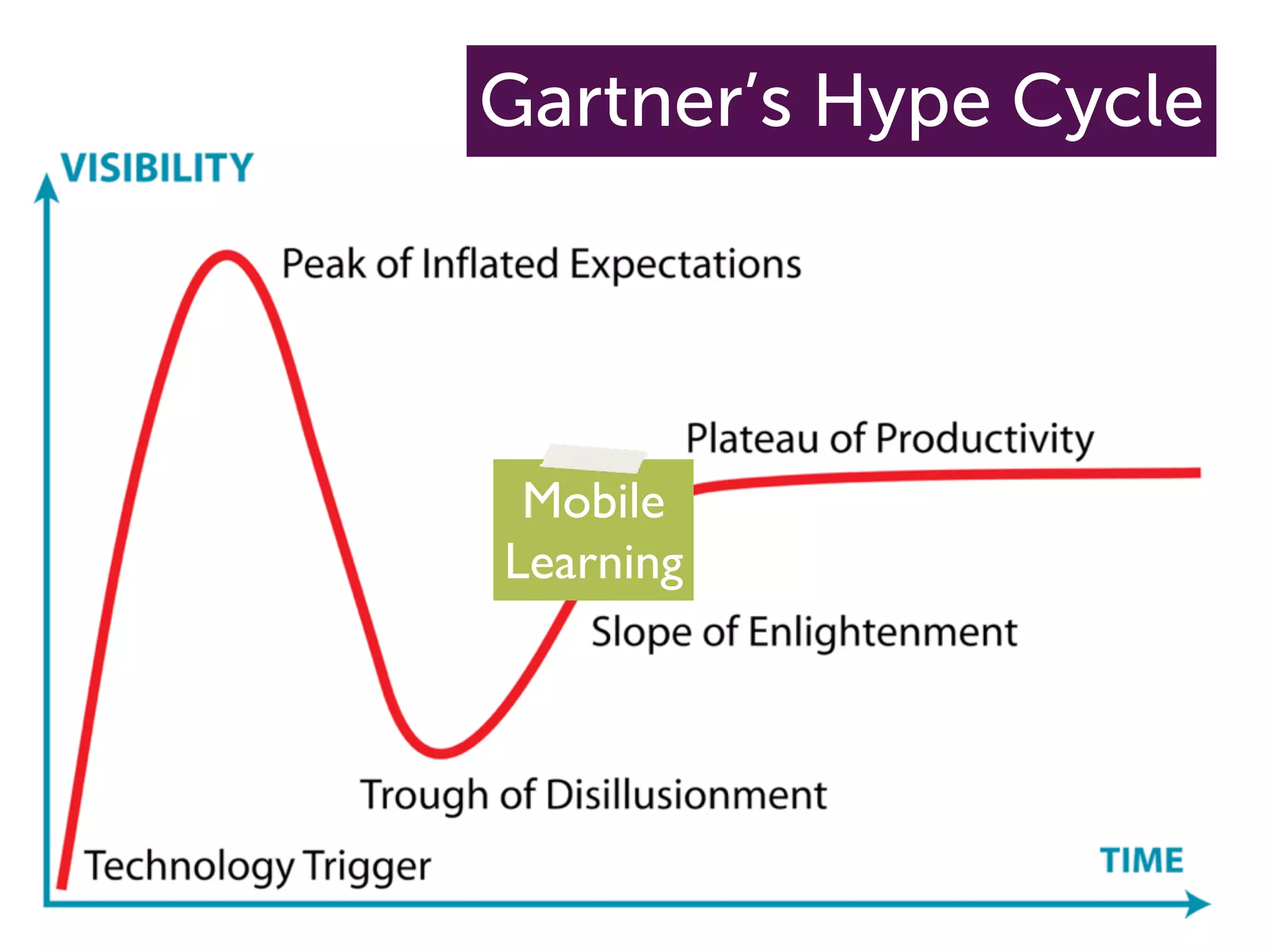
The document discusses the challenges and opportunities of mobile learning, highlighting the expectations of young learners who have grown up with technology. It emphasizes the importance of integrating mobile technology into educational practices to enhance learning experiences and accessibility. Additionally, it addresses common myths surrounding mobile learning, underscoring the need for educational institutions to adapt and innovate in a digital age.









![What is “Early definitions of [mobile learning],
MOBILE
learning? which focused predominantly on the
attributes of mobile technology, have
given way to more sophisticated
conceptualisations suggesting that
mobility is the central issue...
This denotes not just physical mobility
but the opportunity to overcome
physical constraints by having access to
people and digital learning resources,
regardless of place and time.”
KUKULSKA-HULME (2010)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mobilelearninginfokitoverviewforslideshare-110905082211-phpapp02/75/Mobile-Learning-infoKit-12-2048.jpg)

















