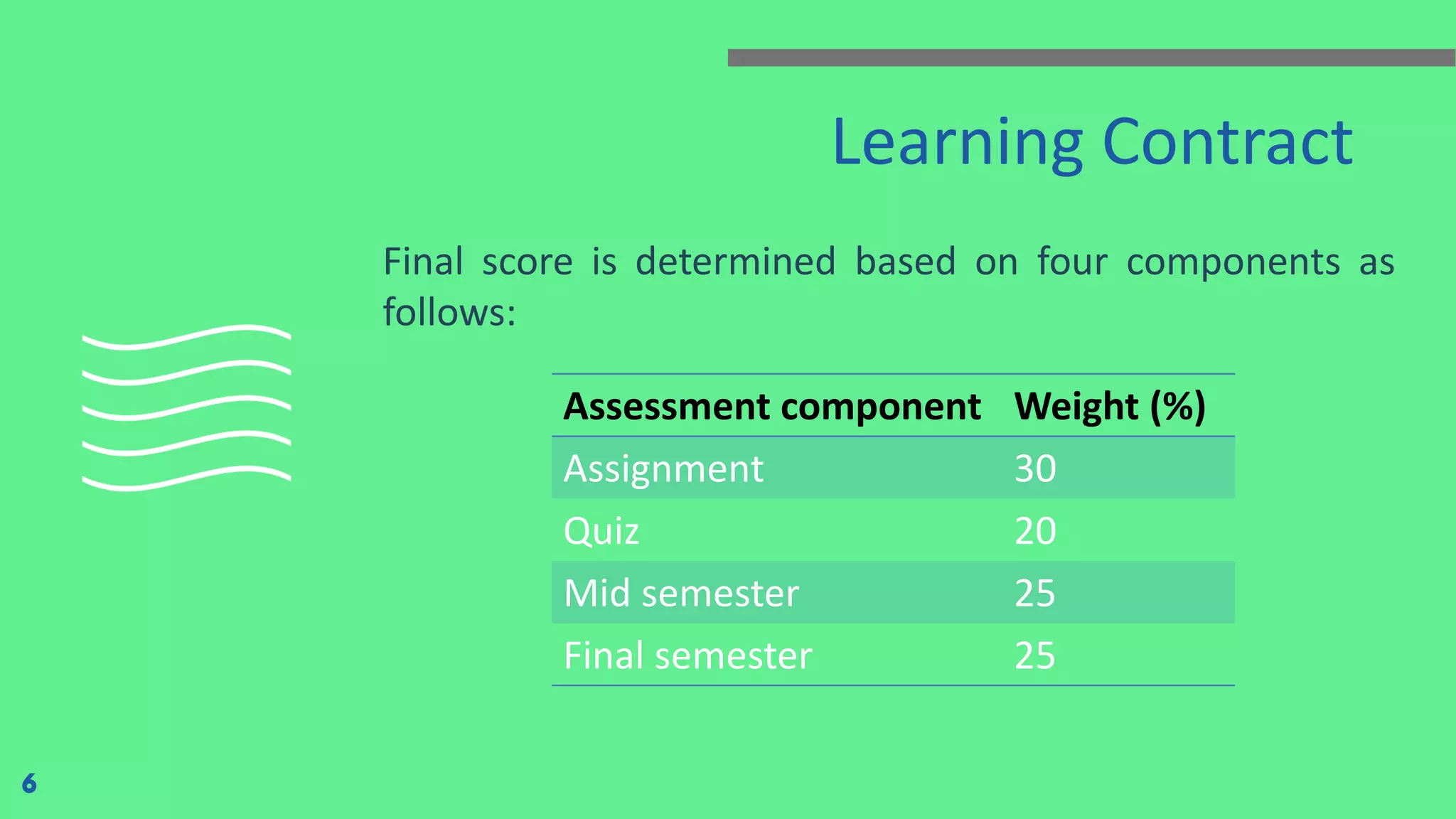
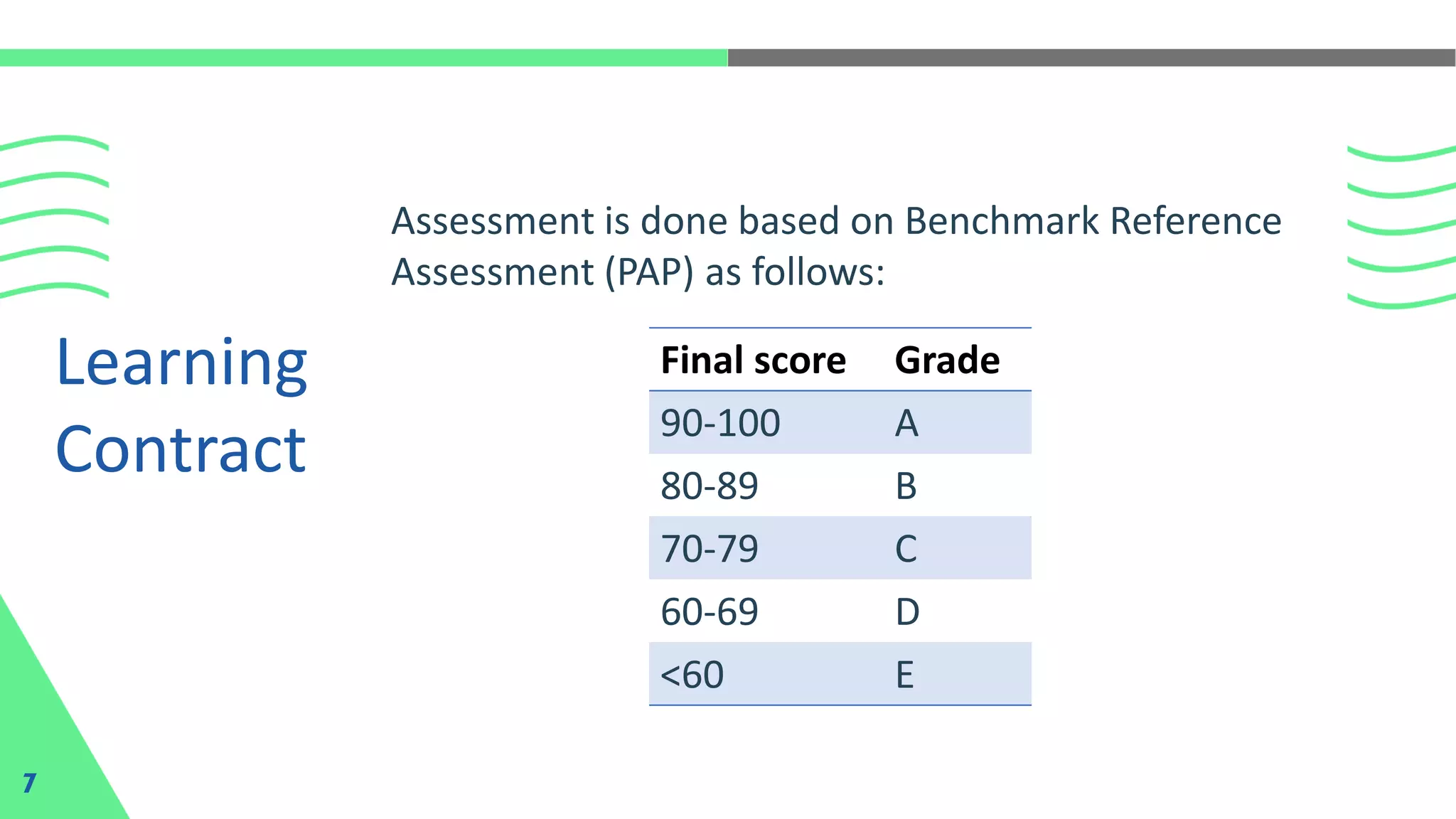
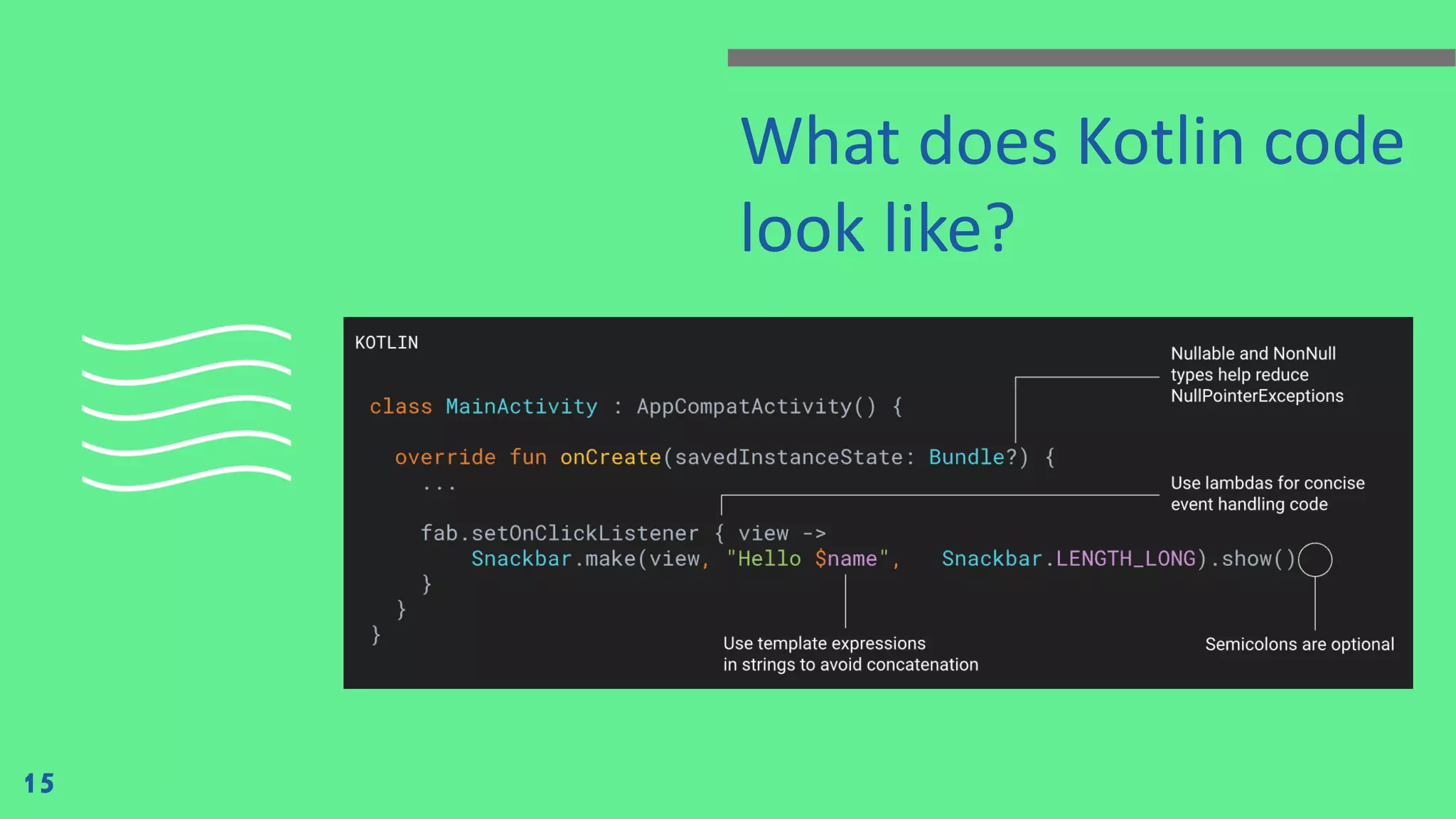
The document outlines the development of mobile-based information systems using Kotlin and Jetpack Compose, focusing on visualizing Firebase data to solve business processes. It details the components of the learning contract, including assessment criteria and penalties for tardiness or assignment delays. Additionally, it highlights Kotlin's advantages for Android development, including its interoperability with Java, code safety, and community support.