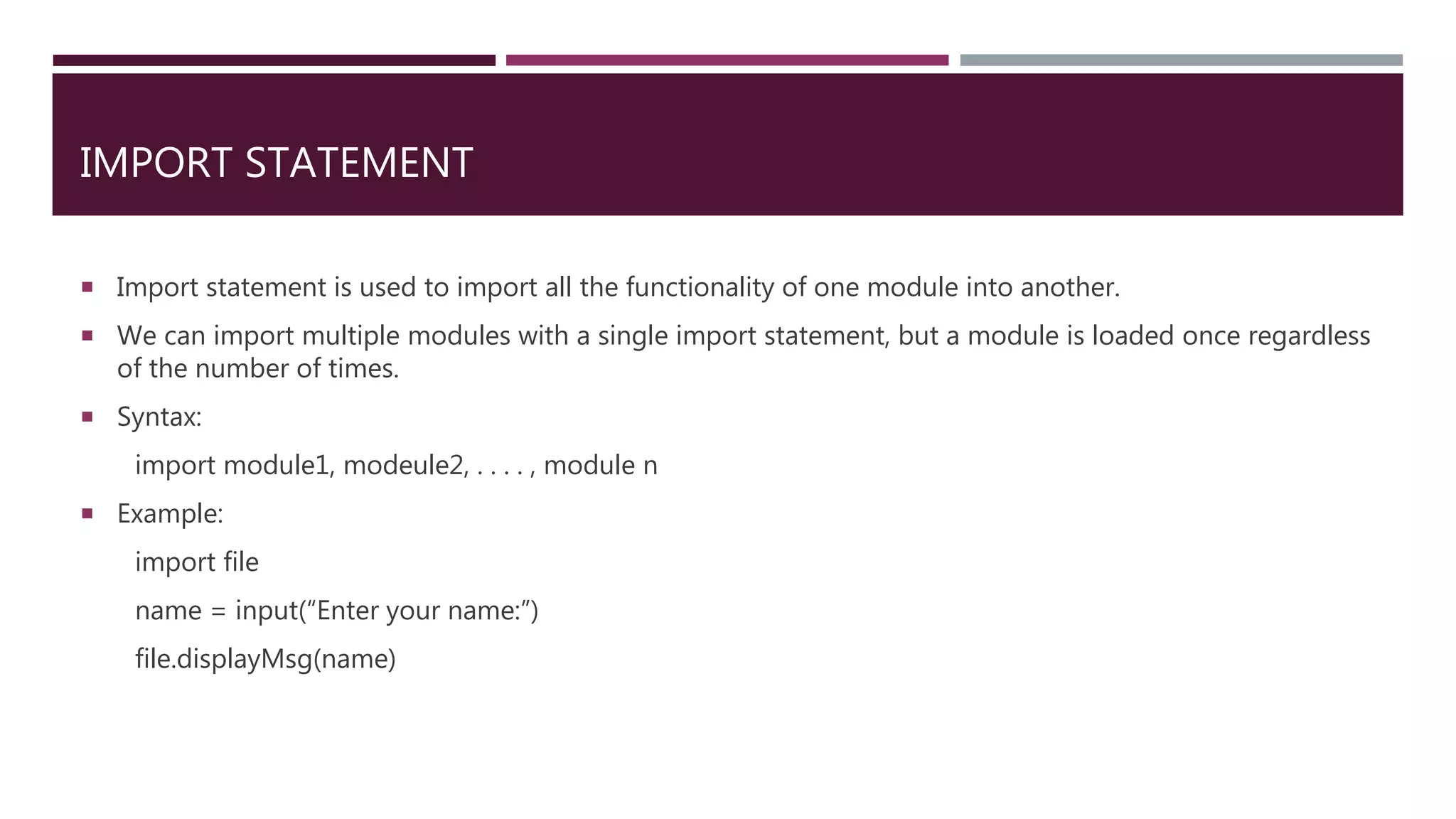
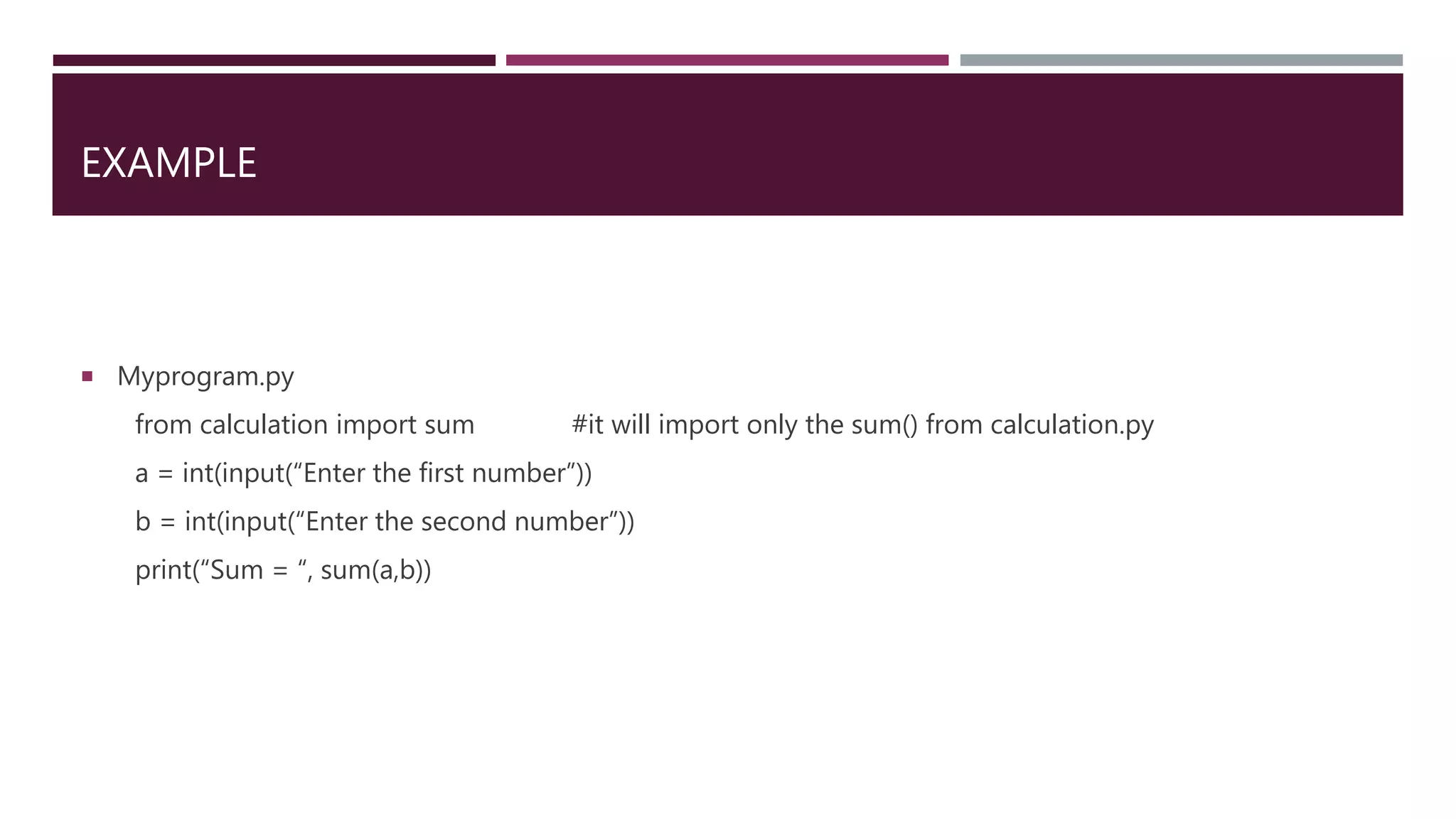
The document explains Python modules, which are program files that encapsulate functions, classes, or variables, enabling logical code organization. It describes how to import modules using import and from-import statements and how to use the import as feature to rename modules. Additionally, it covers the dir() and reload() functions for managing modules and introduces Python packages for organizing code in a hierarchical structure.




![IMPORT AS STATEMENT [RENAMING A MODULE]
Python provides us the flexibility to import some module with a specific name so that we can use this
name to use that module in python source file.
Syntax:
import <module-name> as <specific-name>
Example:
import calculation as cal;
a = int(input(“Enter first number”))
b = int(input(“Enter second number”))
print(“Sum = “, cal.sum(a,b))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5modulesinpython-210827063229/75/Modules-in-Python-Programming-7-2048.jpg)



