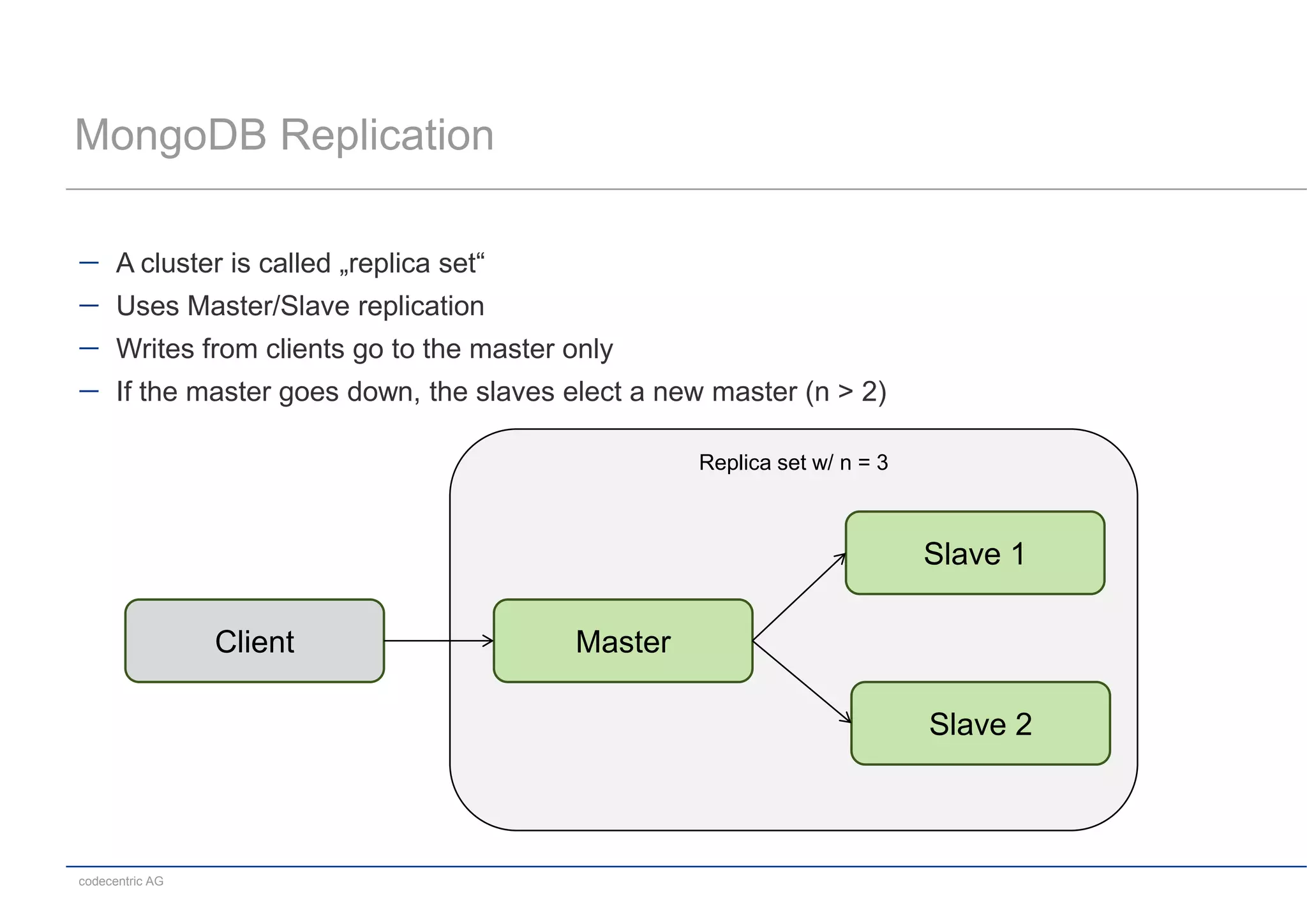
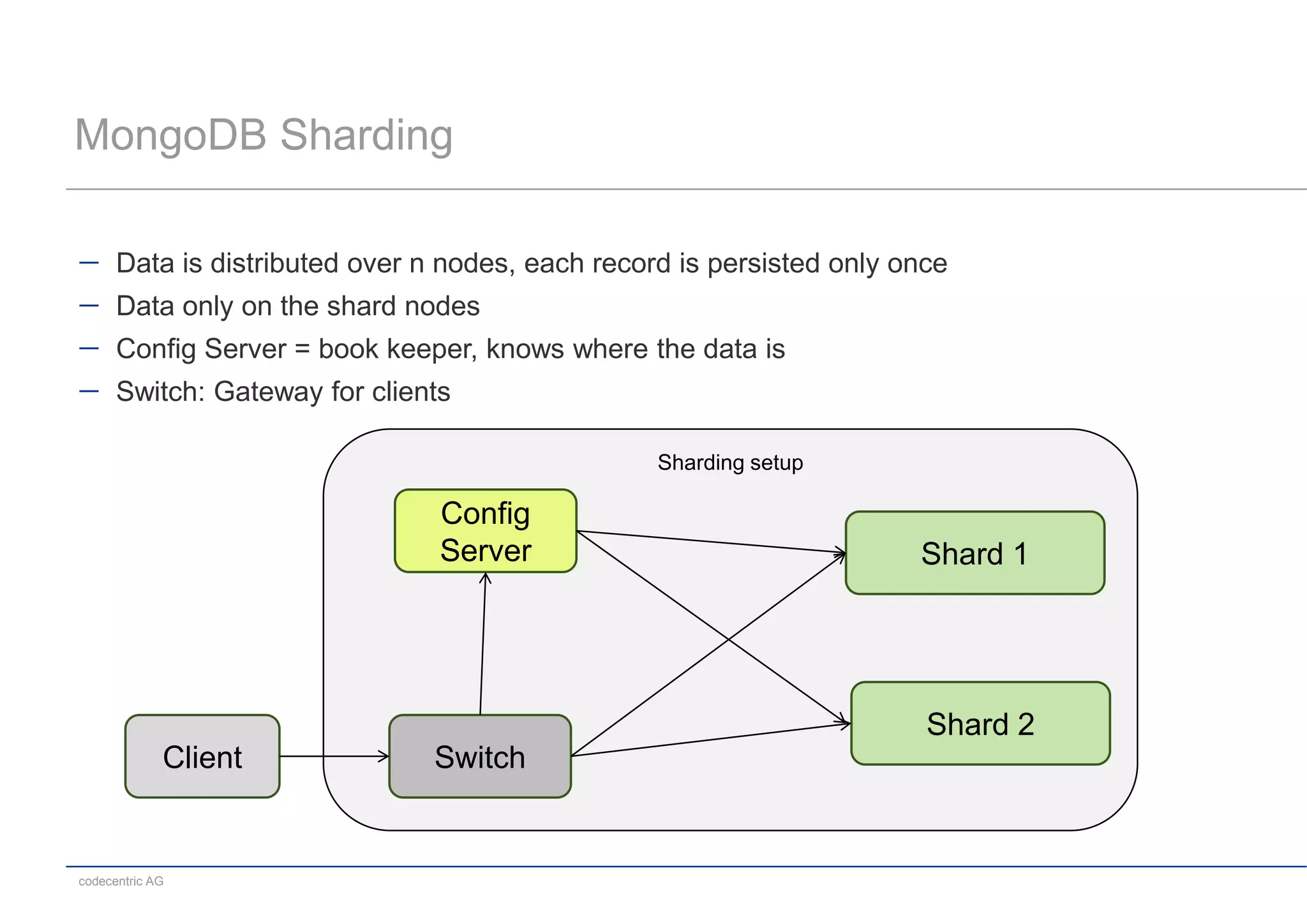
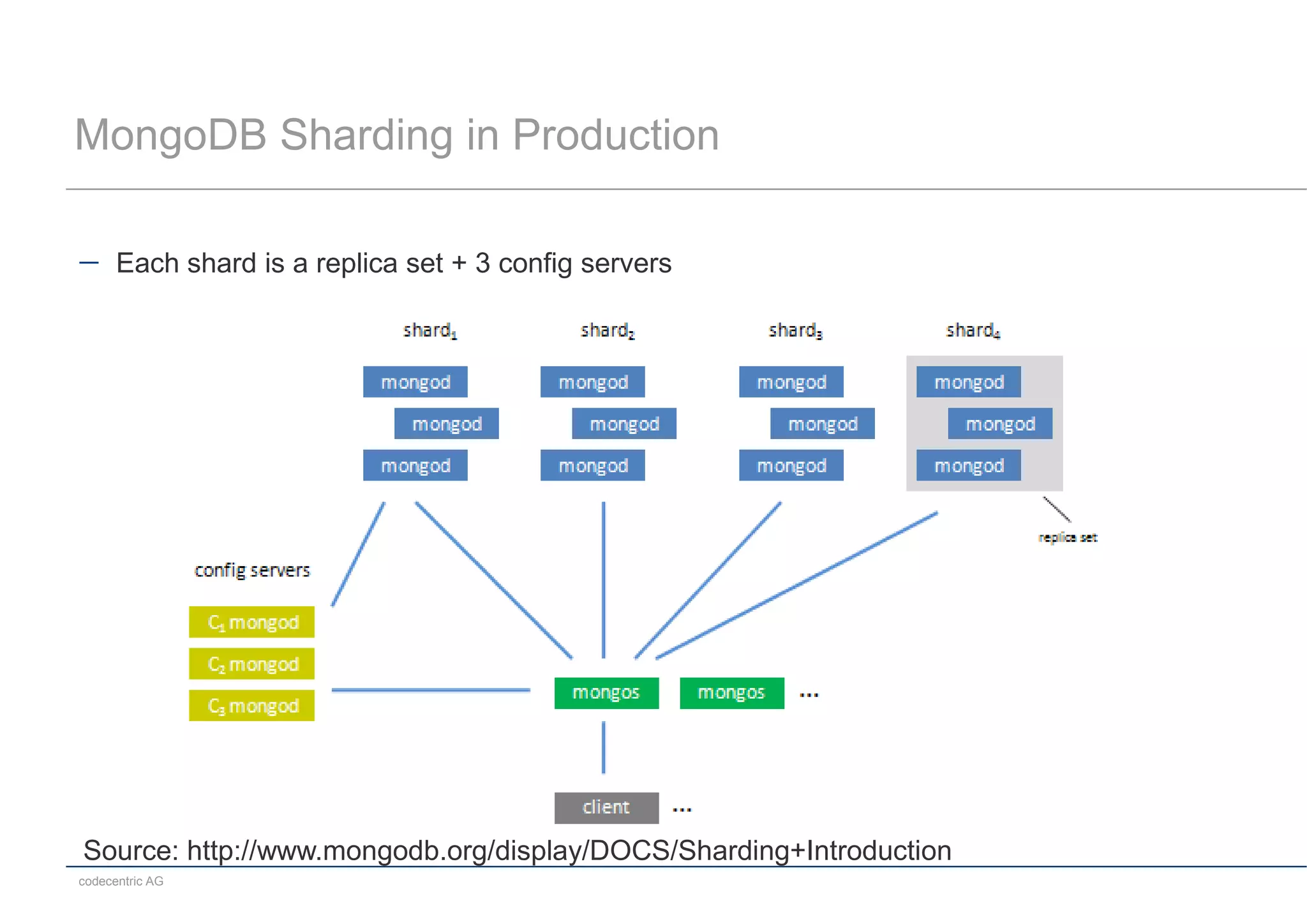
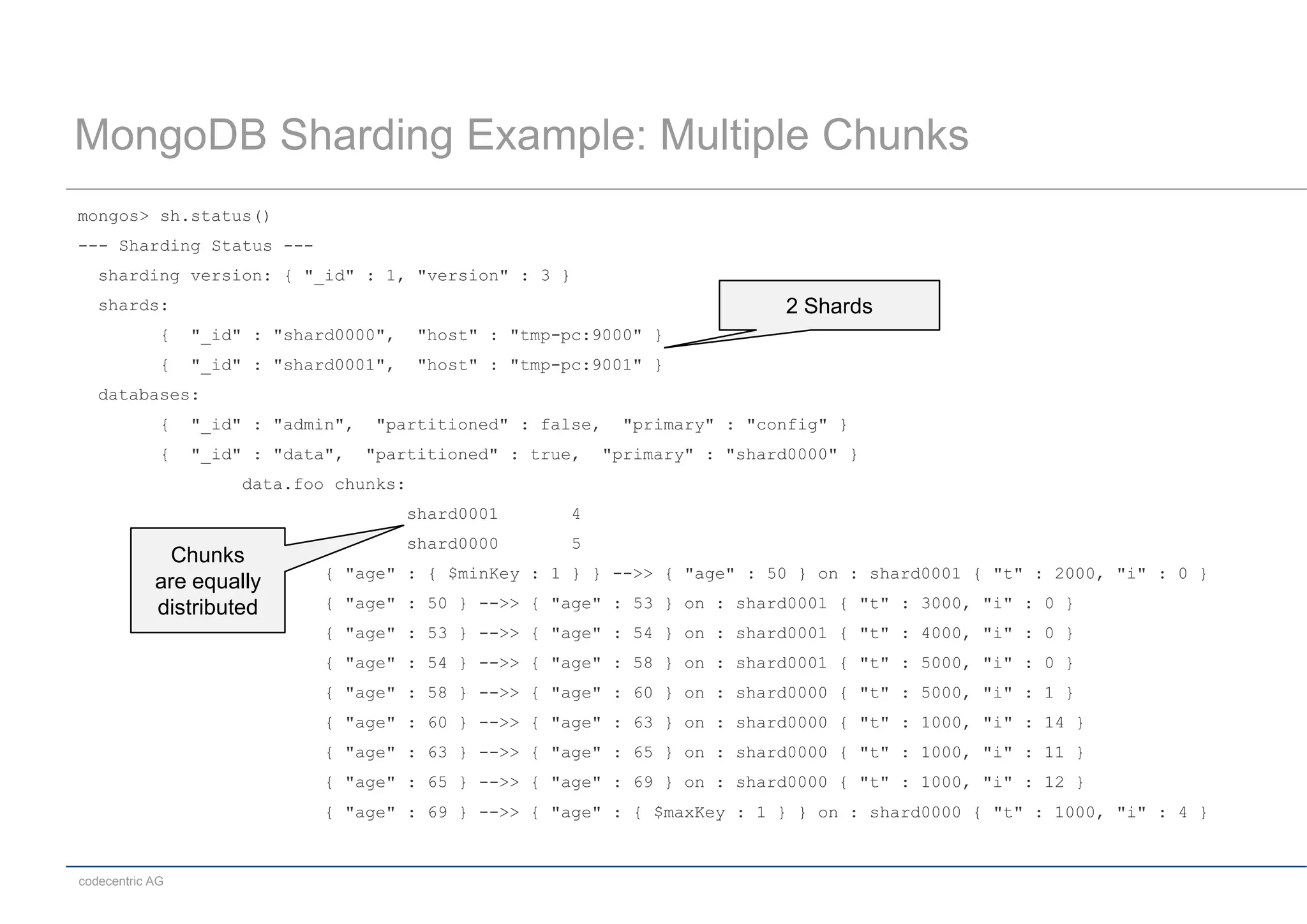
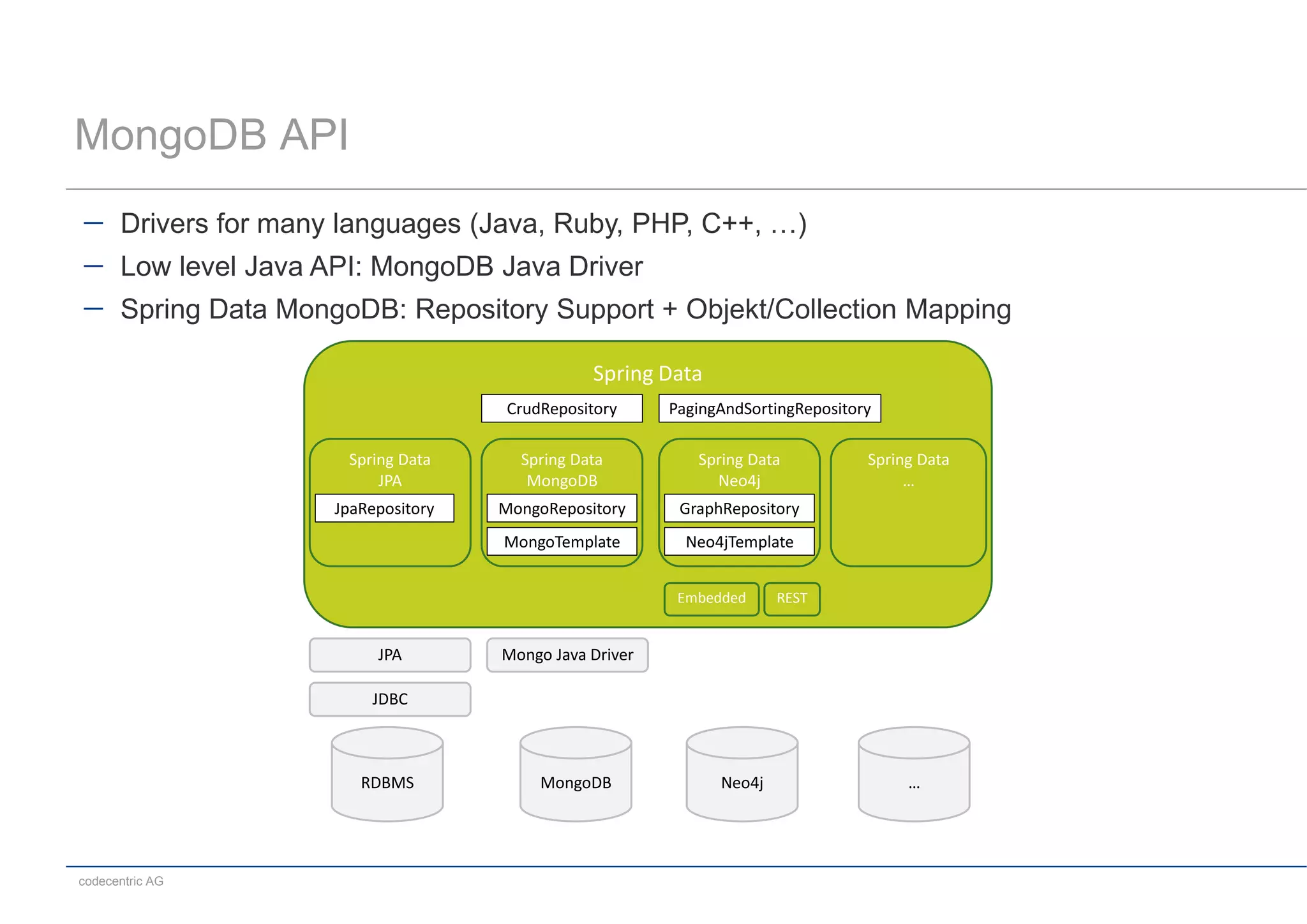
This document summarizes a MongoDB live coding session presented by Tobias Trelle. It introduces MongoDB concepts like documents, collections, CRUD operations, queries including geospatial queries, replication, sharding, and the Java and Spring Data APIs. It also advertises MongoDB user groups in Dusseldorf and Frankfurt organized by codecentric AG.



![What‘s a document?
Single record that can be stored in a collection
JSON = JavaScript Object Notation (internal representation BSON = Binary JSON)
var doc = {
title: „MongoDB_Live_Hacking.pptx“,
tags: [ „cc“, „mongodb“, „nosql“ ],
slides: [
{ nr = 1, header = „MongoDB User Groups by codecentric“},
{ nr = 2, header = „MongoDB at codedcentric WiKi“},
…
]
};
codecentric AG](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodblivecoding-120821014638-phpapp02/75/MongoDB-Live-Hacking-6-2048.jpg)
![Geospatial Queries
Queries based on
2-dimensional coordinates
_id: "A", position: [0.001, -0.002]
_id: "B", position: [0.75, 0.75]
_id: "C", position: [0.5, 0.5]
_id: "D", position: [-0.5, -0.5]
Queries based on distances
& shapes
Details:
http://blog.codecentric.de/en/2012/02/spring-data-mongodb-geospatial-queries/
codecentric AG](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodblivecoding-120821014638-phpapp02/75/MongoDB-Live-Hacking-8-2048.jpg)

![Map/Reduce example
We want to count occurences of tags assigned to our documents:
{name: „Doc 1“, tags: [ „cc“, „mongodb“, „nosql“ ] }
{name: „Doc 2“, tags: [ „cc“, „agile“ ] } Map output:
{name: „Doc 3“, tags: [ „cc“ ] } key = „cc“, value = {count: 1}
key = „mongodb“, value = {count: 1}
key = „nosql“, value = {count: 1}
Map function:
key = „cc“, value = {count: 1}
function() { this.tags.forEach( function(tag) { key = „agile“, value = {count: 1}
emit( tag, {count: 1} ) key = „cc“, value = {count: 1}
})
}
Reduce function: Reduce input:
function(key, values) { key = „cc“, values = [ {count: 1}, {count: 1}, {count: 1} ]
var result = {count: 0};
key = „mongodb“, values = [ {count: 1} ]
values.forEach(function(value) {
key = „nosql“, values = [ {count: 1} ]
result.count += value.count;
key = „agile“, values = [ {count: 1} ]
});
return result;
}
codecentric AG](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodblivecoding-120821014638-phpapp02/75/MongoDB-Live-Hacking-10-2048.jpg)