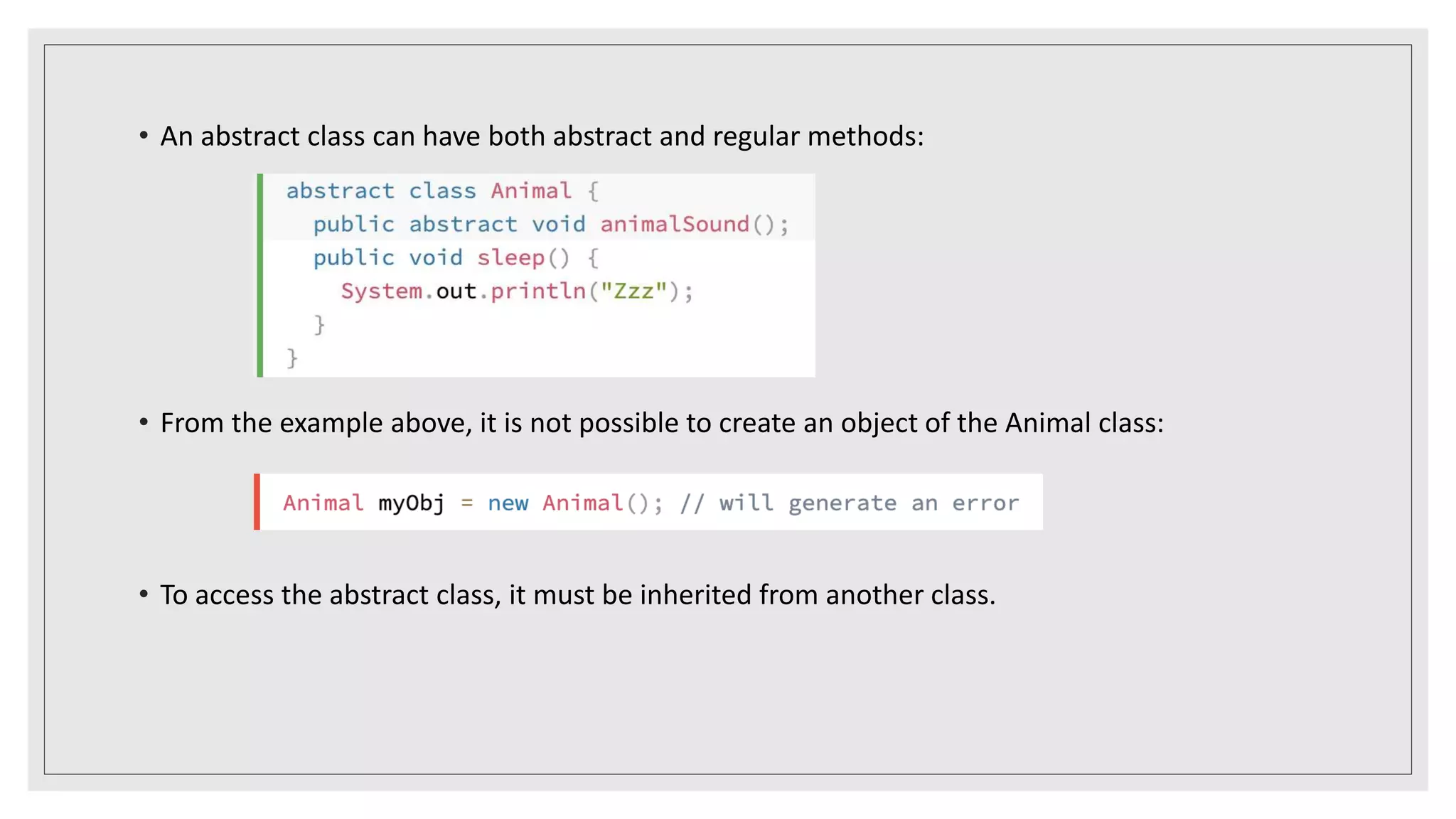
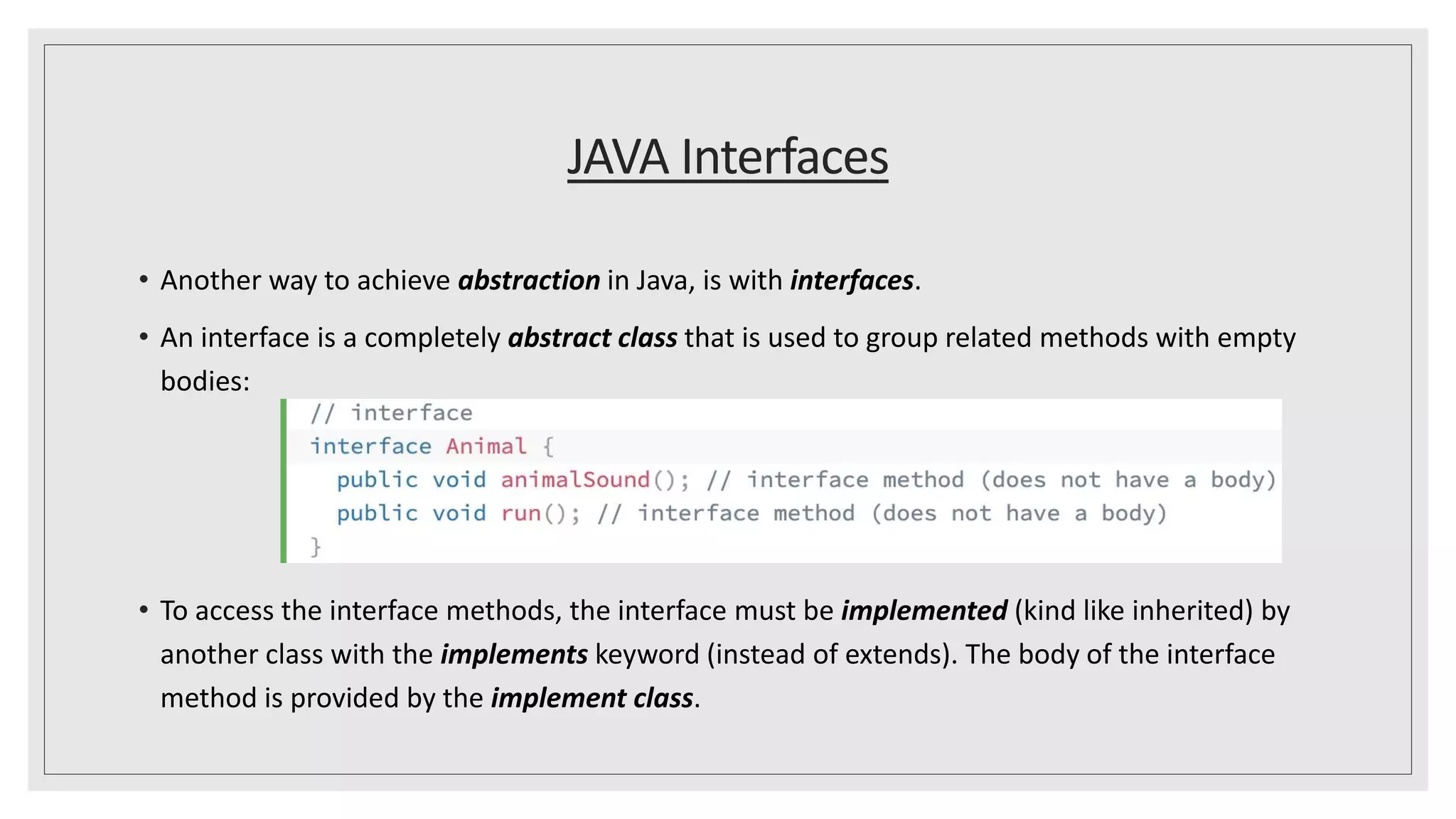
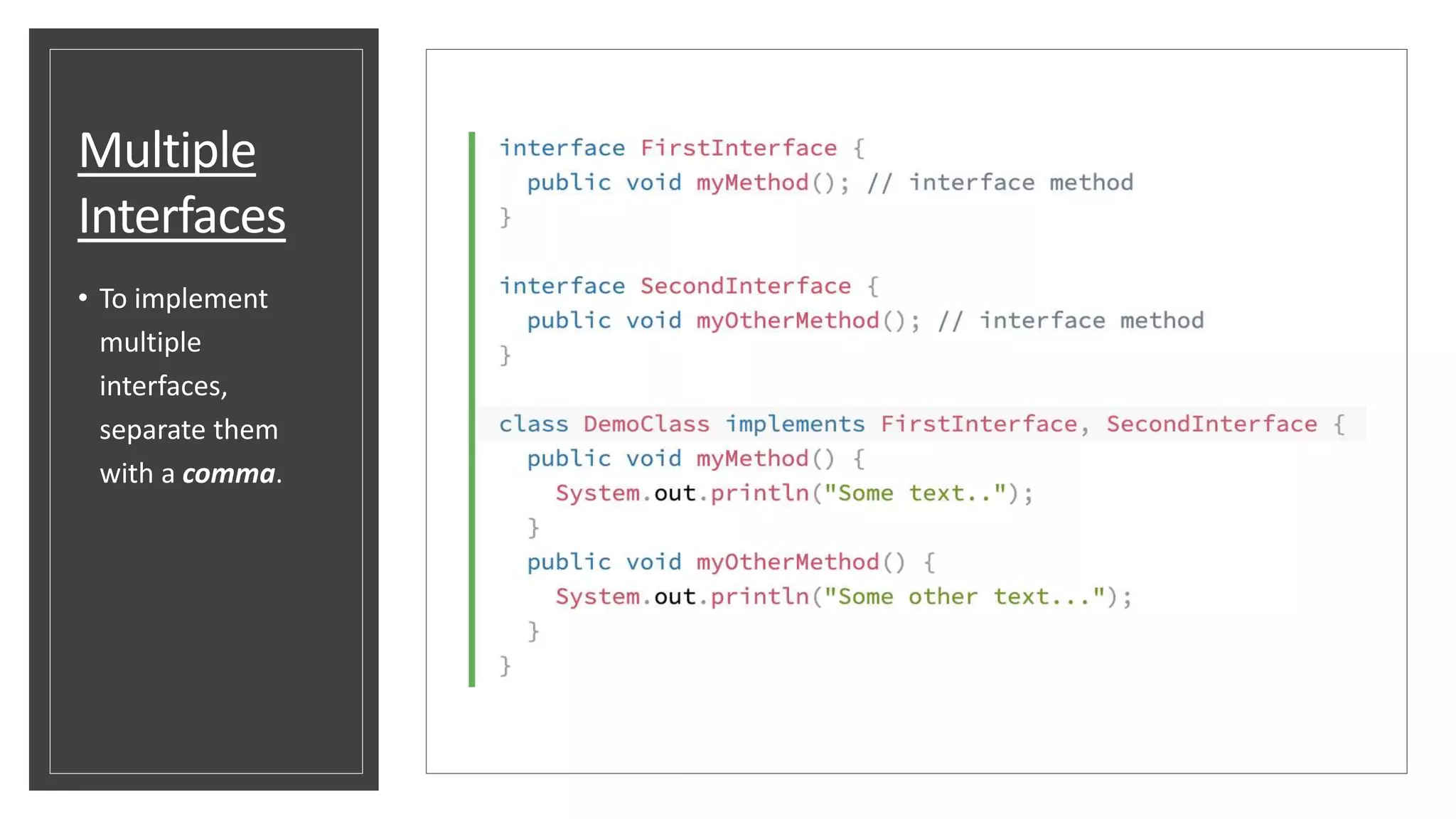
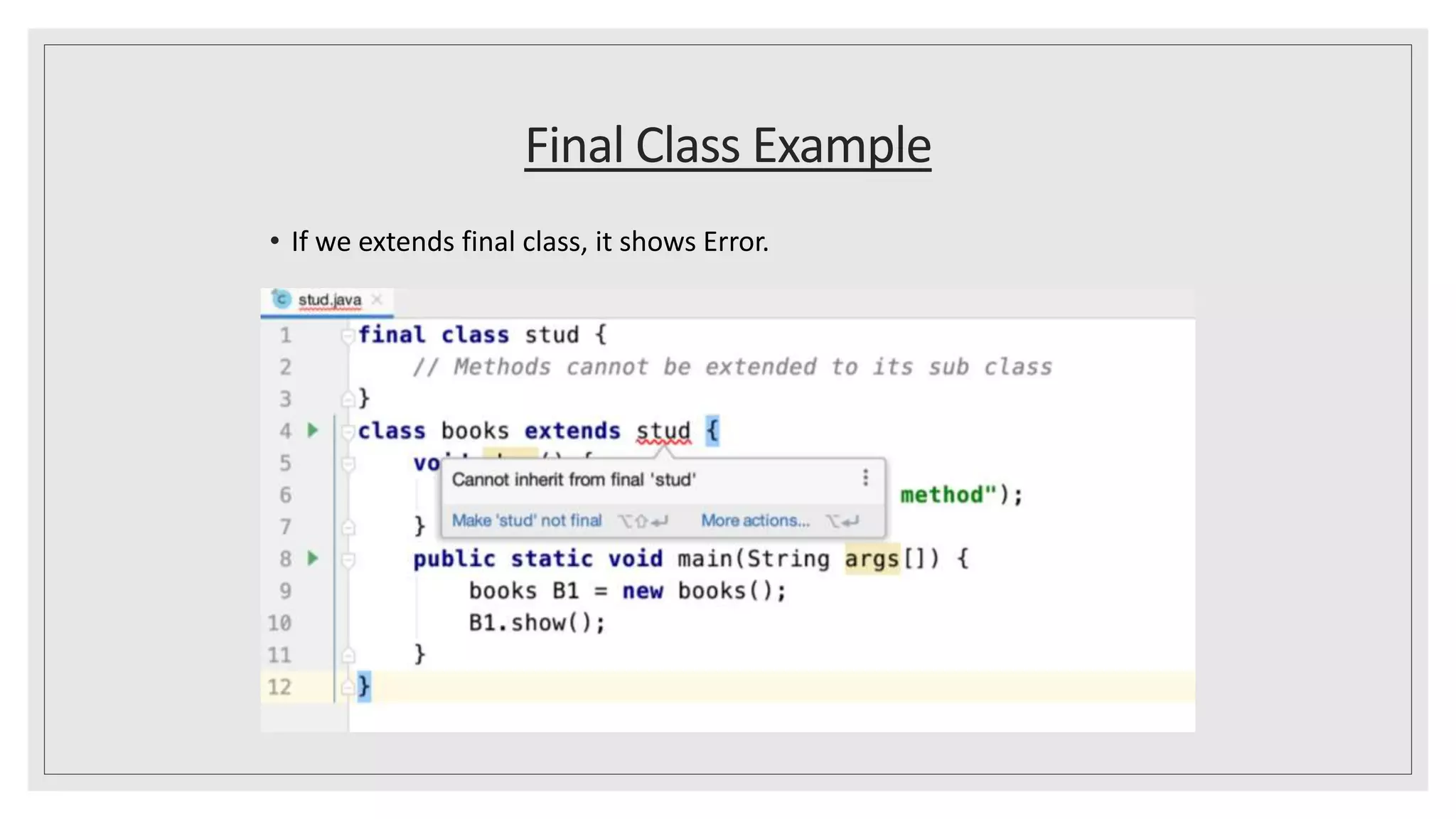
This document discusses abstract classes and methods in Java. It explains that abstract classes cannot be instantiated and can contain both abstract and regular methods, while abstract methods do not have a body. The document also covers interfaces, noting that like abstract classes, interfaces cannot be instantiated but their methods must be overridden by implementing classes. It provides examples of abstract classes, interfaces, and the final keyword, and explains when to use abstraction in Java.