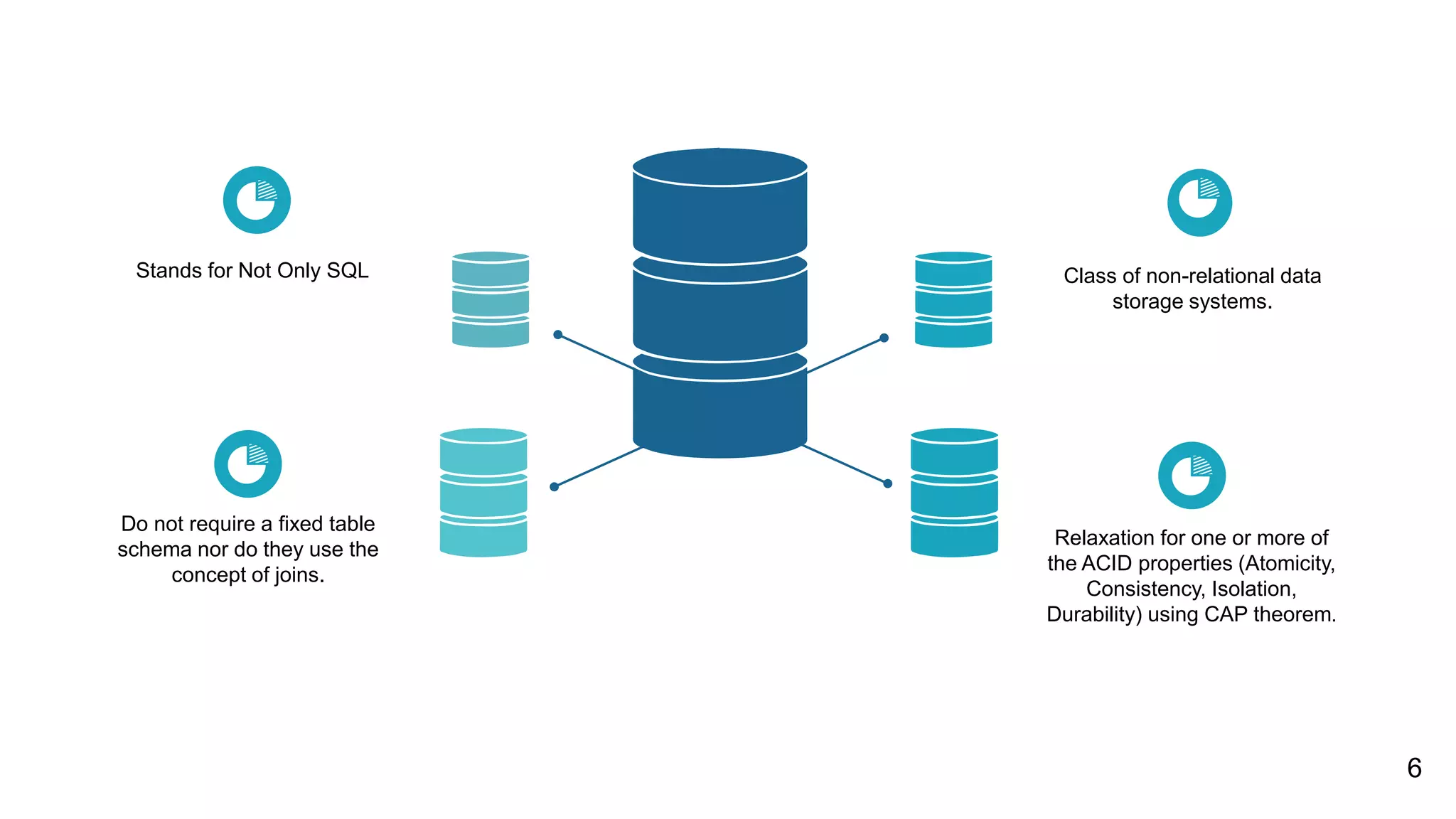
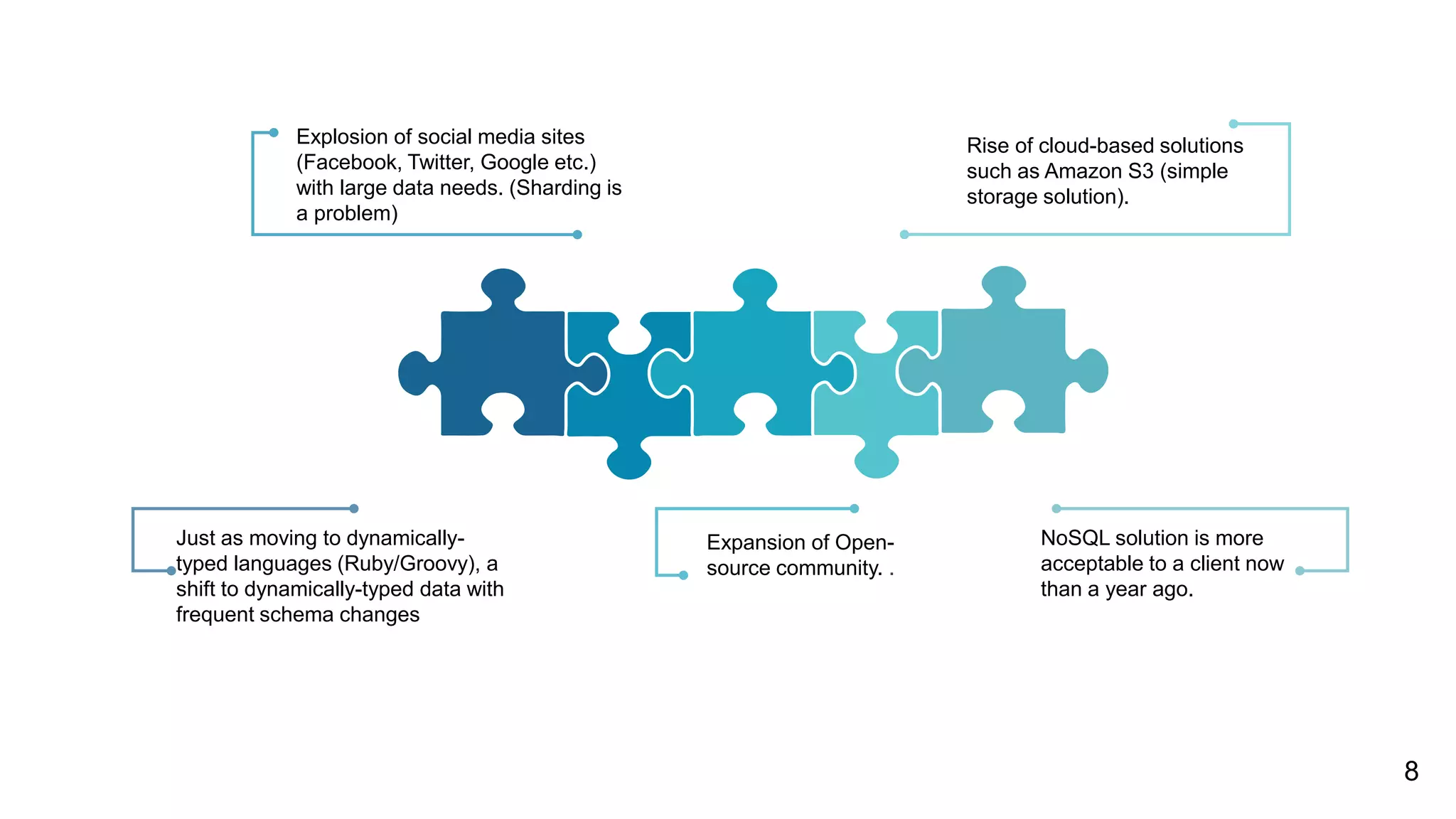
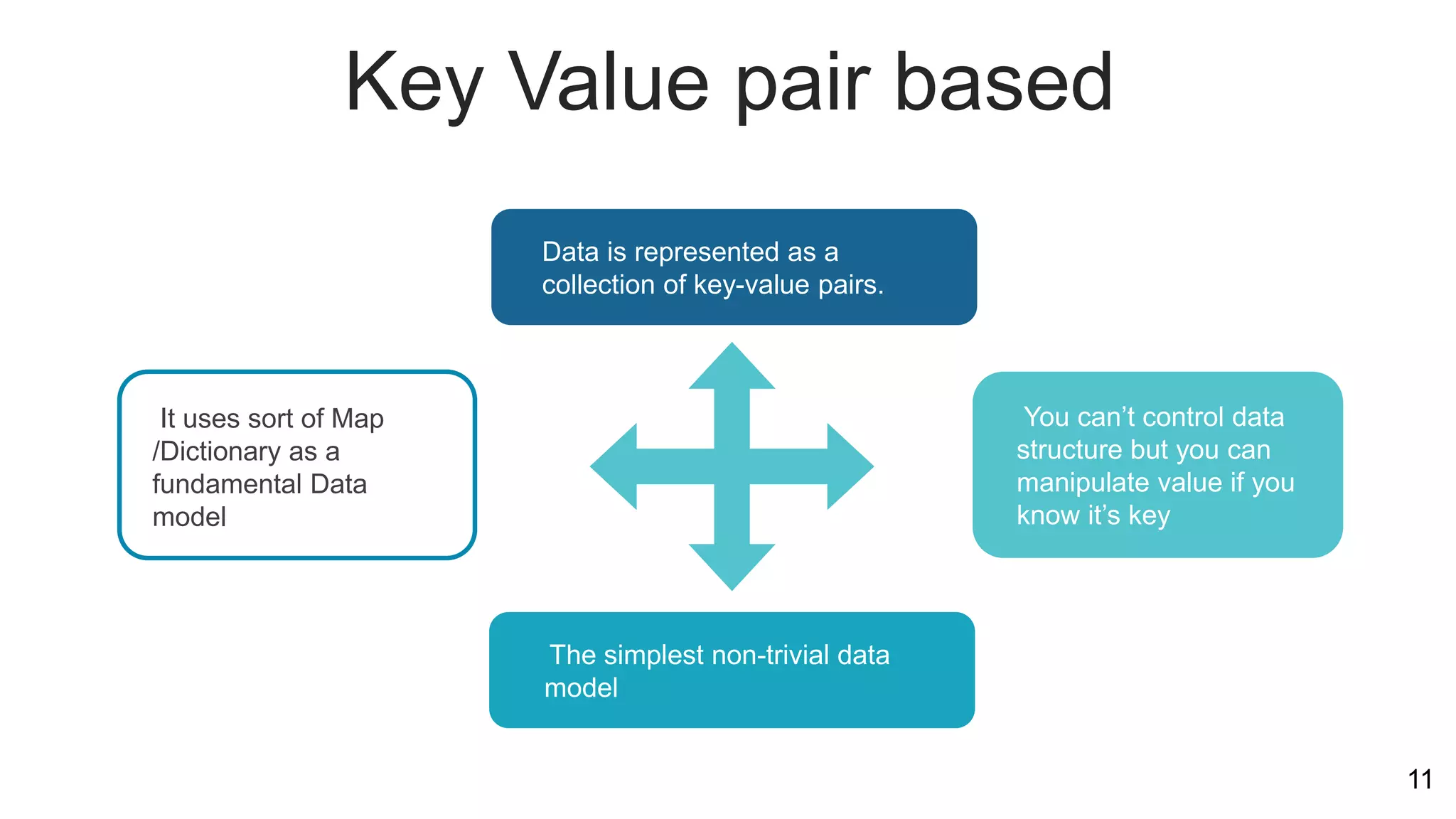
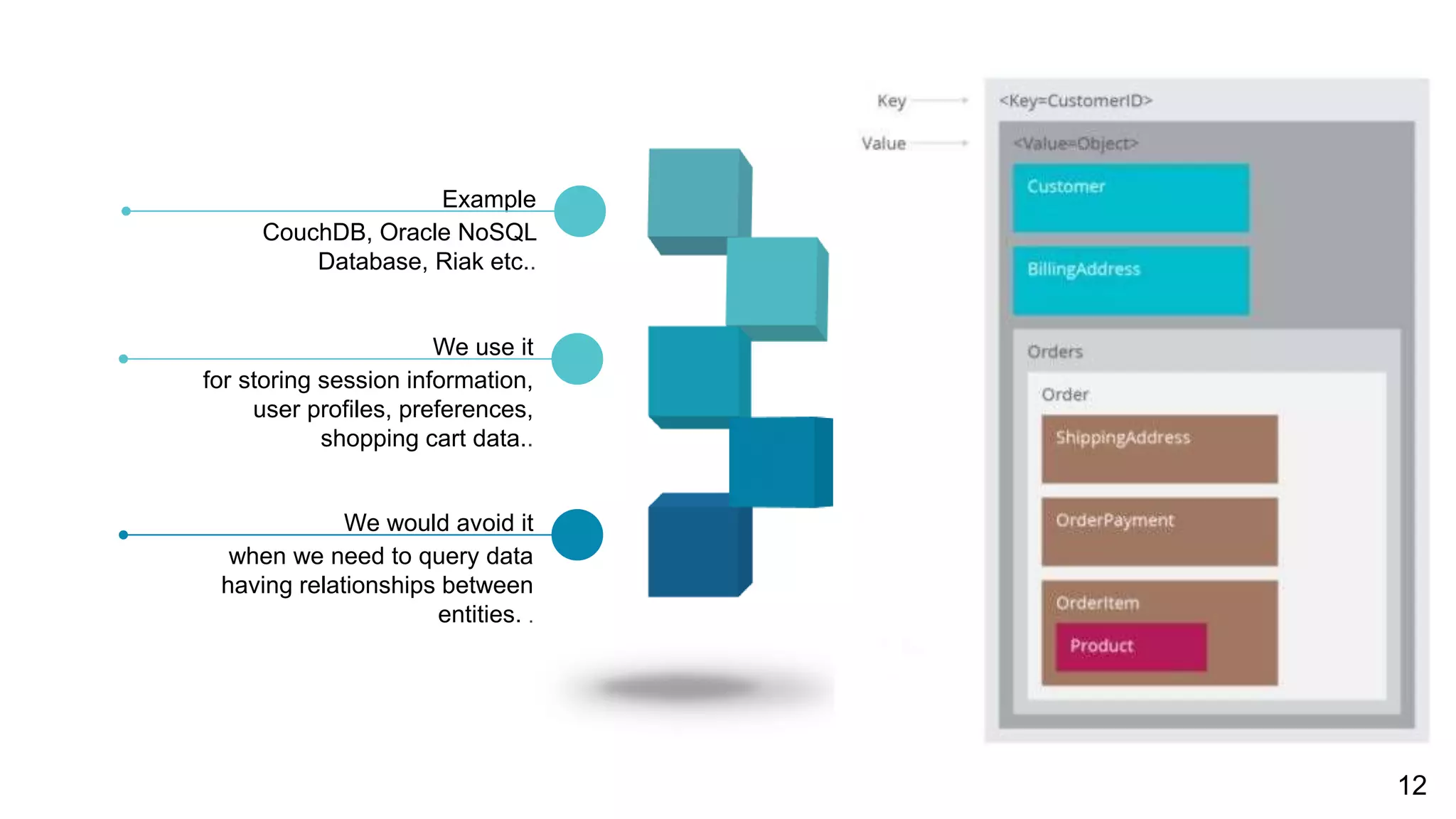
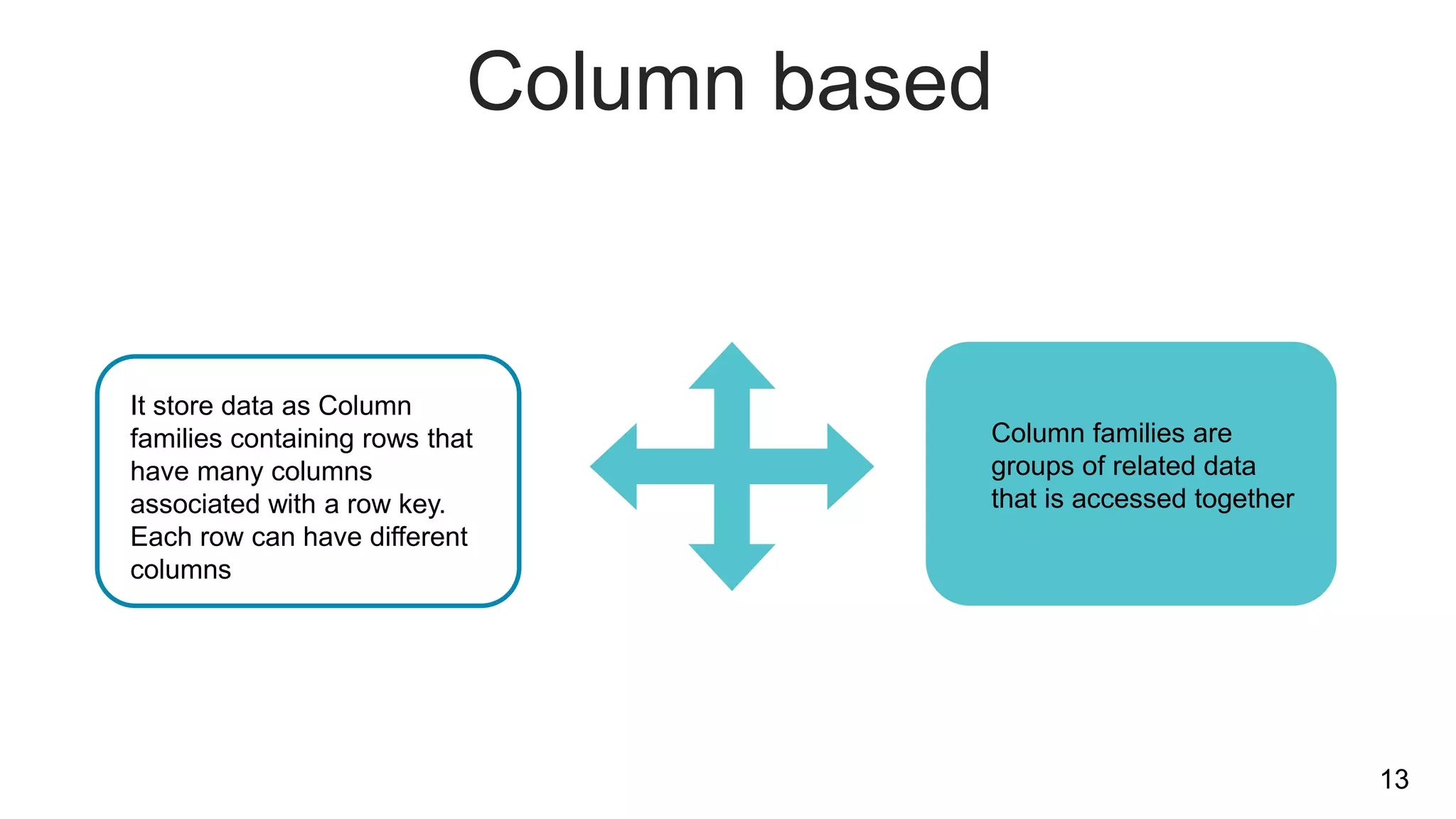
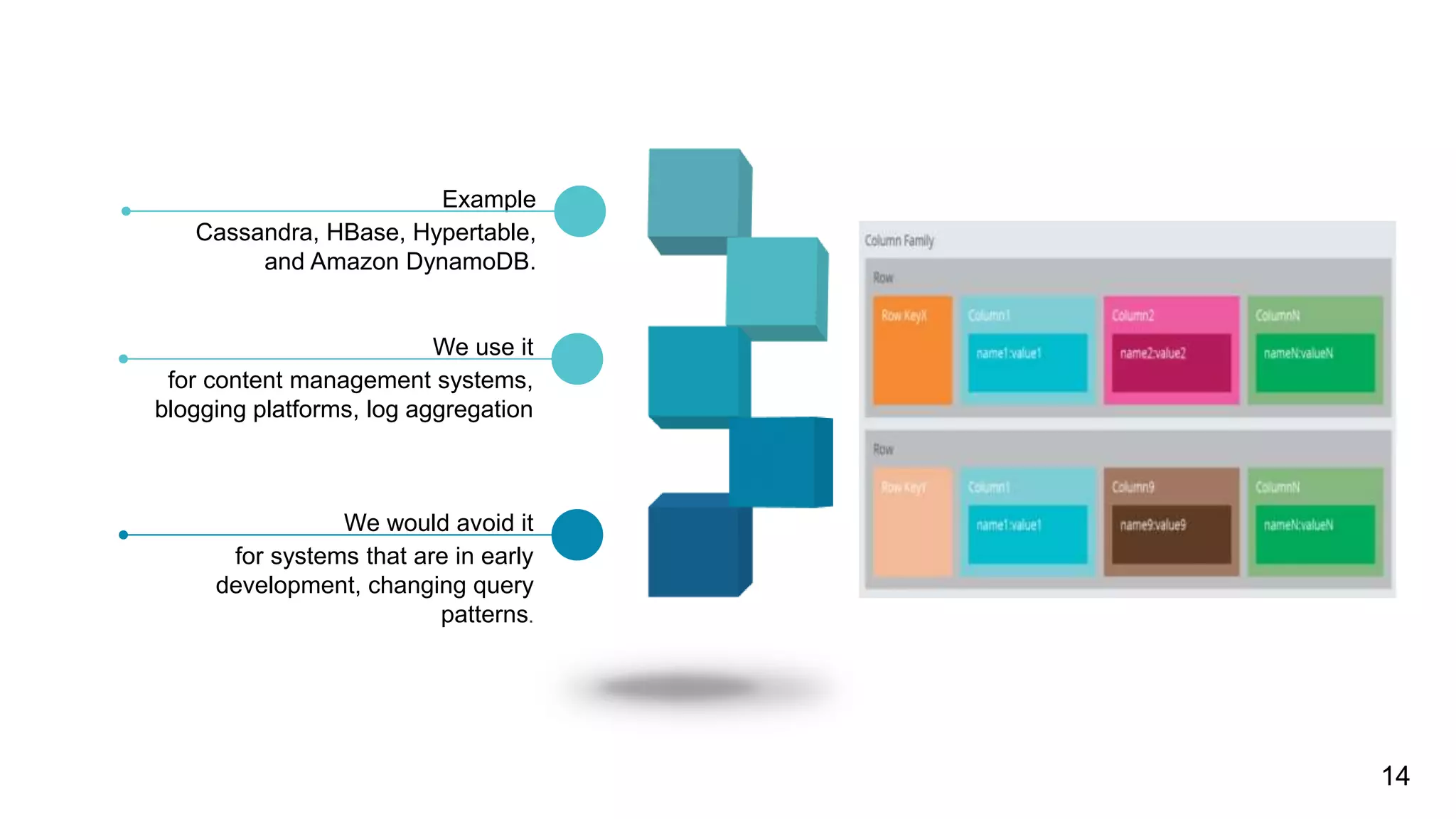
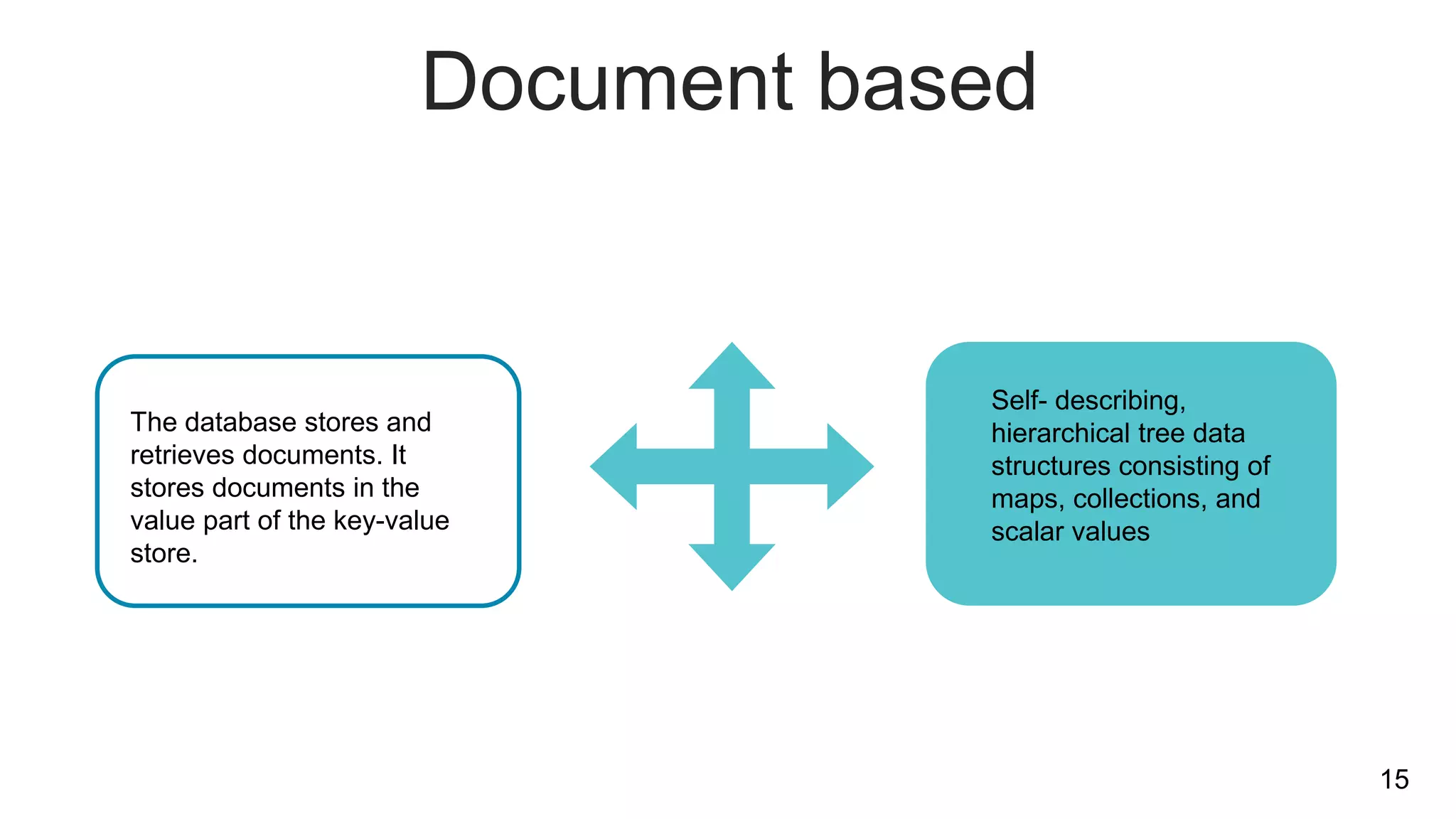
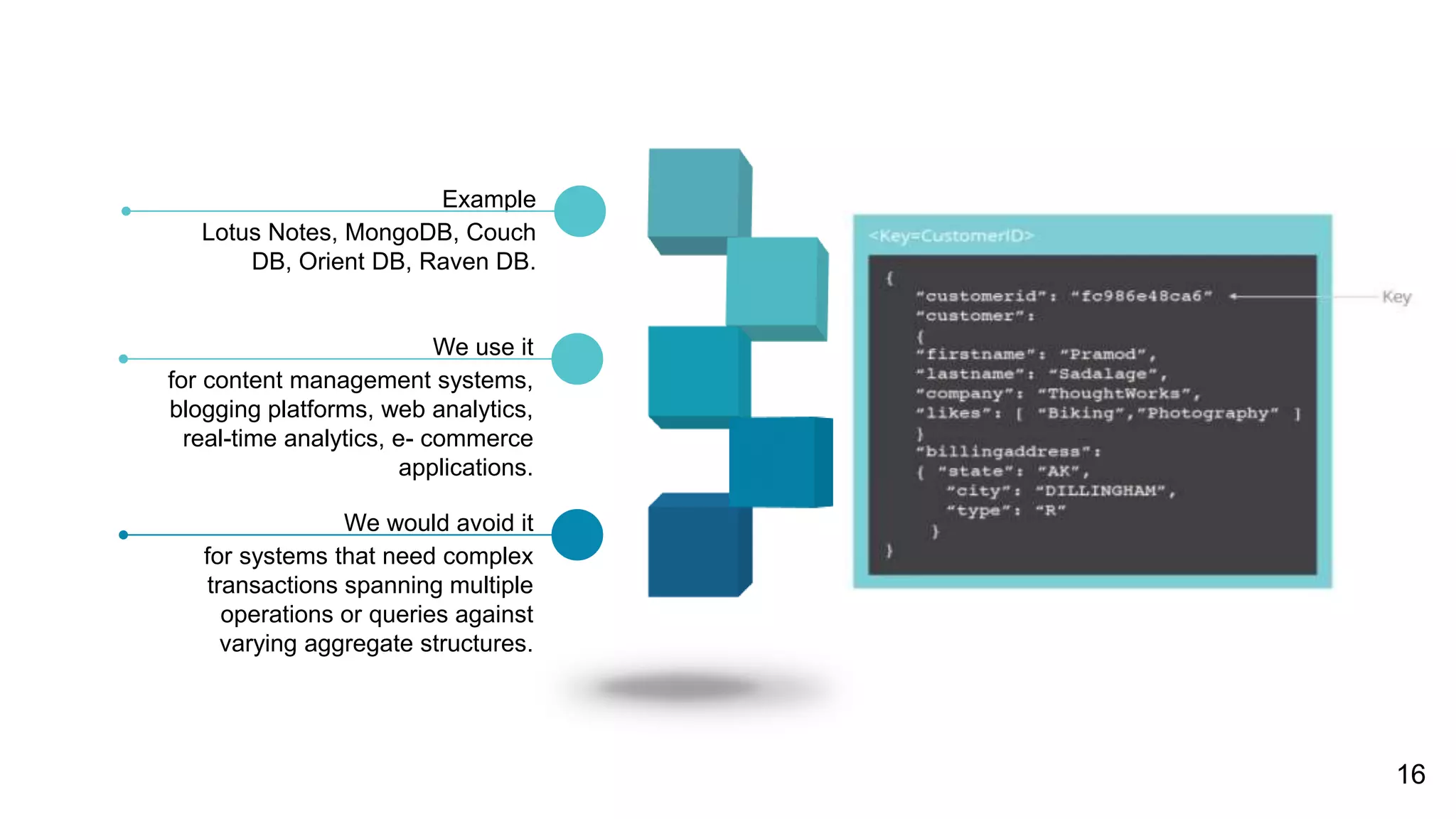
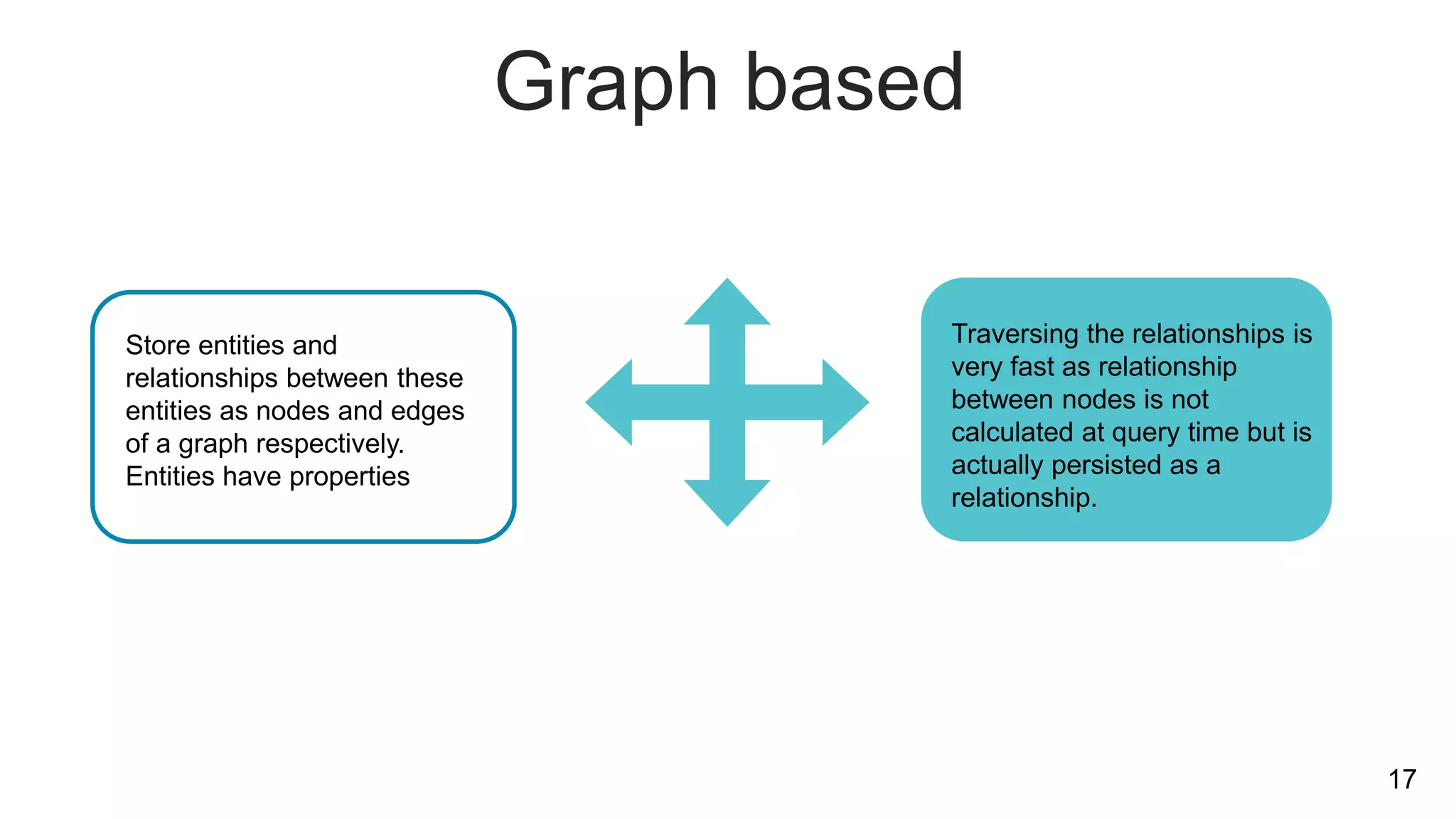
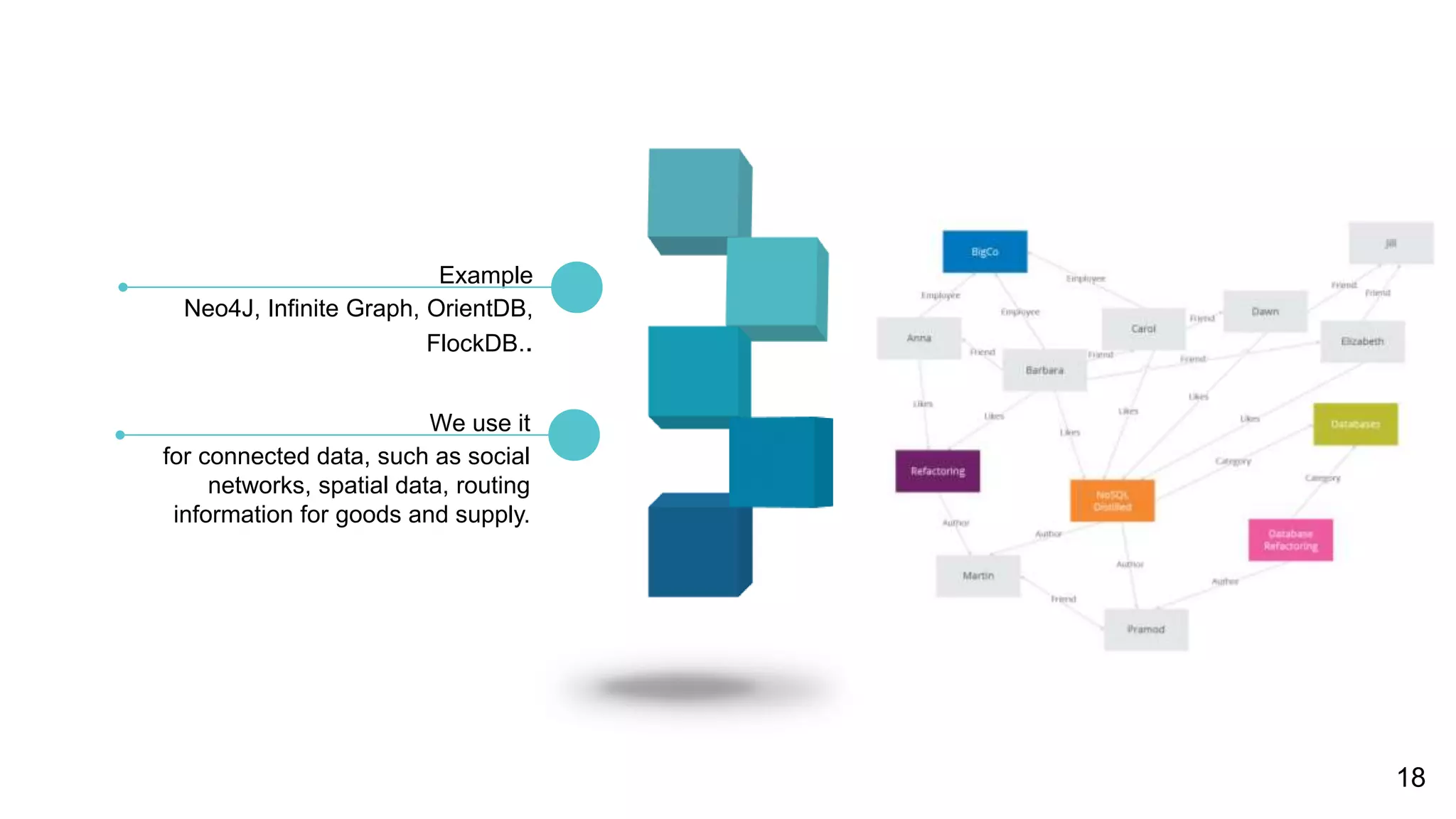
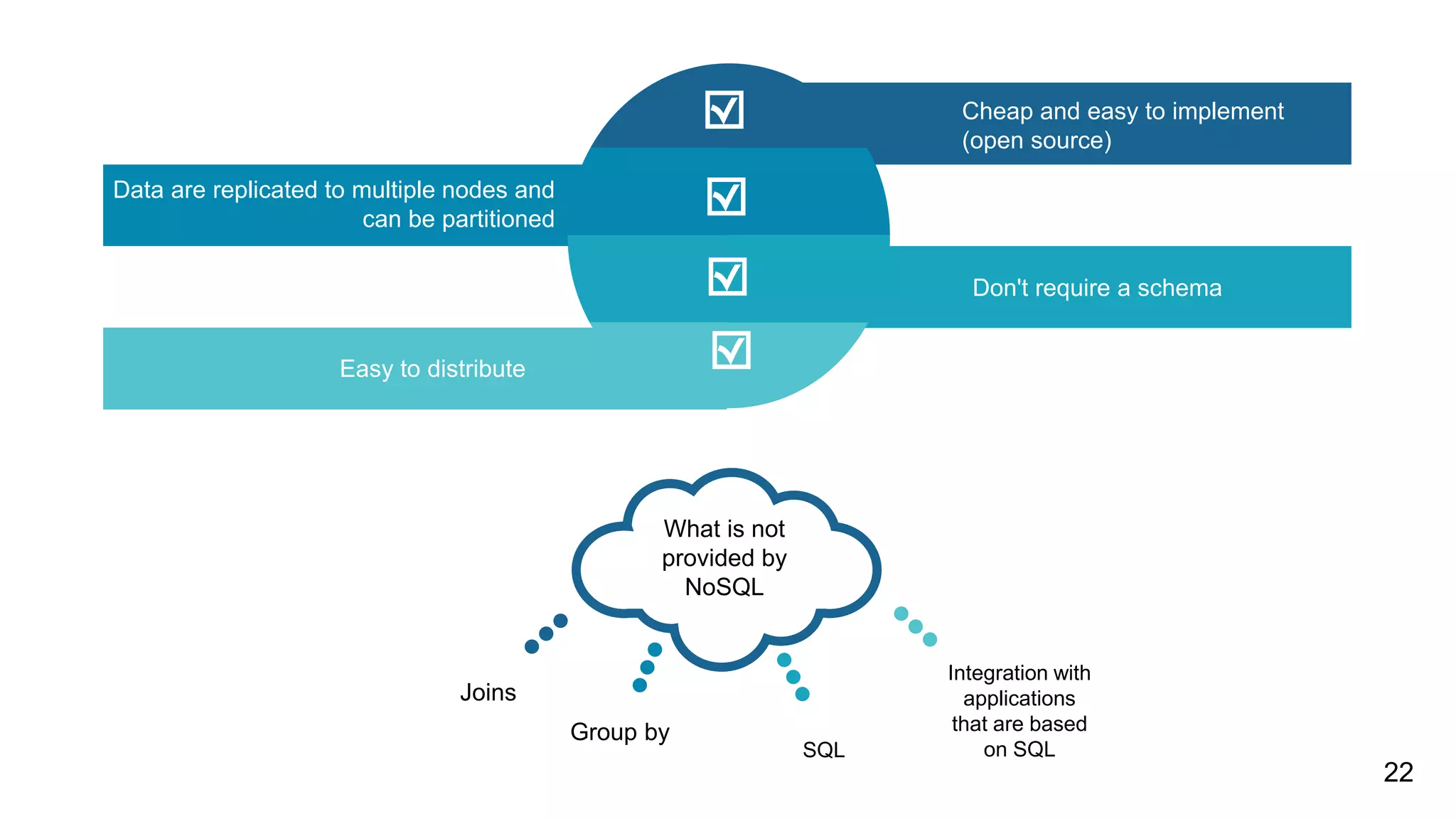
NoSQL databases are non-relational databases that provide an alternative to traditional relational databases. The main types of NoSQL databases are key-value stores, column-oriented databases, document databases, and graph databases. NoSQL databases are best suited for applications that need to store and access large amounts of unstructured or semi-structured data, such as user profiles, session data, logging information and social networking data. They provide advantages like horizontal scaling, high performance and easy implementation compared to relational databases. Both relational and non-relational databases have their place, and a polyglot approach using multiple database technologies is becoming more common.