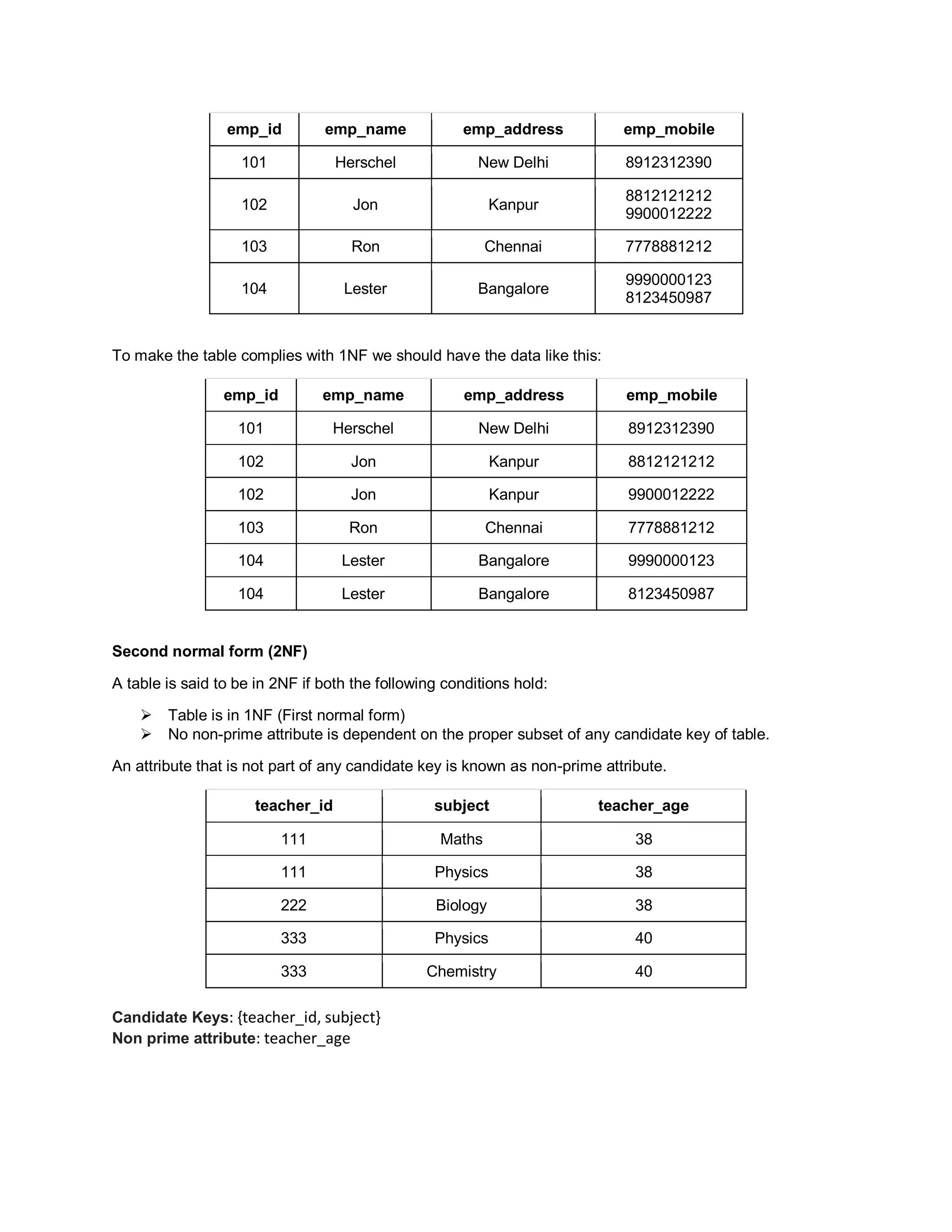
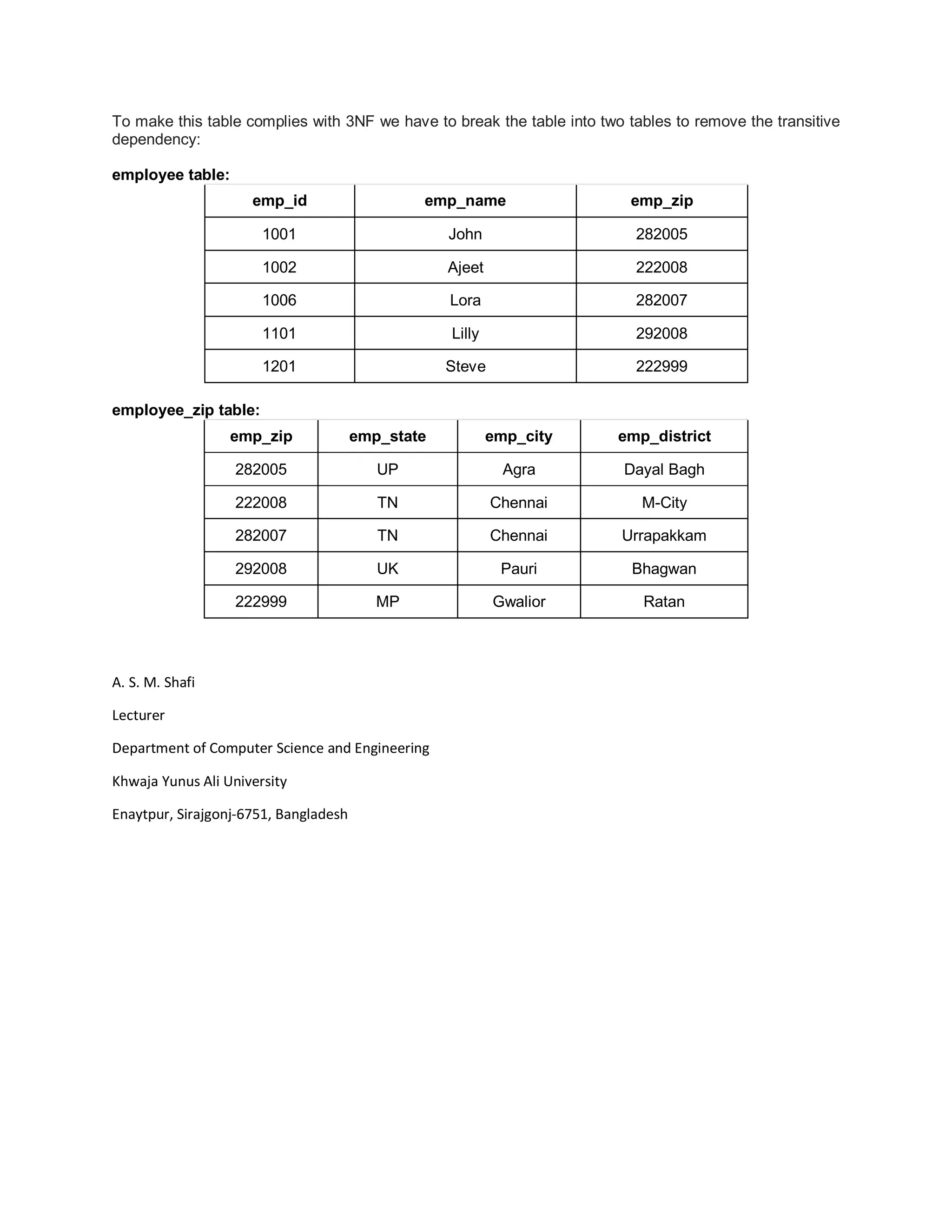
Normalization is the process of structuring a database to minimize duplicate data and reduce data anomalies. It involves breaking tables into smaller, more specific tables and linking them together. The goals of normalization are to minimize duplicate data, ensure data dependencies make logical sense, and simplify table designs to make the database more flexible, easier to maintain and less prone to anomalies. There are several normal forms that are commonly used including first normal form, second normal form, third normal form and Boyce-Codd normal form.