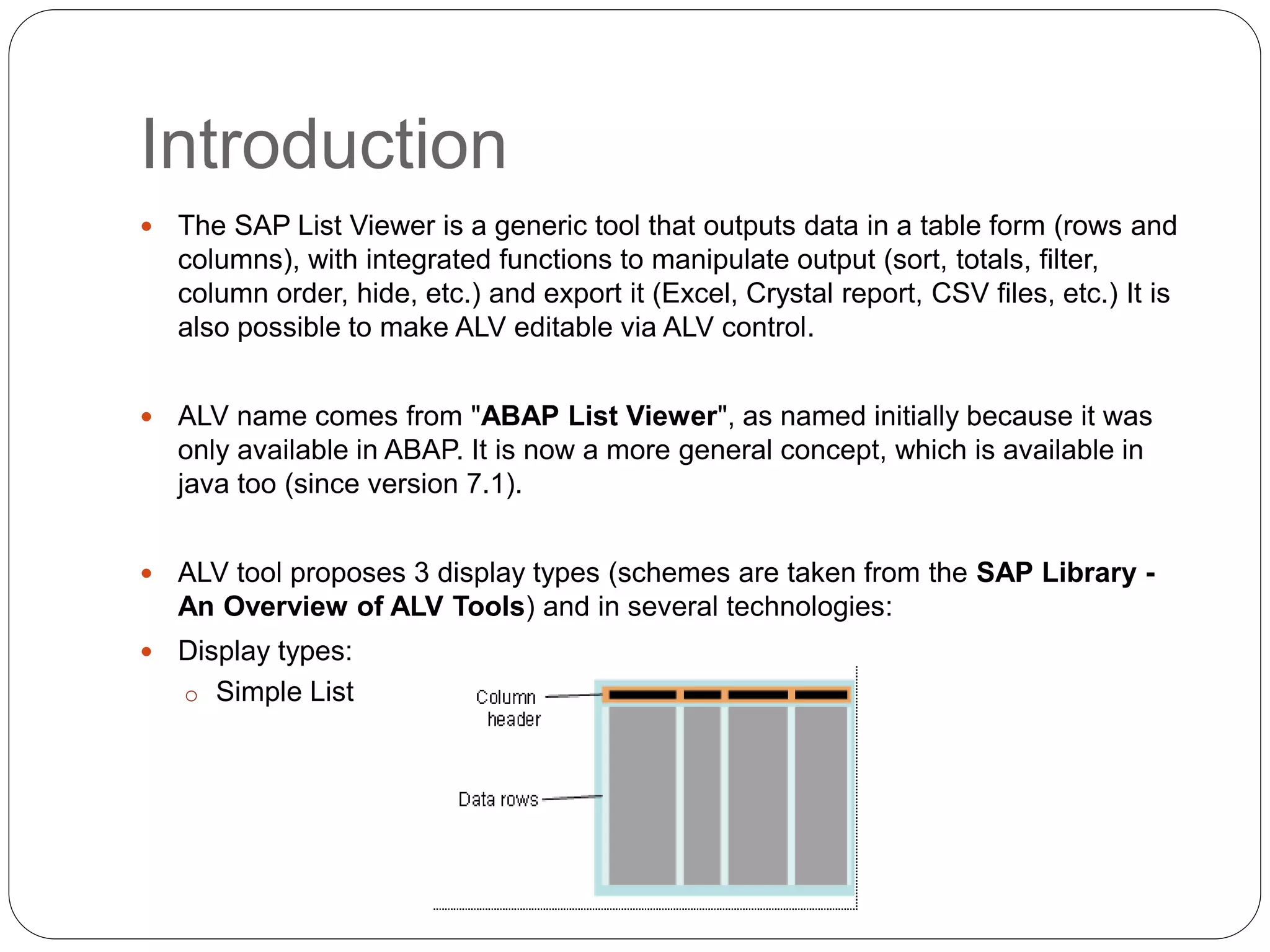
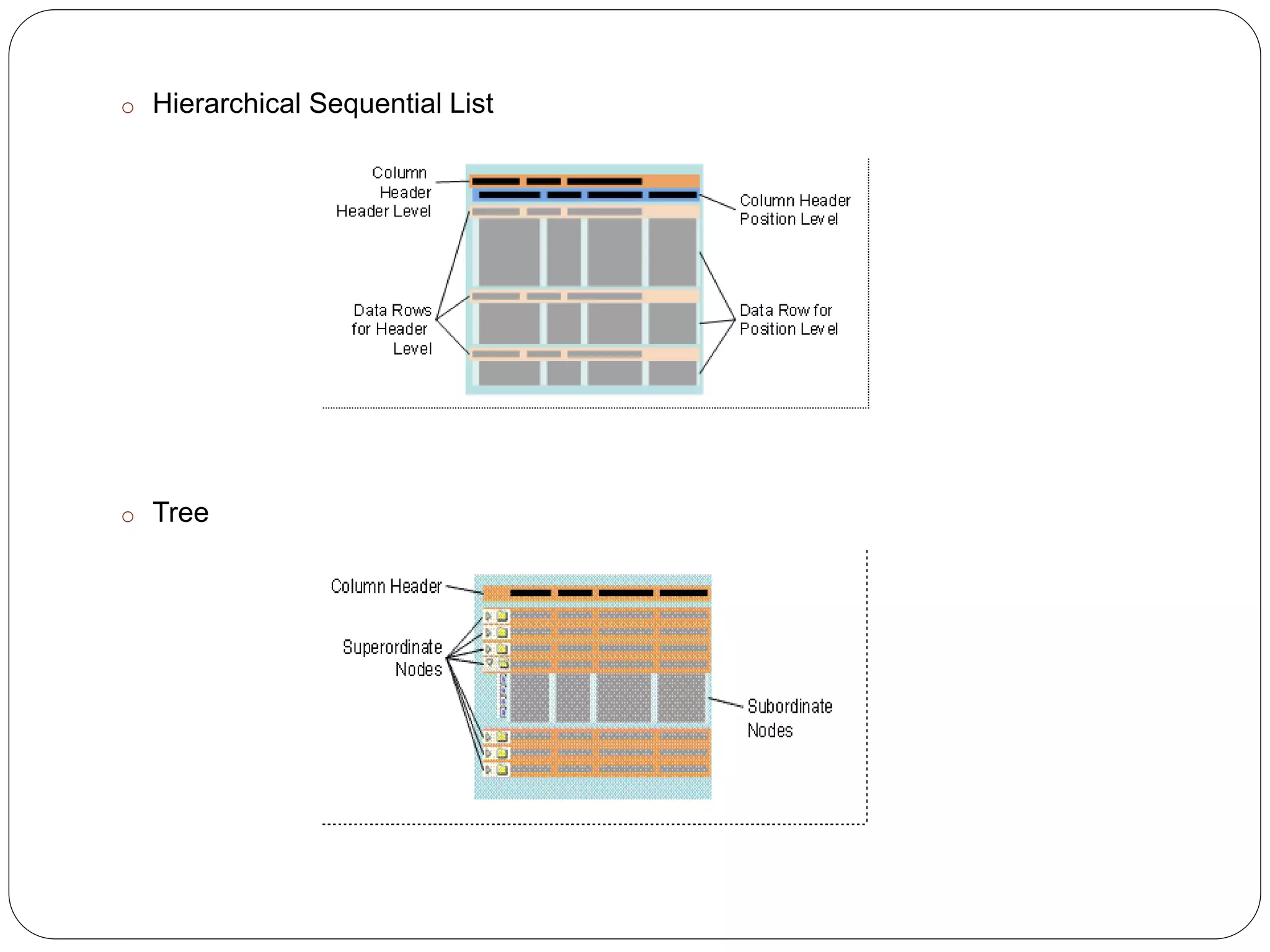
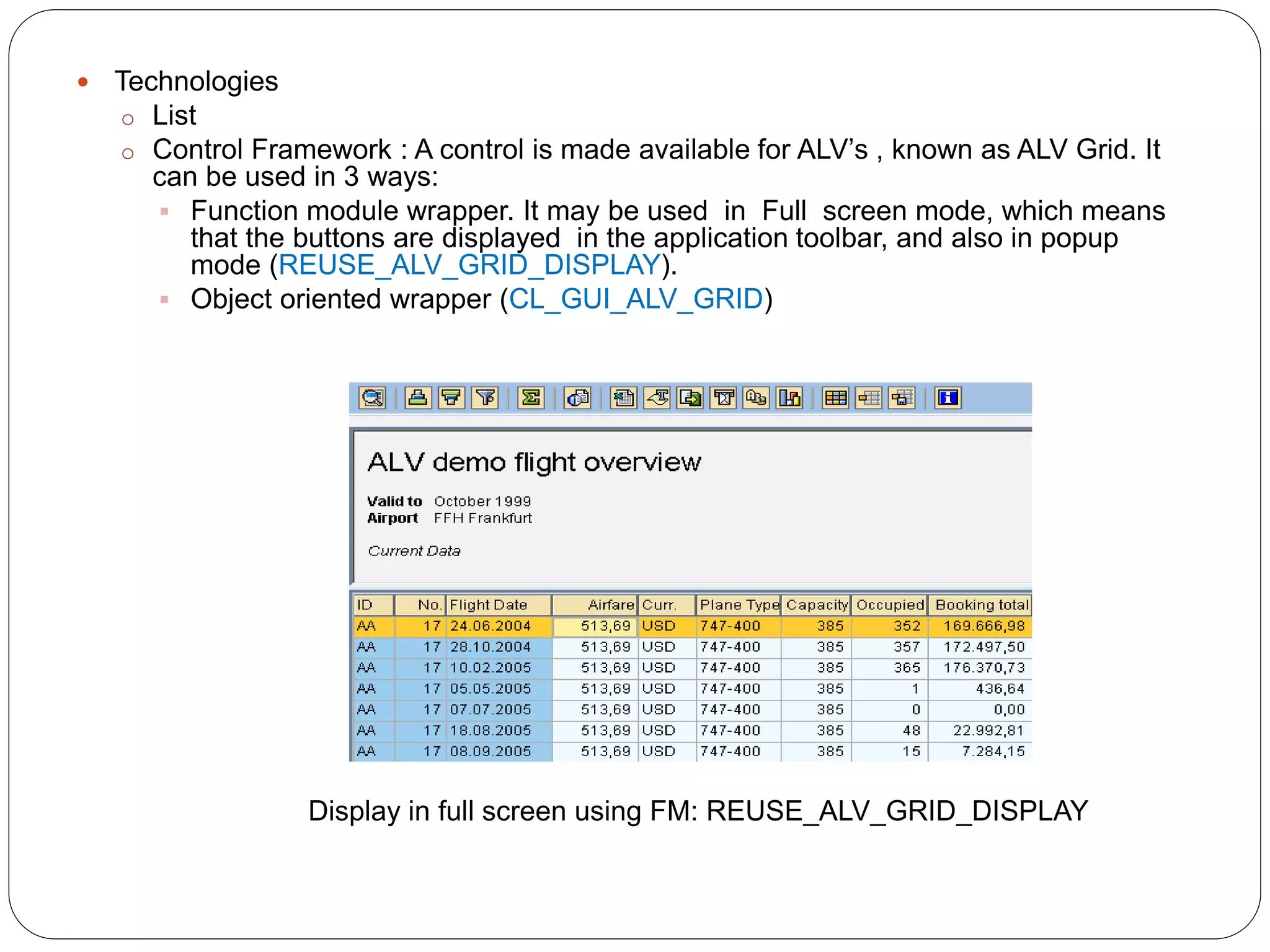
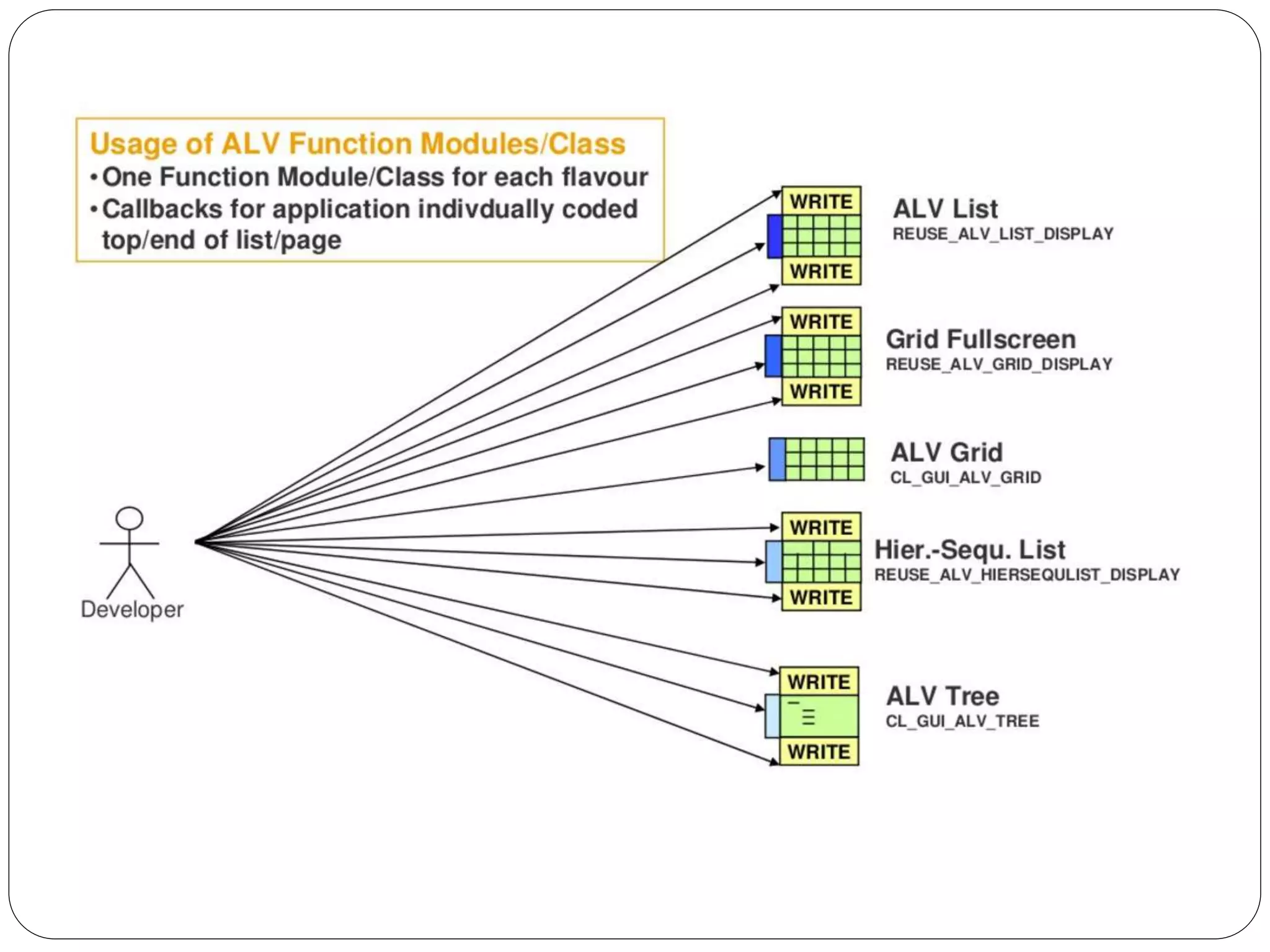
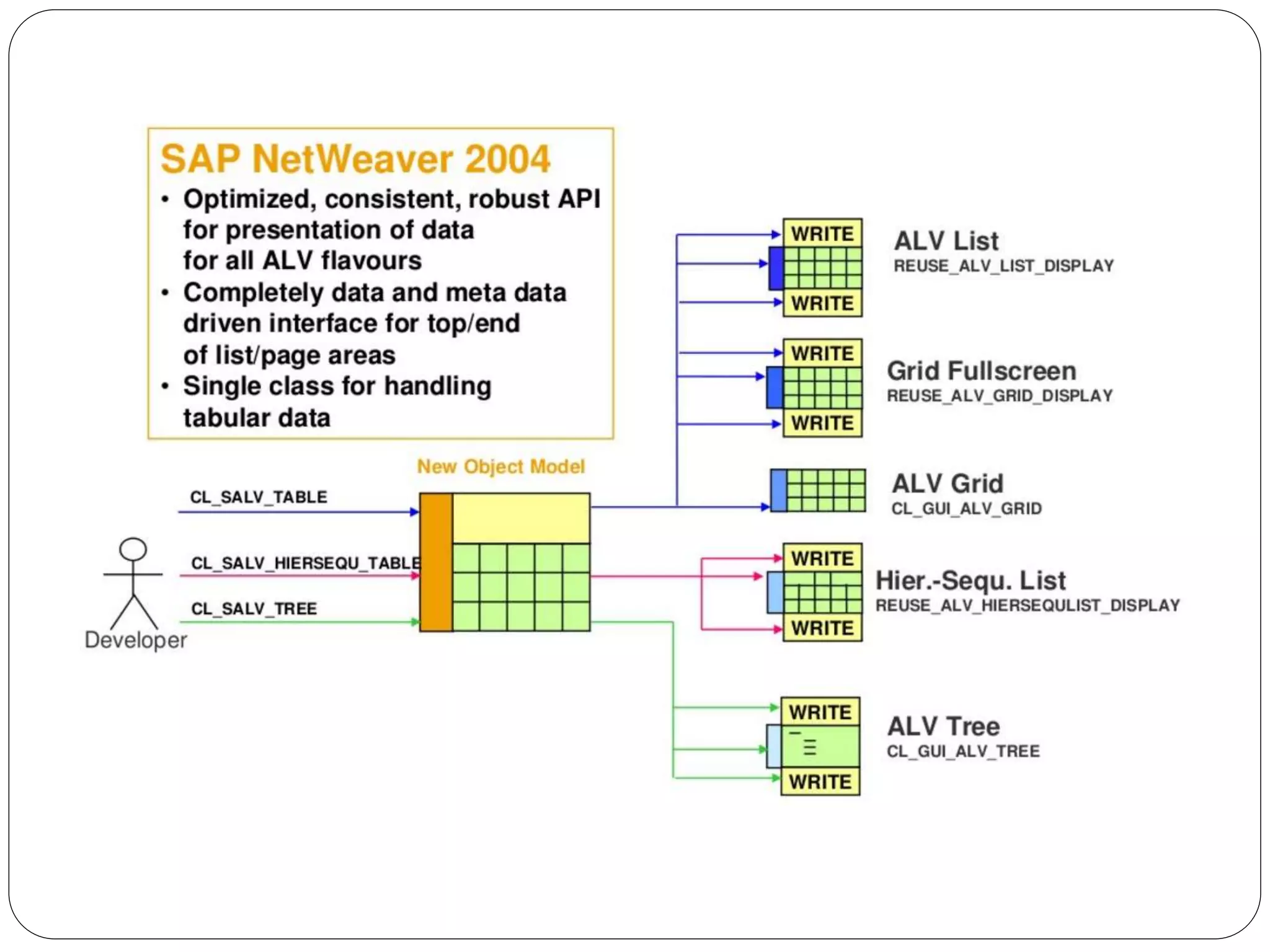
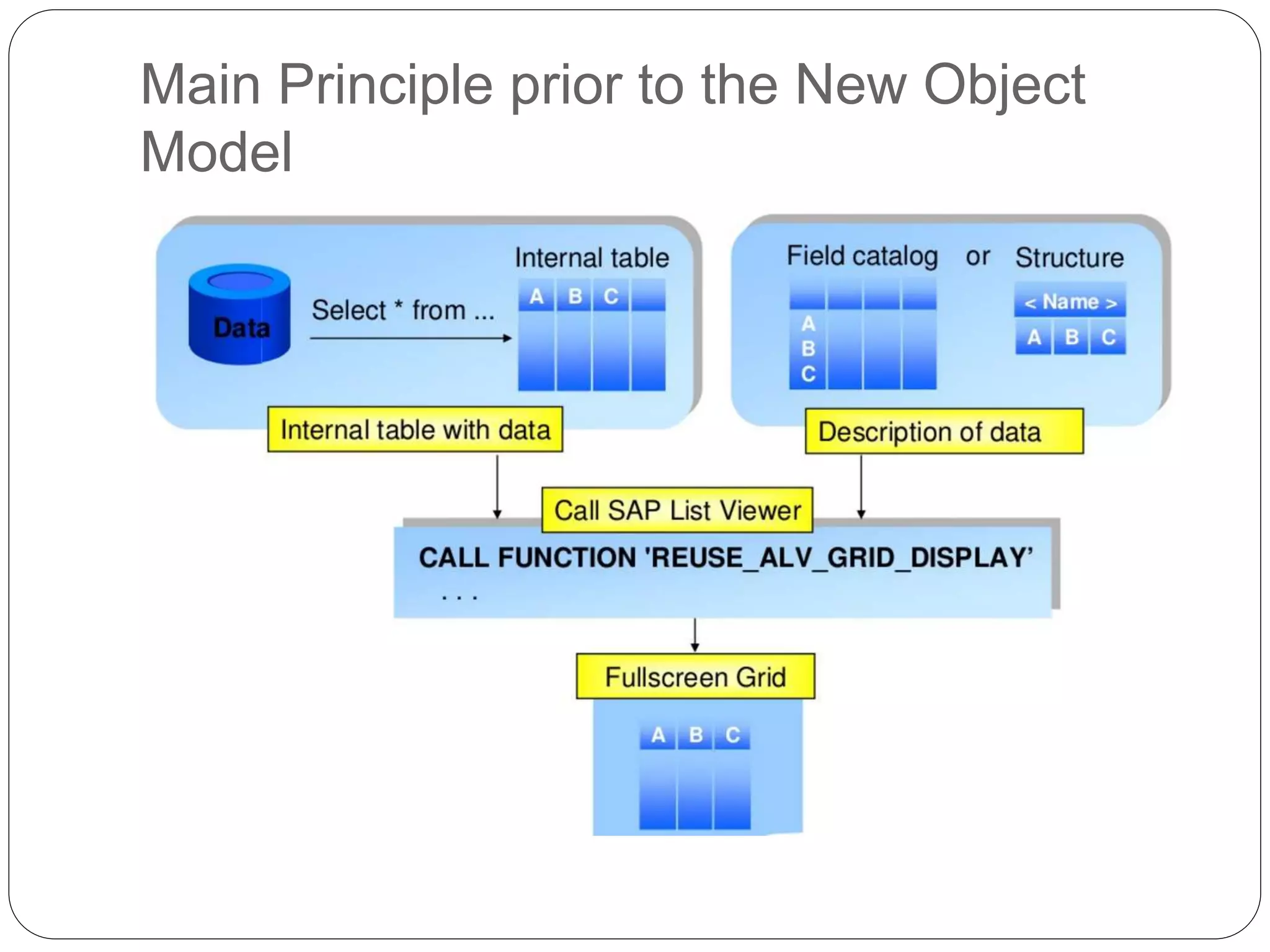
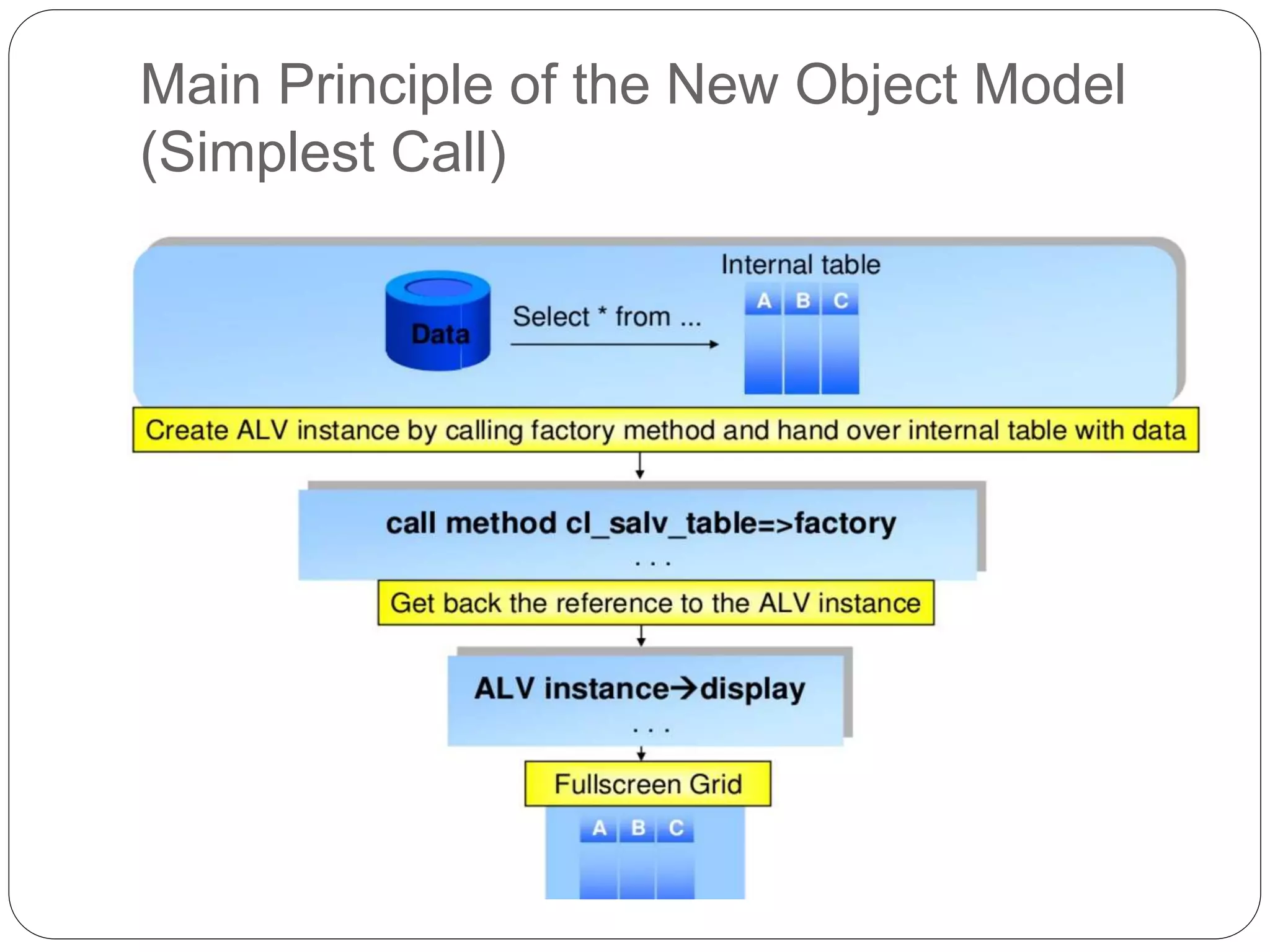
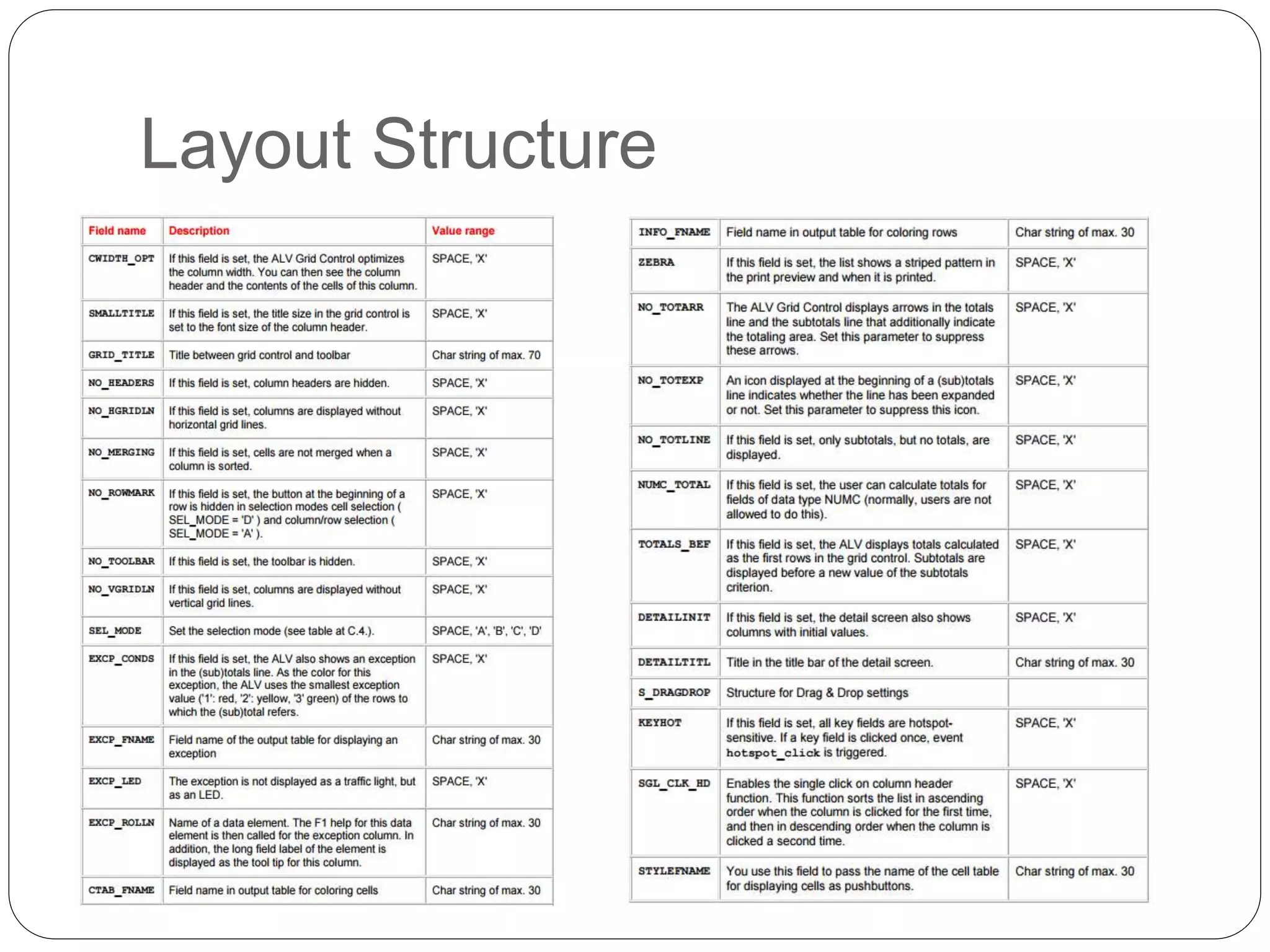
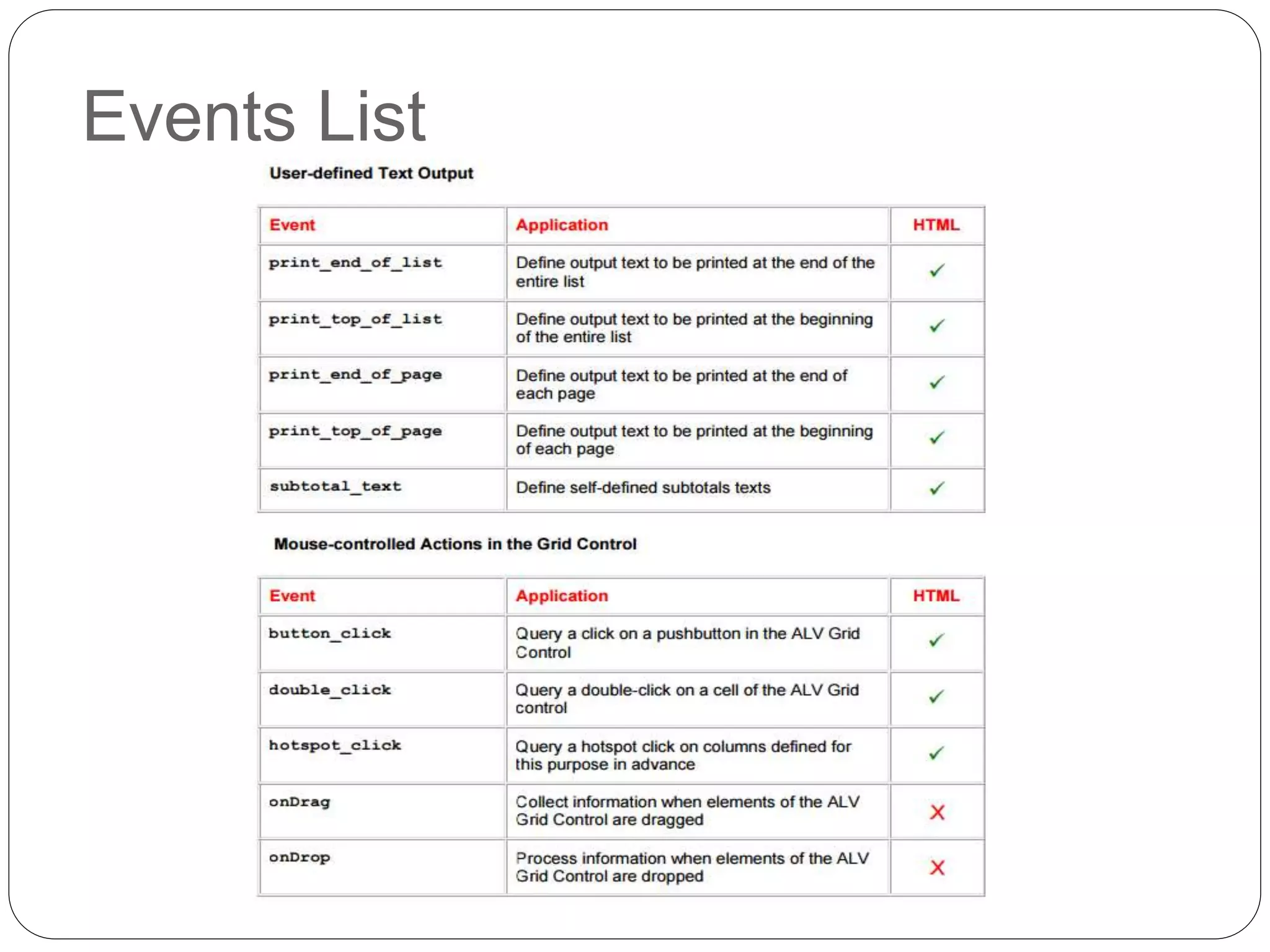
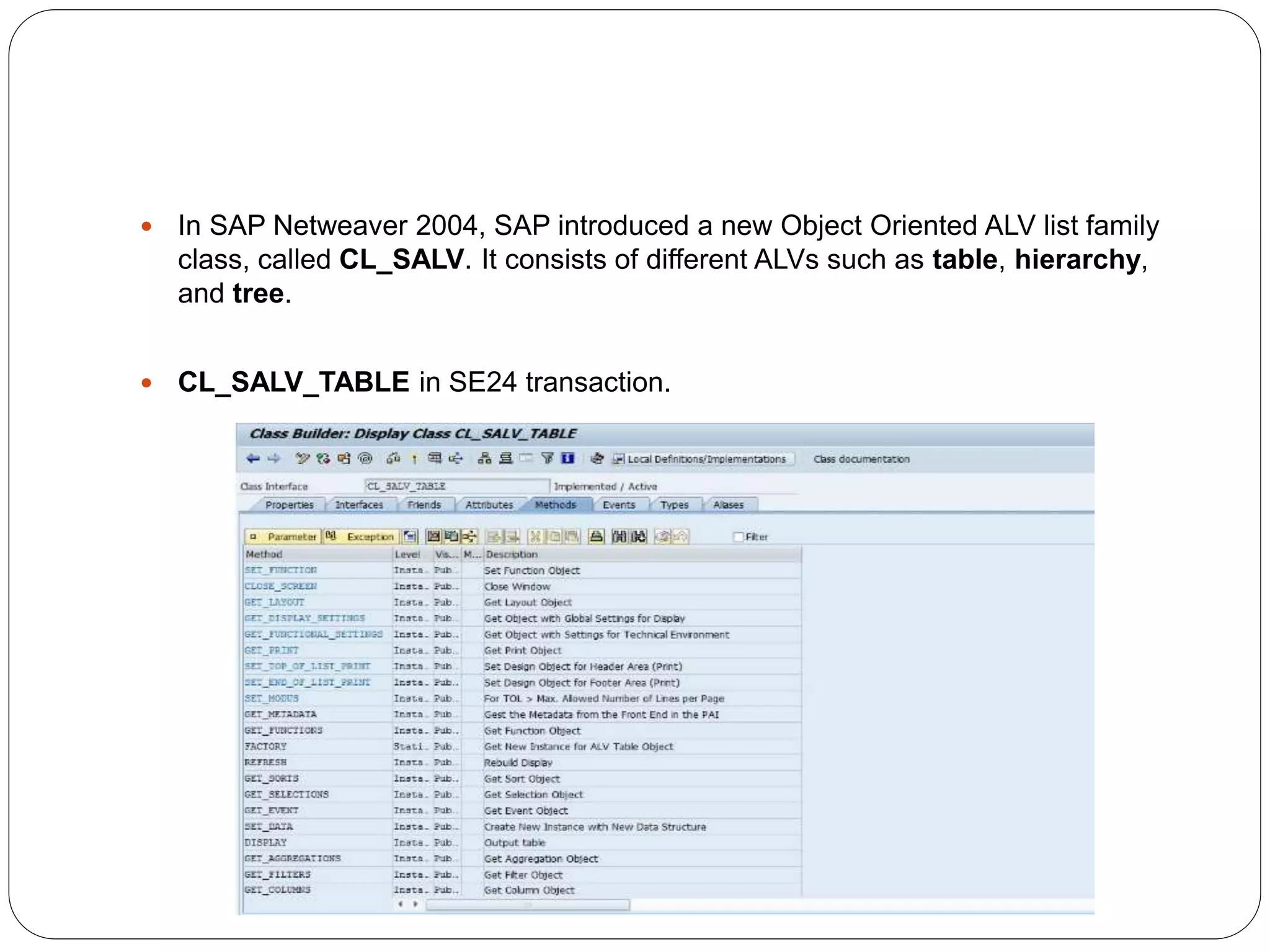
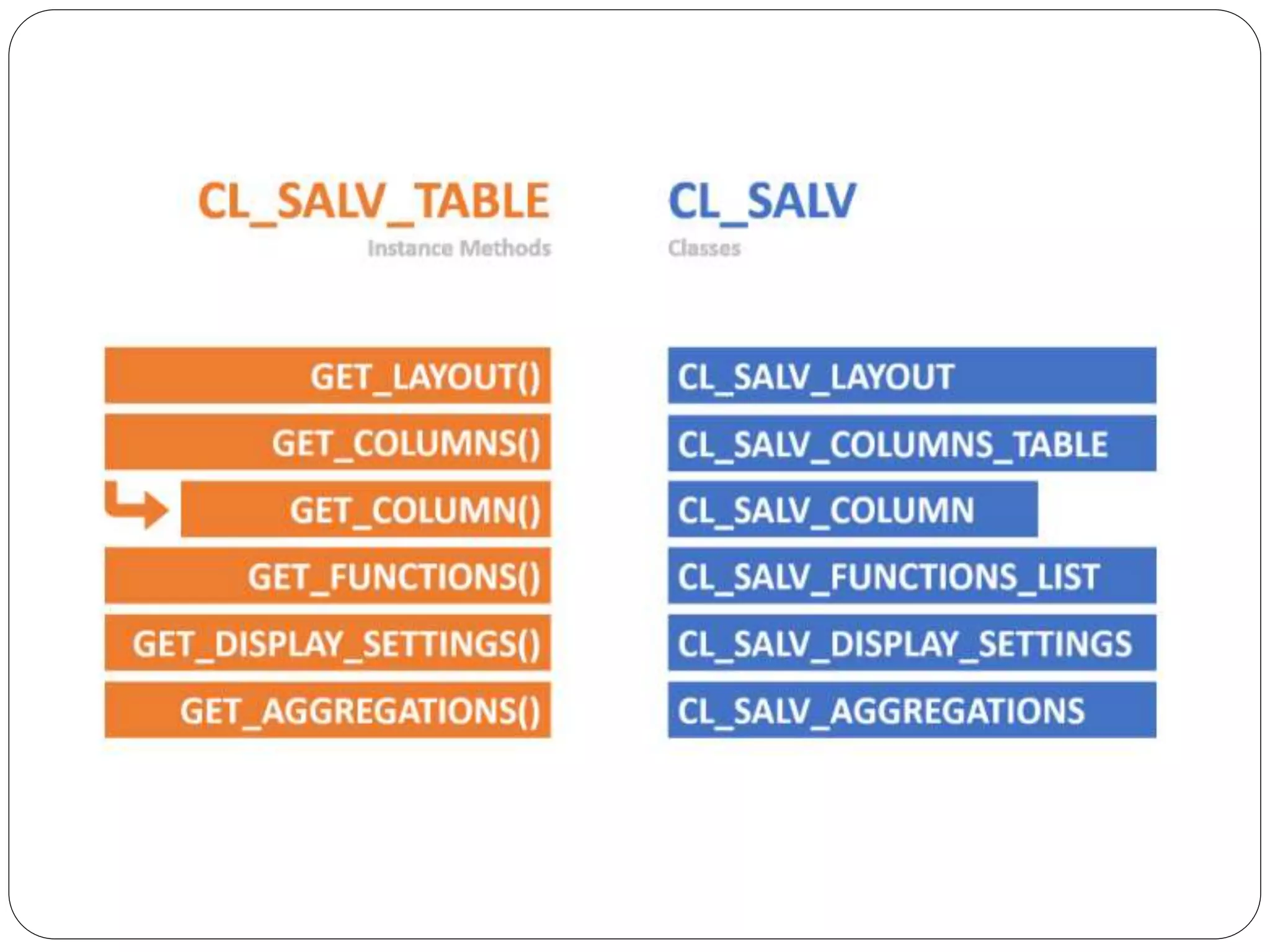
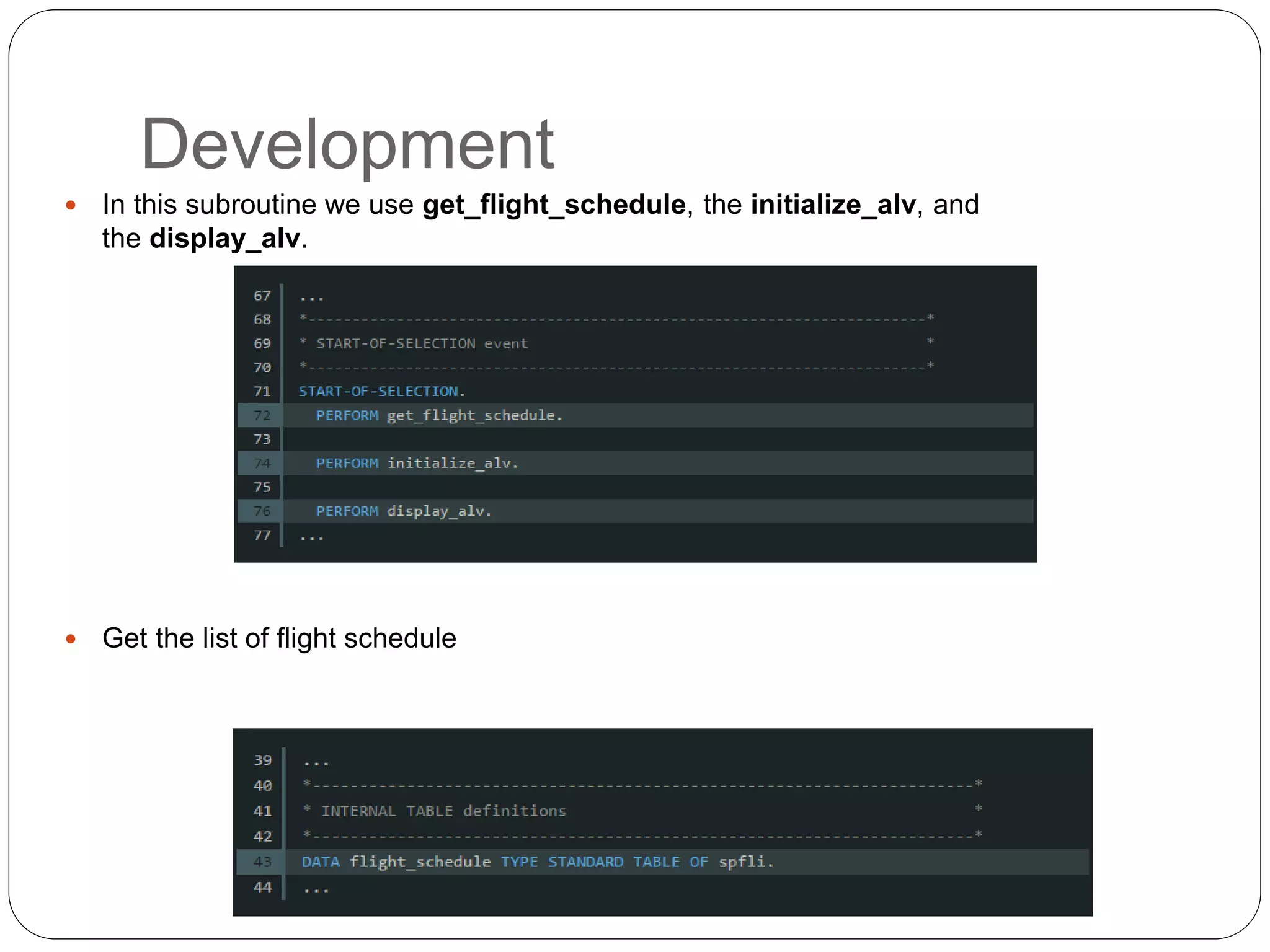
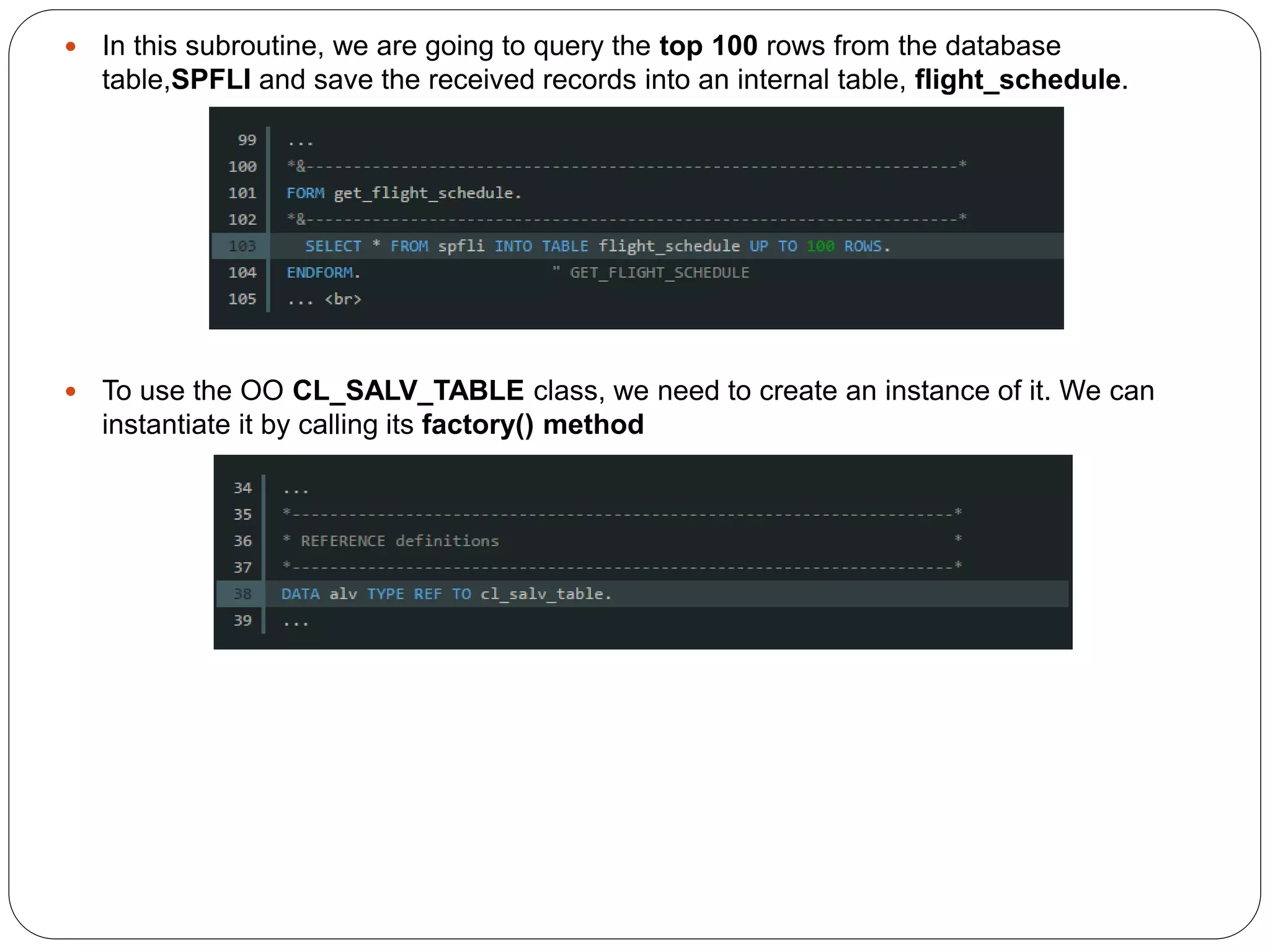
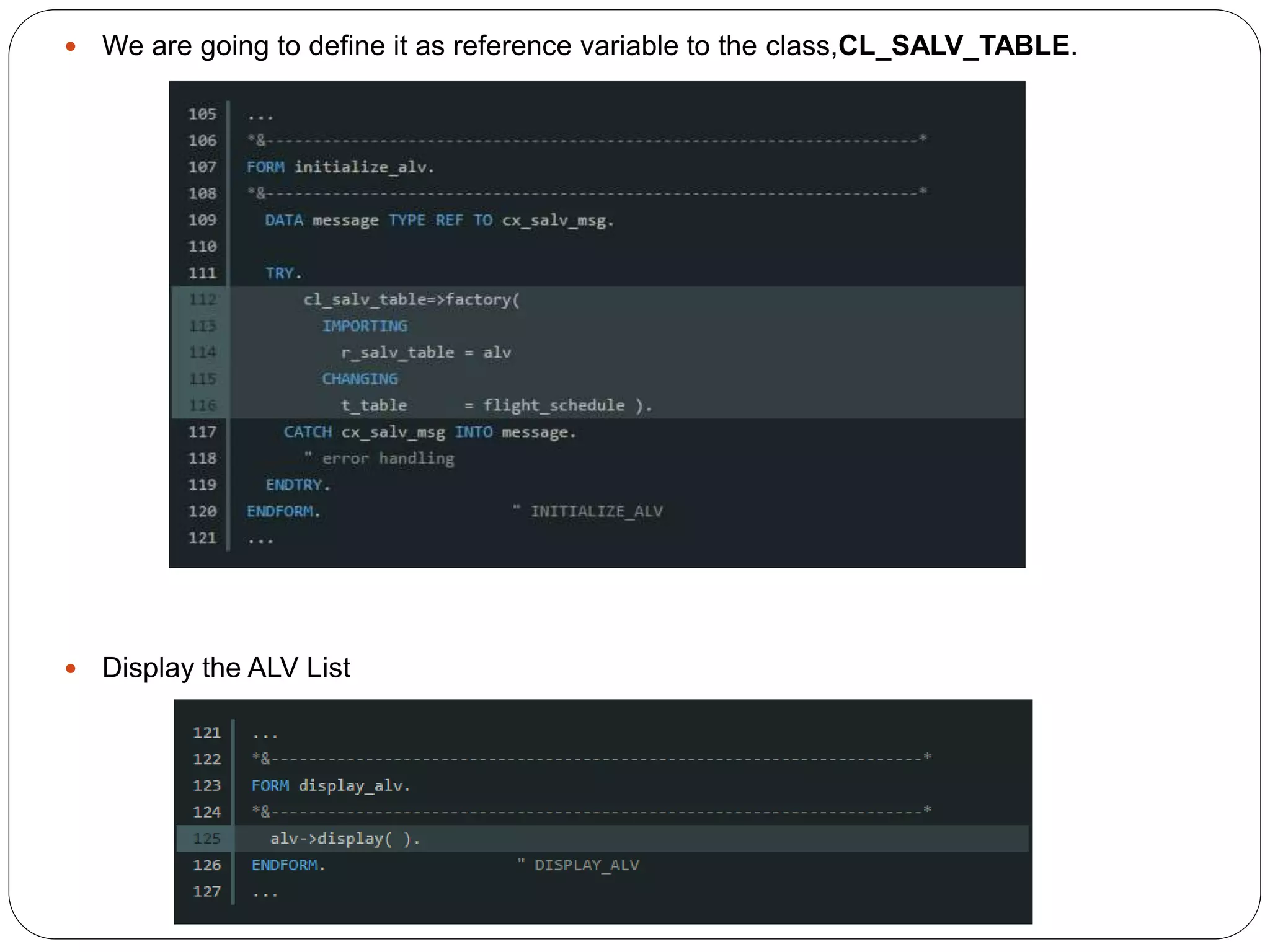
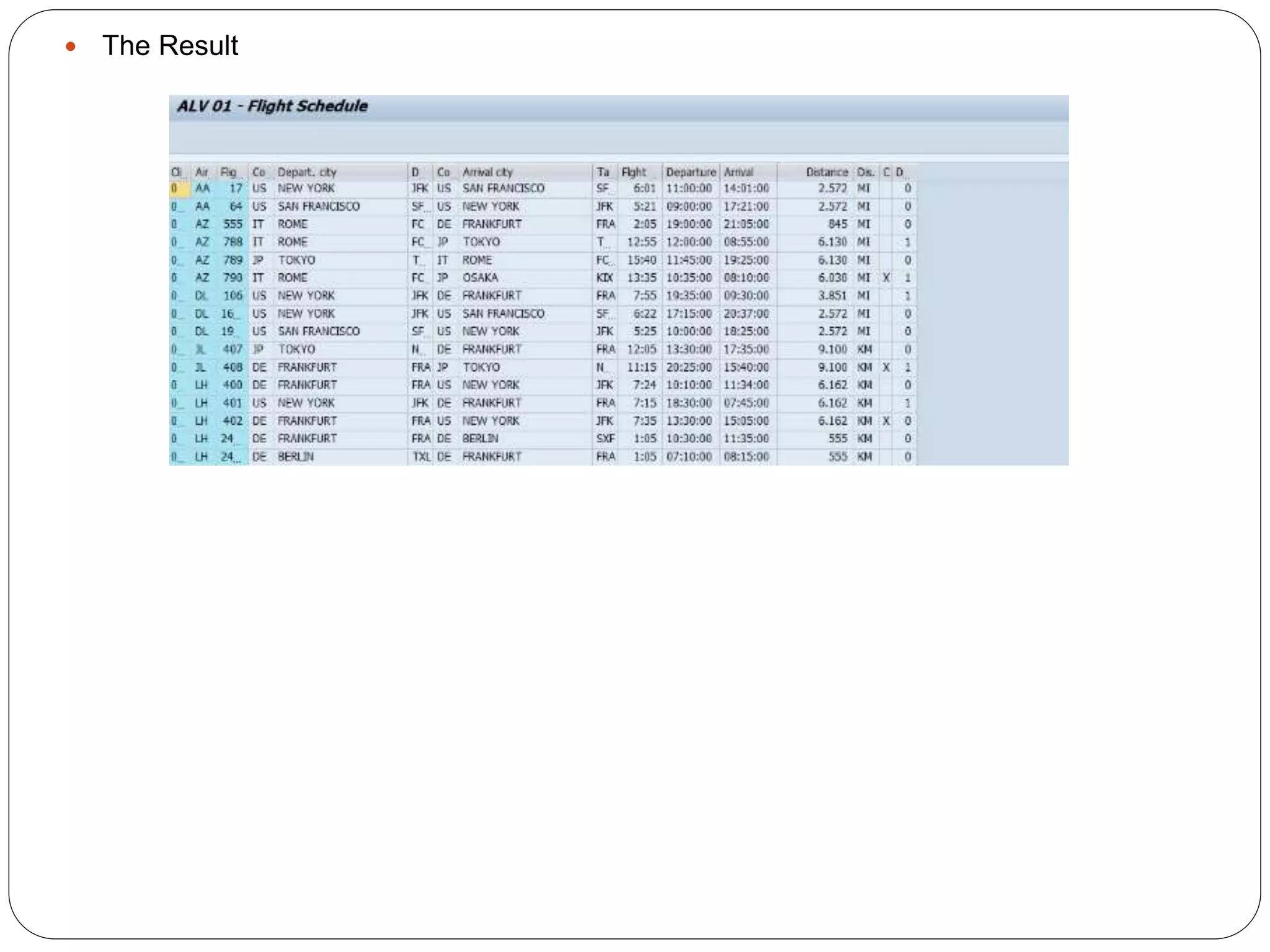
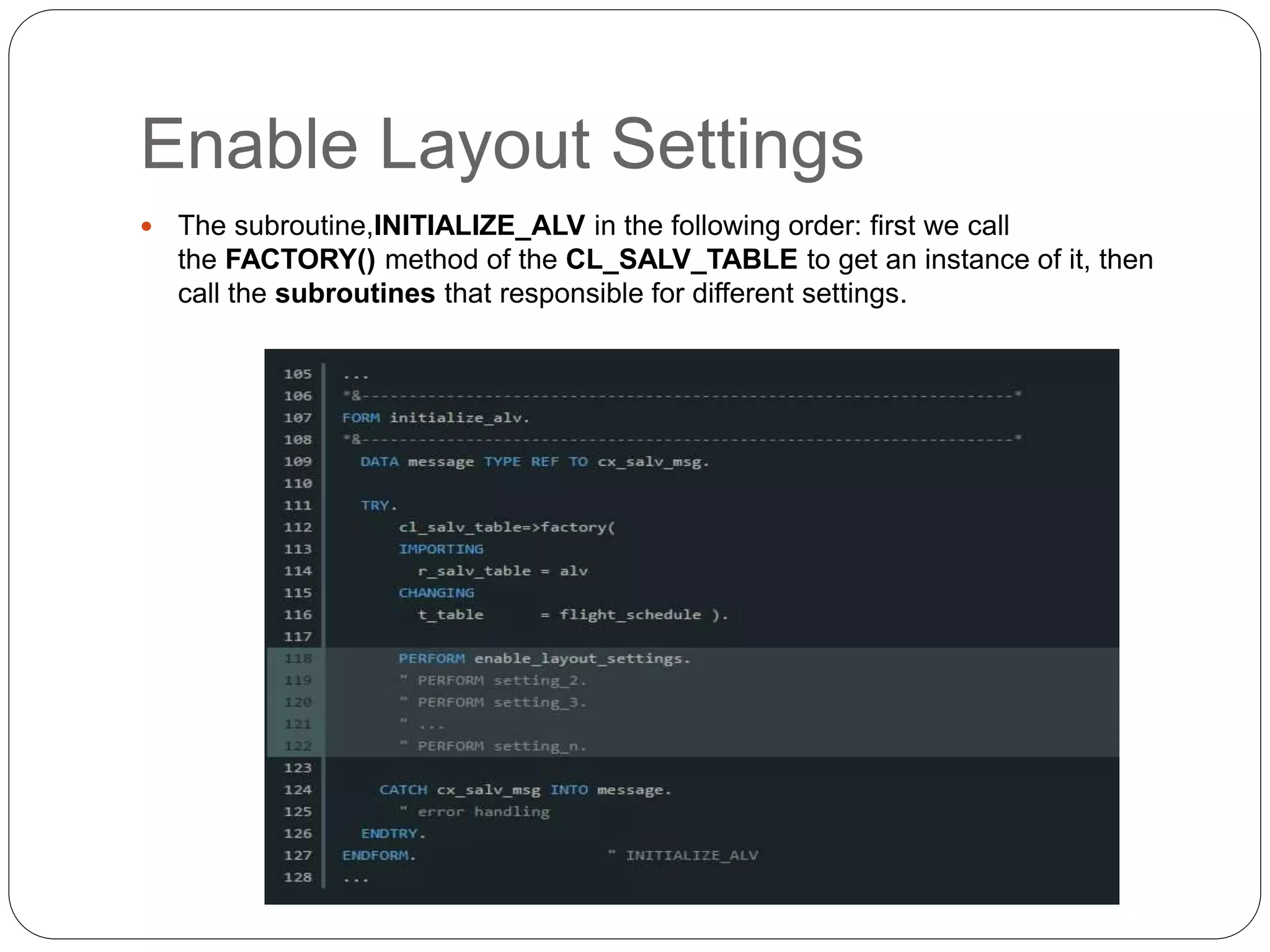
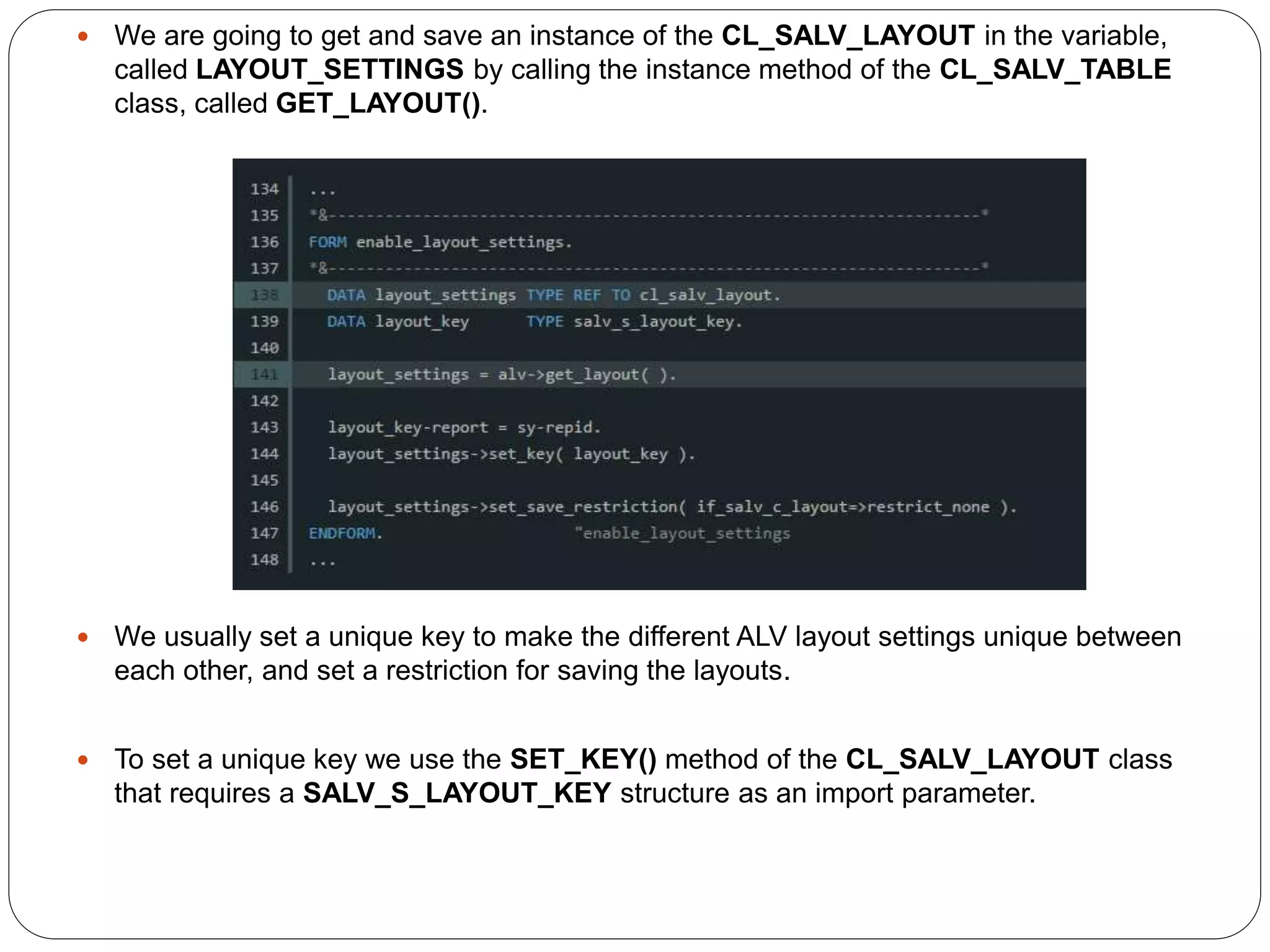
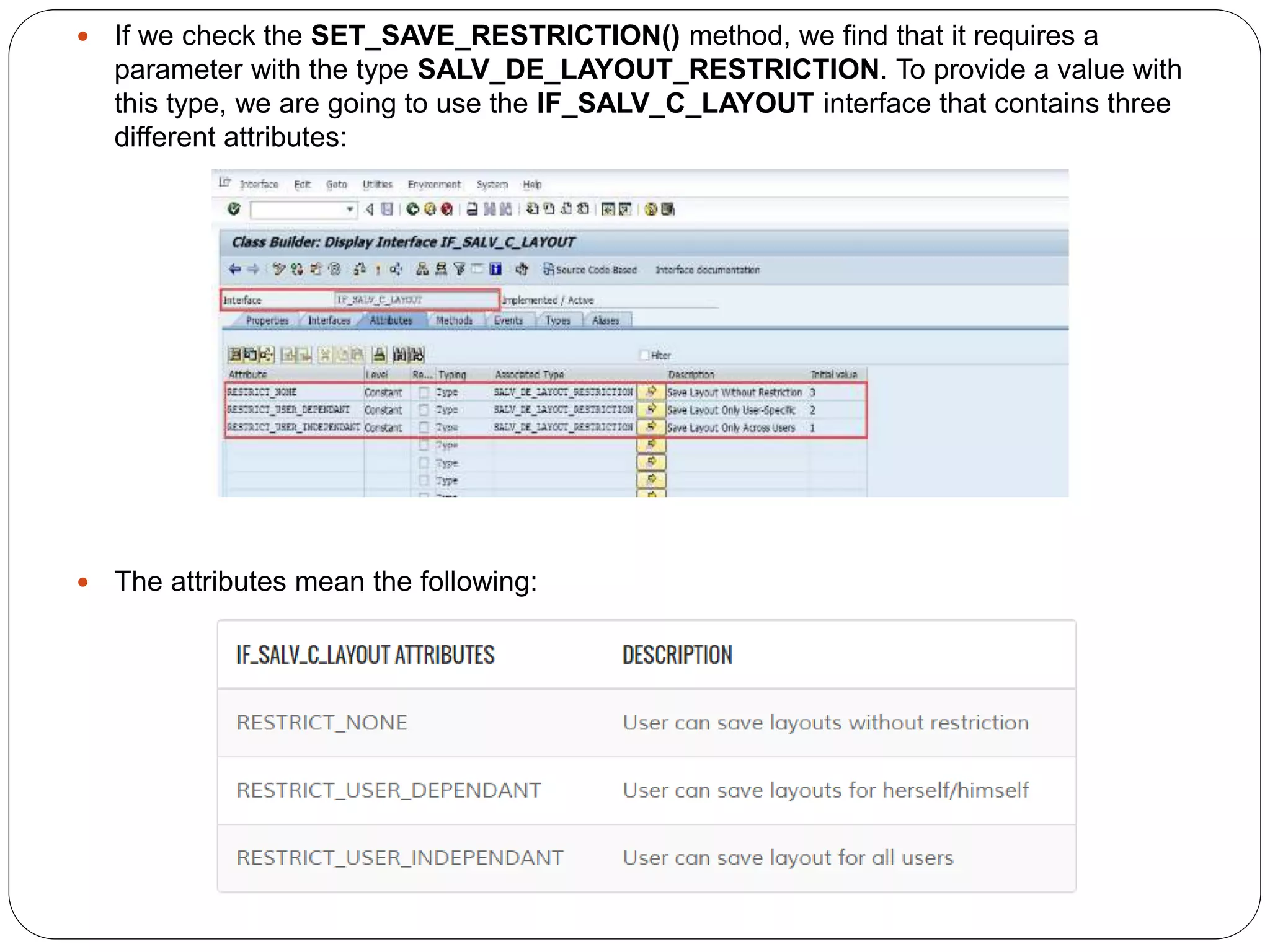
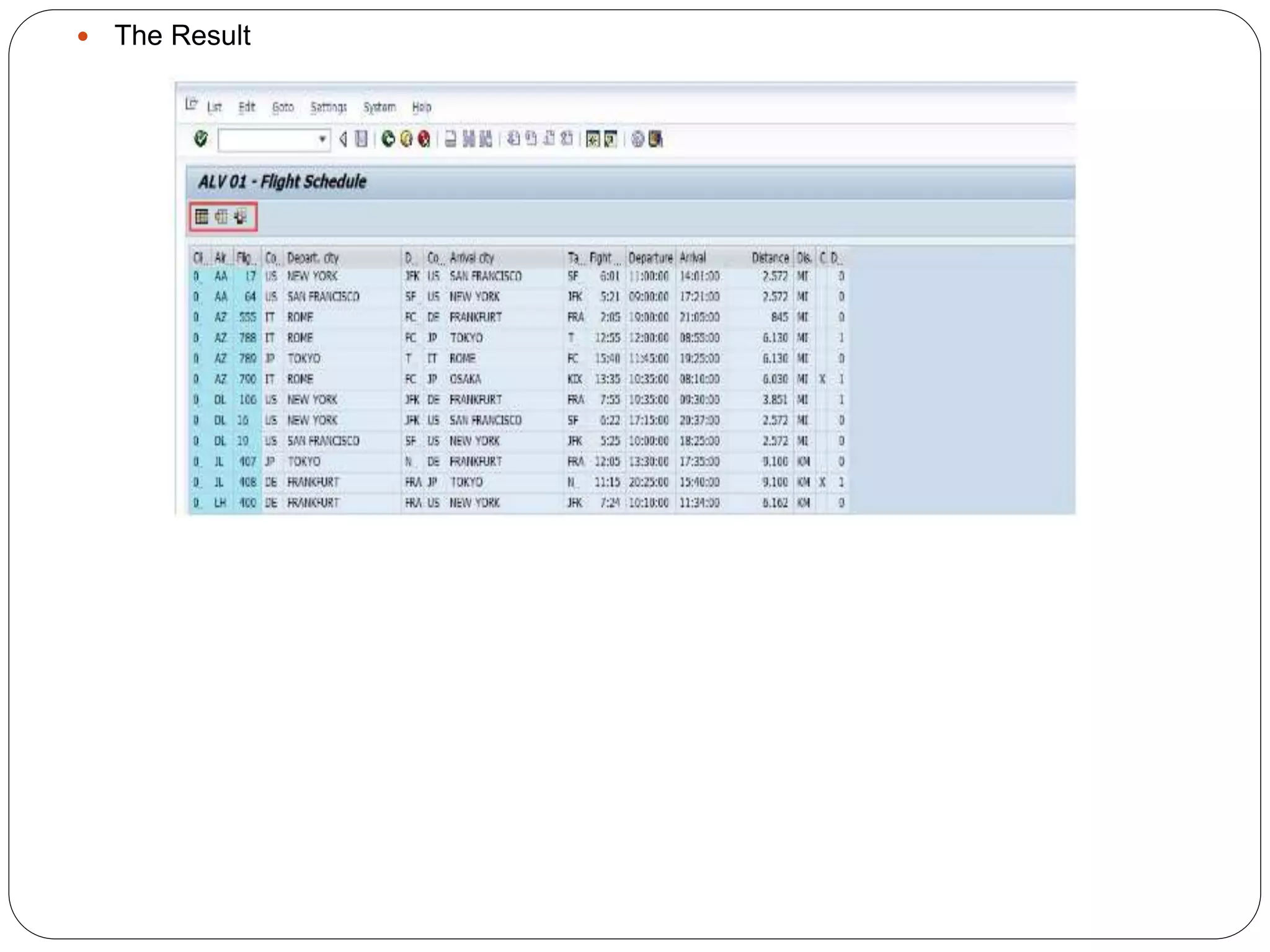
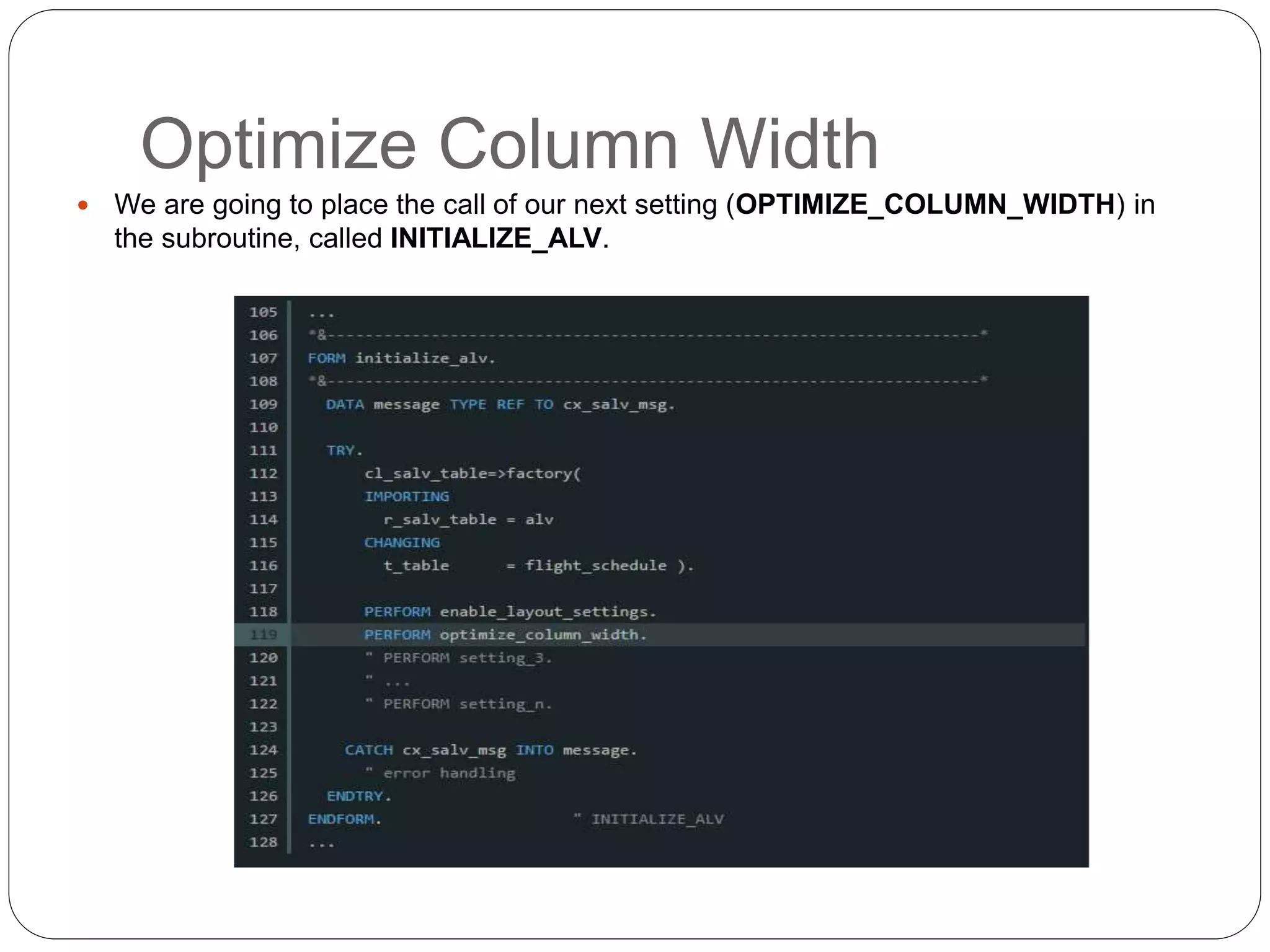
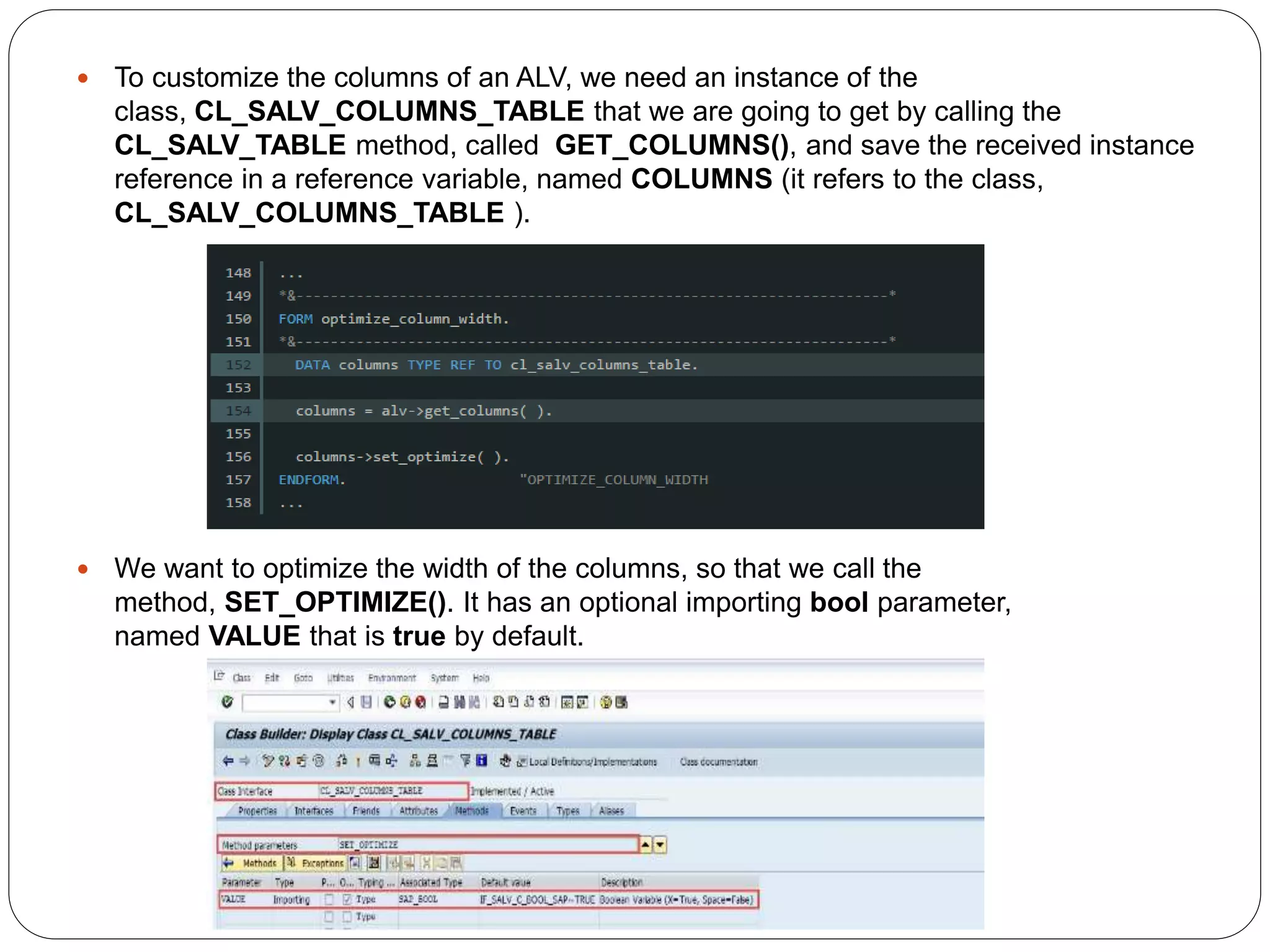
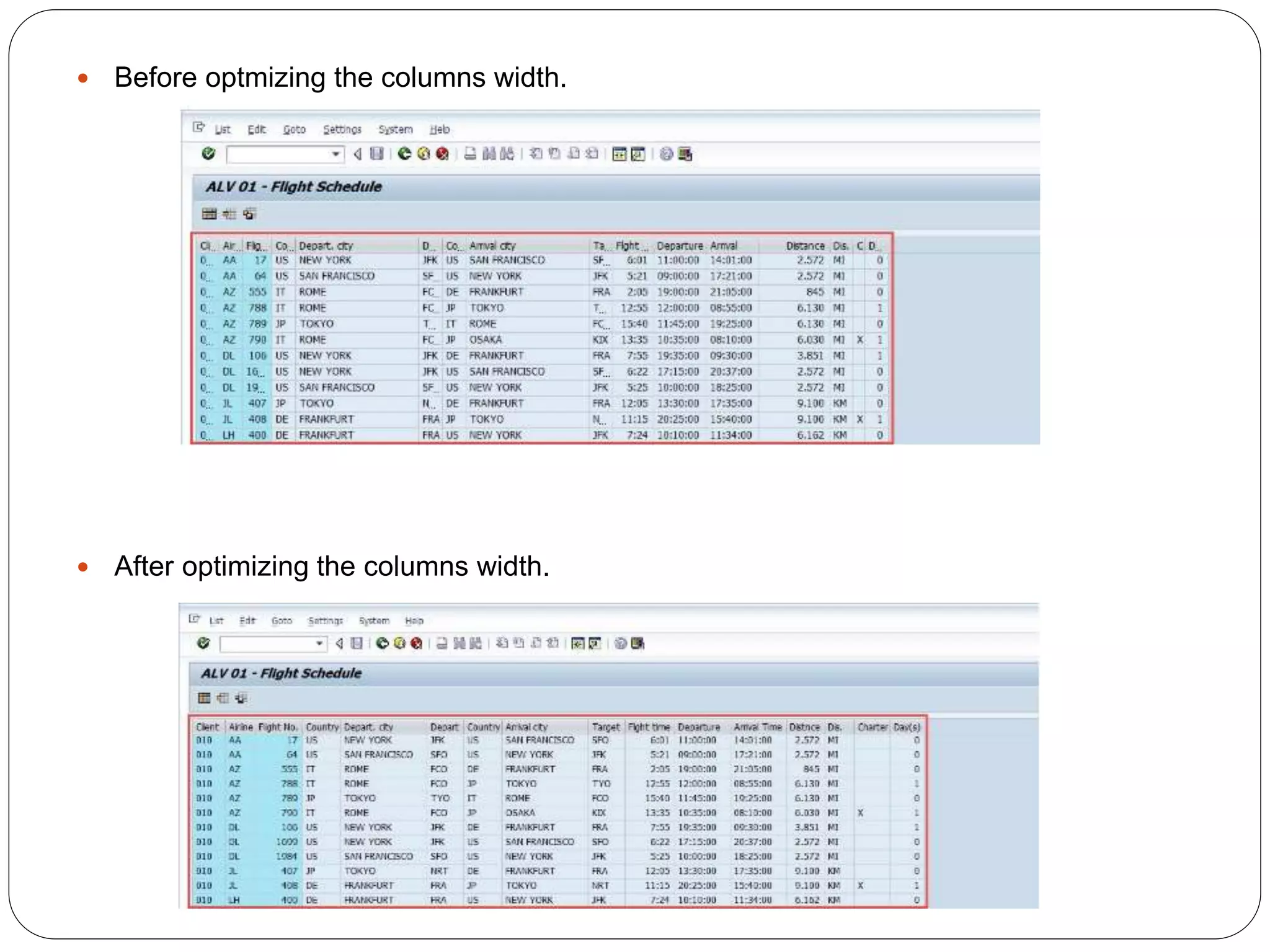
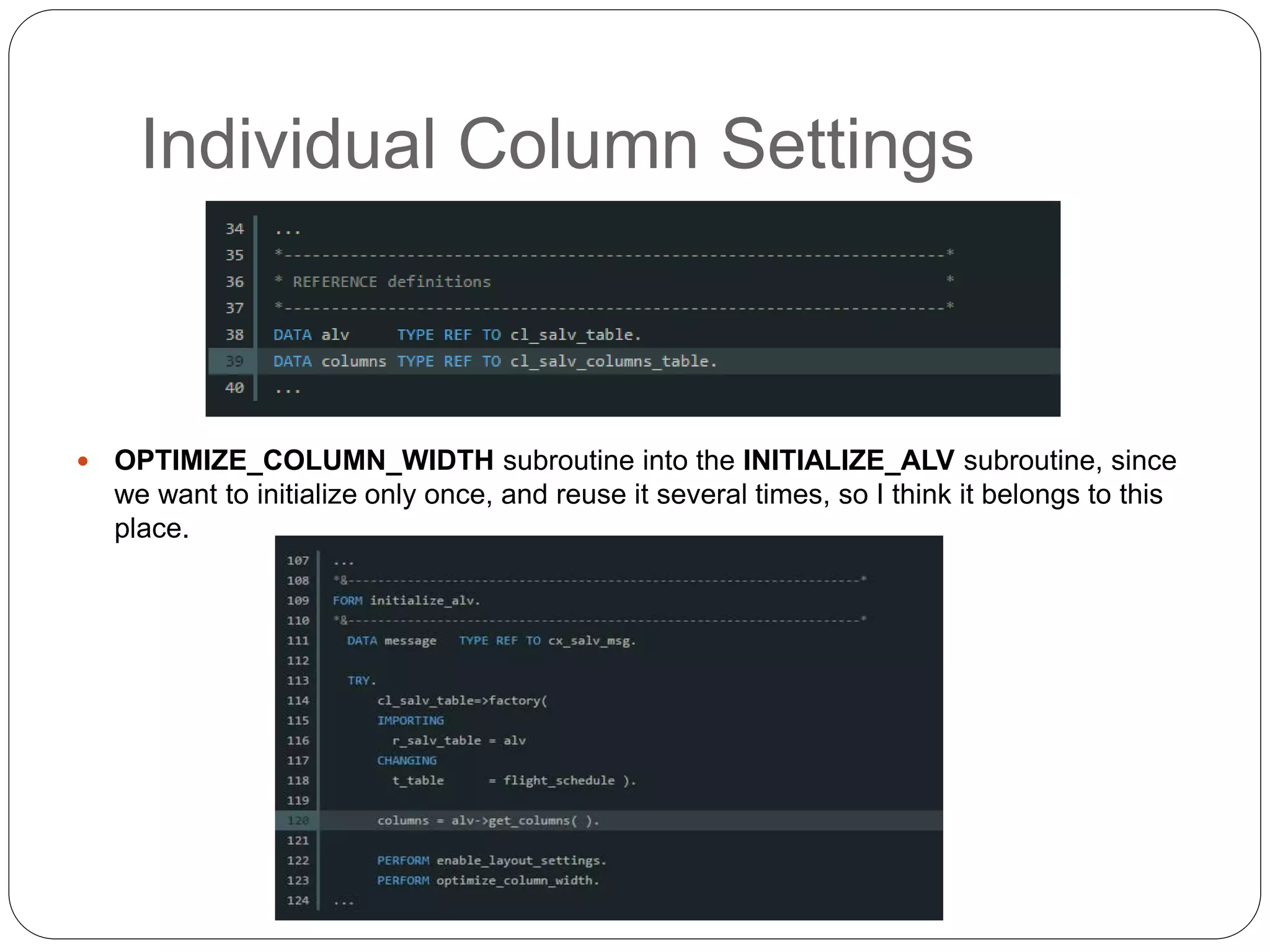
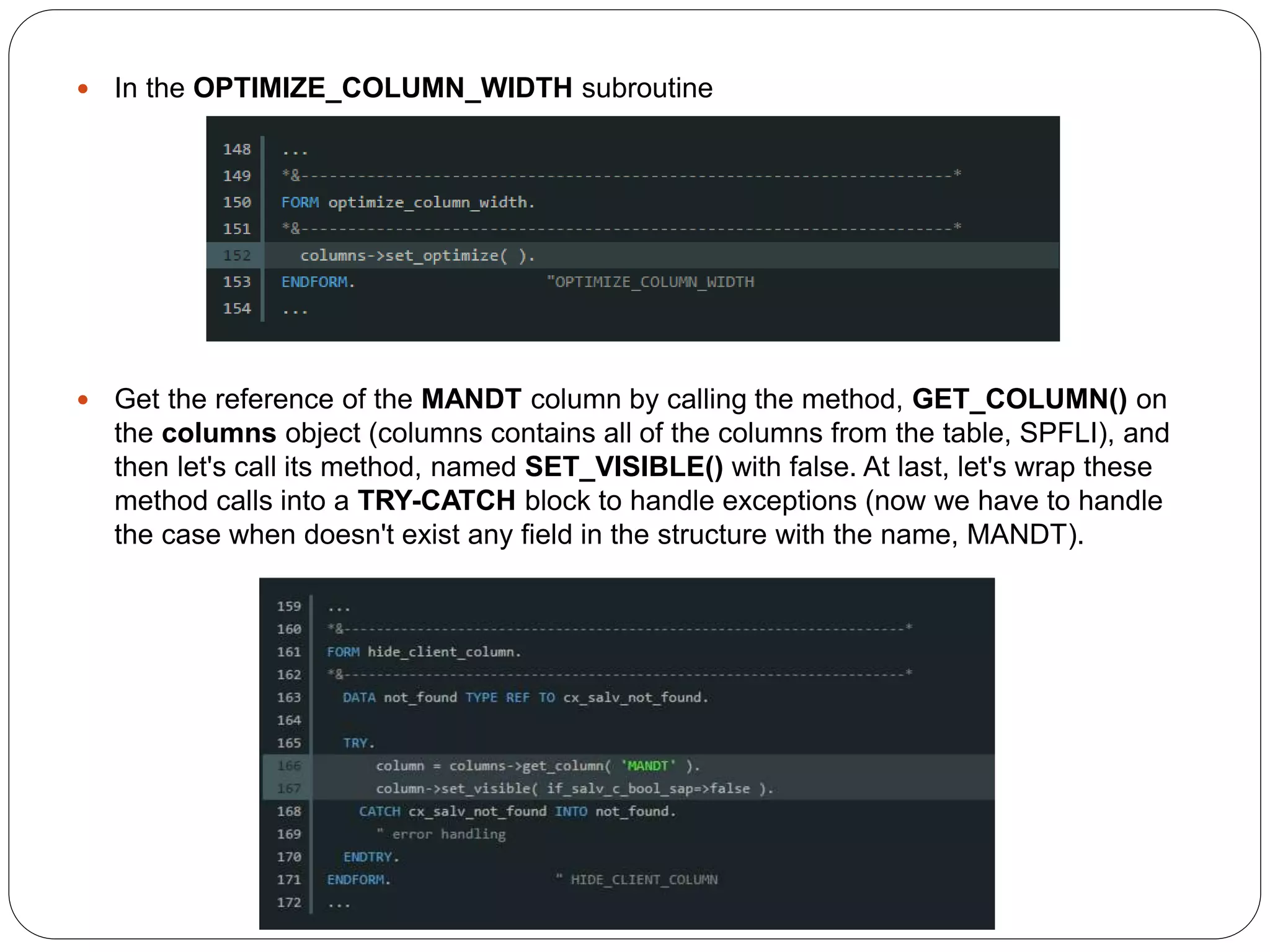
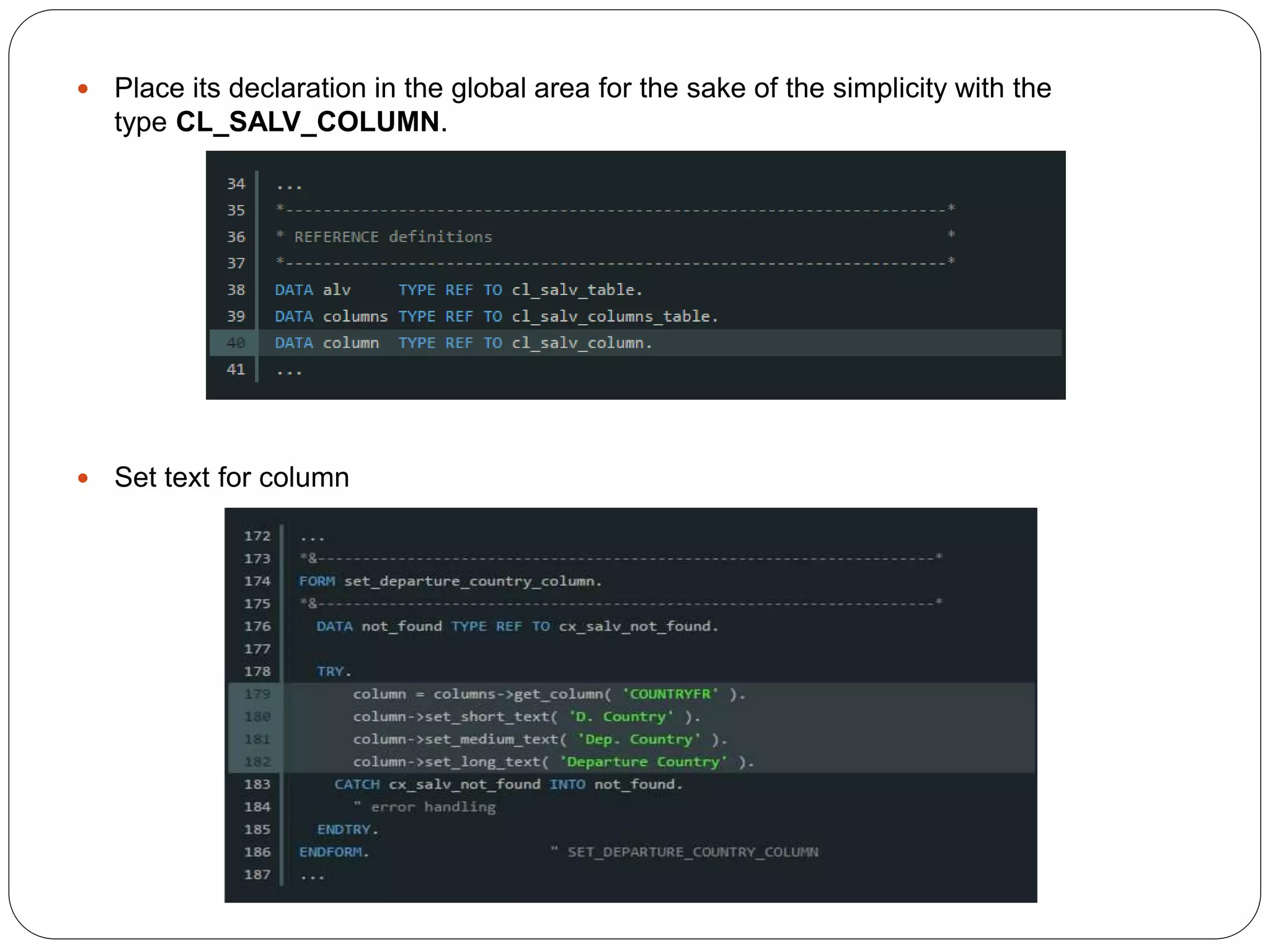
The document provides an overview of the SAP List Viewer (ALV), a tool that displays data in table format with functionalities for manipulation and export. It discusses the ALV's object-oriented model, including components like internal tables, field catalogs, containers, layout structures, and event handlers. Additionally, it details the creation and customization of ALV grids using classes such as cl_gui_alv_grid and cl_salv_table, highlighting essential methods for data display and layout optimization.