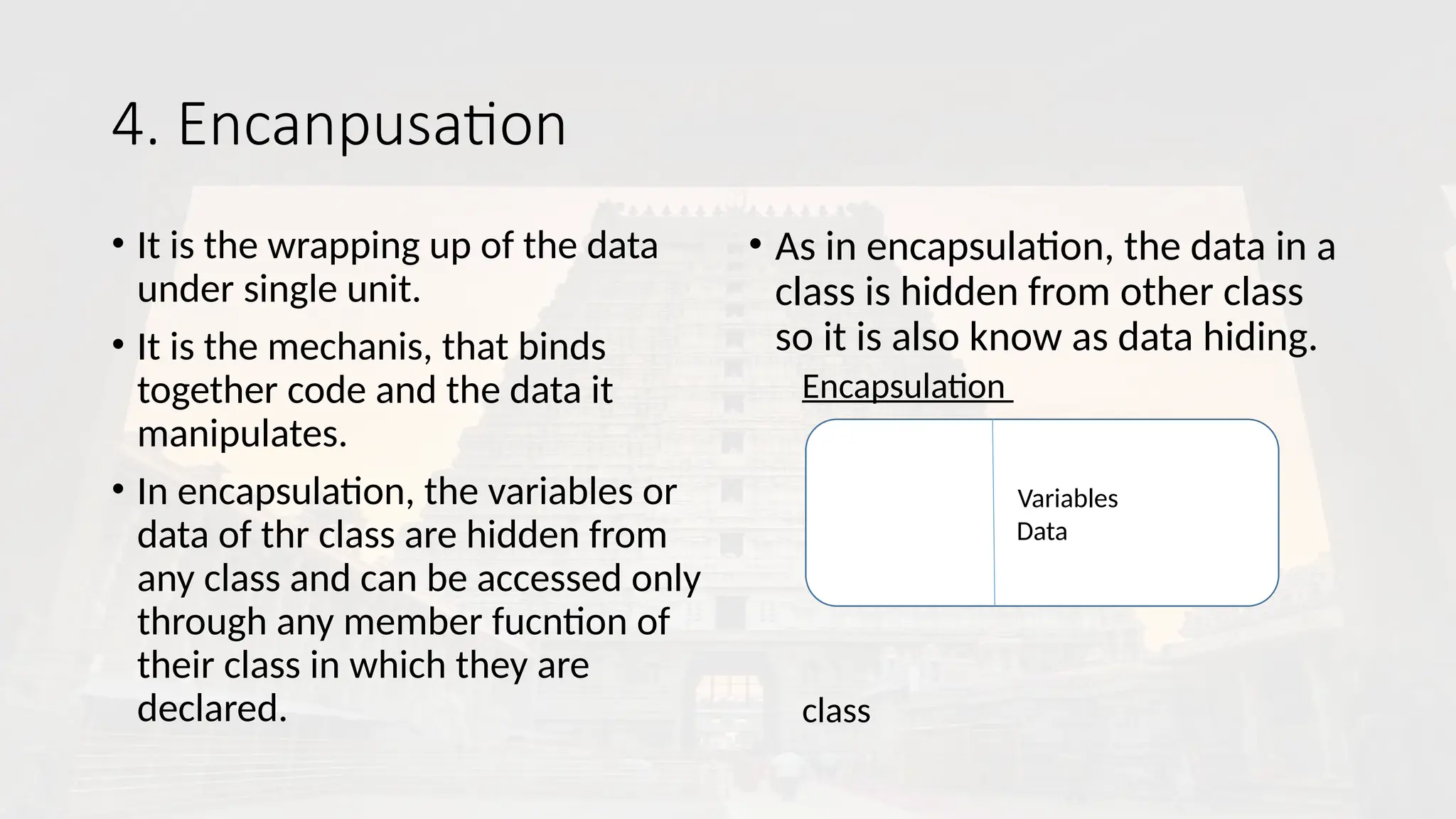
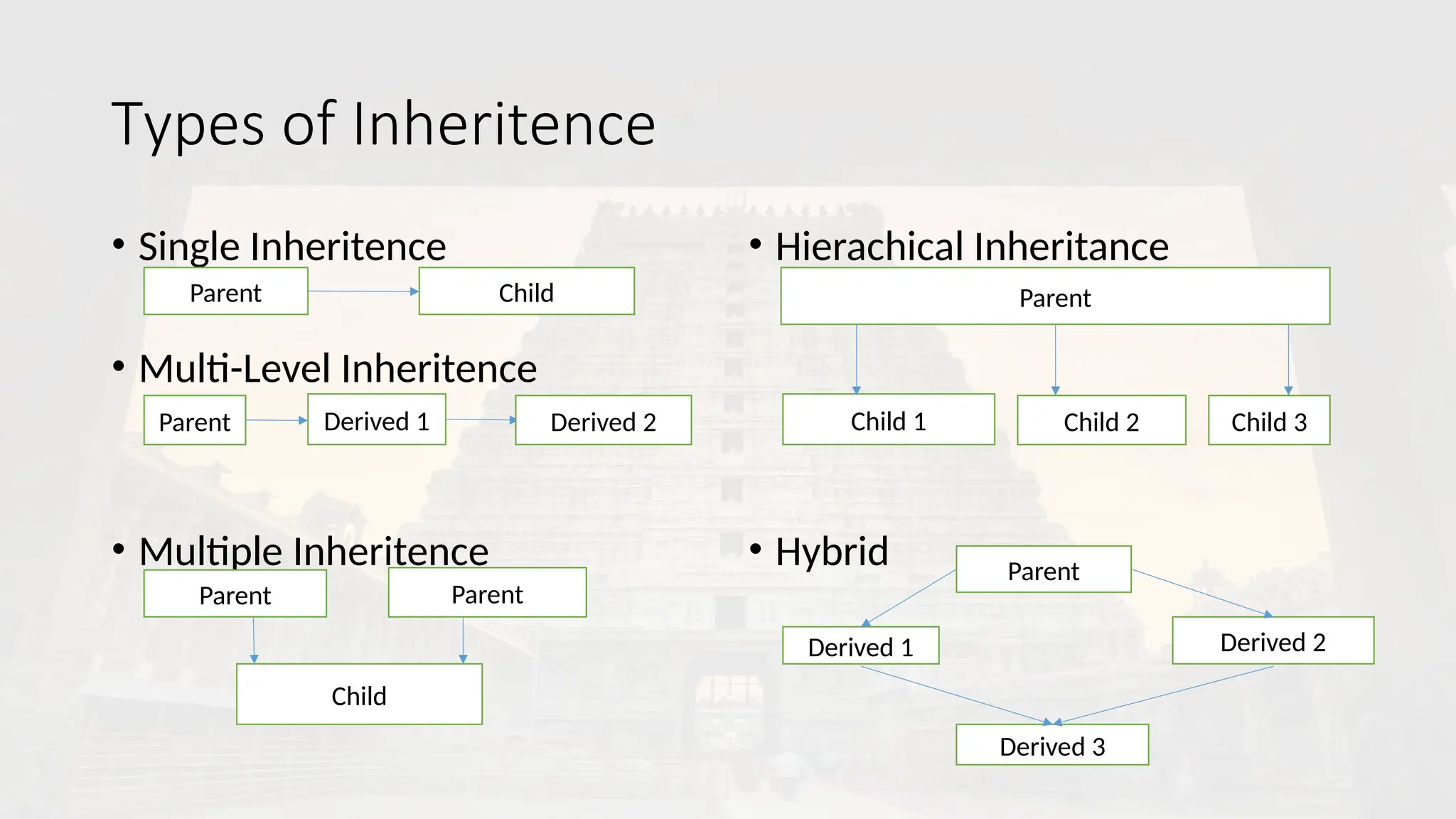
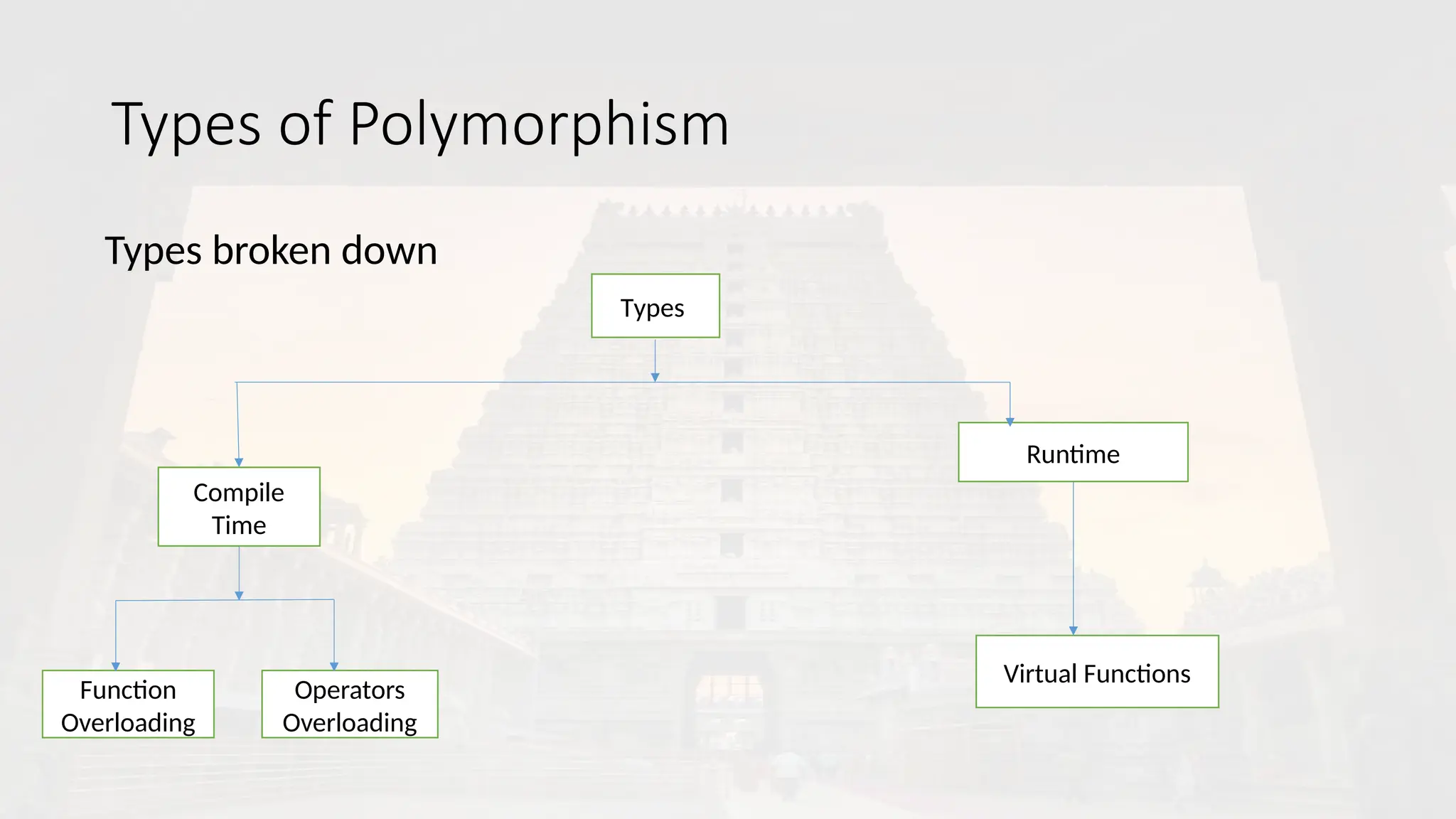
It refers to language that uses object in programming. OOP aims to implement real world entities like inheritance, hiding, polymorphism in programming.
OOP aims to bind together data and functions that operate on them so that no other part of code can access this data except function.