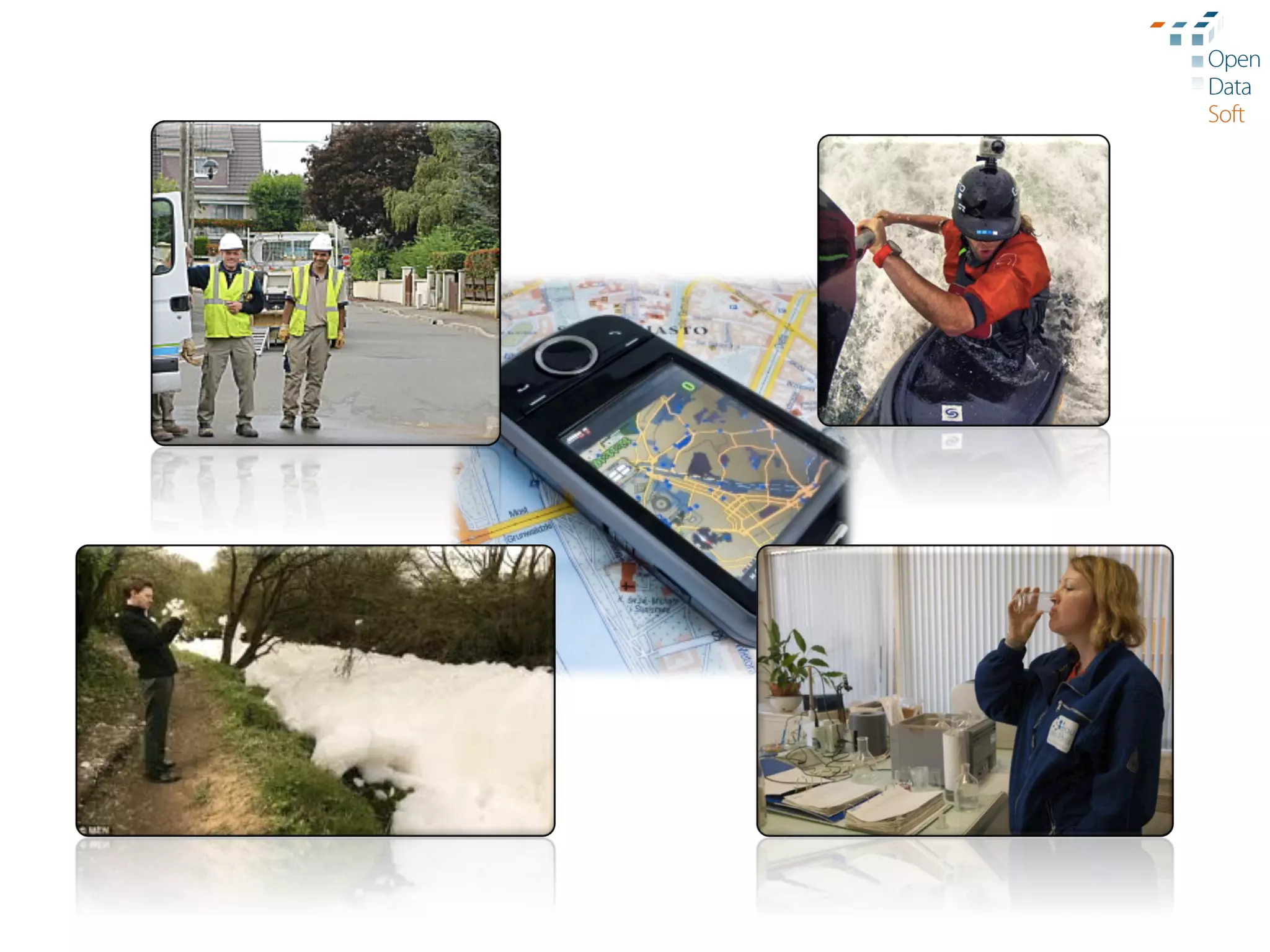
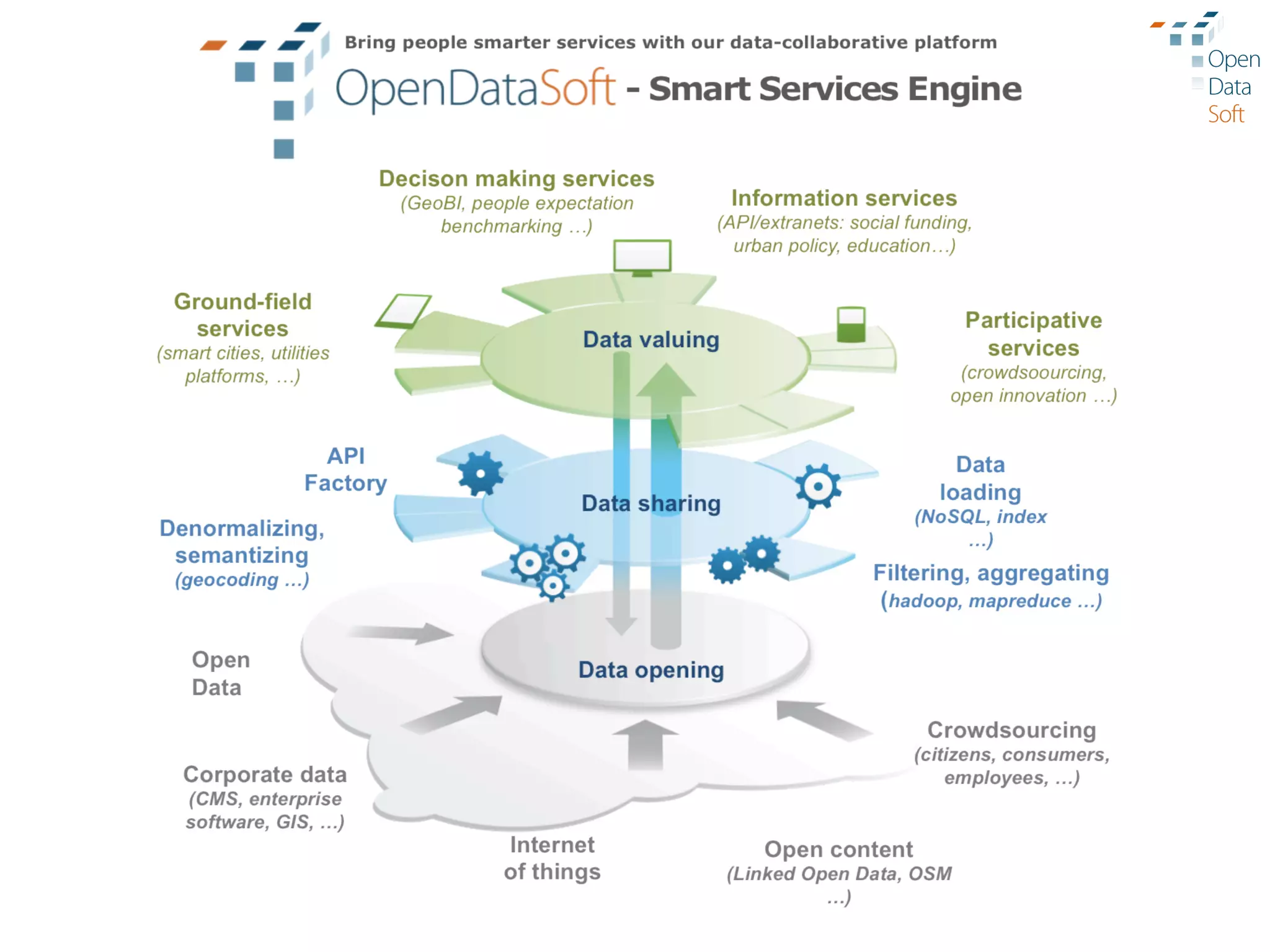
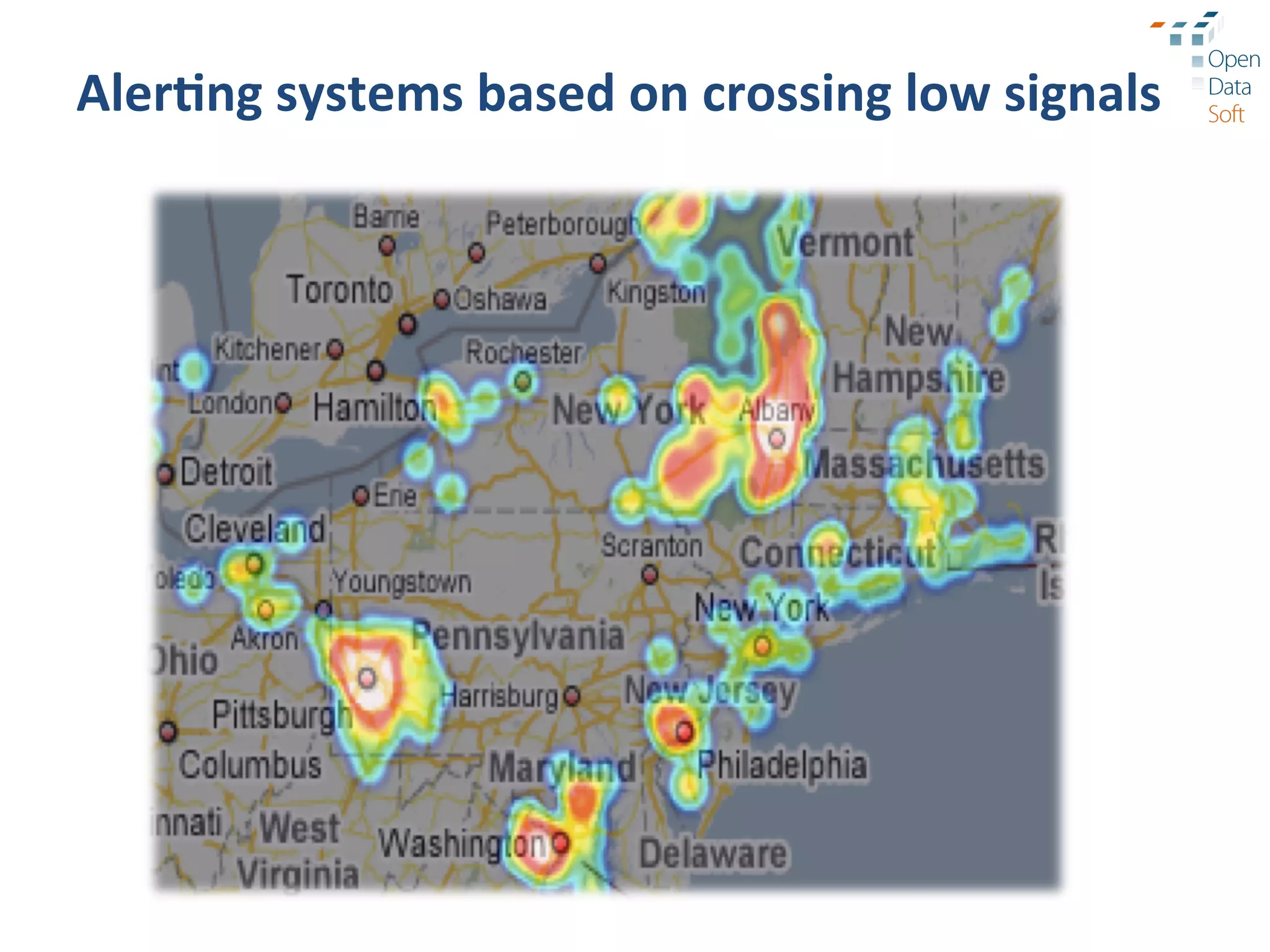
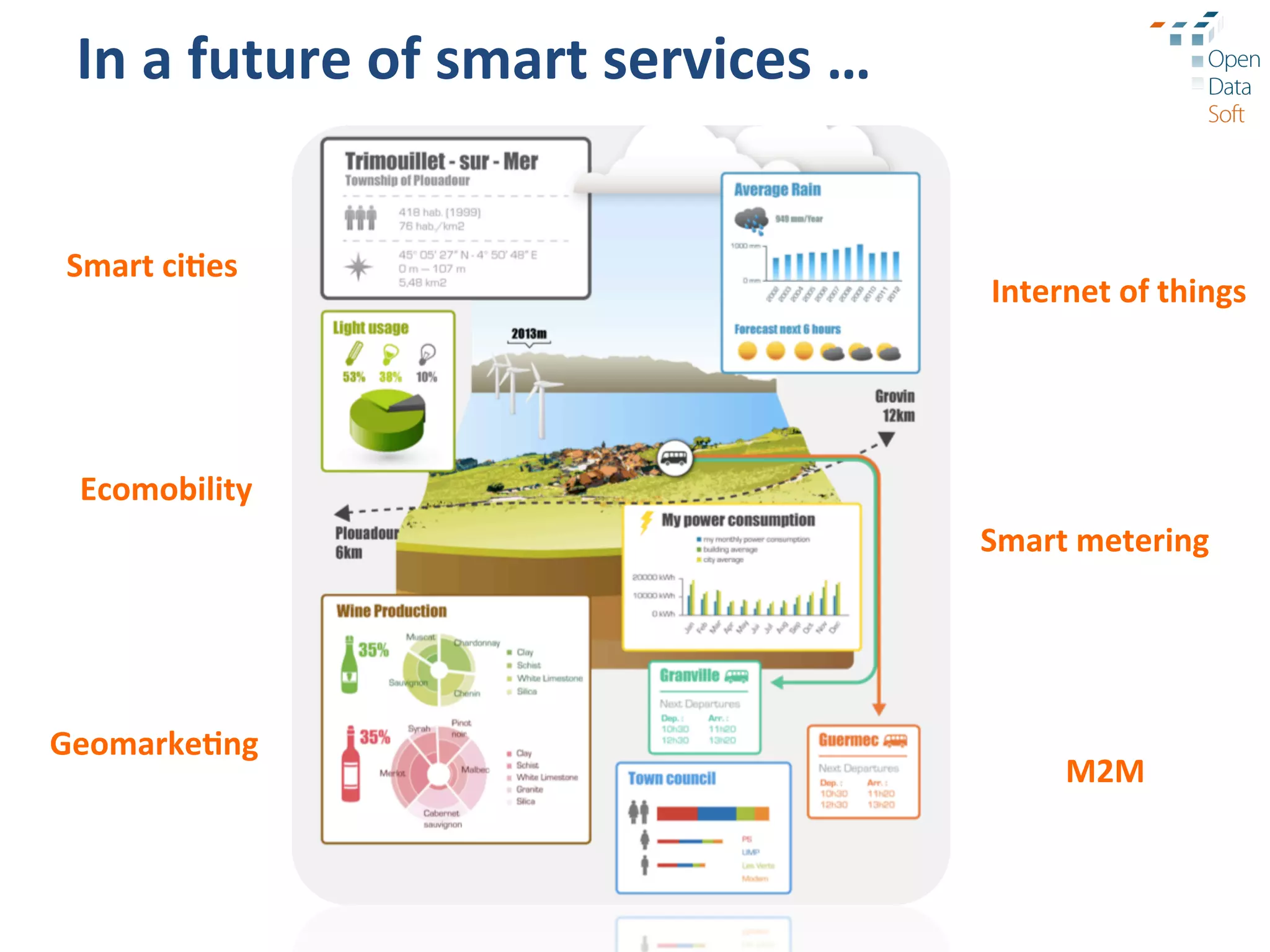
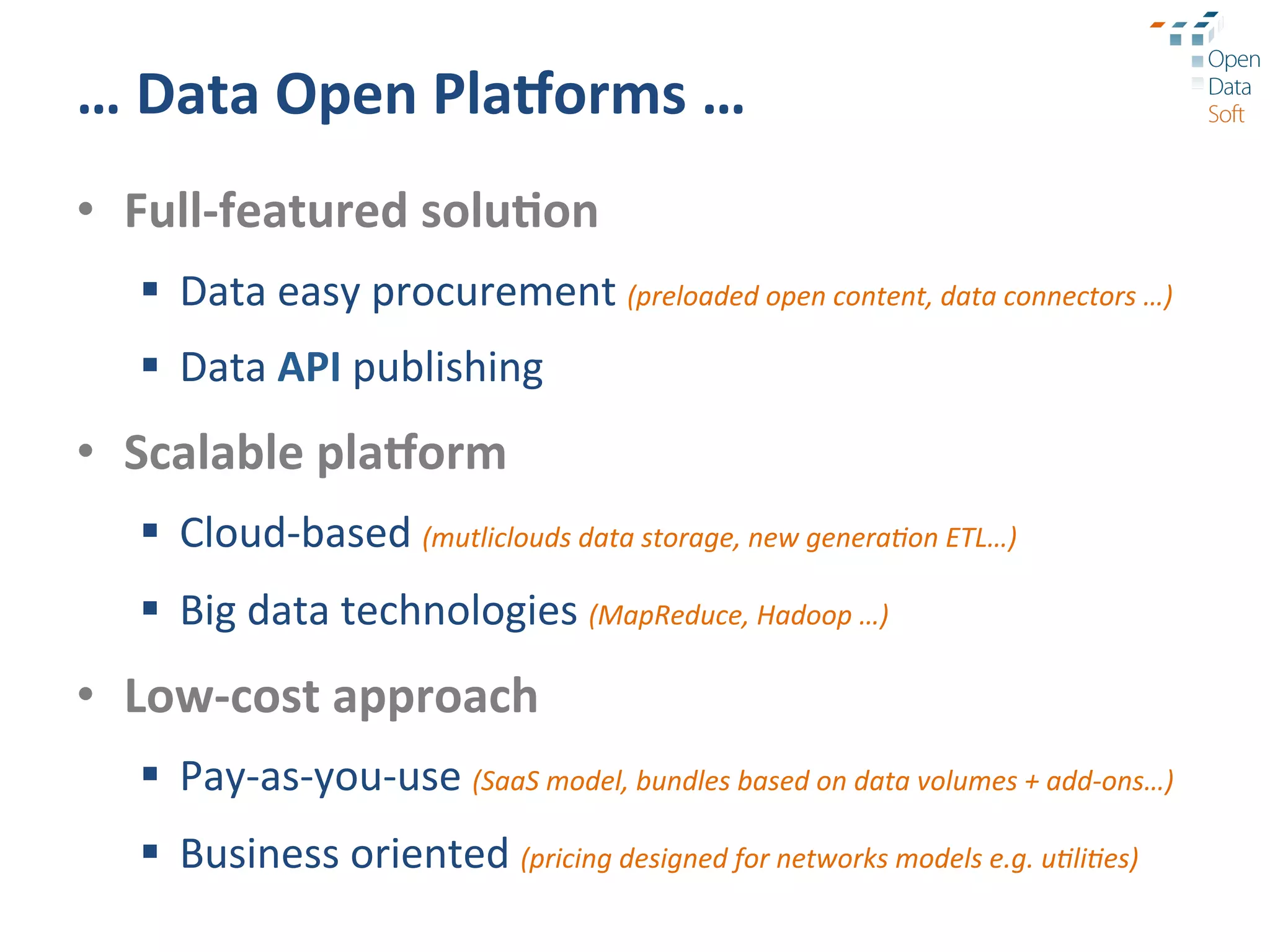
The document discusses the importance and advantages of open data platforms, emphasizing their role in driving innovation and enabling data-centric services. It highlights the integration of big data technologies and cloud computing to enhance data management, access, and governance. Additionally, it outlines the potential for new business models and improved decision-making through accessible data processes and APIs.