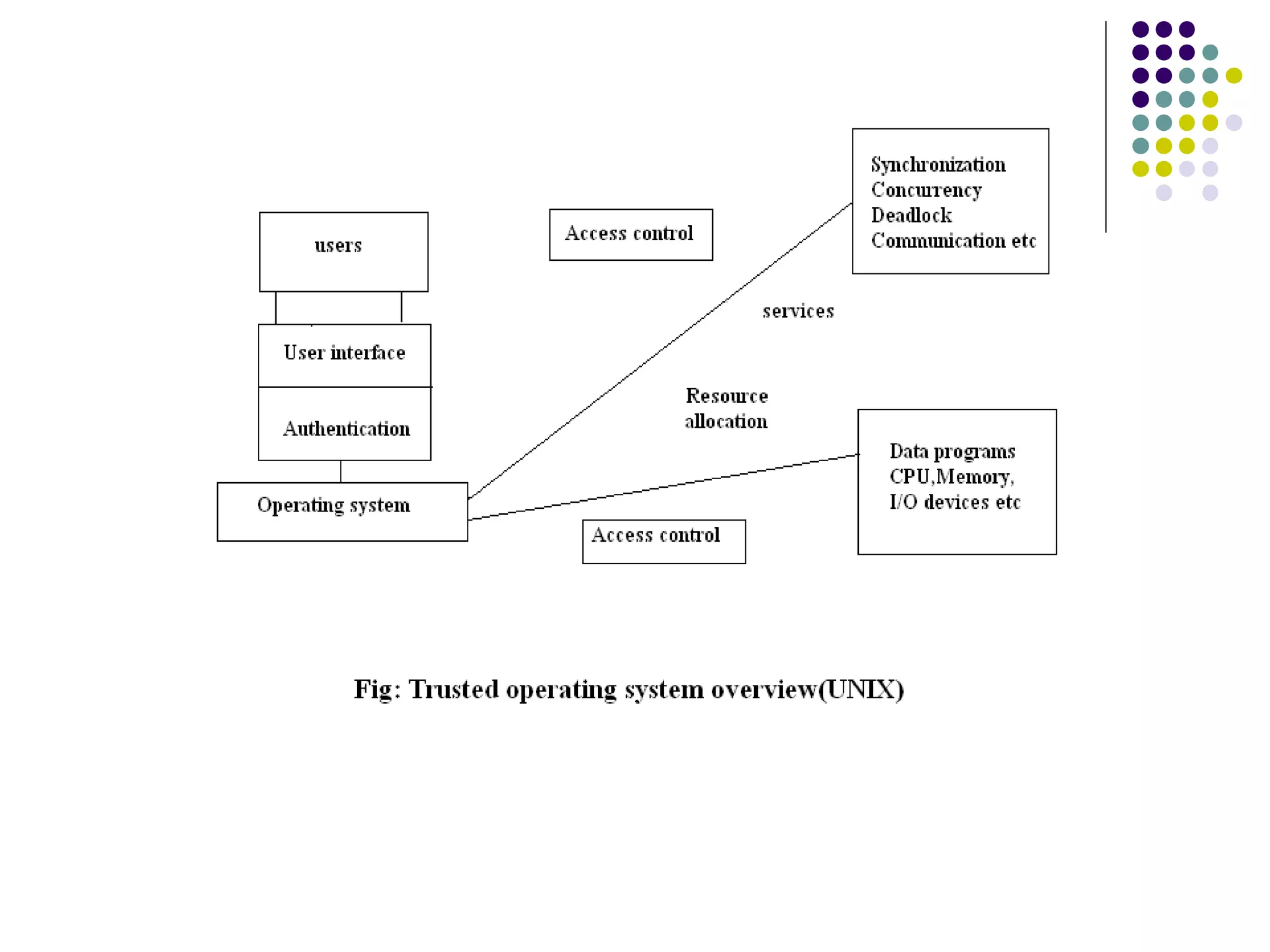
Vulnerabilities exist in operating systems like Linux, UNIX and Windows. A vulnerability is a weakness that allows an attacker to compromise a system's security. Vulnerabilities occur at the intersection of a system flaw, an attacker's access to the flaw, and their ability to exploit it. Common UNIX vulnerabilities include setuid problems, trojan horses and terminal troubles. Windows is vulnerable to password issues, peer-to-peer file sharing exploits, and Outlook/Outlook Express bugs. Linux has flaws like missing permission checks, uninitialized data, and memory mismanagement. Control is important for operating systems to balance robustness, predictability and efficiency. The trusted computing base (TCB) aims to enforce security by containing all elements