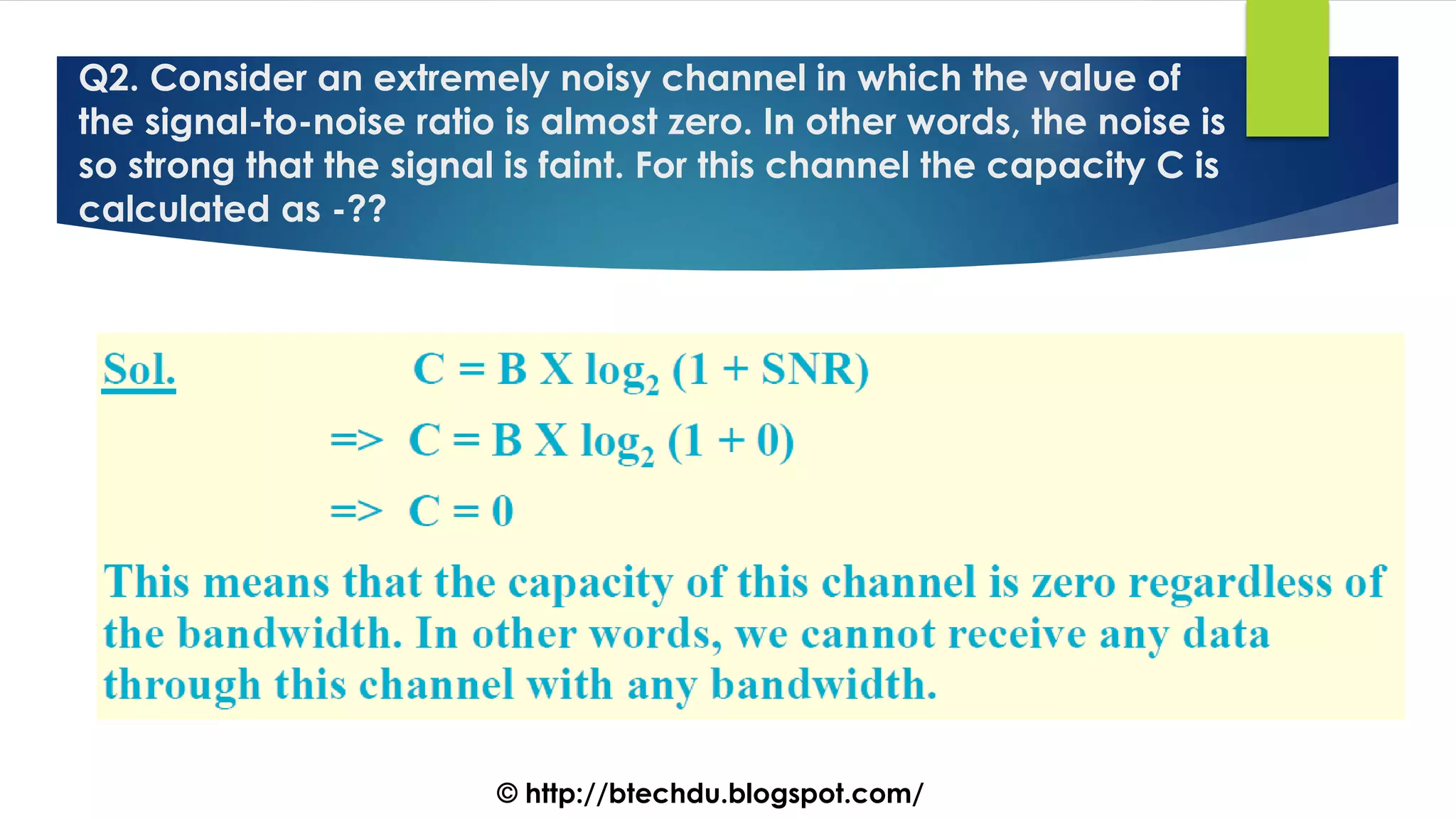
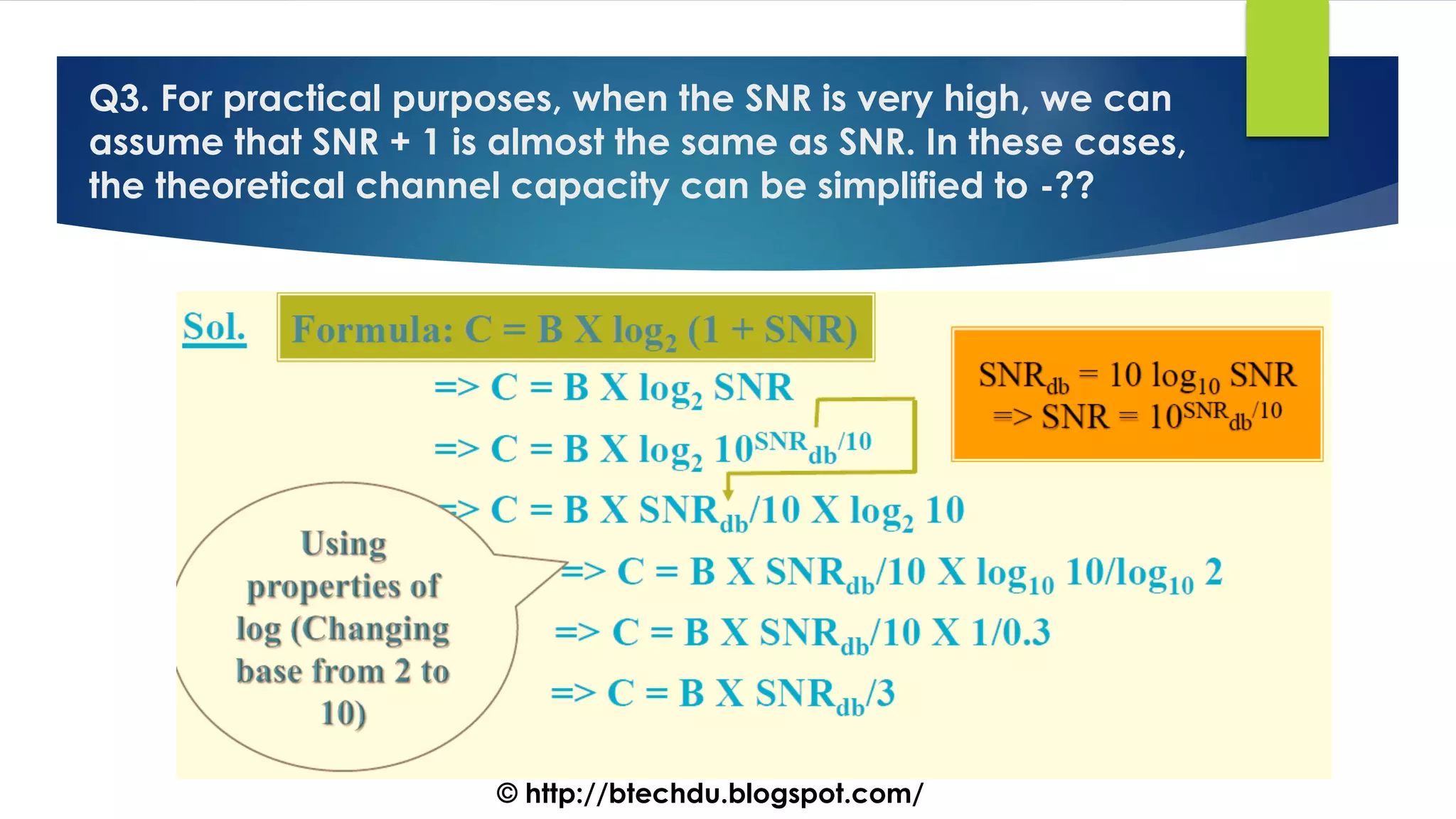
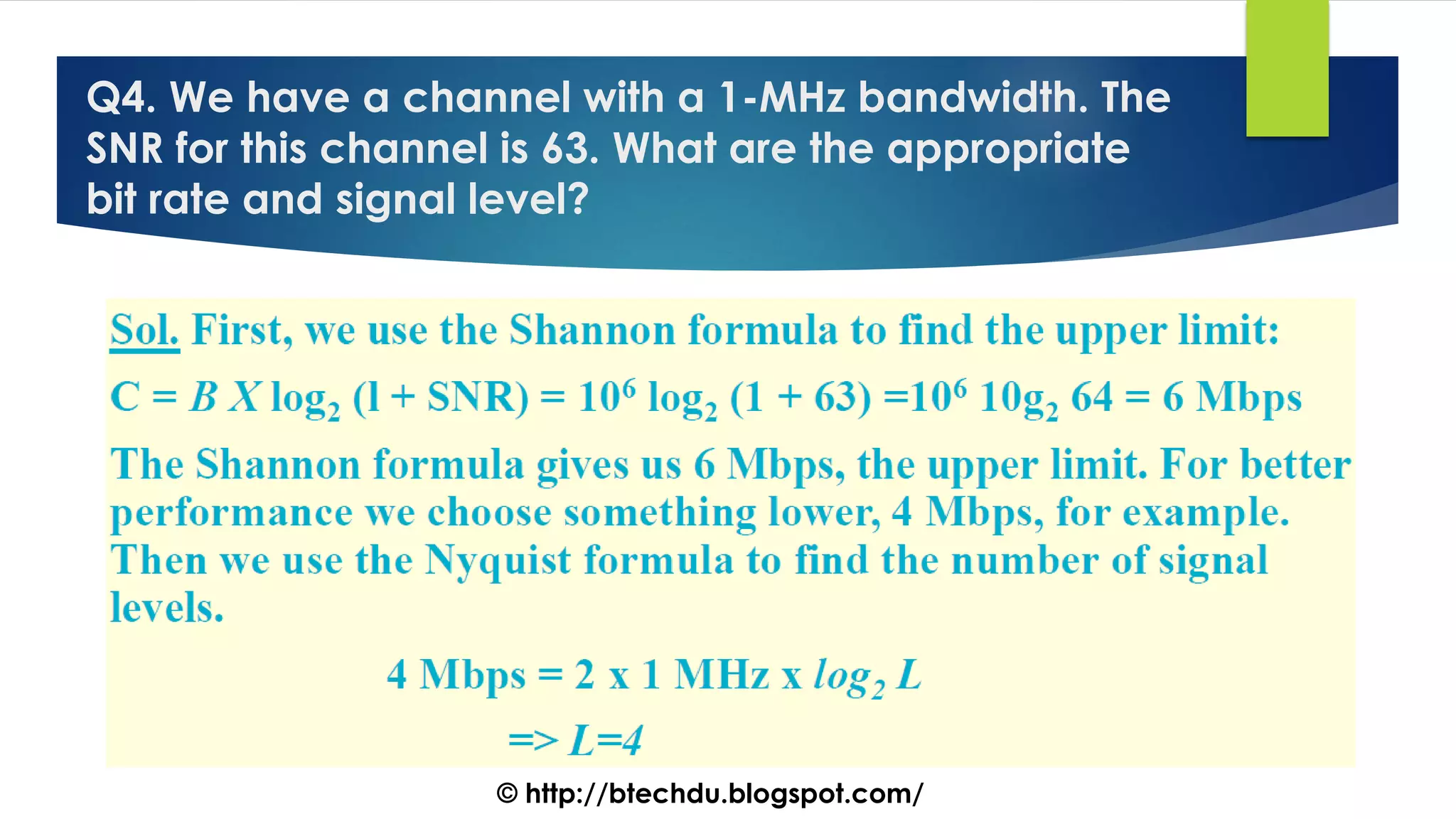
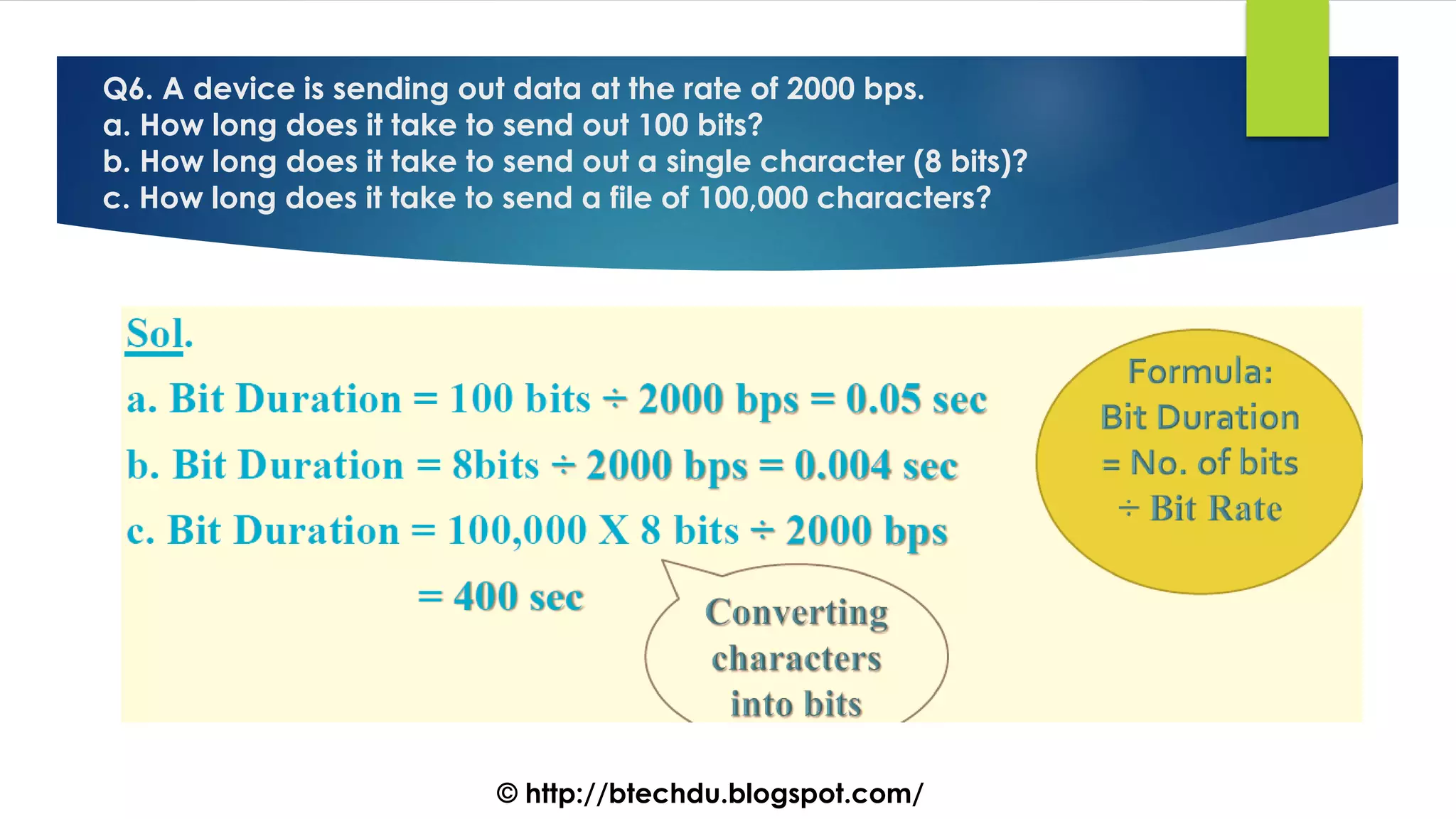
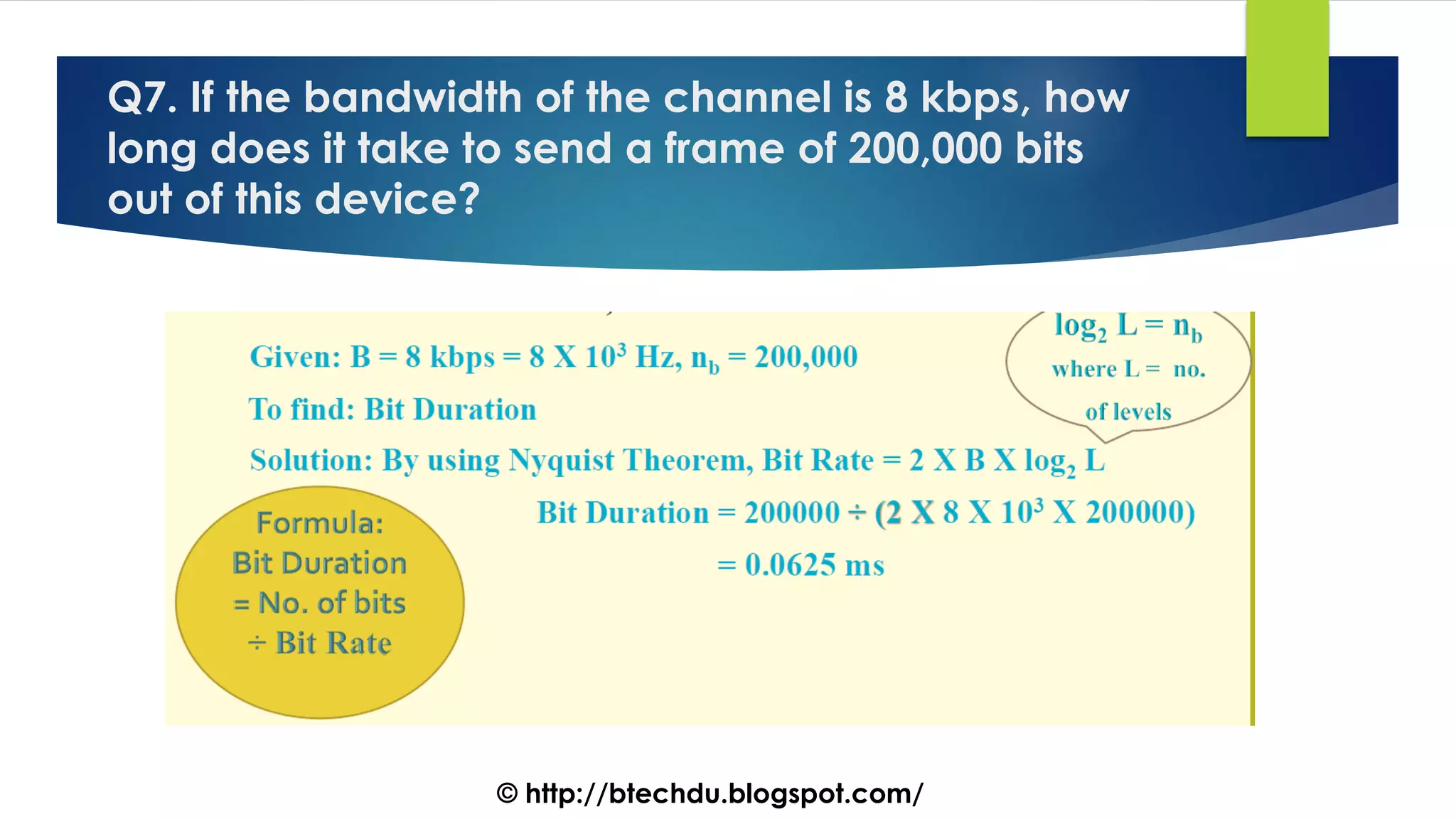
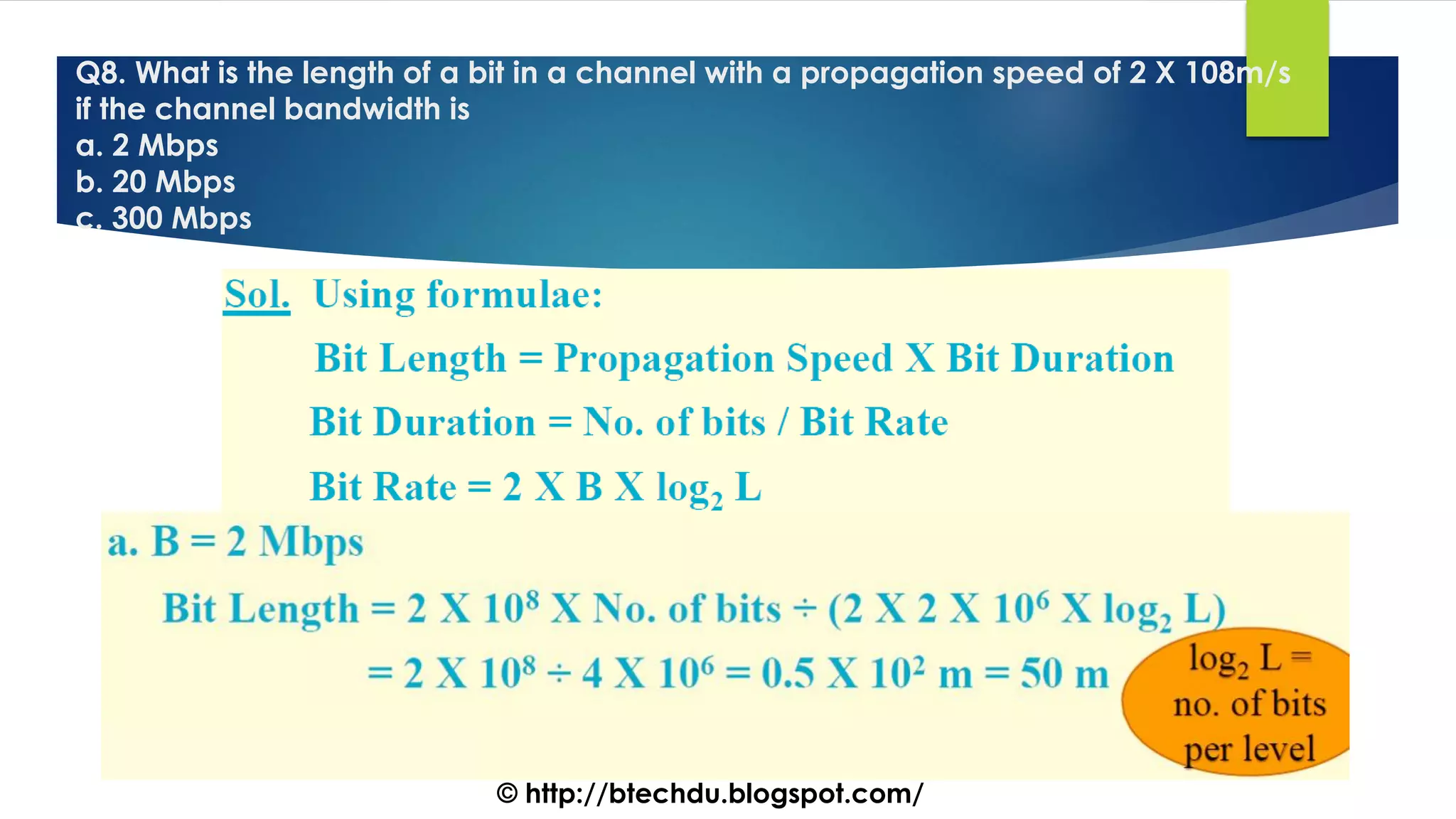
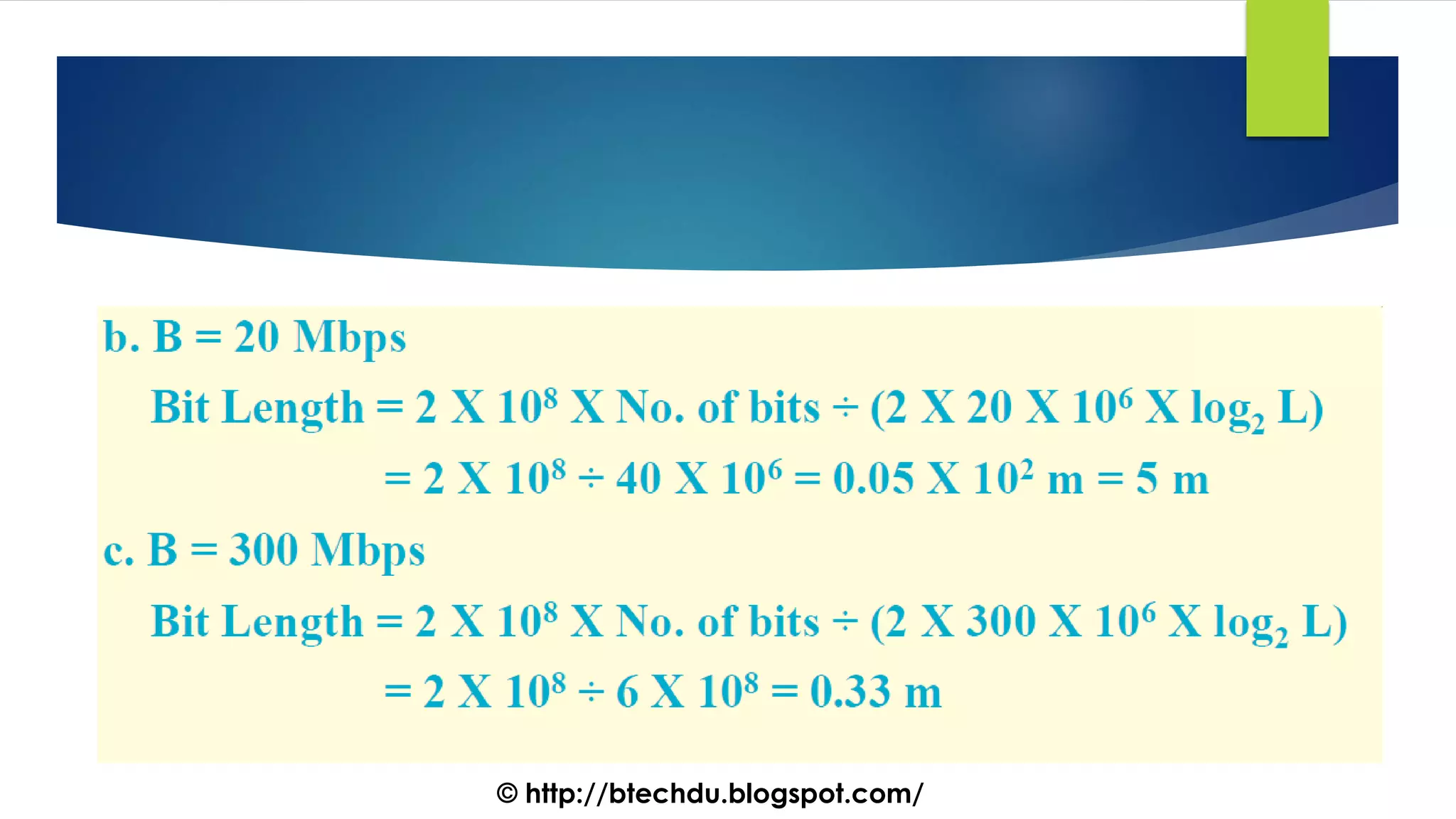
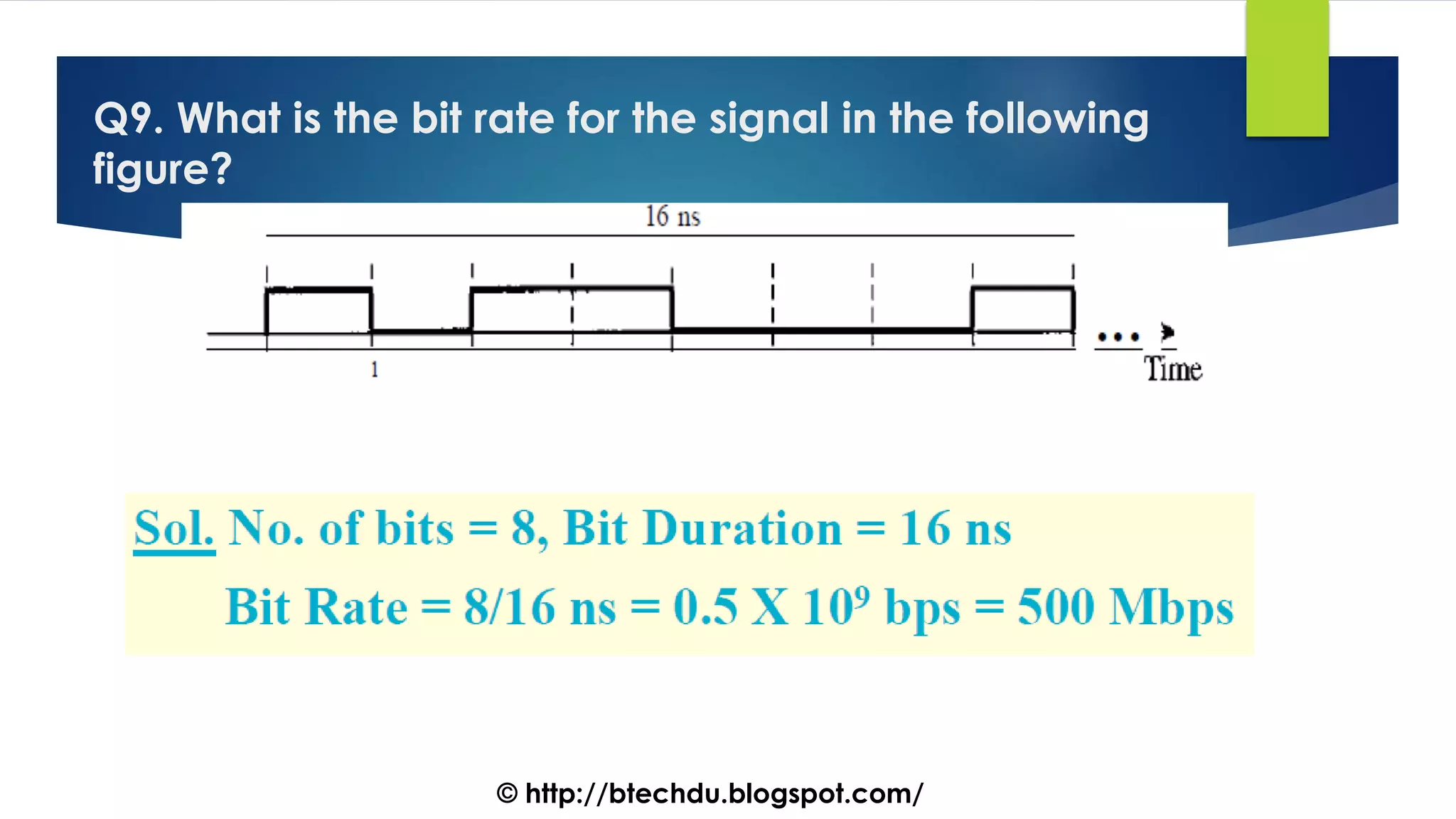
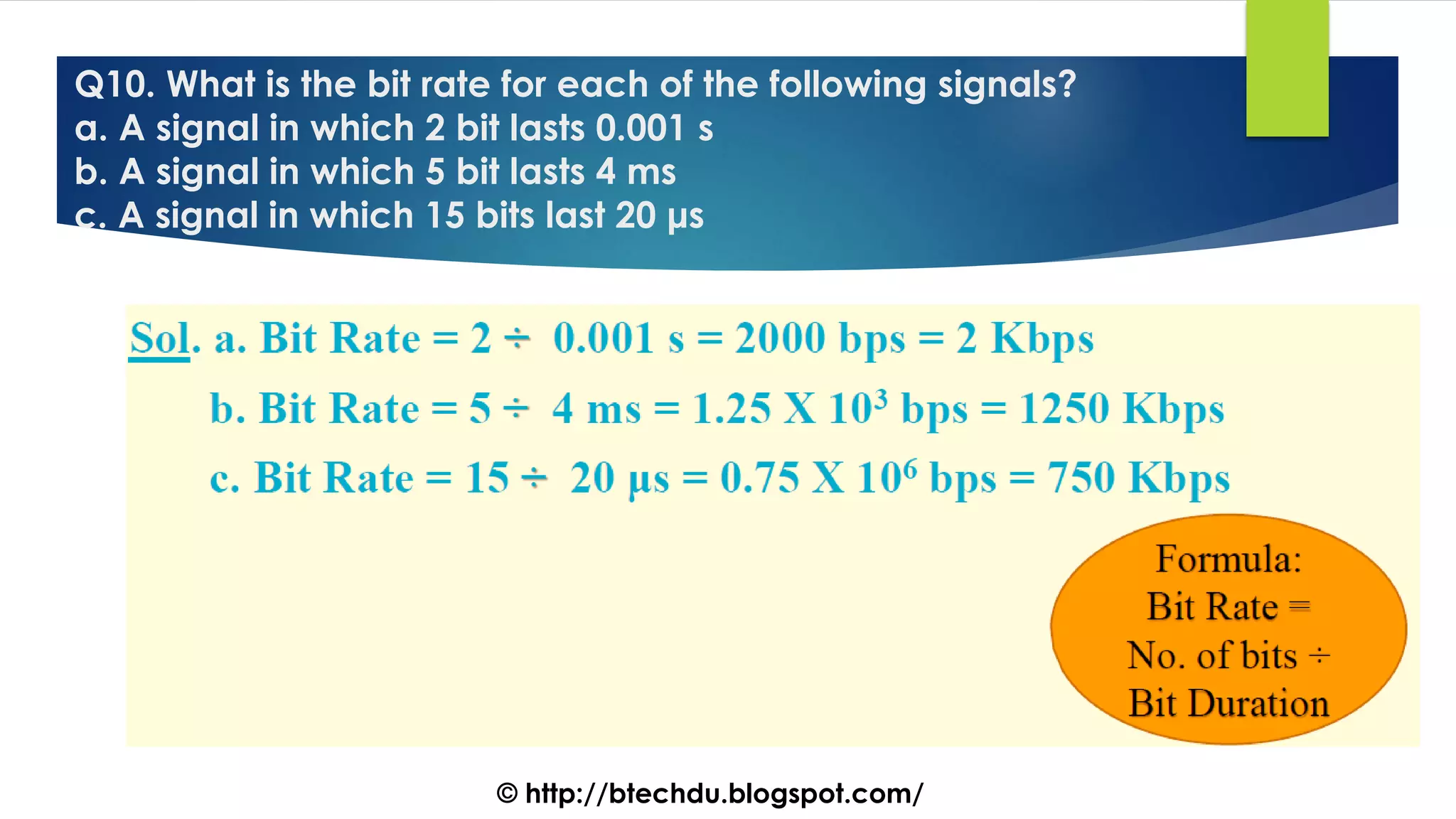
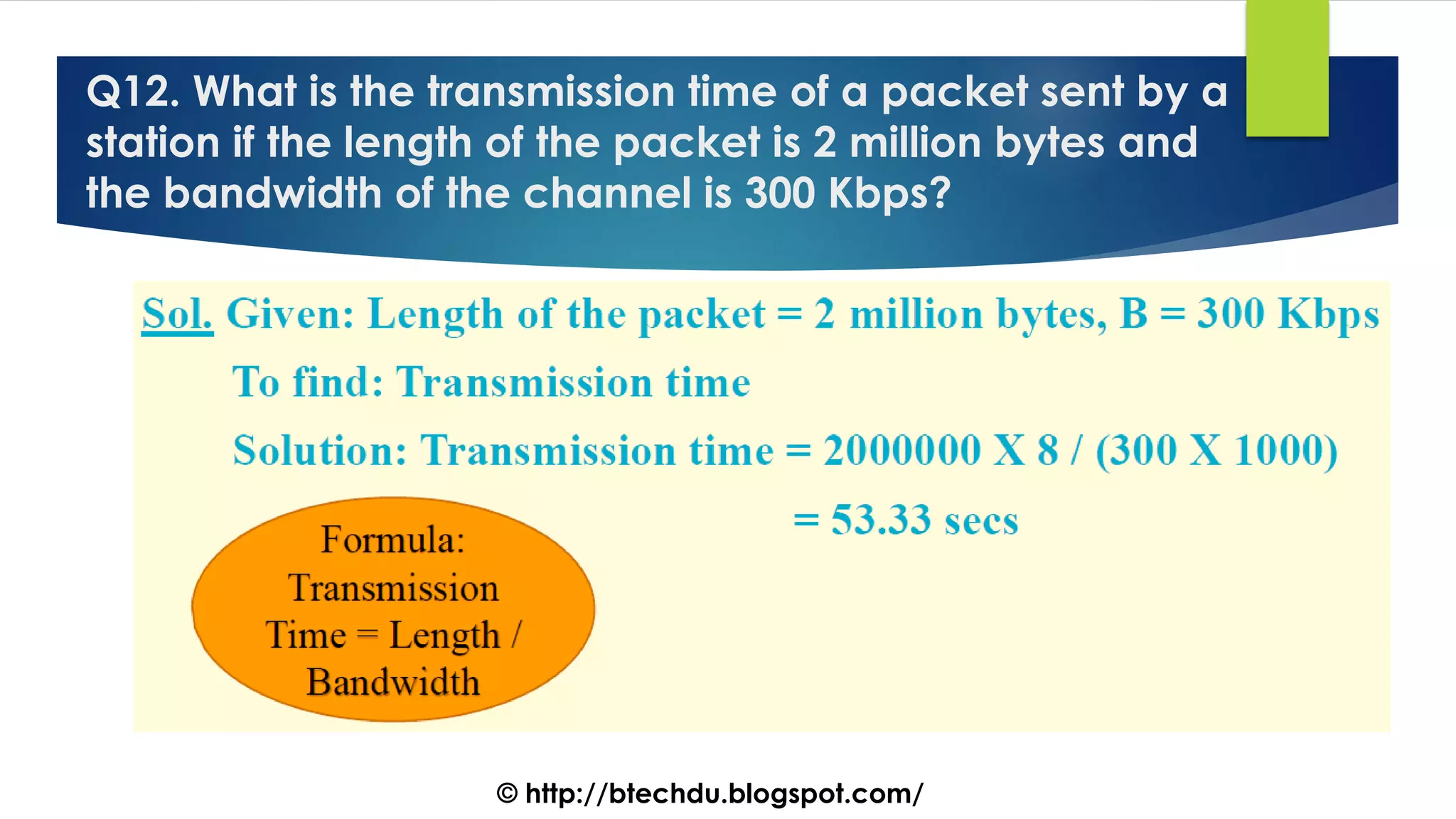
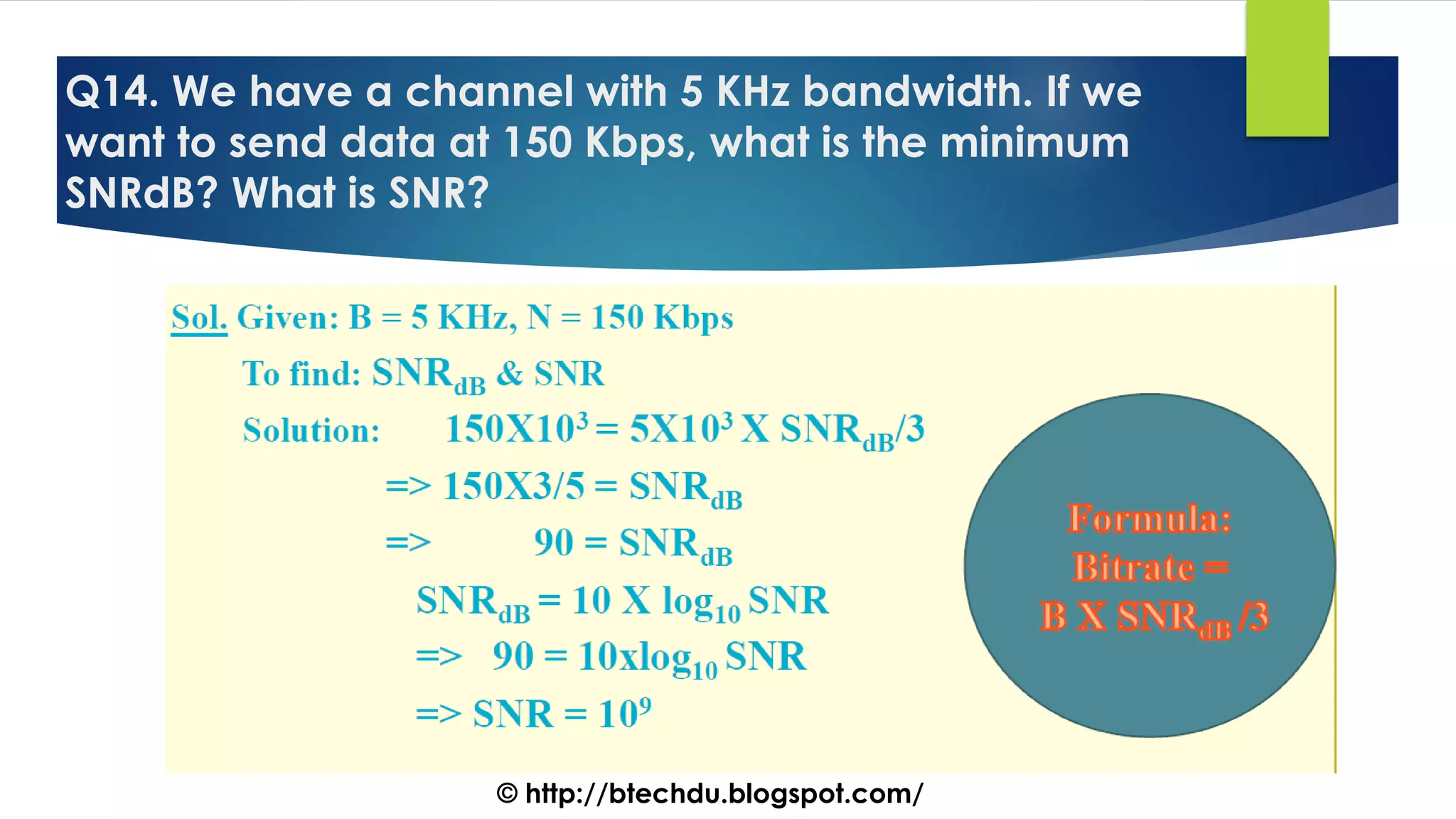
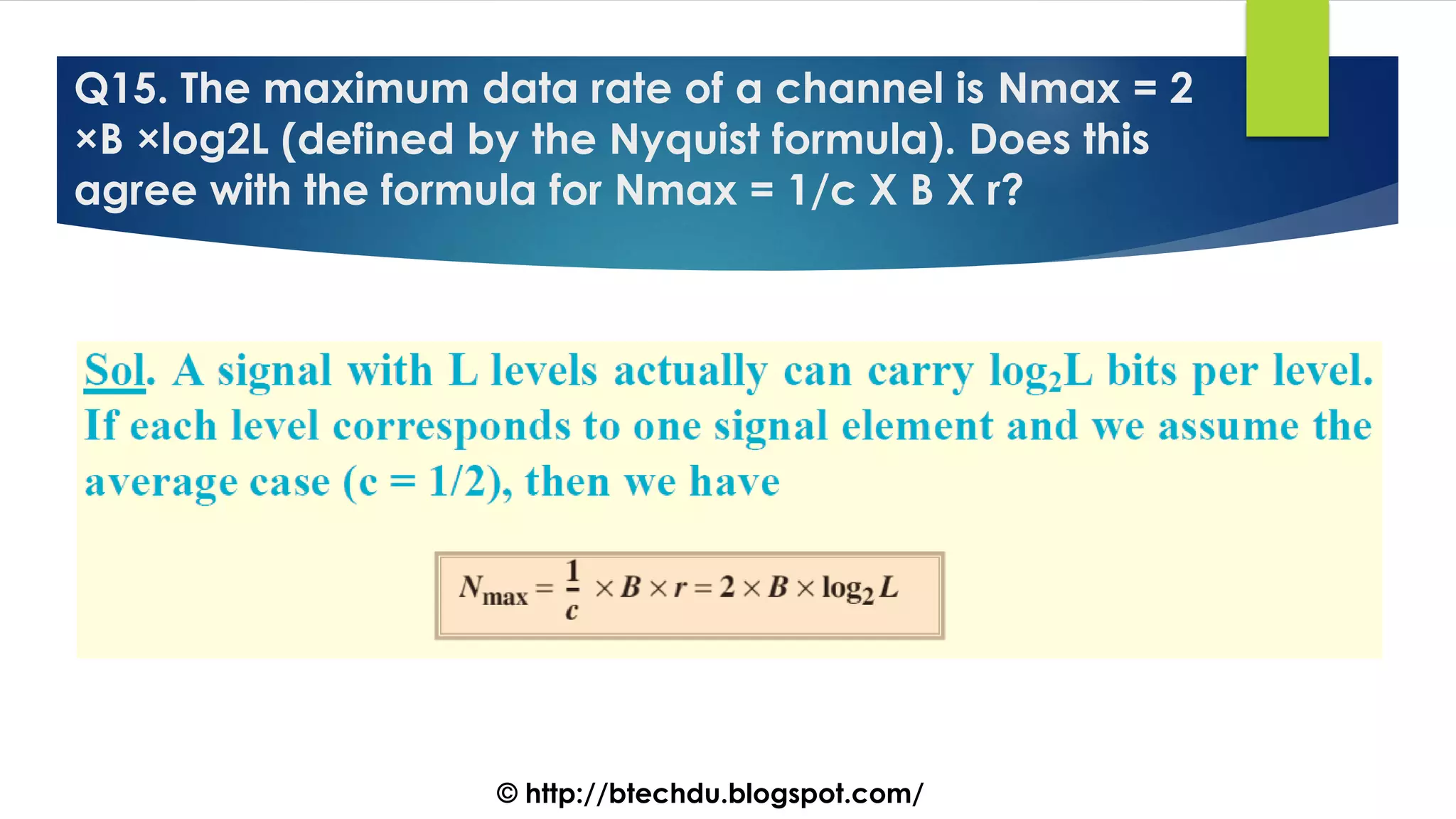
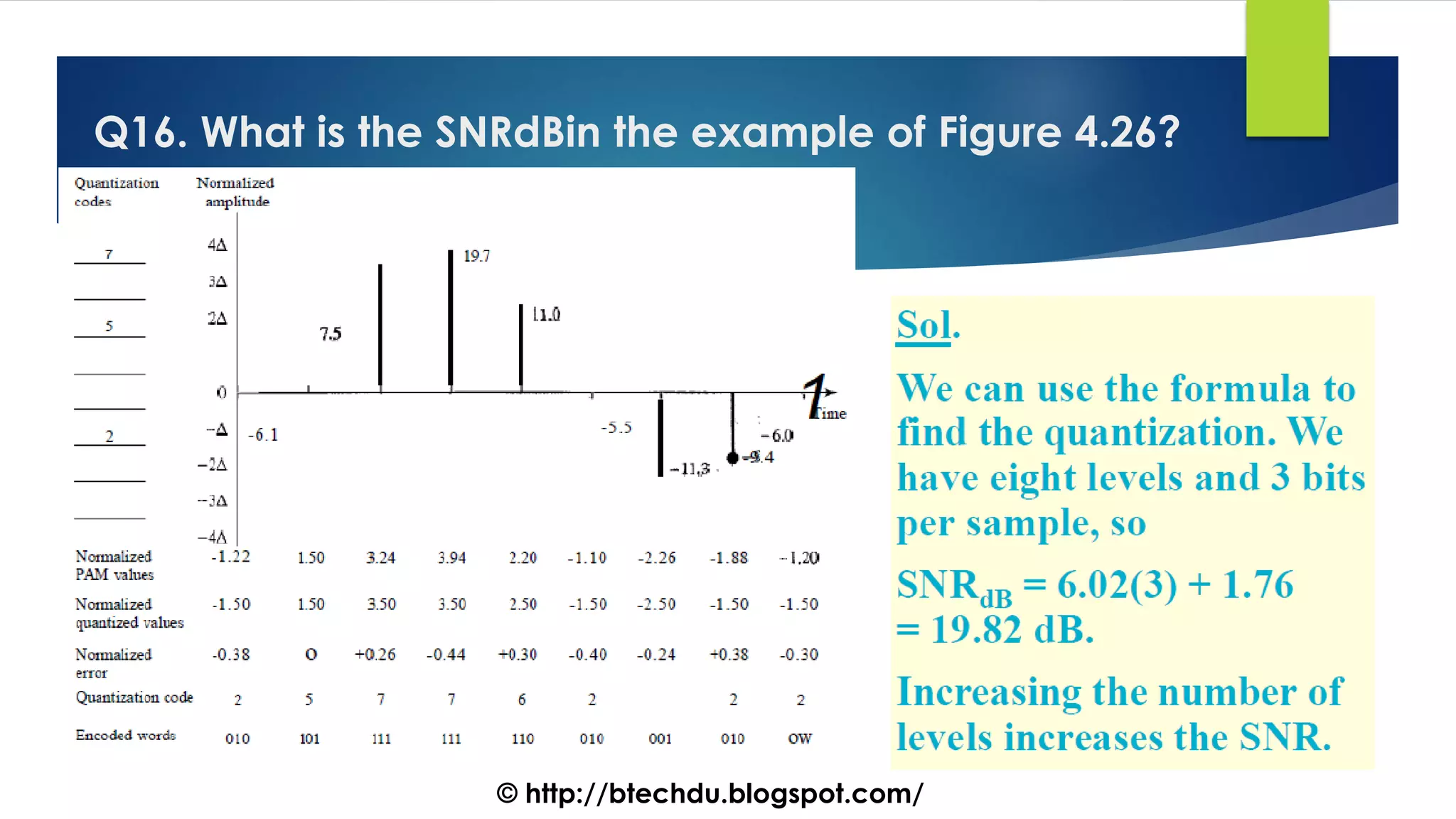
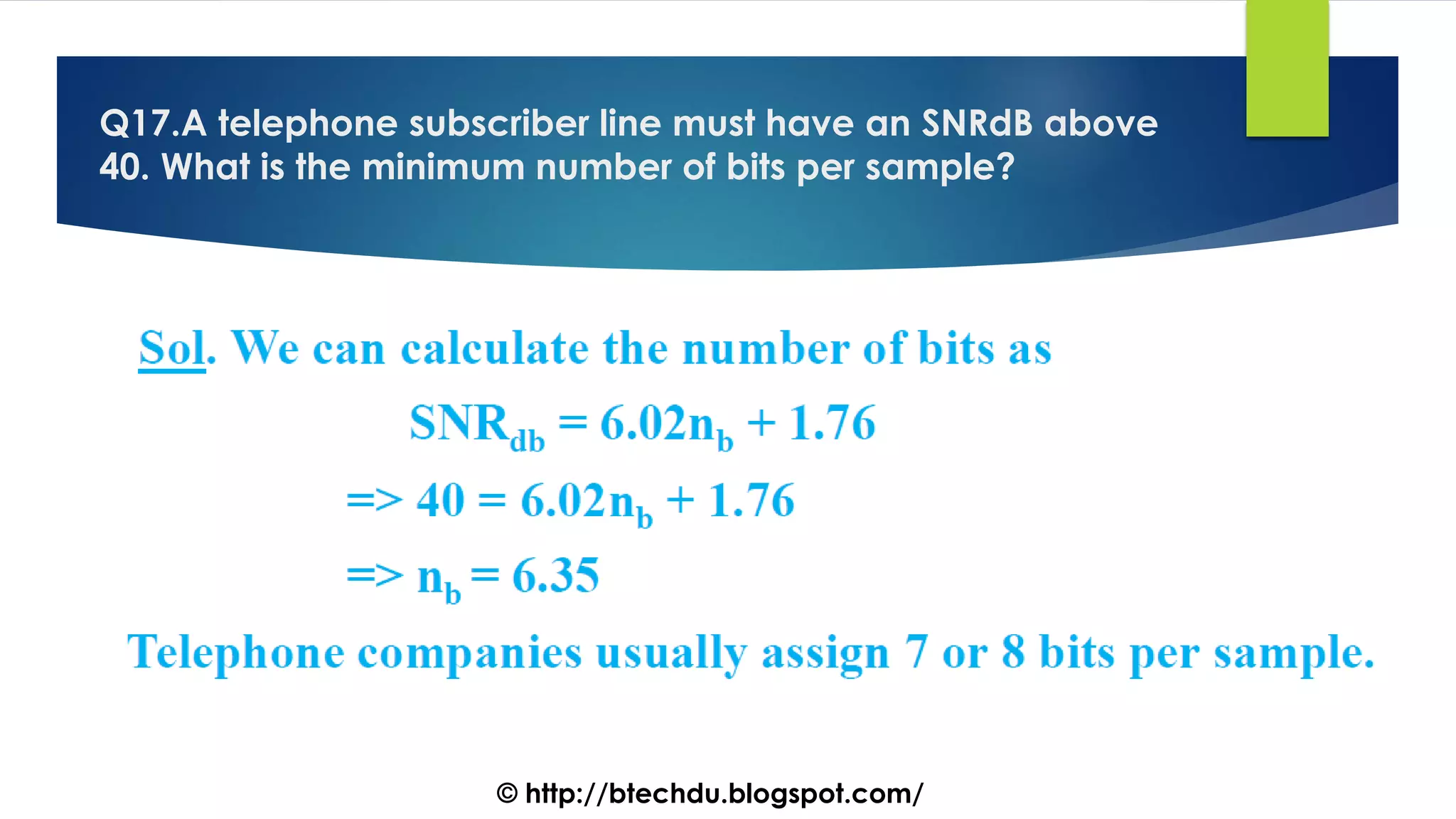
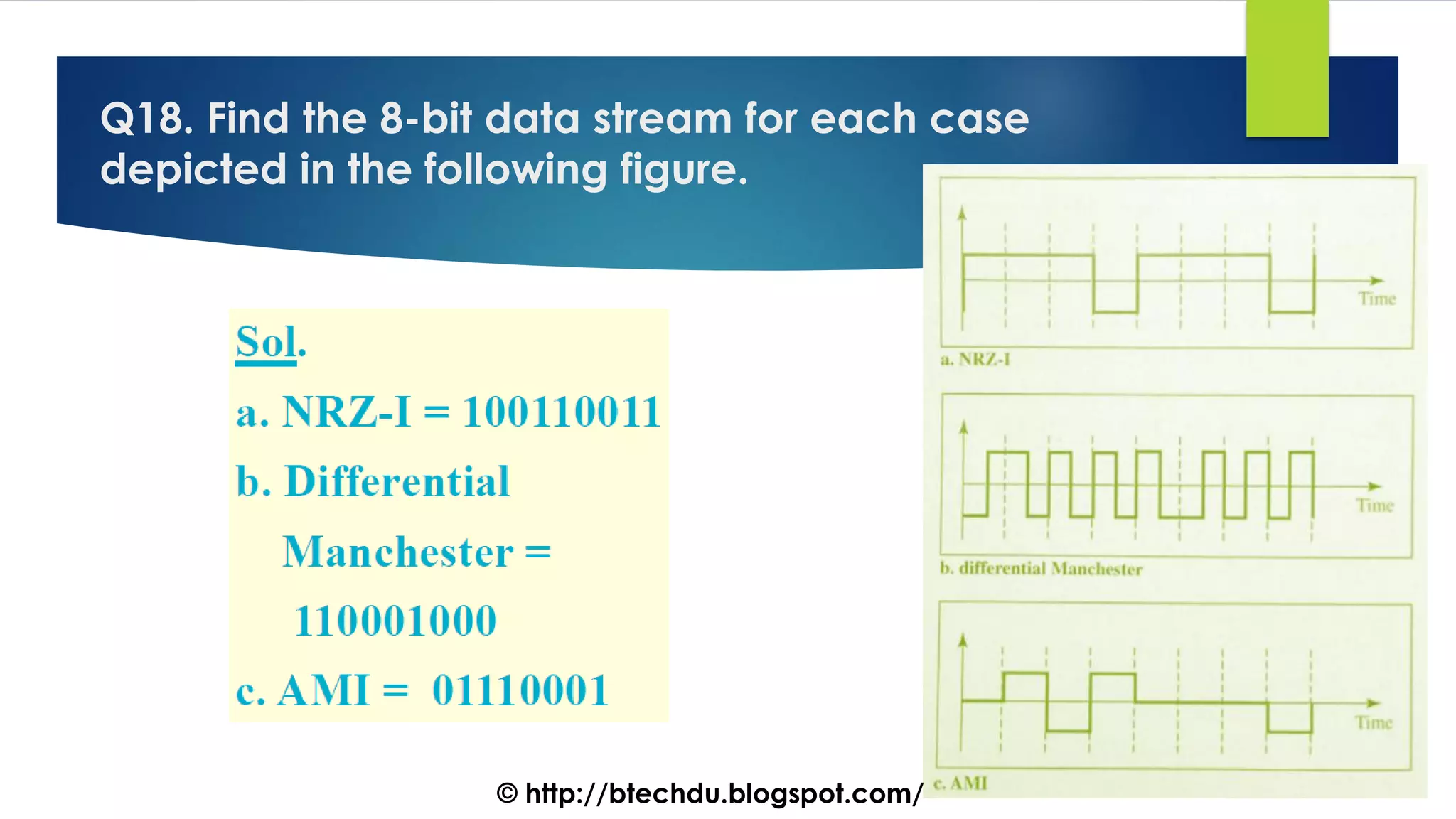
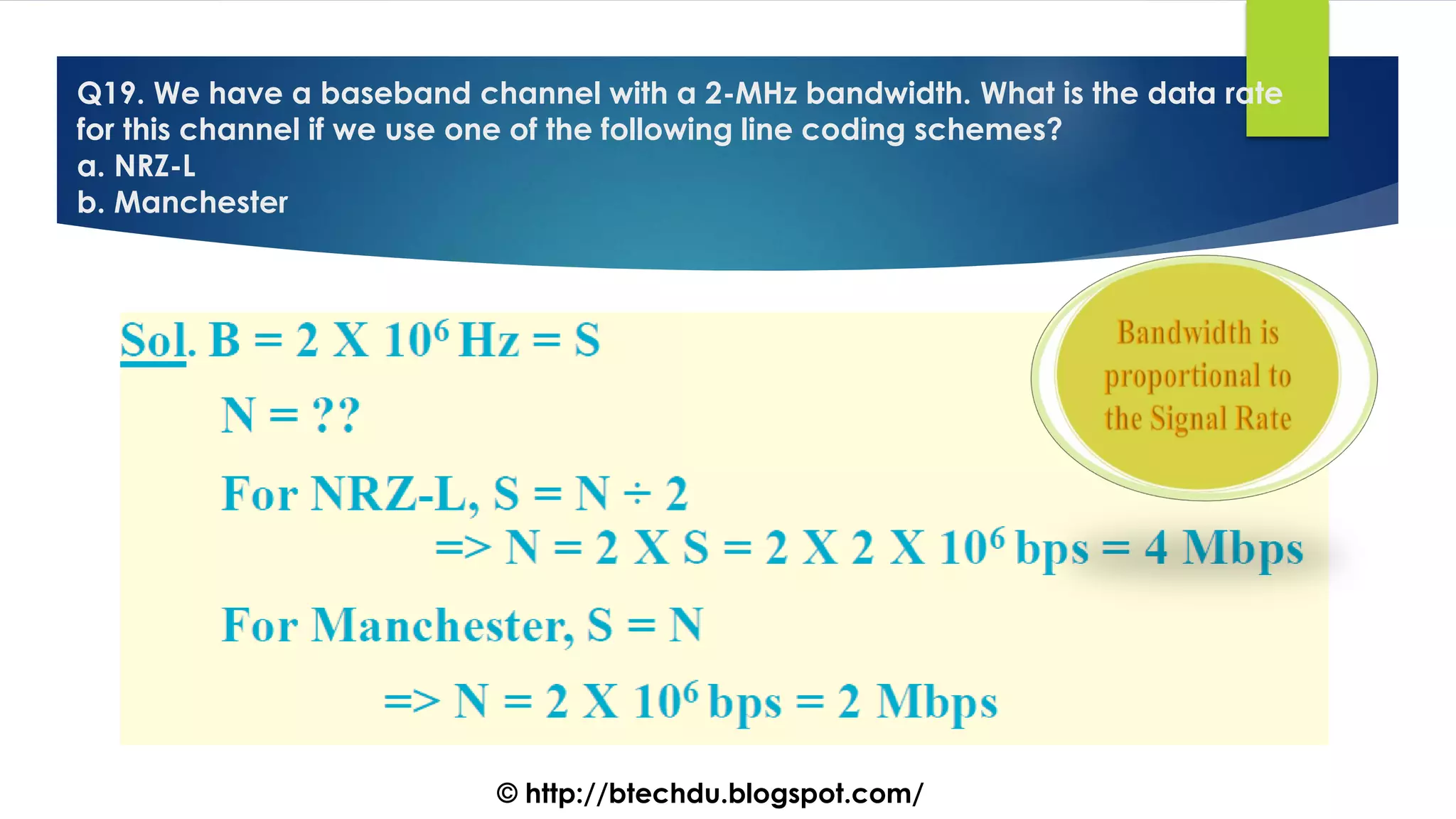
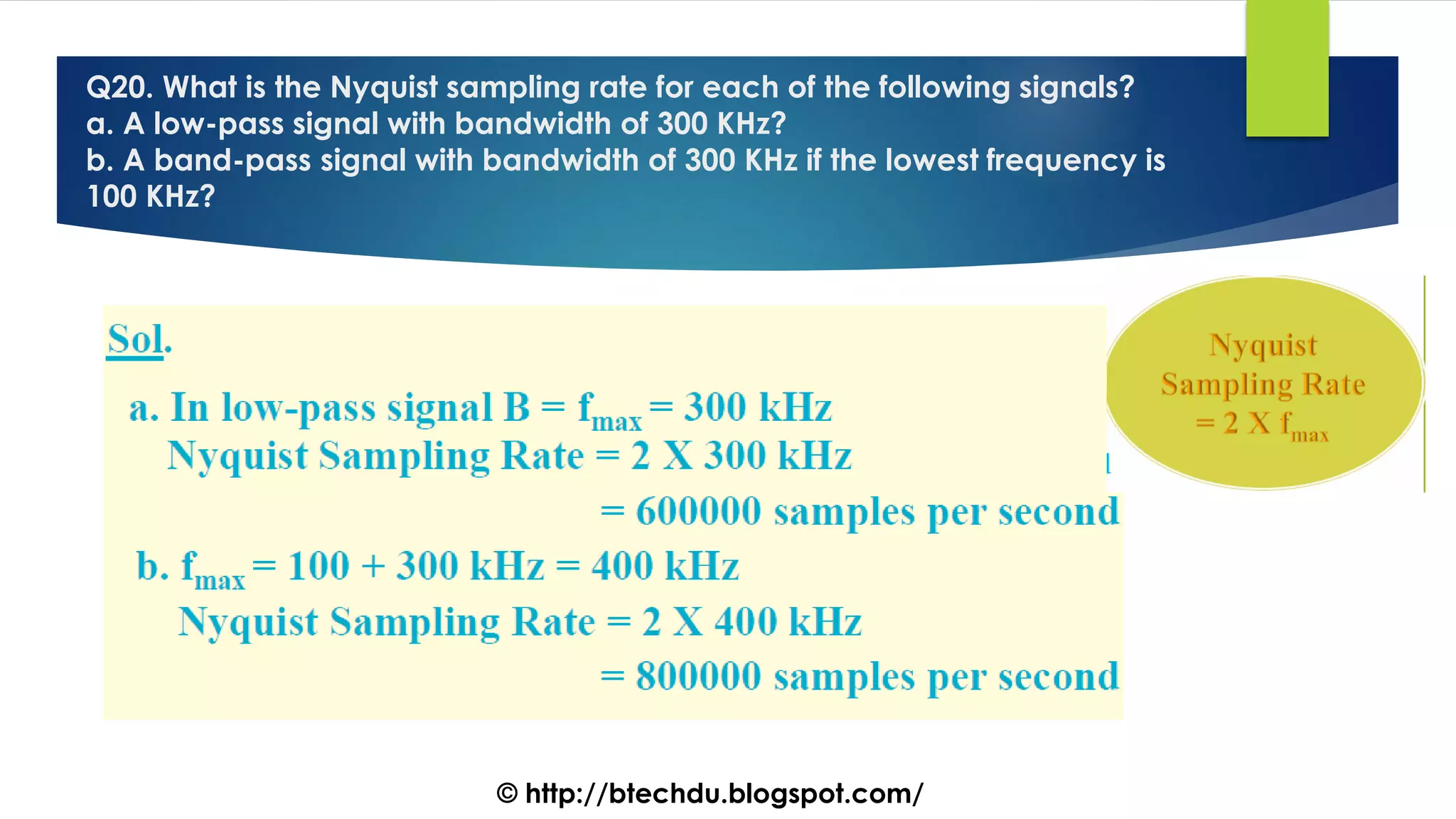
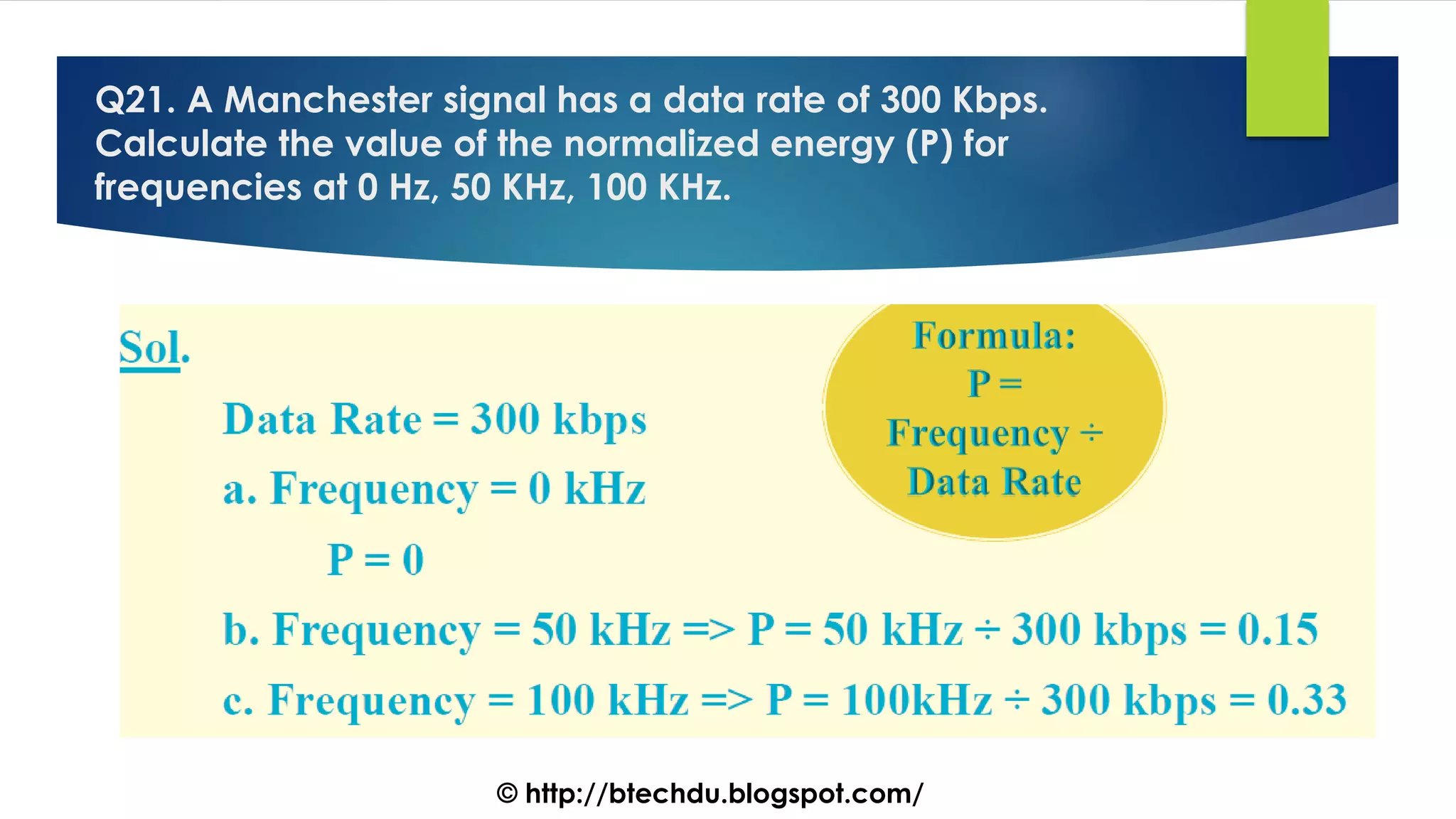
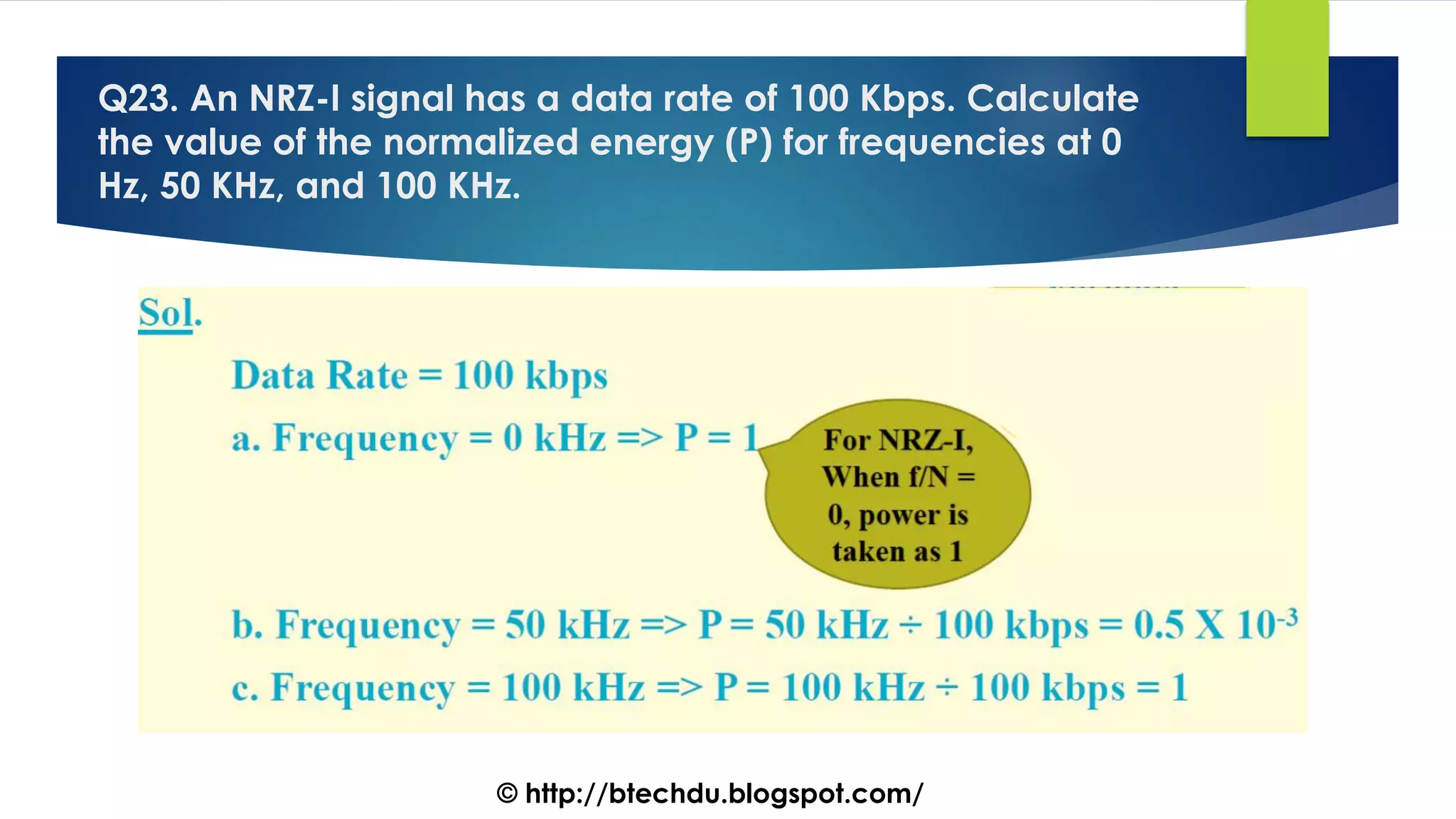
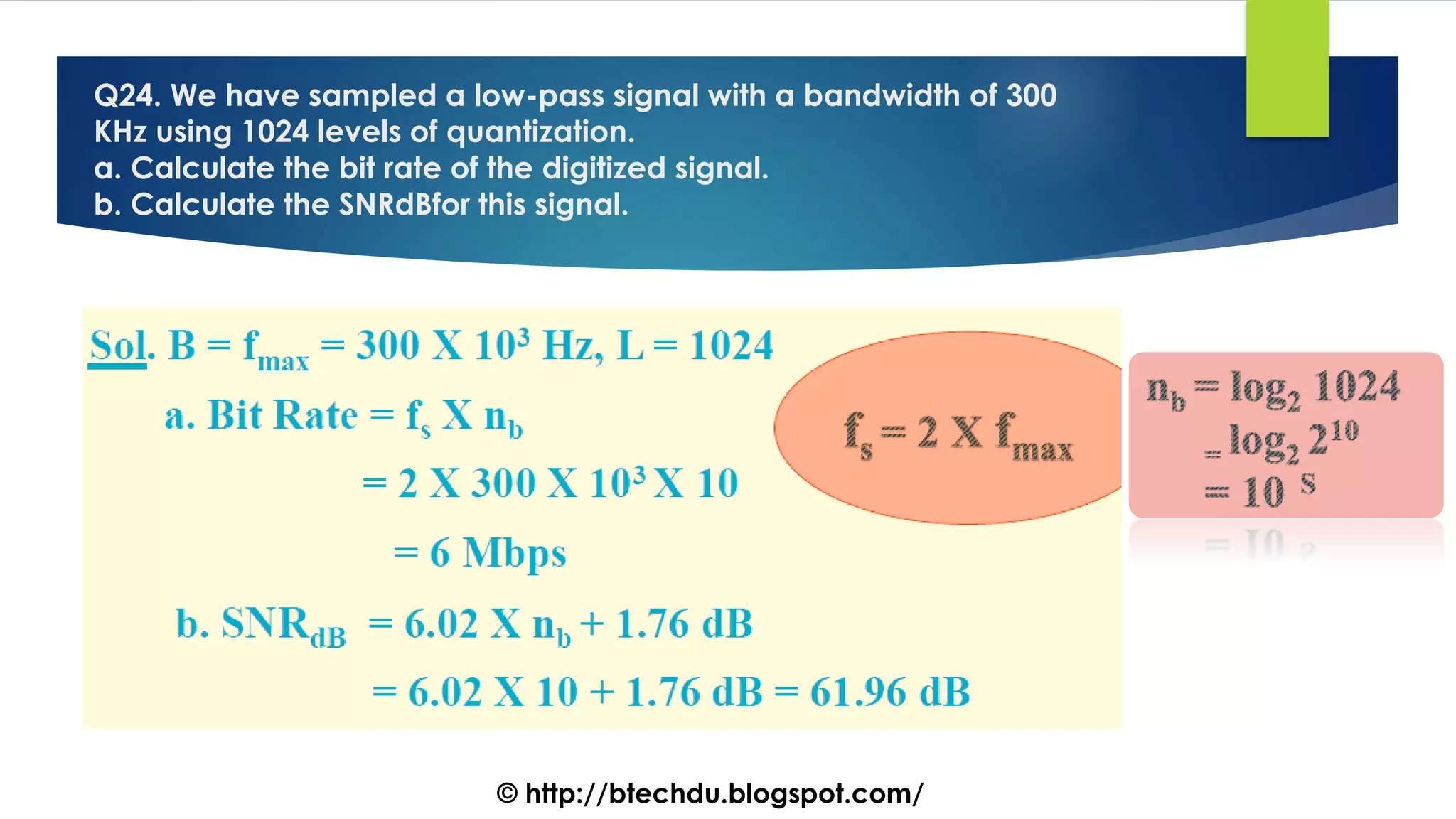
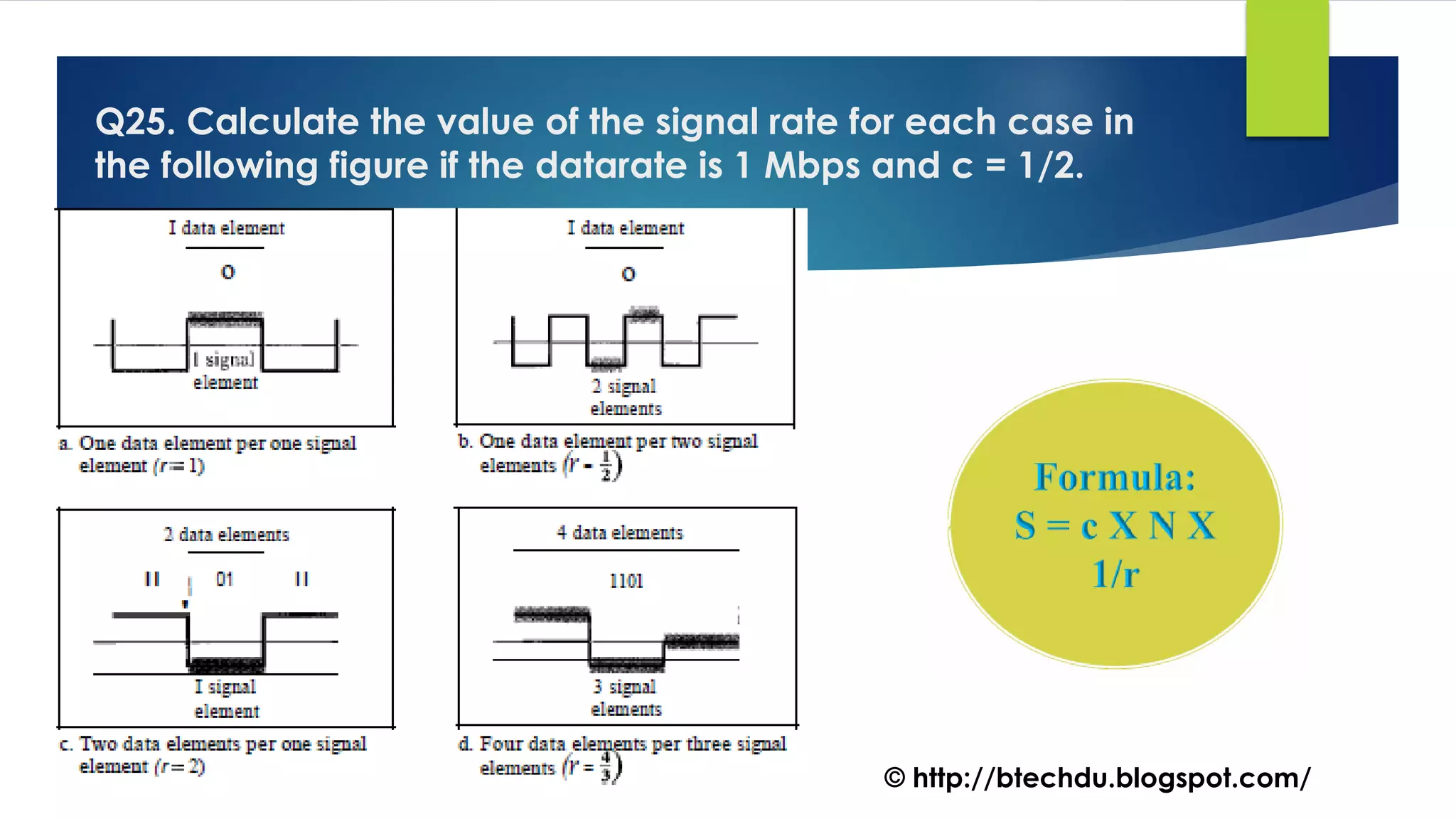
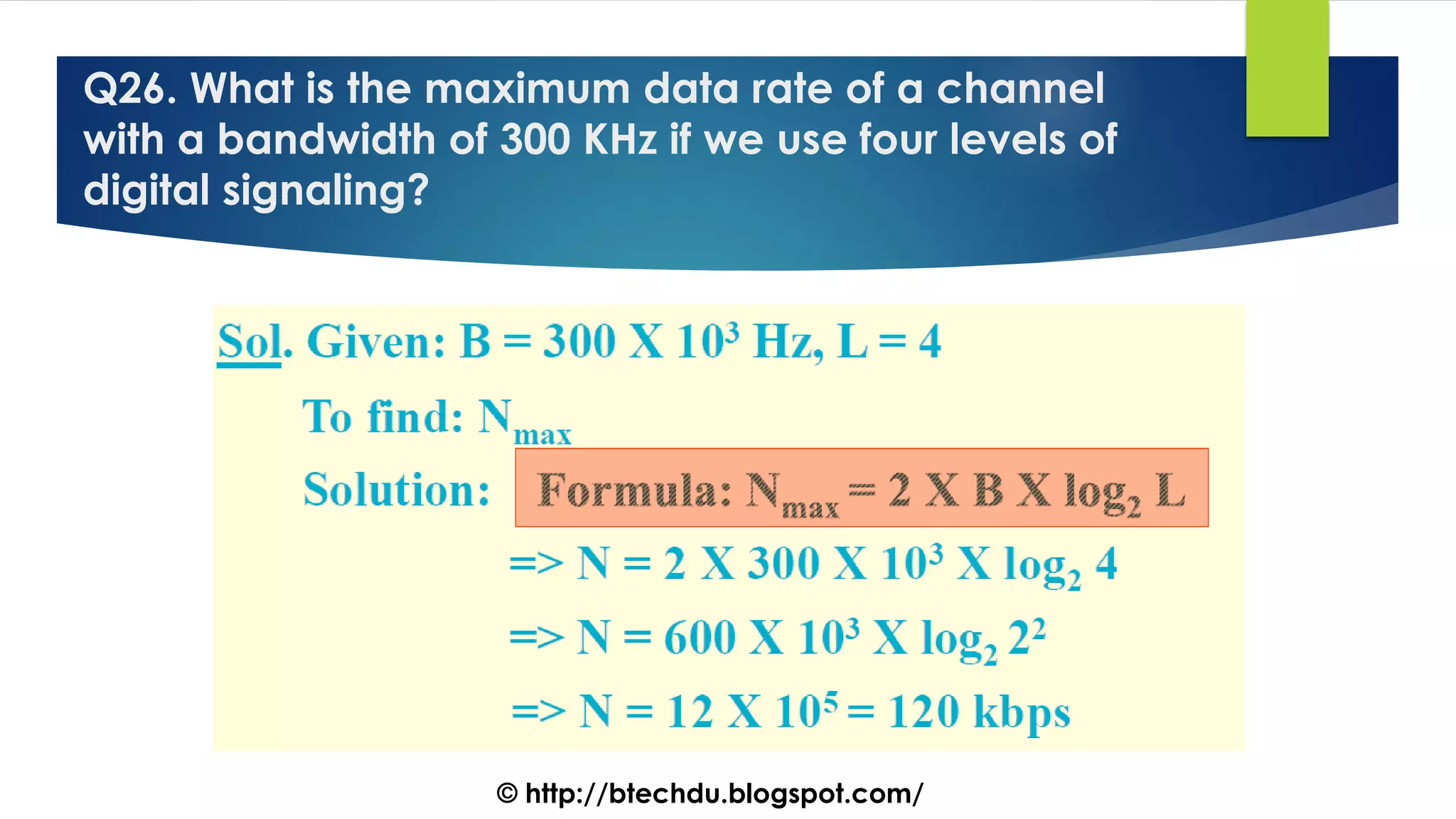
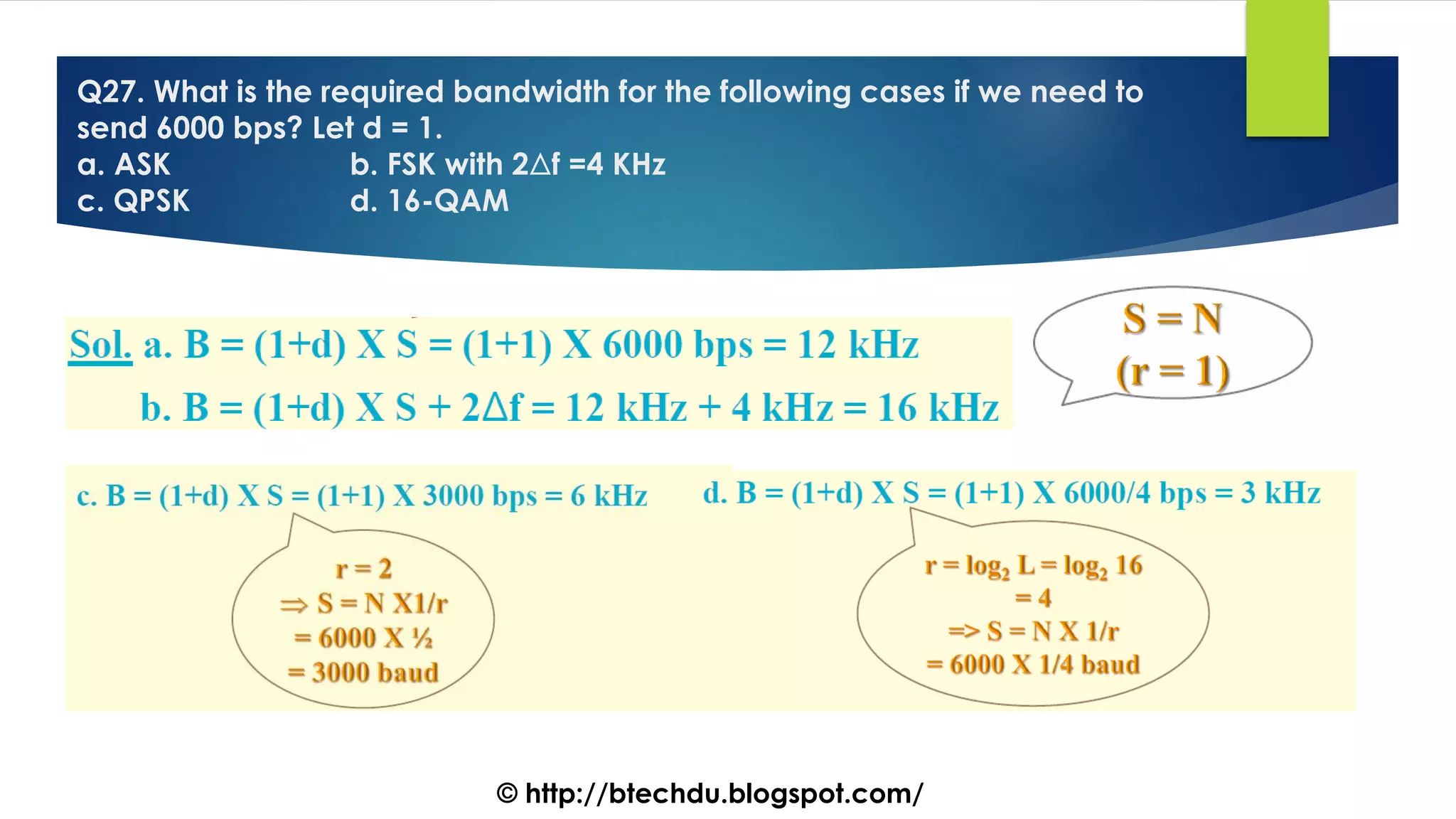
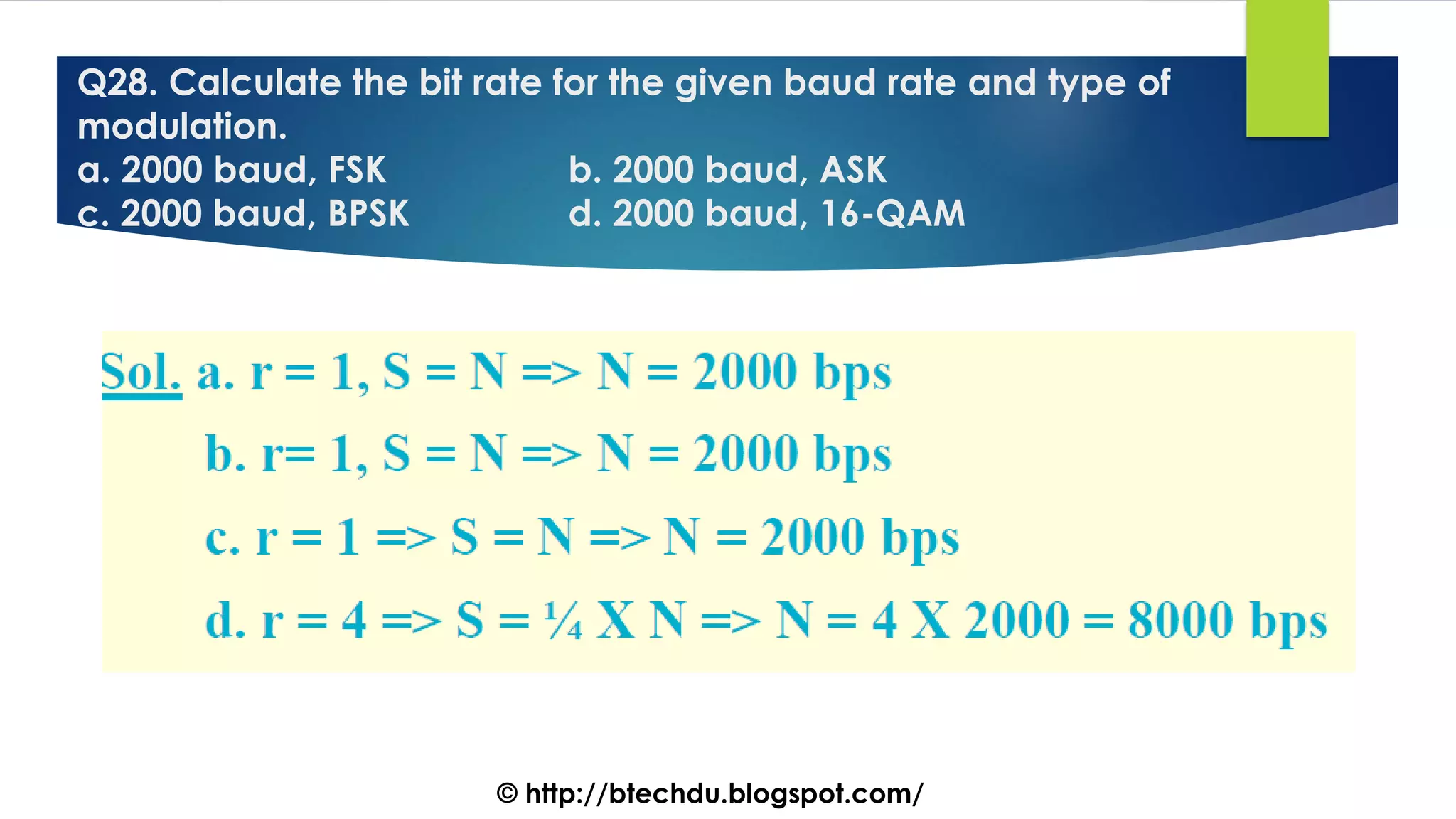
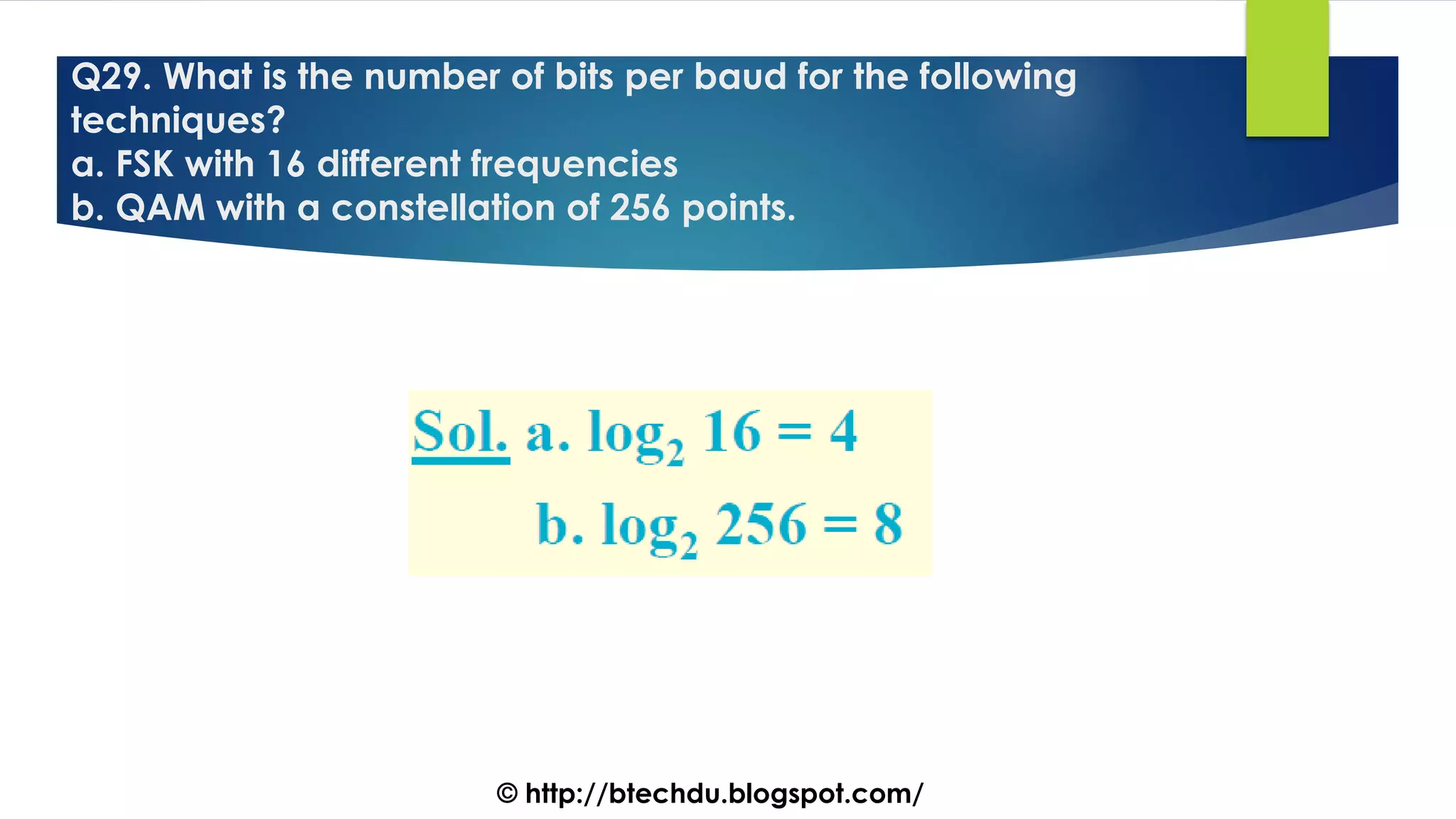
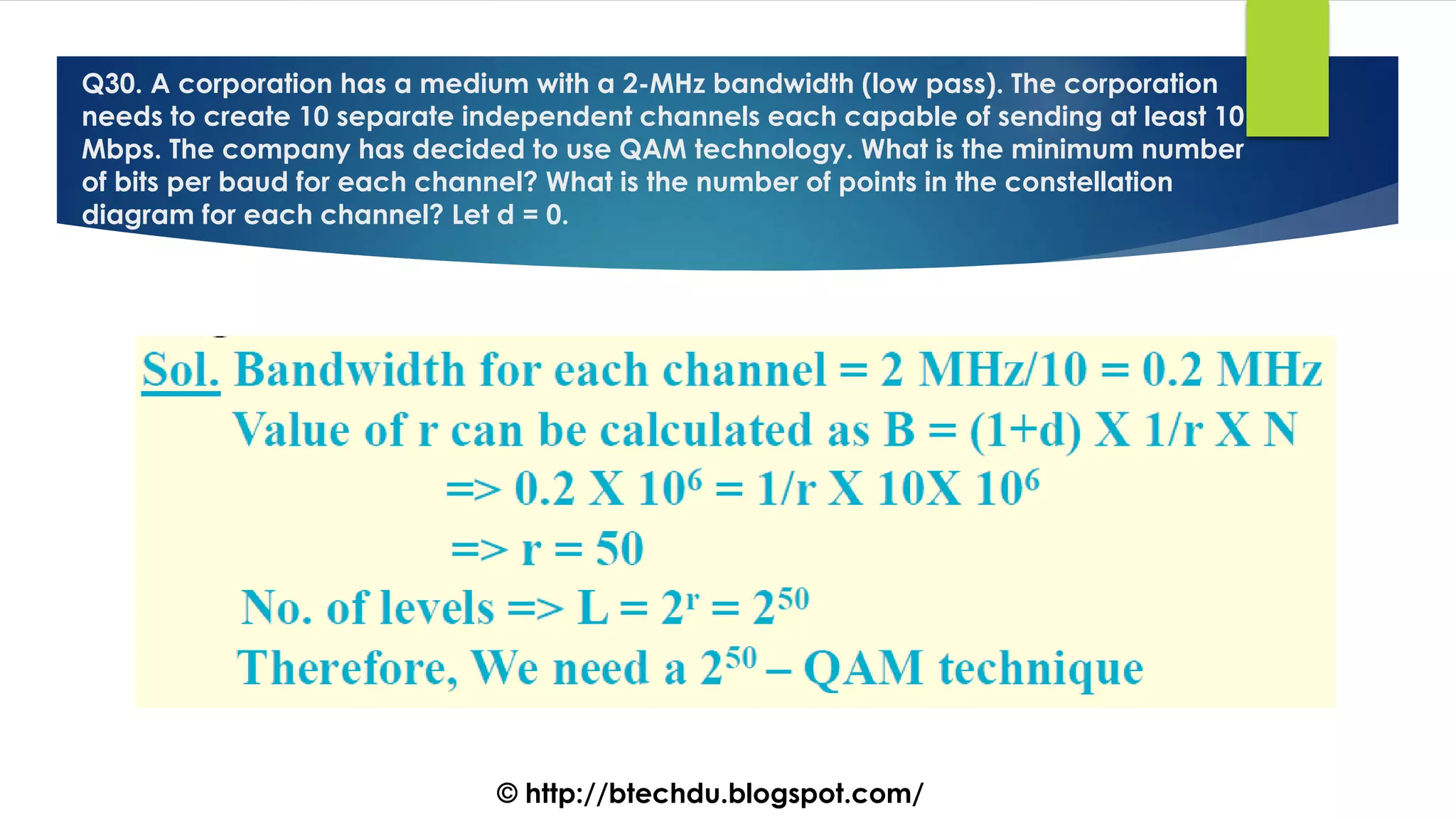
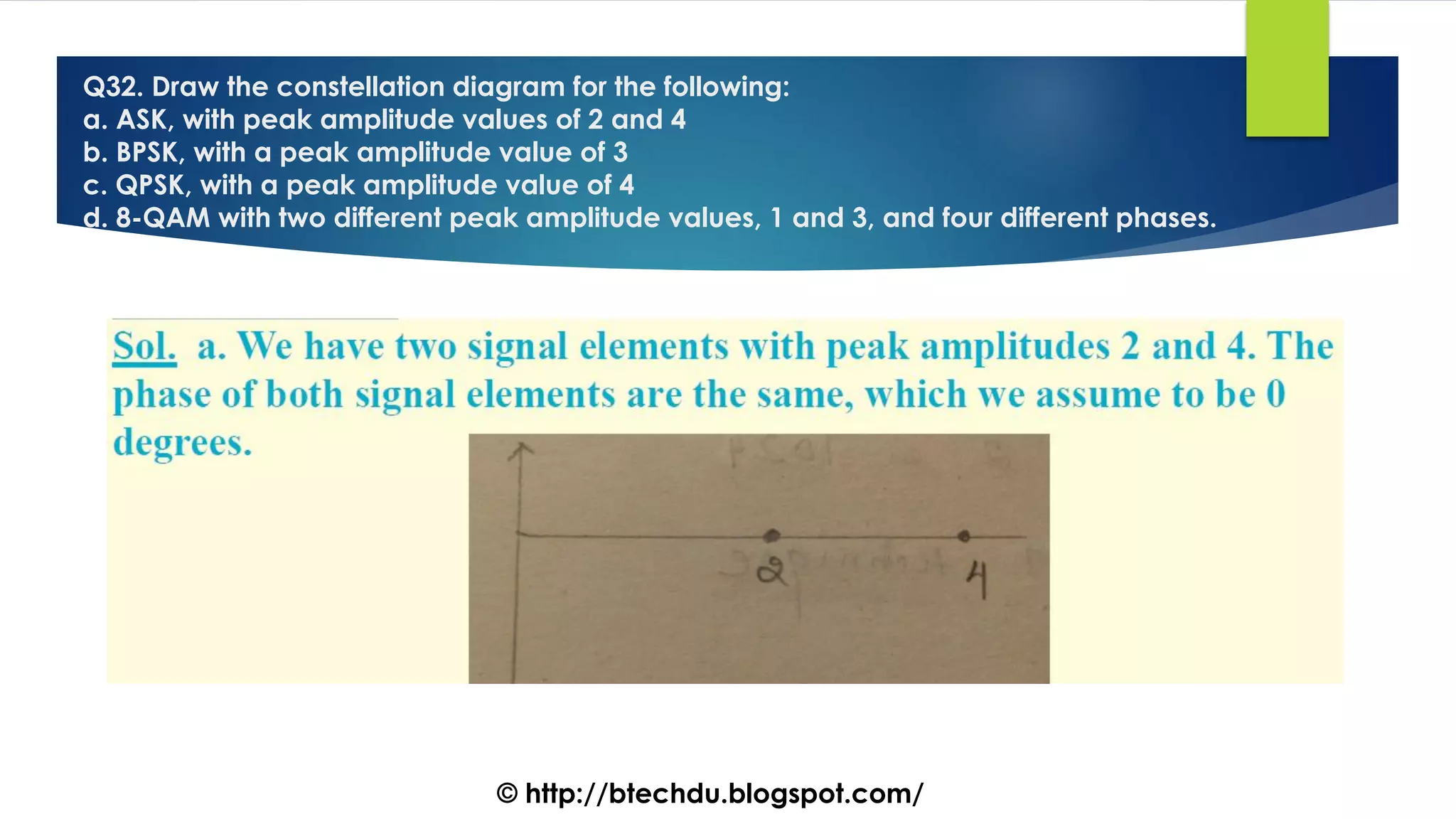
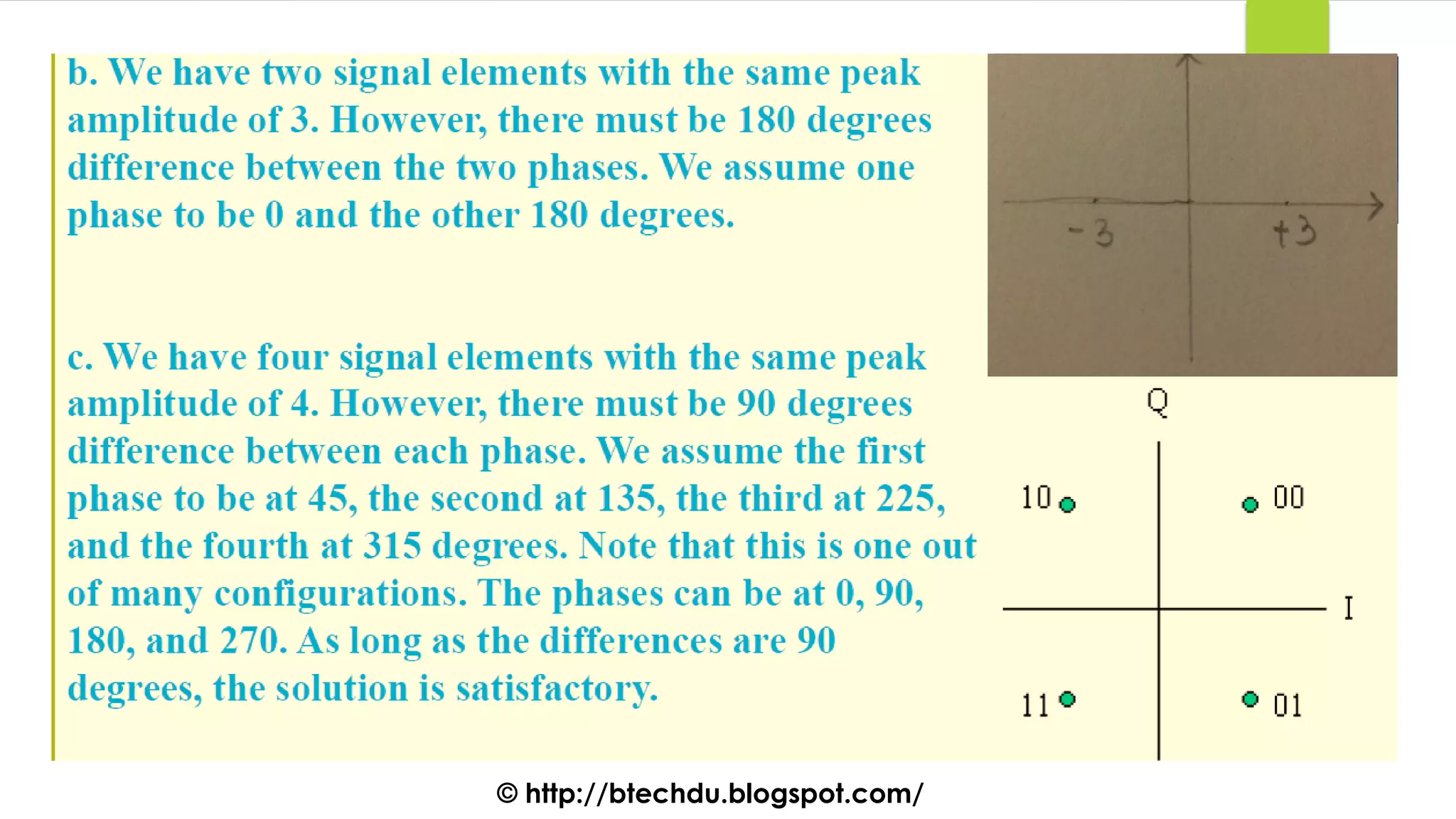
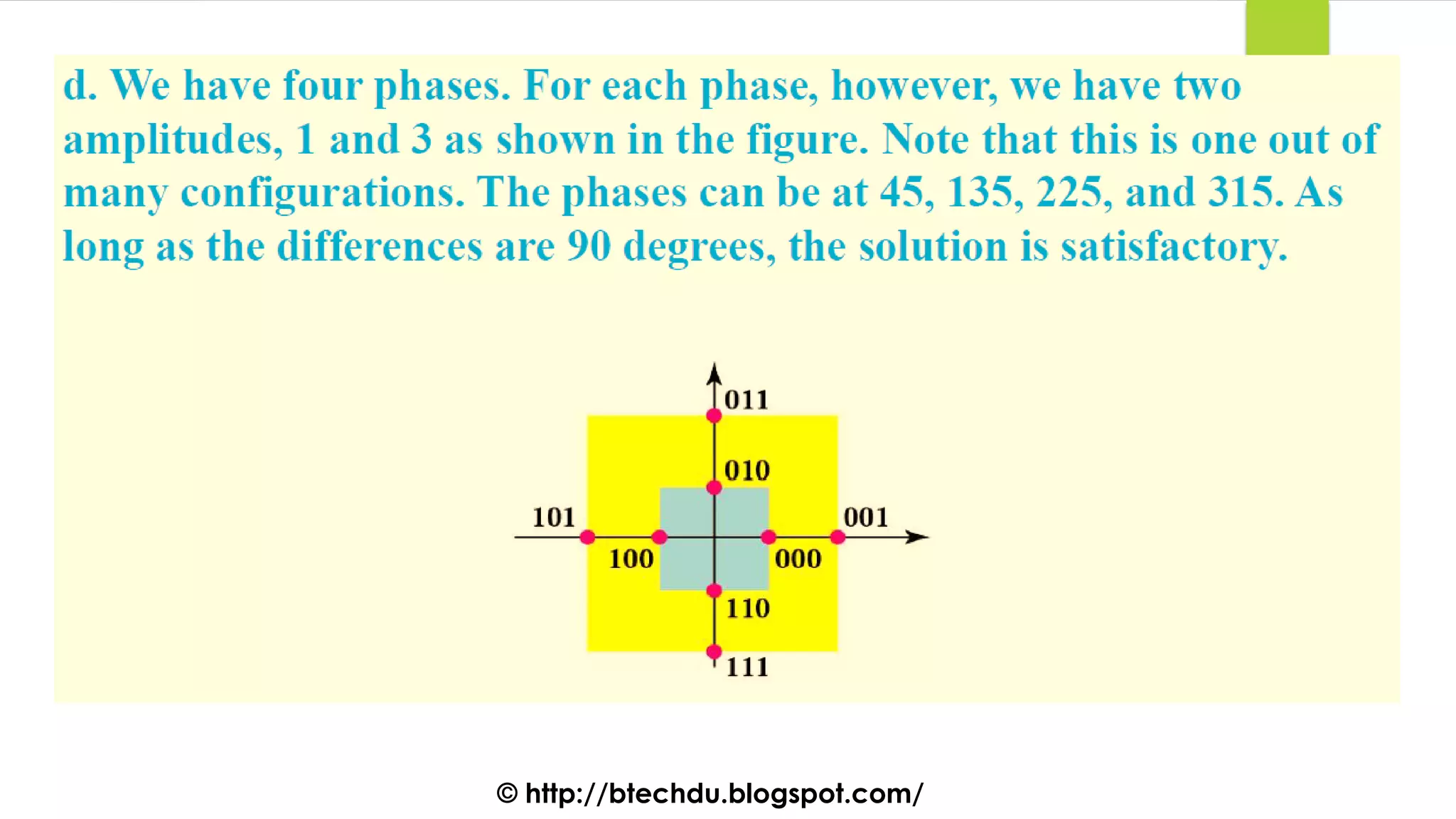
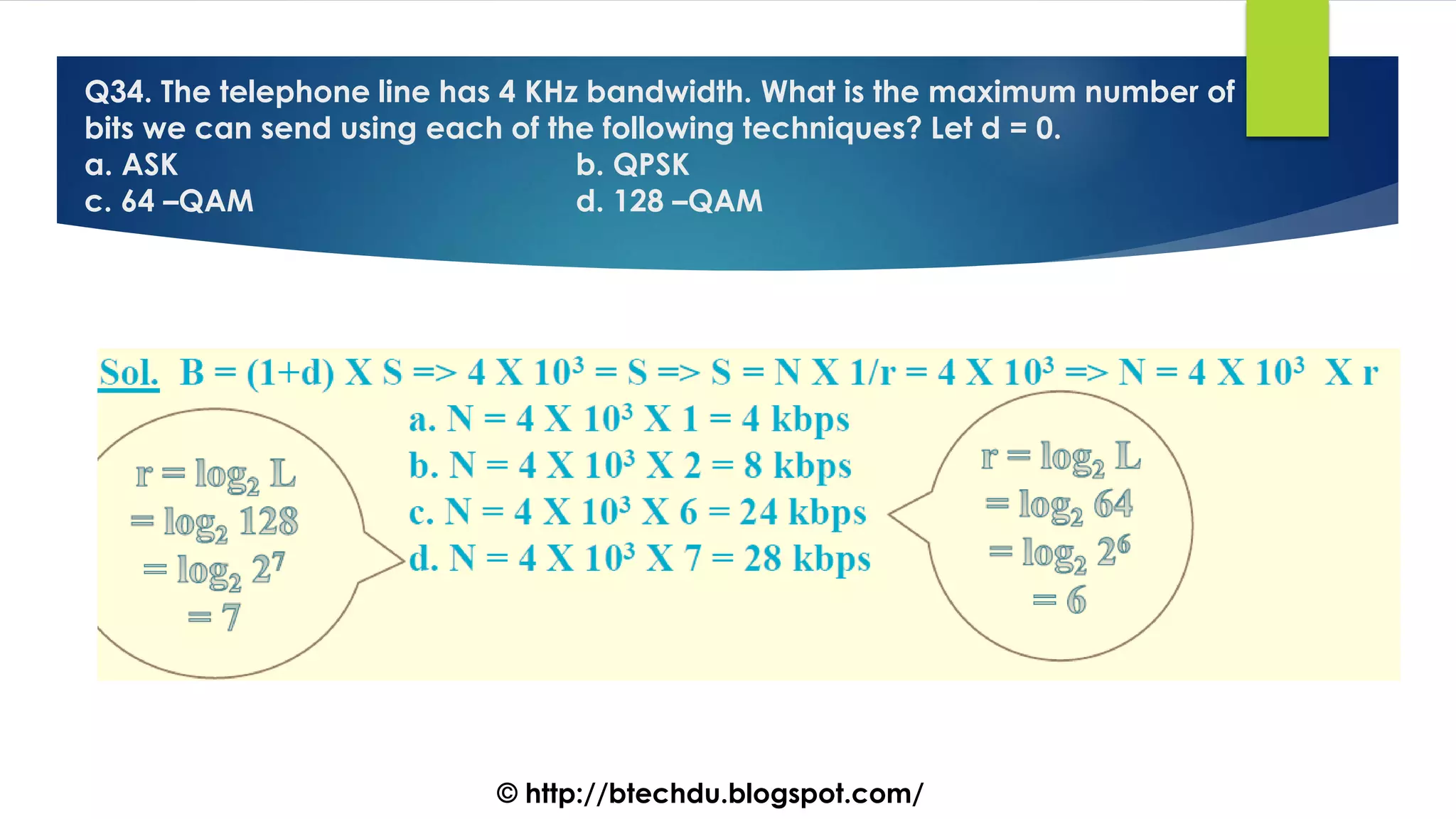
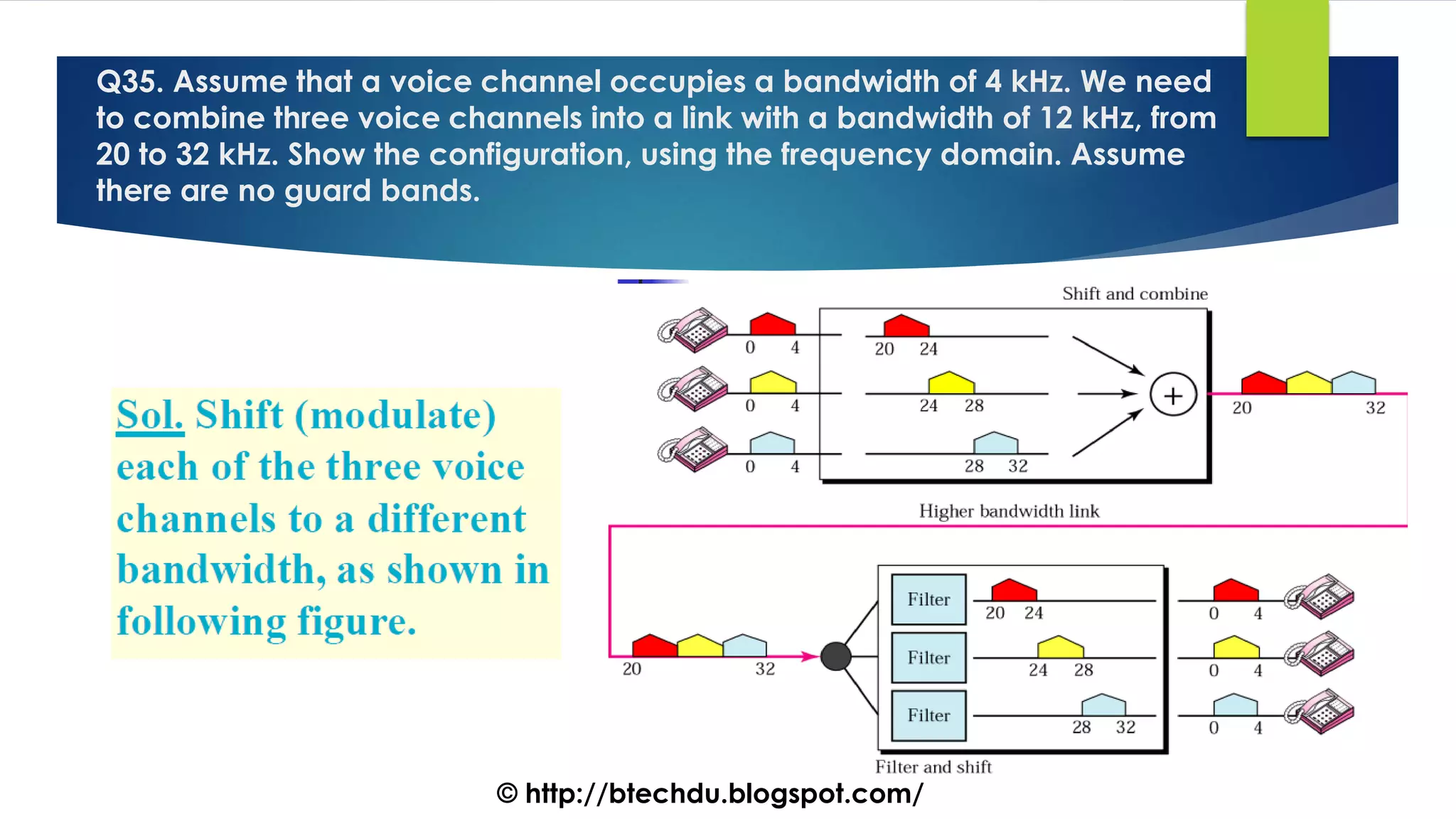
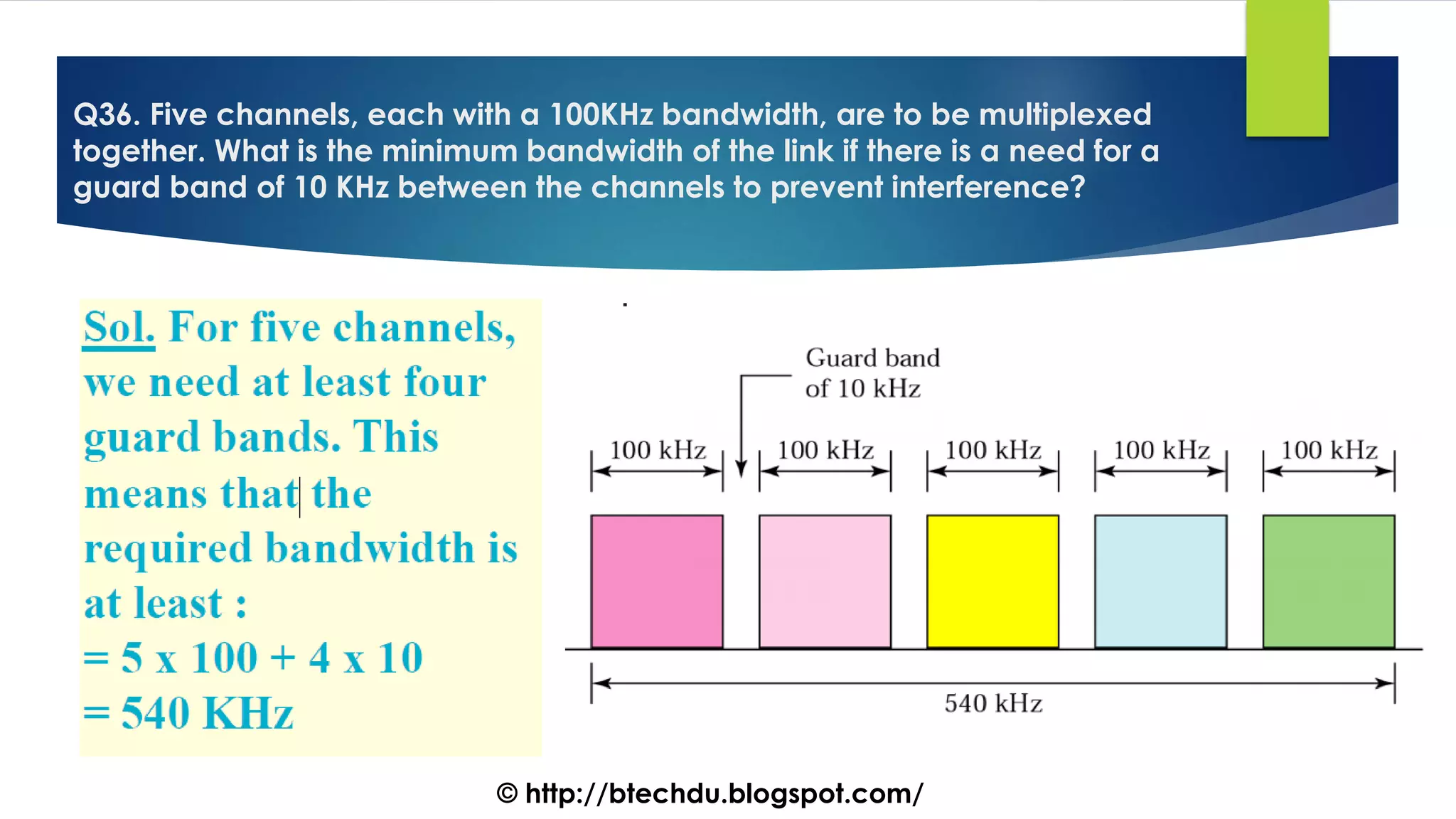
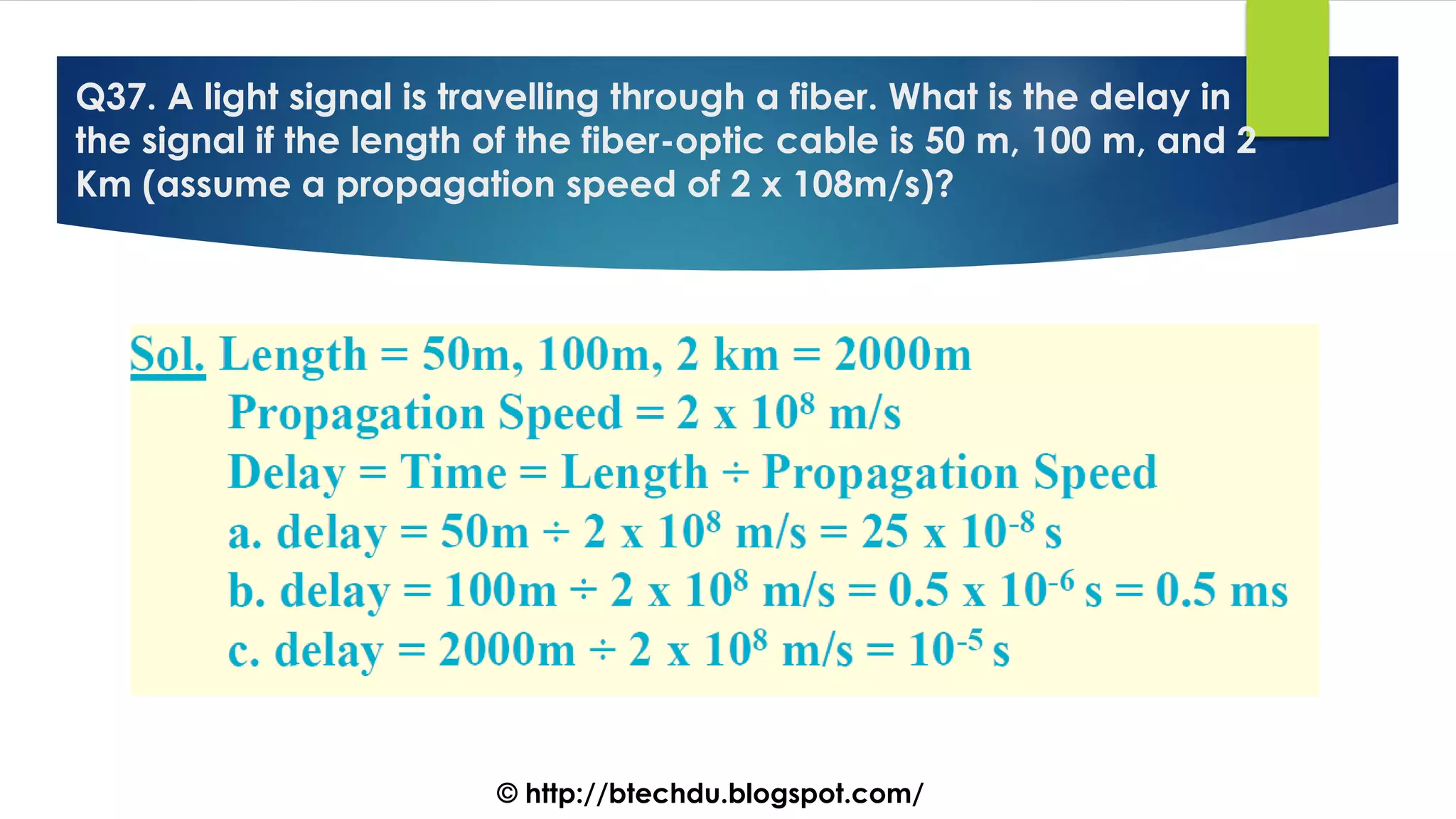
The document comprises a series of questions focused on physical layer concepts in data communication and networking. It addresses various topics such as signal-to-noise ratio, bandwidth, data rates, modulation techniques, and multiplexing, aimed at B.Tech computer science students at the University of Delhi. Each question seeks to explore theoretical and practical aspects of digital and analog transmission methods.