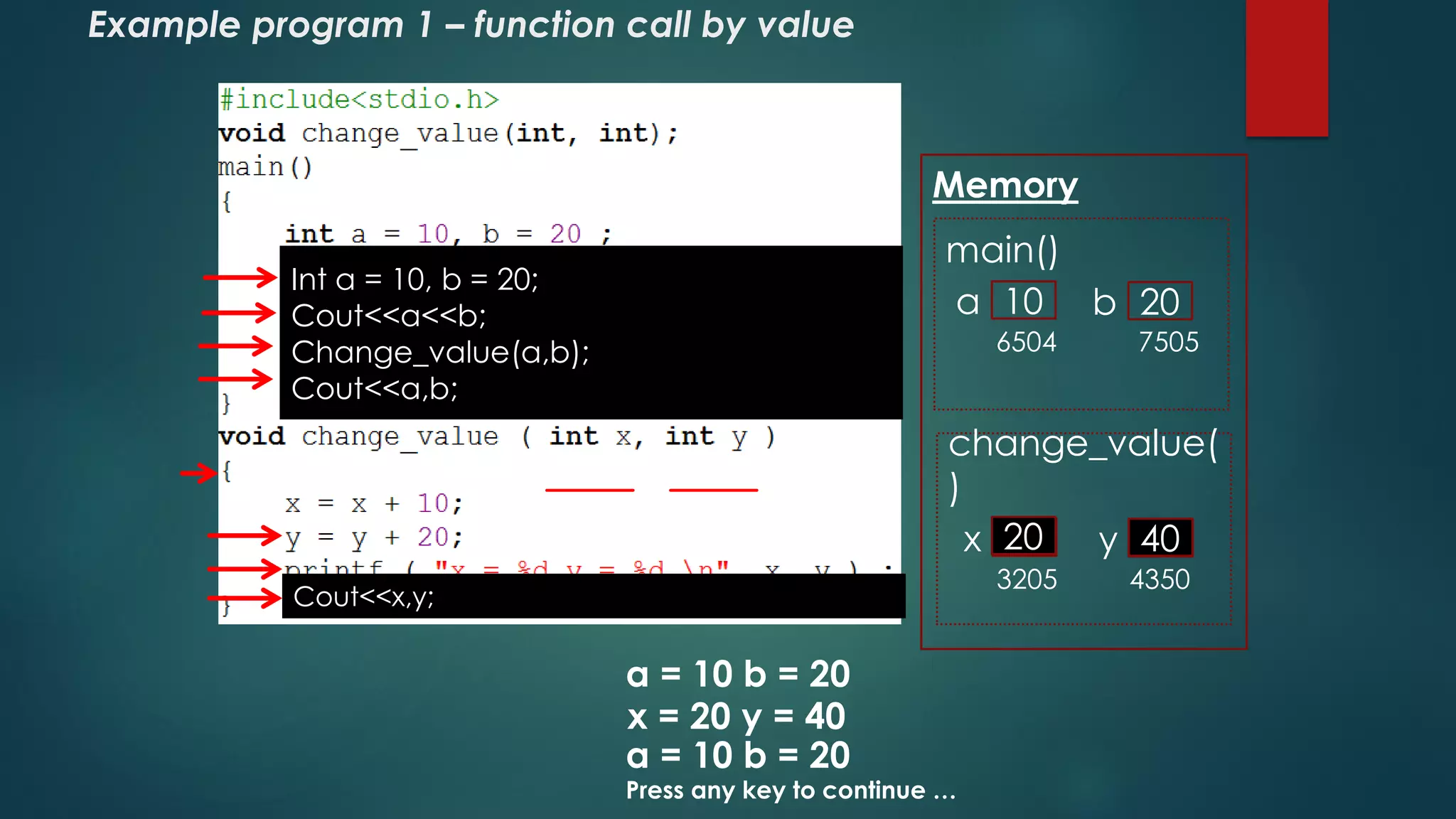
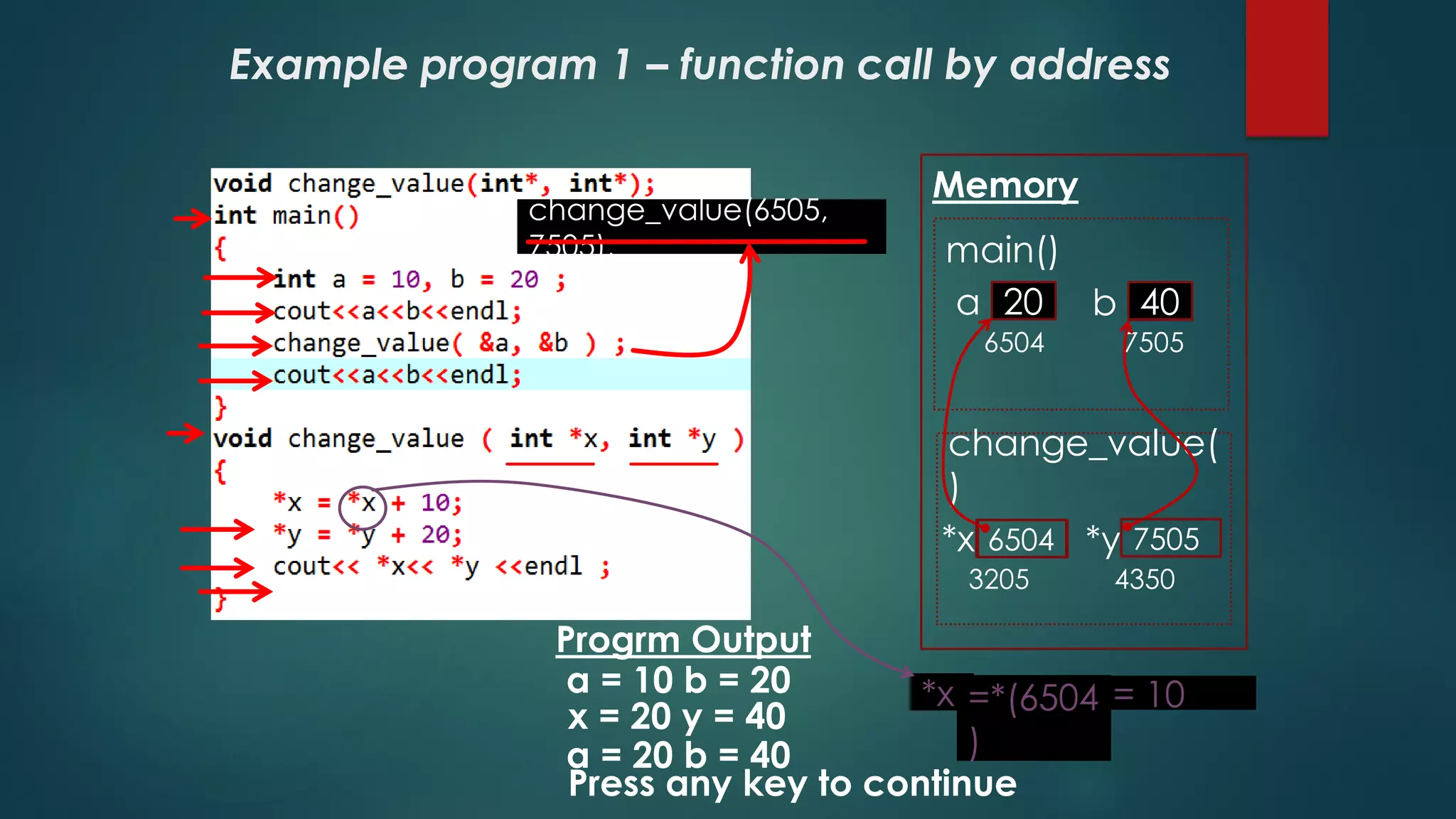
The document explains pointers in C++, defining a pointer as a variable that stores a memory address and introducing the declaration syntax. It covers the usage of operators for accessing memory addresses and values, as well as pointer initialization and function calls by value and address. Additionally, it describes arrays of pointers, demonstrating how each element can store different object memory addresses.








![Array of Pointers
An array of pointers is an array in which each element is a pointer. Each
element in the array can store a memory address. The array can store the
memory addresses of different objects of same type.
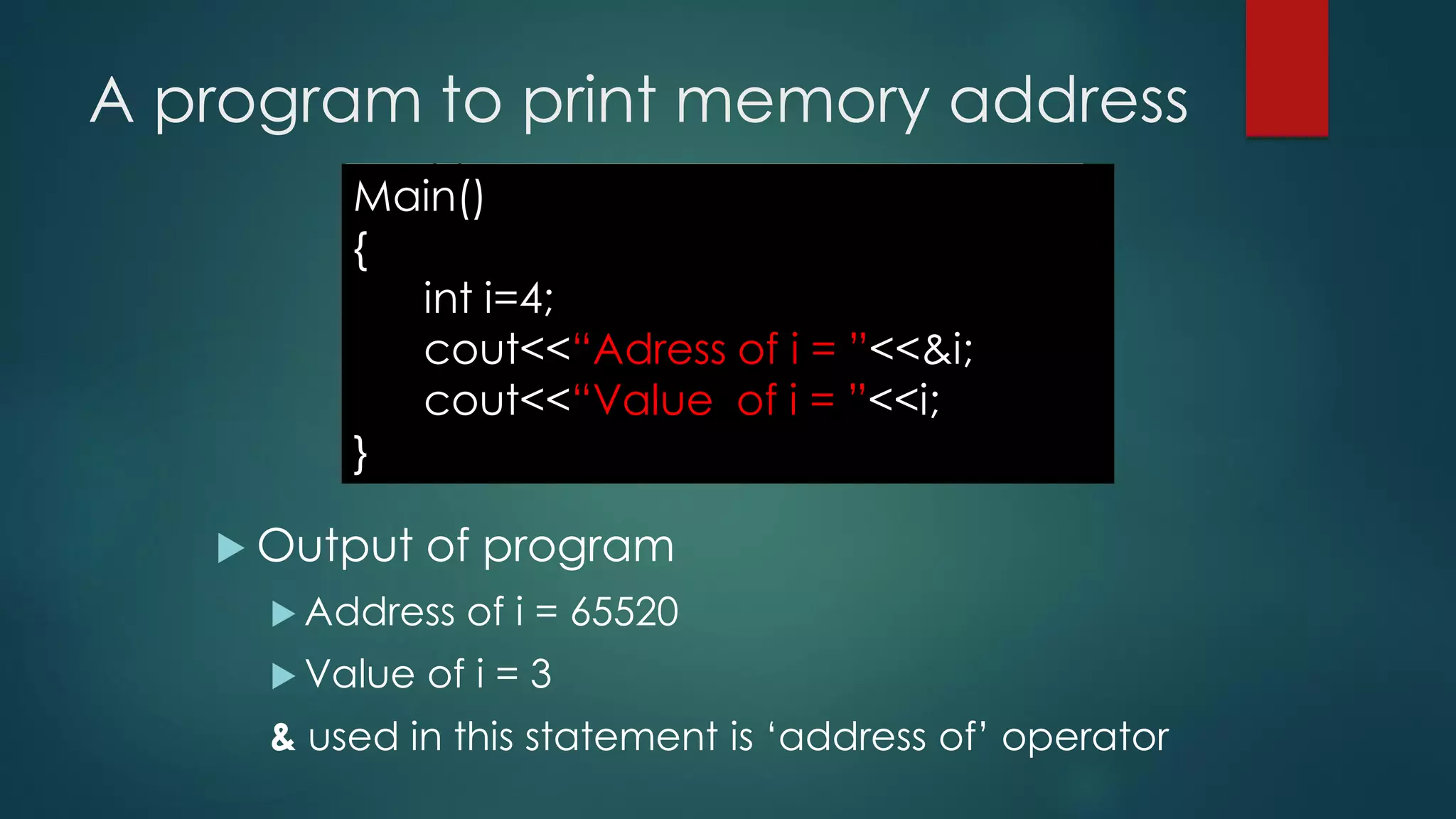
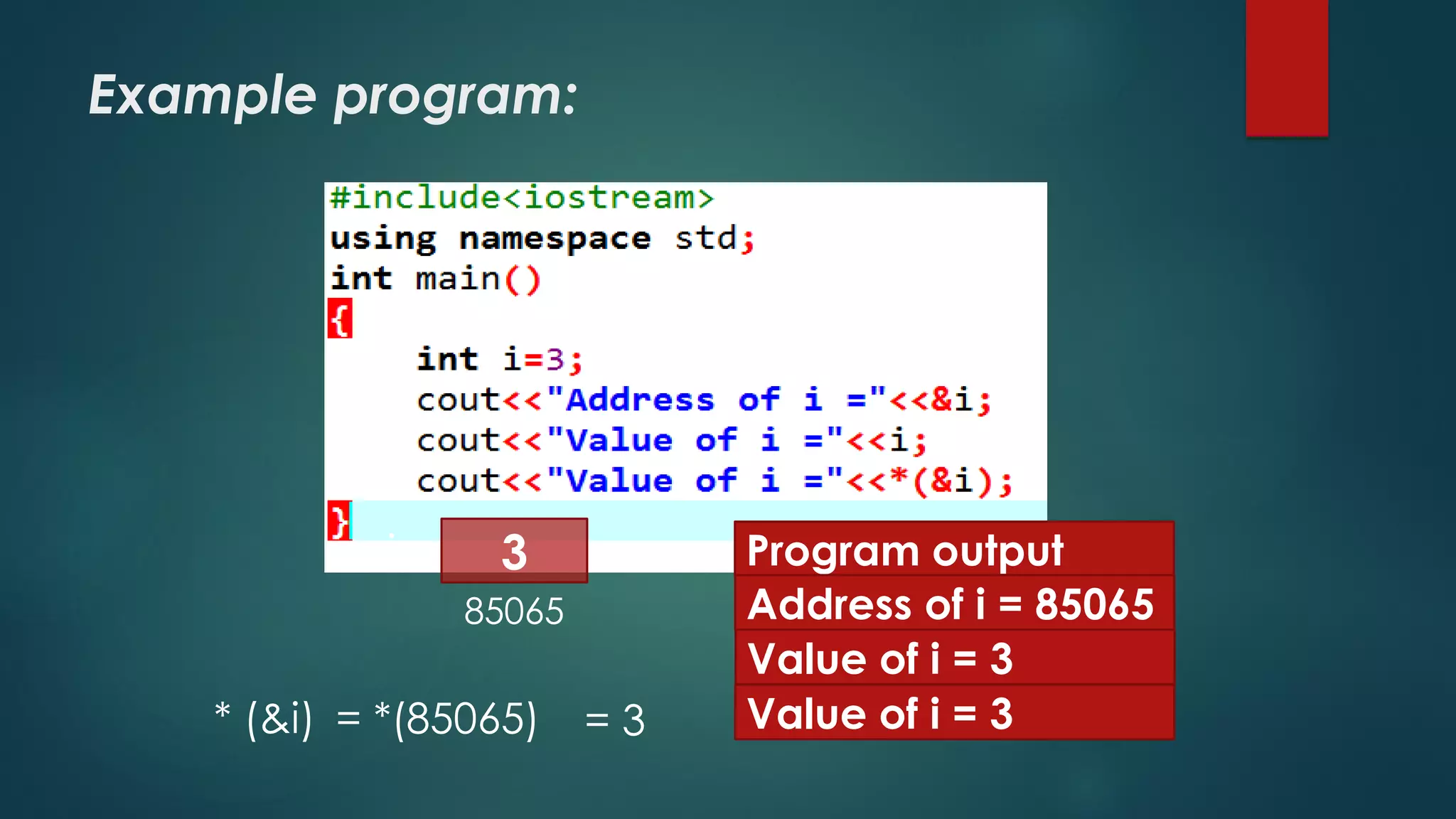
Example:
Int main()
{
int *ptr [3],a, b, c, i;
ptr [0]=&a;
ptr [1]=&b;
ptr [2]=&c;
Cout<<“Enter 3 integers:”<<endl;
Cin>>a>>b>>c;
Cout<<“You entered the following values:”;
For(i=0;i<3;i++)
Cout<<*ptr [ i ] ;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationpointers-190522195014/75/Pointers-in-Programming-13-2048.jpg)
