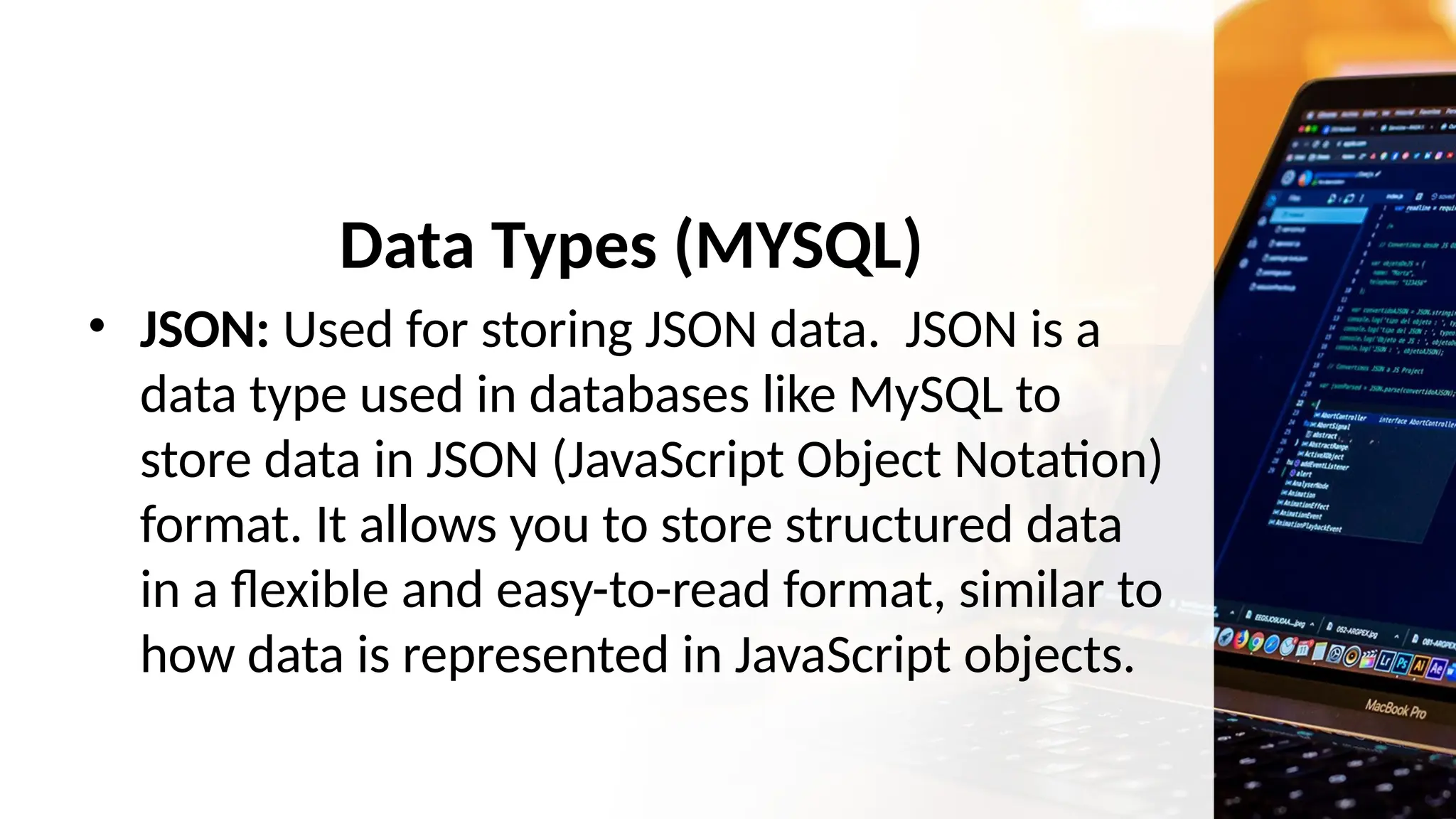
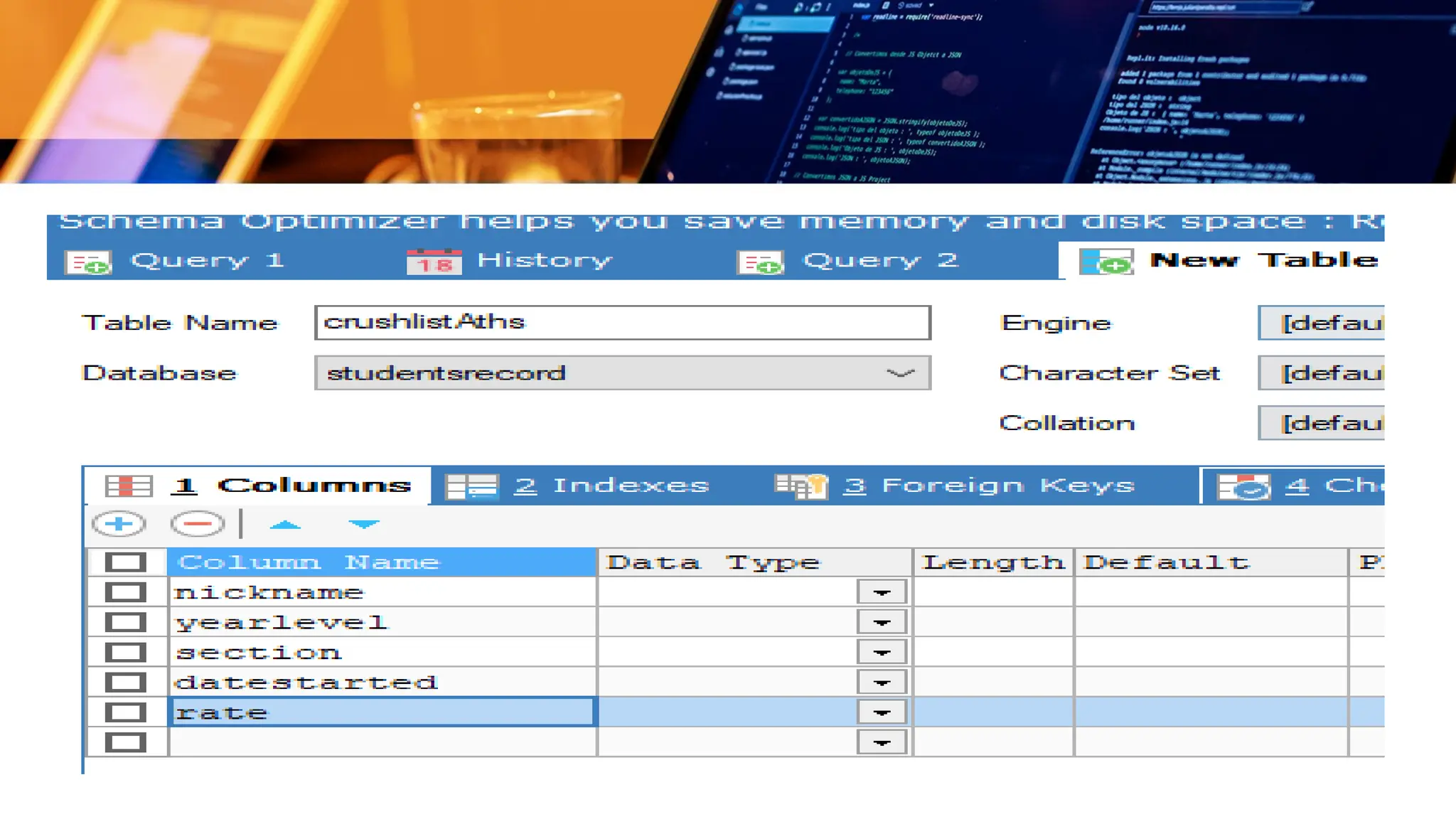
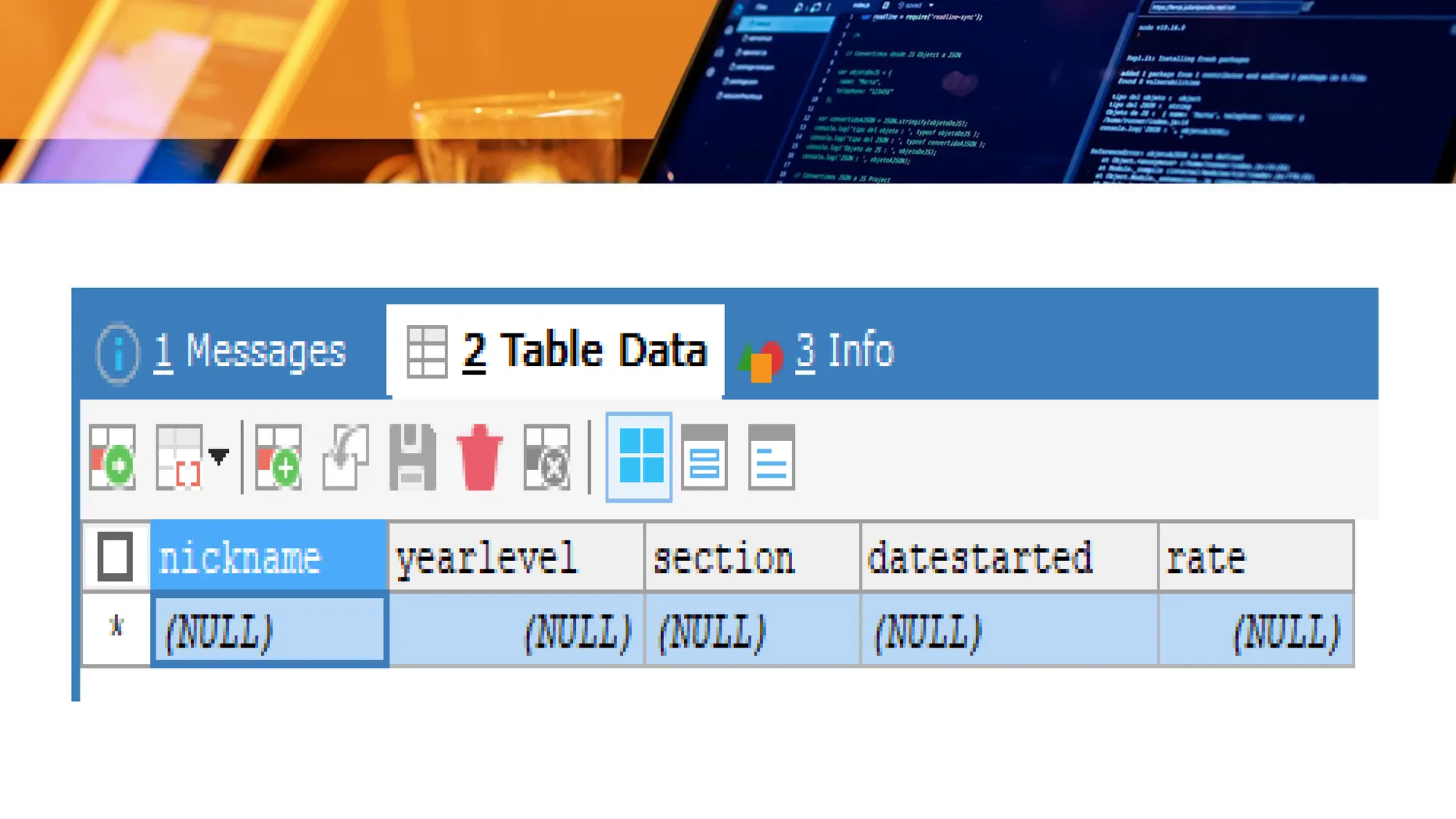
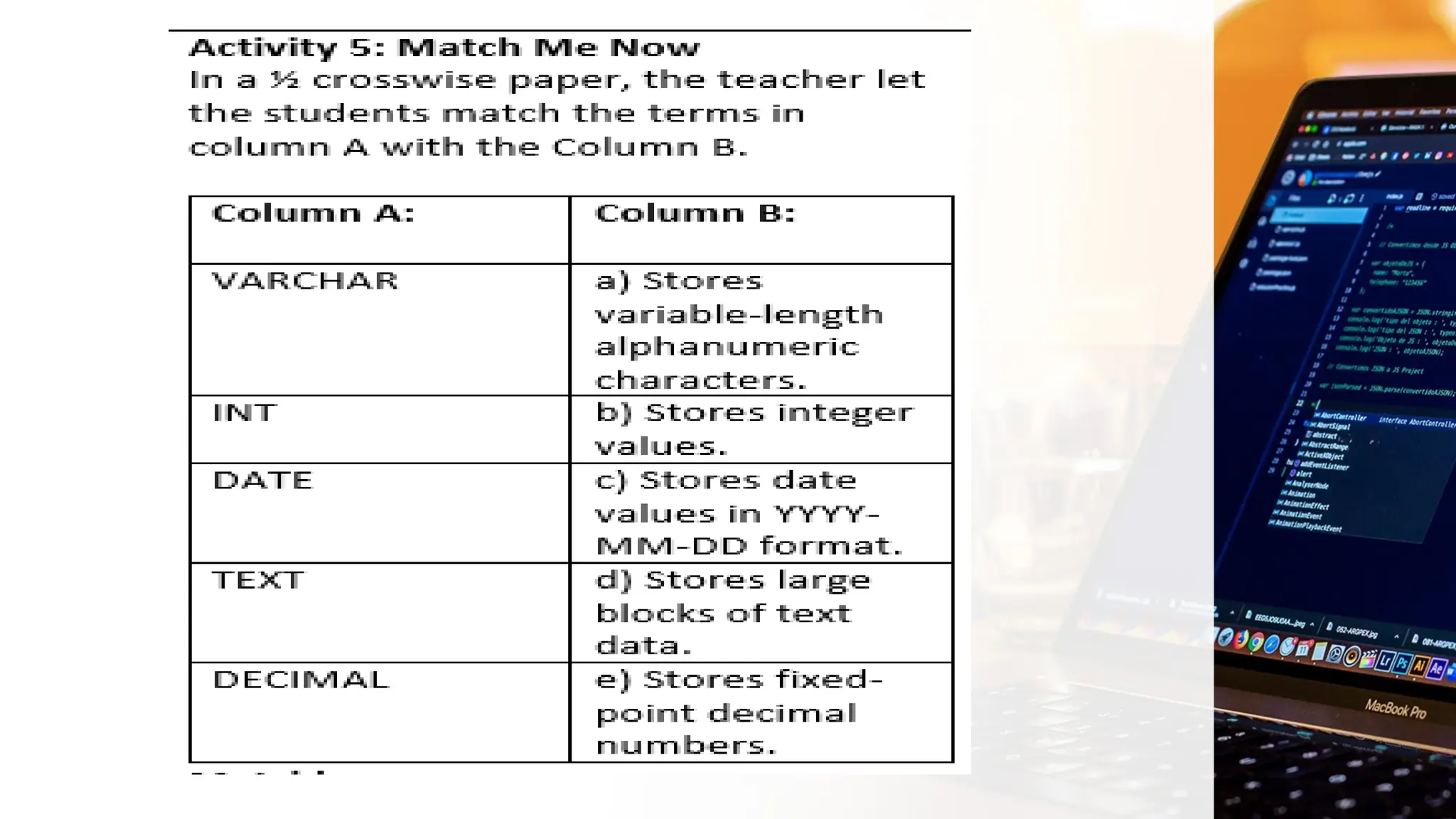
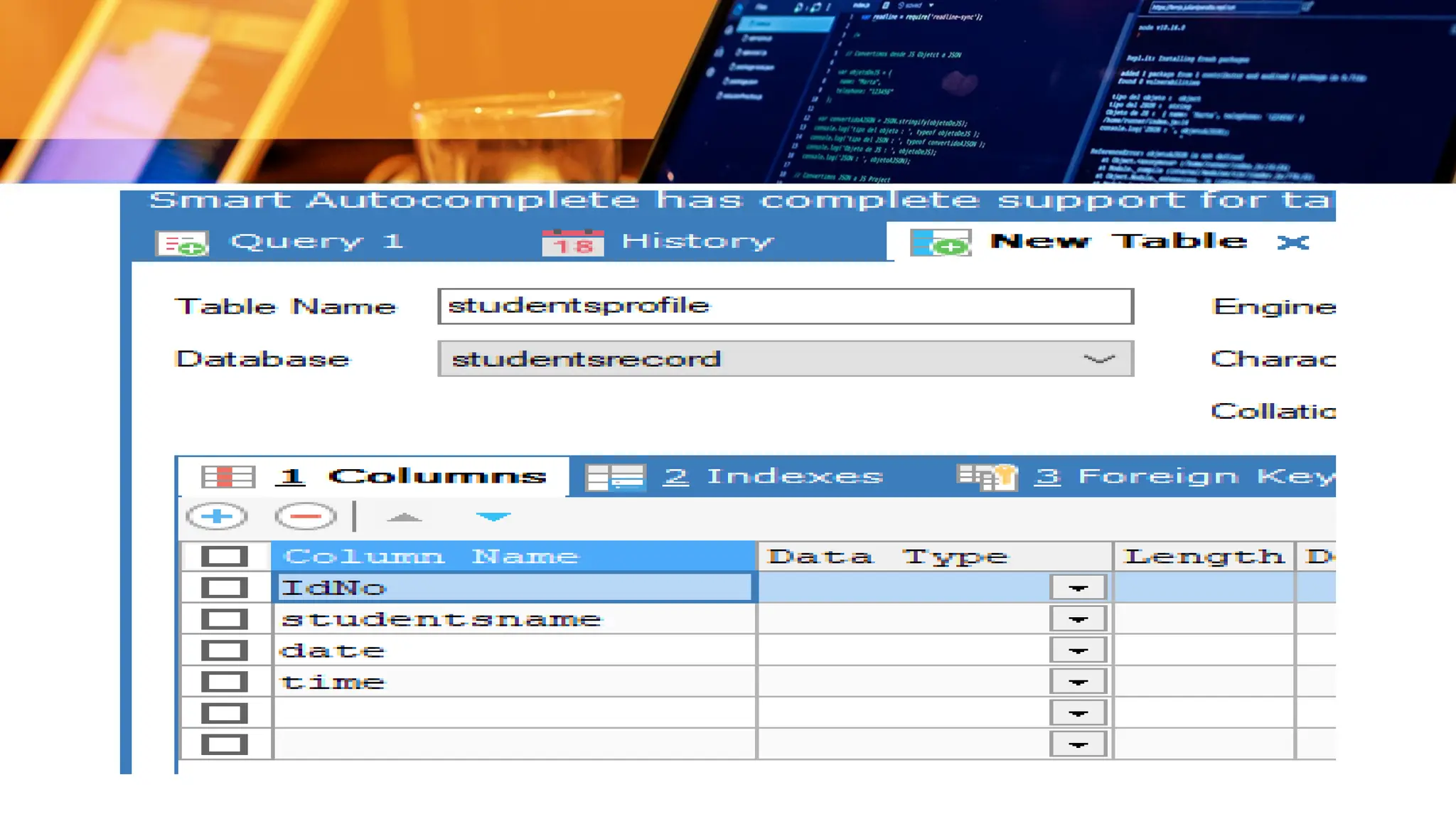
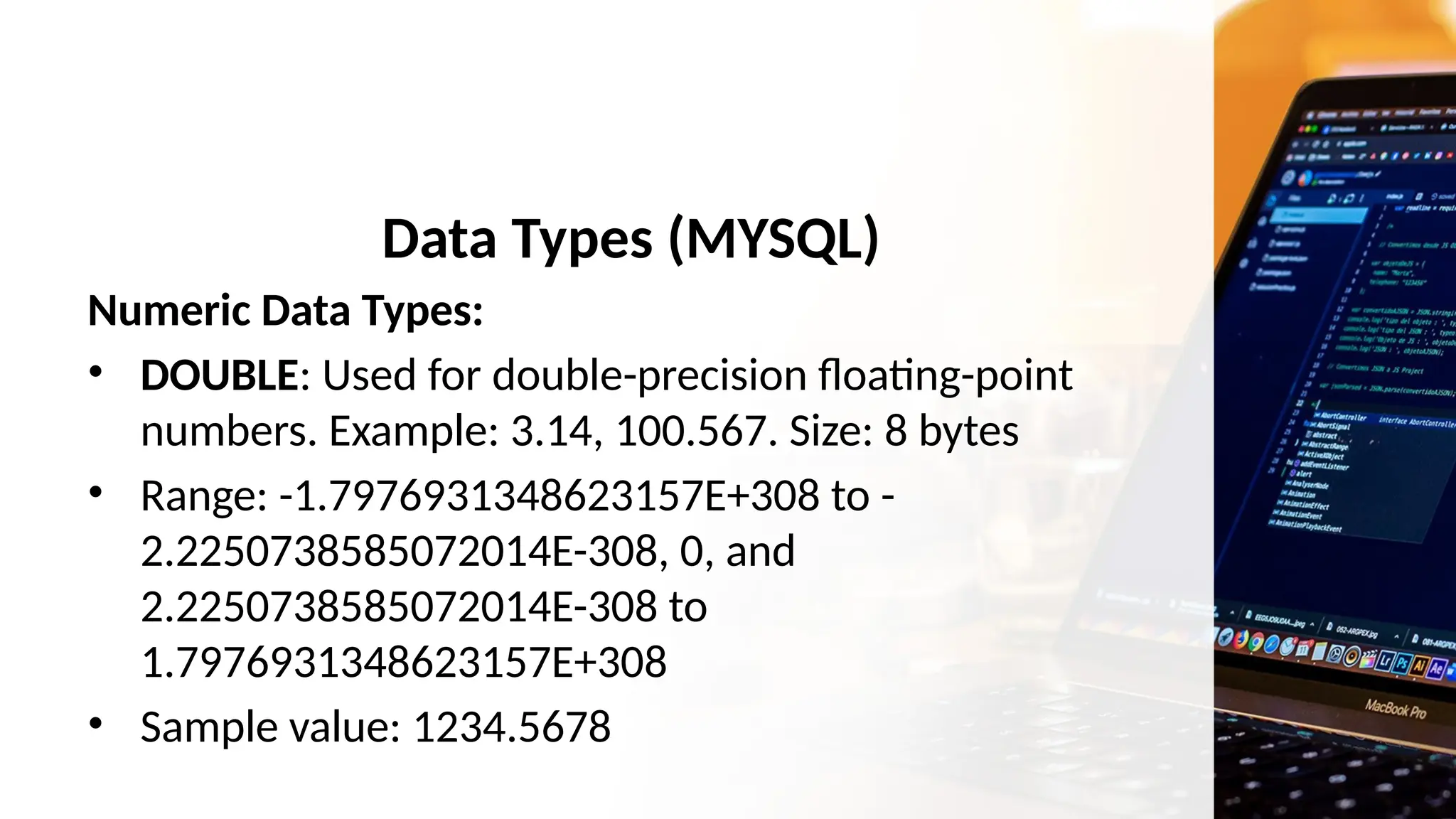
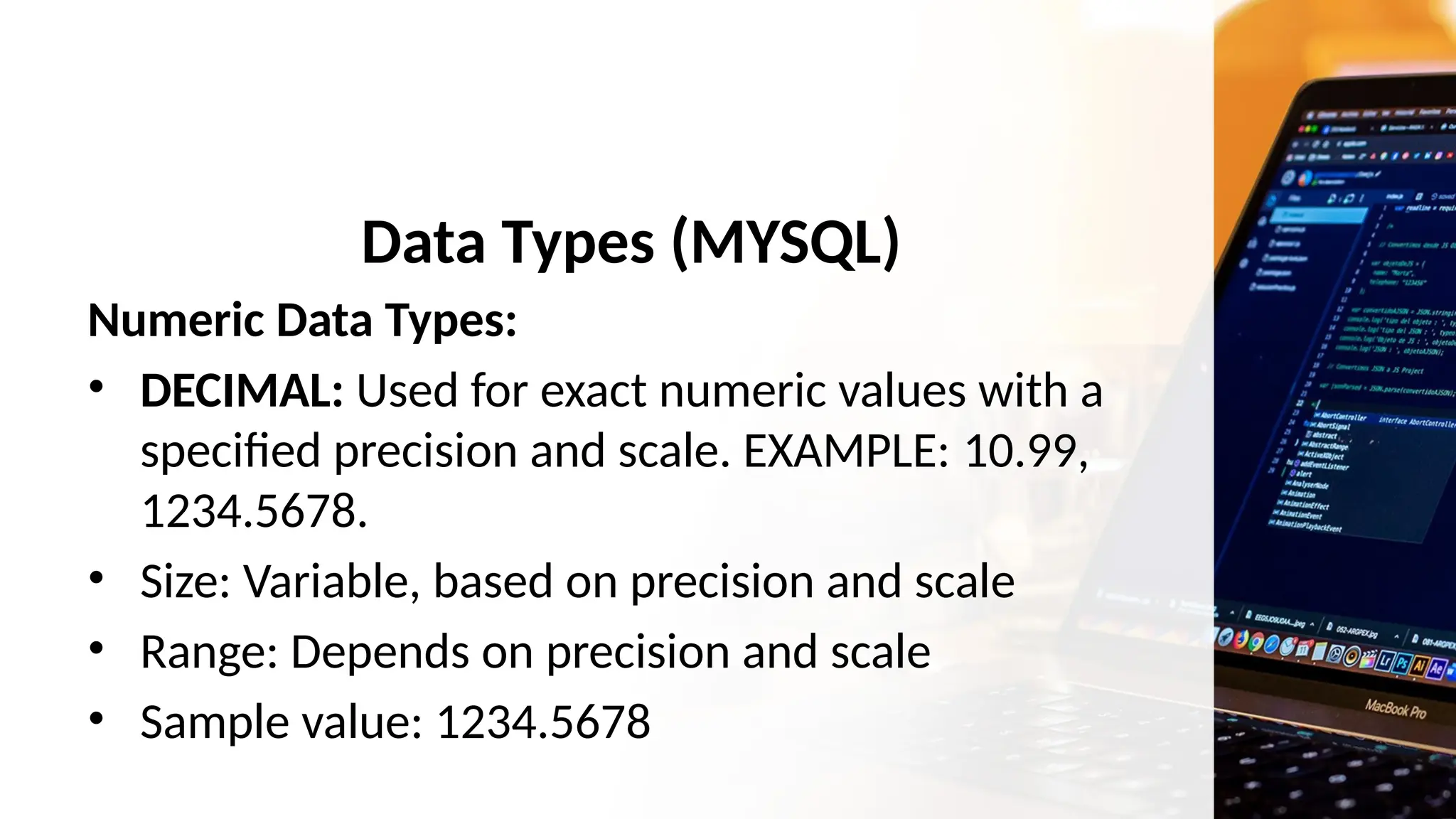
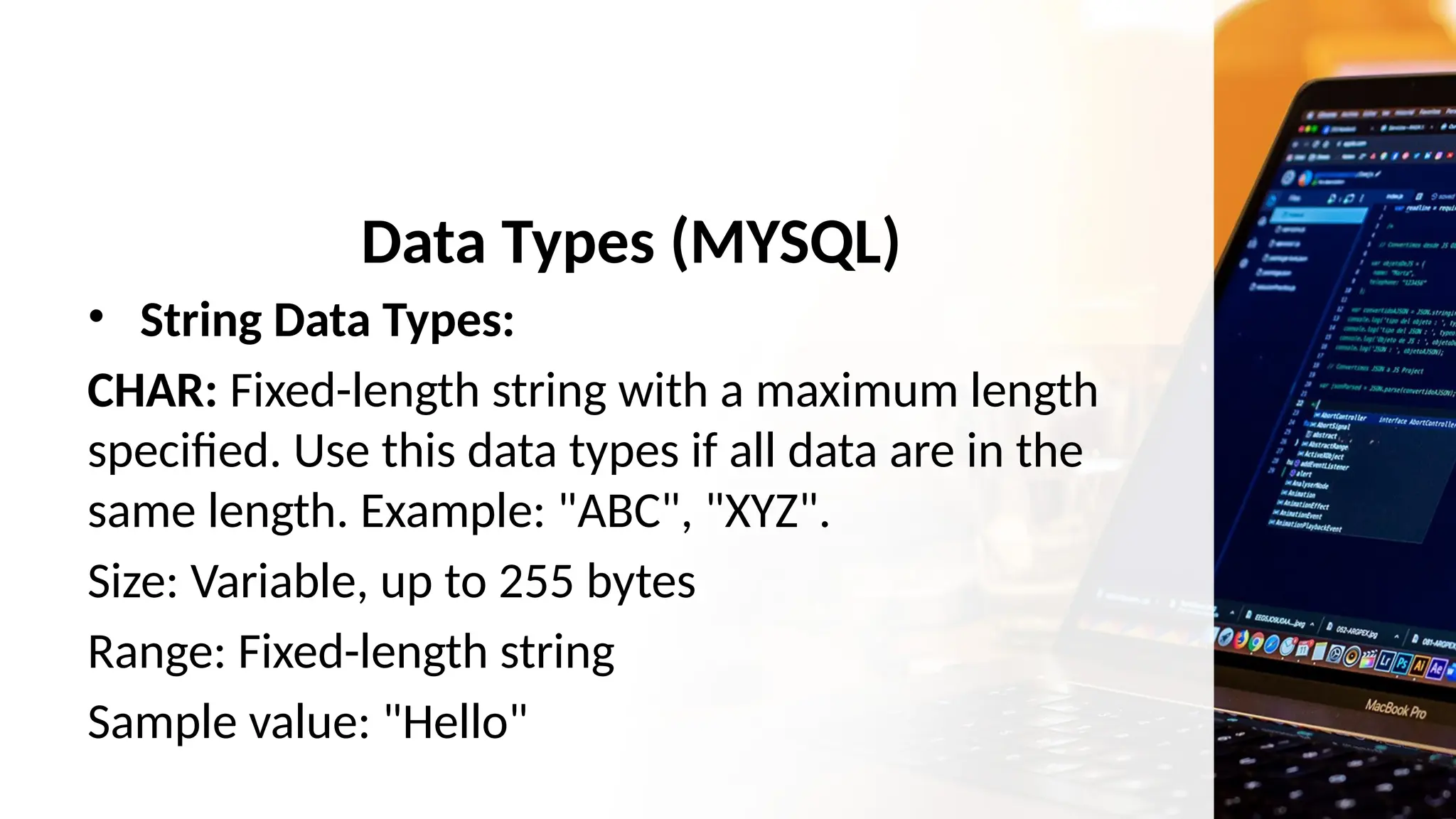
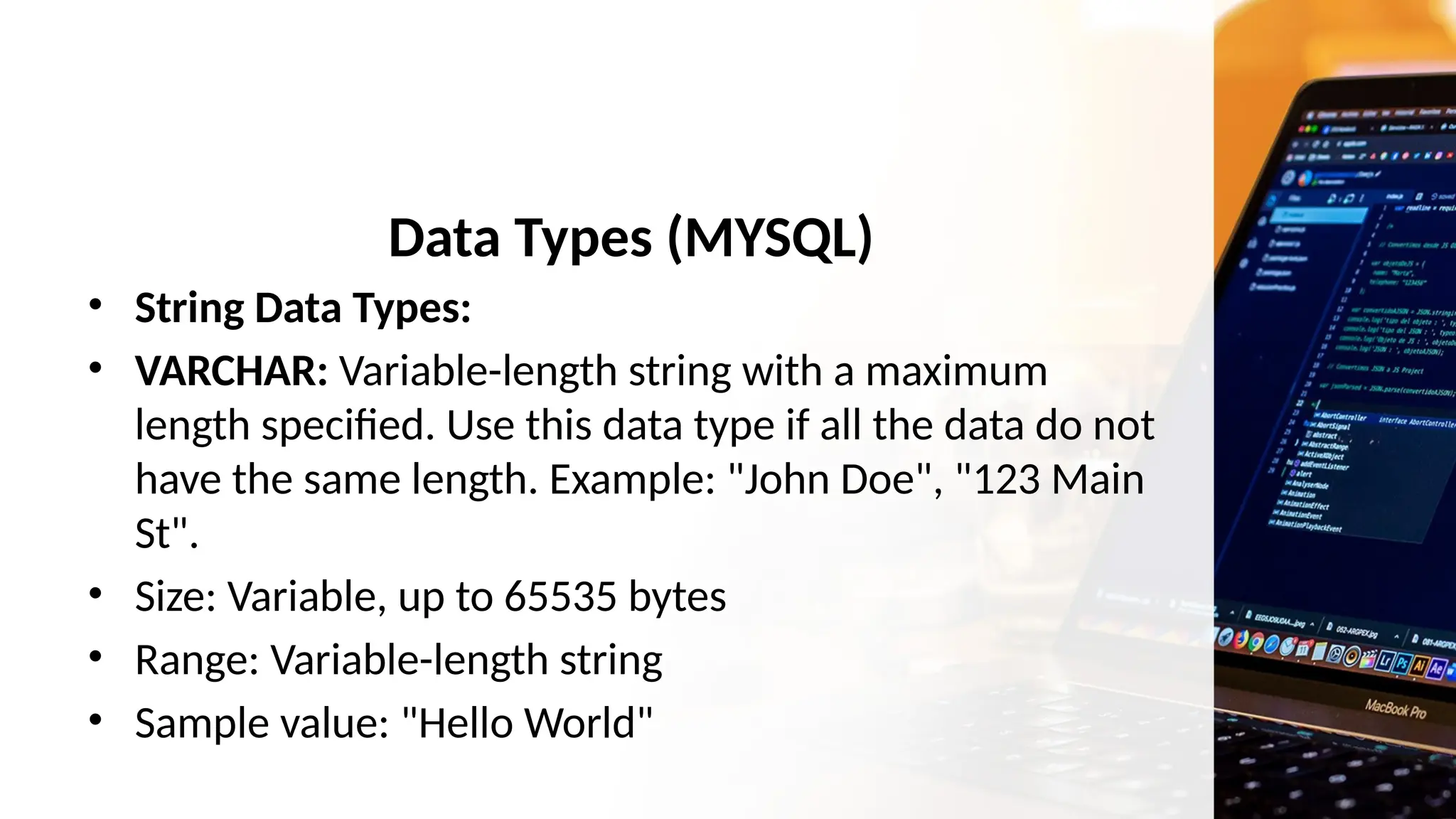
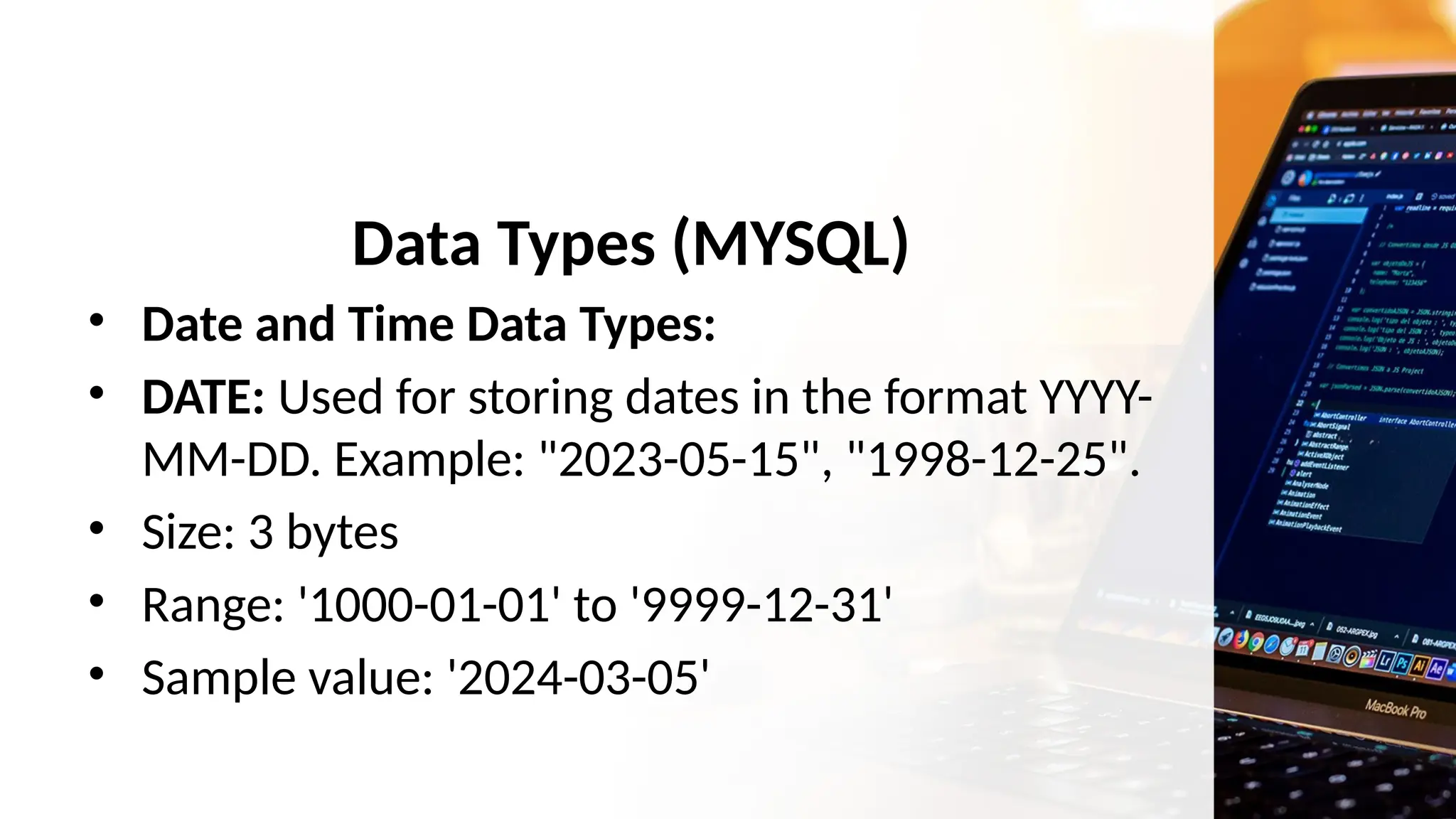
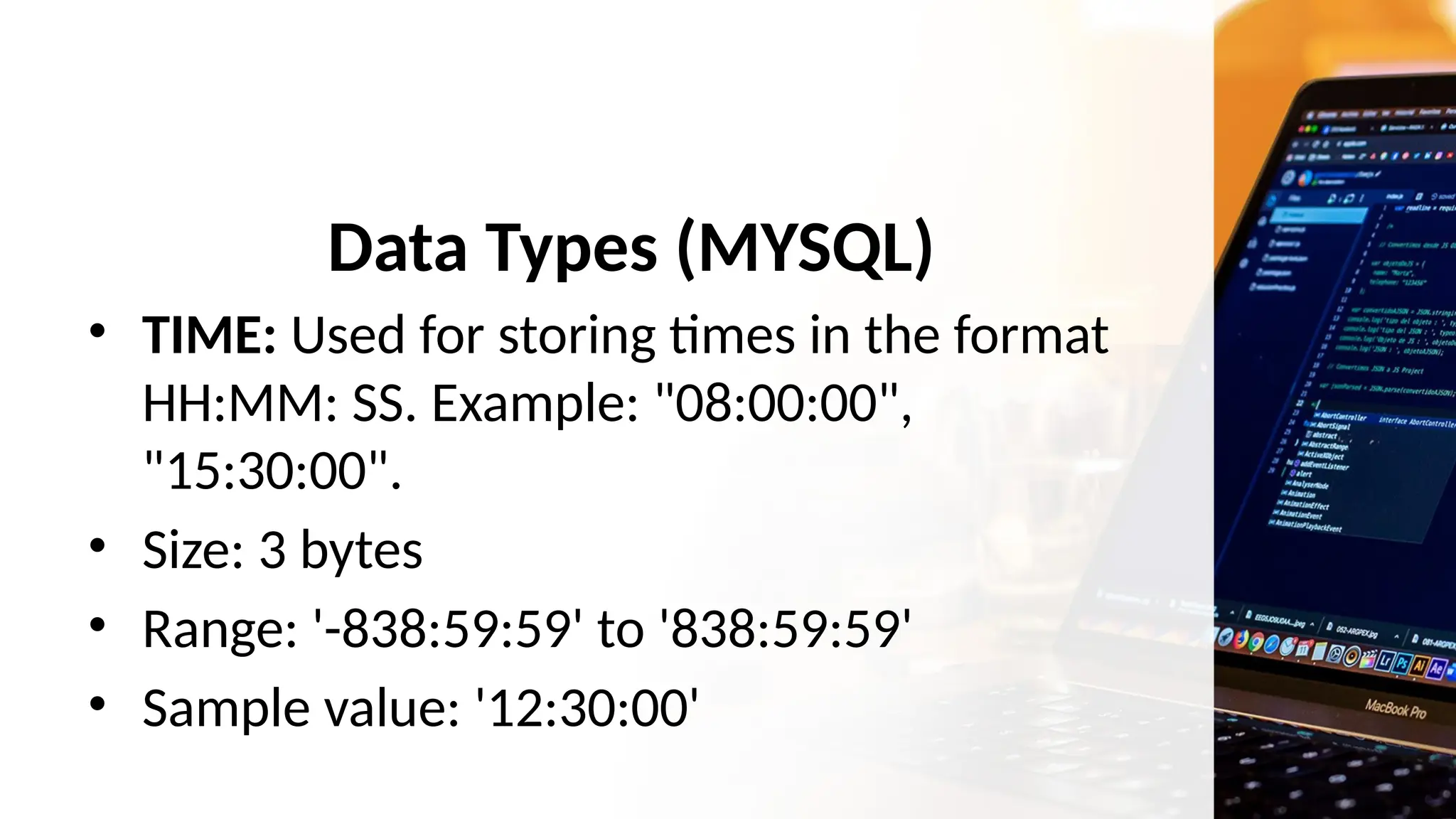
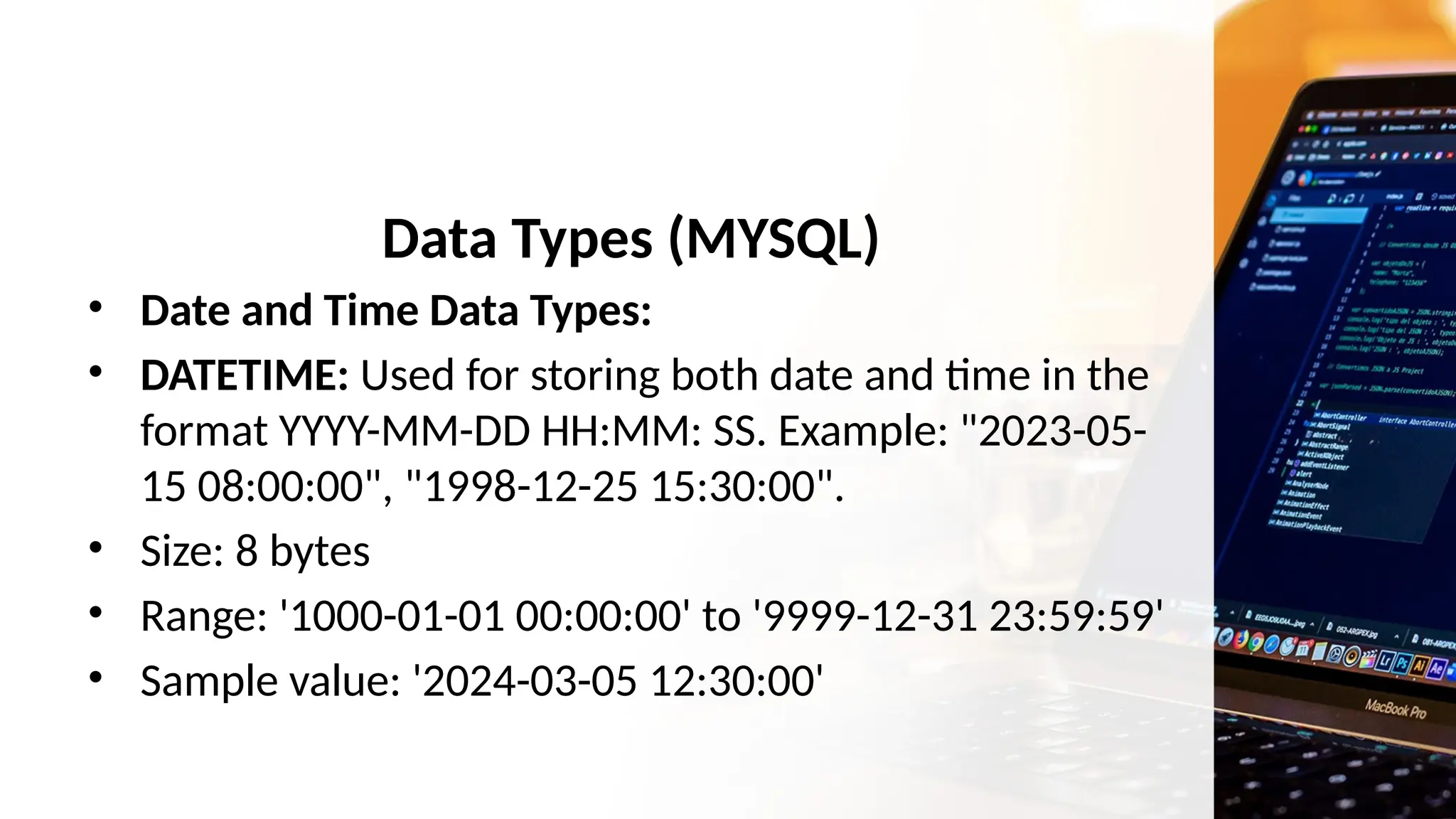
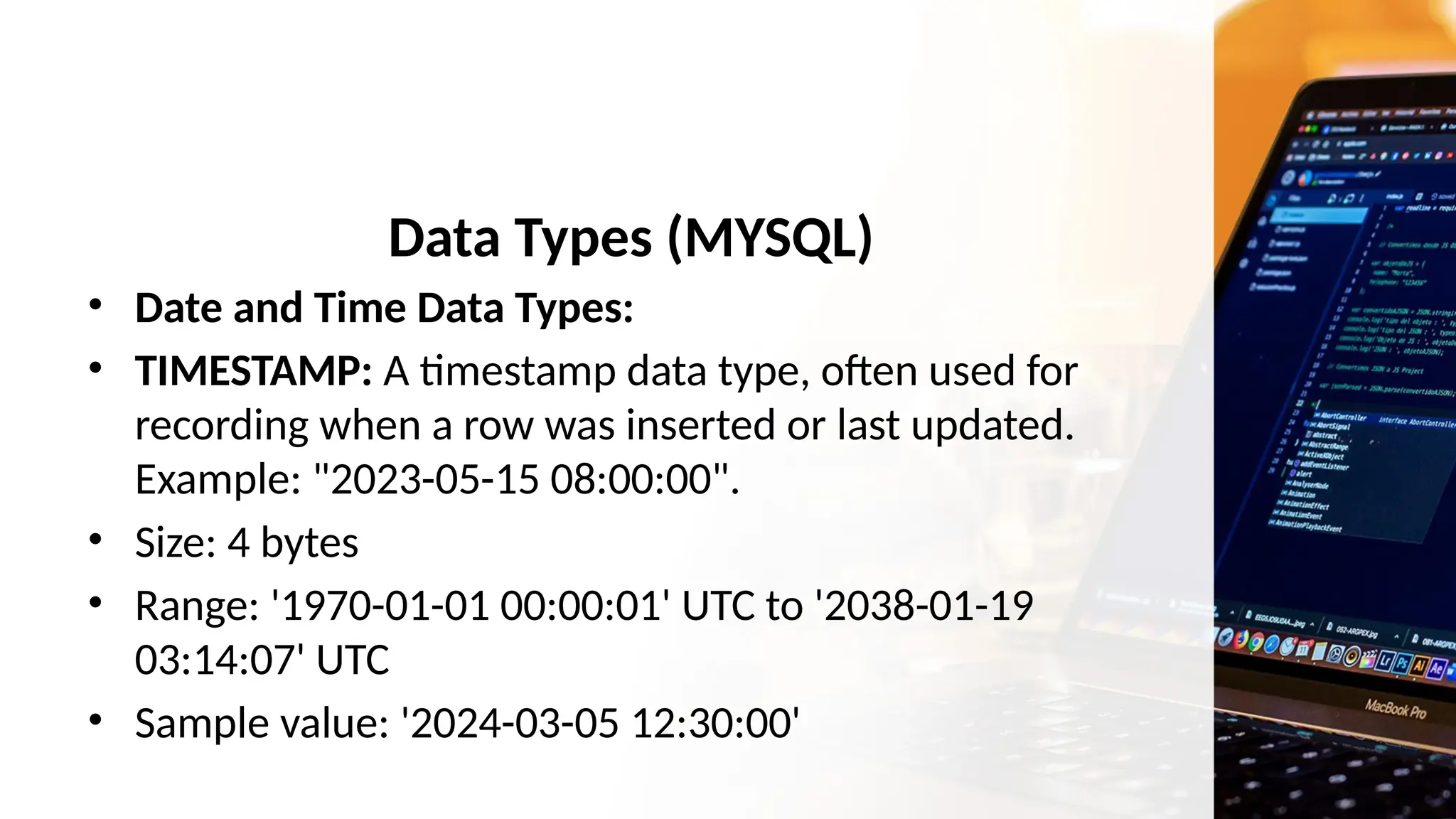
The document outlines a lesson plan focusing on different types of data used in MySQL, incorporating two engaging activities to enhance student understanding. Students will learn about various data types such as numeric, string, and date/time through songs and hands-on exercises, like identifying the appropriate data type for given tasks. Objectives include recognizing different data types, understanding their importance, and discussing their applications in MySQL.









![Data Types (MYSQL)
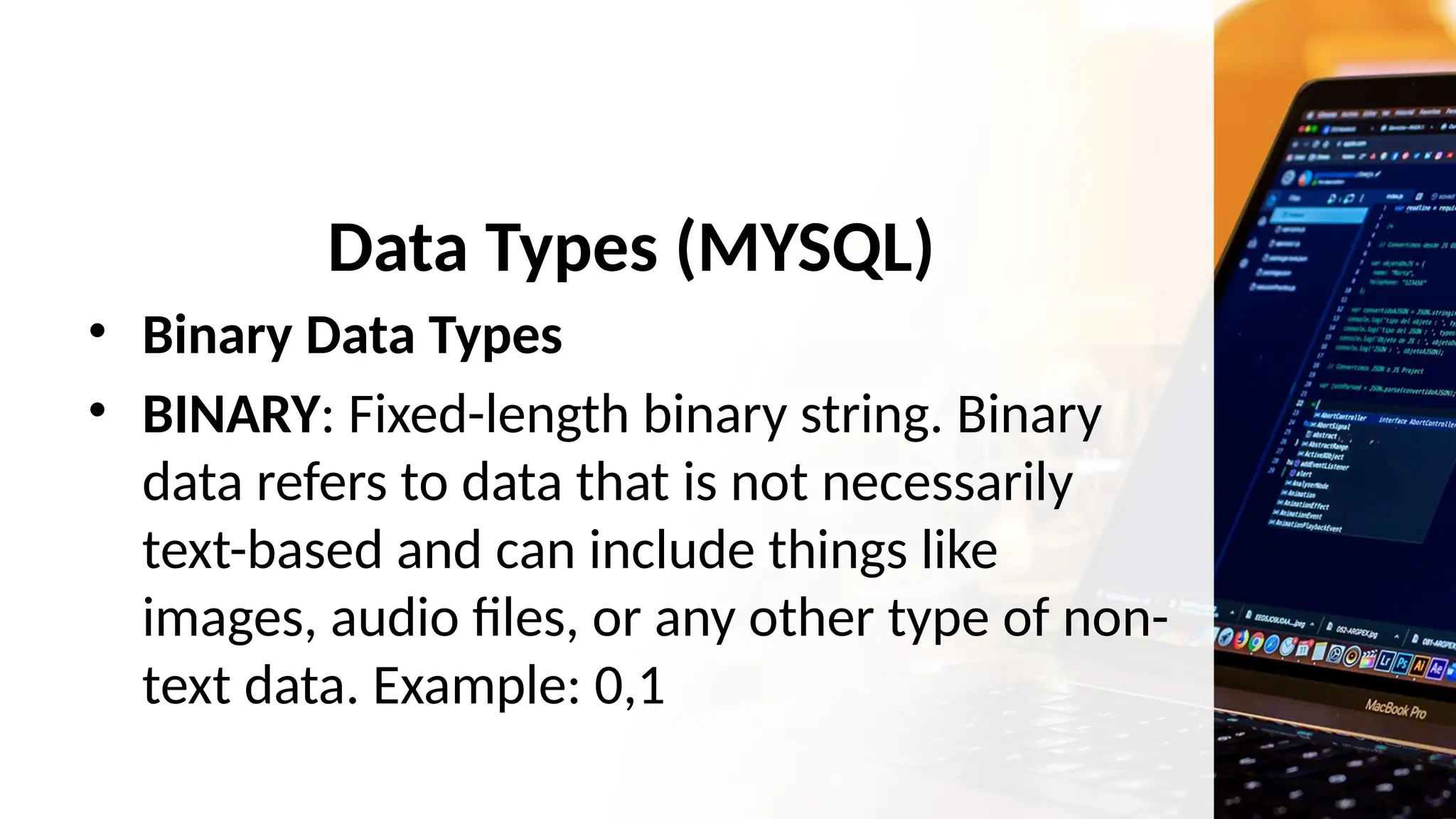
• Binary Data Types
• VARBINARY: Variable-length binary string.
VARBINARY would be ideal for storing these
images because it can accommodate different
sizes without wasting storage space.
• BLOB: Used for storing large binary objects like
images or files. Example: [IMAGES].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptcreateive-240902004523-221145ab/75/PPT-CREATEIVEhahhahahahhahahahahahaha-pptx-20-2048.jpg)