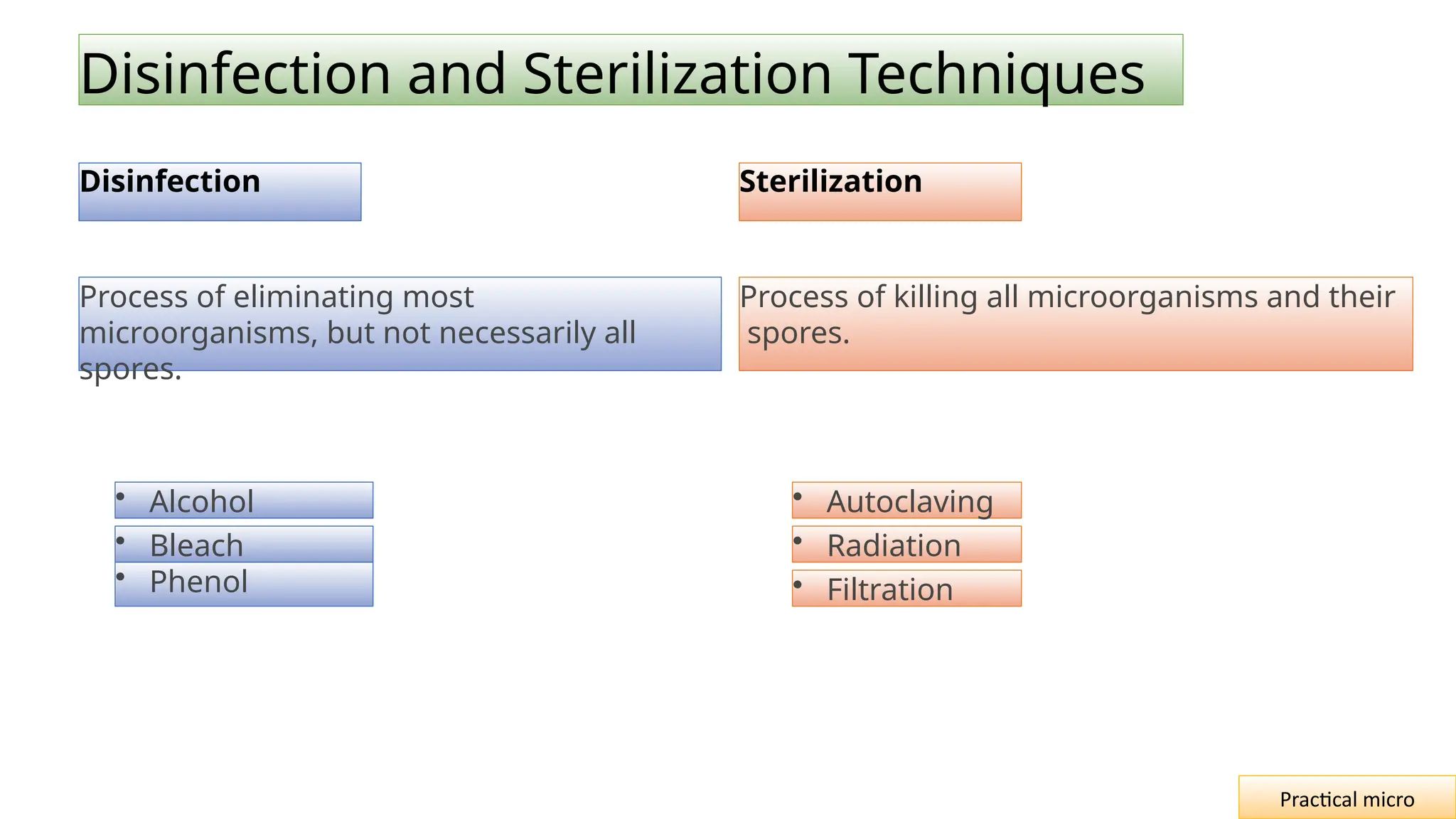
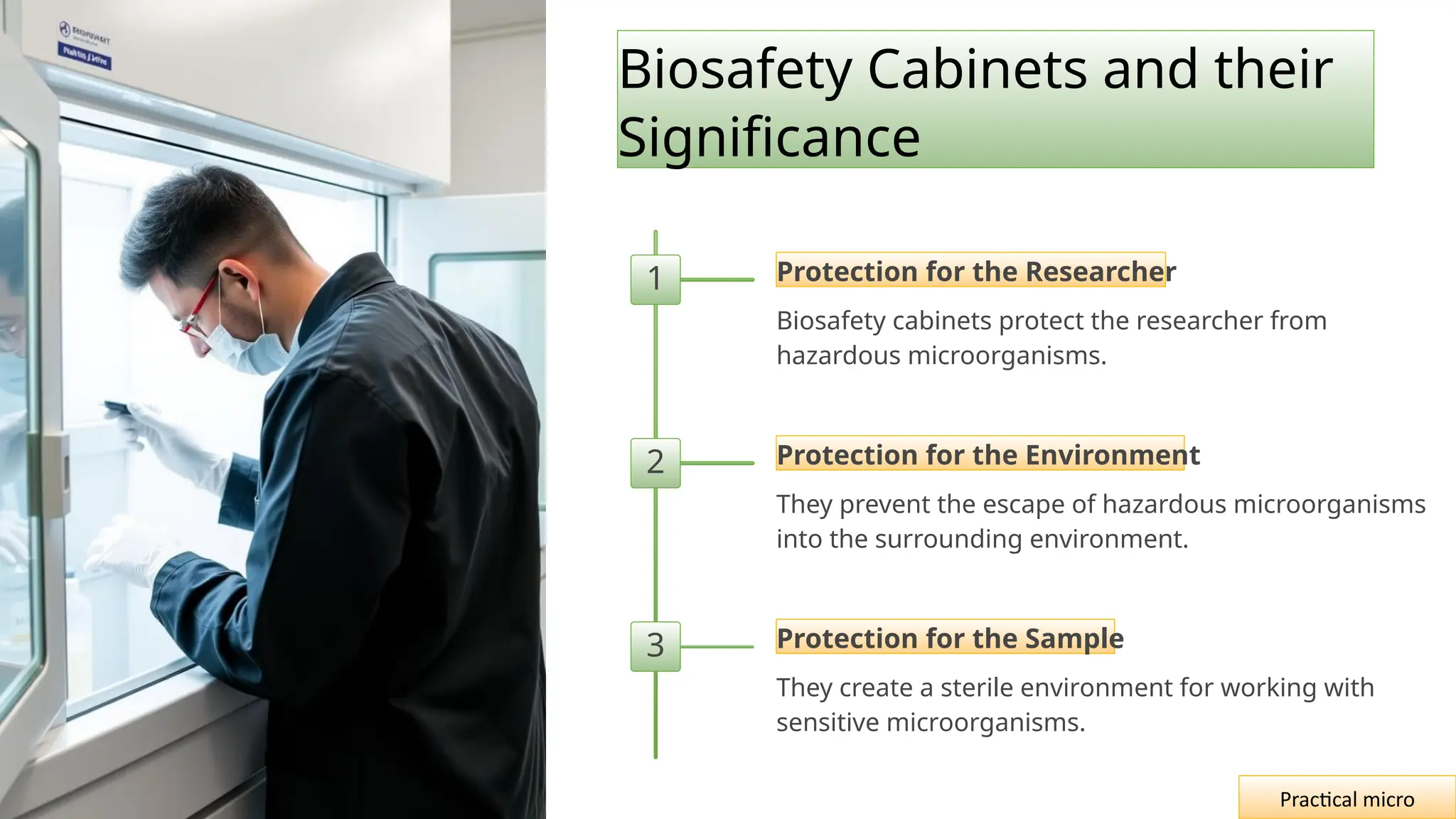
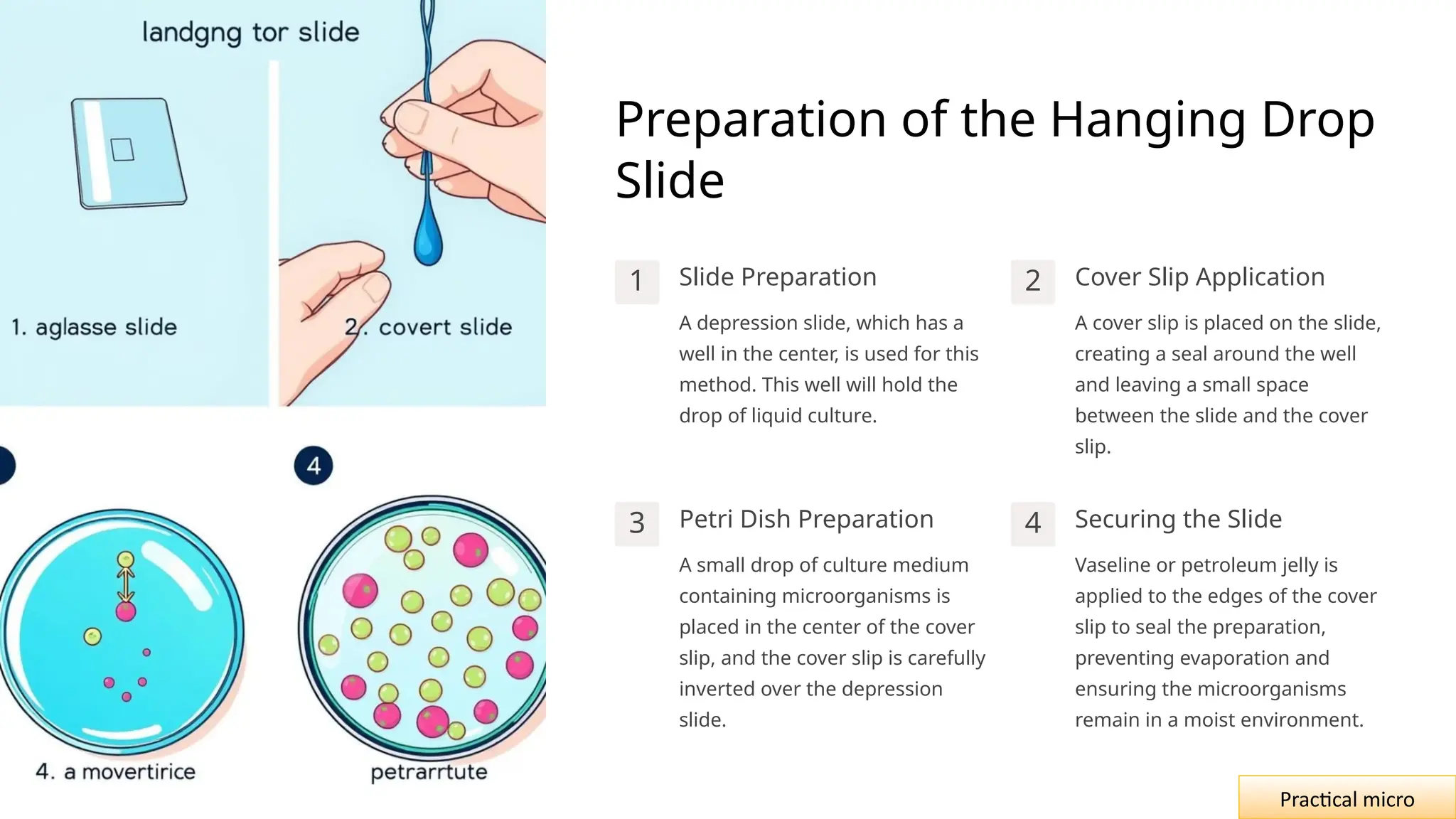
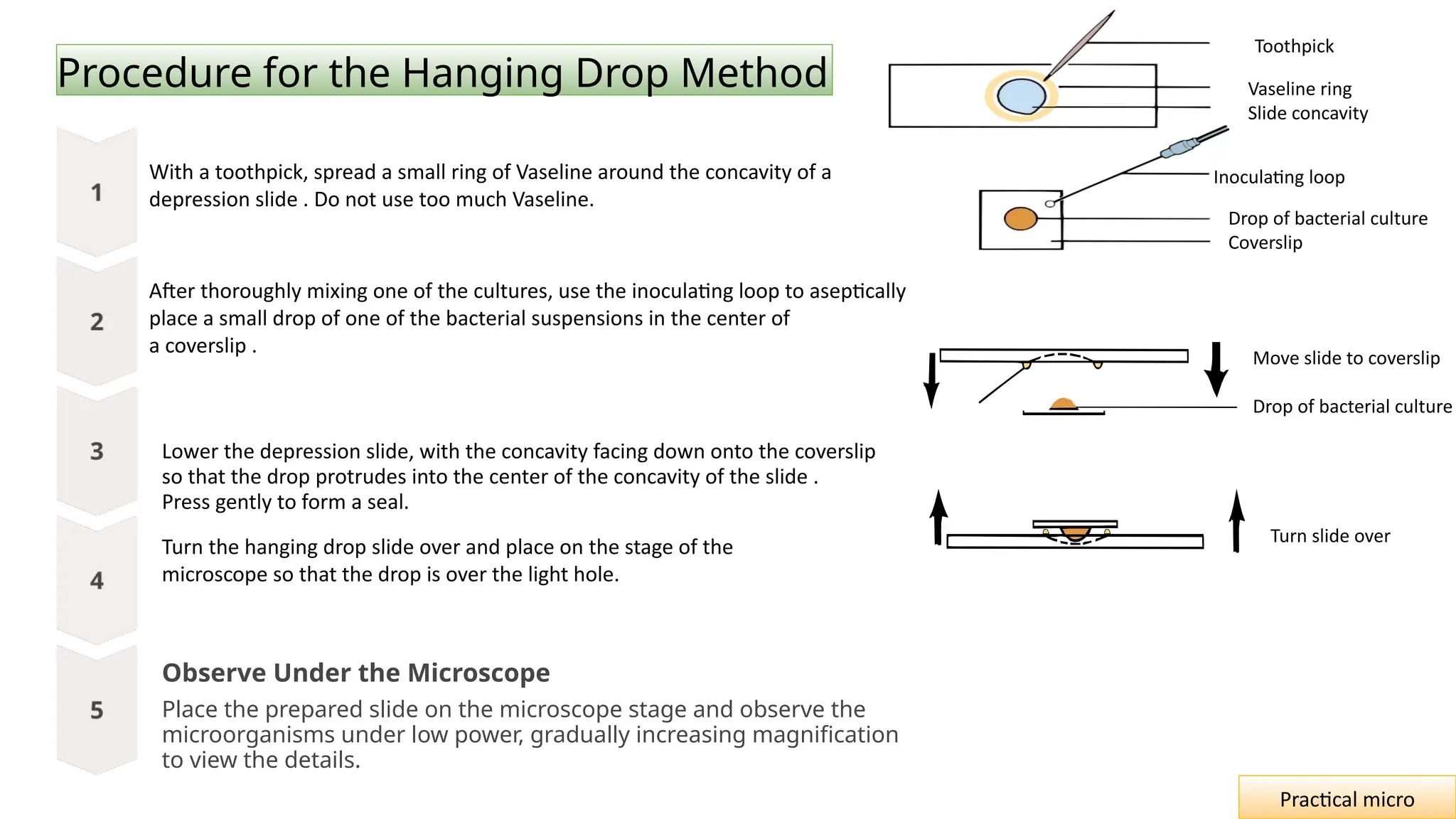
The document outlines essential safety measures and laboratory practices in microbiology, emphasizing the importance of personal protective equipment and proper handling of biohazardous materials. It details the hanging drop method as a key technique for observing the motility and behavior of microorganisms, discussing its preparation, advantages, and limitations. The document underscores the significance of these practices for researchers, environmental safety, and experimental integrity.