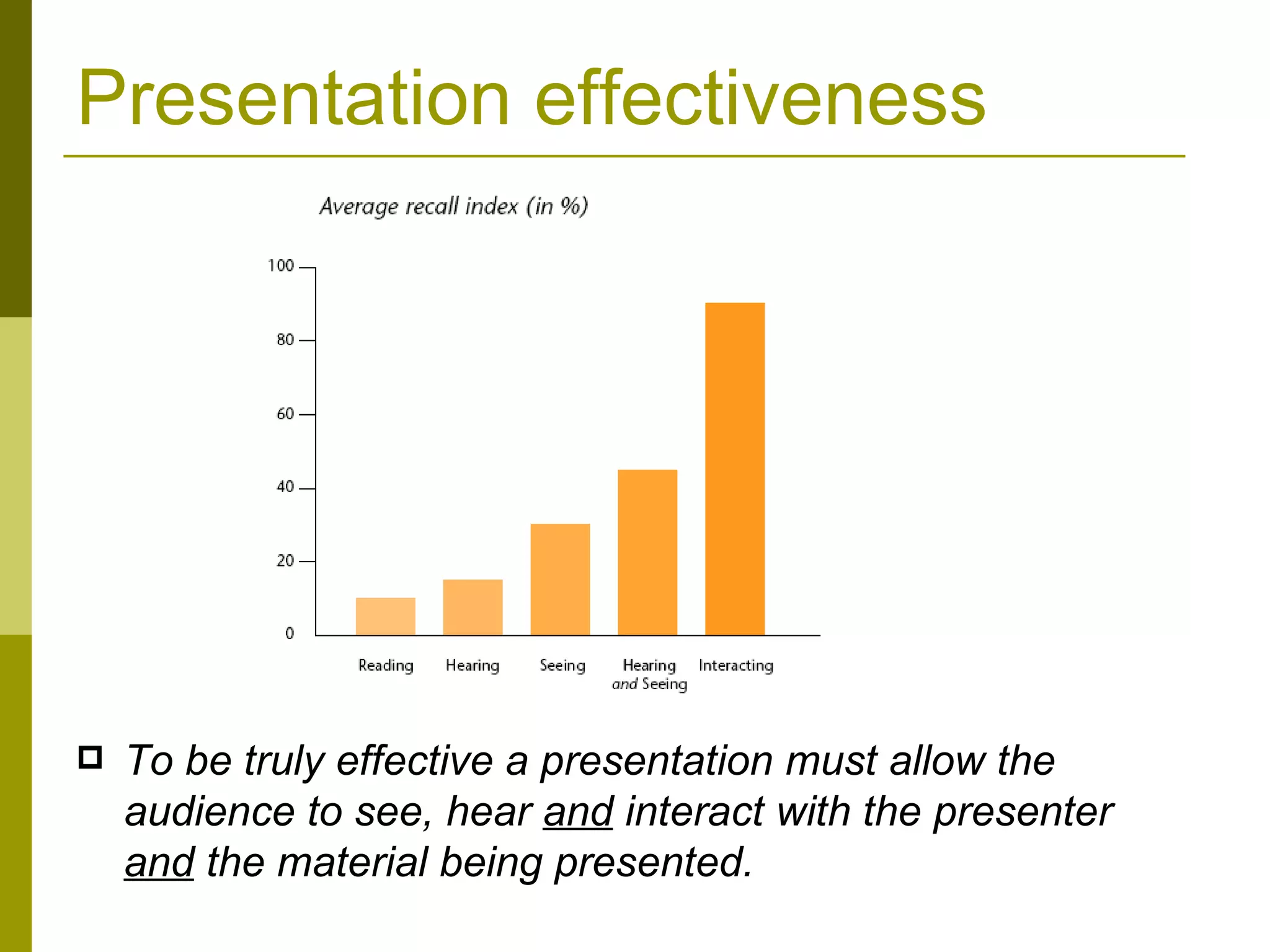
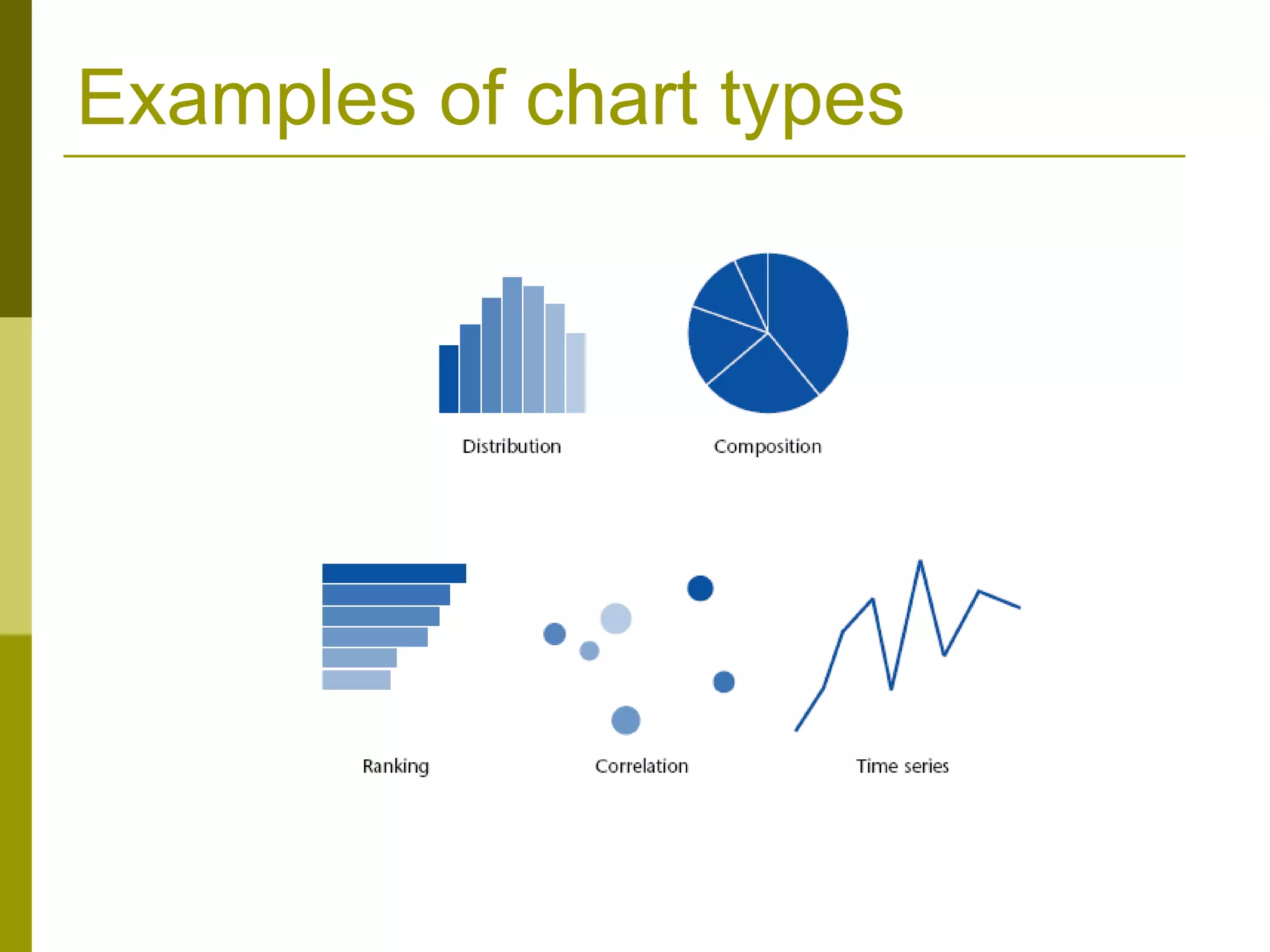
The document provides guidance on creating effective presentations with a focus on content, layout, and delivery. It discusses choosing objectives and key messages tailored to the audience. For layout, it recommends using a consistent template with varied graphics and limited colors and animation. Delivery tips include making a strong first impression, using body language to engage the audience, and speaking clearly while practicing beforehand. The overall message is that an effective presentation balances these three elements: content tailored to the audience, visually appealing layout, and confident delivery.