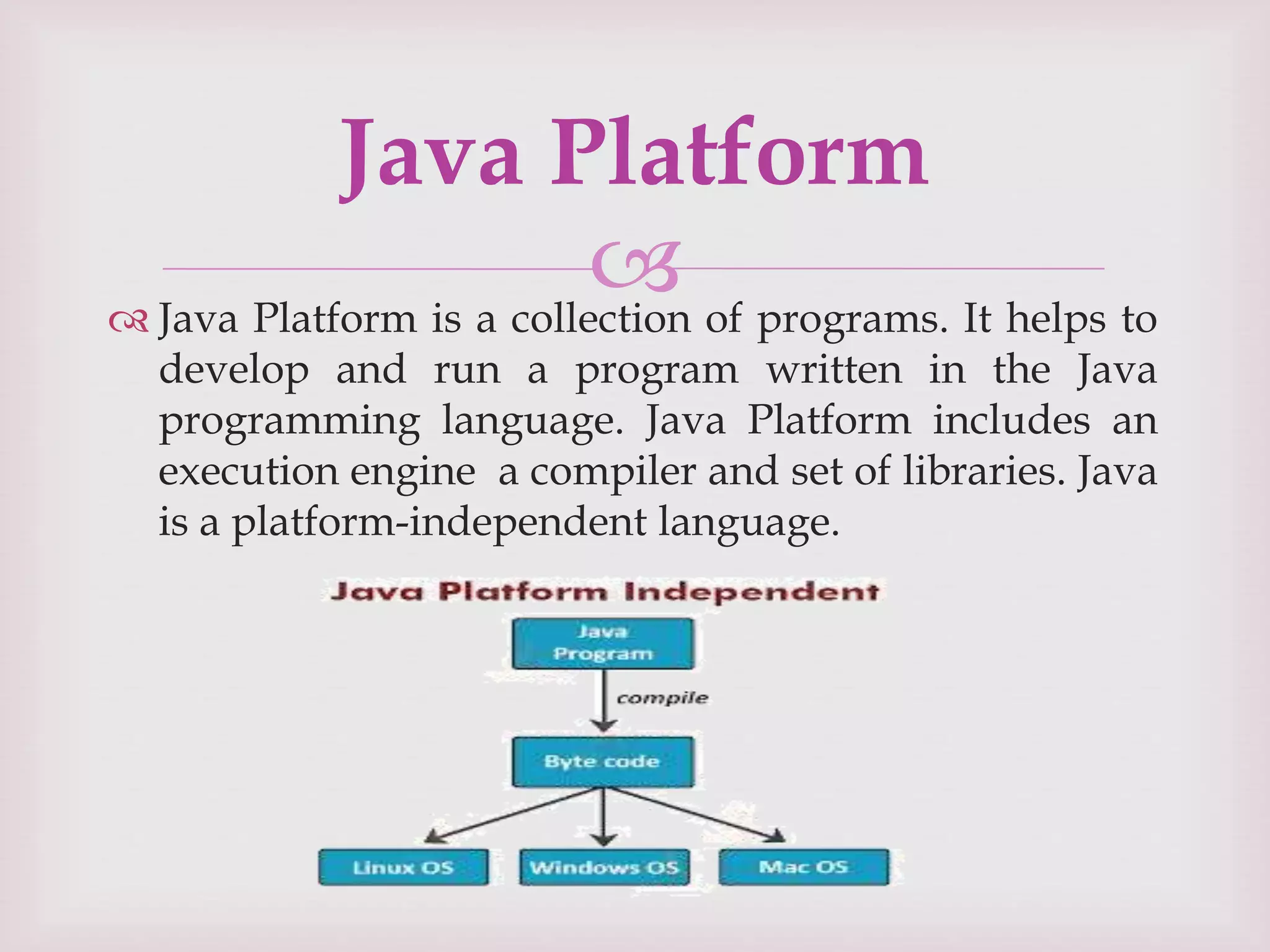
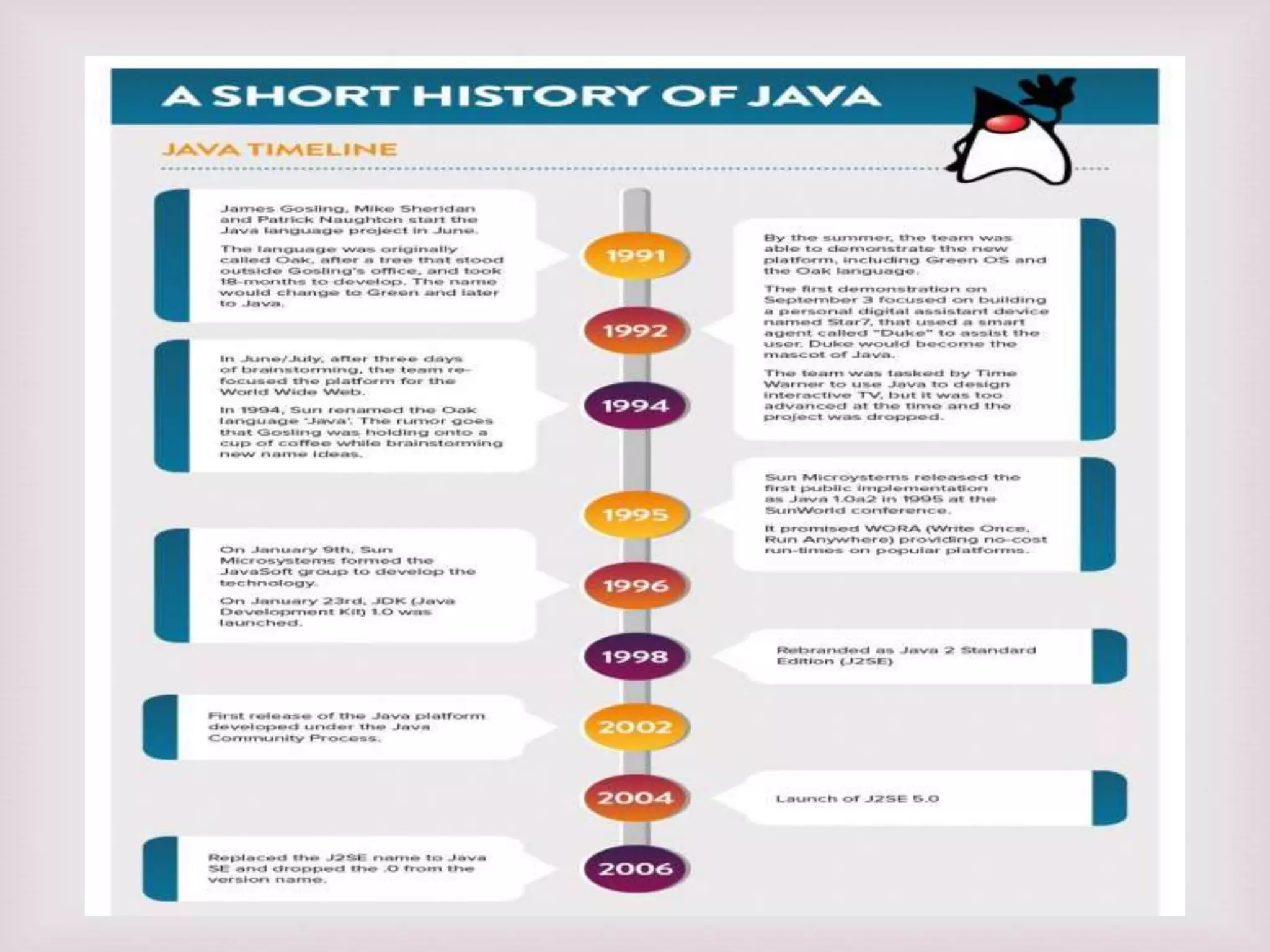
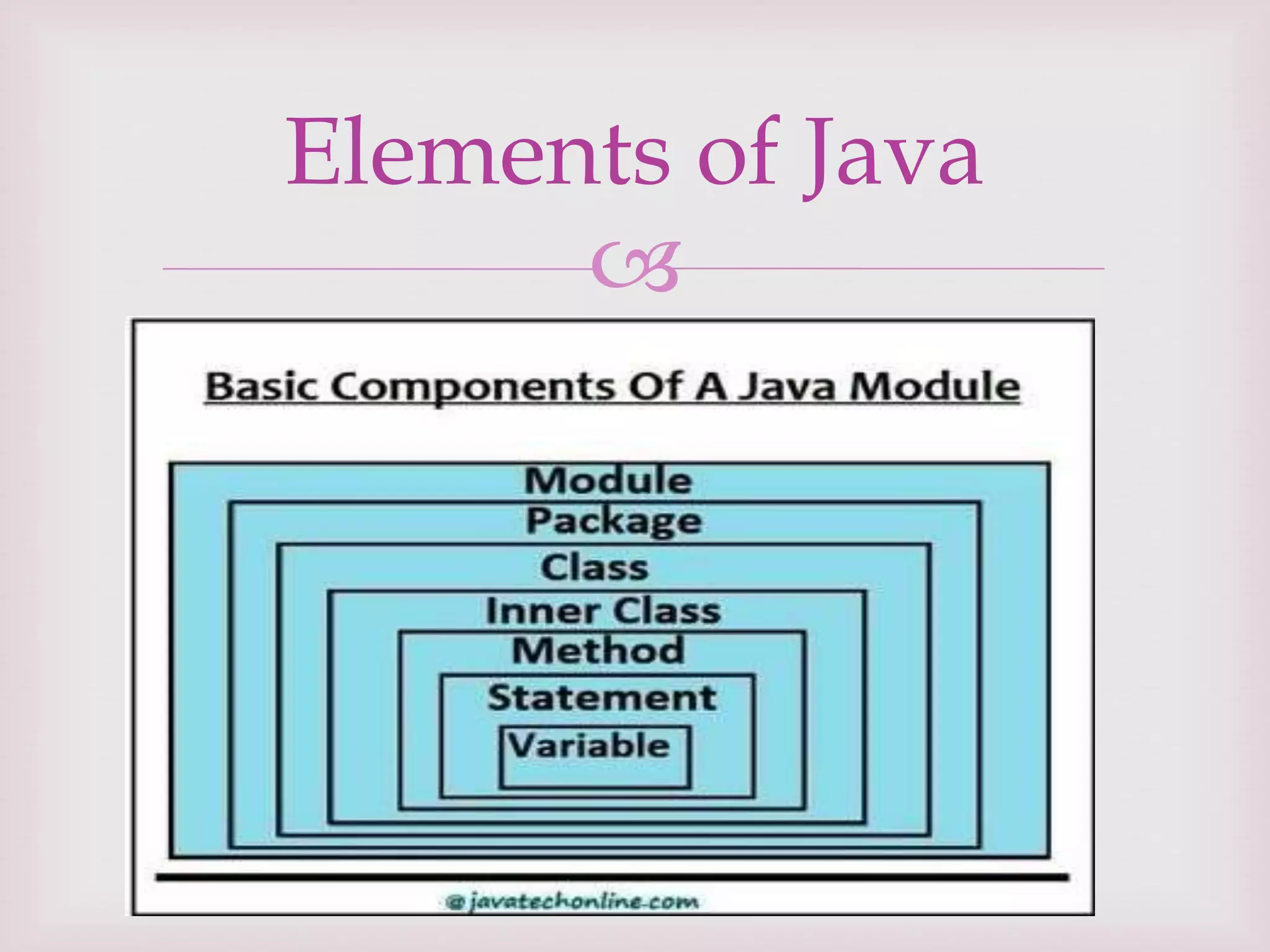
This document provides an overview of the Java programming language. It discusses that Java was created by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in 1991 and was originally called Oak. The document outlines the different editions of Java including Java Standard Edition, Java Enterprise Edition, and Java Micro Edition. It also describes the main types of Java applications and summarizes the key principles, features, and elements of object-oriented programming and the Java language.