This document provides an overview of programming in a Linux environment at Seoul National University, focusing on concepts such as using the Vim editor, compiling programs with GCC, and managing projects with Makefiles and Git. It covers essential commands, configuration tips, and examples in multiple programming languages. Additionally, it discusses the benefits of Linux, available resources for learning, and version control with Git and GitHub.





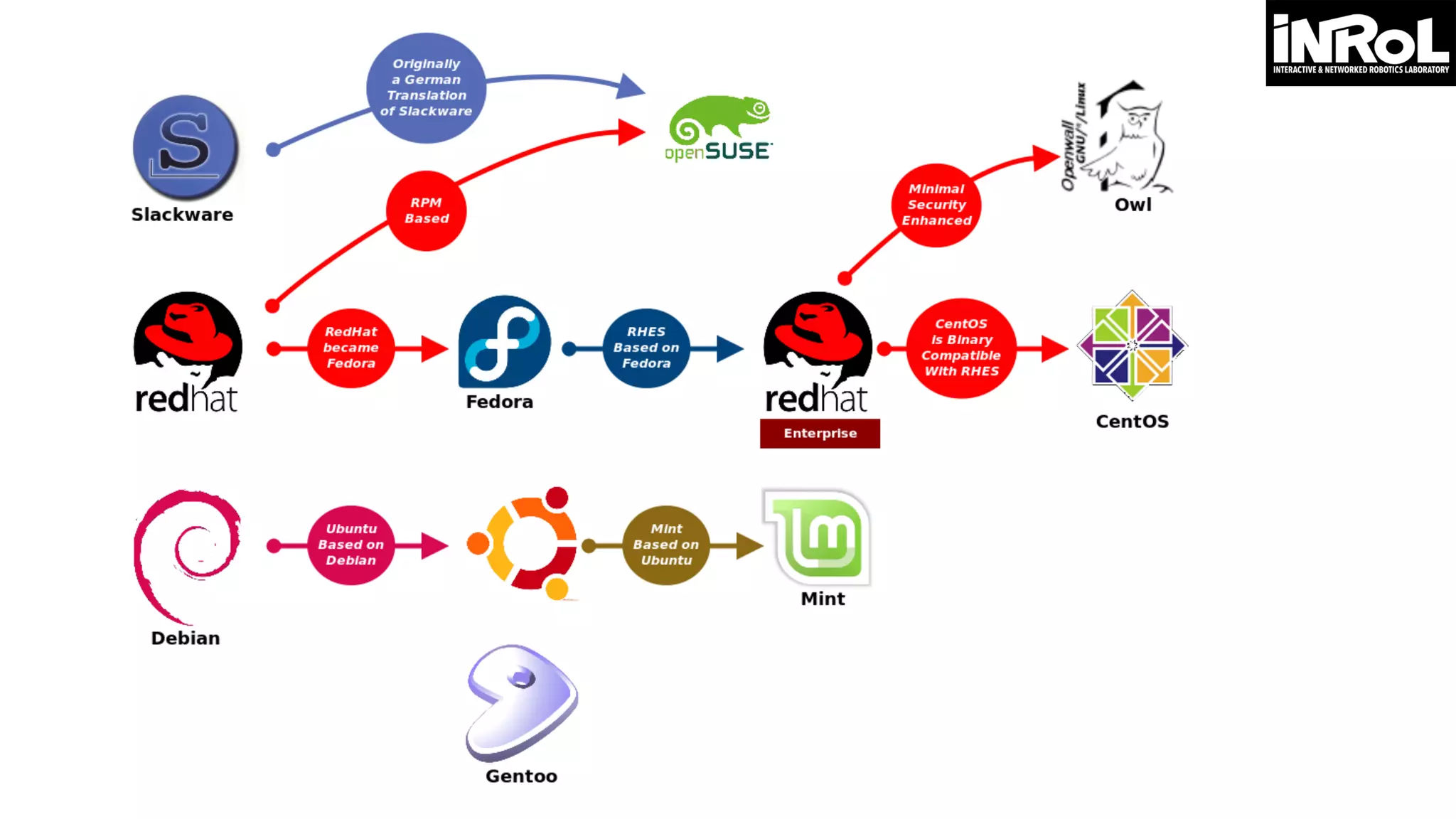
















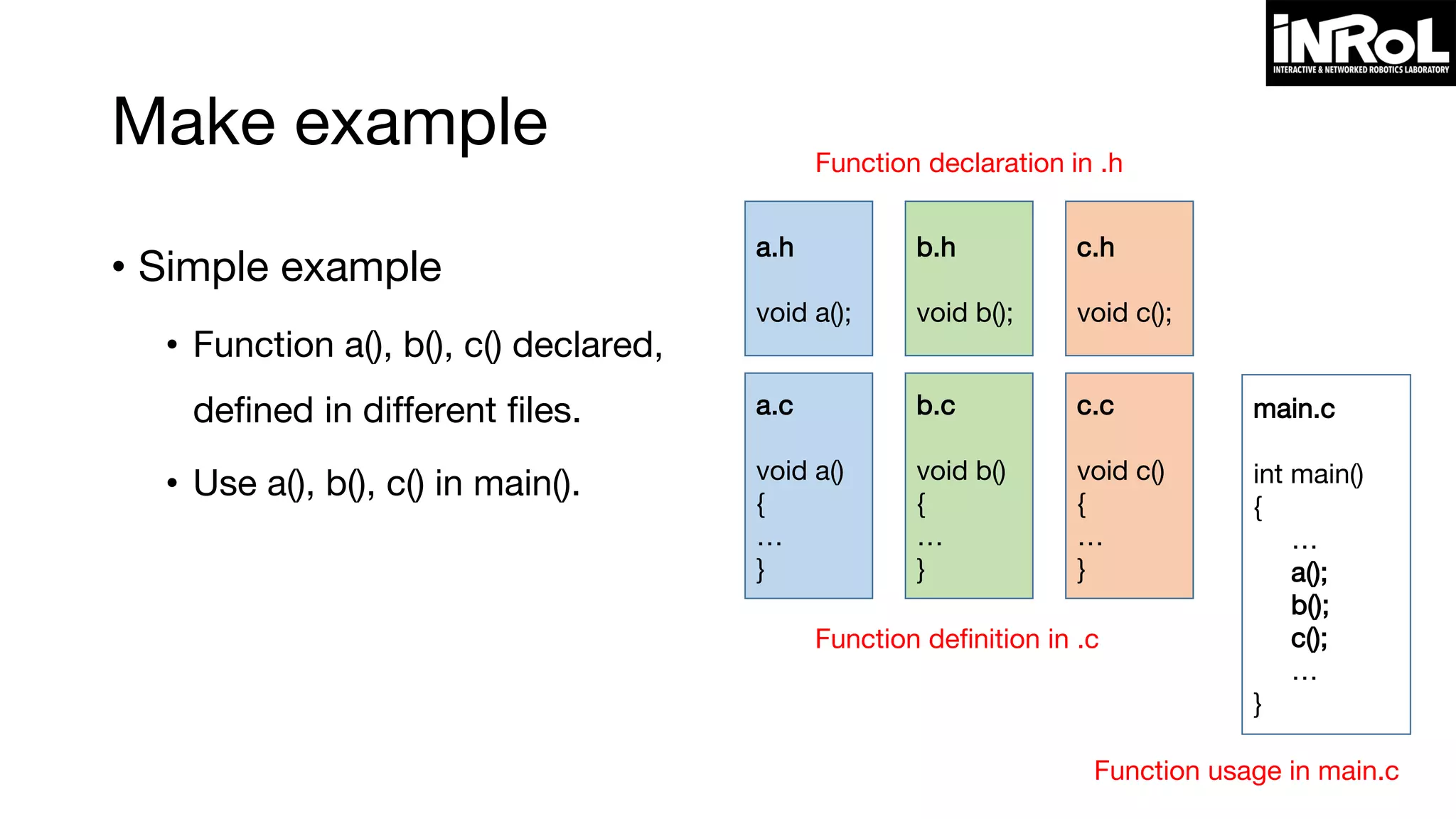
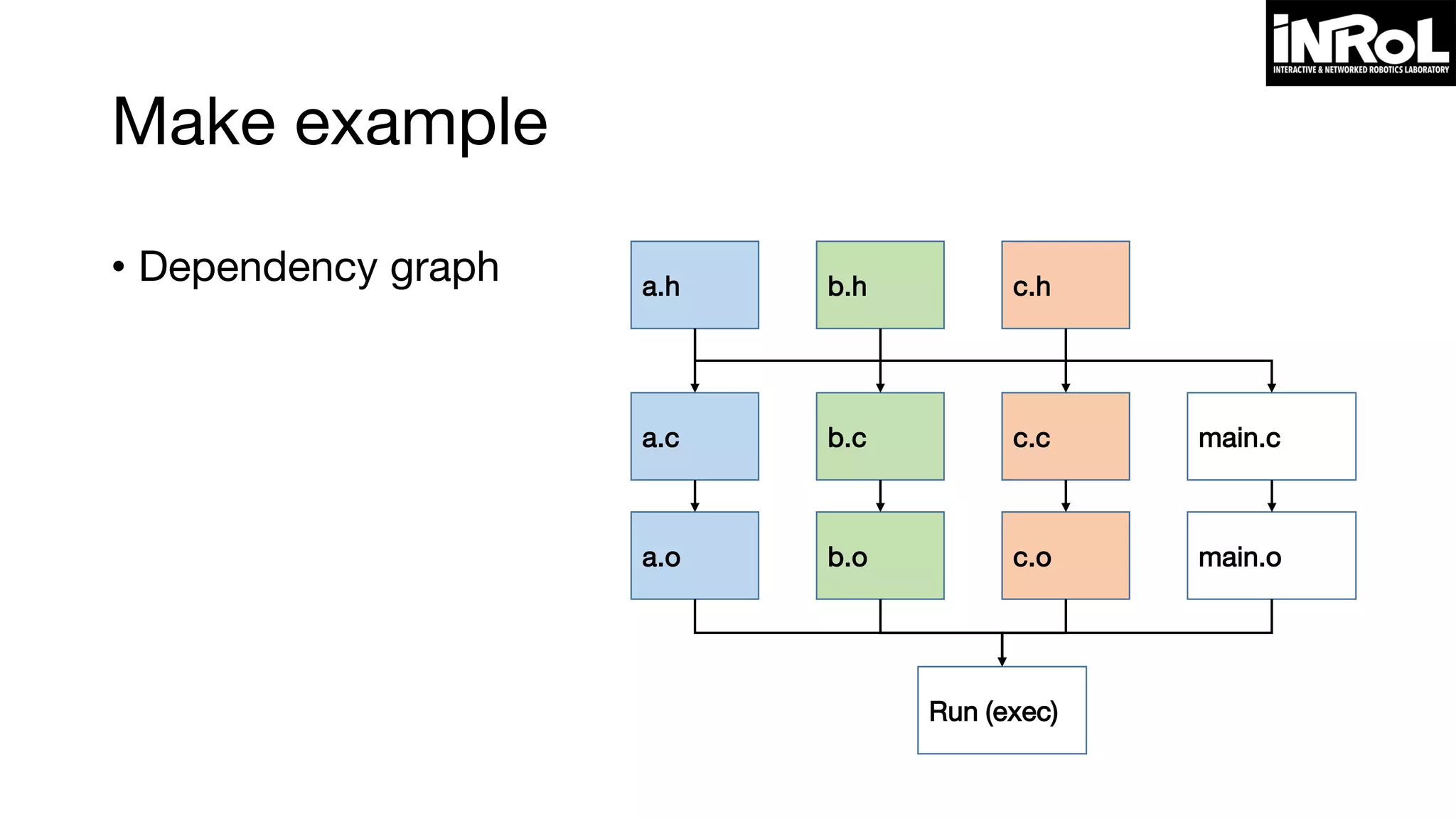
![Writing makefile
target-name ... : list-of-dependencies ...
[TAB] command (gcc command: tab is necessary)
...
...
target-name: name of result file (object file or executable file)
list-of-dependency: dependency for target
command: gcc command for compiling](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginlinuxenvironment-160112082101/75/Programming-in-Linux-Environment-32-2048.jpg)