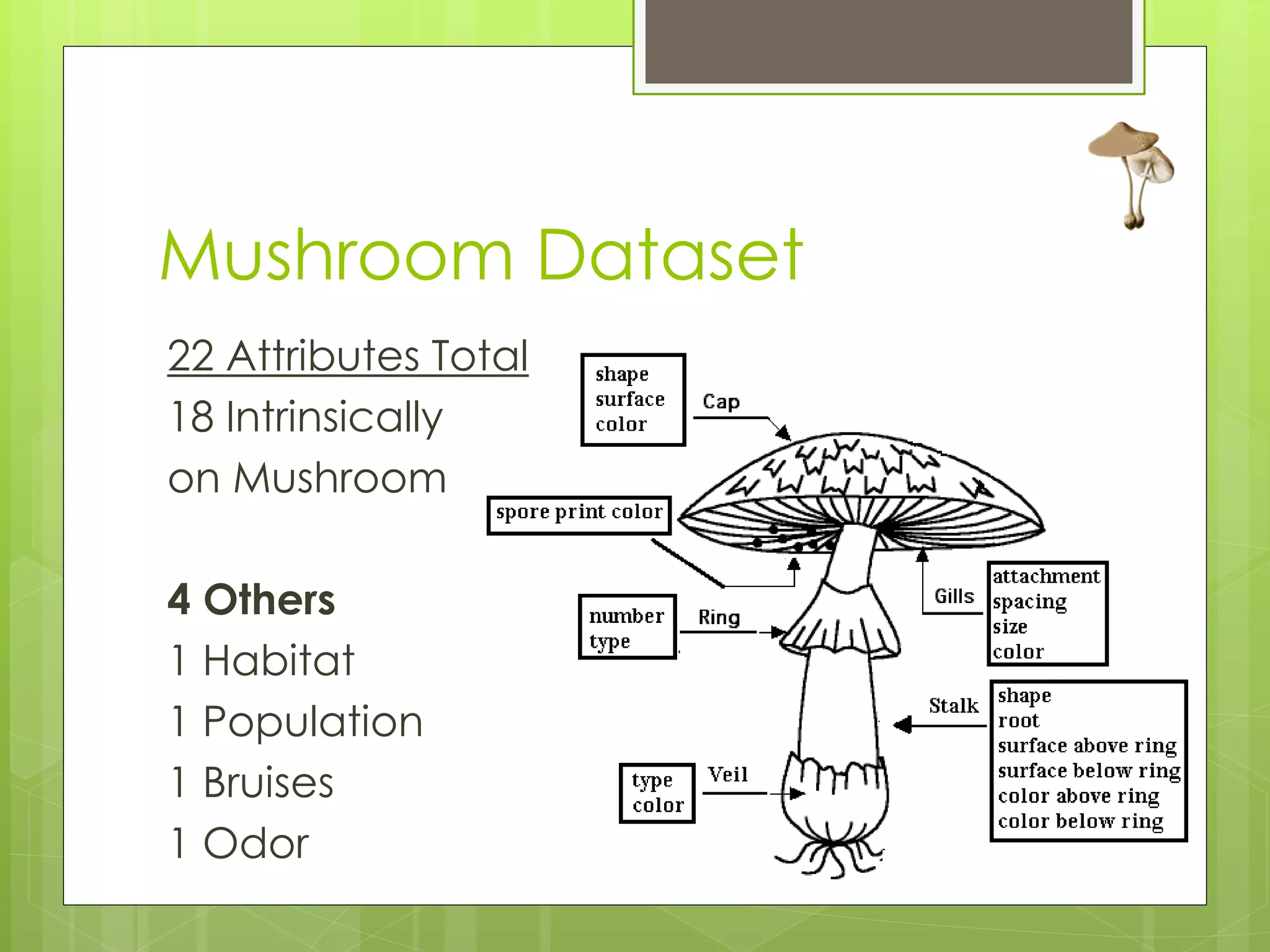
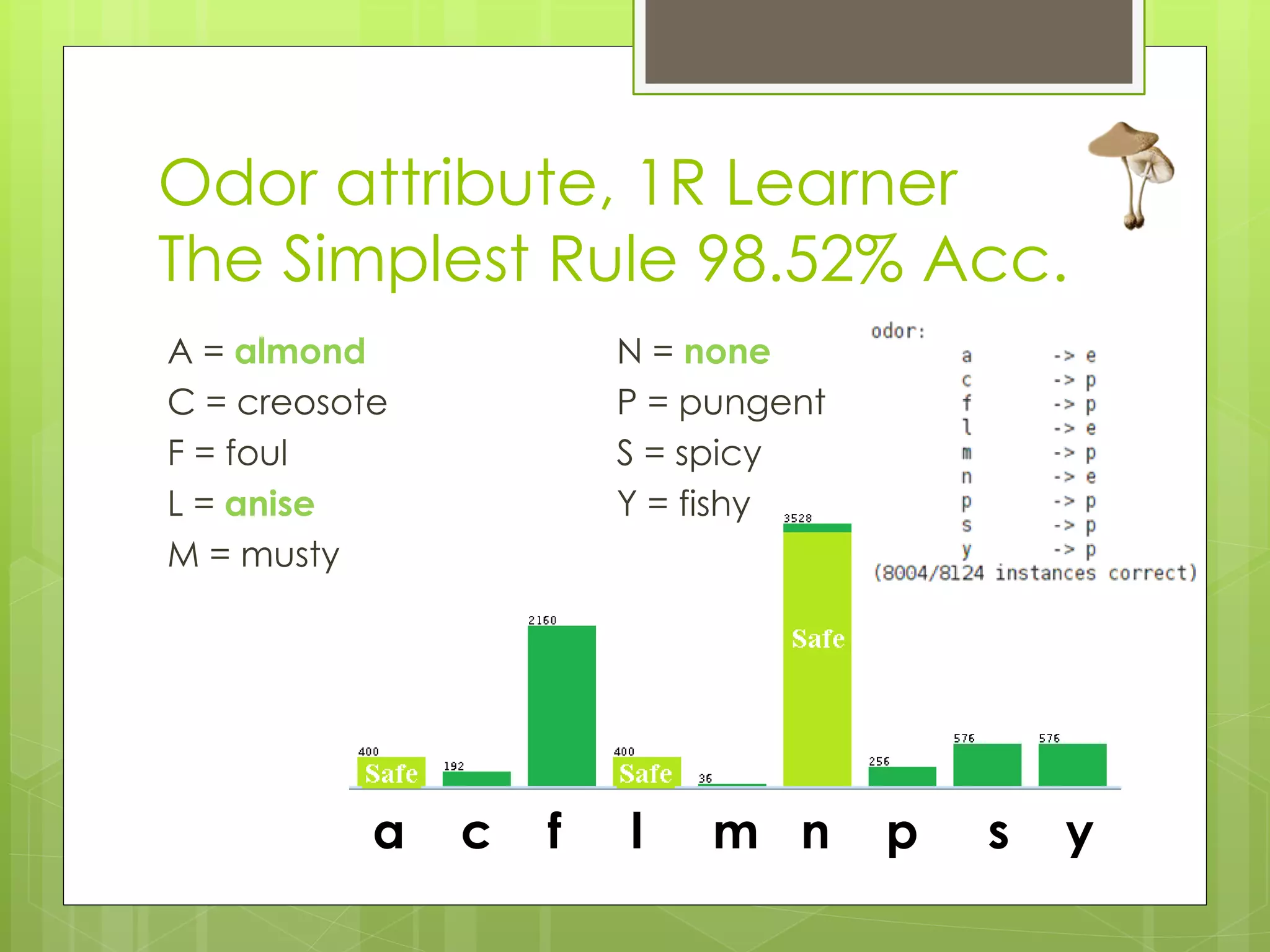
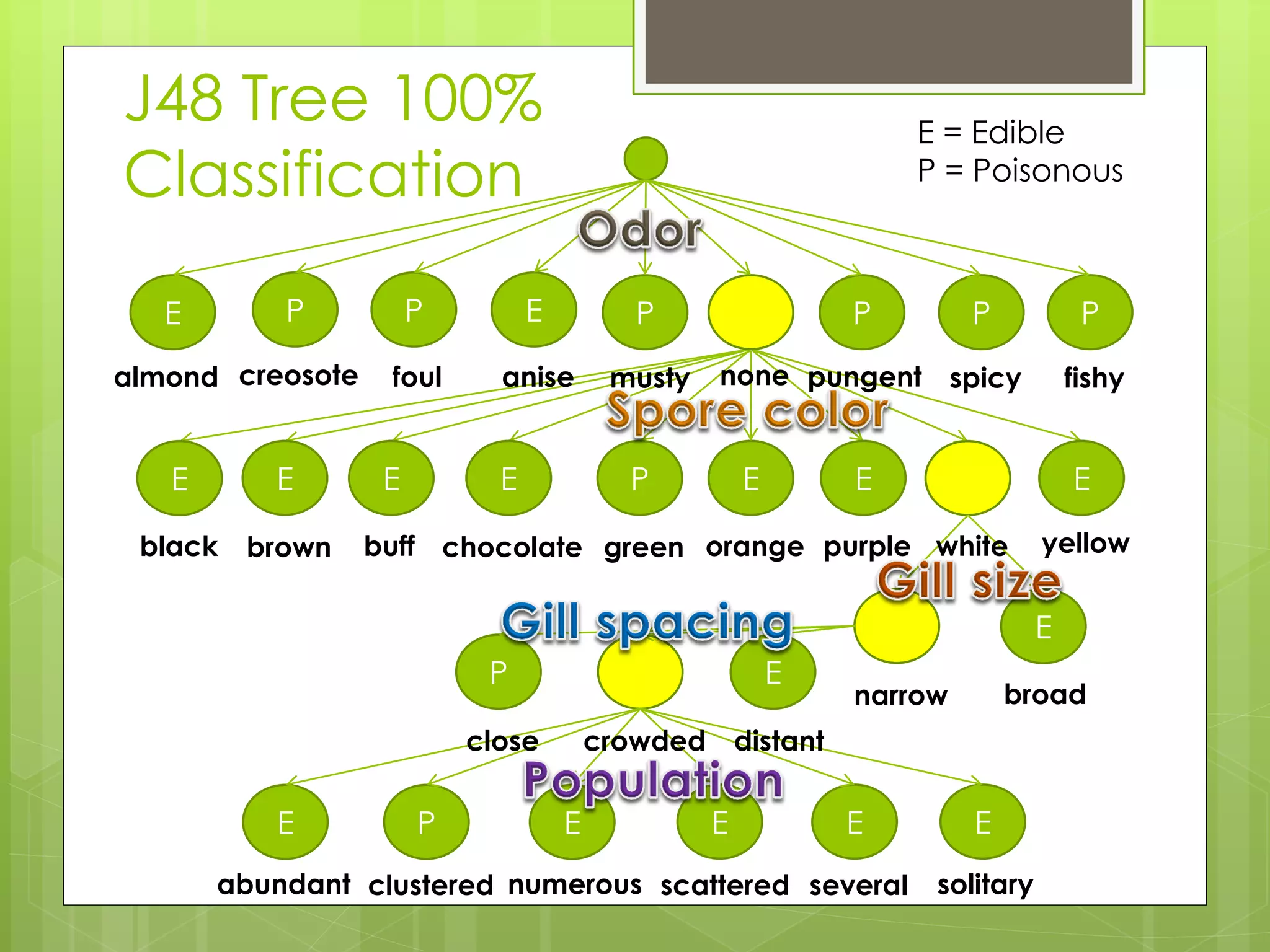
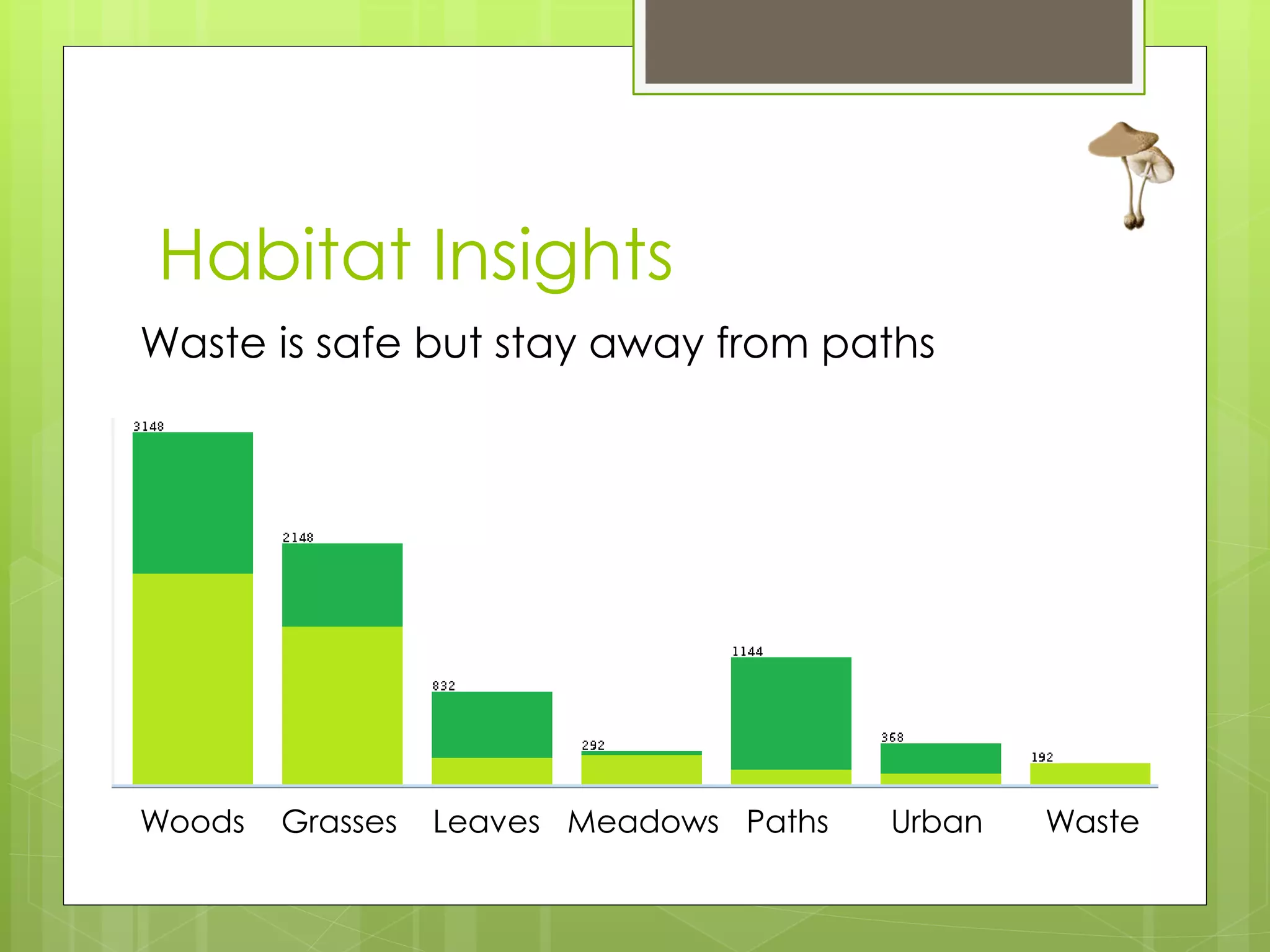
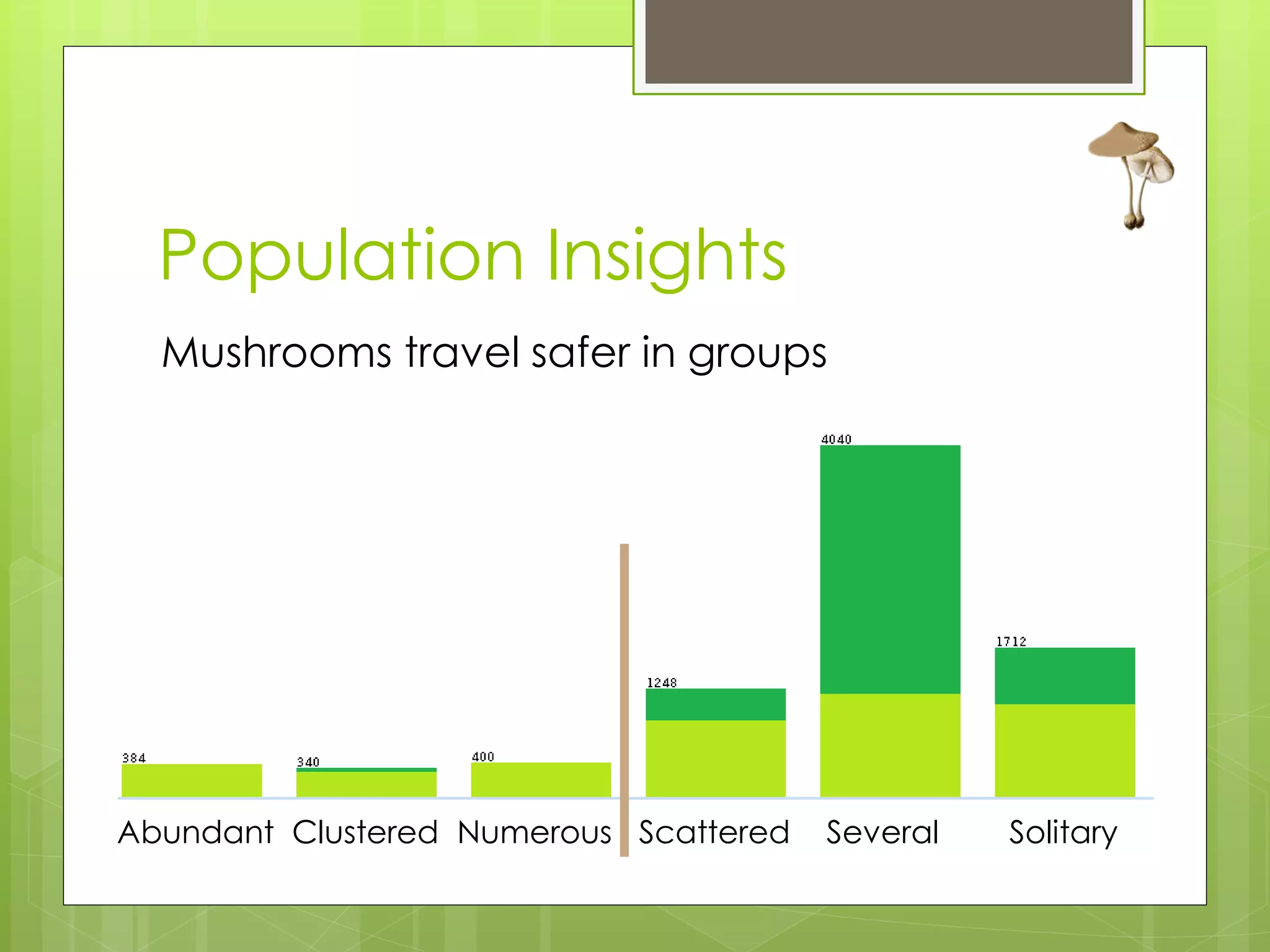
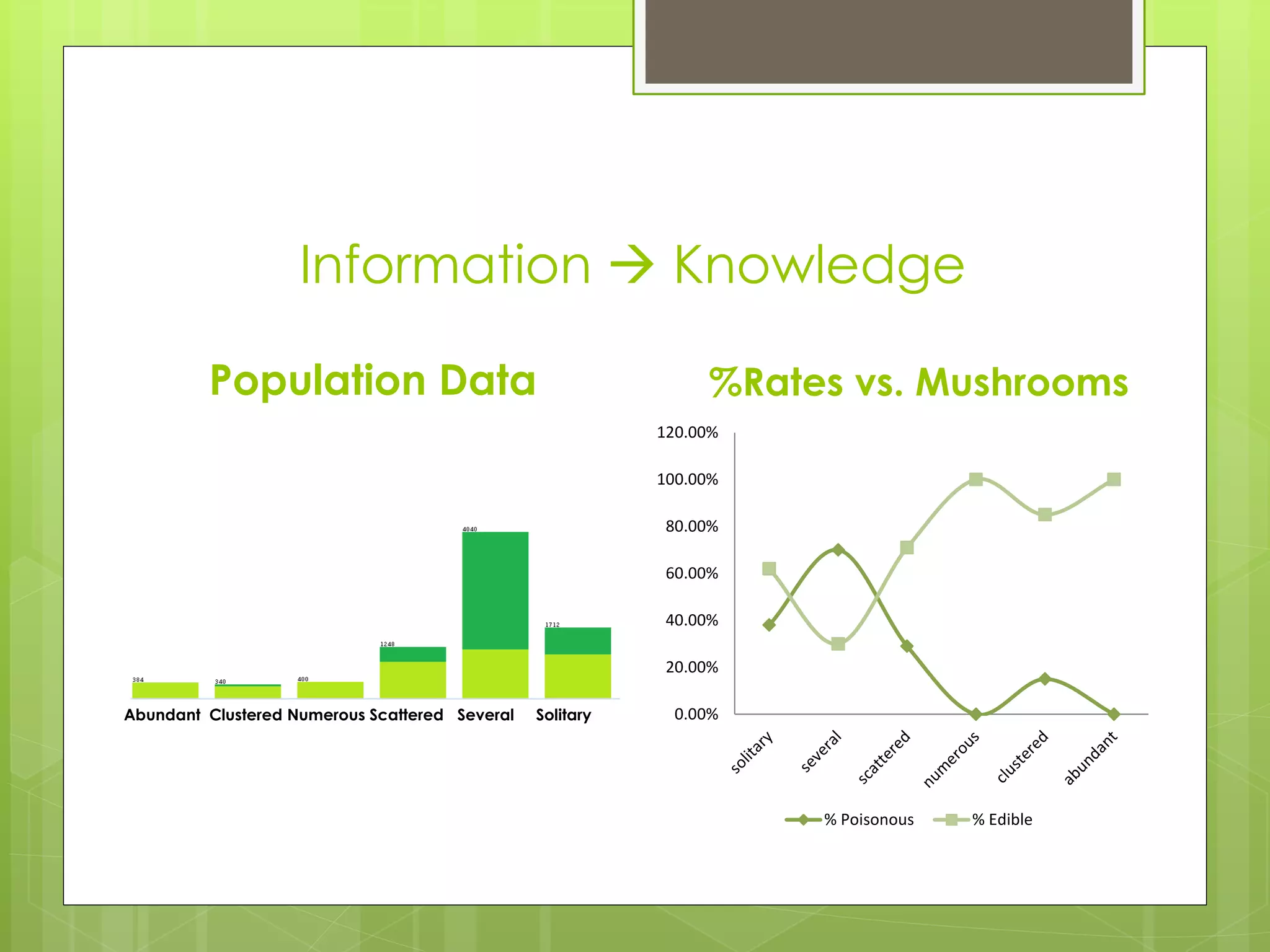
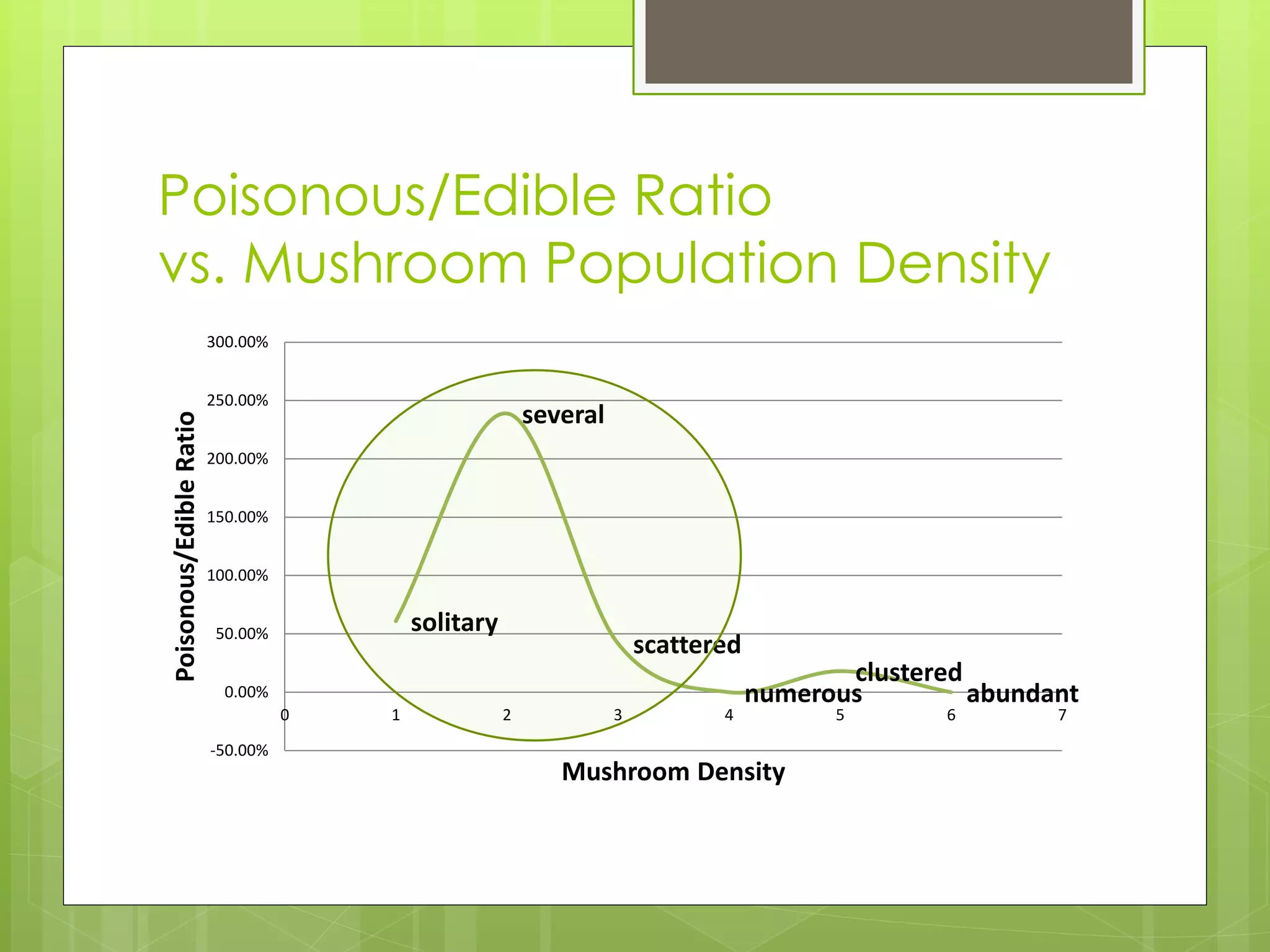
This document discusses a project analyzing a mushroom dataset containing descriptions of 23 species of gilled mushrooms to determine if they are edible or poisonous. The dataset includes 8,124 instances with 22 attributes describing intrinsic mushroom characteristics and external factors. A decision tree model achieved 100% accuracy in classification by considering attributes like odor, habitat, population density, and cap/stalk features. Further analysis found odor and spore print color were the most statistically significant but not practical for identification in the field. Future work aims to develop easier visual classification methods using attributes like habitat, population density, and cap/stalk characteristics.