Python is a high-level programming and scripting language that was developed by Guido van Rossum in the early 1990s. It is versatile, suitable for applications in web development, data science, artificial intelligence, and more, and is used by companies like Google and YouTube. Python's features include easy readability, extensive libraries, and simple syntax, making it accessible for beginners and widely adopted for various programming needs.












![Standard Data types
String – ‘MyString’, and “MyString”
List – [ 69, 6.9, ‘mystring’, True]
Tuple – (69, 6.9, ‘mystring’, True) immutable
Set/frozenset – set([69, 6.9, ‘str’, True])
frozenset- ([69, 6.9, ‘str’, True]) –no duplicates &
unordered
Dictionary or hash – {‘key 1’: 6.9, ‘key2’: False} -
group of key and value pairs
9 March 2019Python](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonnewest-190309160454/75/PYTHON-FOR-BEGINNERS-BASICS-OF-PYTHON-22-2048.jpg)
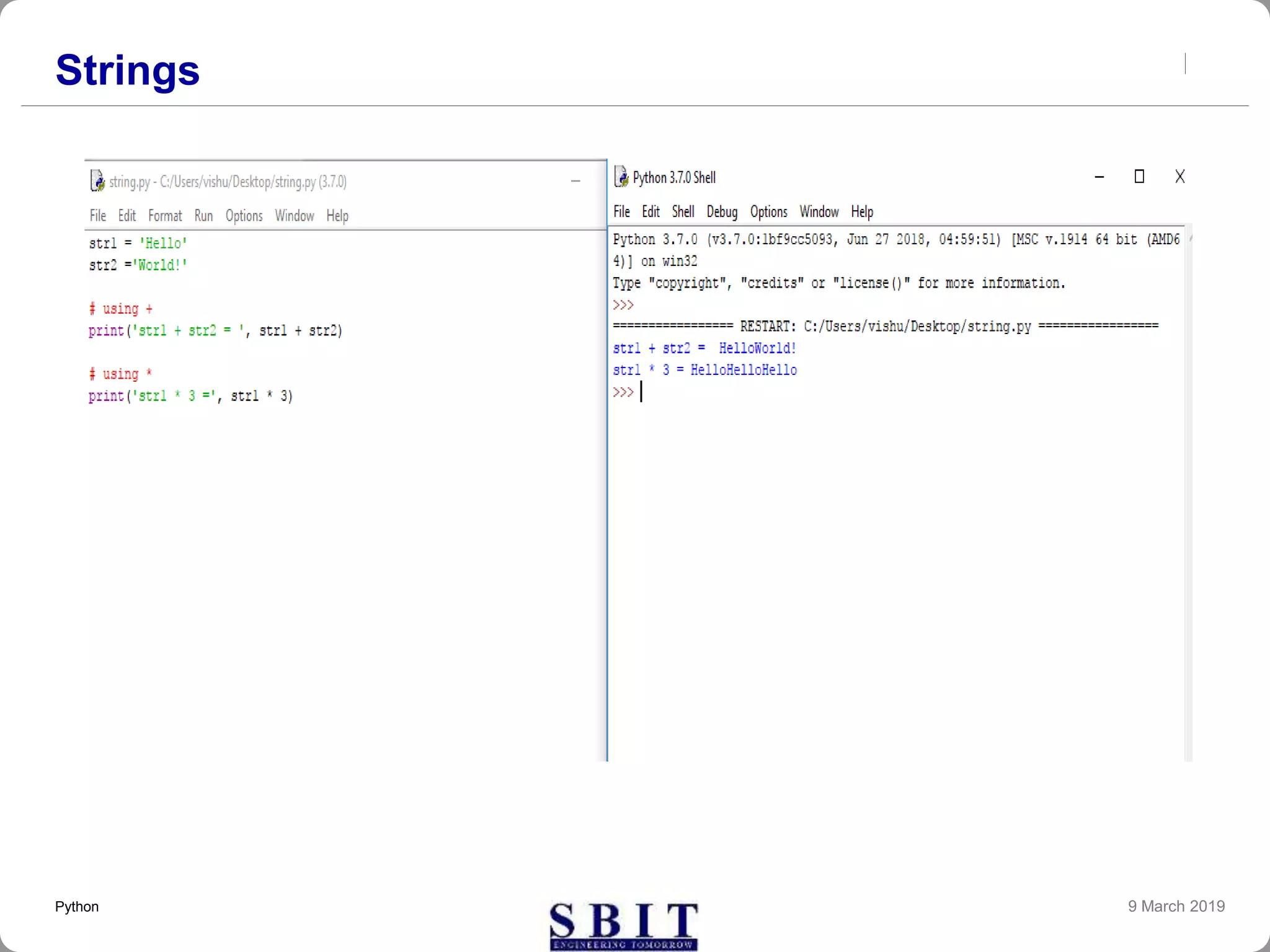
![Strings
Strings in Python are identified as a contiguous set of
characters represented in the quotation marks.
Python allows for either pairs of single or double
quotes. Subsets of strings can be taken using the
slice operator ([ ] and [:] ) with indexes starting at 0 in
the beginning of the string and working their way from
-1 at the end.
The plus (+) sign is the string concatenation operator
and the asterisk (*) is the repetition operator.
9 March 2019Python](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonnewest-190309160454/75/PYTHON-FOR-BEGINNERS-BASICS-OF-PYTHON-23-2048.jpg)
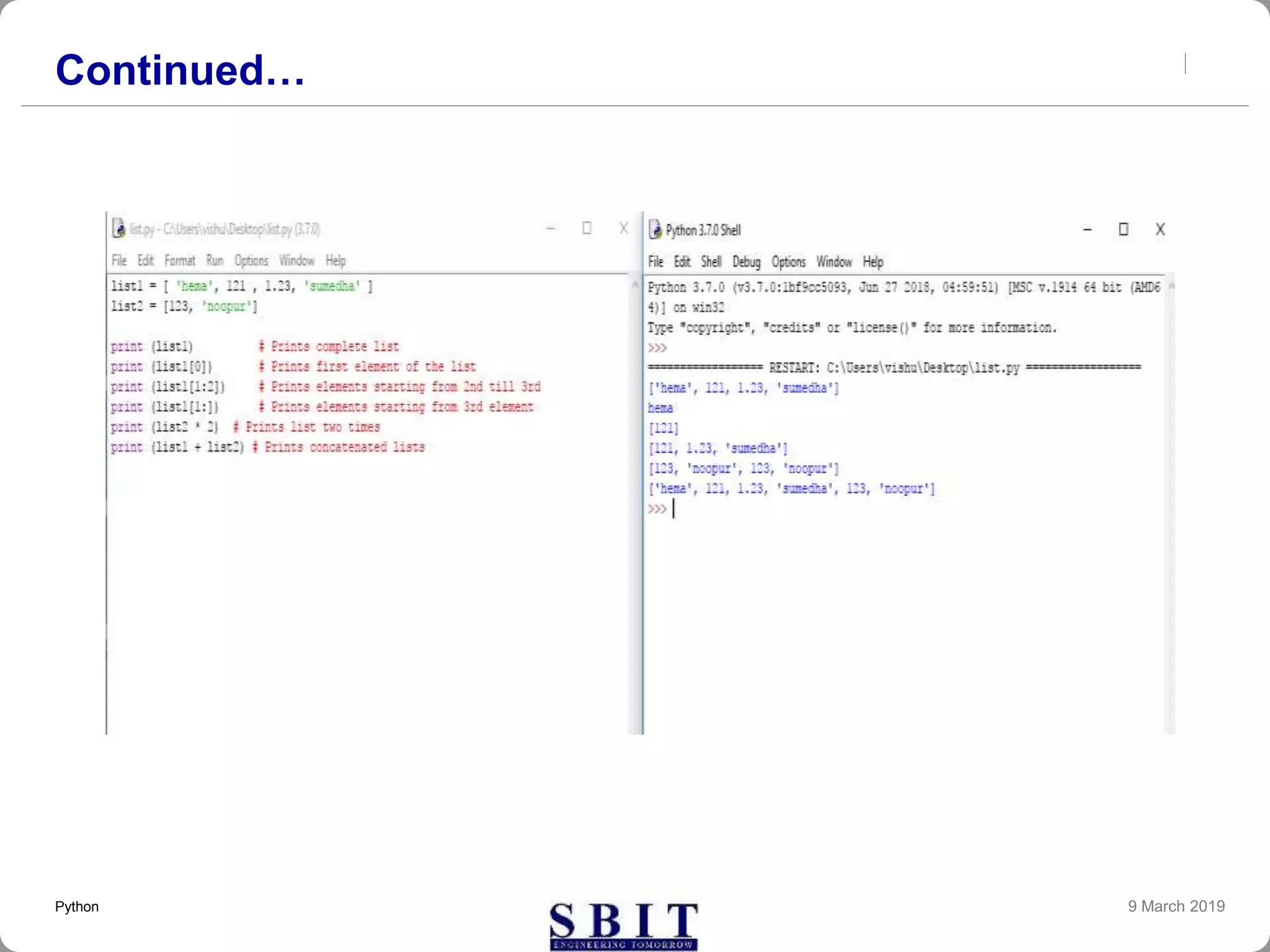
![Lists
lists are the most versatile of Python's compound data
types. A list contains items separated by commas and
enclosed within square brackets ([ ]). To some extent, lists
are similar to arrays in C. One difference between them is
that all the items belonging to a list can be of different data
type.
The values stored in a list can be accessed using the slice
operator ([ ] and [:]) with indexes starting at 0 in the
beginning of the list and working their way to end -1. The
plus (+) sign is the list concatenation operator, and the
asterisk (*) is the repetition operator.
9 March 2019Python](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonnewest-190309160454/75/PYTHON-FOR-BEGINNERS-BASICS-OF-PYTHON-25-2048.jpg)





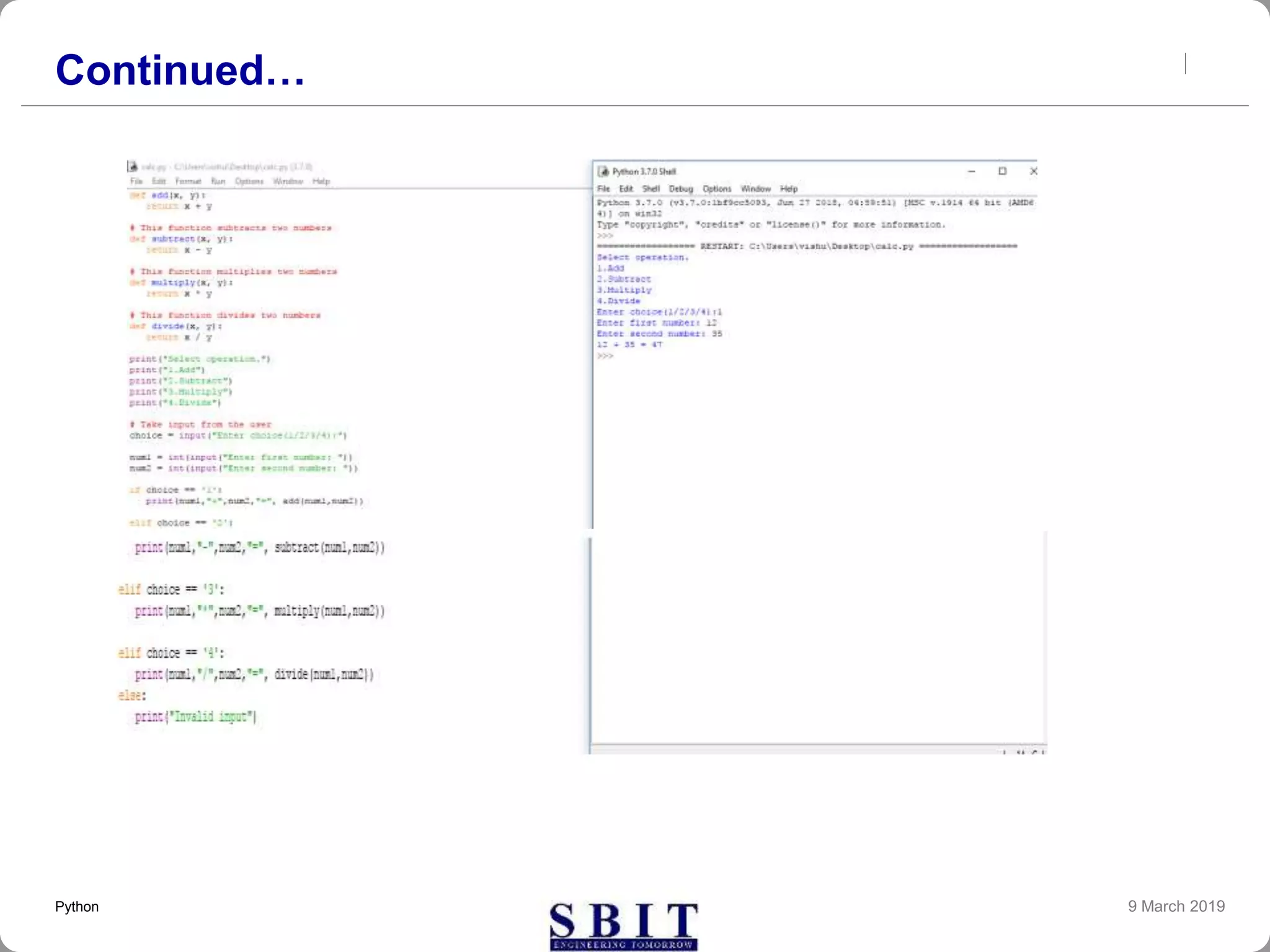
![Defining a function
You can define functions to provide the required
functionality. Here are simple rules to define a function in
Python.
Function blocks begin with the keyword def followed by the
function name and parentheses ( ( ) ).
Any input parameters or arguments should be placed within
these parentheses. You can also define parameters inside
these parentheses.
The code block within every function starts with a colon (:)
and is indented.
The statement return [expression] exits a function,
optionally passing back an expression to the caller. A return
statement with no arguments is the same as return None.
9 March 2019Python](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonnewest-190309160454/75/PYTHON-FOR-BEGINNERS-BASICS-OF-PYTHON-34-2048.jpg)