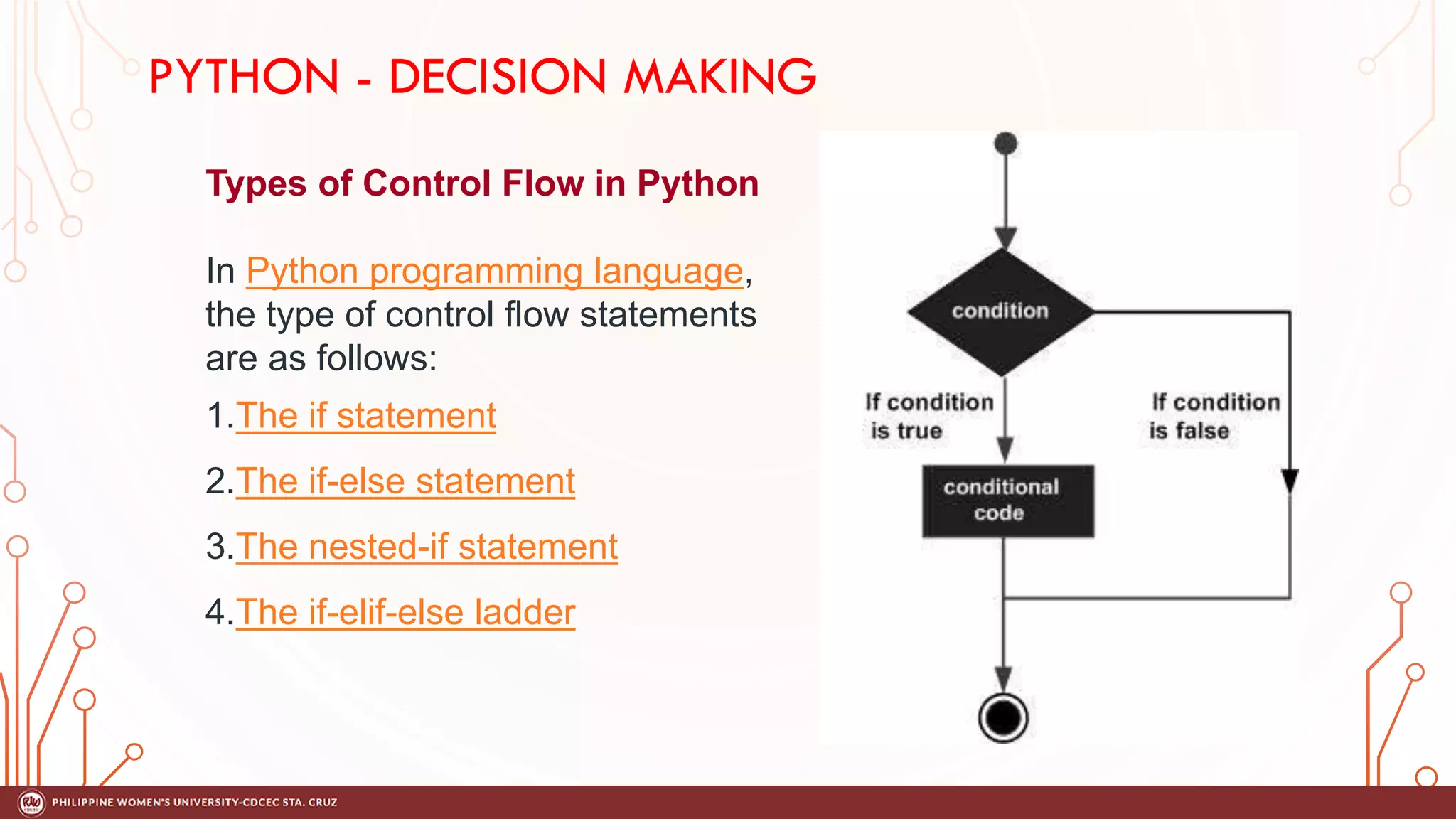
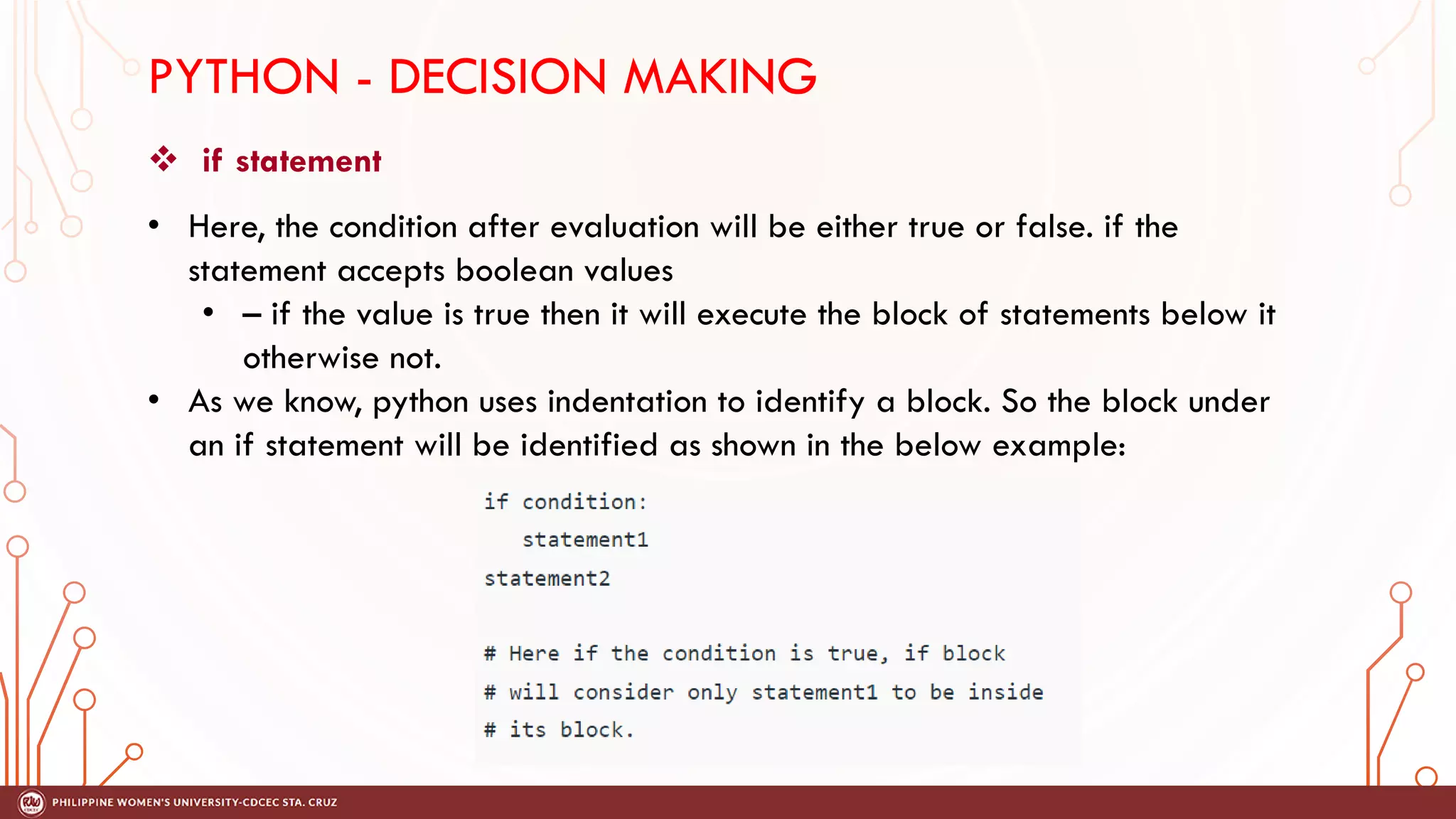
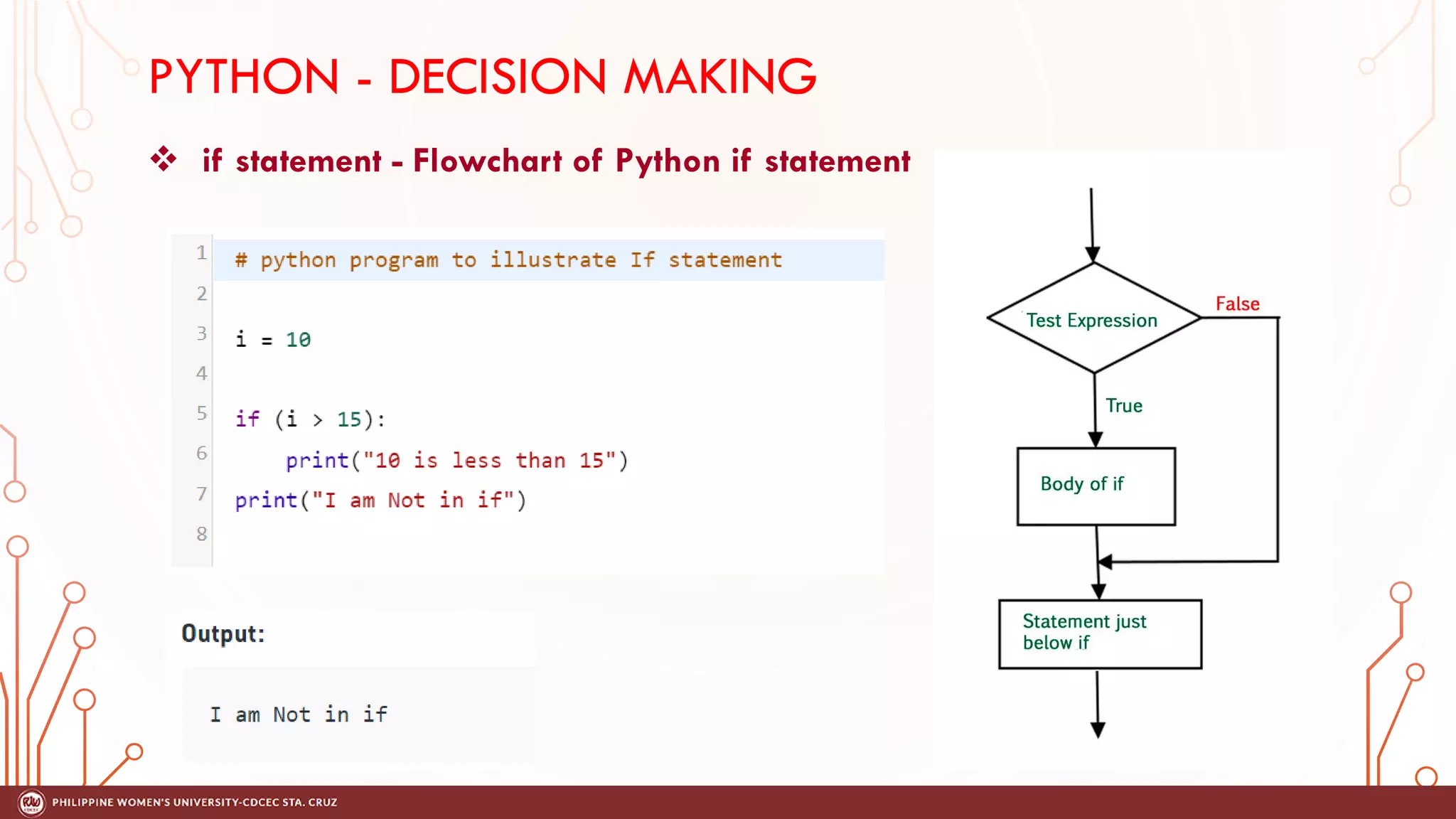
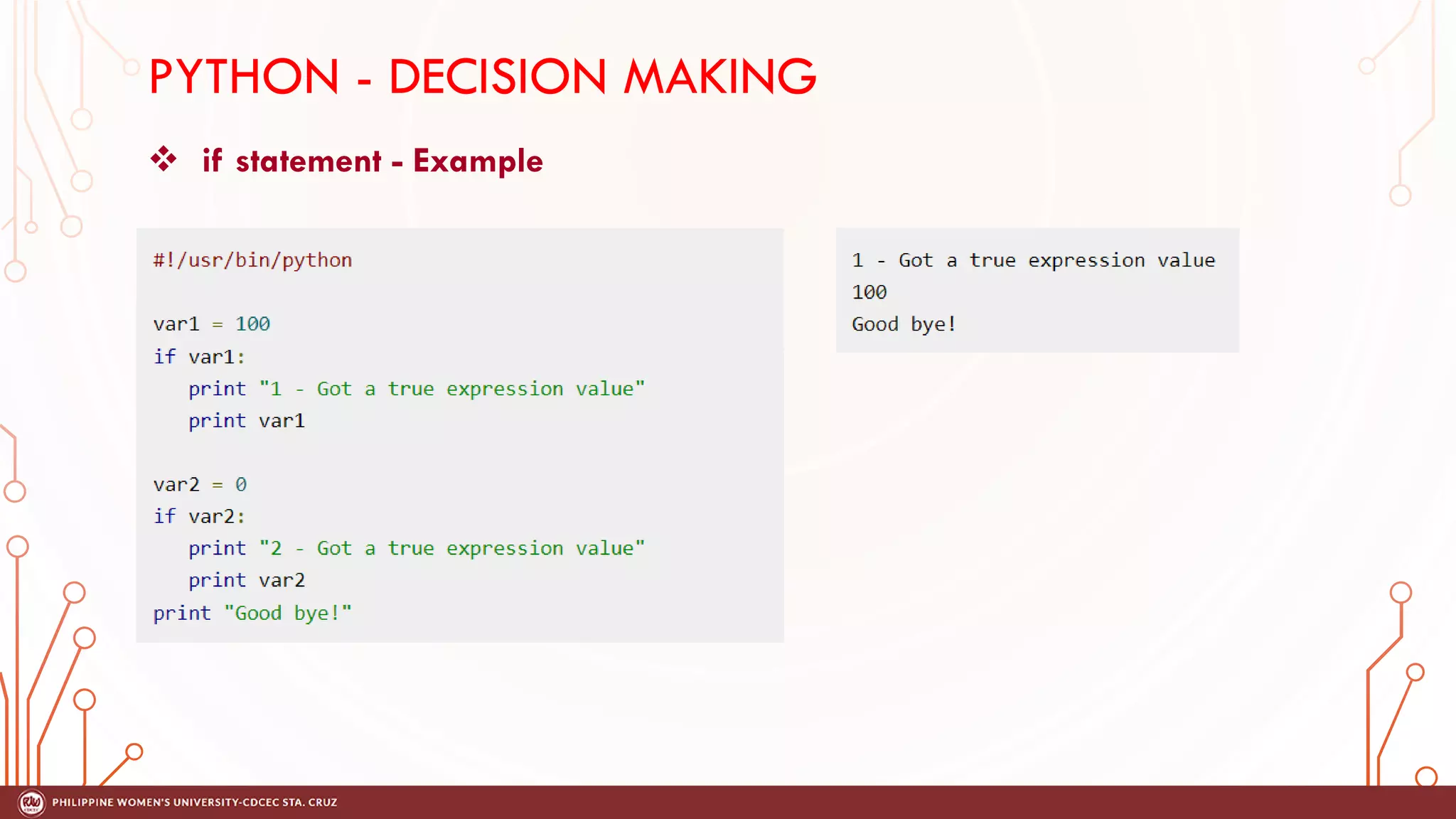
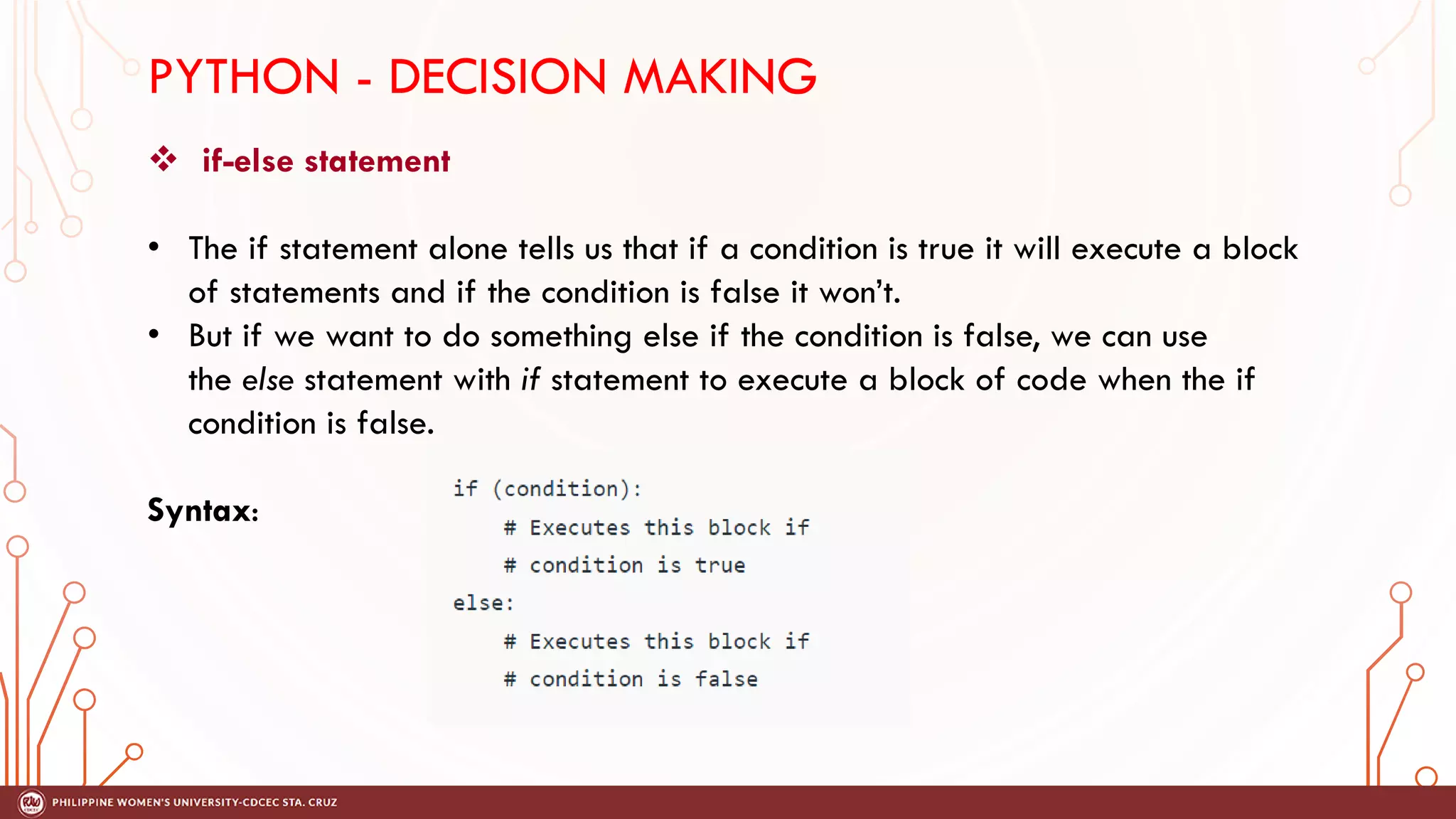
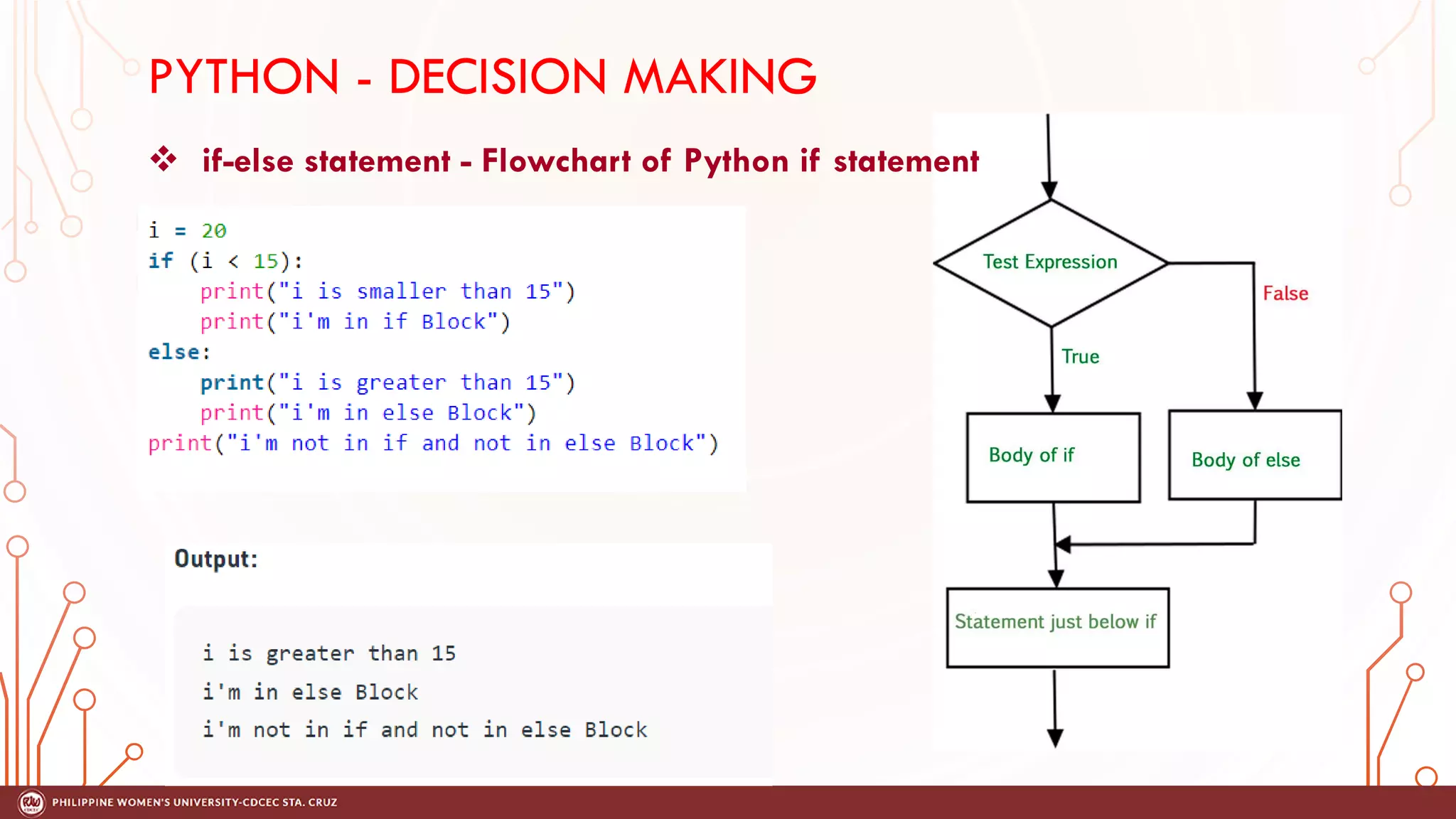
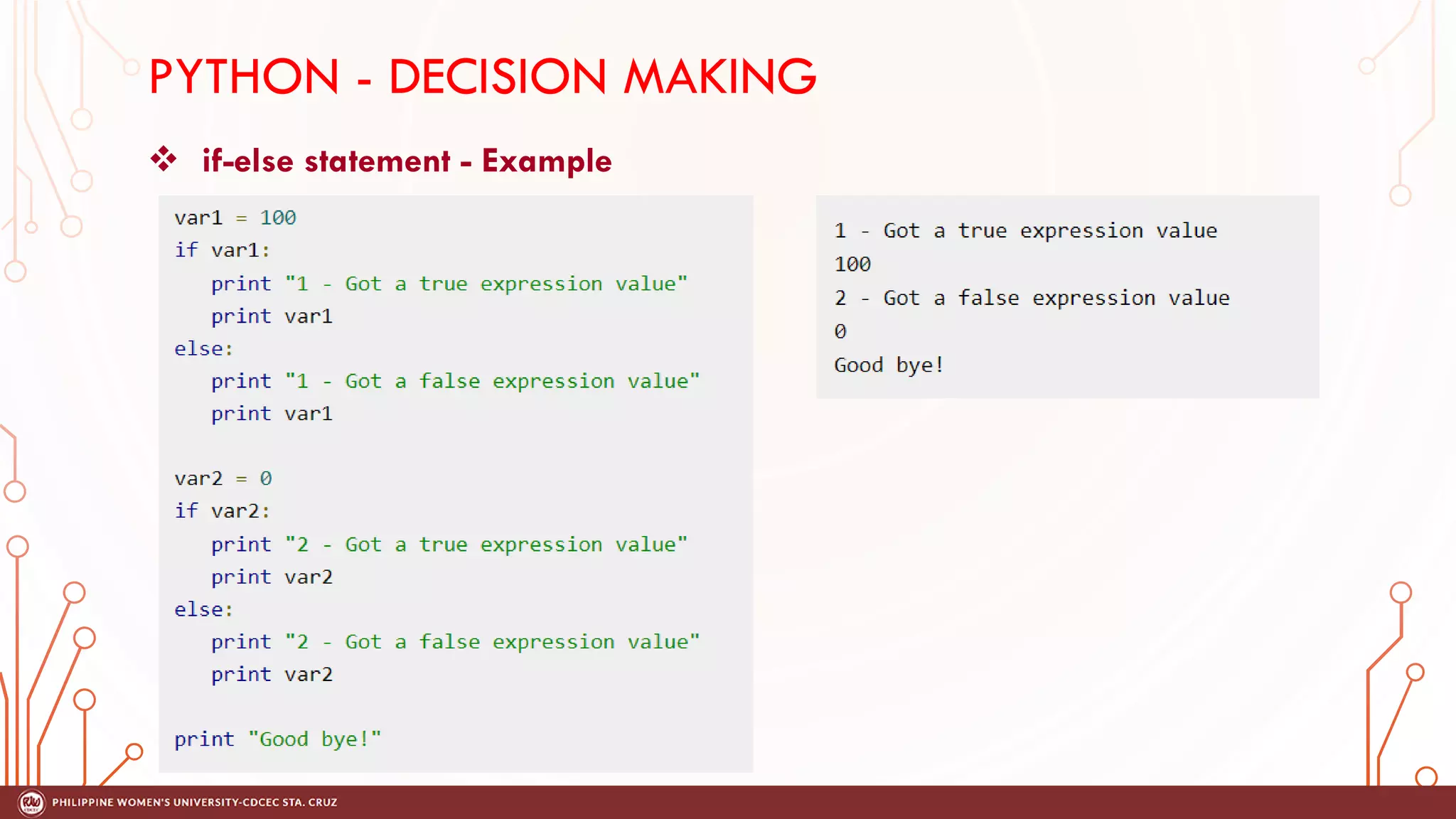
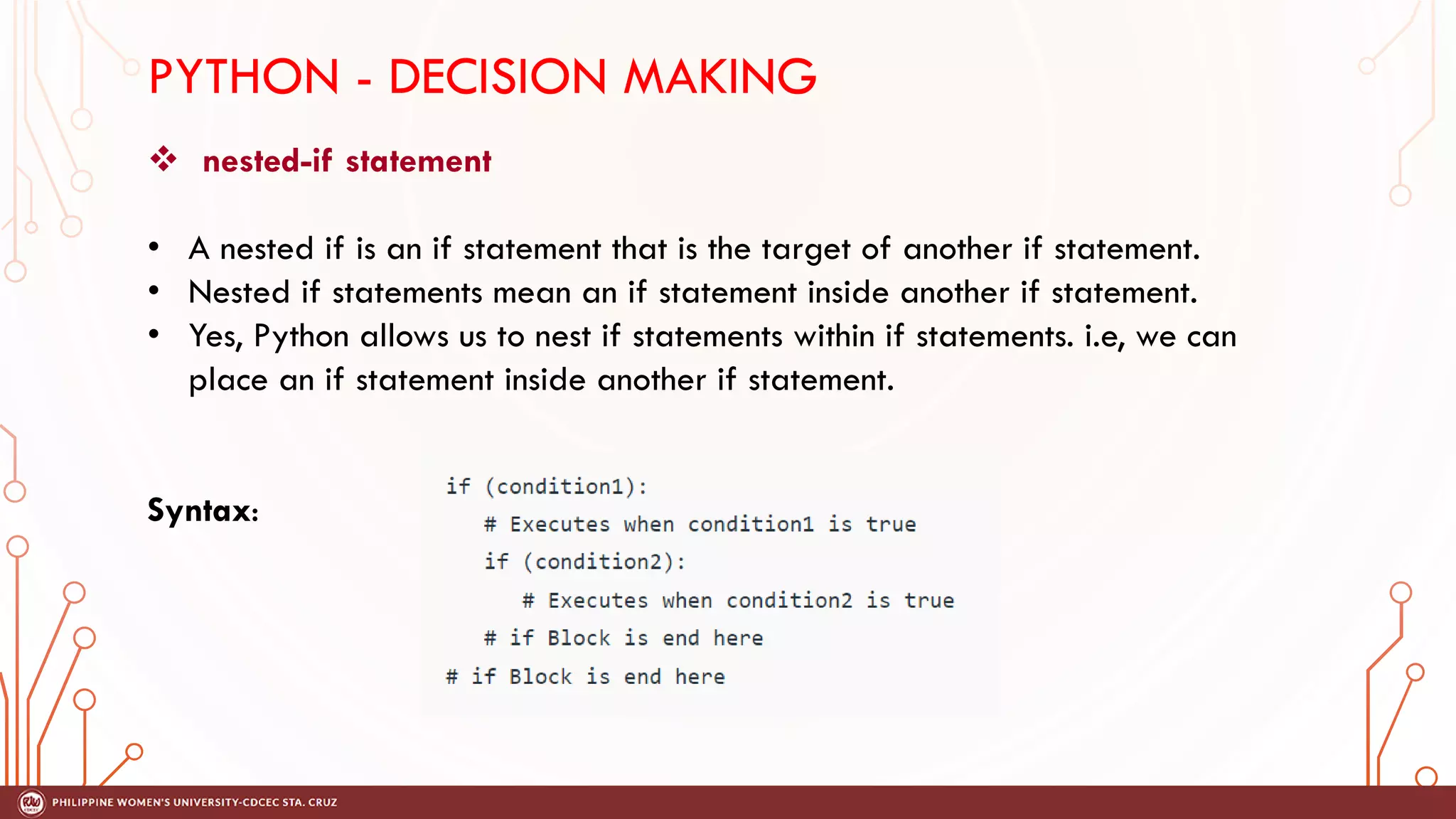
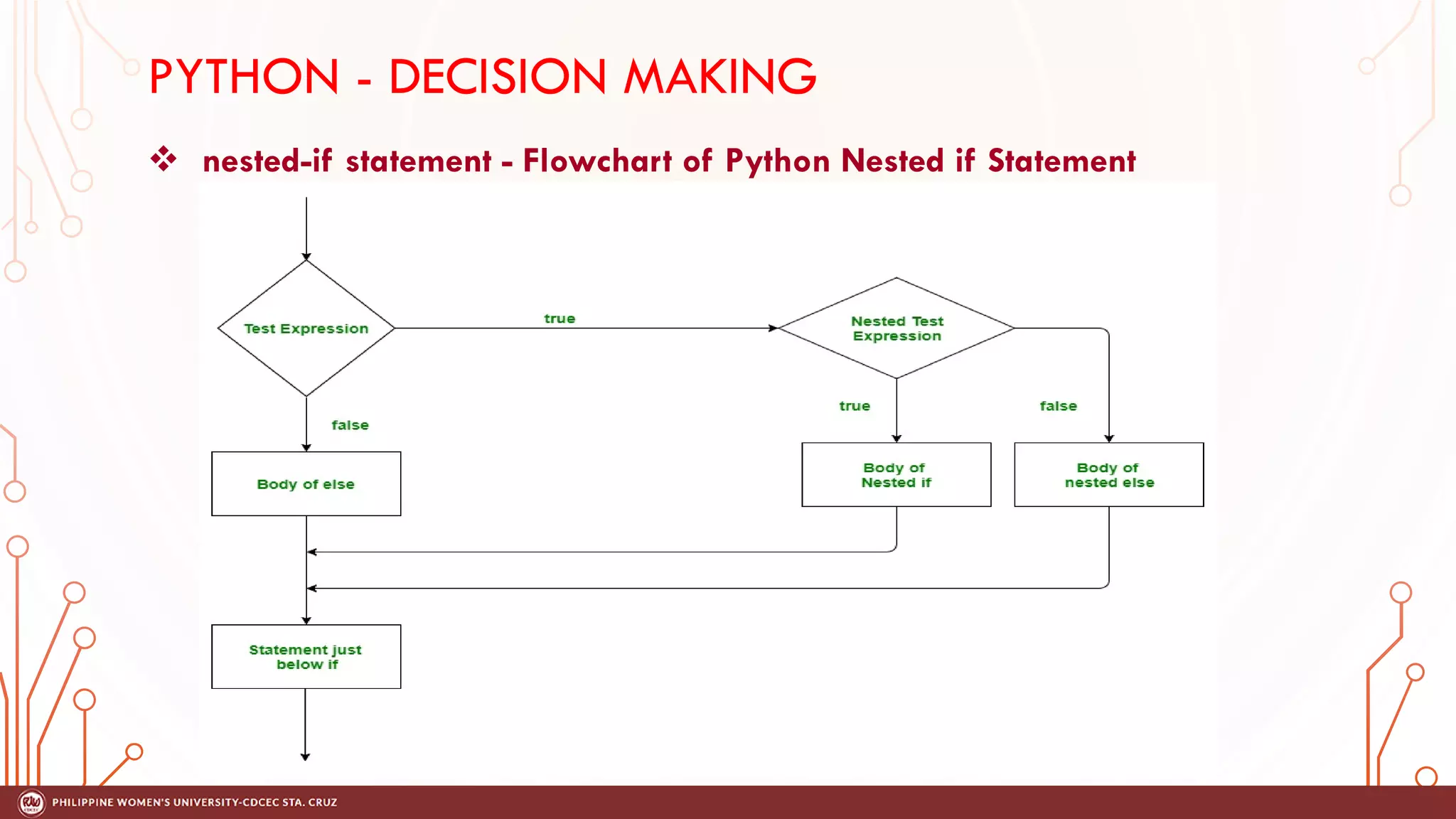
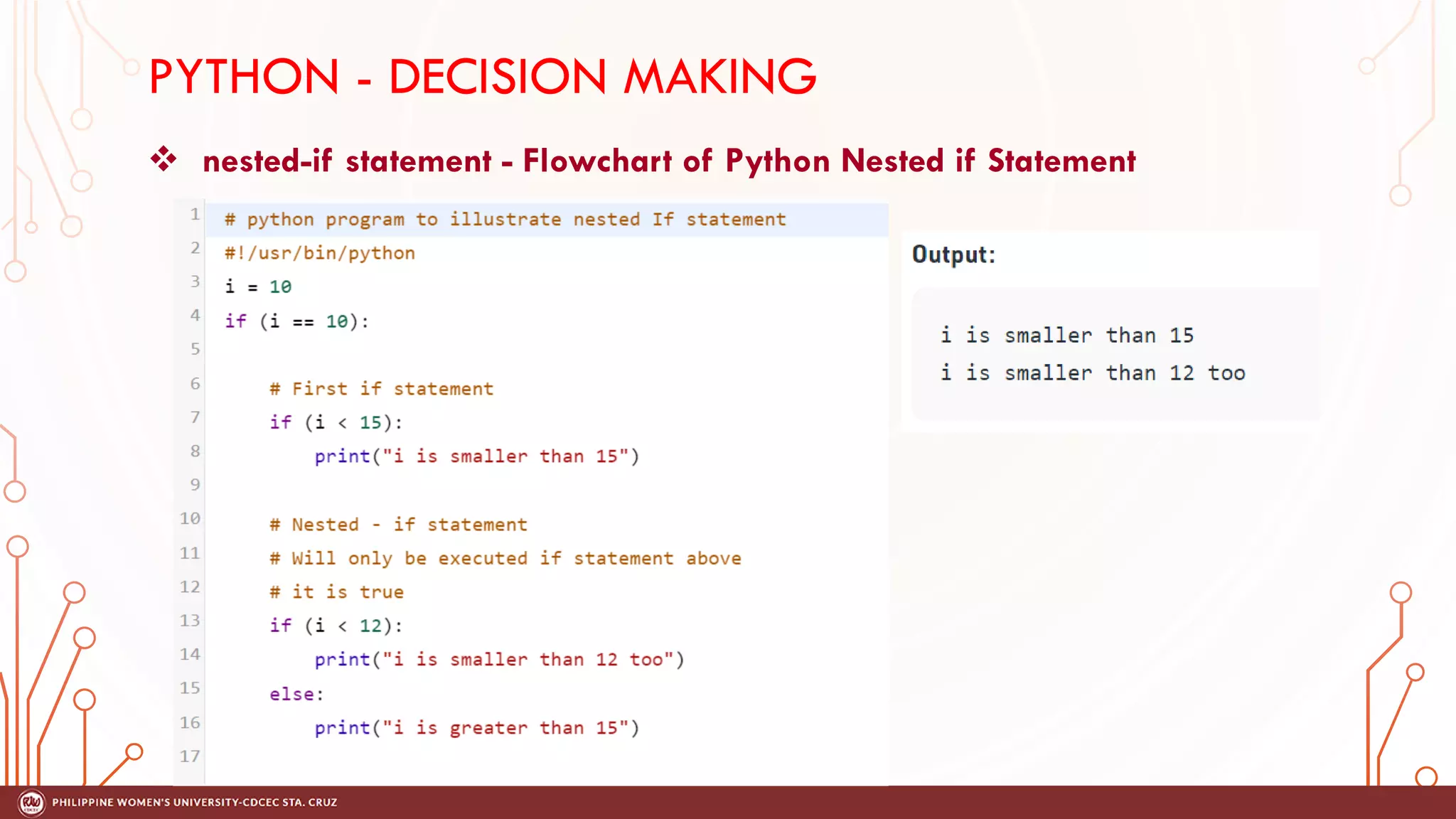
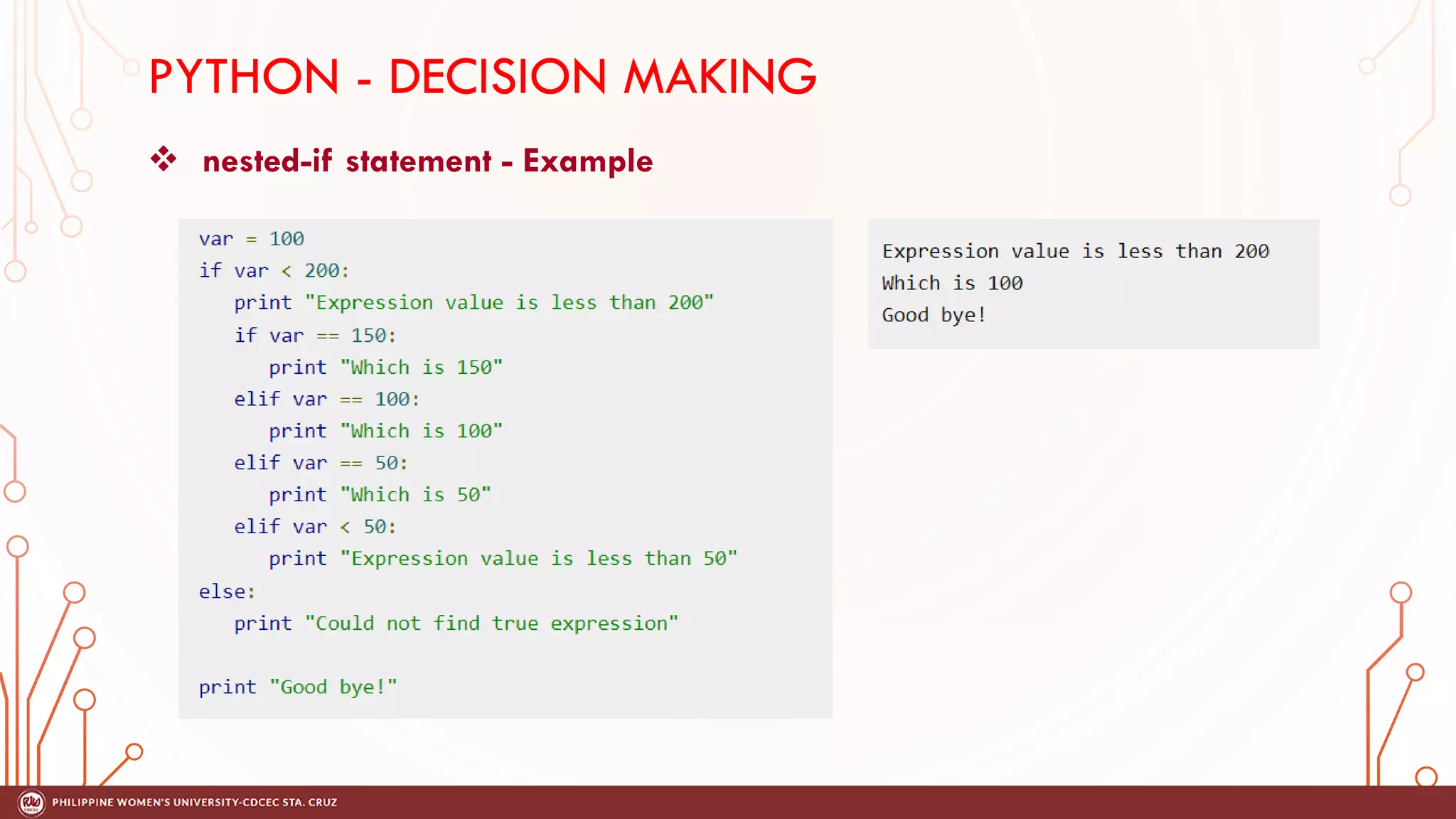
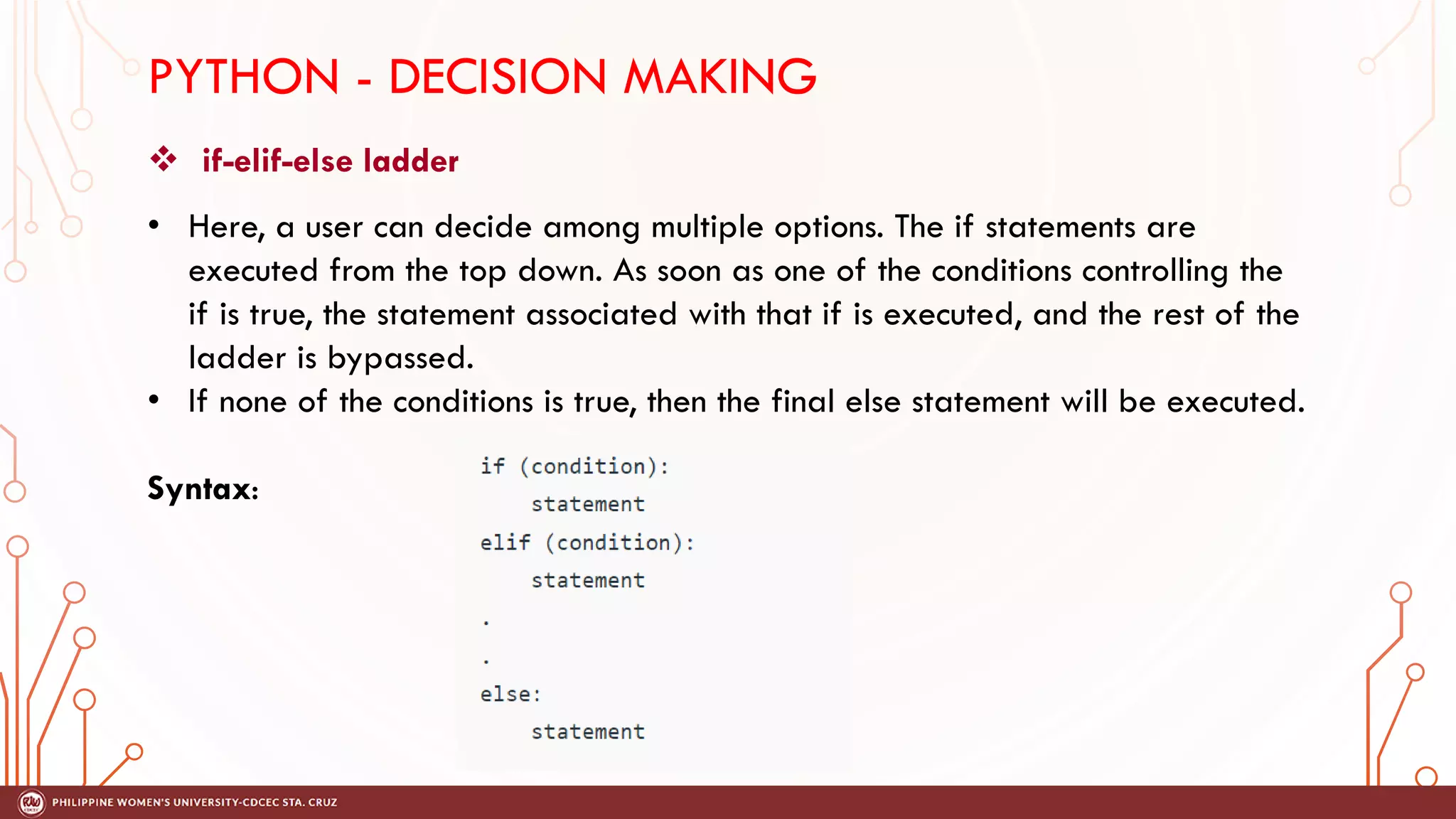
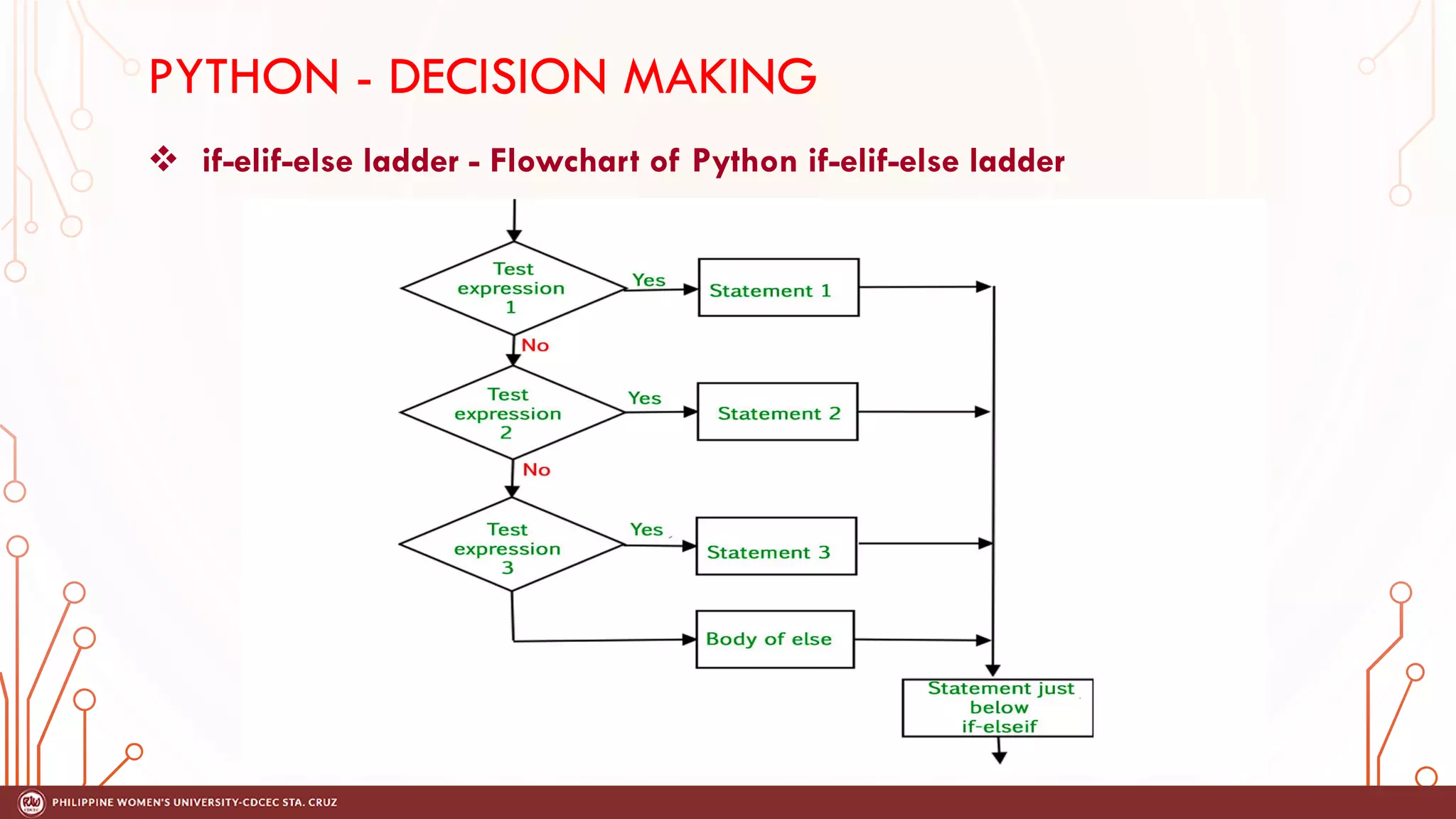
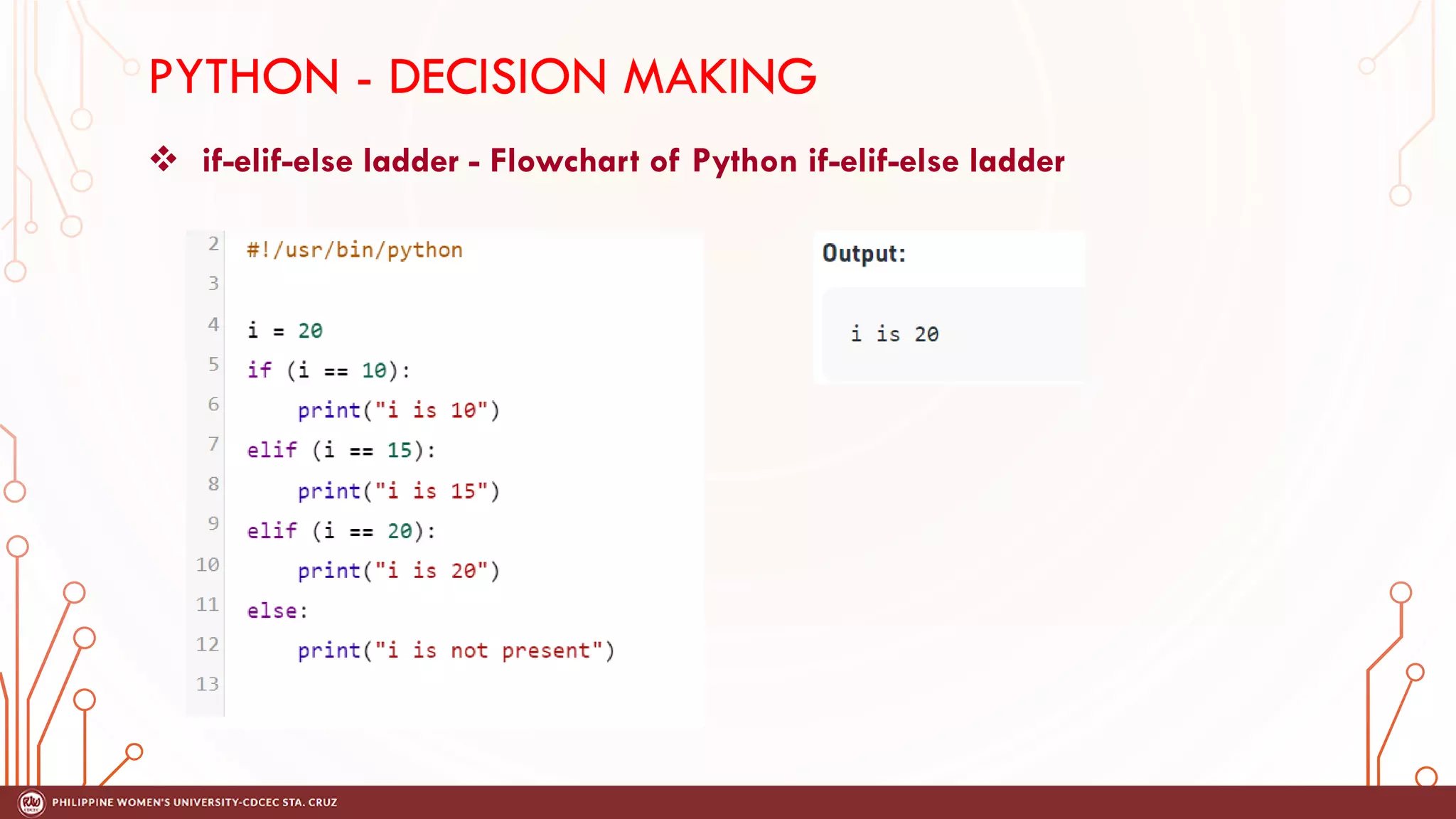
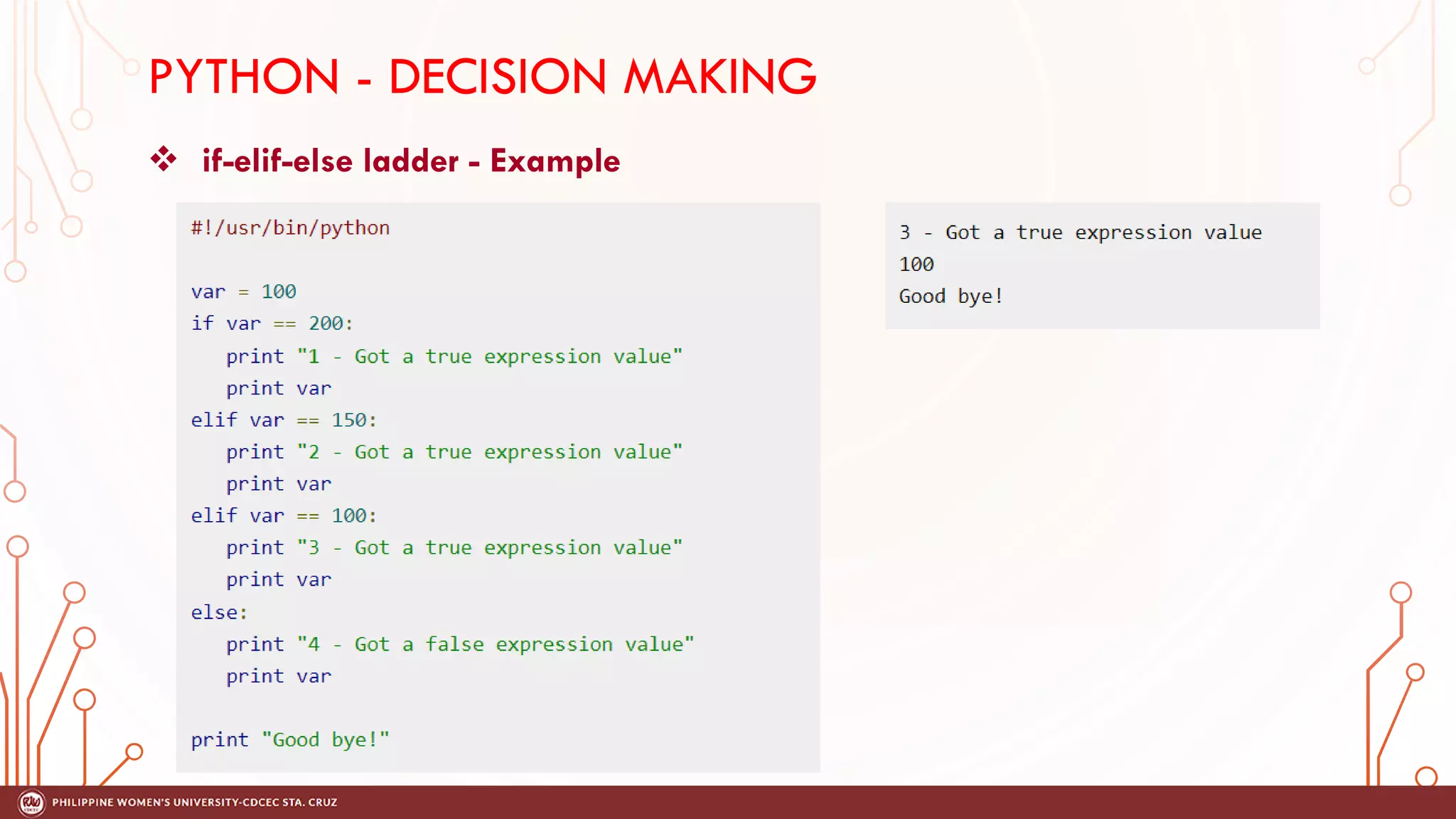
This document discusses decision making and control flow in Python programming. It covers the basic decision making statements like if, if-else, nested if, and if-elif-else ladder. The if statement executes code if a condition is true, while if-else adds else blocks for false conditions. Nested if allows if statements within other ifs. The if-elif-else ladder sequentially tests multiple conditions and executes the first true block. Examples and flowcharts are provided for each statement type.