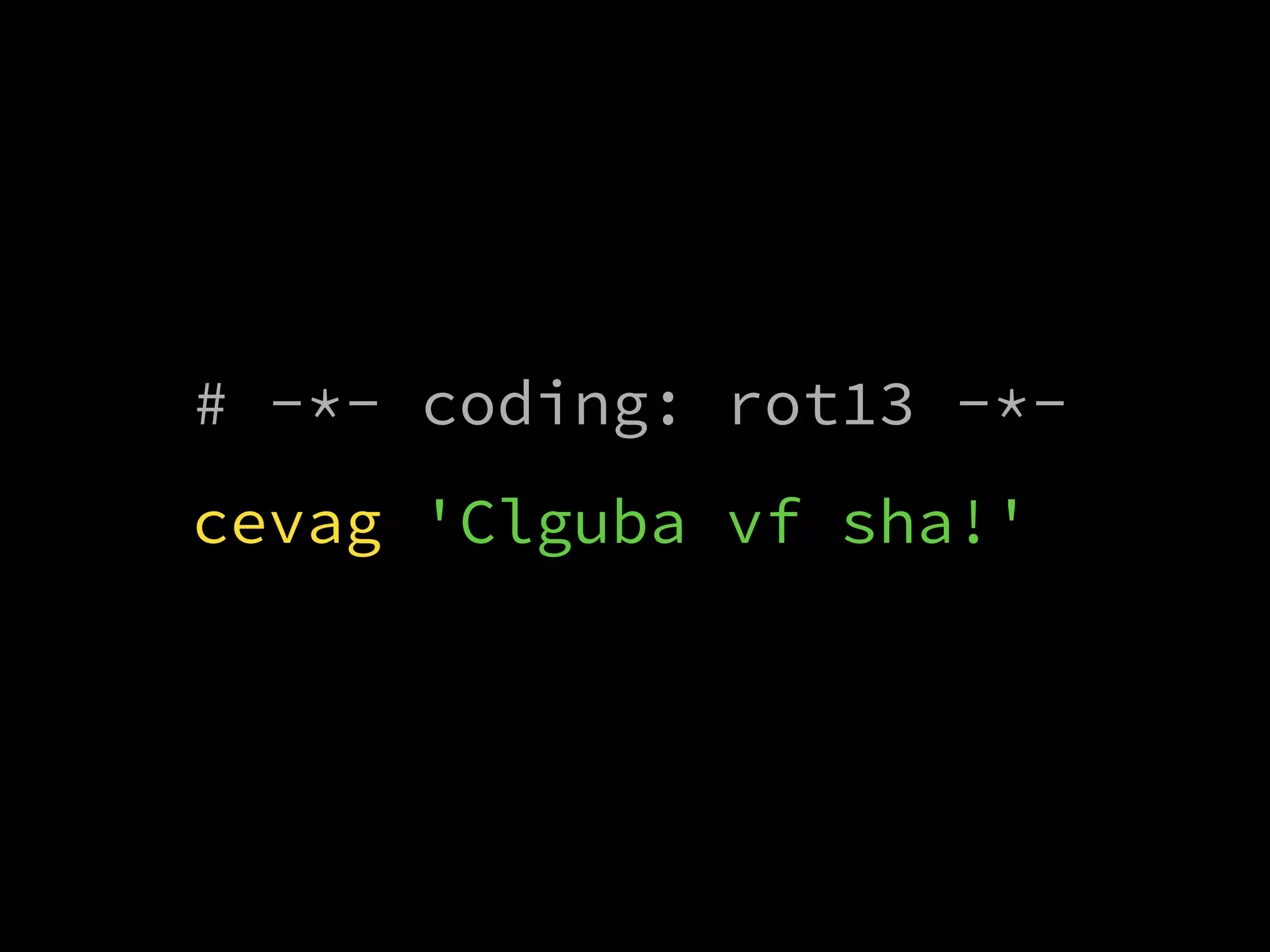
This document contains a collection of Python tidbits and examples including:
- Examples of list comprehensions, generators, slicing, unpacking, and decorators
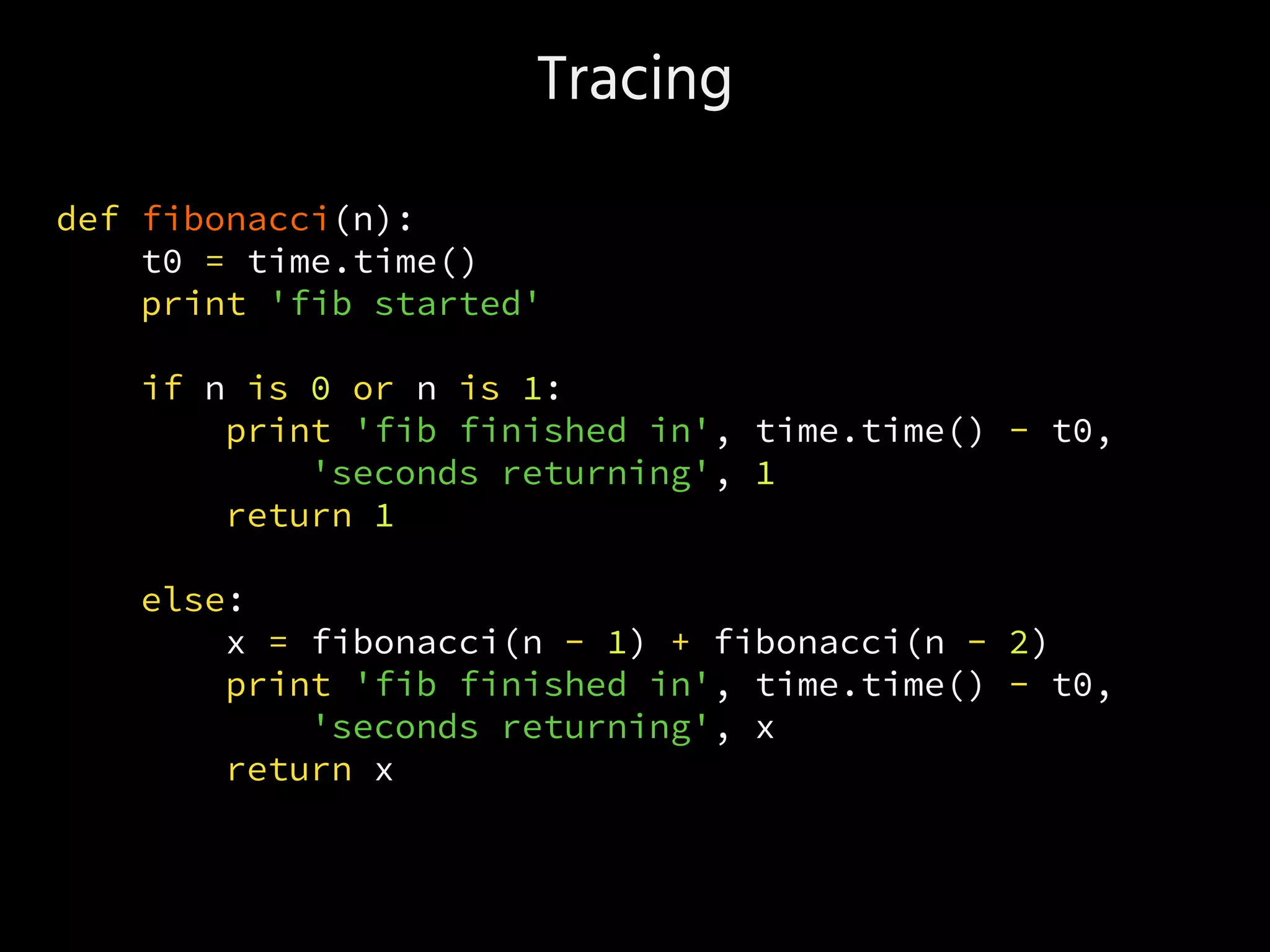
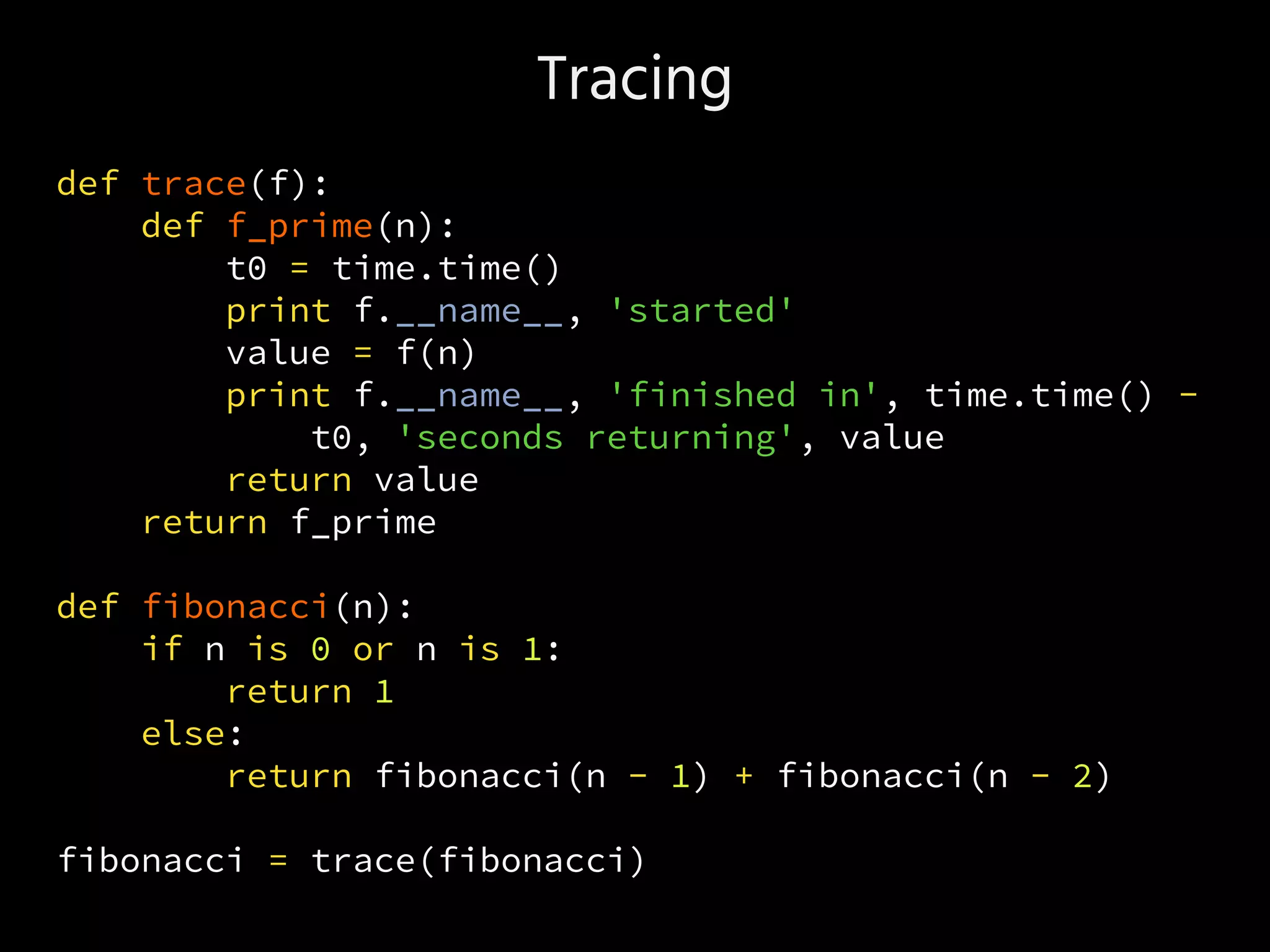
- Tracing a Fibonacci function using a decorator
- Examples demonstrating tuples, dictionaries, strings, iterators, and performance
- Brief mentions of additional Python topics like debugging, web frameworks, documentation tools, and libraries







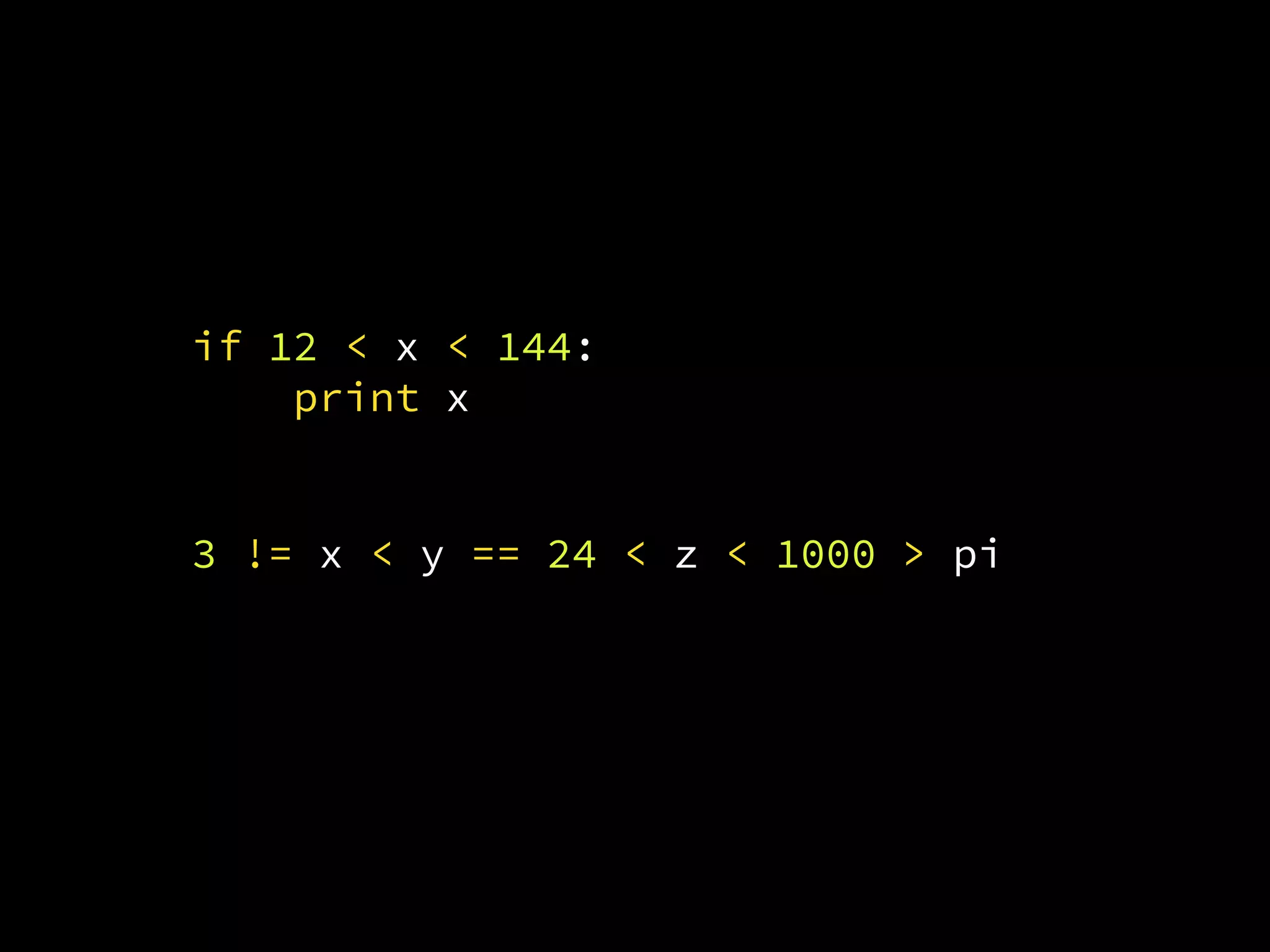


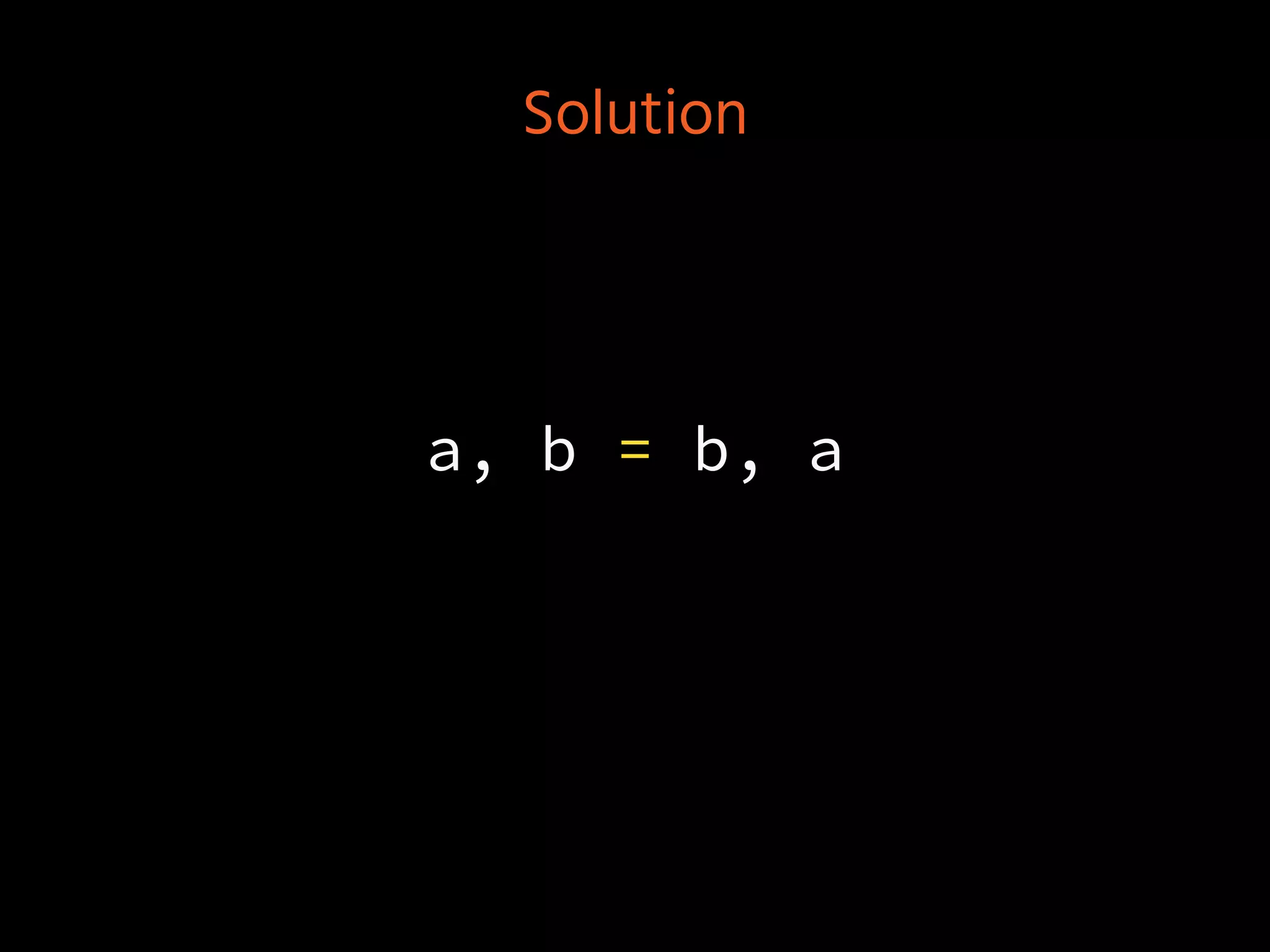




![[start:end:step]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-19-2048.jpg)
!['Michigan Hackers'[6:13]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-20-2048.jpg)
!['Michigan Hackers'[6:13]
0123456789abcdef](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-21-2048.jpg)
!['Michigan Hackers'[:-5]
0123456789abcdef](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-22-2048.jpg)
!['Michigan Hackers'[-5:]
0123456789abcdef](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-23-2048.jpg)
!['Michigan Hackers'[::2]
0123456789abcdef](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-24-2048.jpg)
![[::-1]
reversed()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-25-2048.jpg)


![Imperative
cubes = []
for x in range(100):
cubes.append(x ** 3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-28-2048.jpg)

![List comprehension
cubes = [x ** 3 for x in range(100)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-30-2048.jpg)
![With a predicate
cubes = []
for x in range(100):
if x % 2:
cubes.append(x ** 3)
cubes = map(lambda x: x ** 3,
filter(lambda x: x % 2, range(100)))
cubes = [x ** 3 for x in range(100) if x % 2]
cubes = [x ** 3 for x in range(100)][1::2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-31-2048.jpg)
![Sum of two dice
table = []
for i in range(1, 7):
row = []
for j in range(1, 7):
row.append(i + j)
table.append(row)
[[i + j for i in range(1, 7)]
for j in range(1, 7)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-32-2048.jpg)
![word = 'abracadabra'
[word[:i] for i in range(len(word), 0, -1)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-33-2048.jpg)



![Unpack argument lists
def add(a, b):
return a + b
nums = [1, 2]
add(*nums)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-37-2048.jpg)


![Decomposition
x, xs = things[0], things[1:]
x, *xs = things](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-40-2048.jpg)
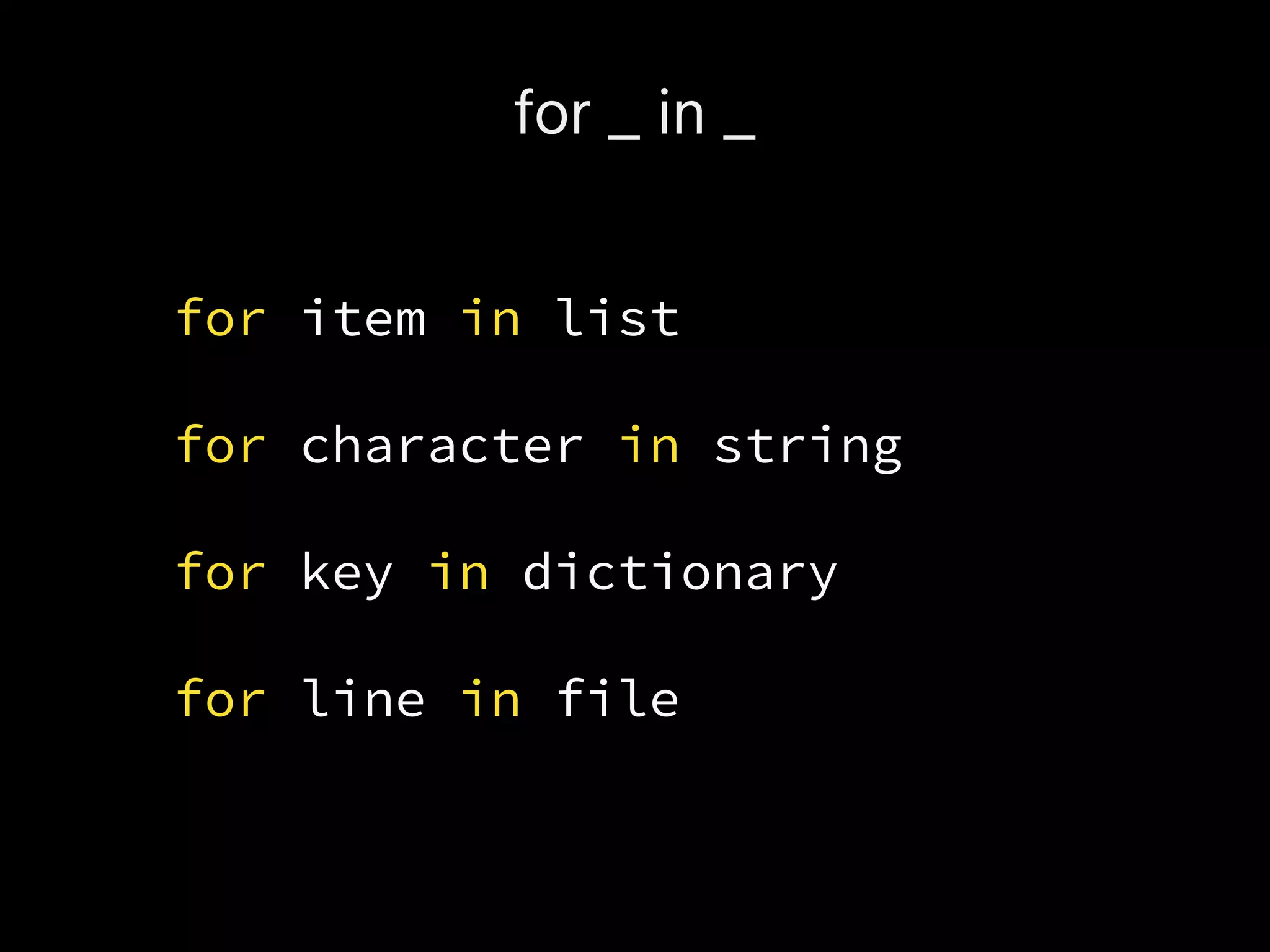
![__iter__
nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
iterator = iter(nums)
iterator.next()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-43-2048.jpg)
![Implementing range
class simple_range:
def __init__(self, n):
self.n = n
self.data = [i for i in range(n)]
def __iter__(self):
return iter(self.data)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-44-2048.jpg)
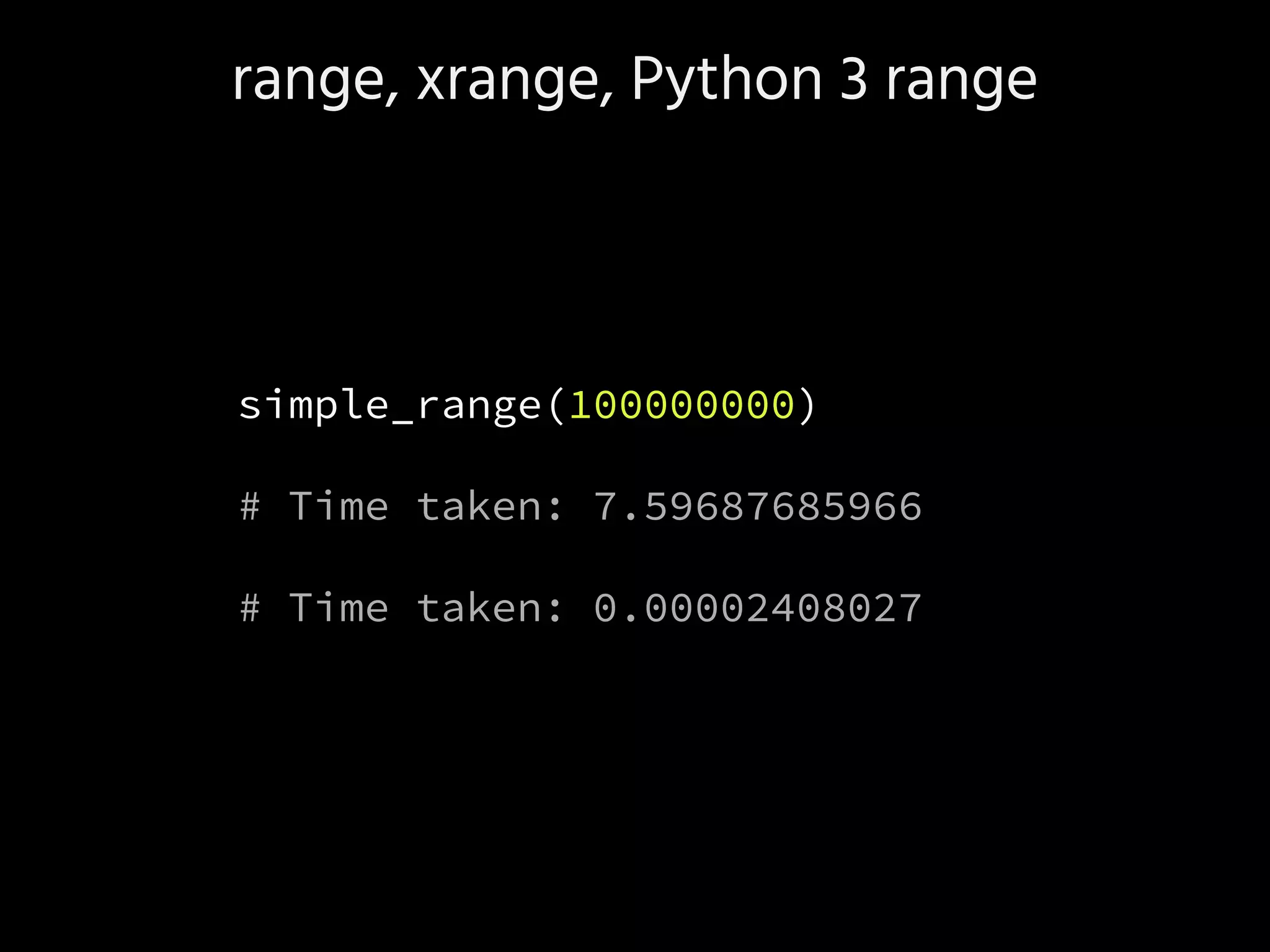
![Performance
import time
class simple_range:
def __init__(self, n):
t0 = time.time()
self.n = n
self.data = [i for i in range(n)]
print 'Time taken:', time.time() - t0
def __iter__(self):
return iter(self.data)
simple_range(100000000)
# Time taken: 7.59687685966](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-45-2048.jpg)





![A more complicated generator
def alphagen(start, end=None):
s = list(reversed(start))
while end is None or s != list(reversed(end)):
yield ''.join(reversed(s))
if s == list('z' * len(s)):
s = list('a' * (len(s) + 1))
else:
for i, ch in enumerate(s):
if ch is 'z':
s[i] = 'a'
else:
s[i] = chr(ord(ch) + 1)
break](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-52-2048.jpg)





![' '.join([''.join(reversed(word)) for word in s.split()])
' '.join(reversed(s.split()))
reversed(s)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-60-2048.jpg)
![import random
random.choice(['Ankit', 'Abby', 'Edward',
'Andrew', 'Omkar', 'Jason'])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axnk7puprv6a0ivaevsa-signature-285bb2060e7b0b854e157309721a8c1b0f638a00fb200047611a7e4f8d3ed502-poli-160806223028/75/Python-Tidbits-61-2048.jpg)

