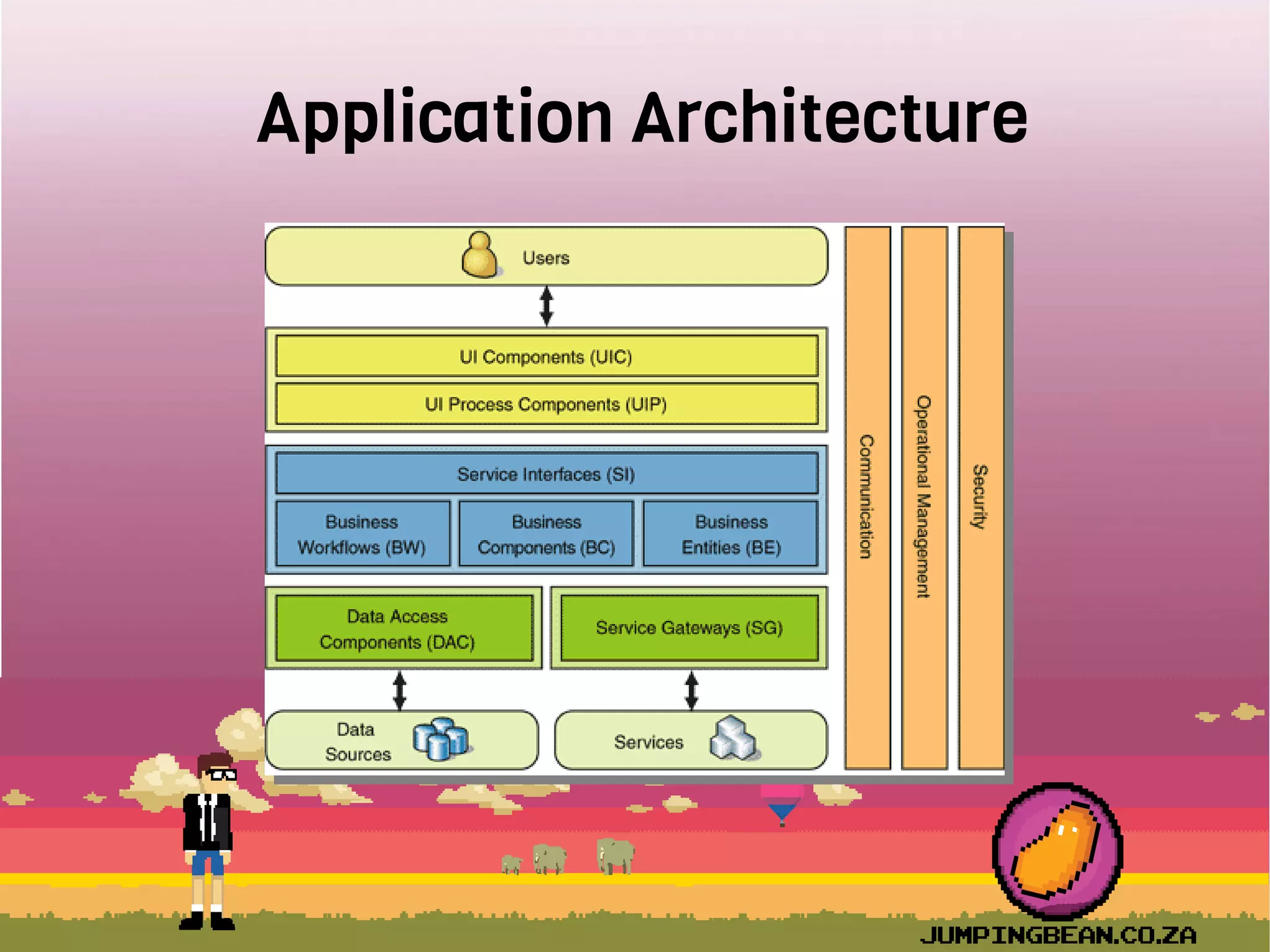
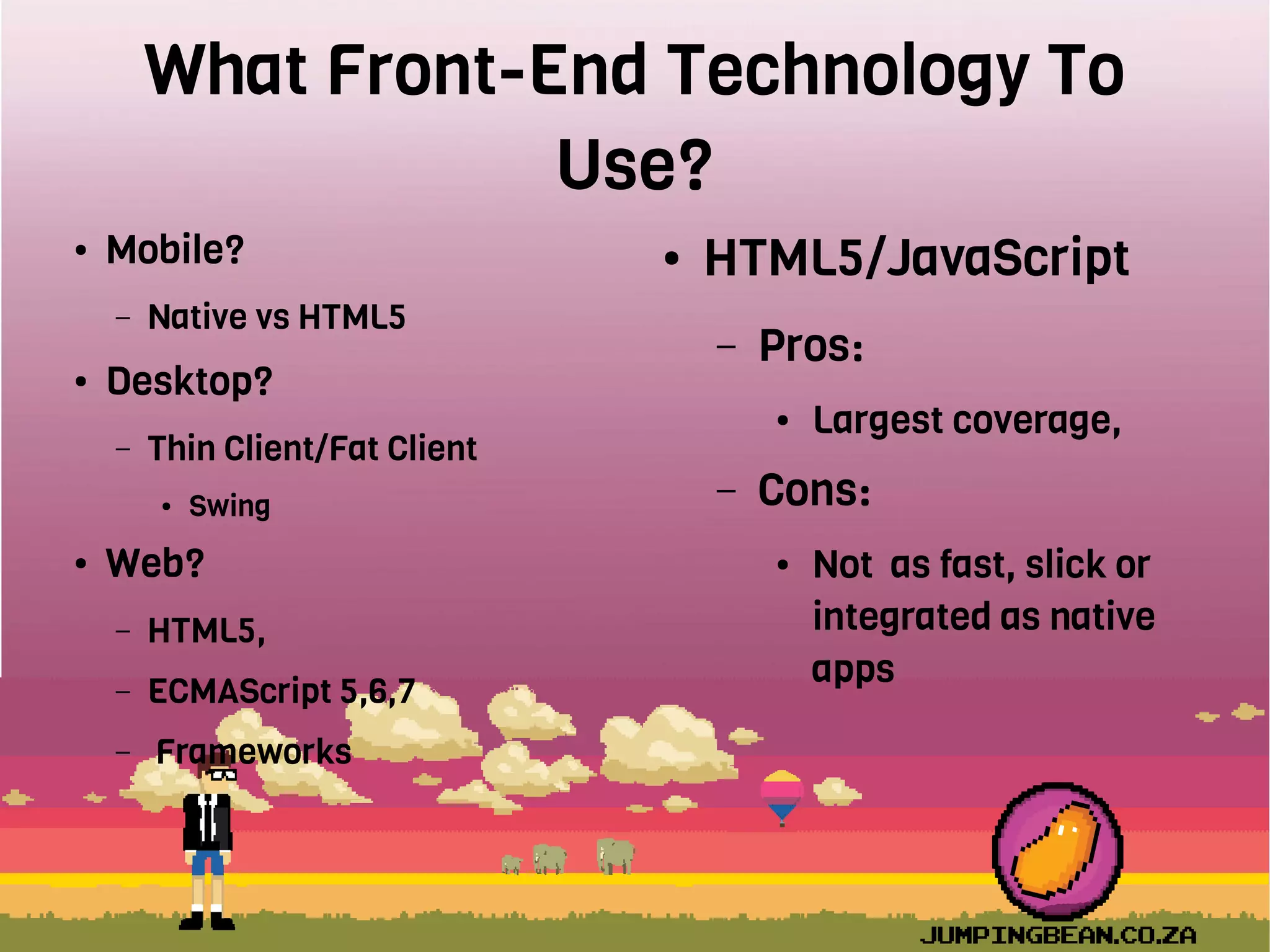
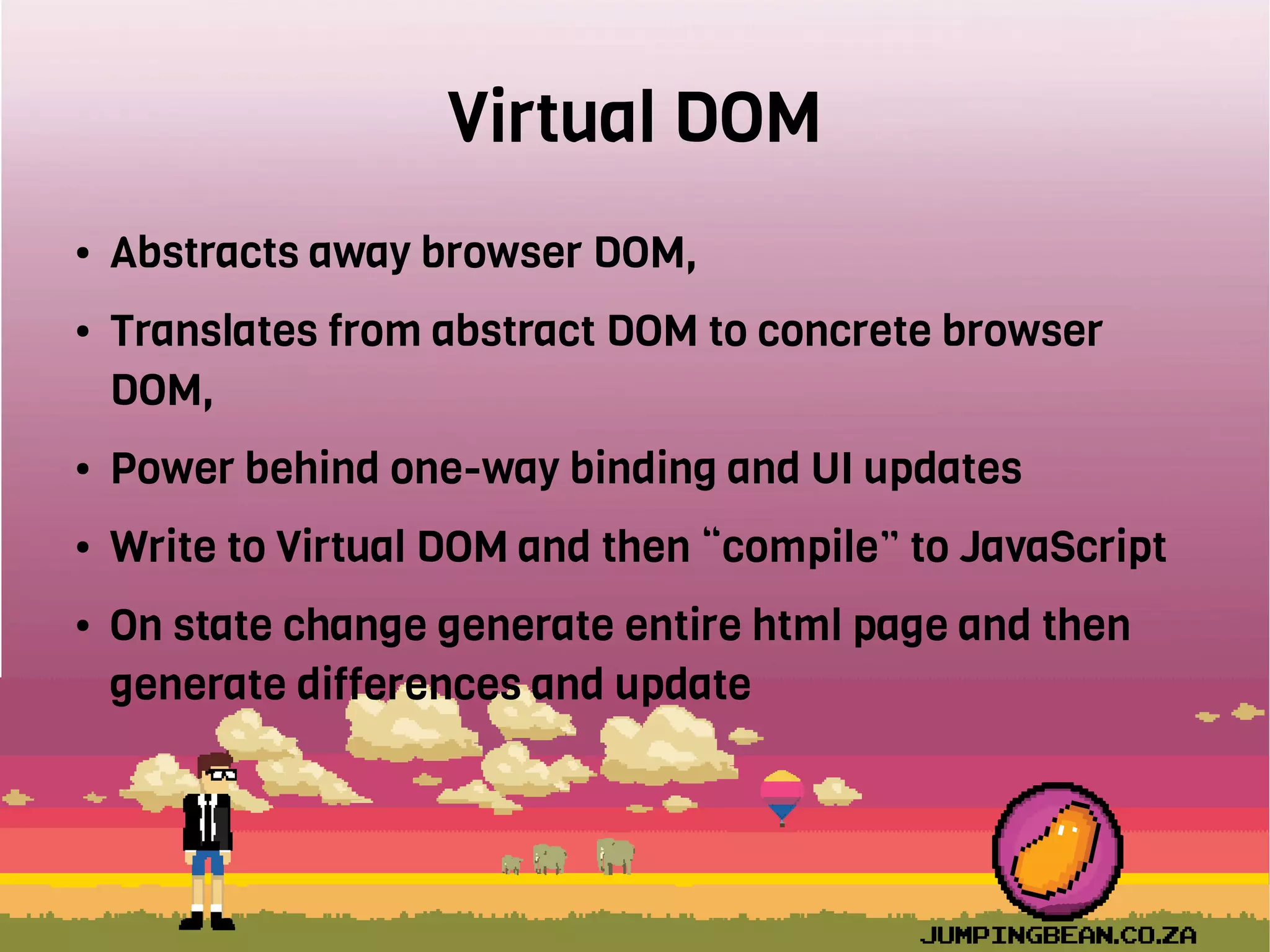
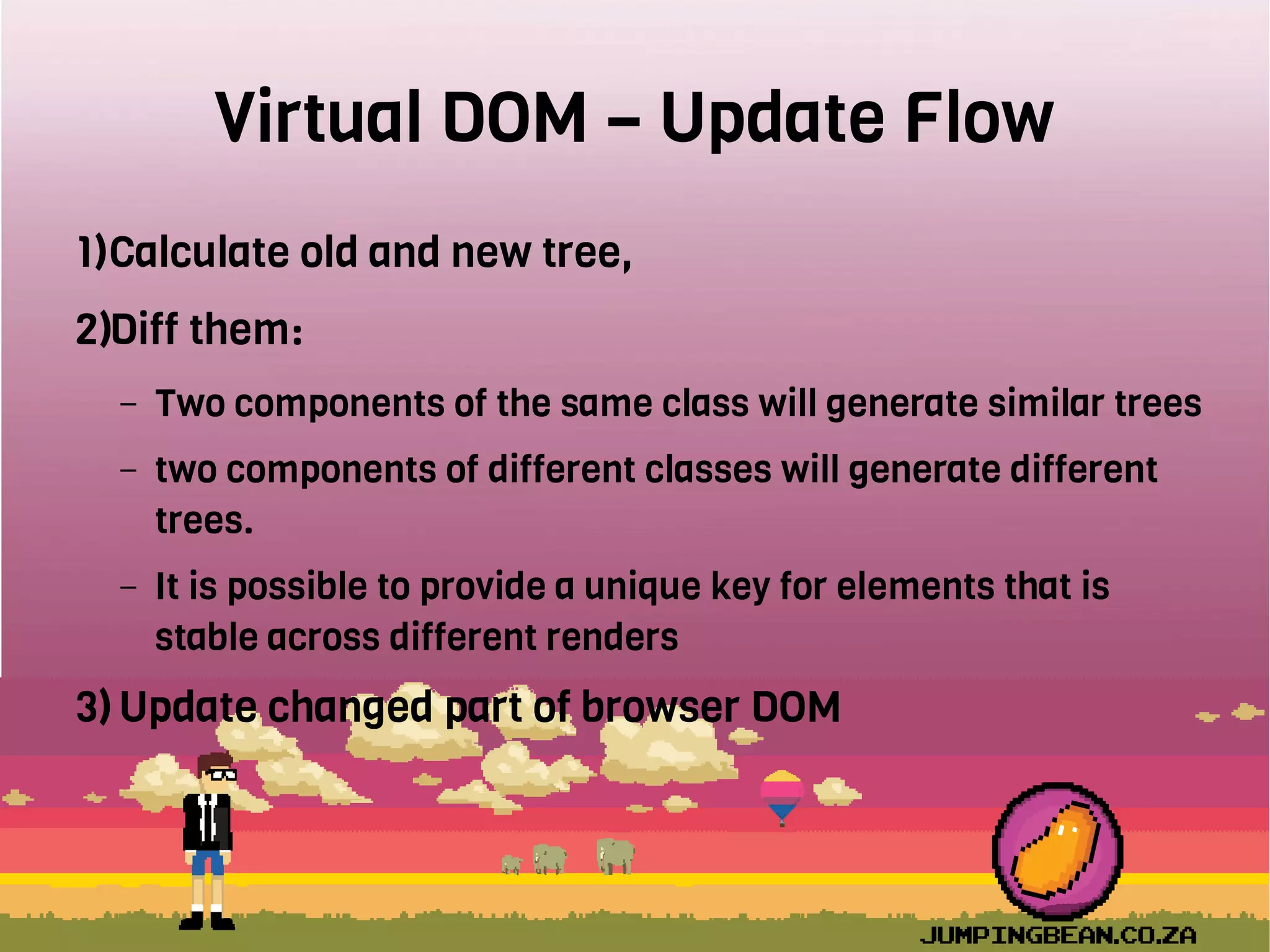
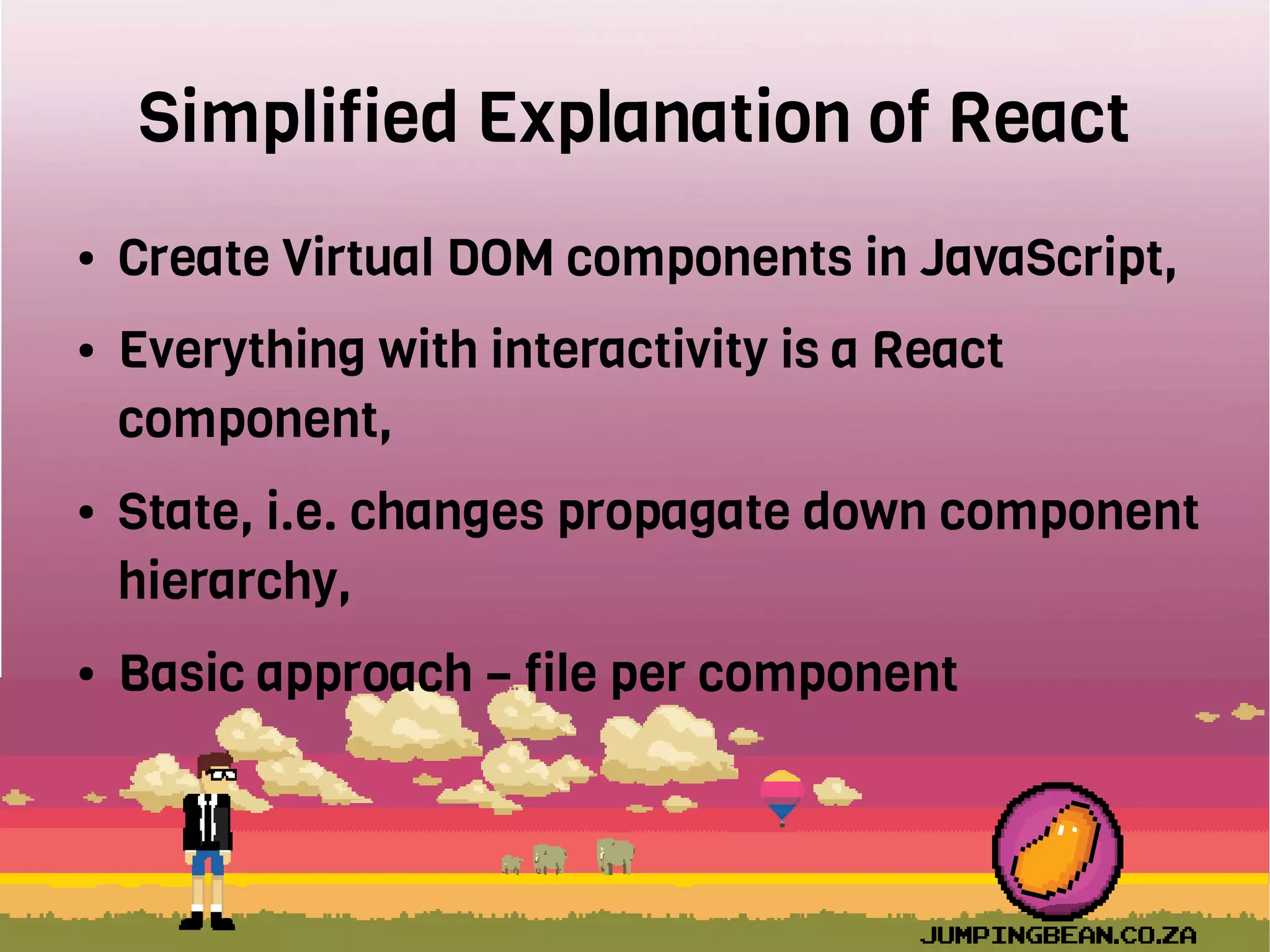
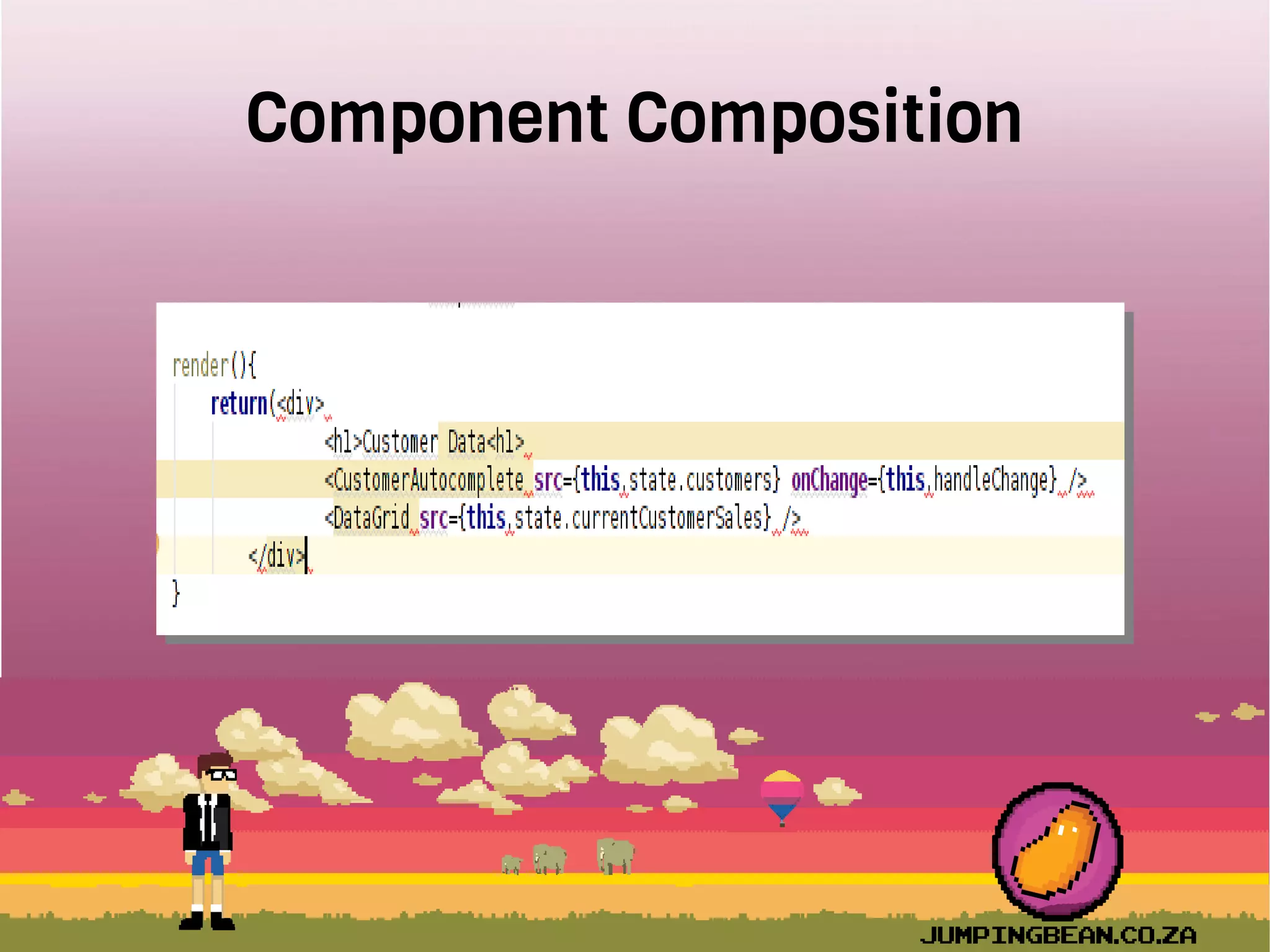
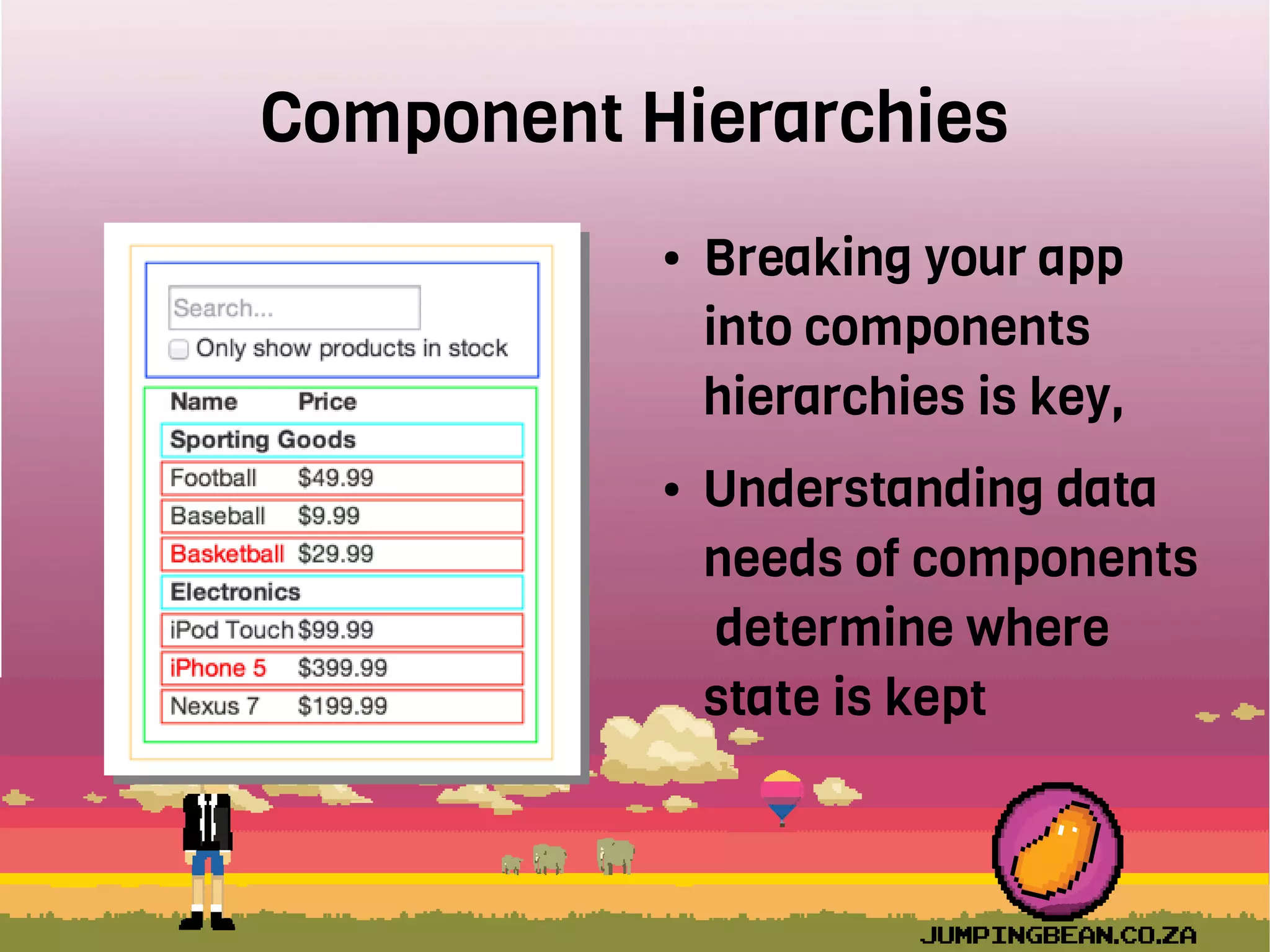
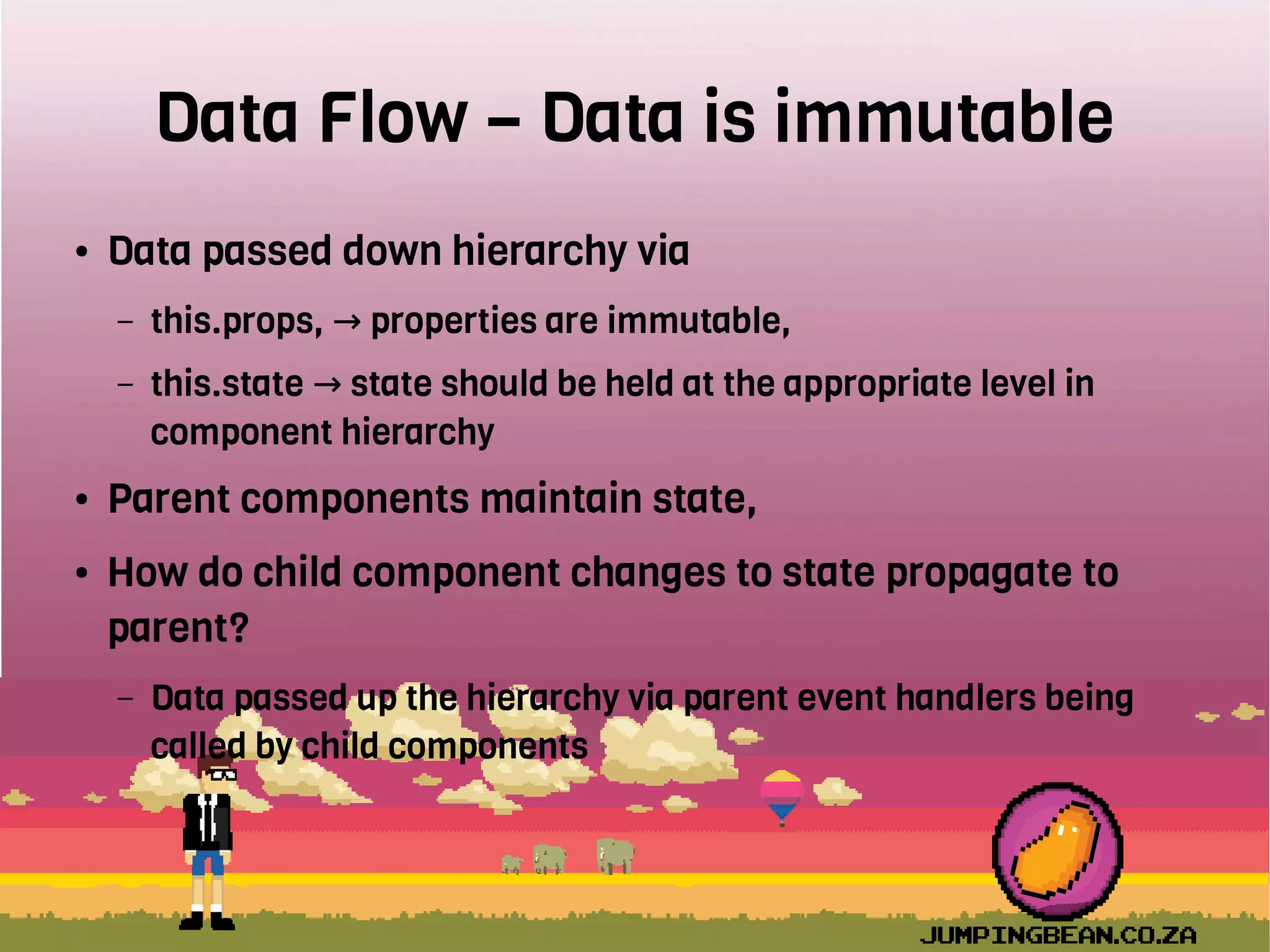
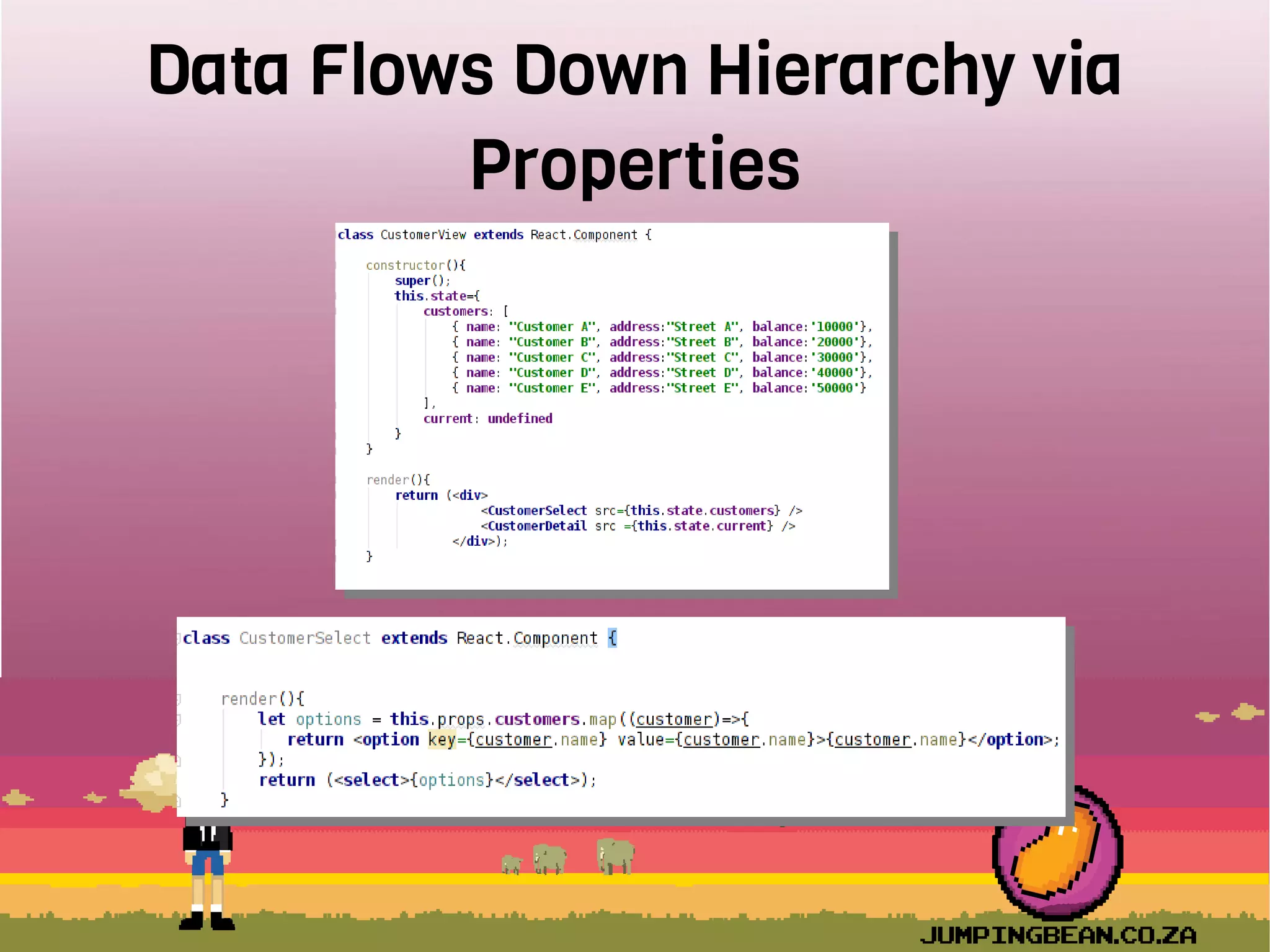
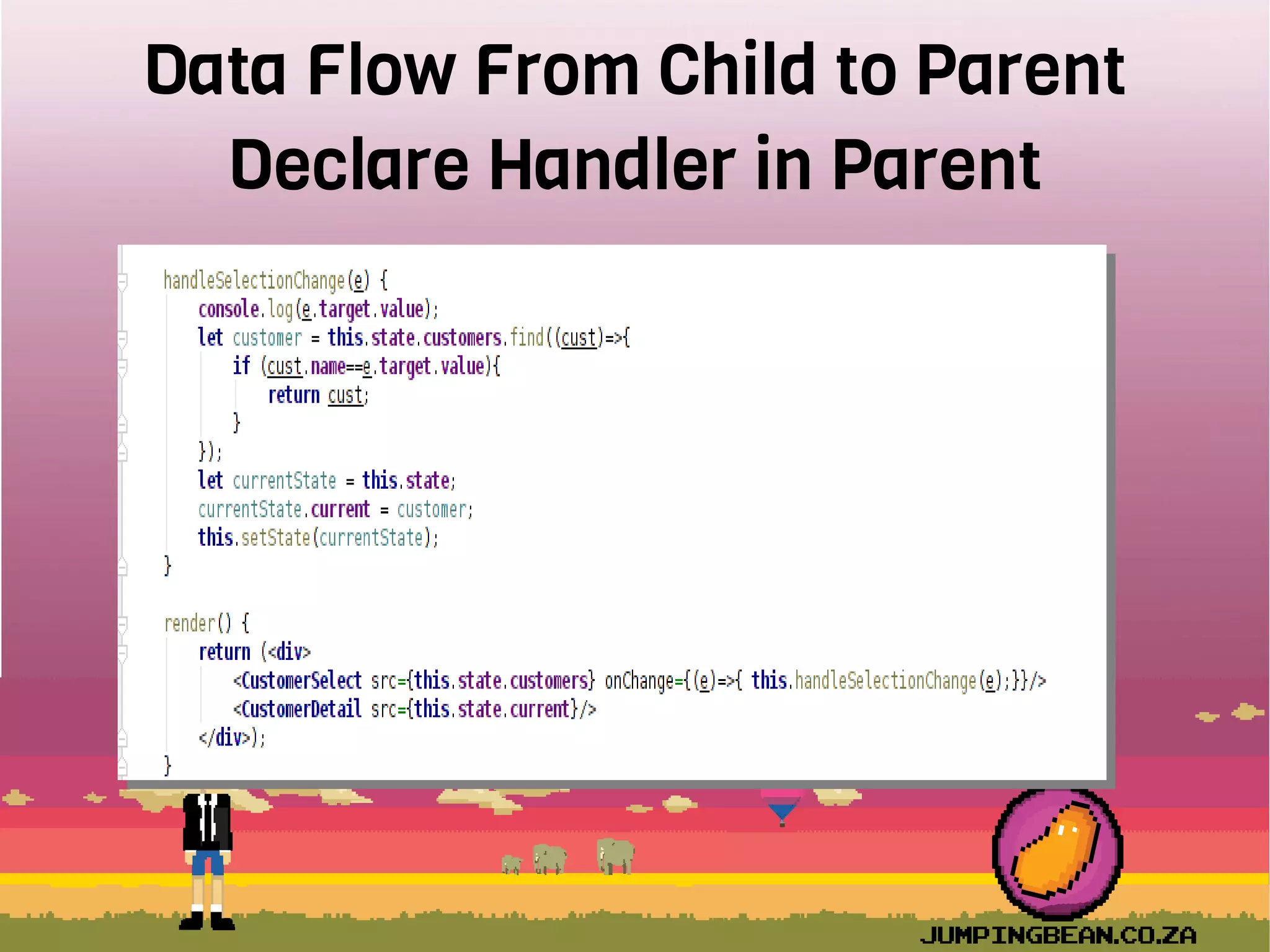
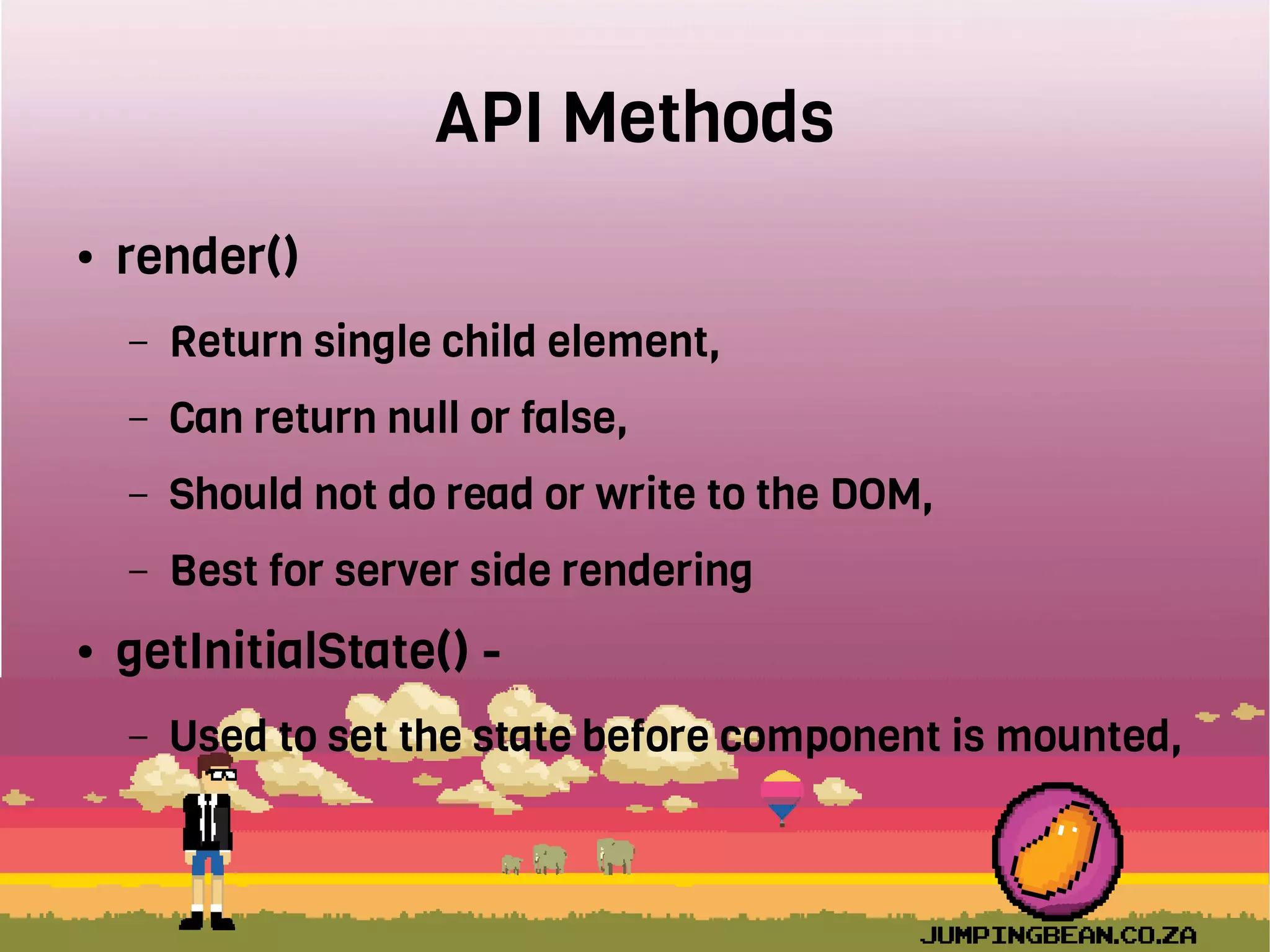
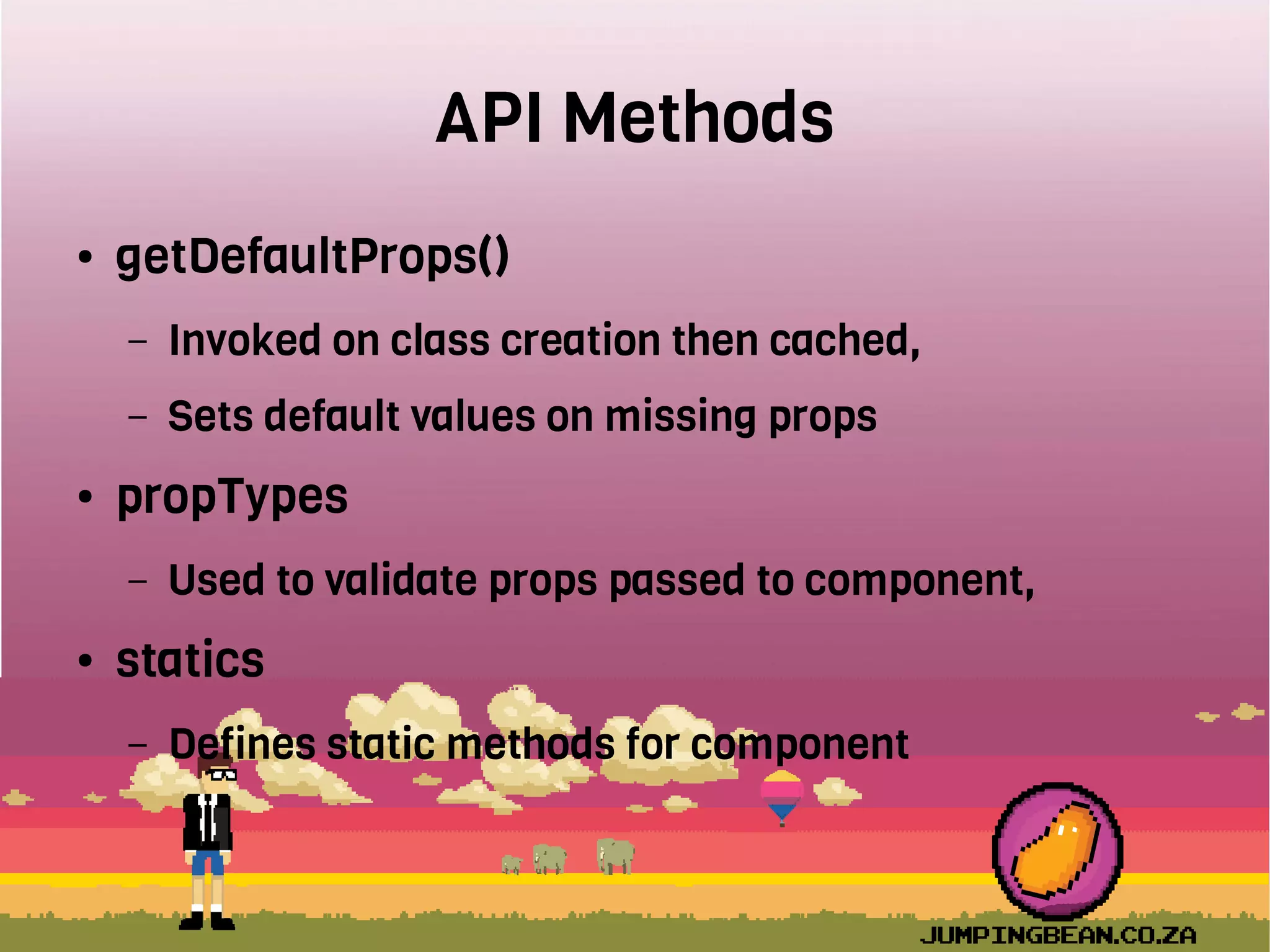
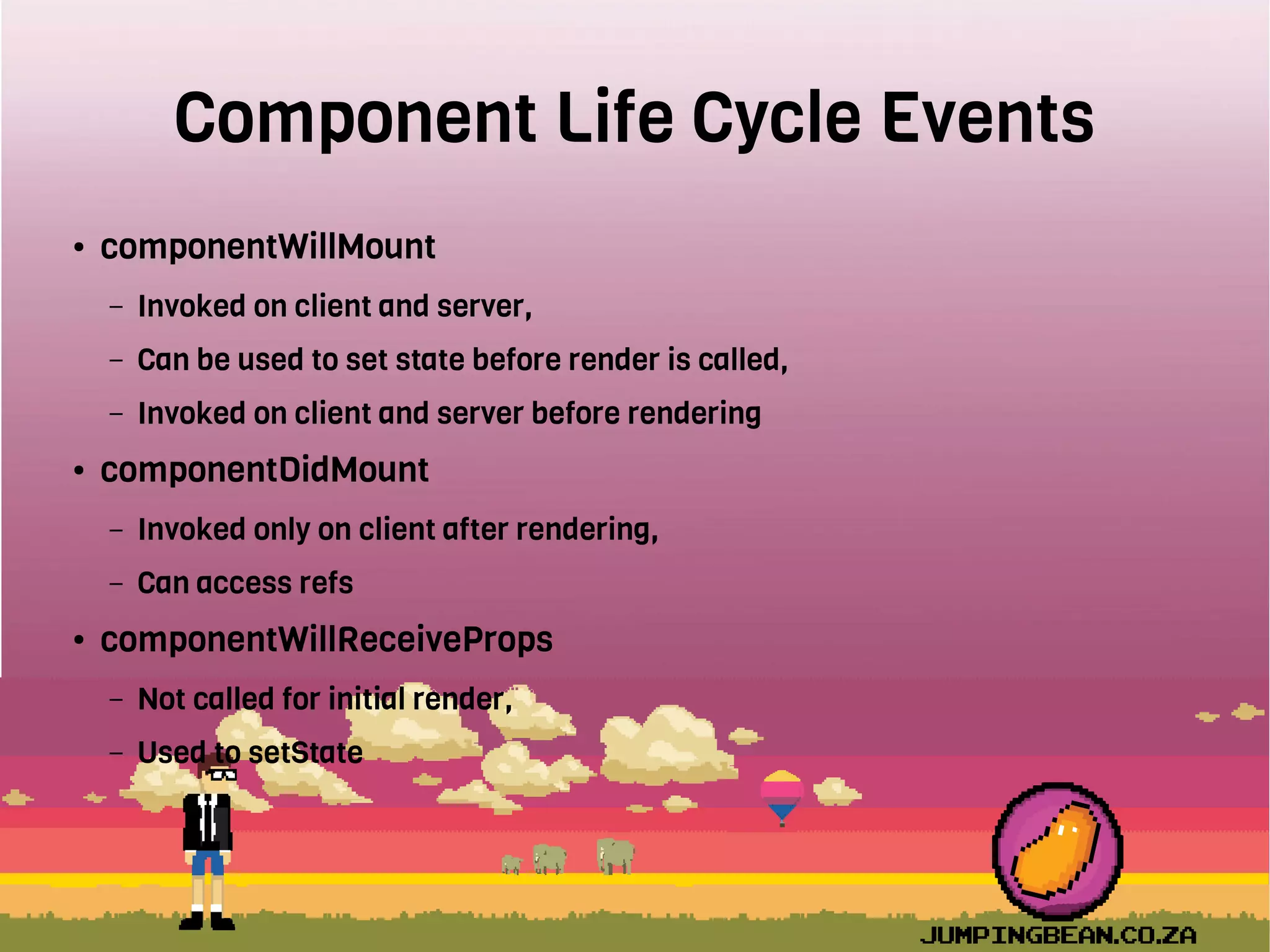
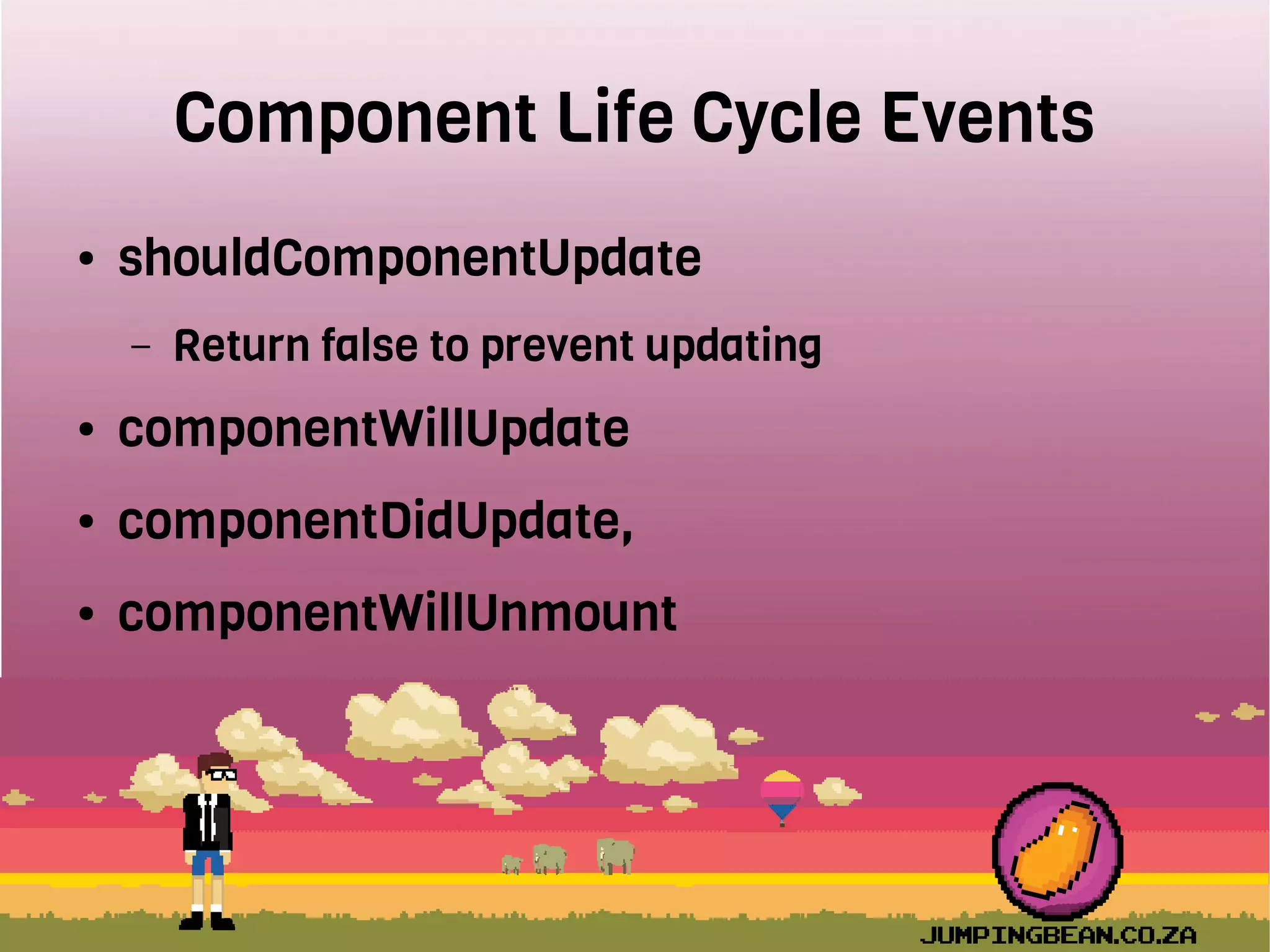
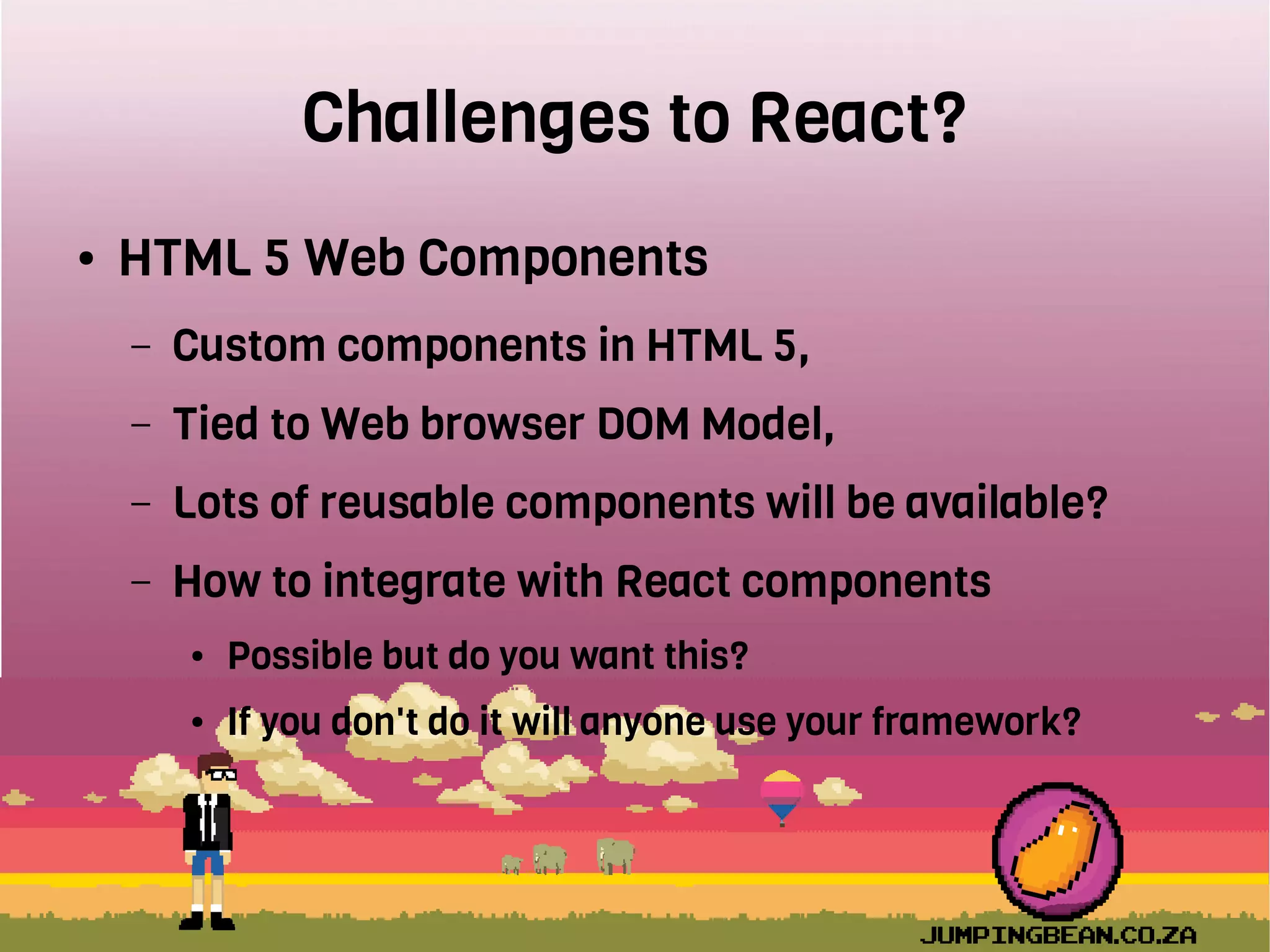
The document provides an introduction to React, highlighting its role as a JavaScript library from Facebook for building user interfaces, primarily for single-page applications. It contrasts React with other frameworks, emphasizing its one-way data binding, virtual DOM, and component-based architecture, which simplify UI development and updates. The document also touches on the component lifecycle, data flow management, and potential challenges in integrating React with HTML5 components.