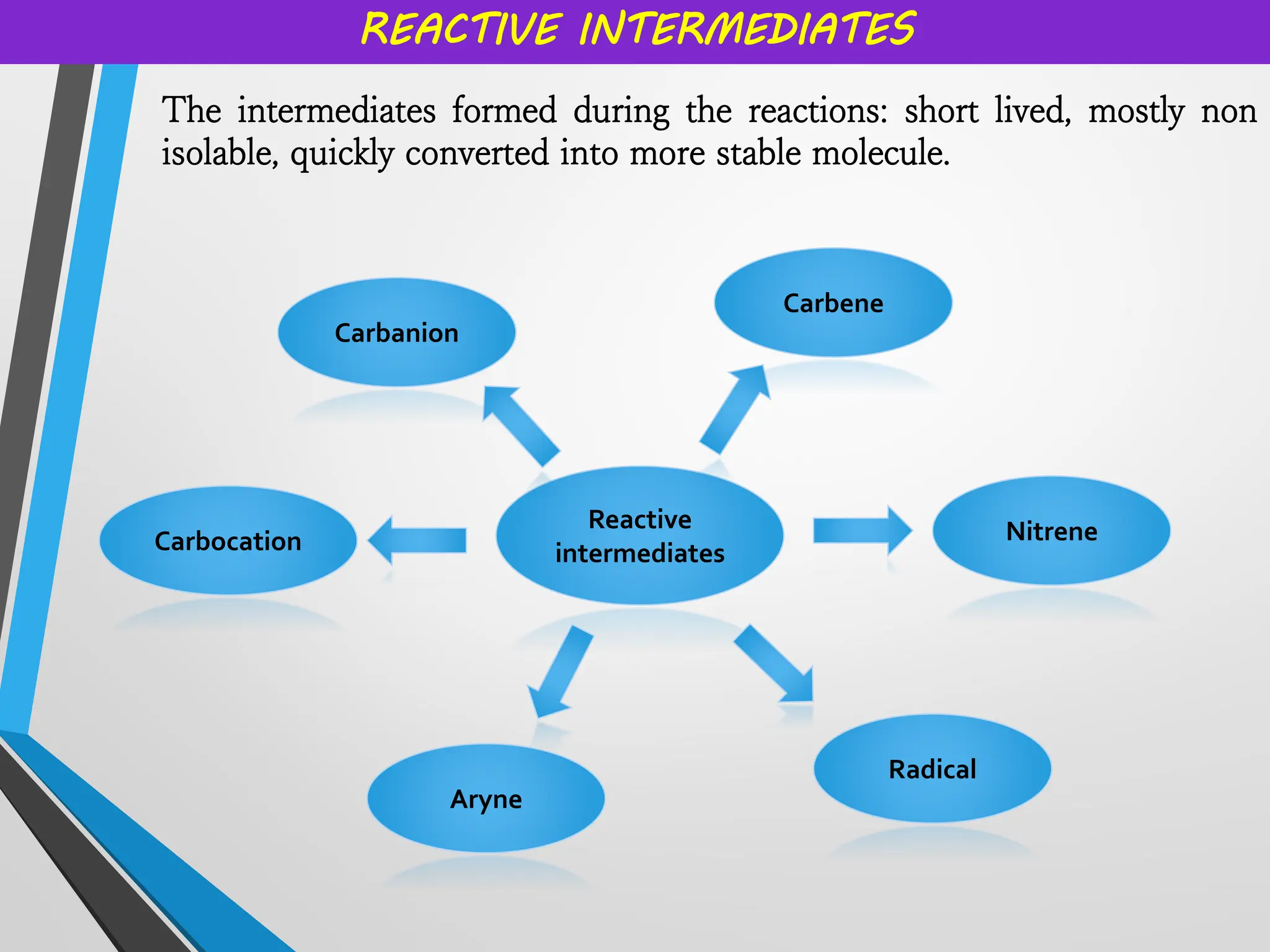
Reactive intermediates and their applications by Dr. Anand S. Burange
Topics covered: Carbocation history, work of George Olah, carbocation synthesis, Carbene and carbanion, Wagner Meerwein,Friedel Crafts reaction, Simmons Smith Cyclopropanation, Appel reaction, Pinalcol-pinacolone rearrangement, and many more.
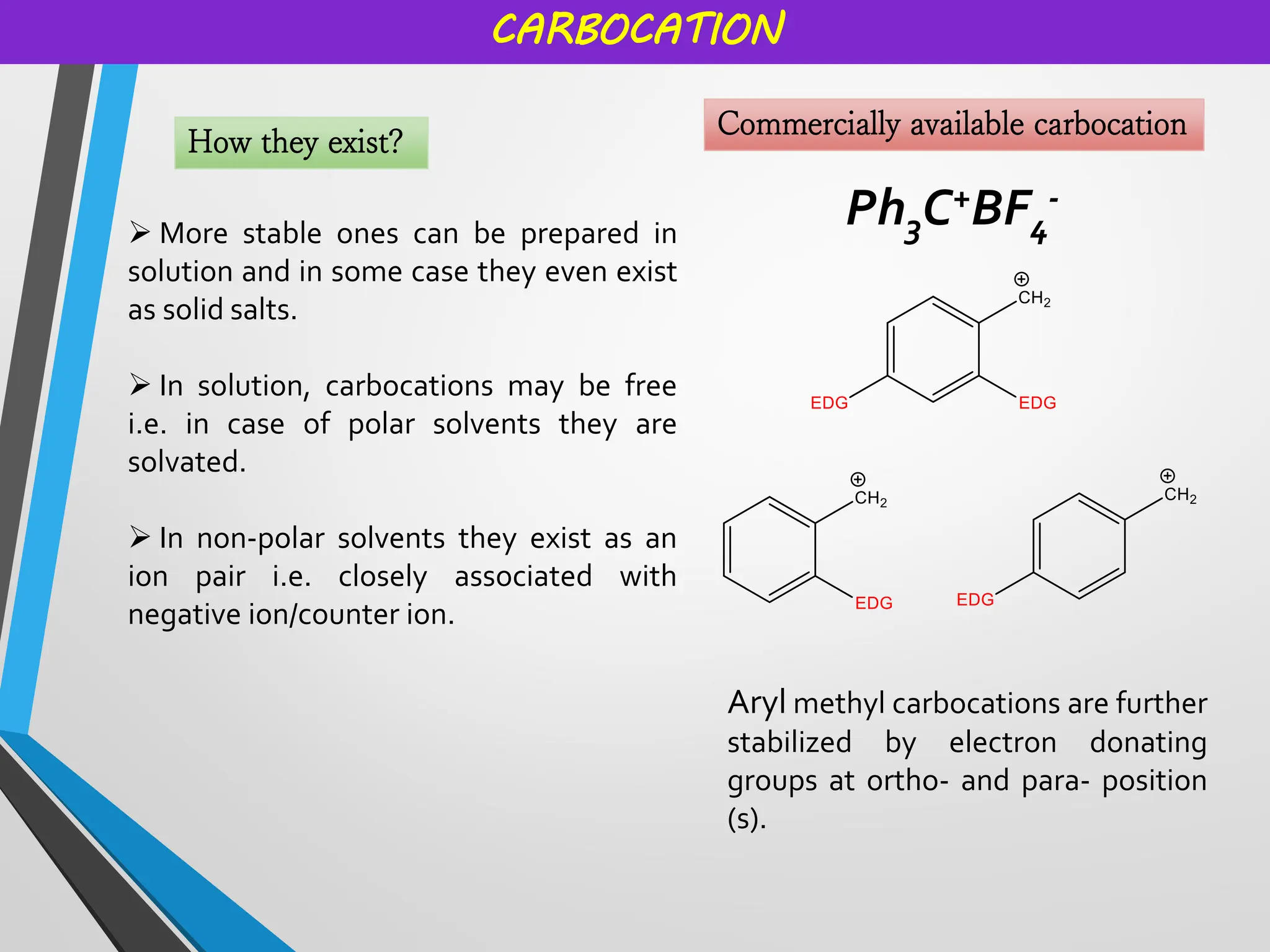
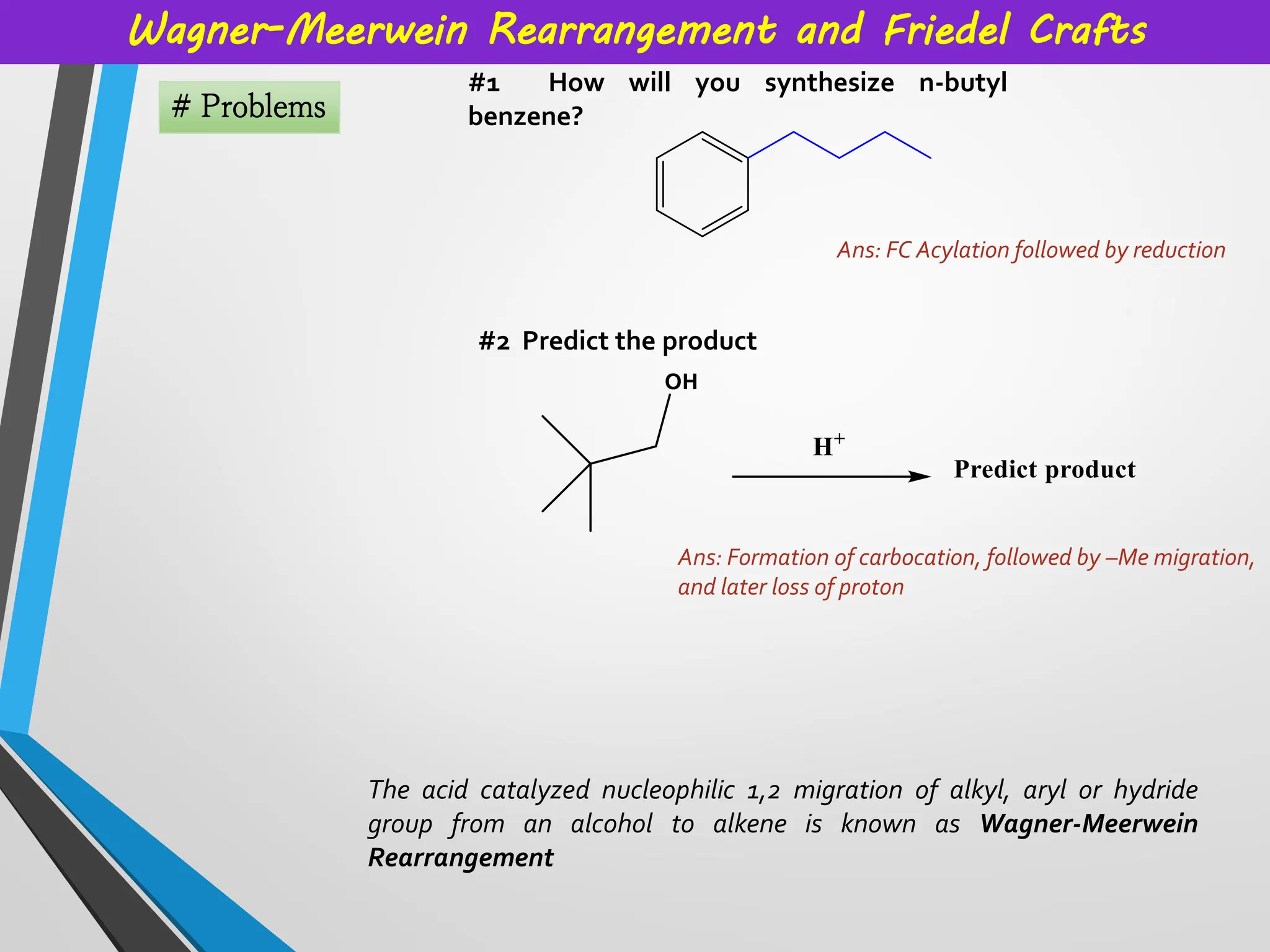
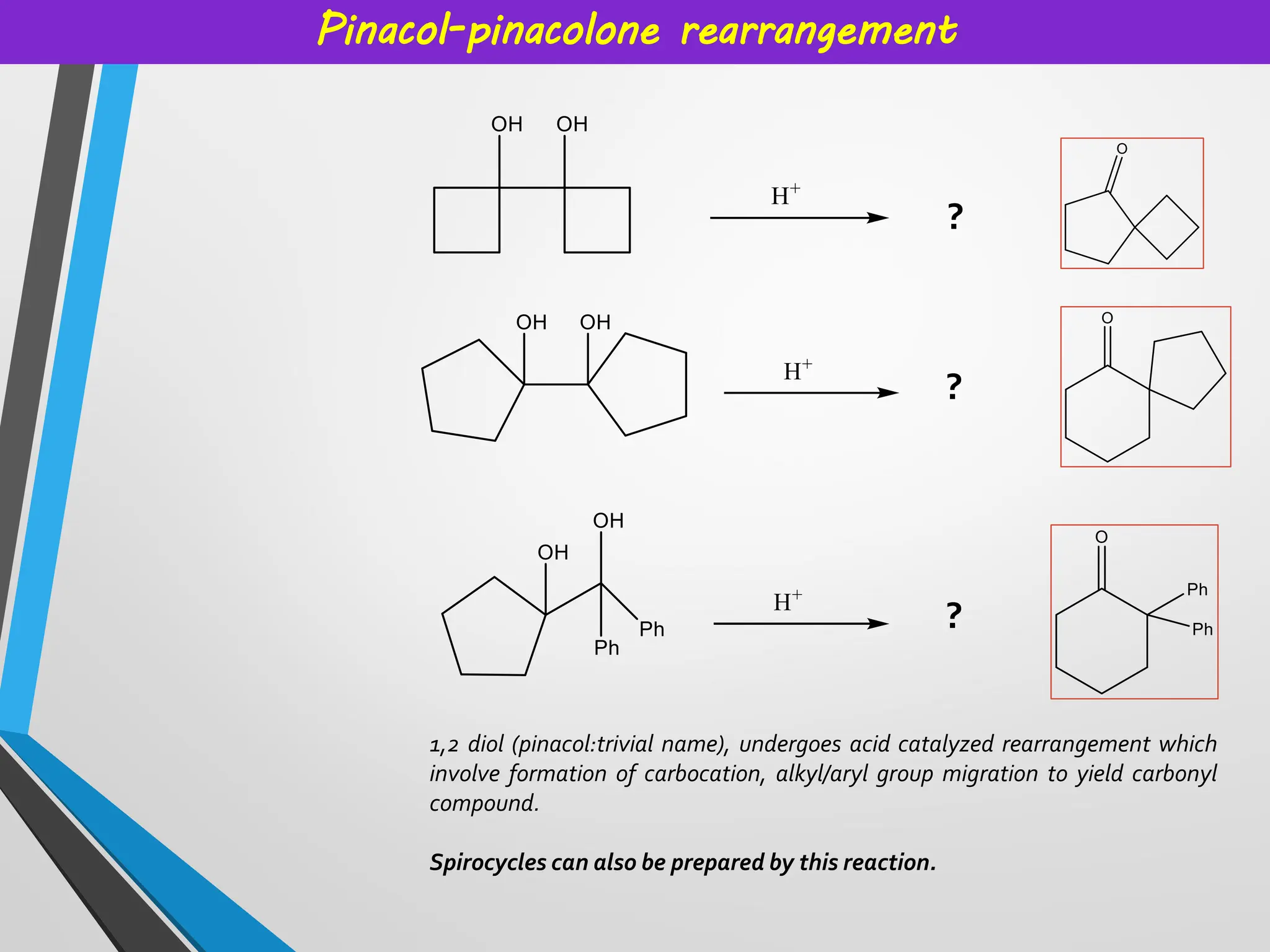
![CARBOCATION
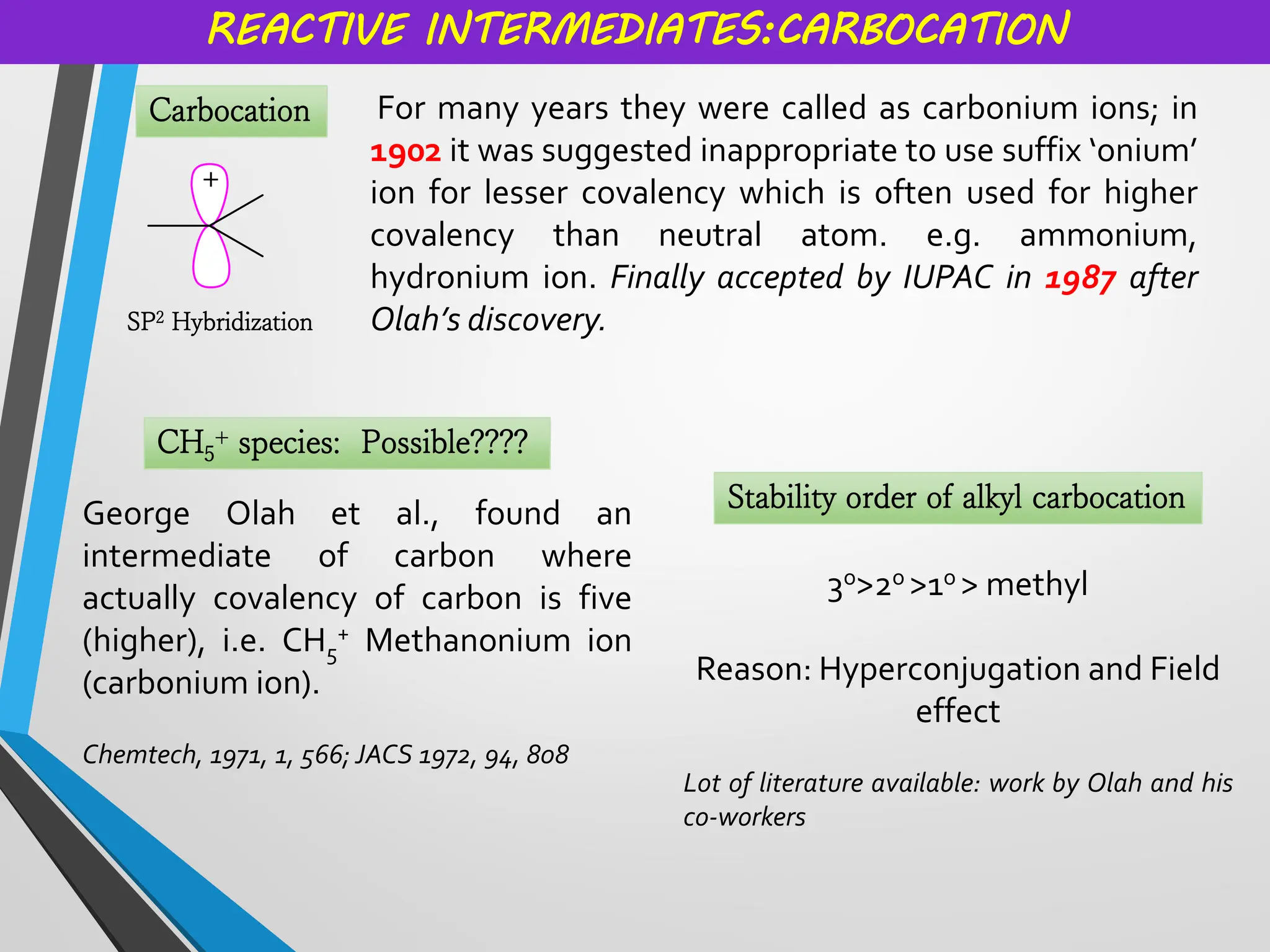
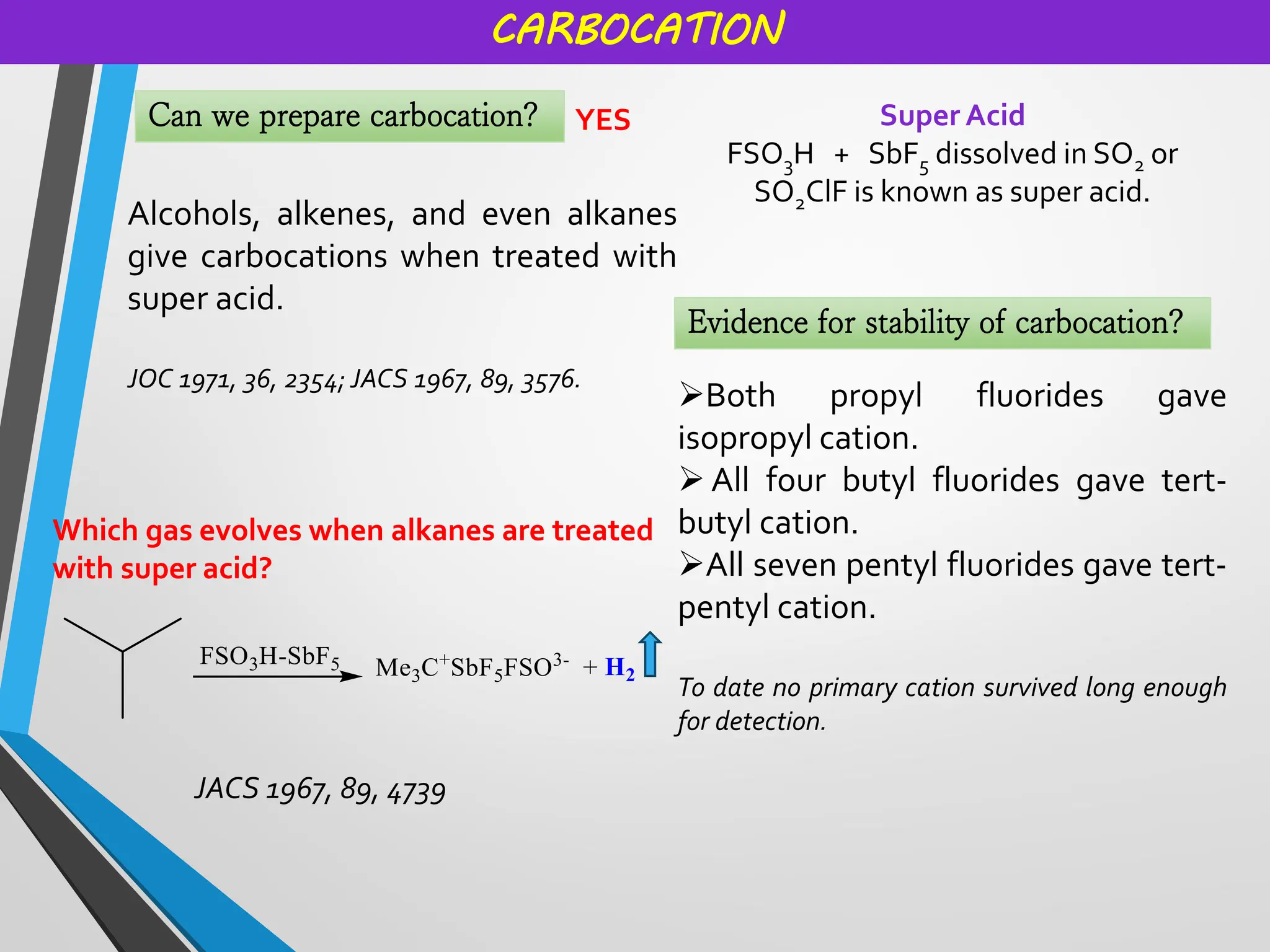
Acyl-cation
Acyl or acetyl cation is as stable as tert-butyl cation.
Q. Which of the following carbocations do not exist? Which one is more stable?
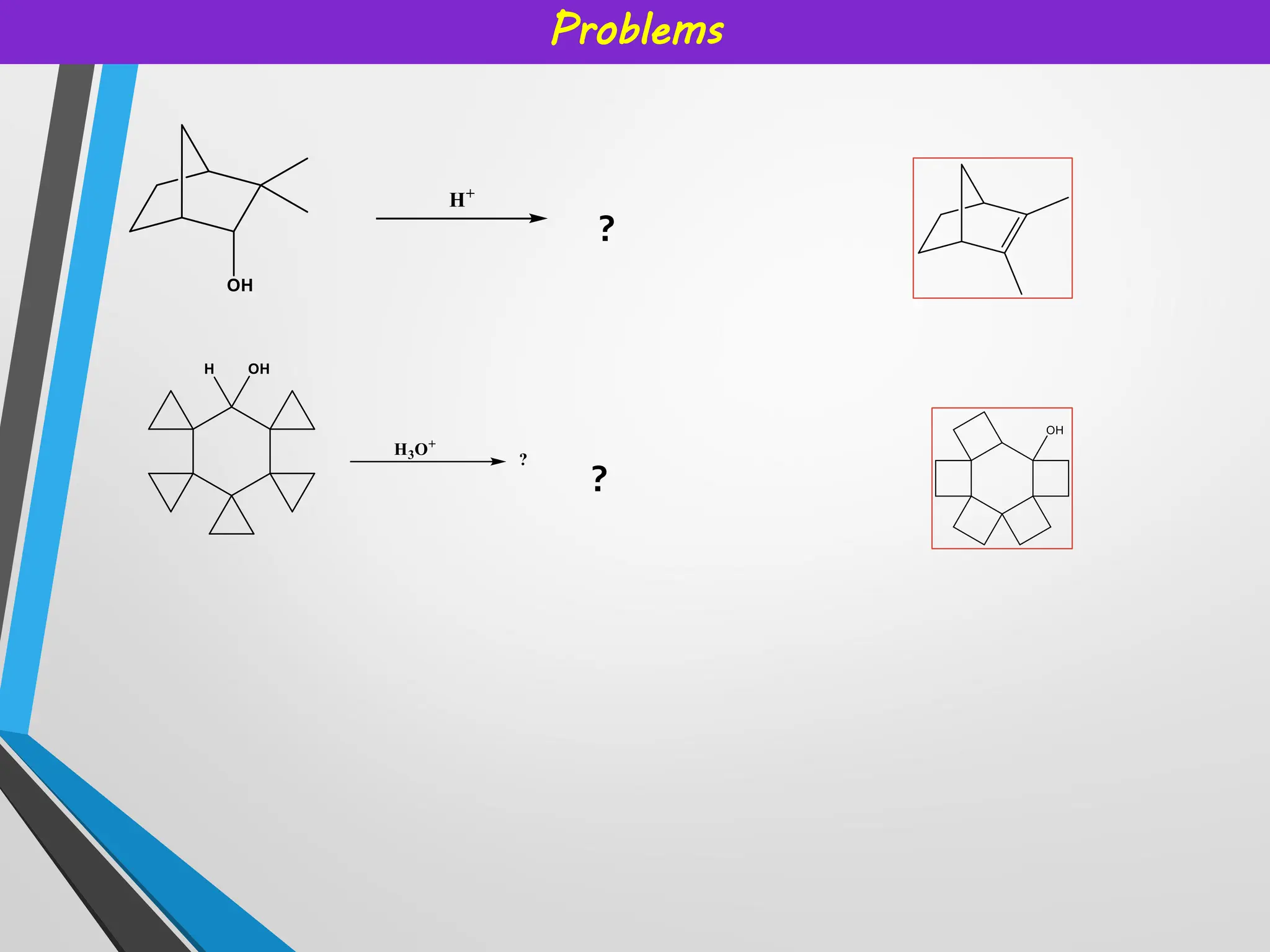
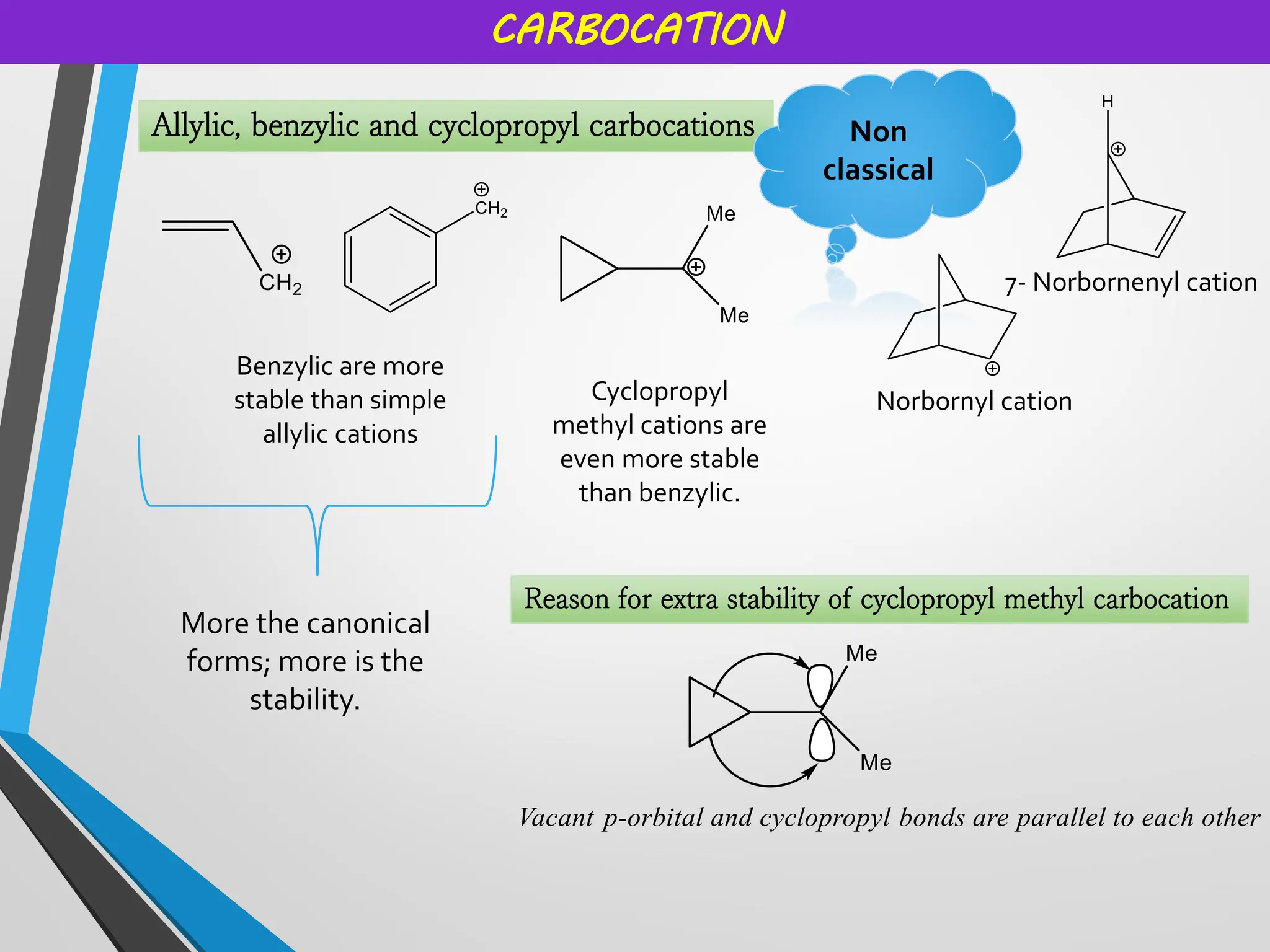
• It is impossible to form carbocation at bridgehead atoms in [2.2.1] systems
since they can not be planar.
• However, larger bridgehead carbocations can exist.
• Cyclopropyl group provides extra stability already discussed in previous
slide.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactiveintermediatesburange-251018110403-d4961c22/75/Reactive-intermediates-and-their-applications-6-2048.jpg)