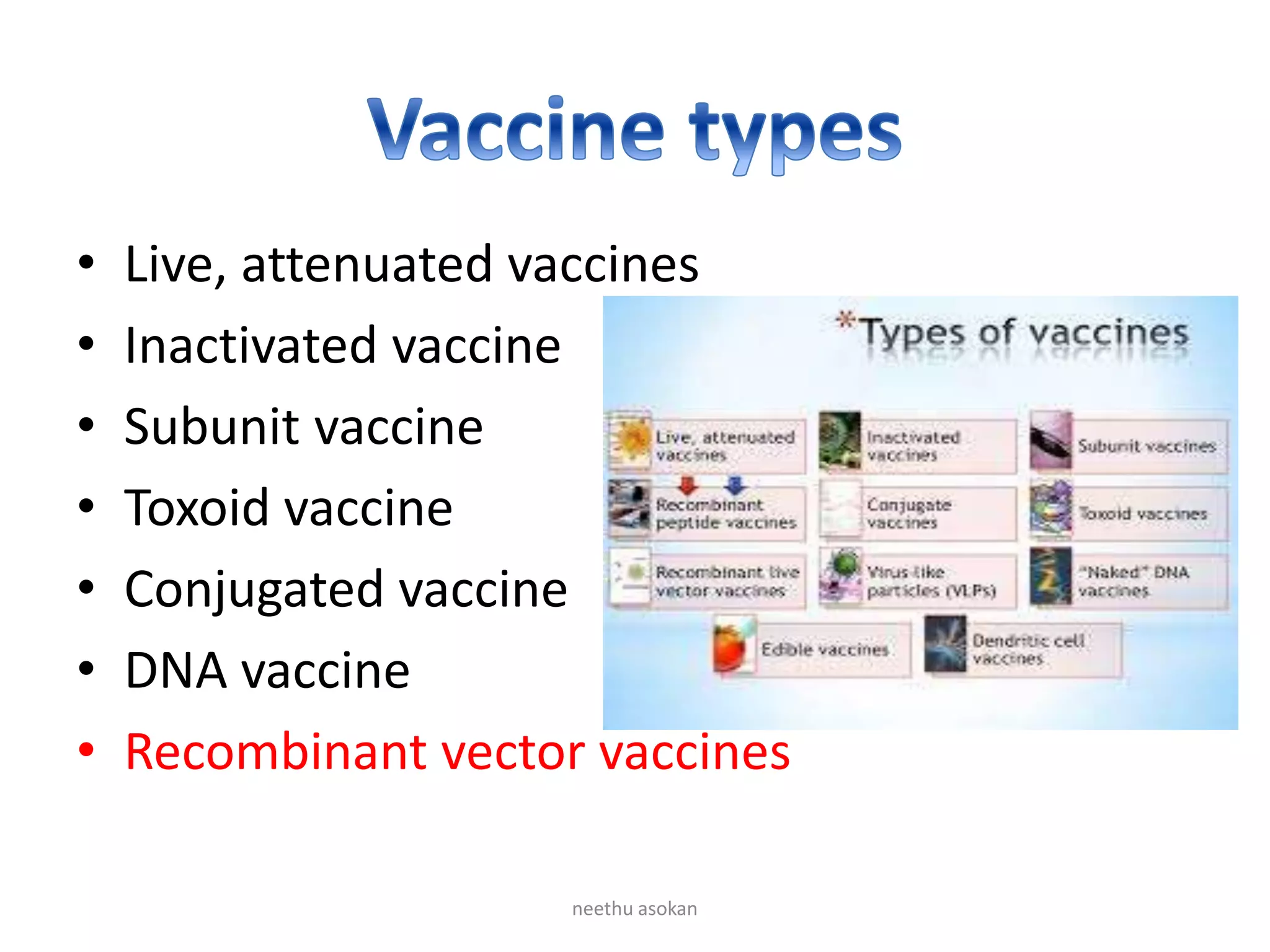
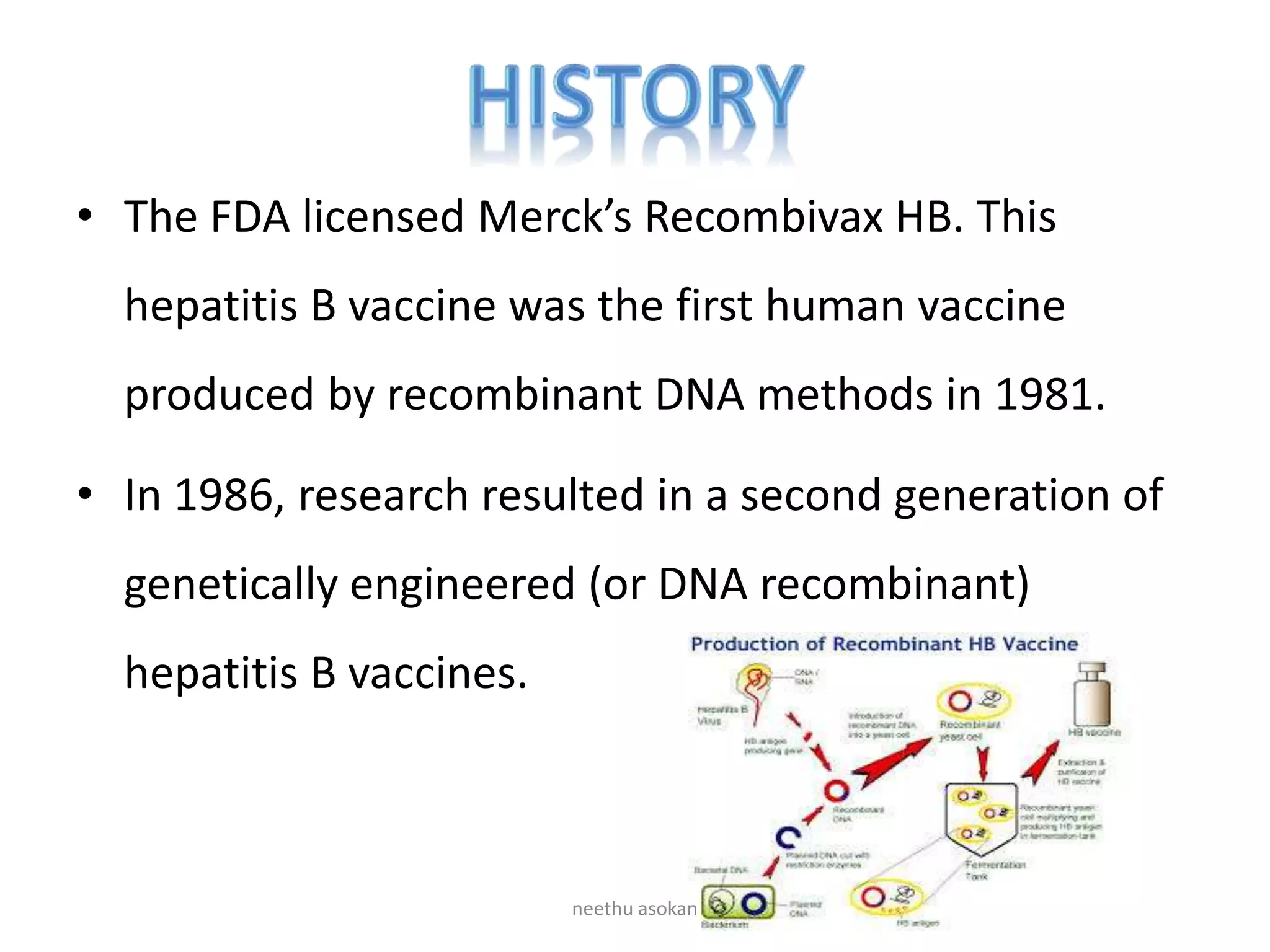
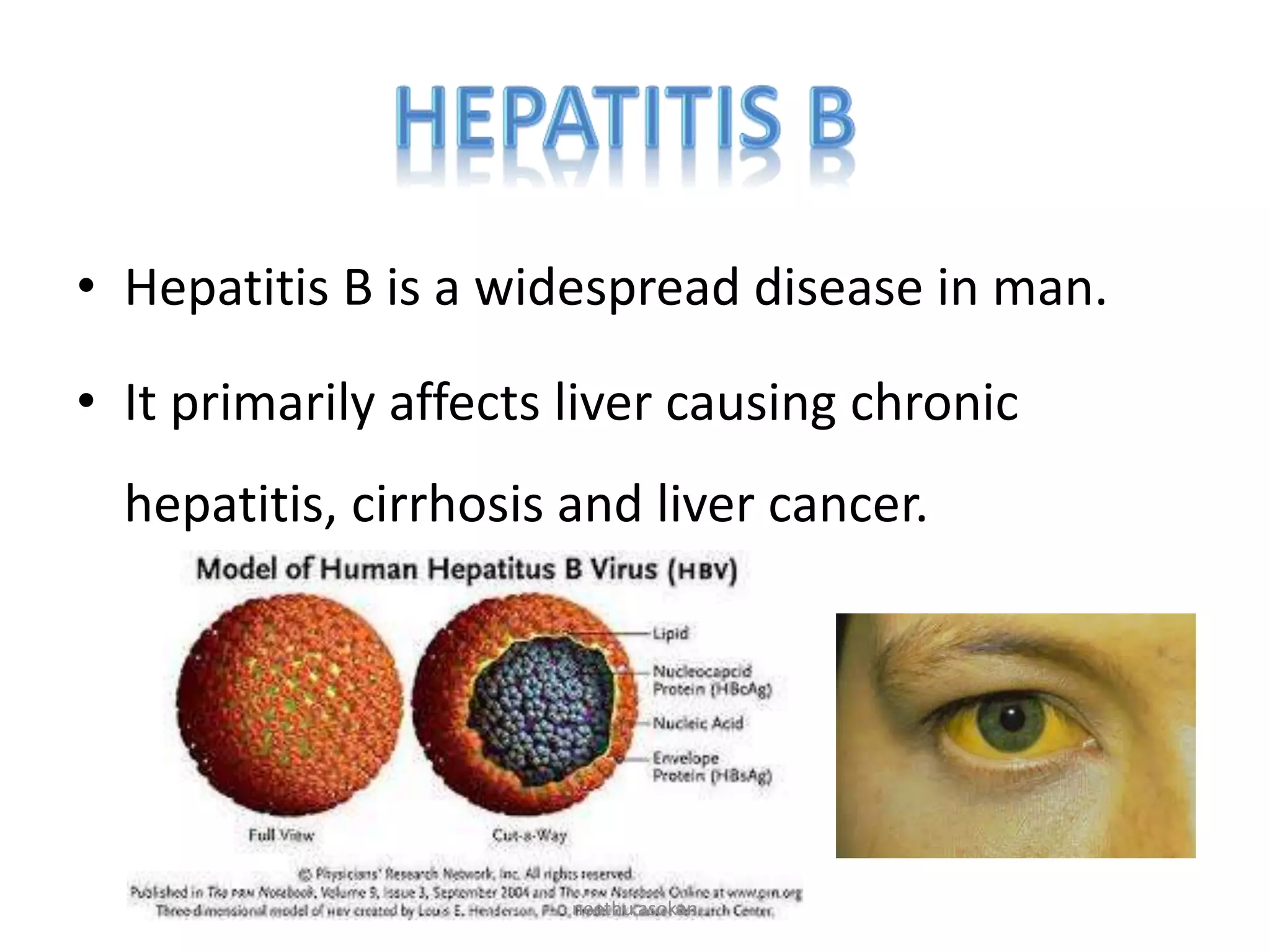
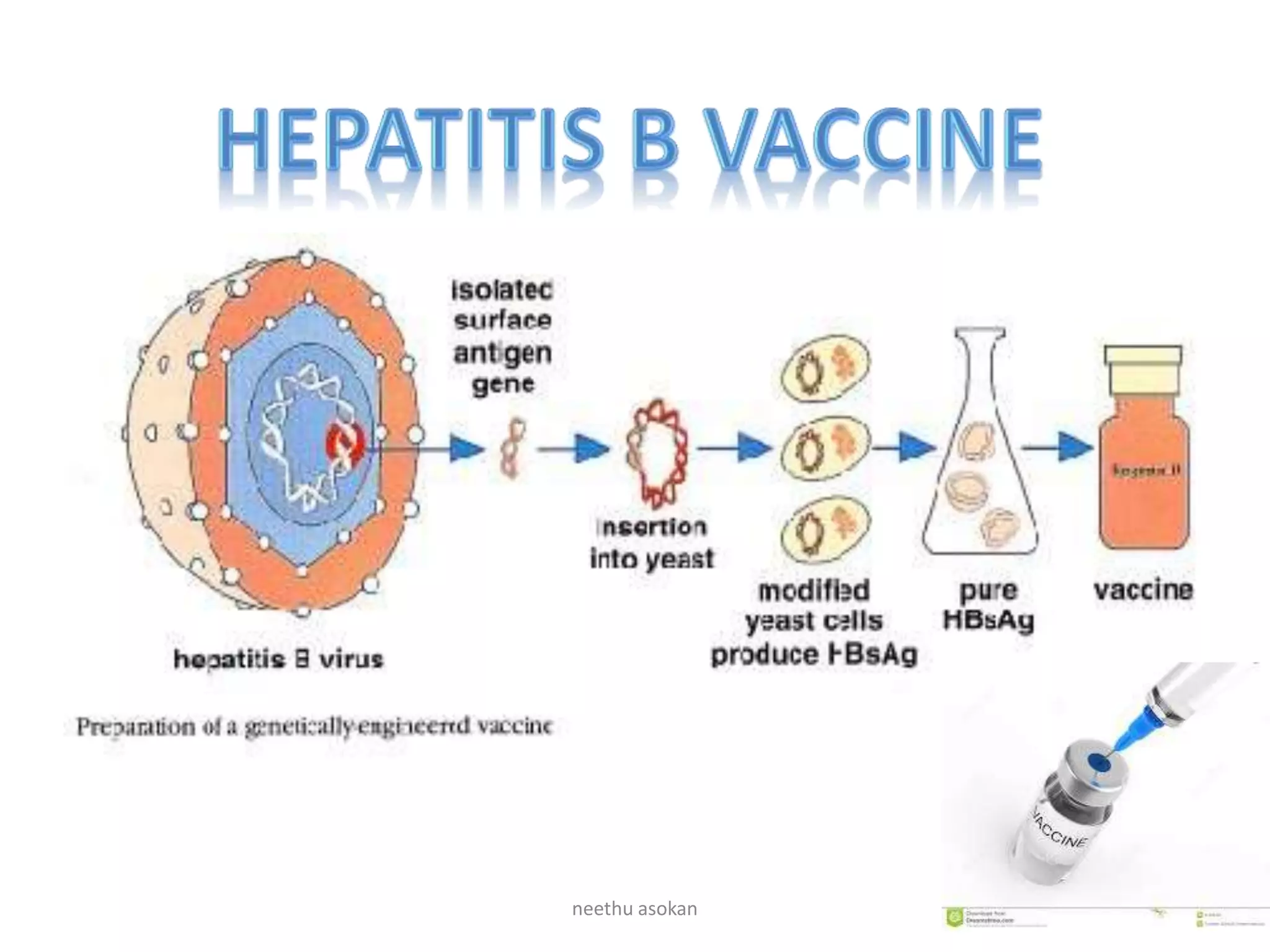
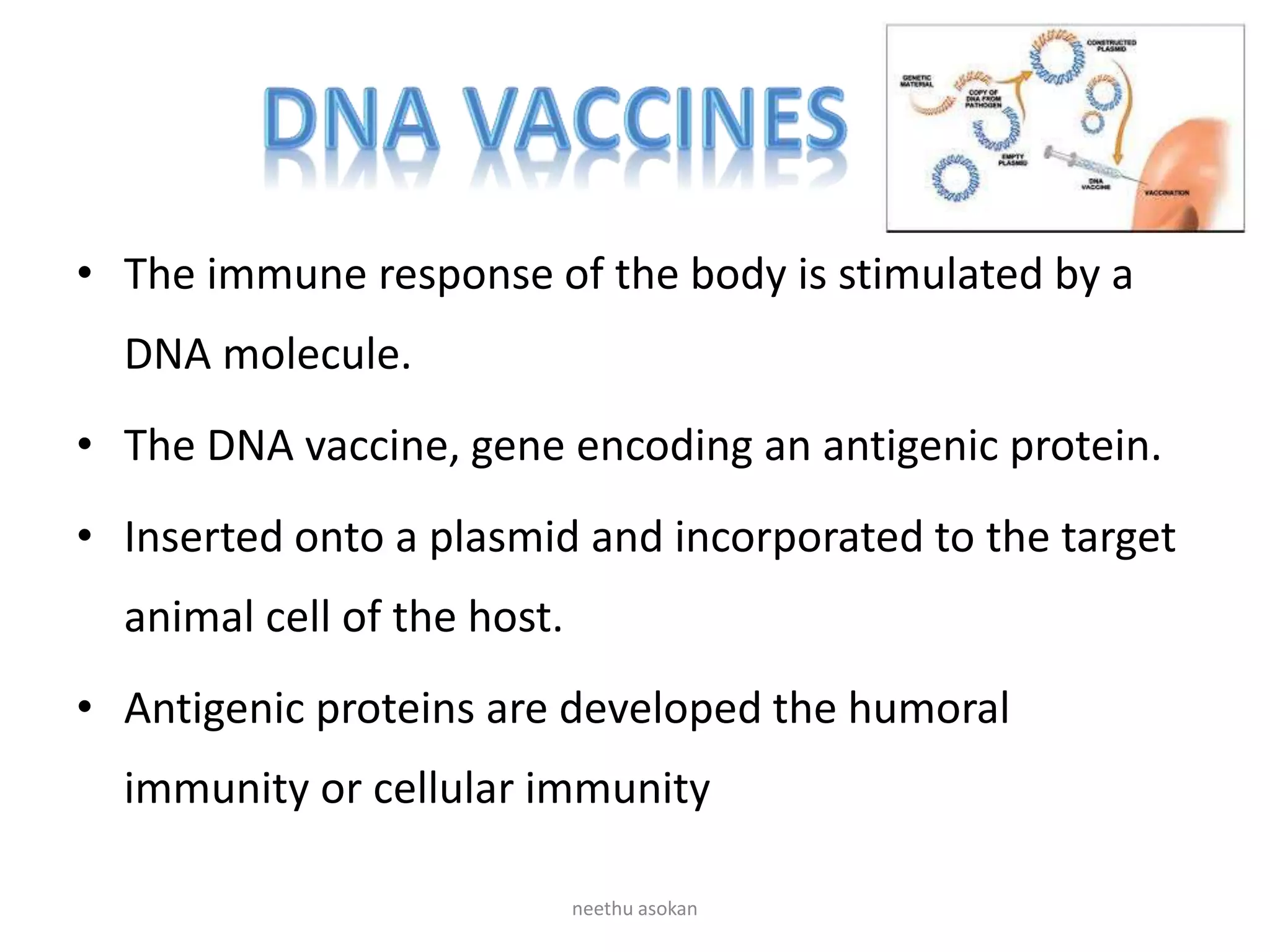
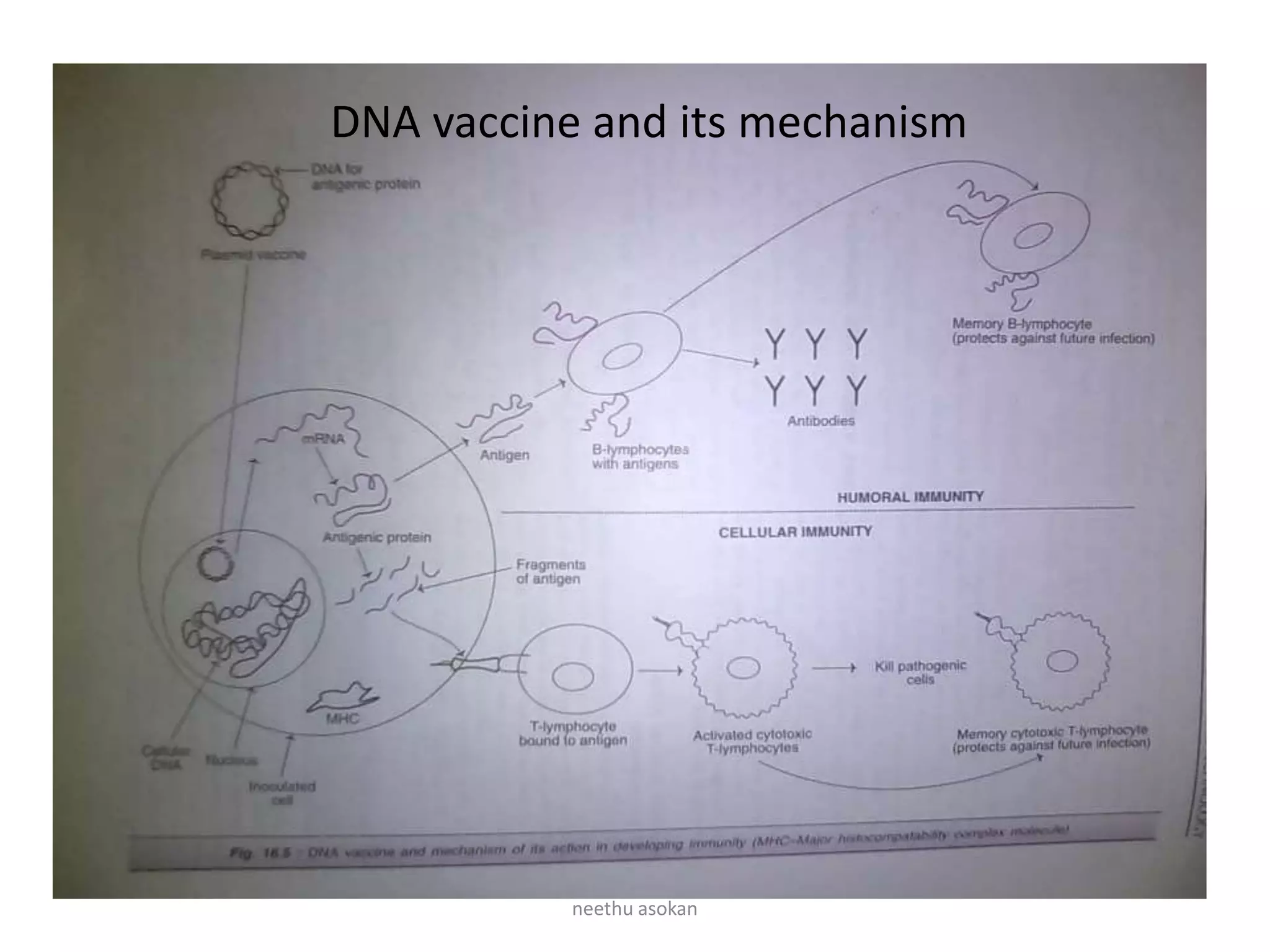
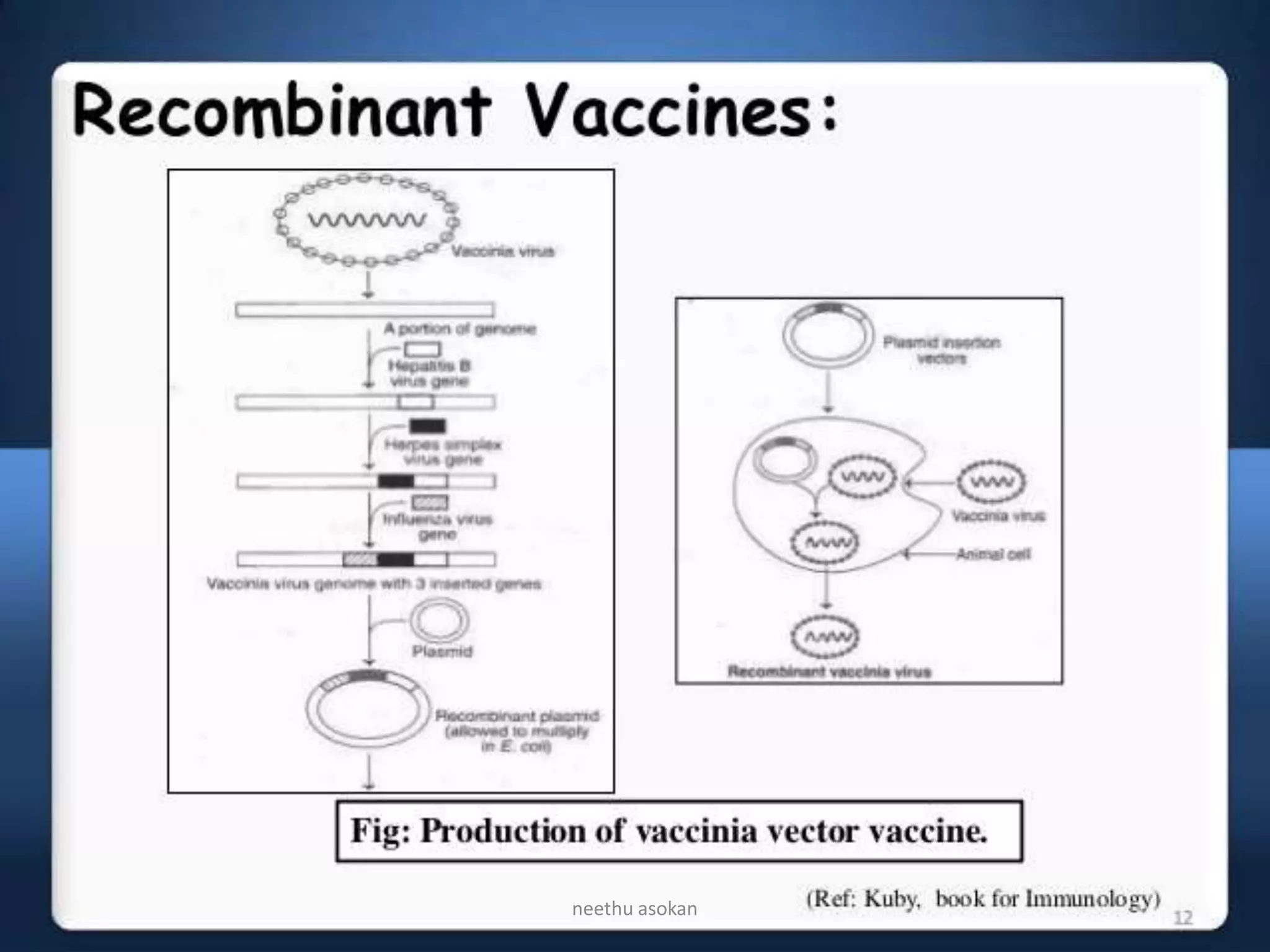
Recombinant vaccines are produced using genetic engineering techniques. The first licensed human recombinant vaccine was for hepatitis B in 1981. Recombinant vaccines include subunit vaccines containing pathogen proteins or peptides, attenuated recombinant vaccines using genetically modified non-pathogenic organisms, and vector recombinant vaccines utilizing viral vectors carrying foreign antigen genes. Recombinant vaccines offer advantages like purity, stability and safety compared to traditional vaccines.