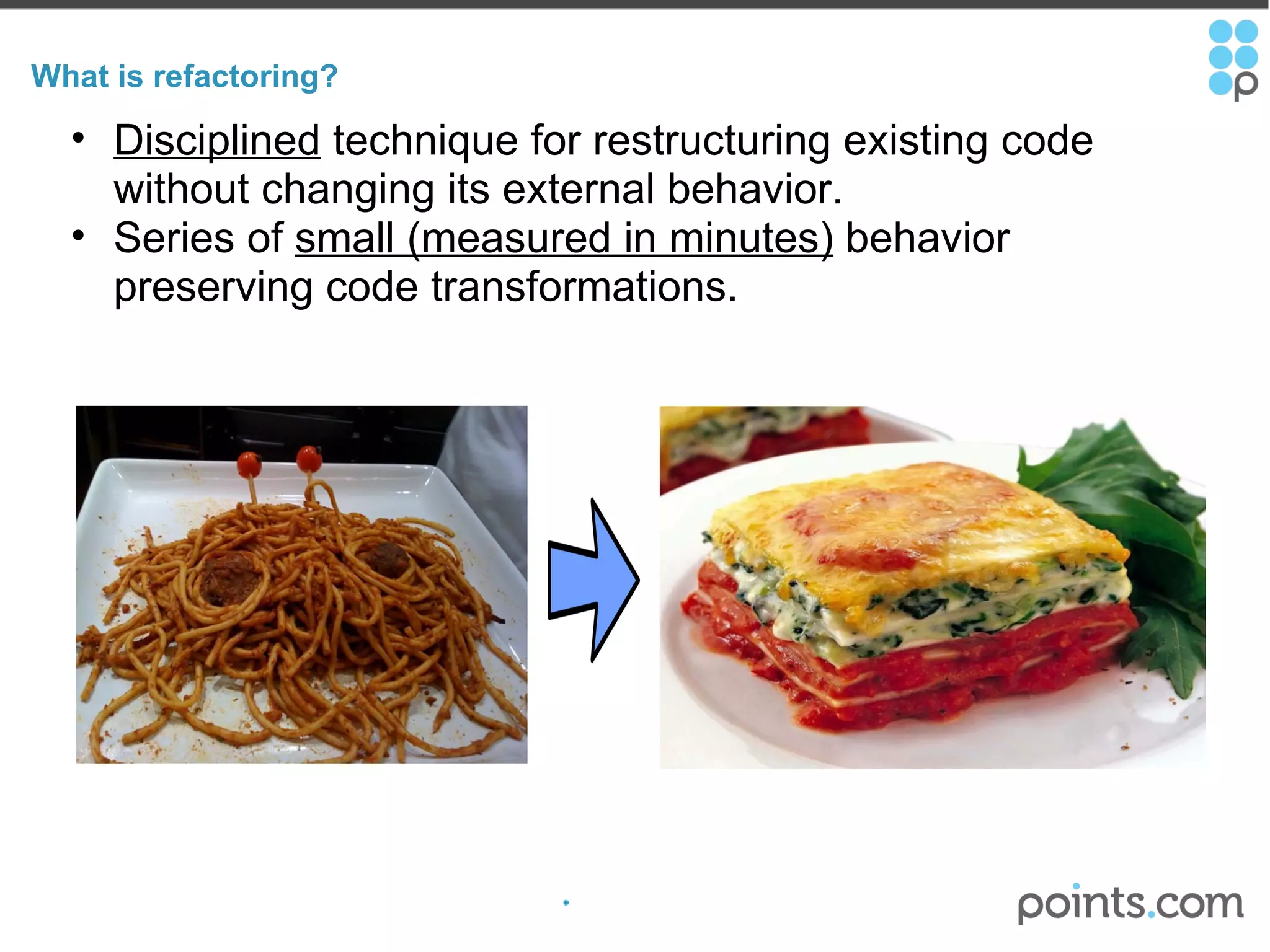
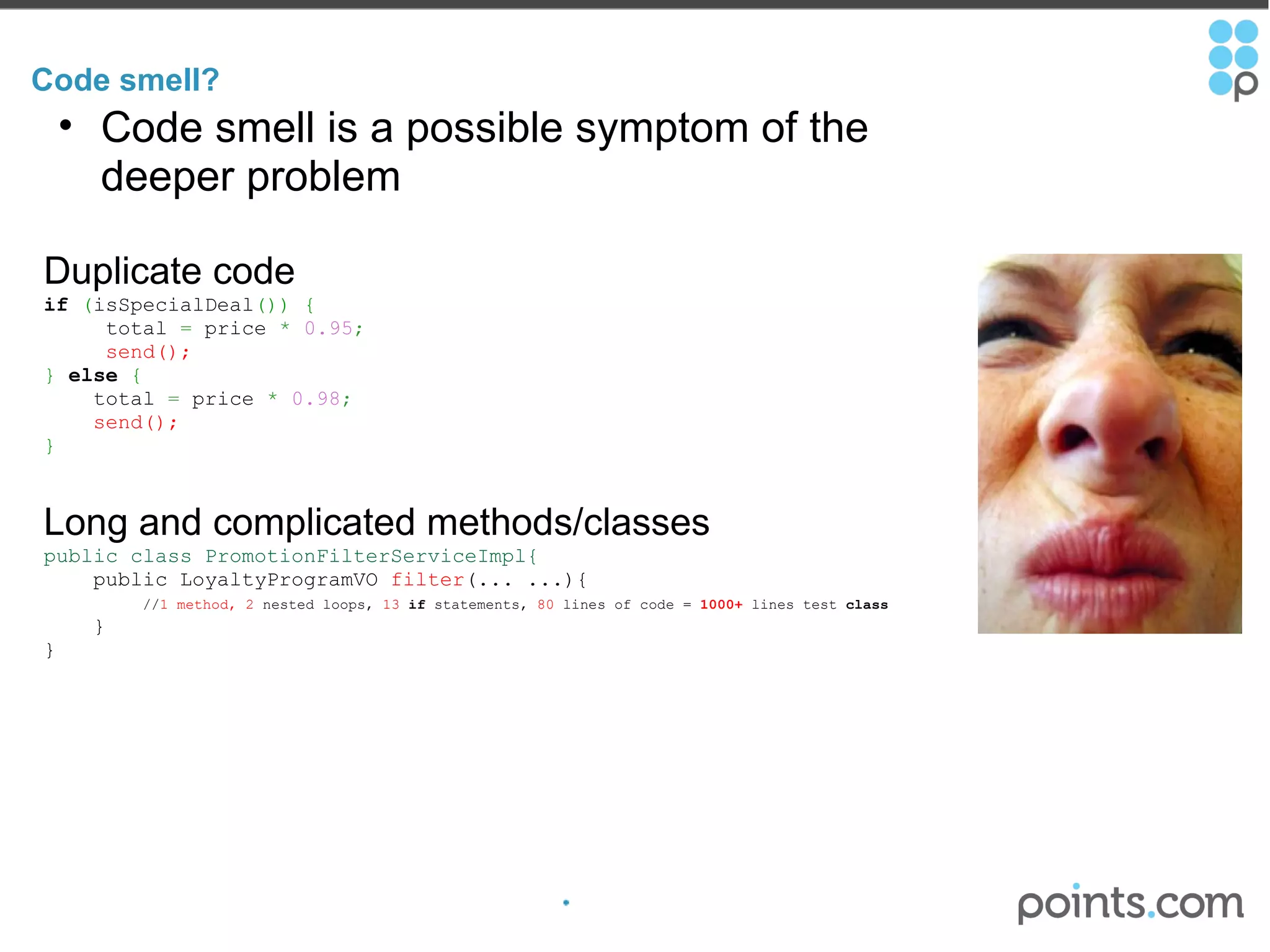
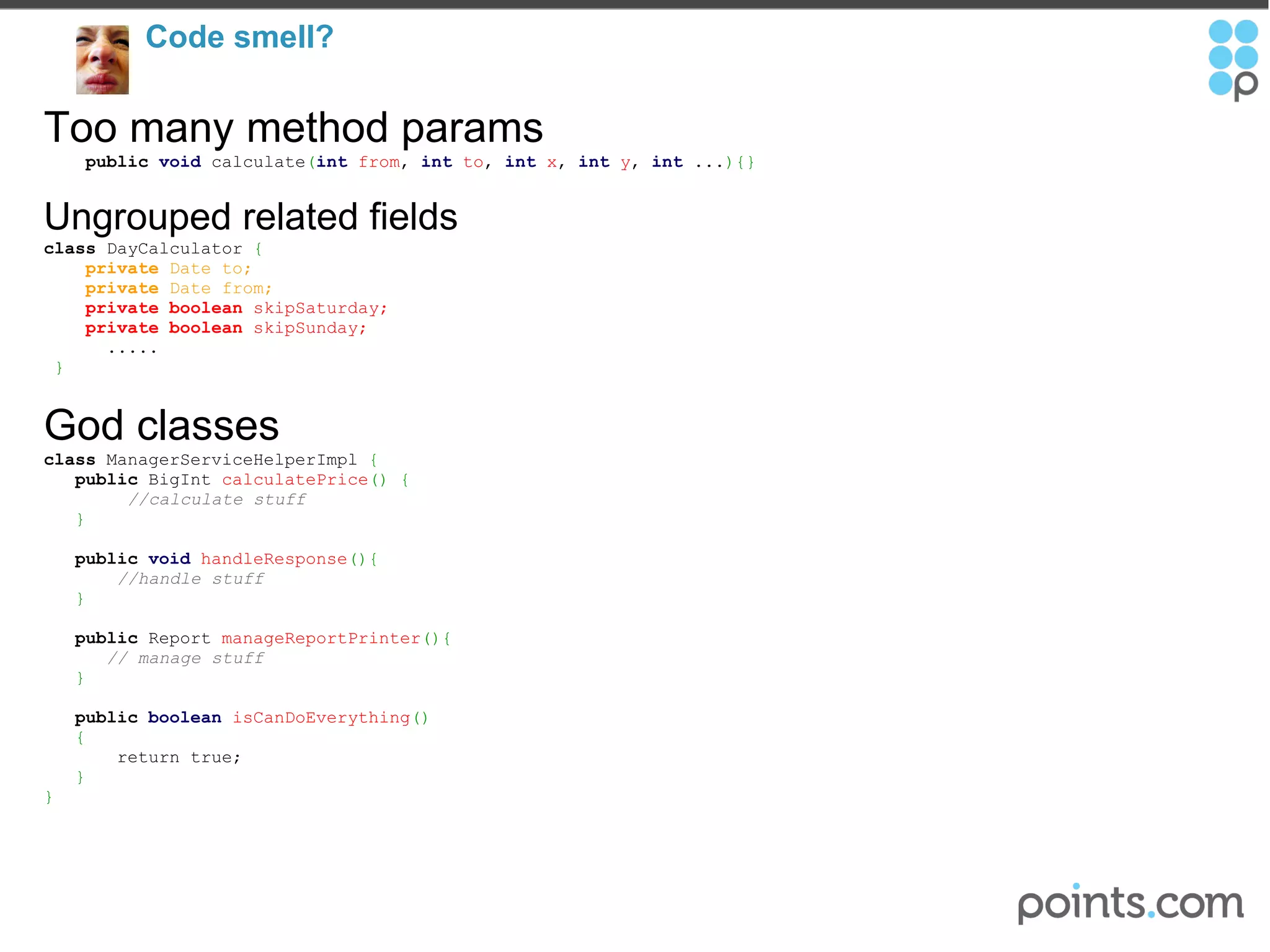
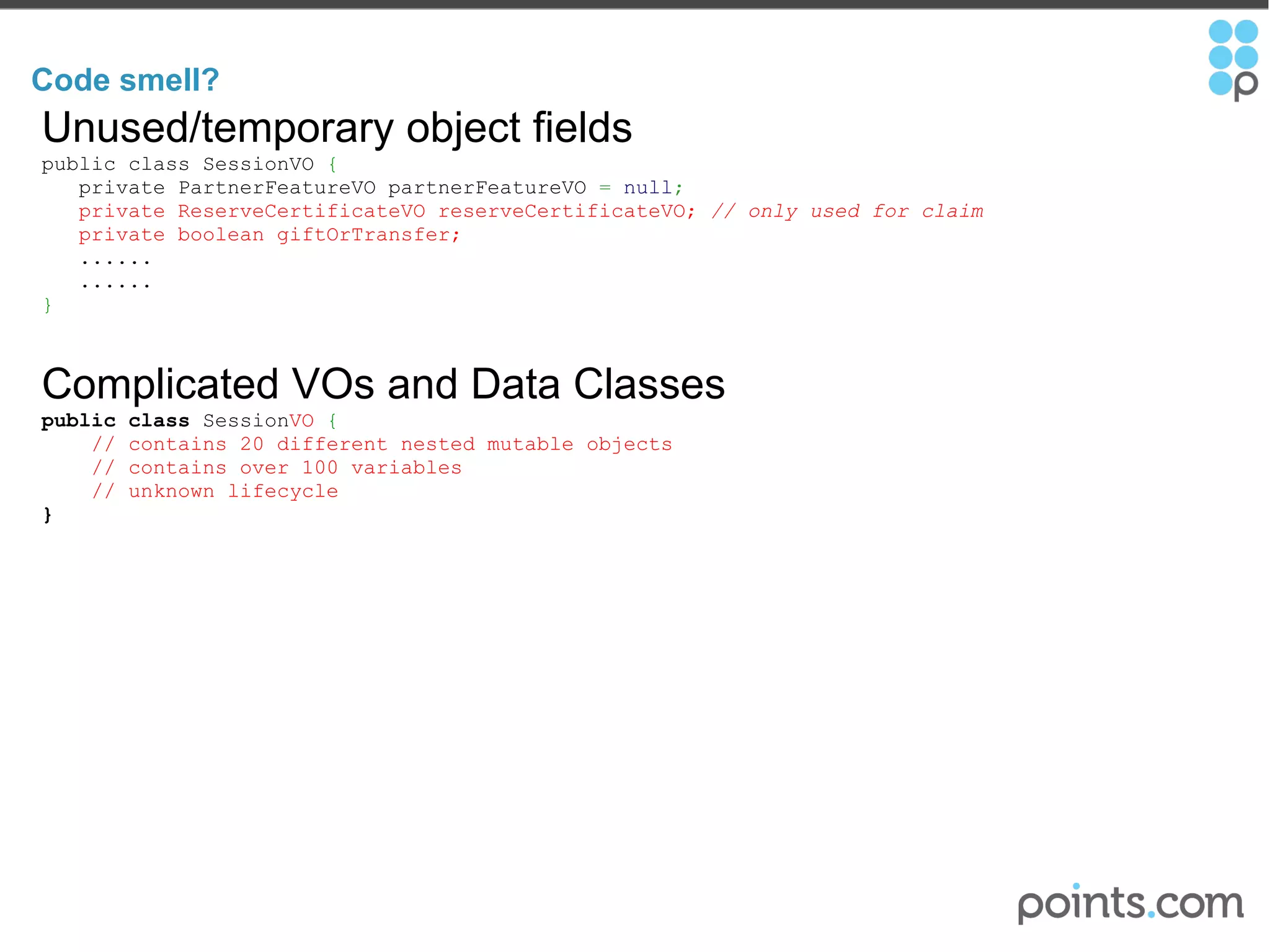
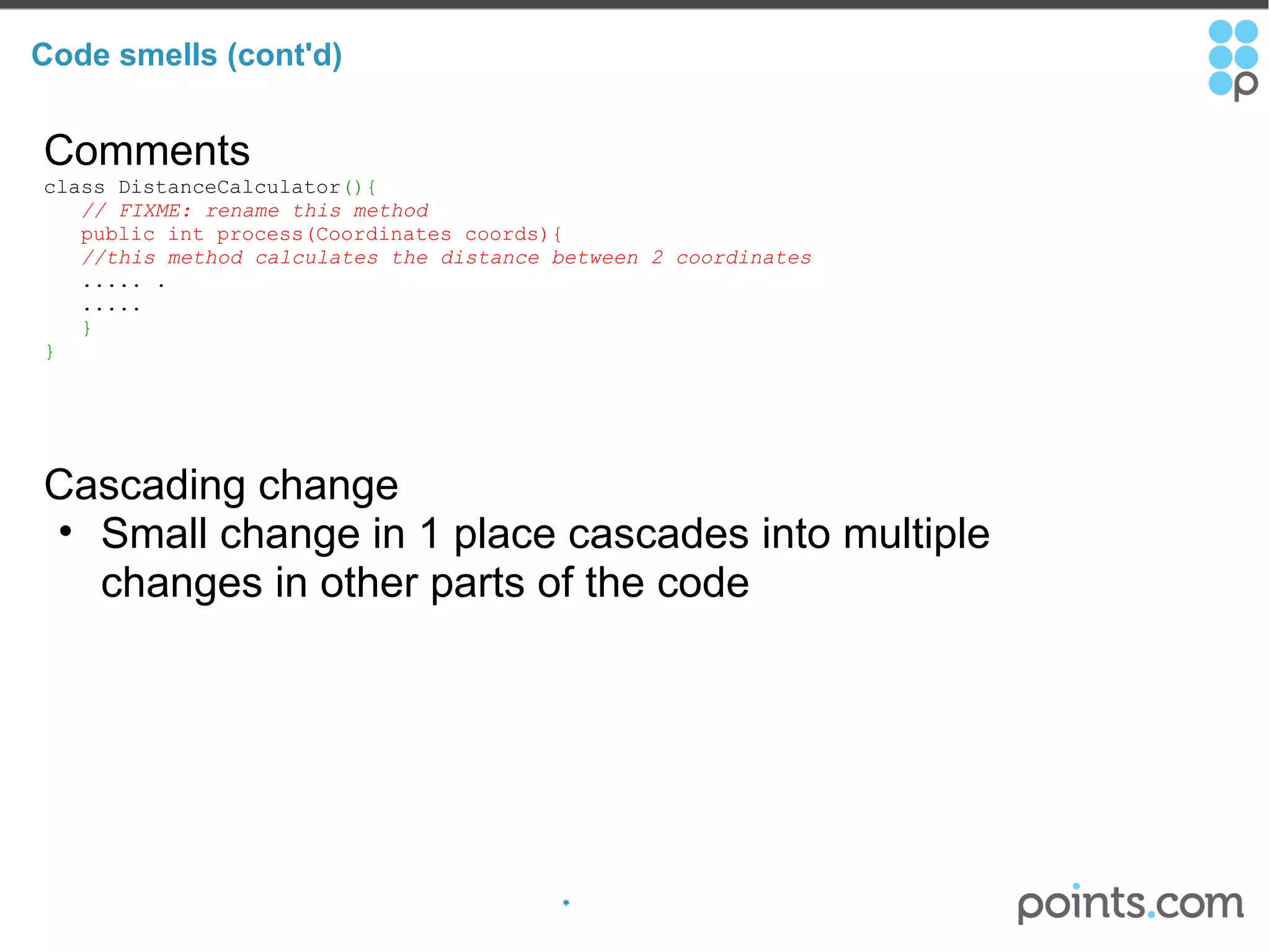
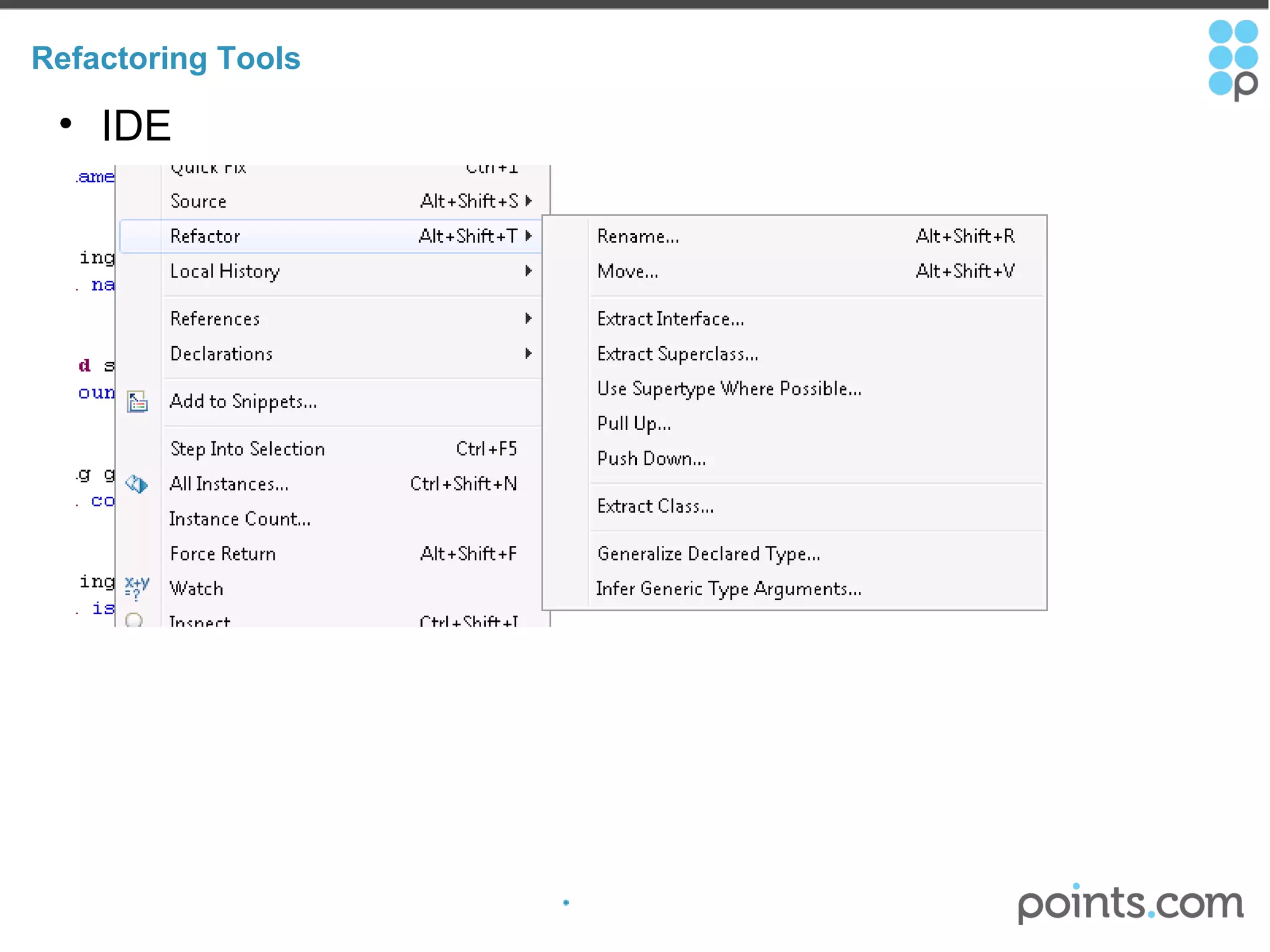
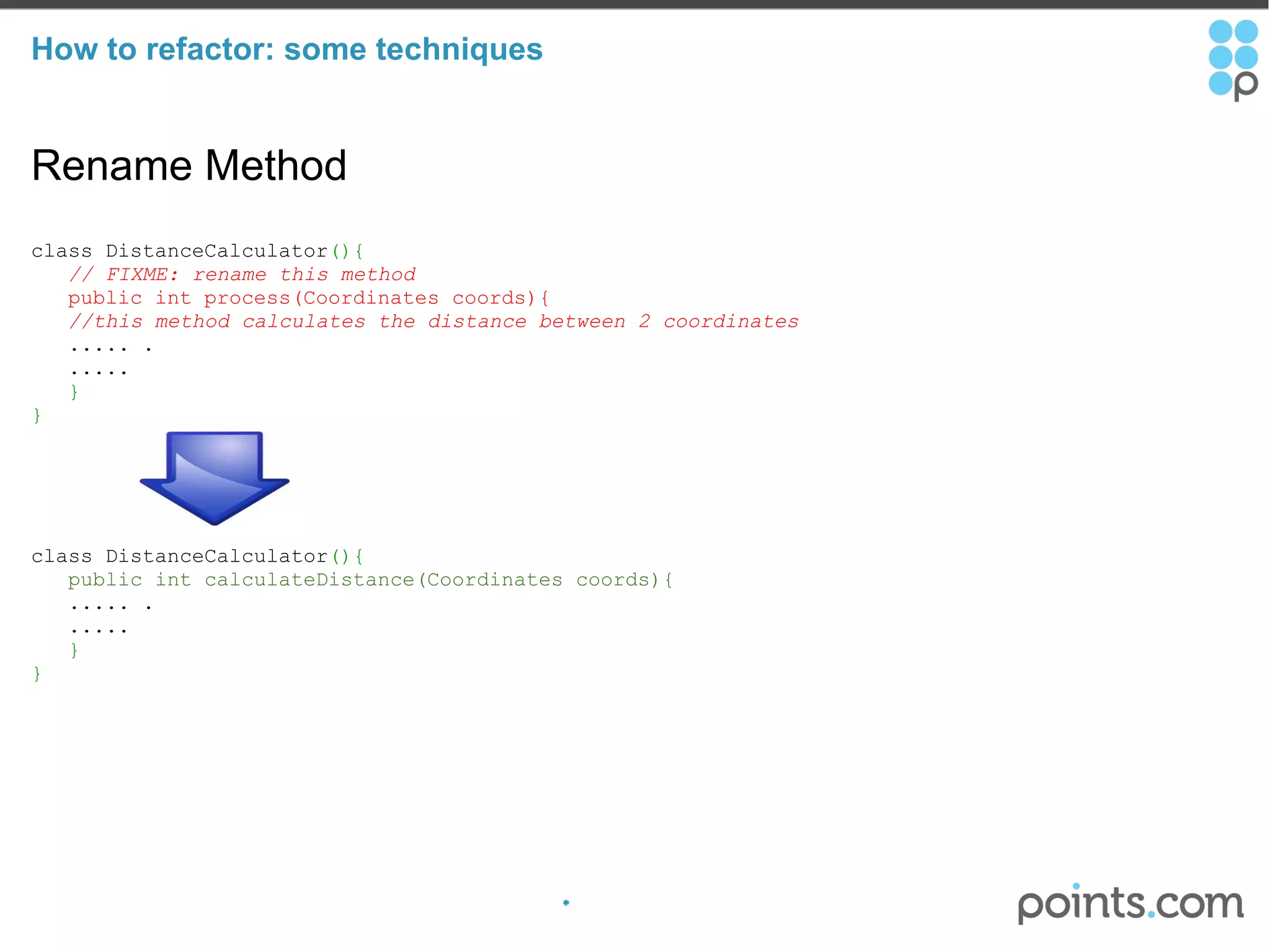
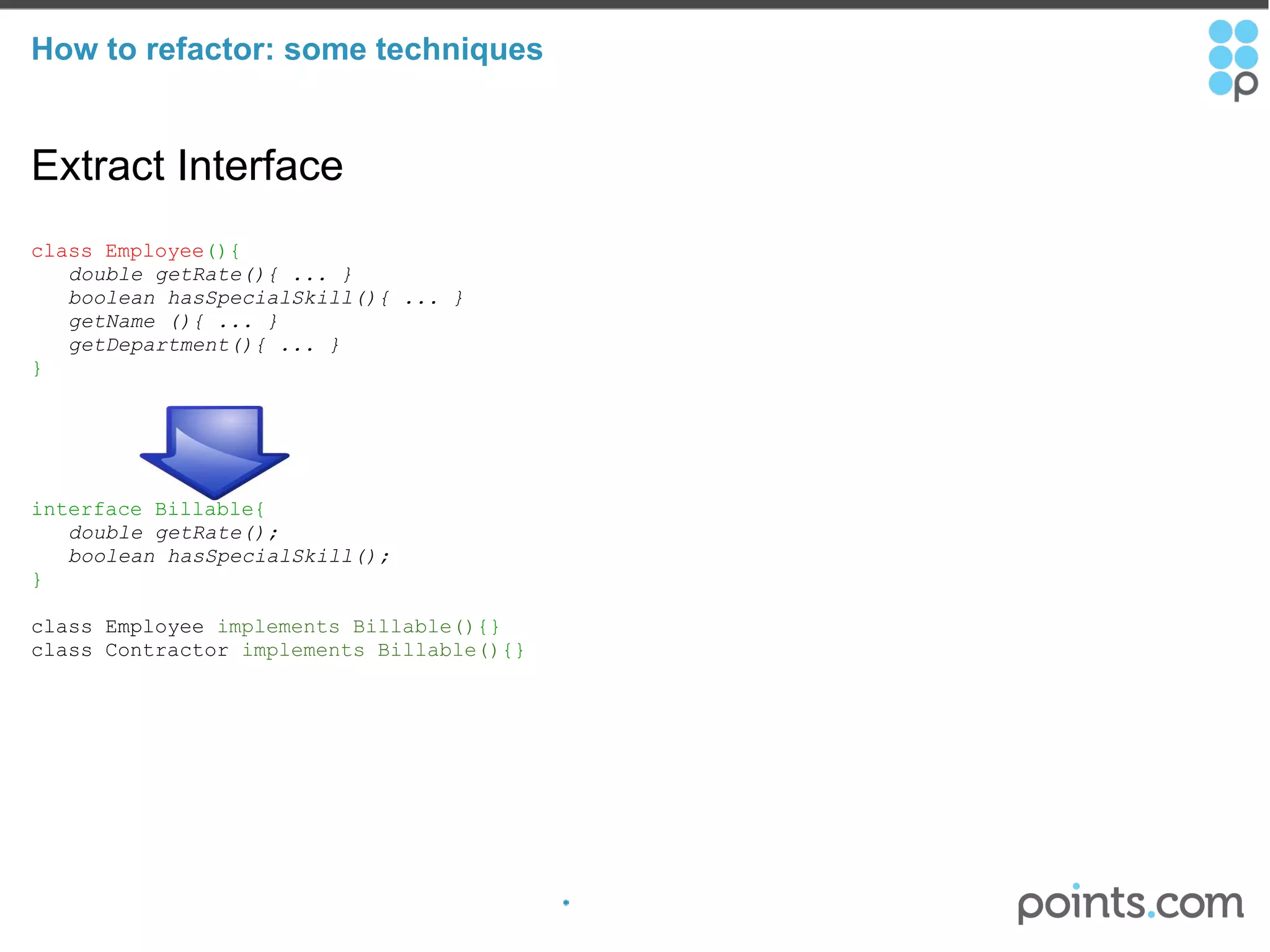
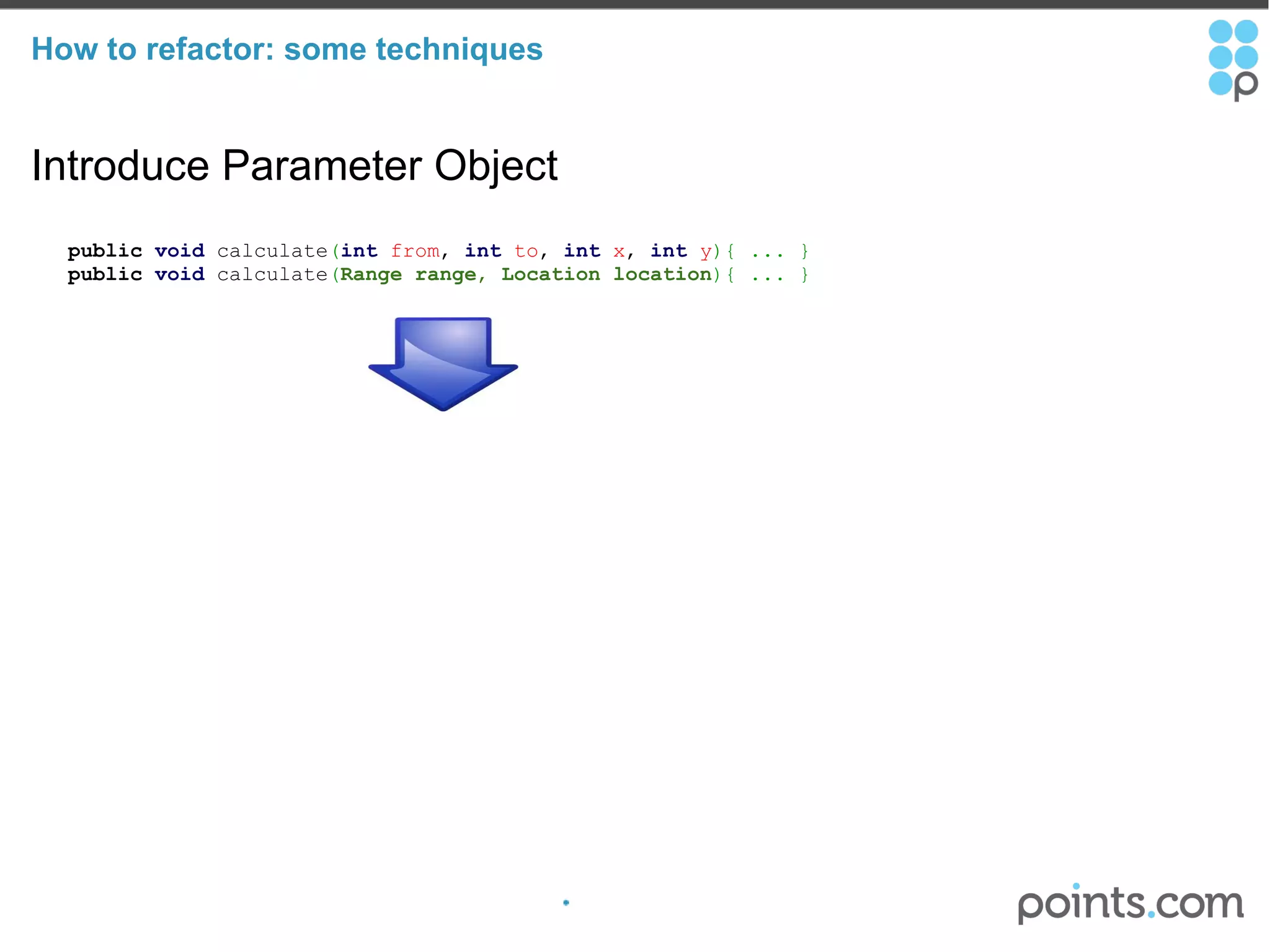
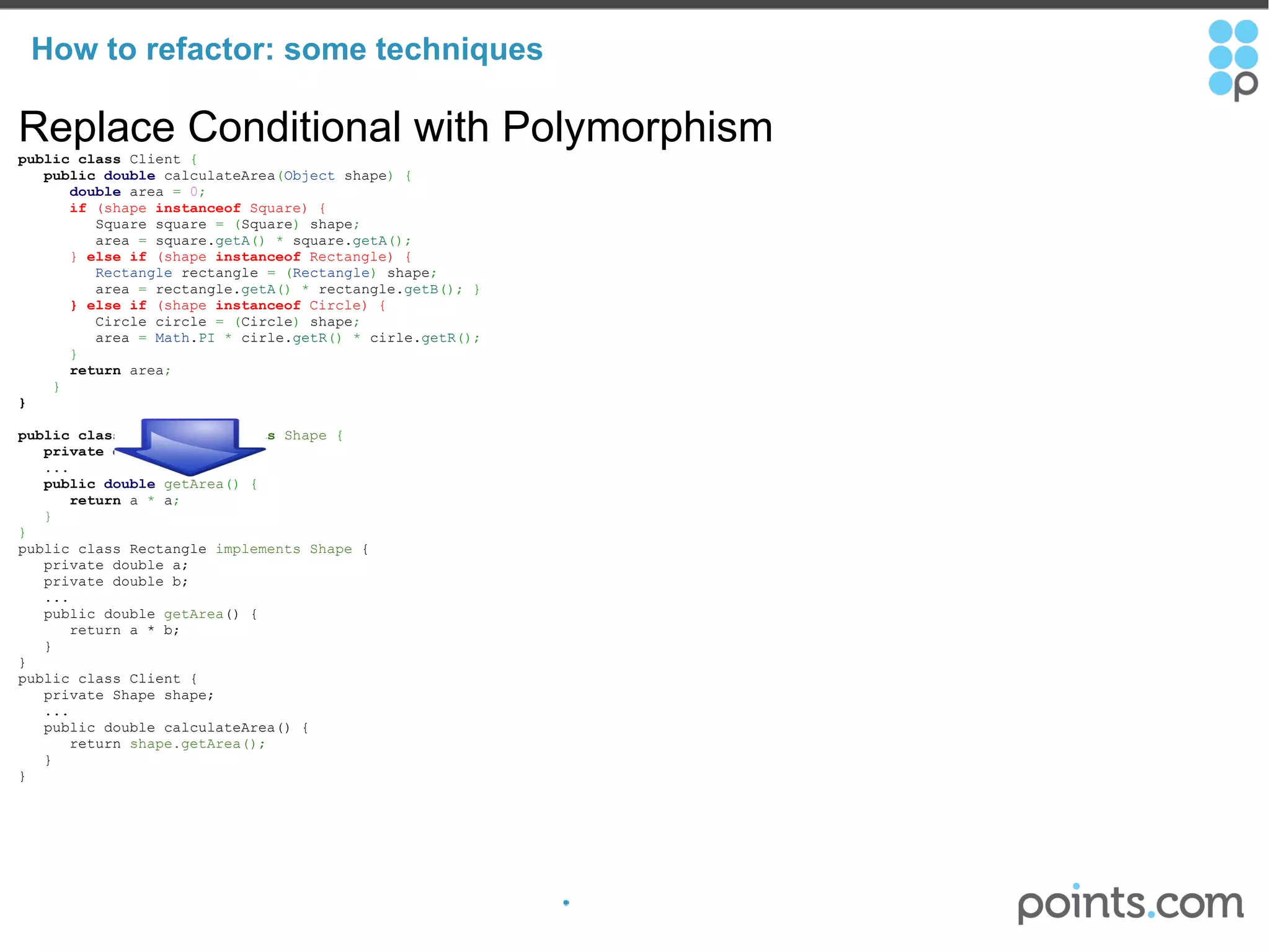
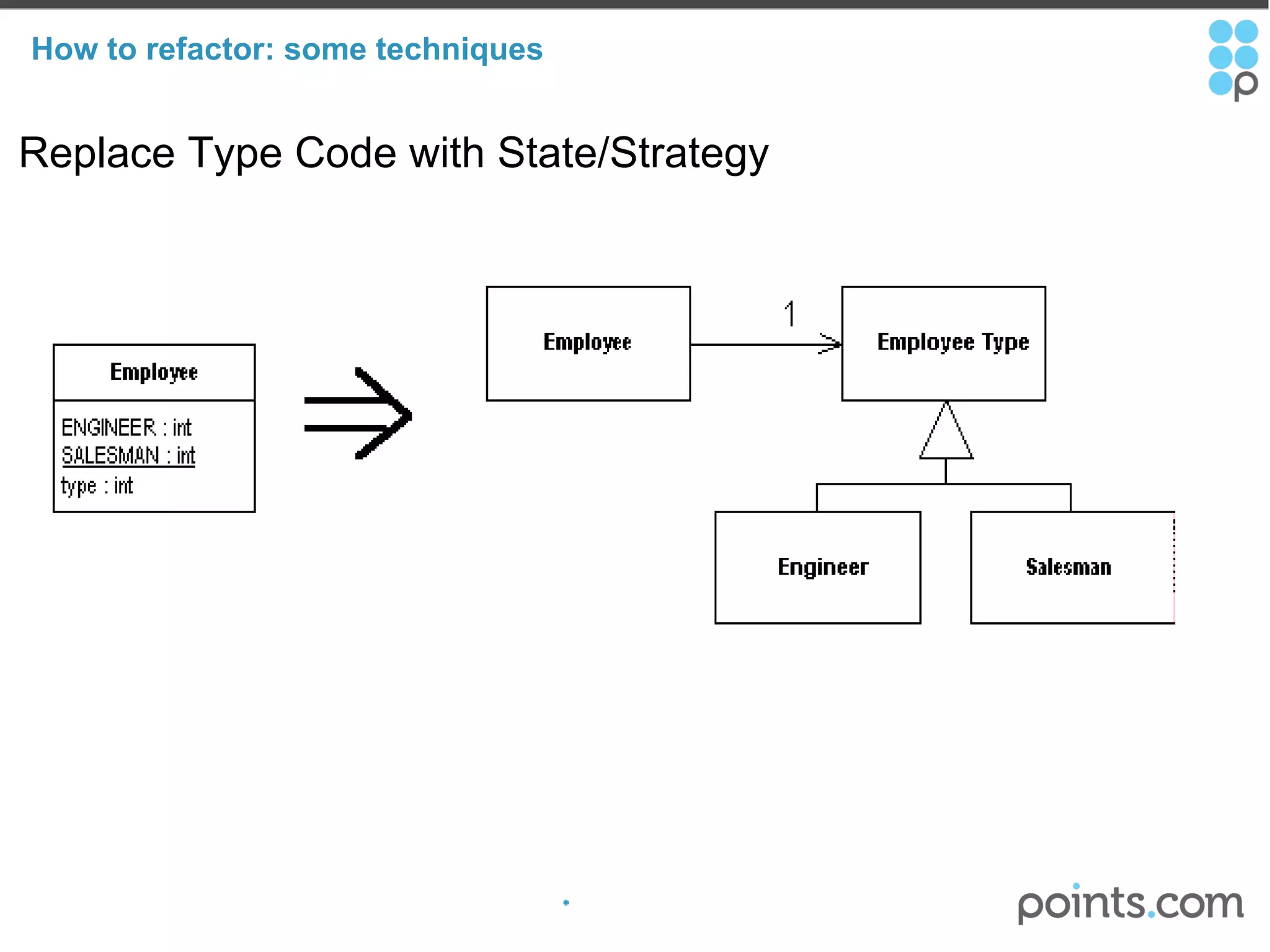
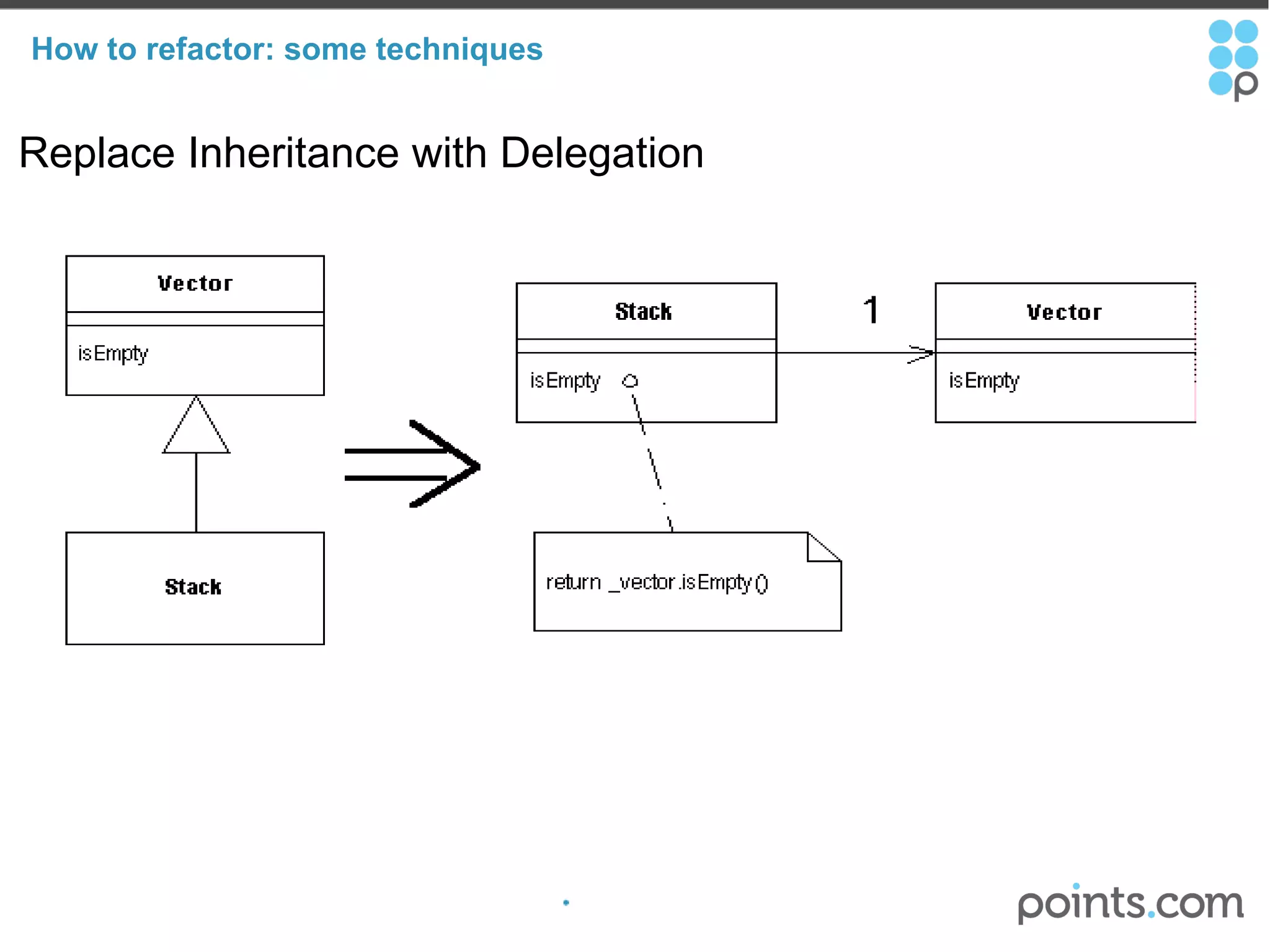
The document discusses refactoring code to improve its quality without changing its external behavior. It defines refactoring and explains why it is important to make code easier to understand and maintain over time. It provides examples of "code smells" that indicate needs for refactoring and discusses techniques for refactoring code, such as renaming methods, extracting interfaces, replacing conditionals with polymorphism, and using tools to help with the process.