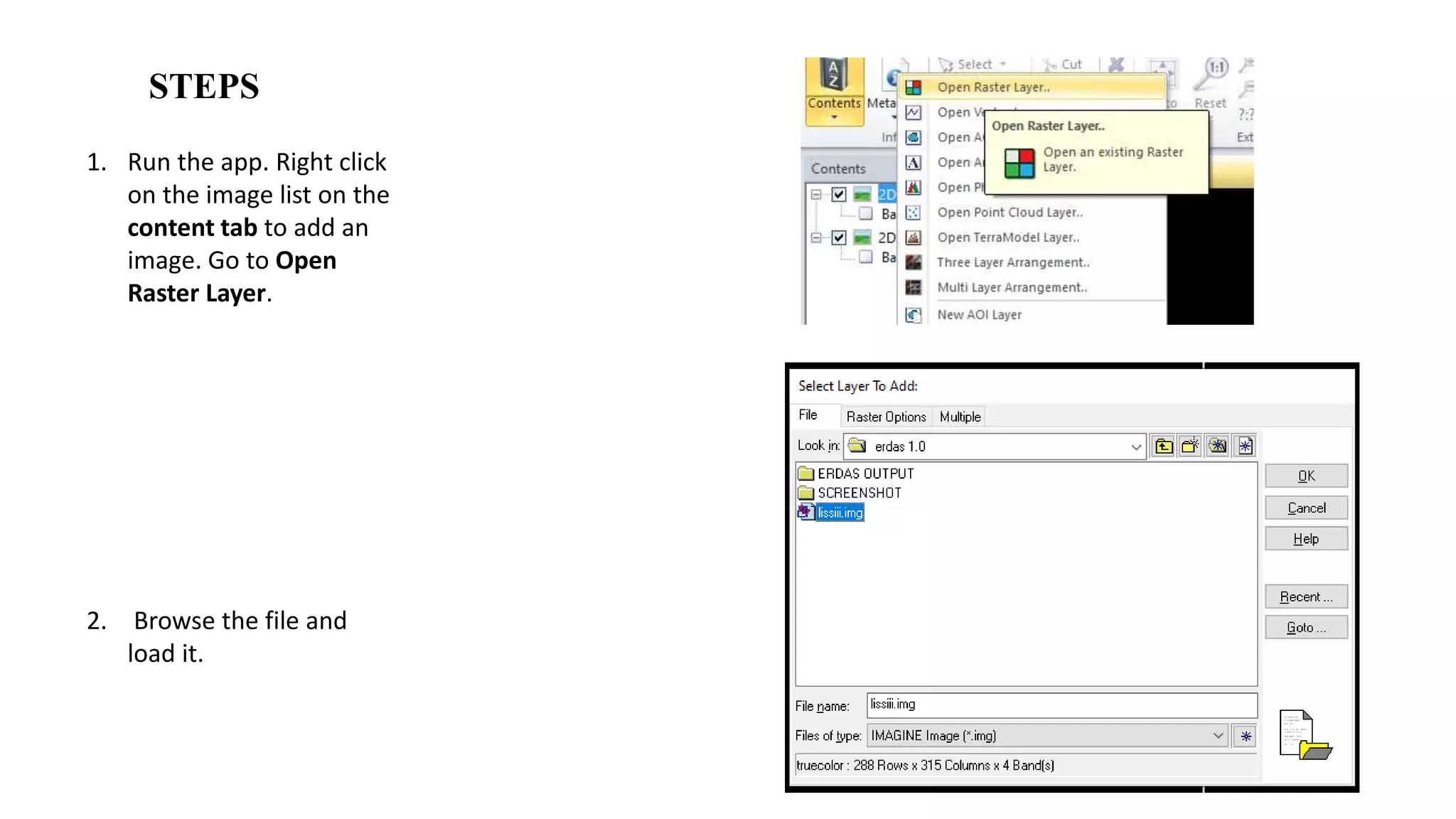
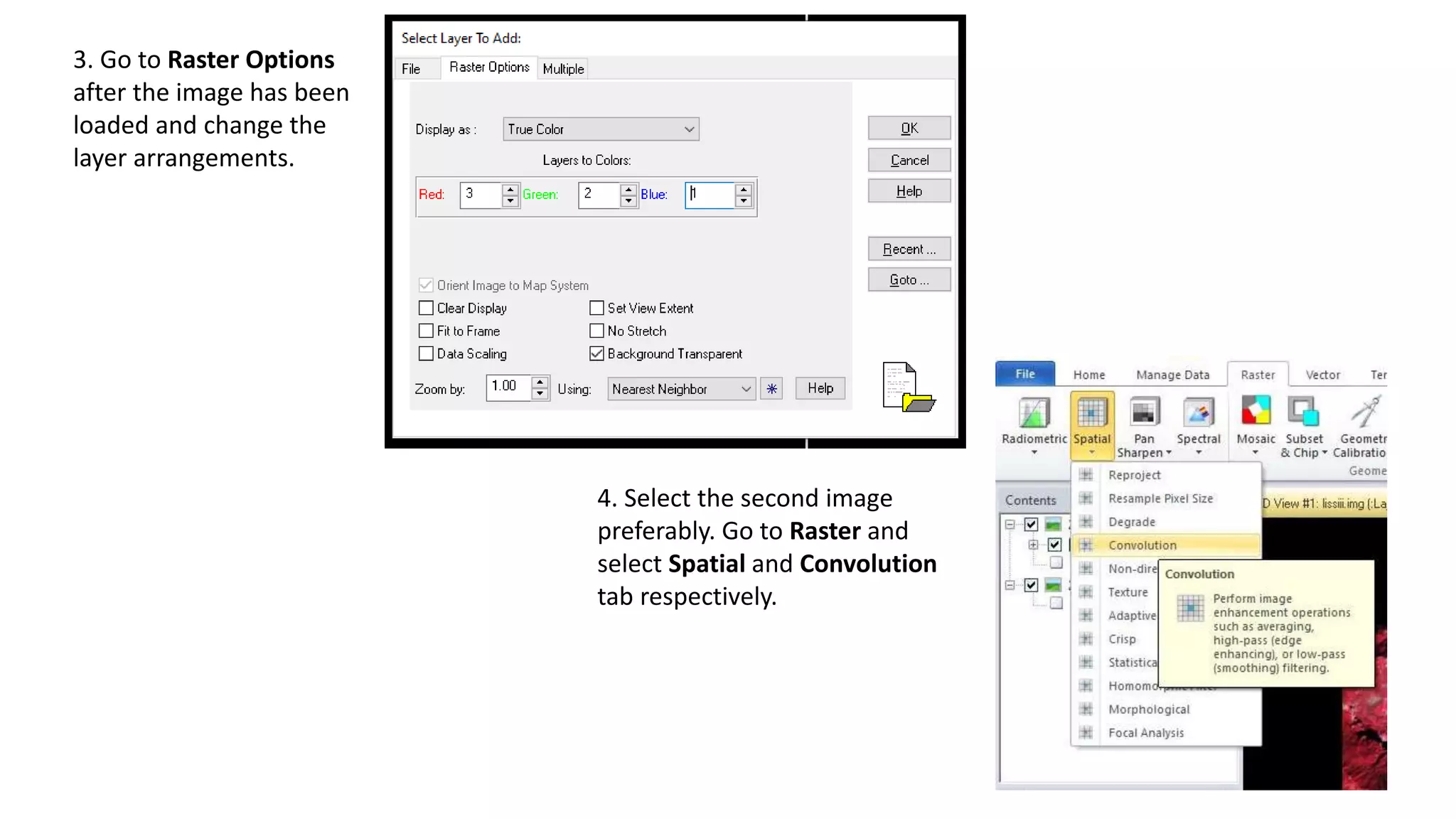
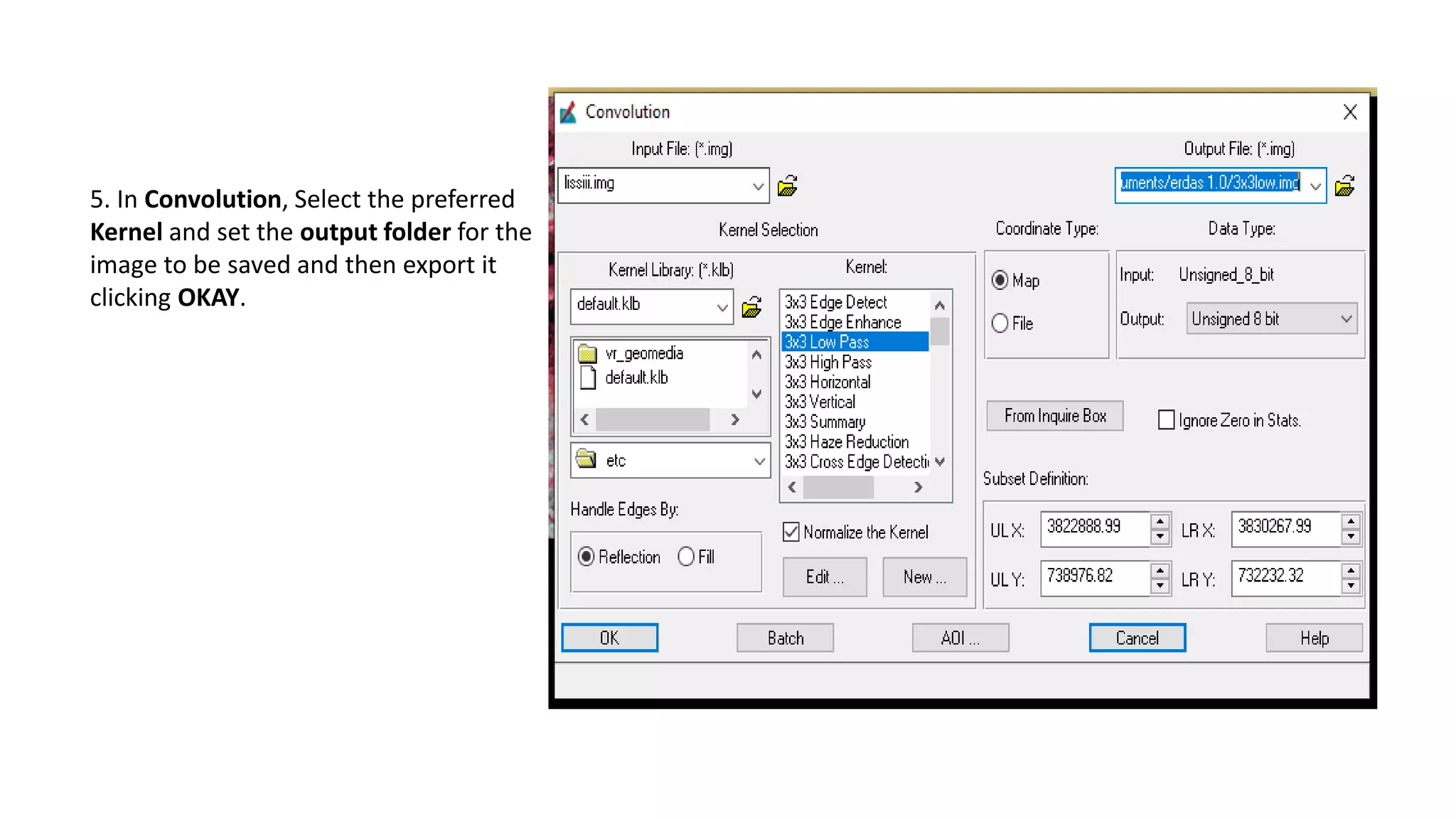
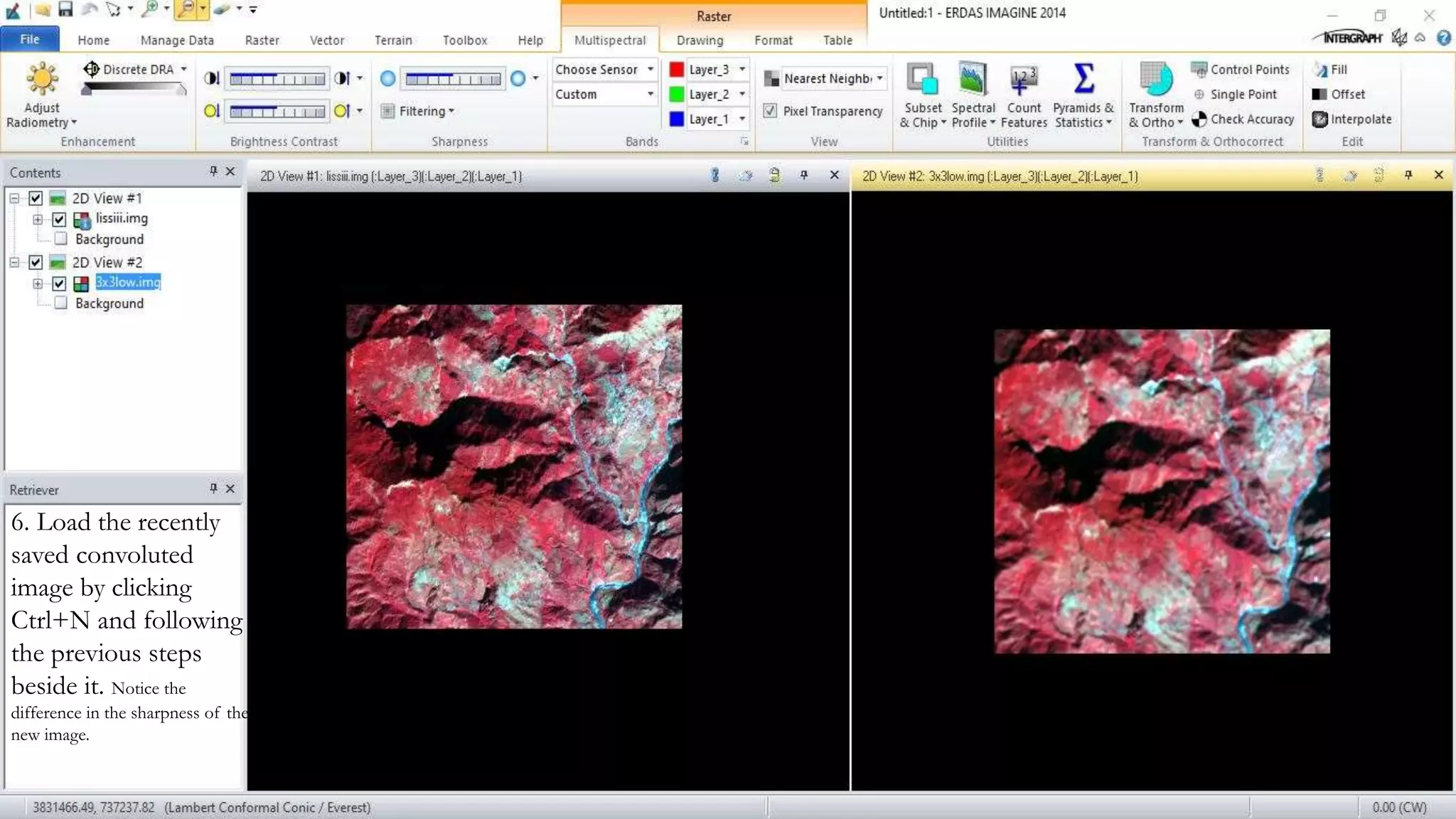
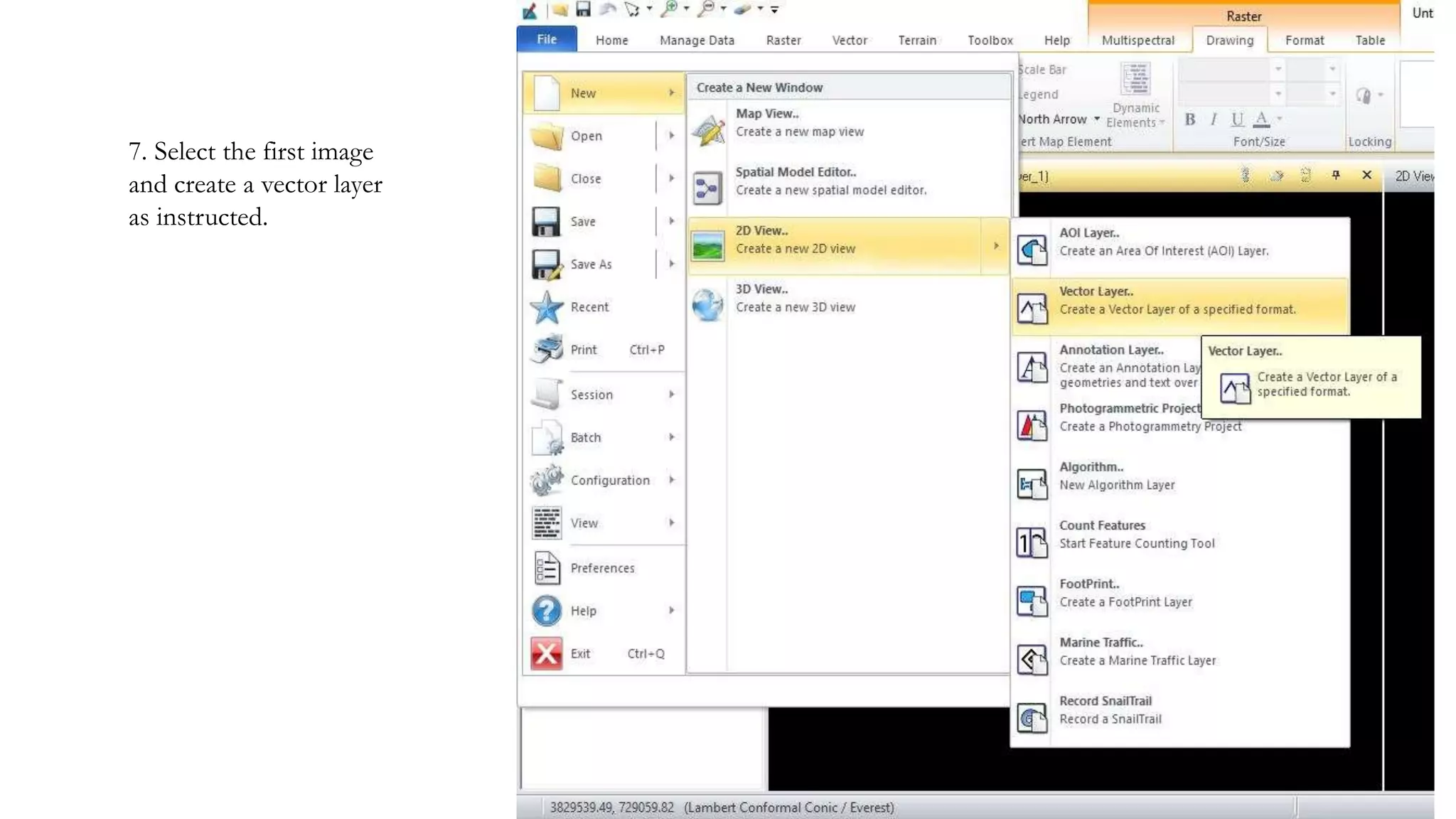
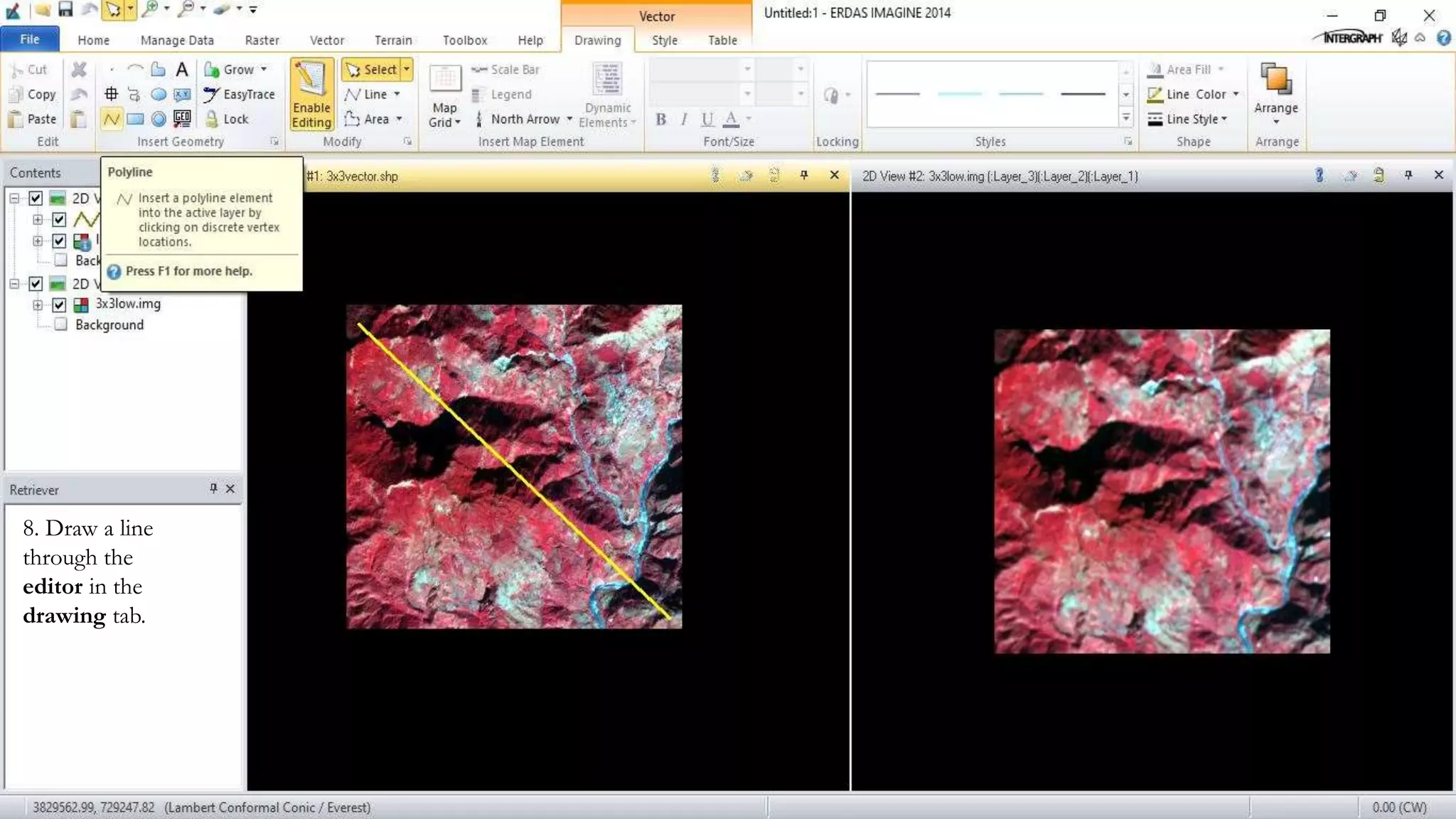
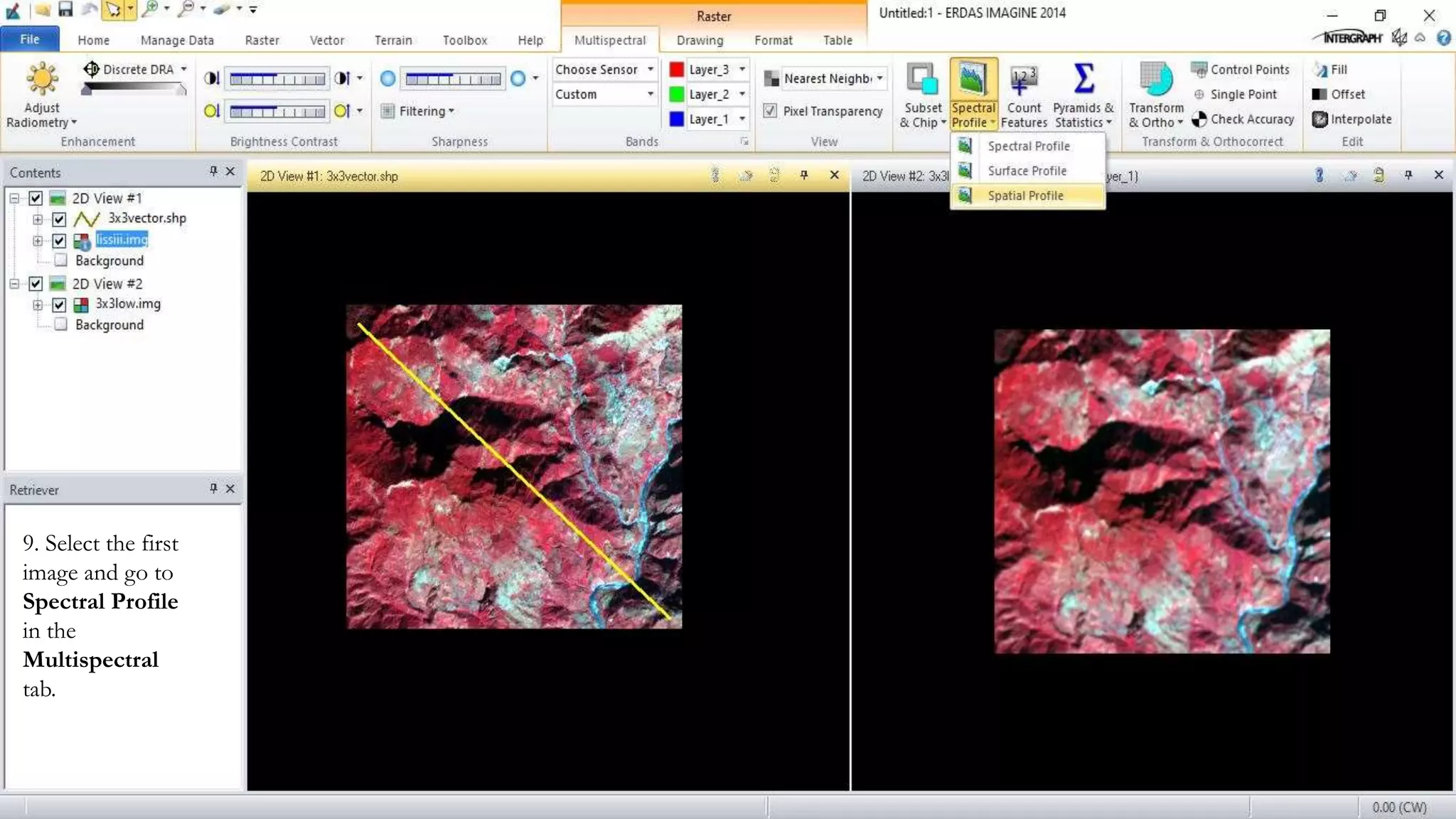
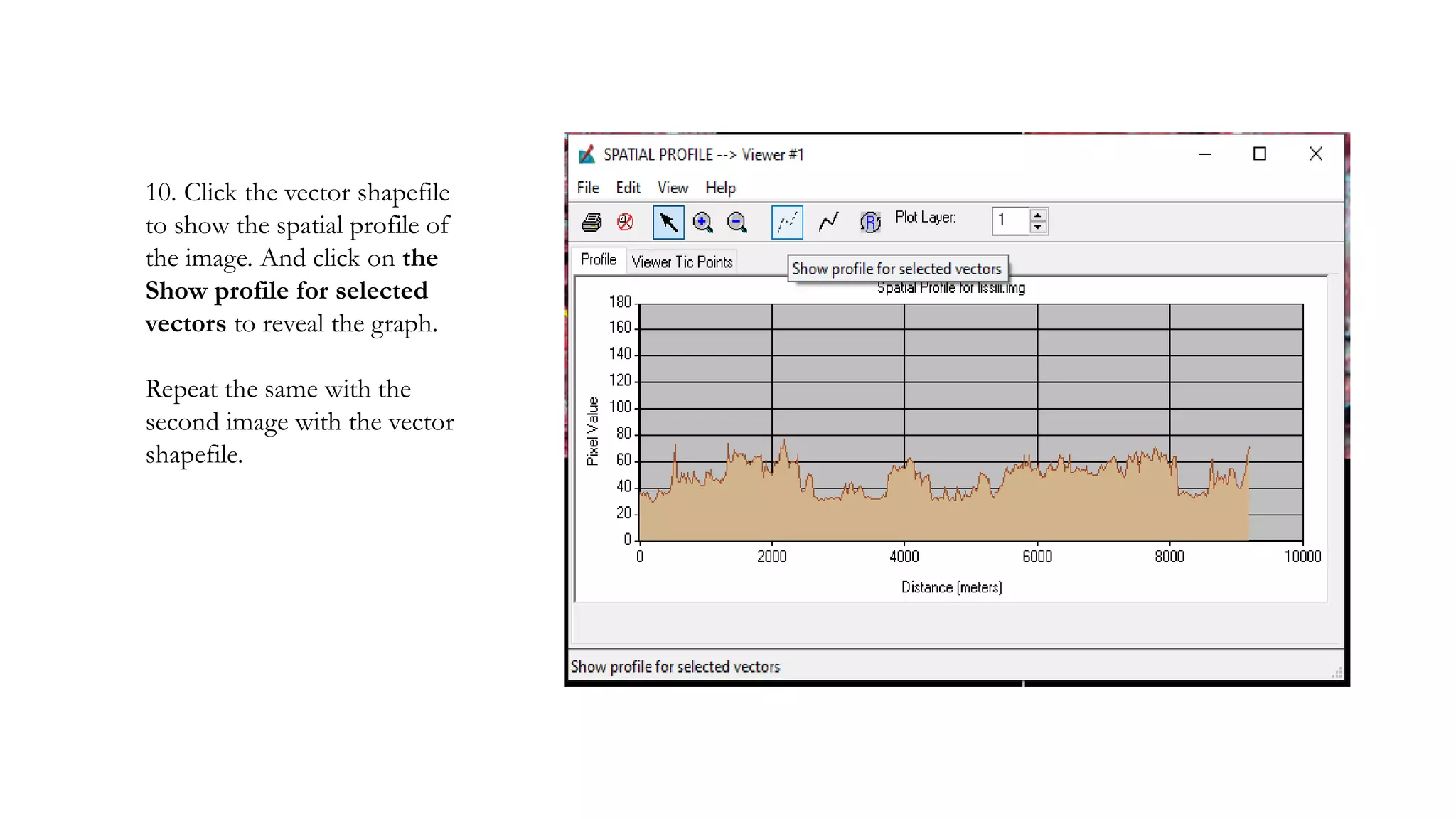
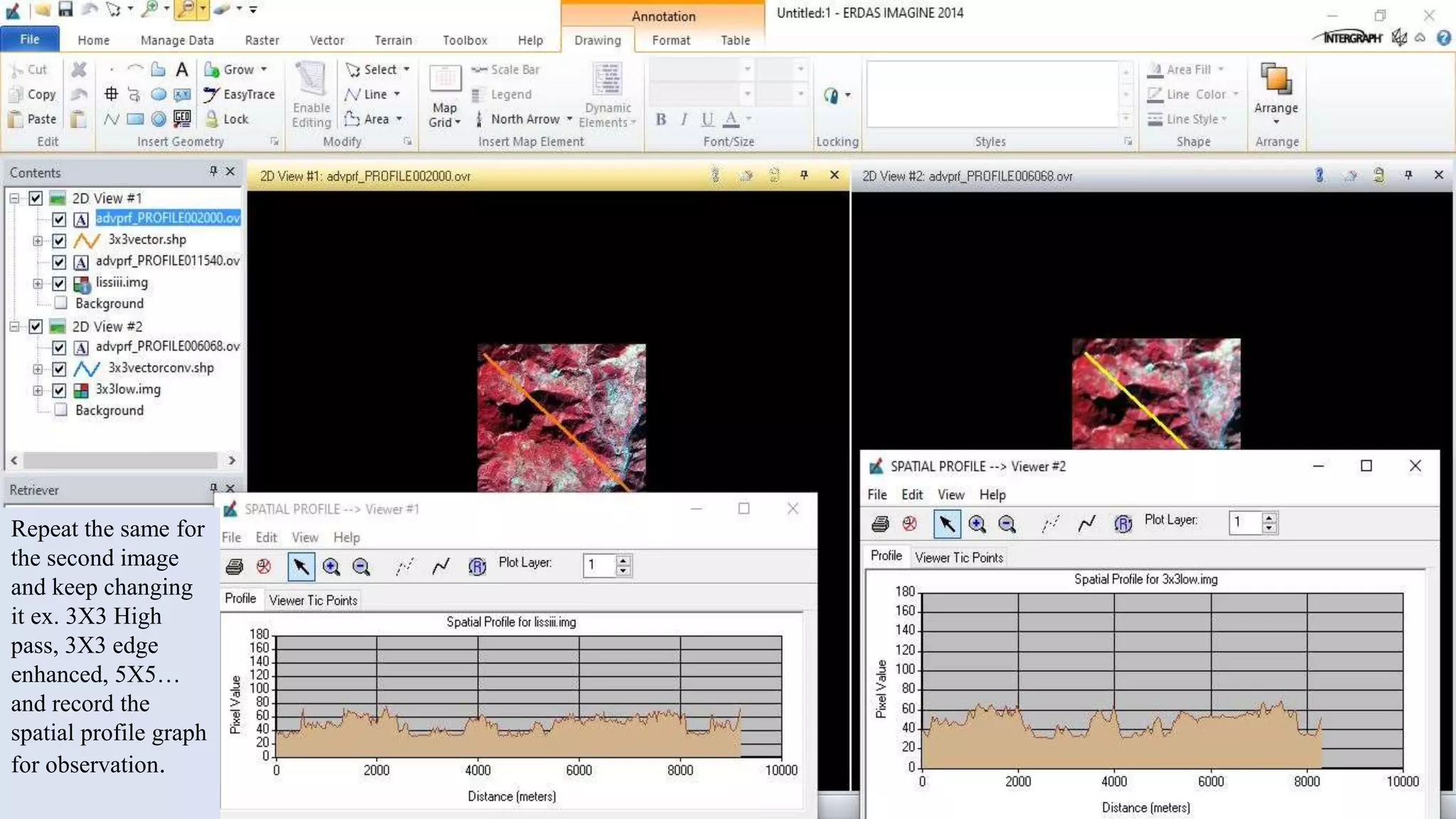
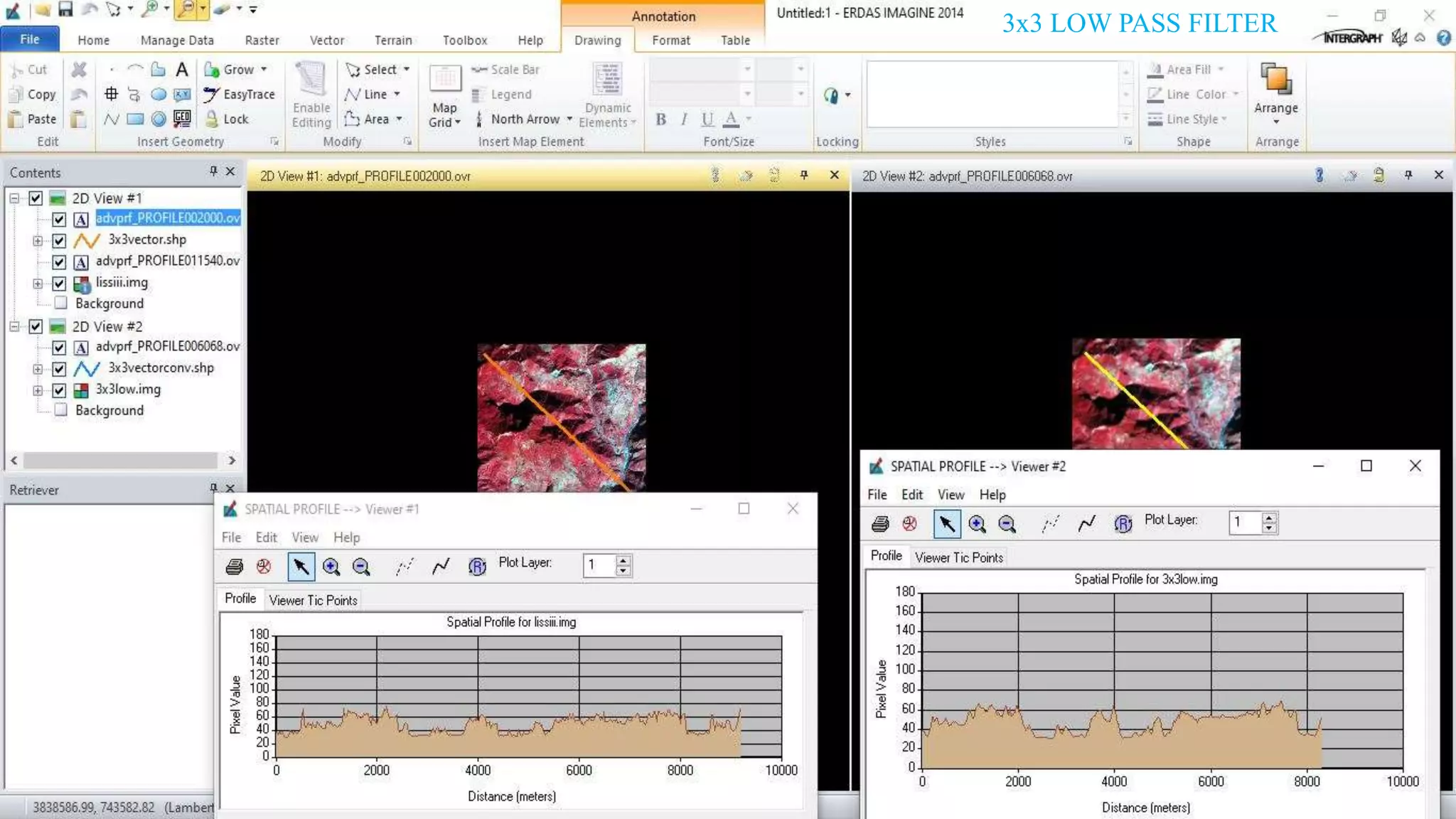
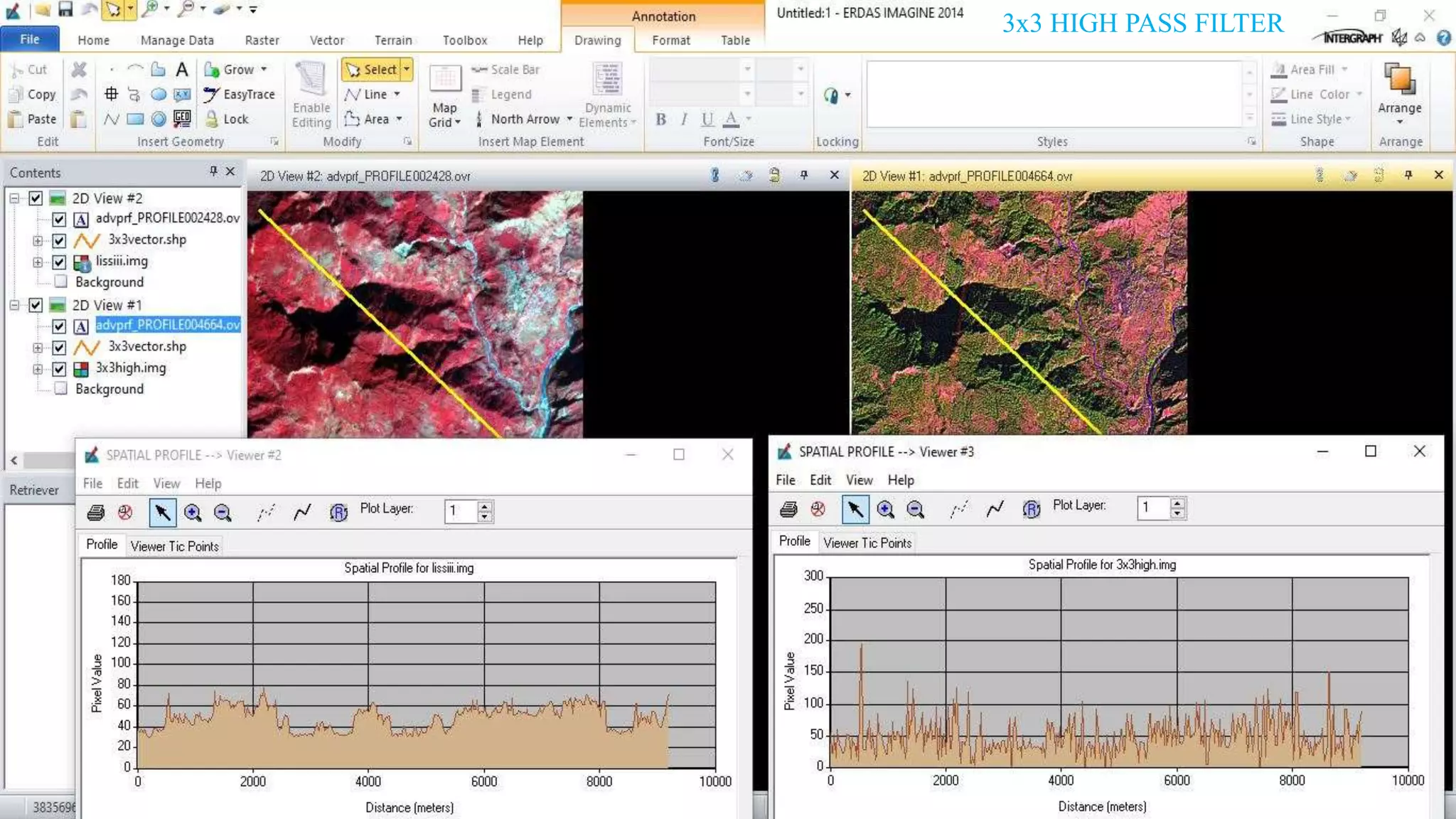
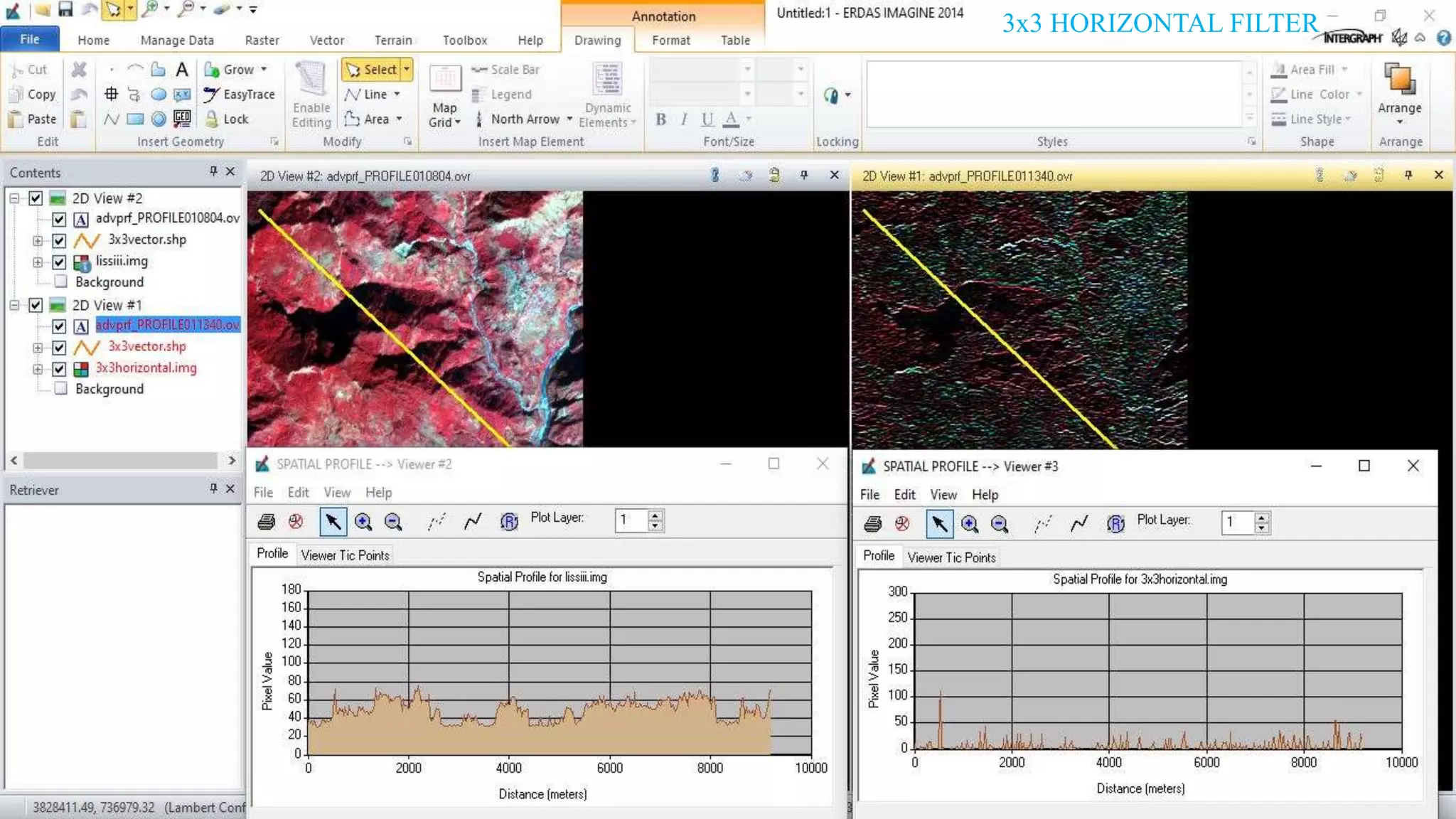
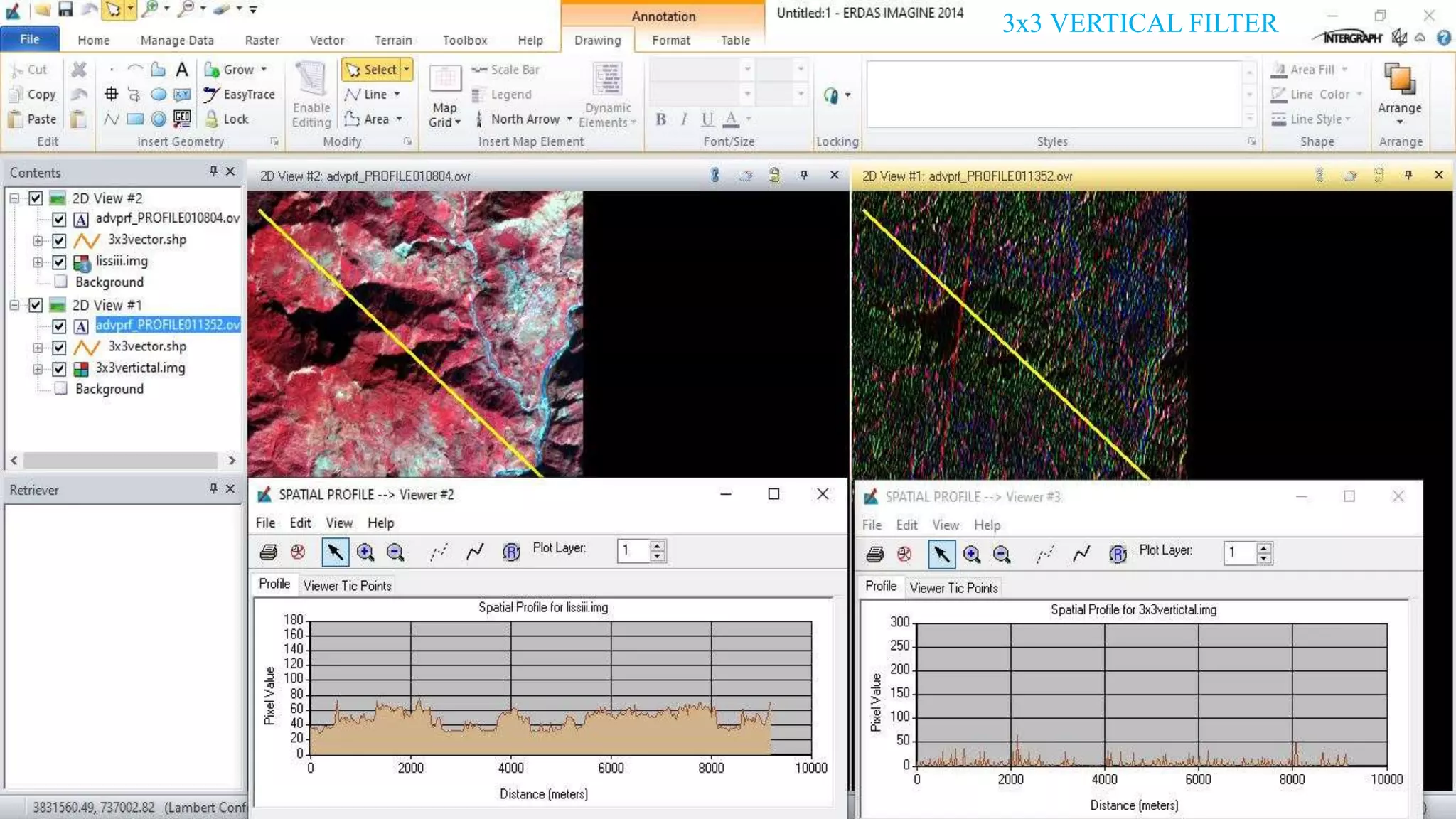
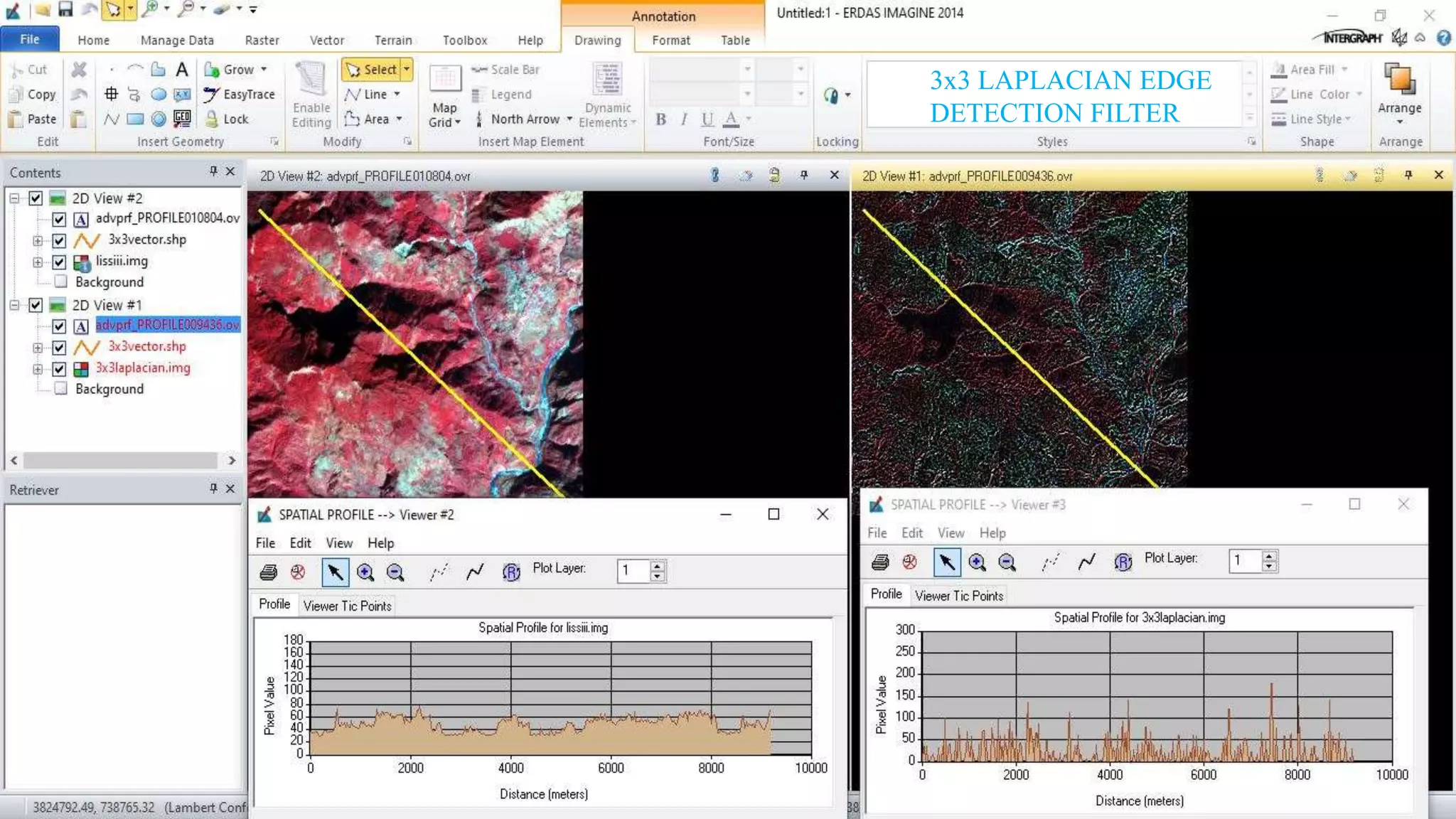
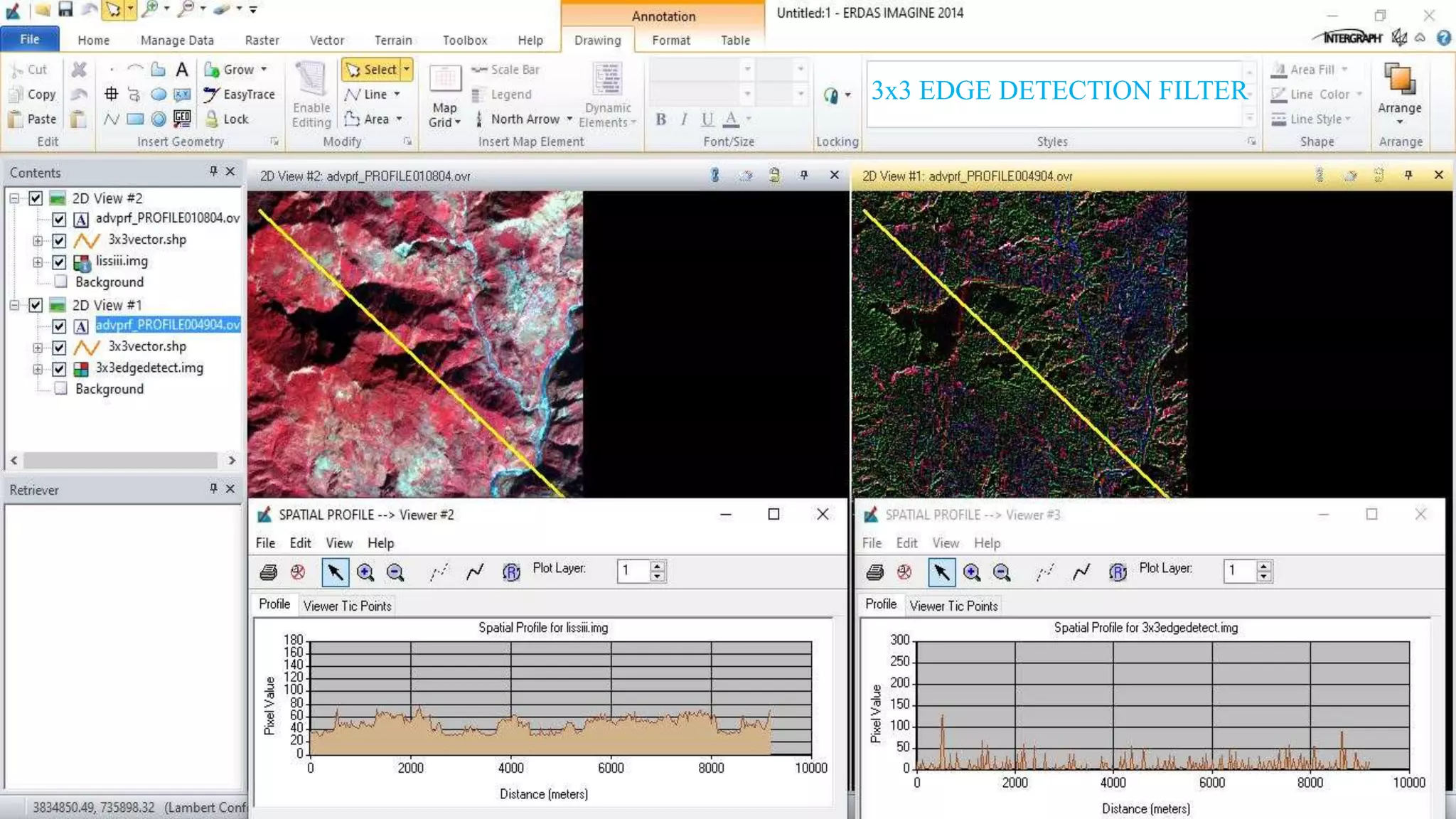
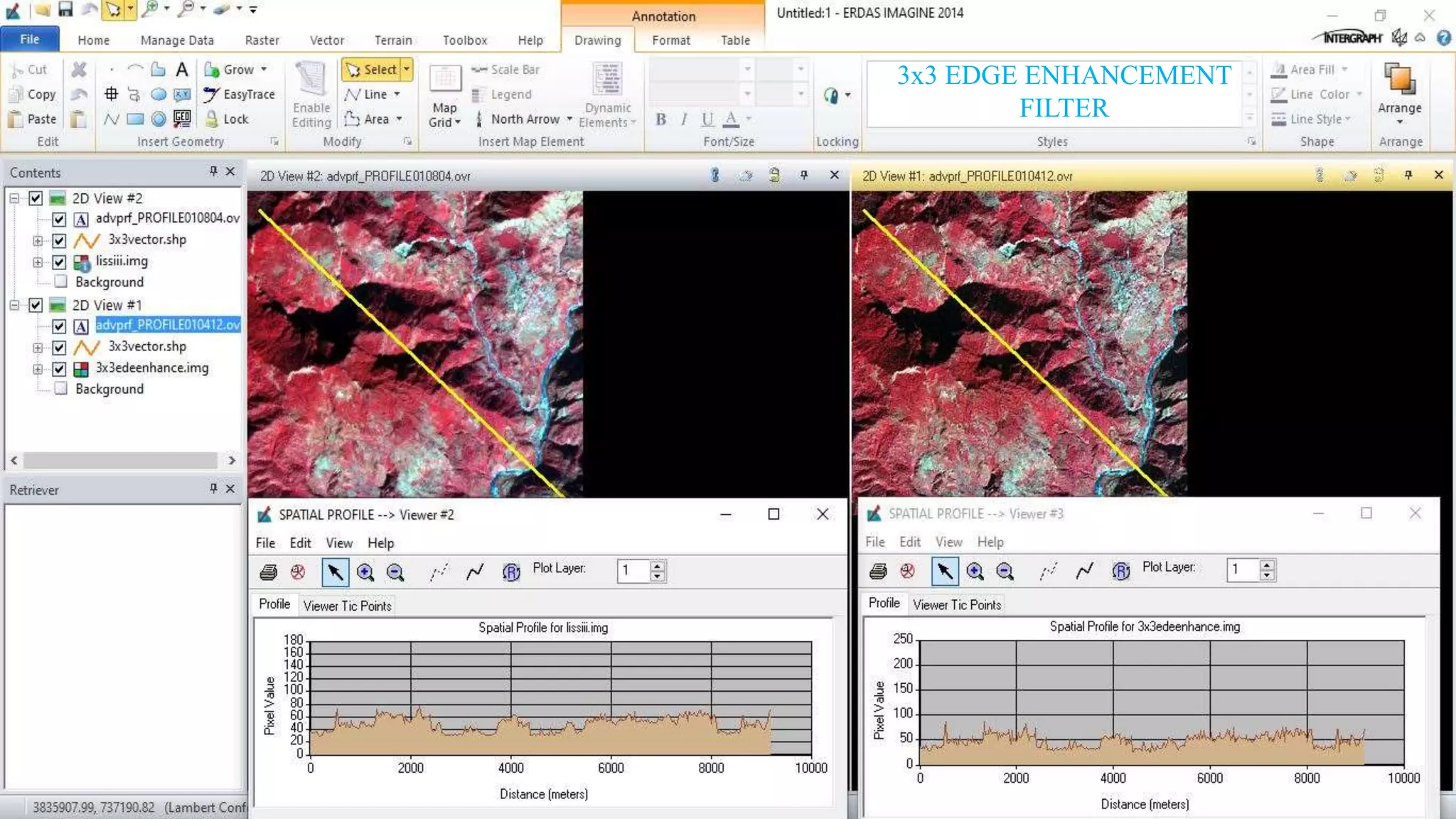
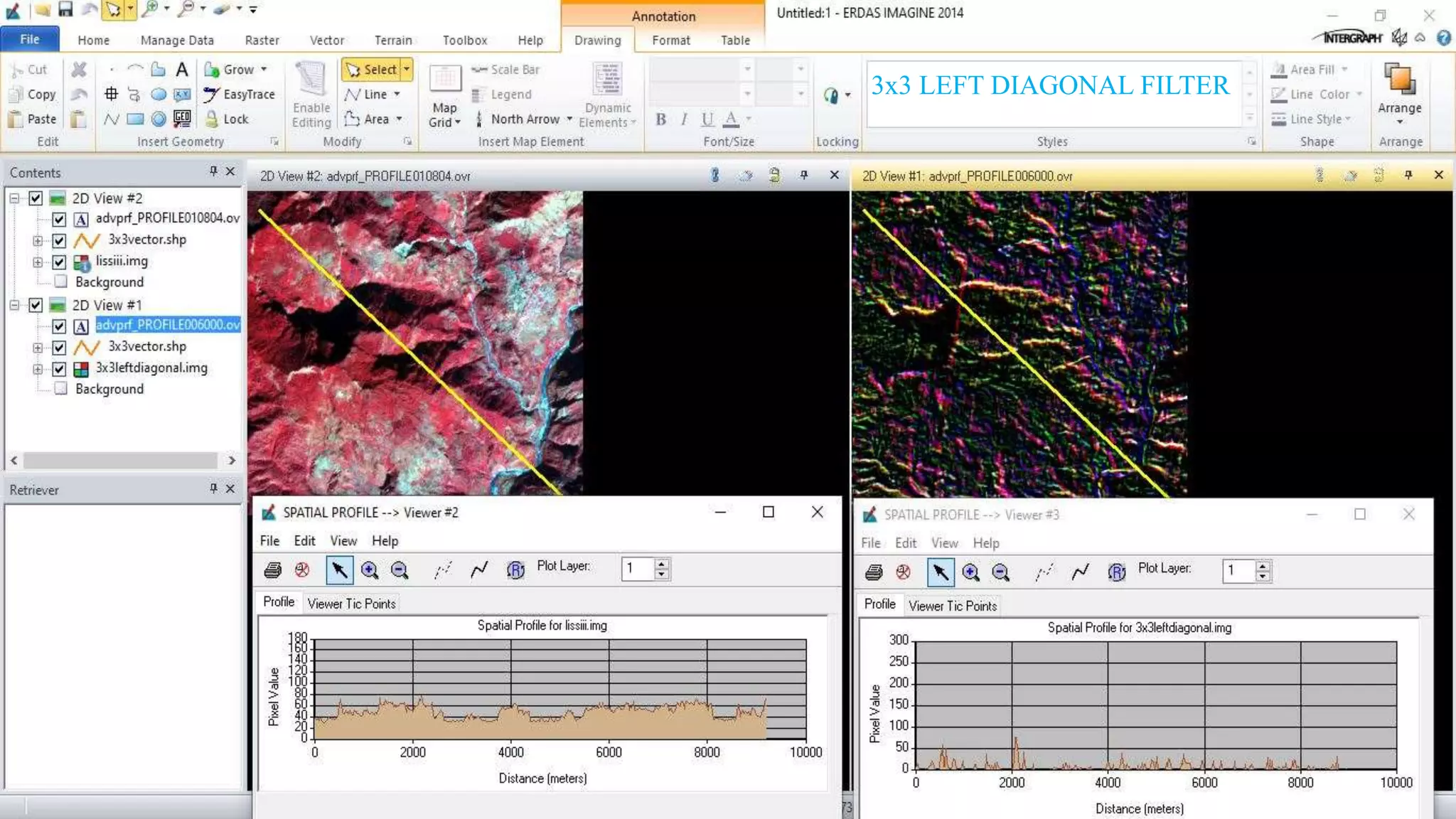
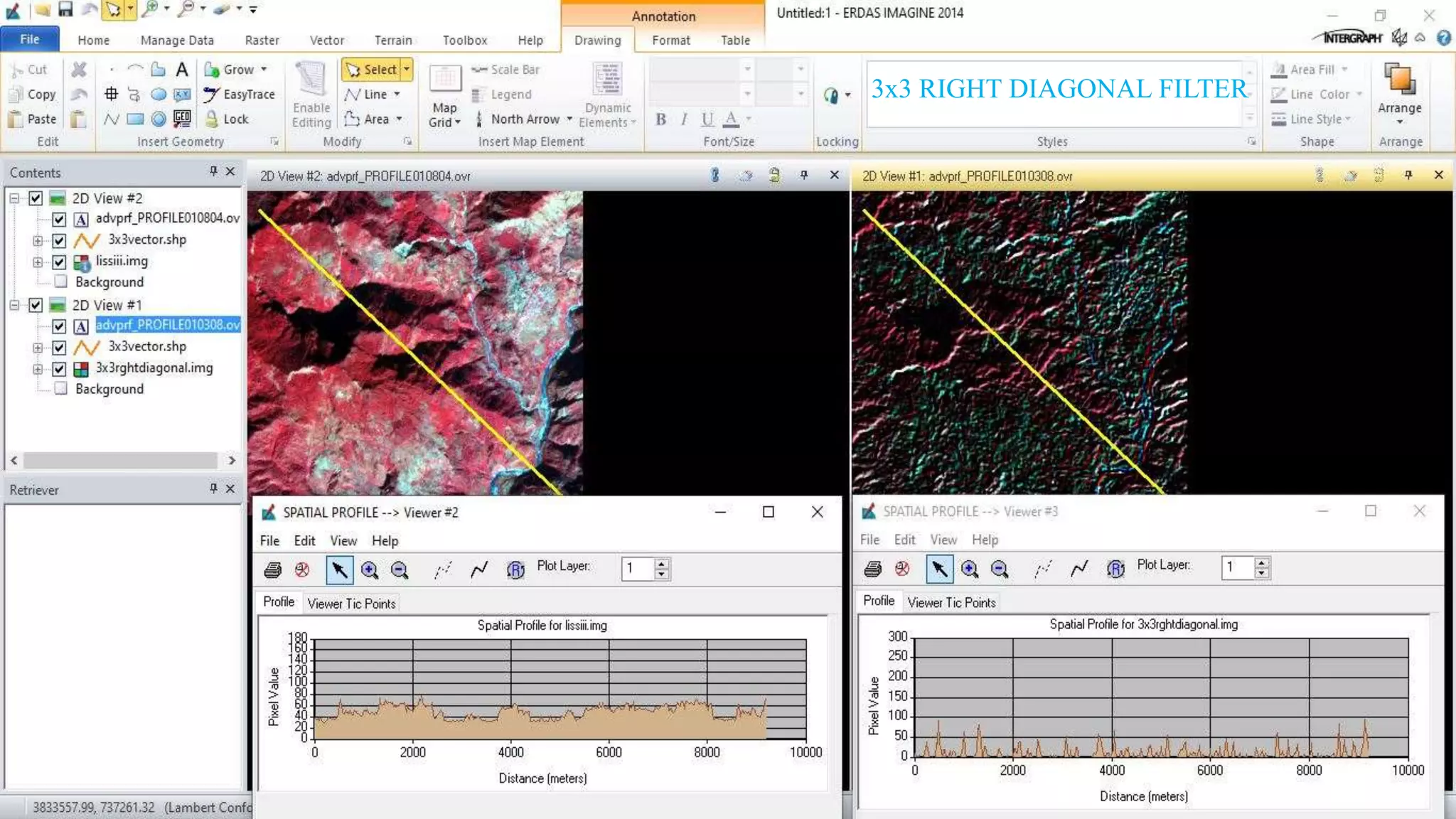
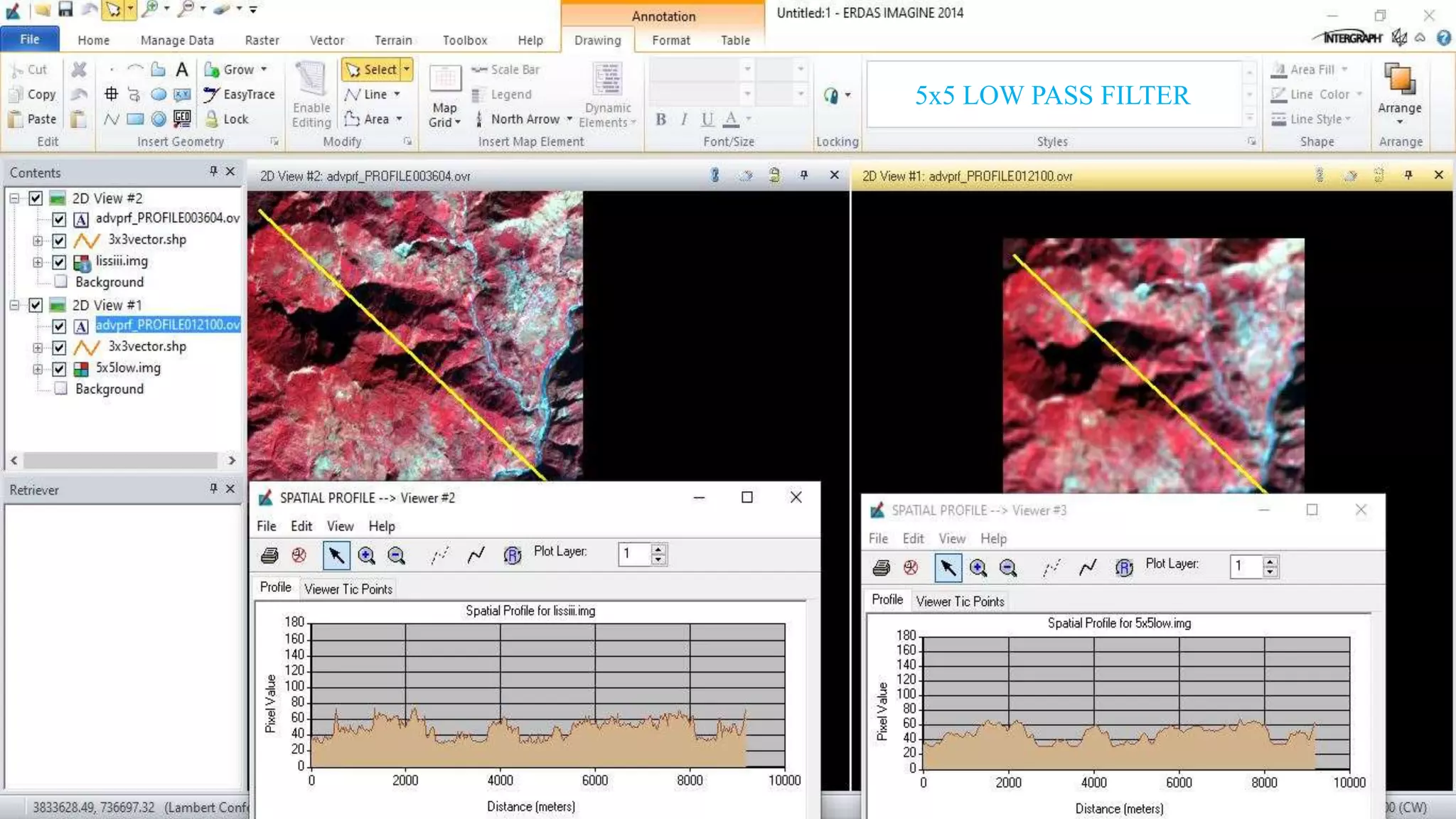
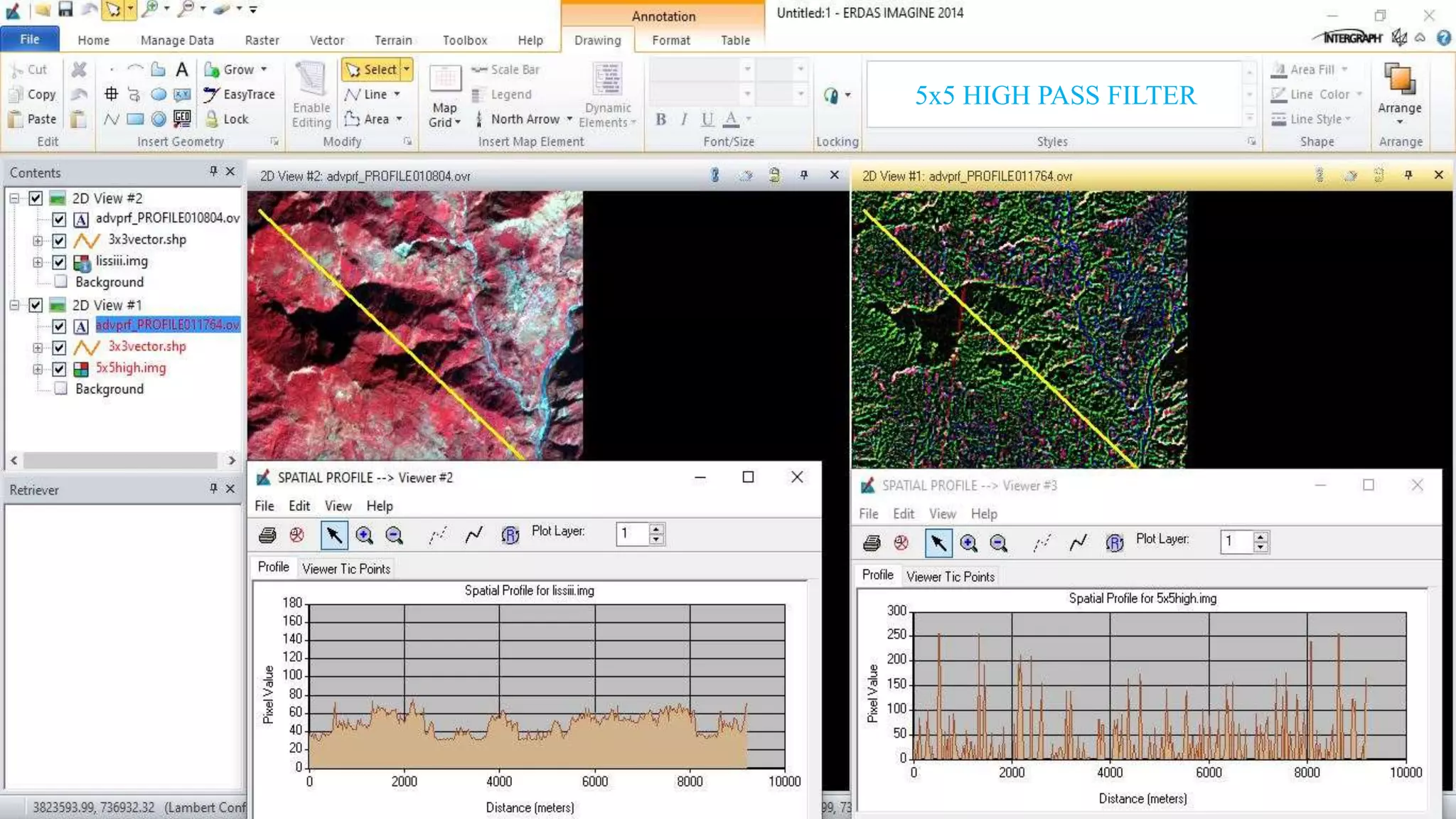
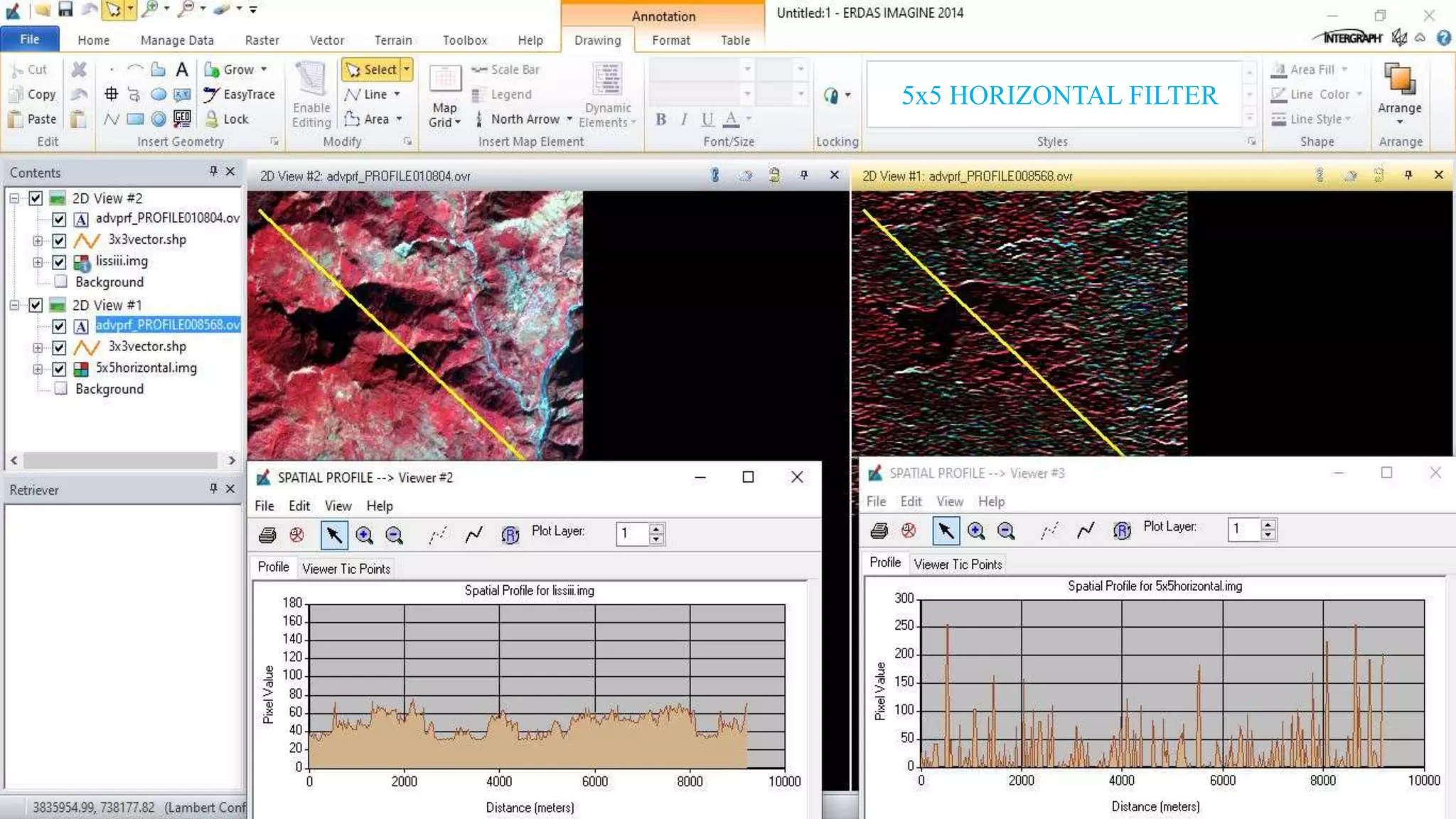
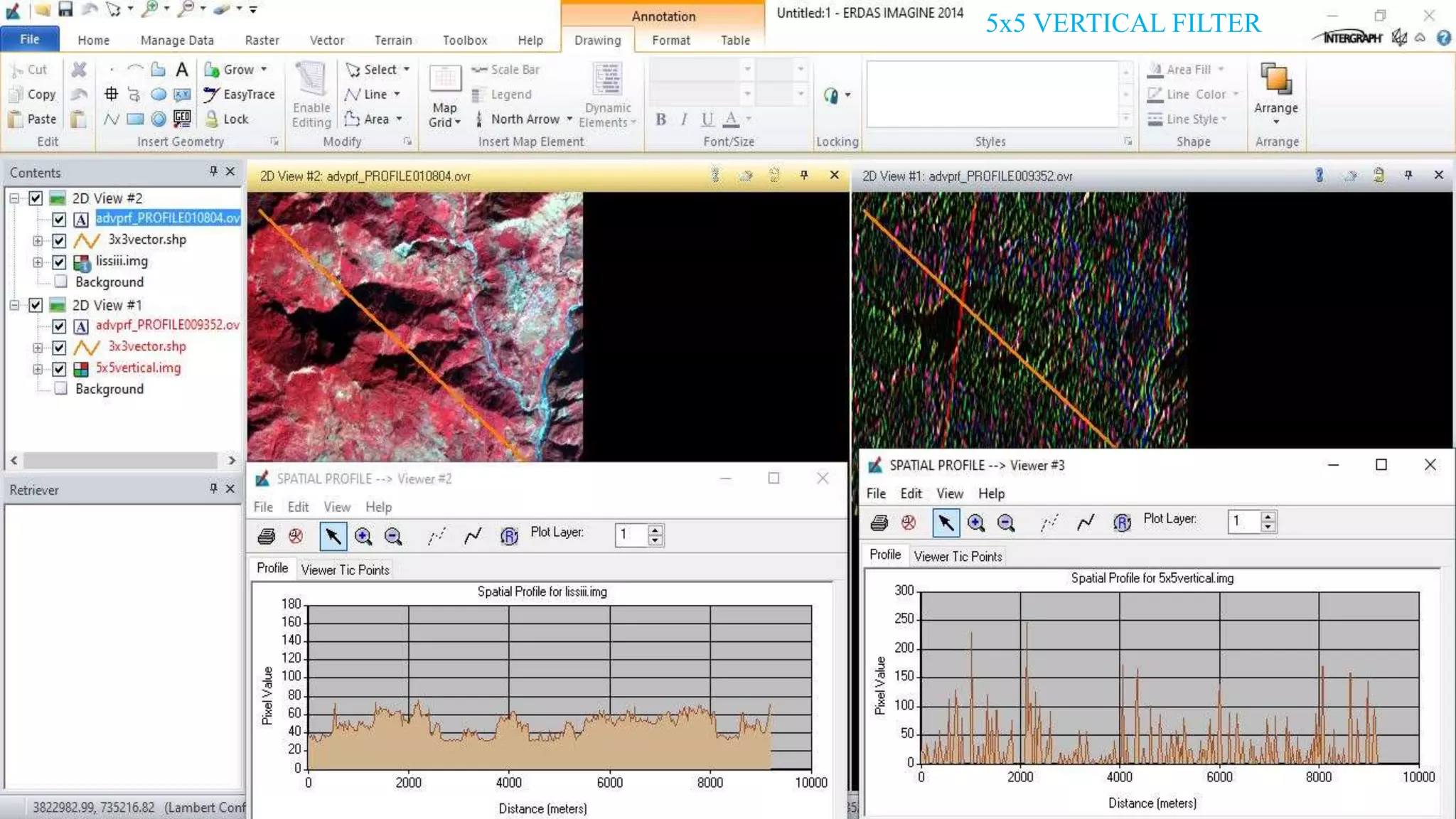
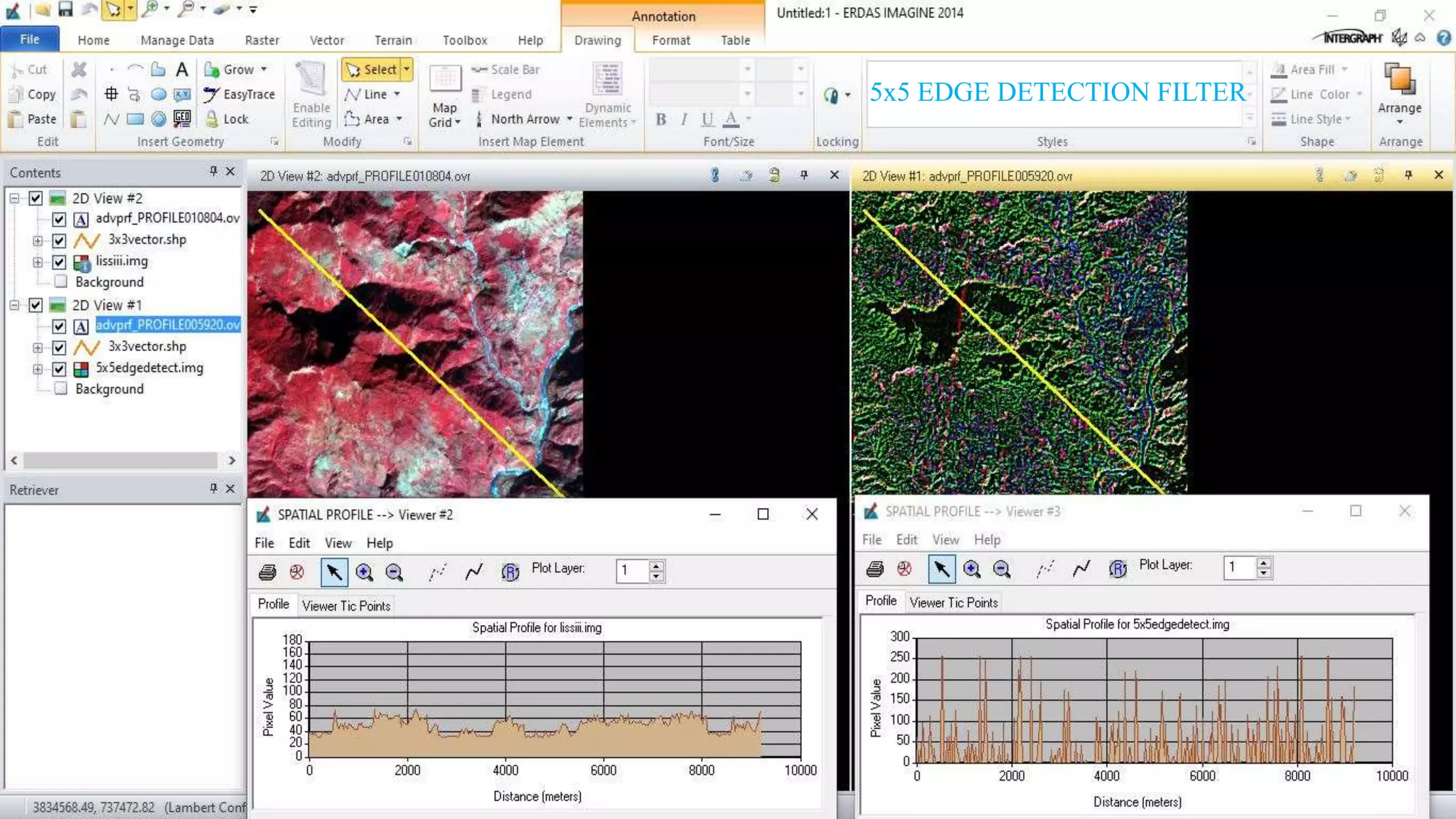
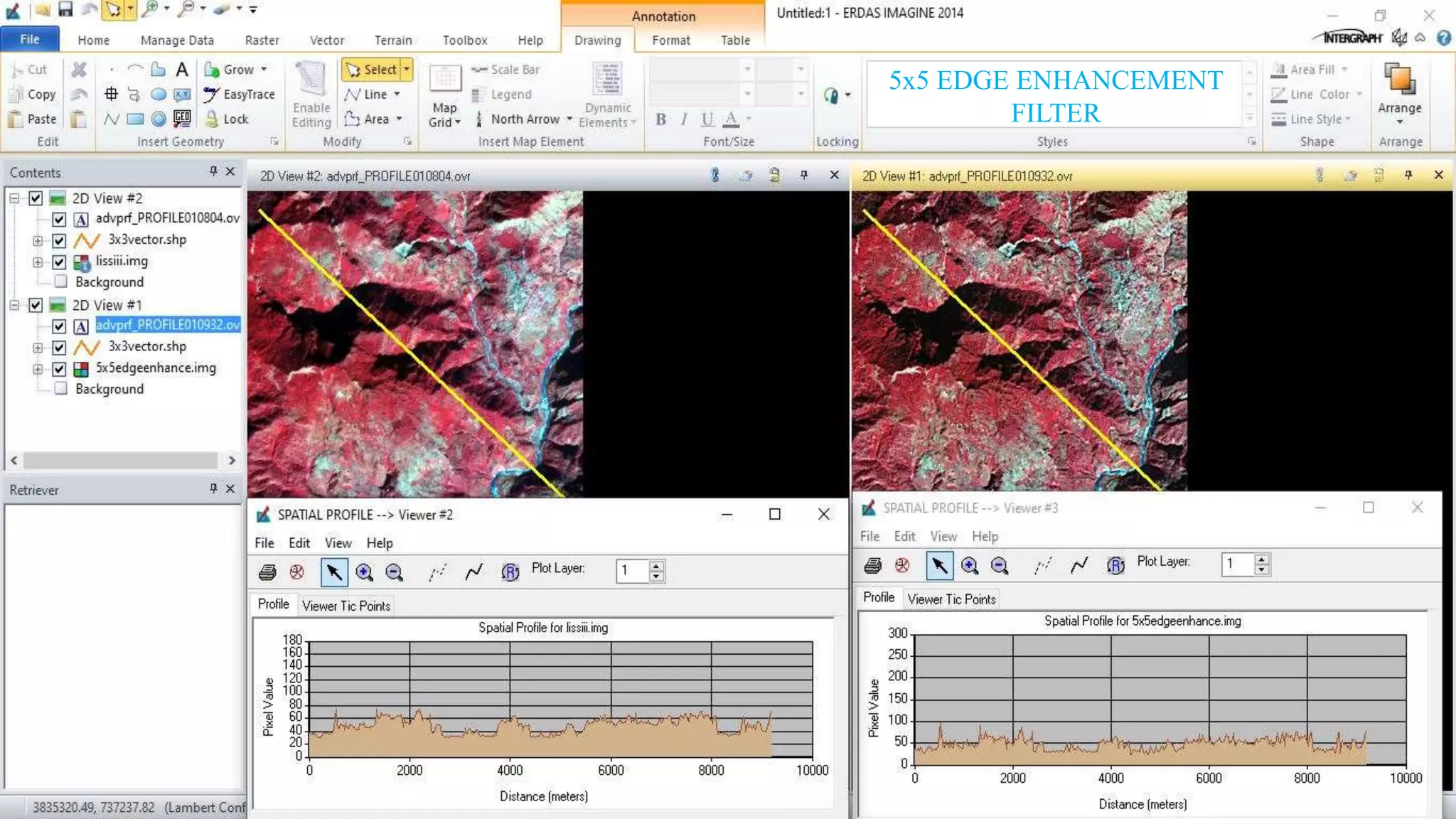
The document discusses the advantages of digital image filtering, highlighting how specific enhancements can improve visual interpretation based on application needs. It details various filtering techniques, including low-pass and high-pass filters, which serve to either smooth or sharpen images respectively, as well as directional and edge detection filters. Additionally, the document provides a step-by-step guide for utilizing these techniques through a specific software application.