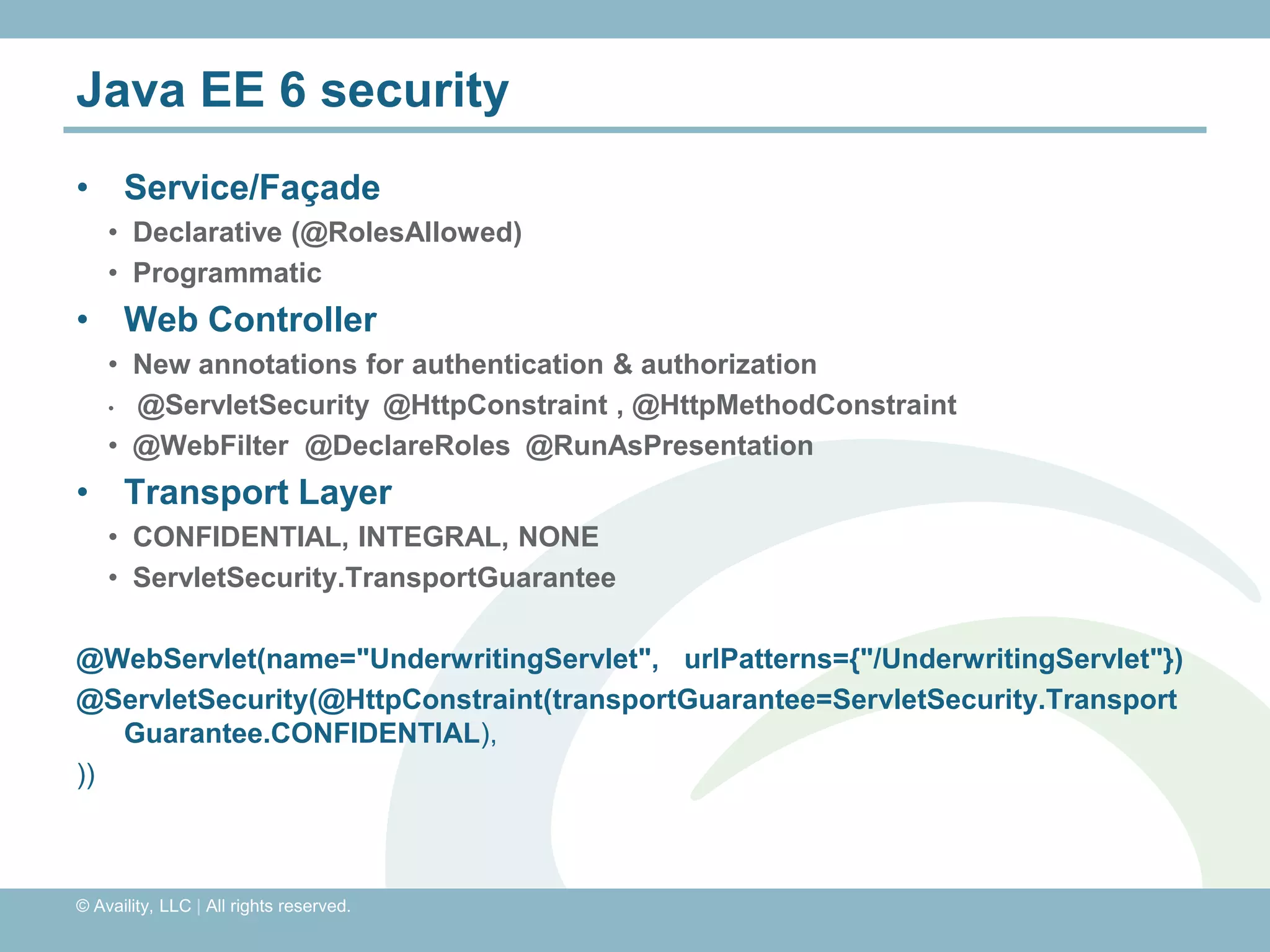
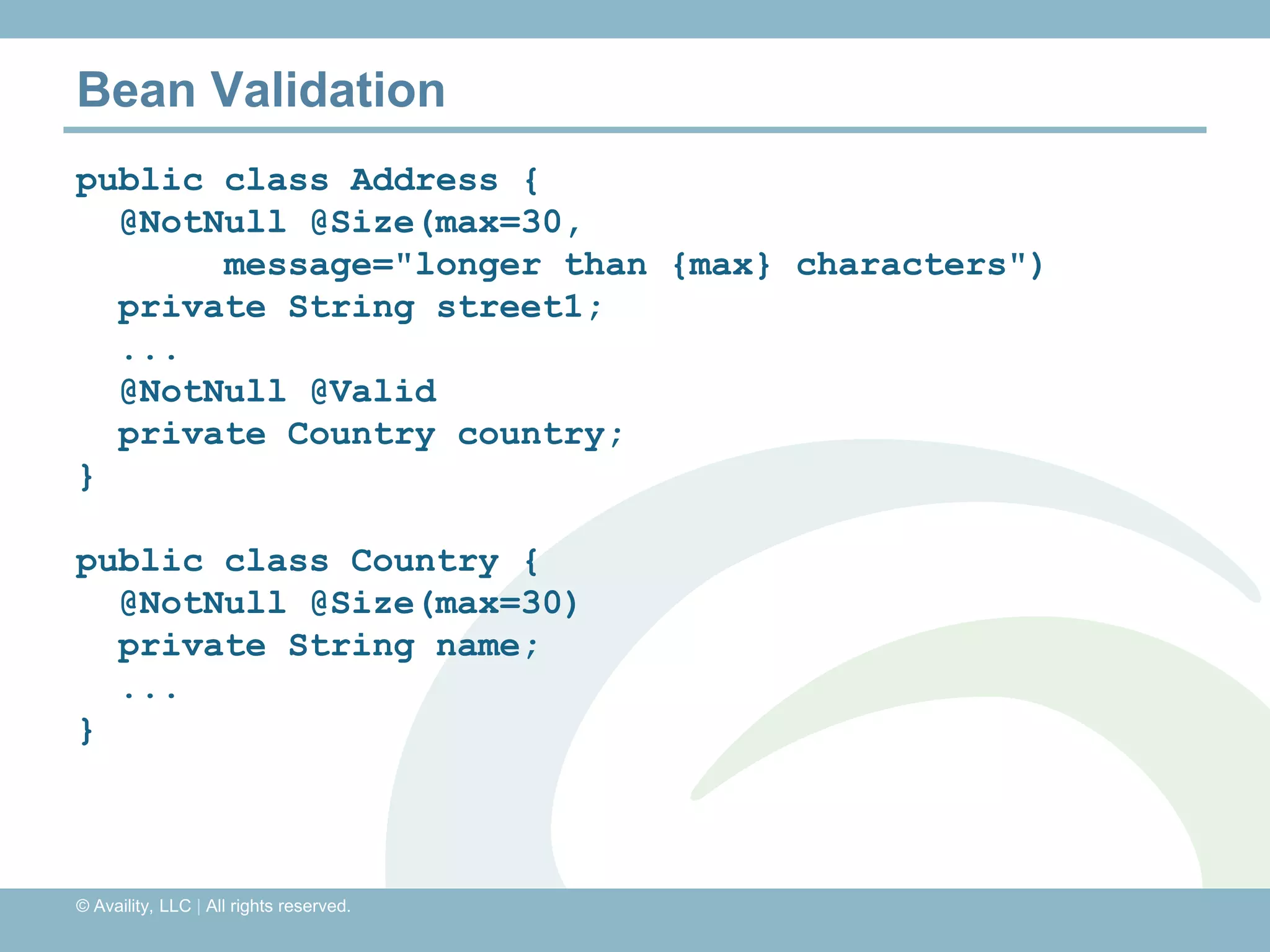
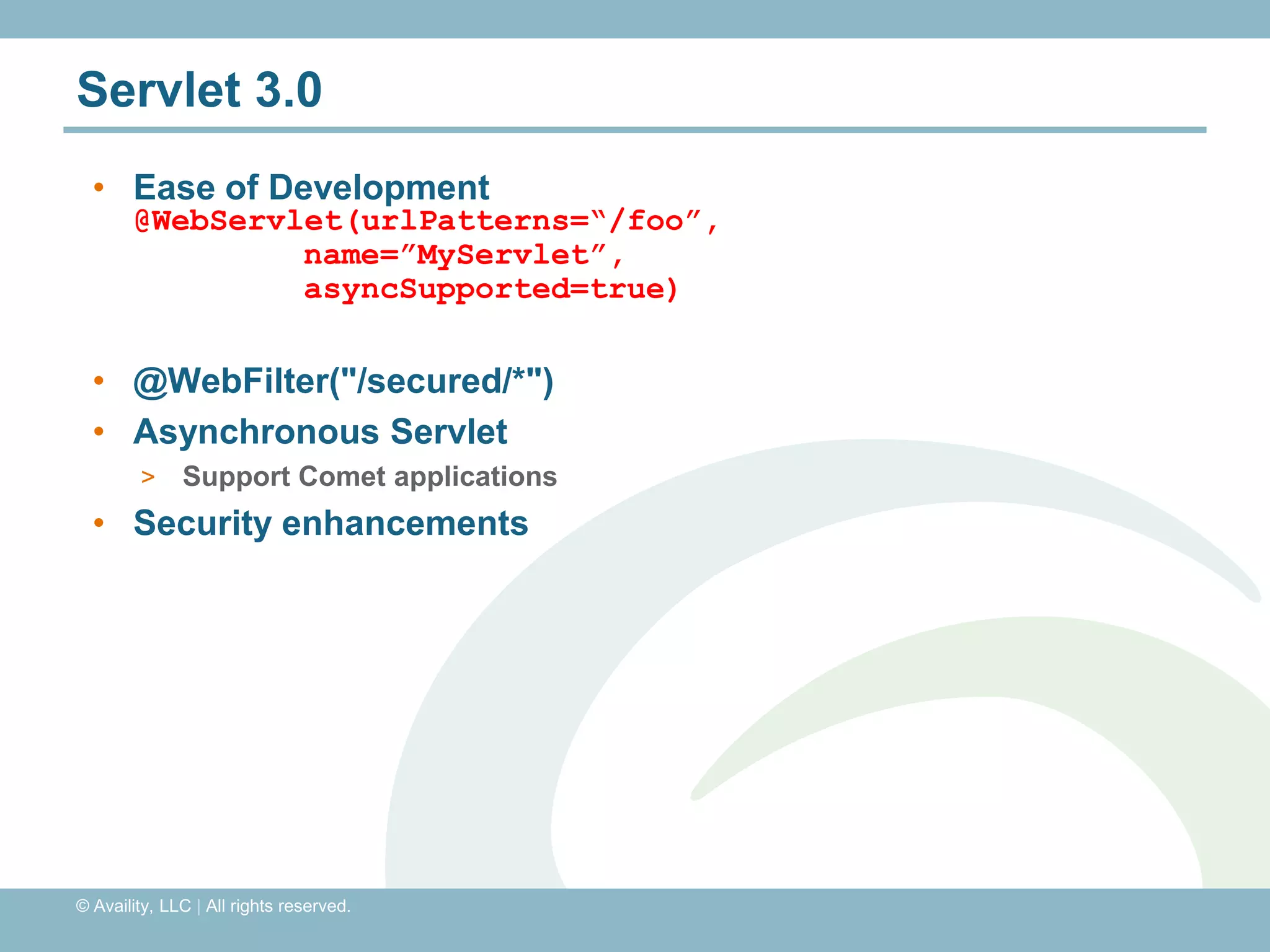
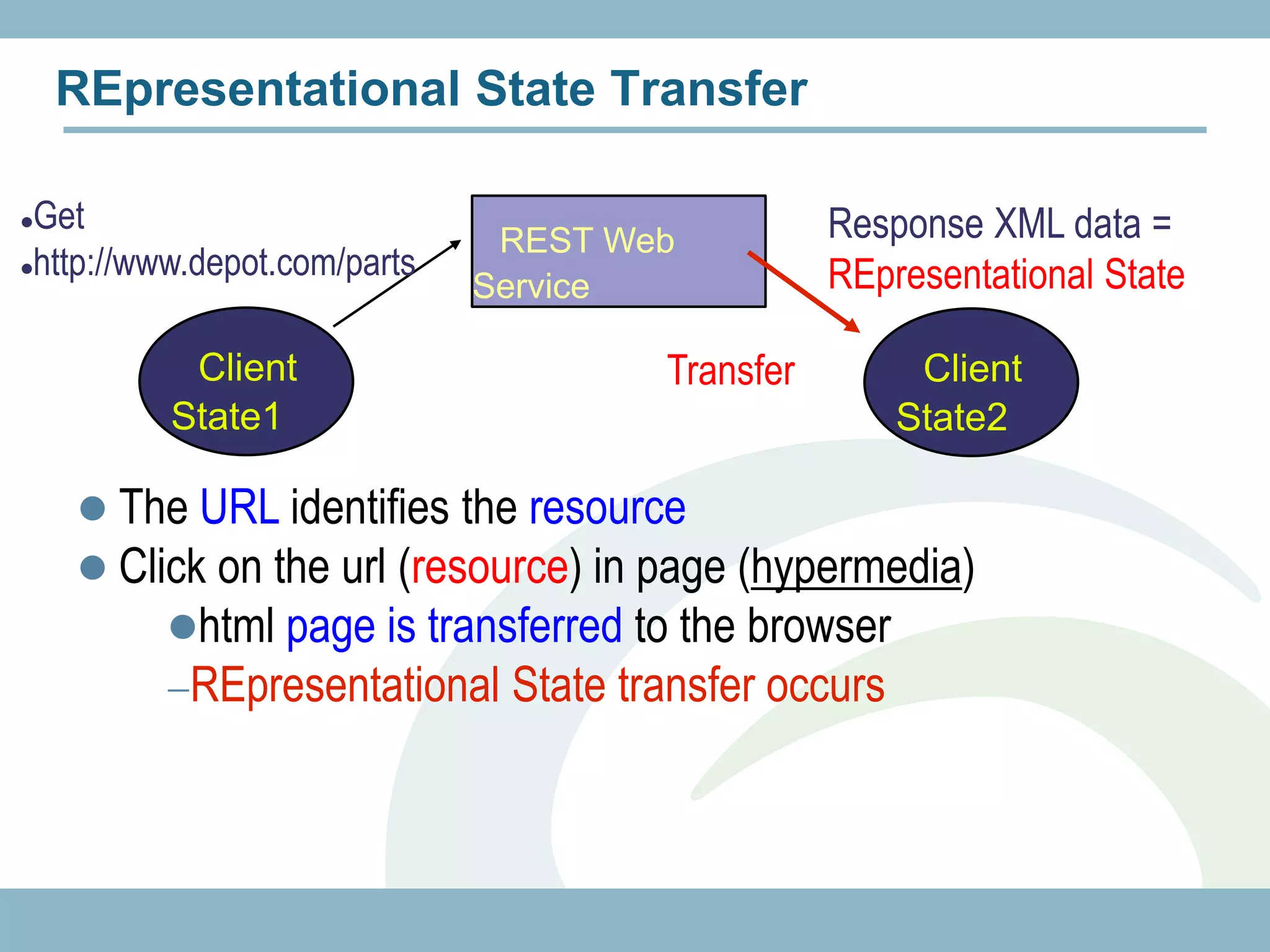
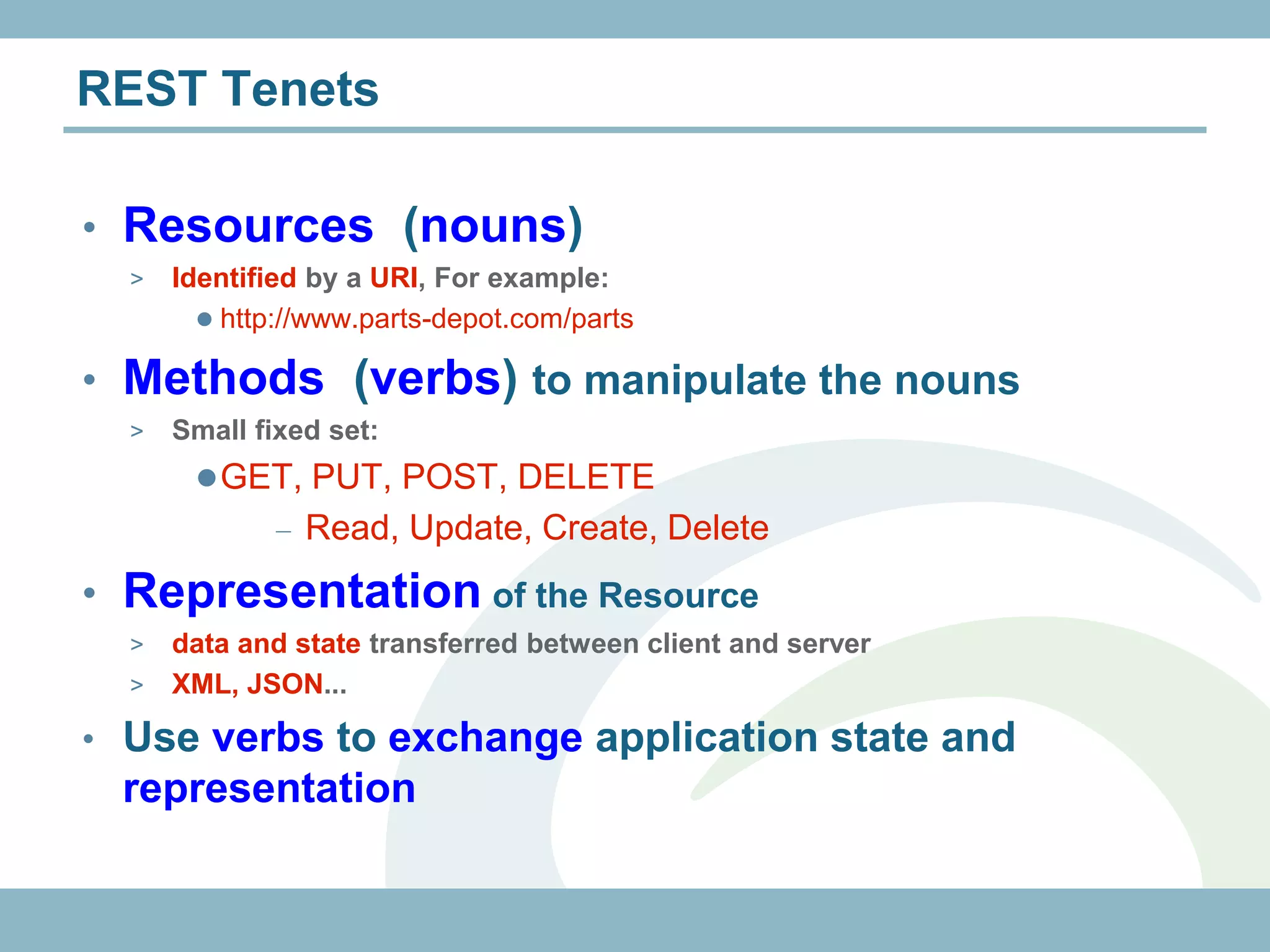
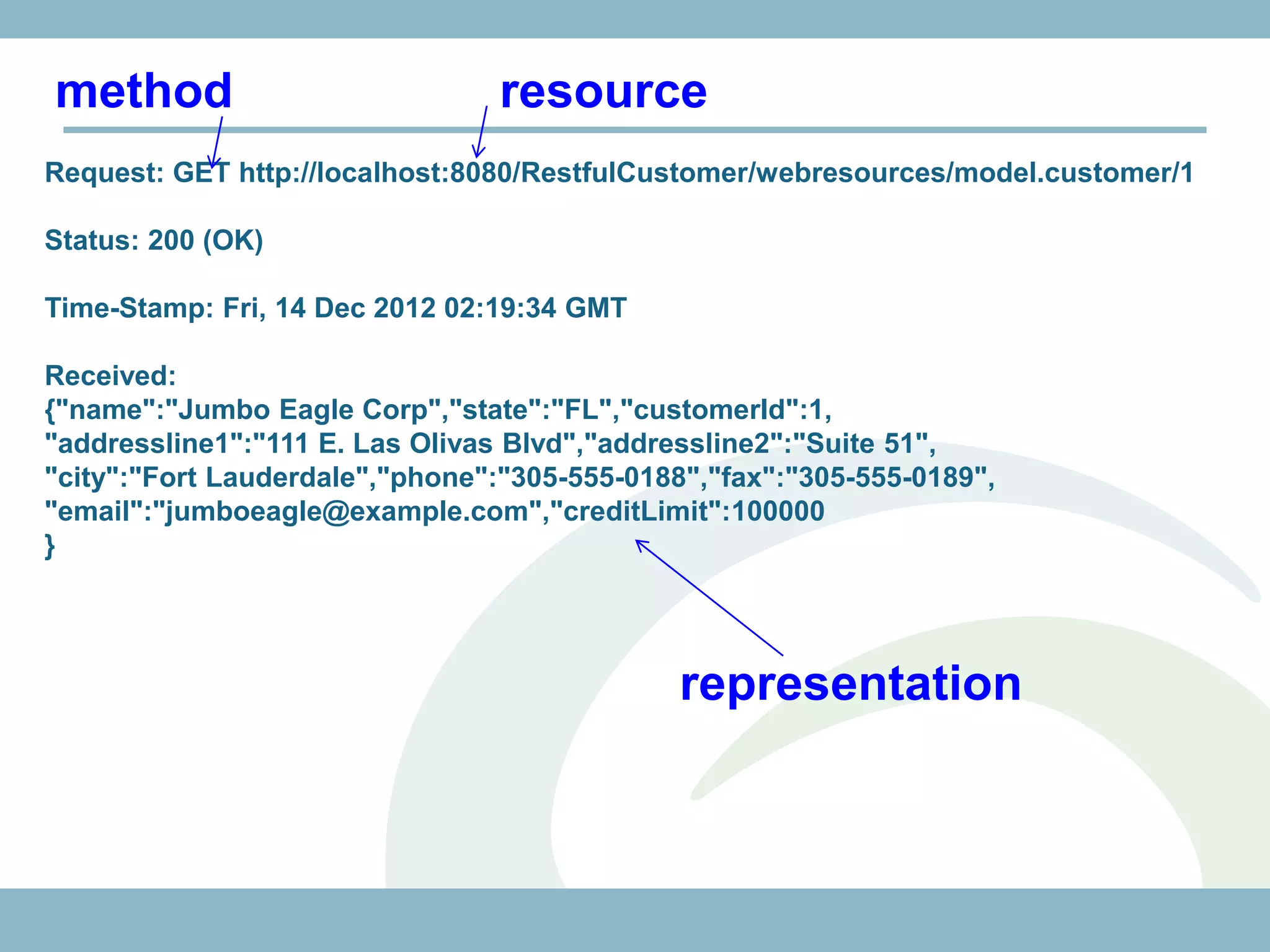
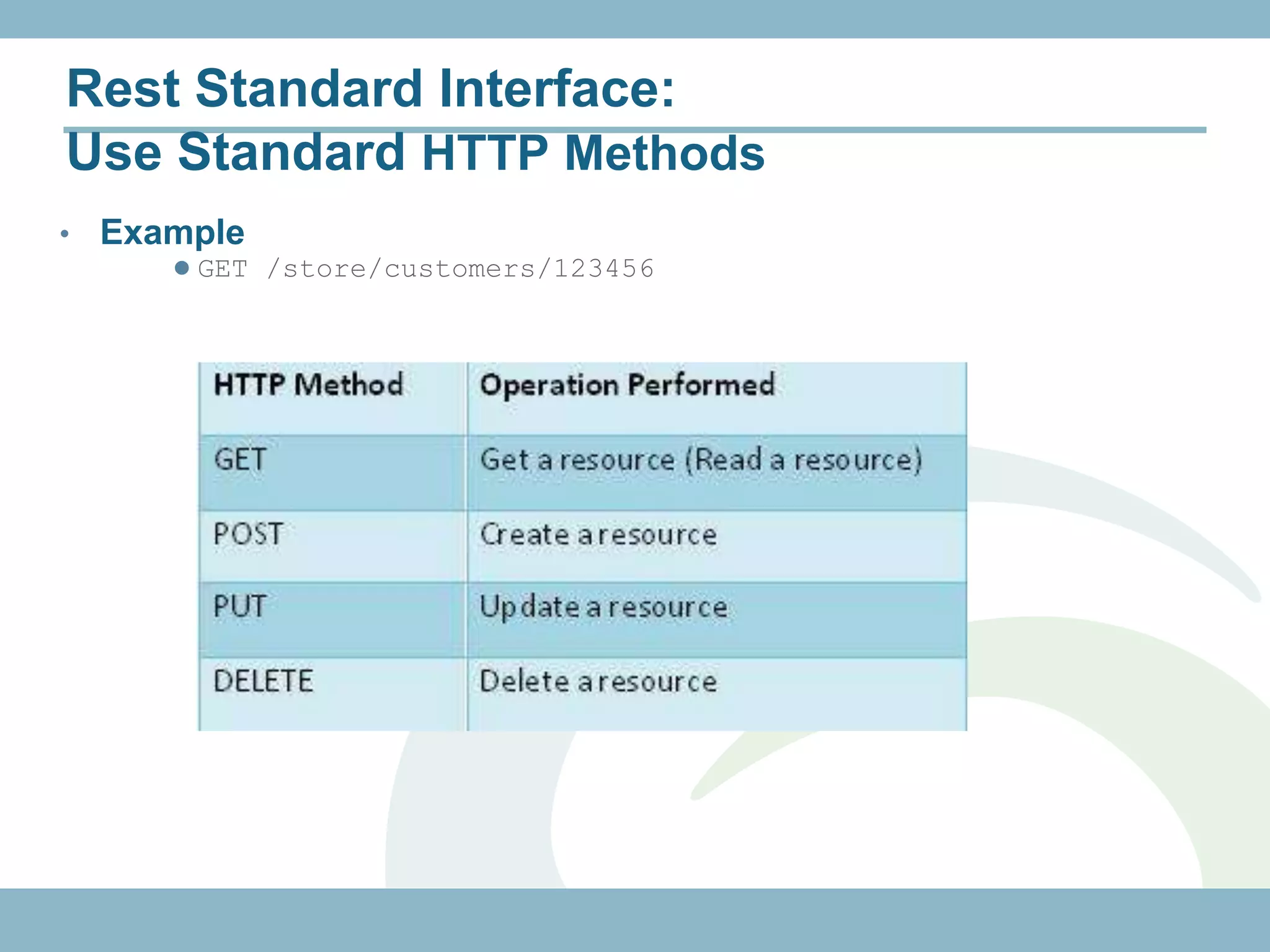
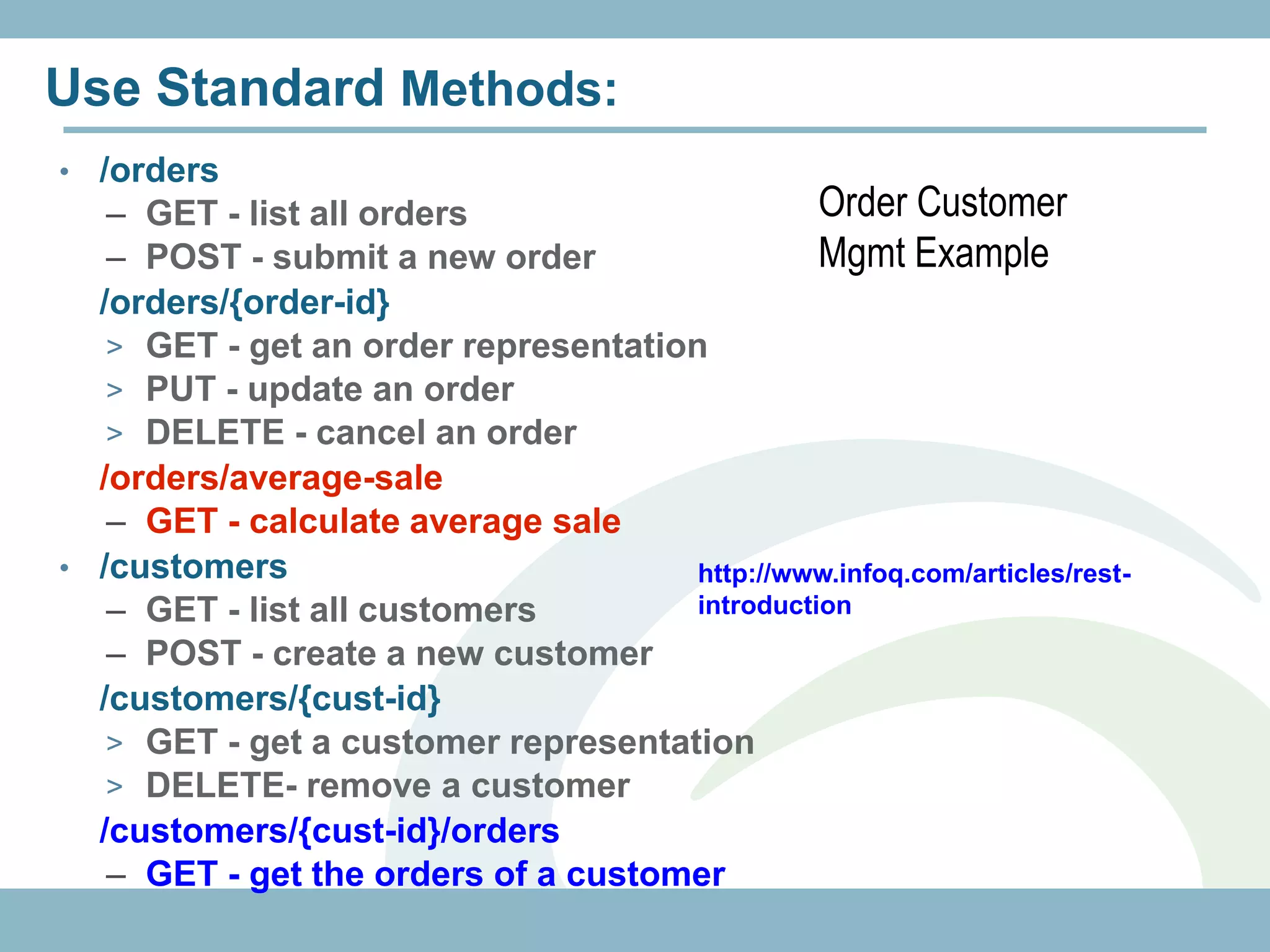
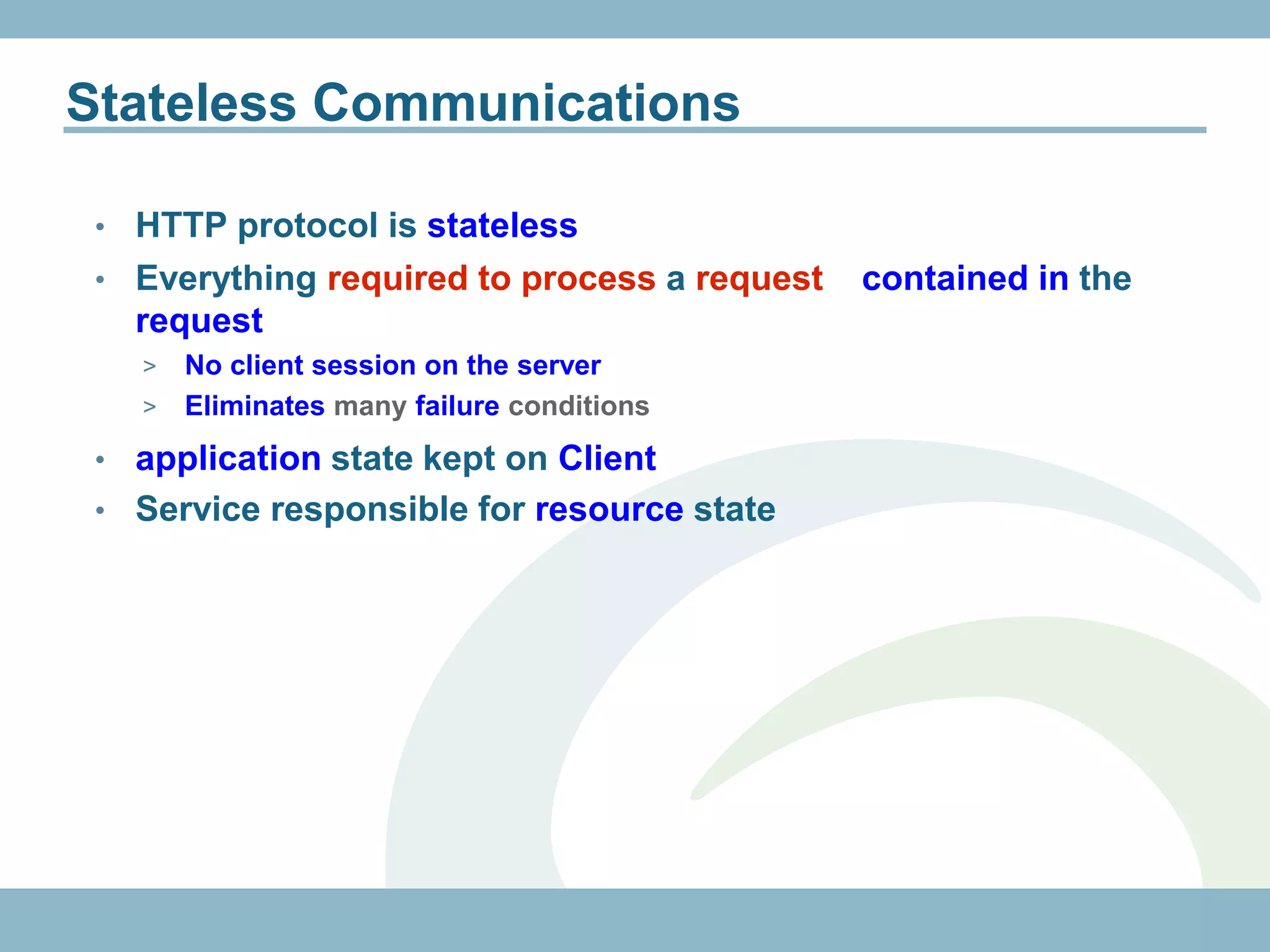
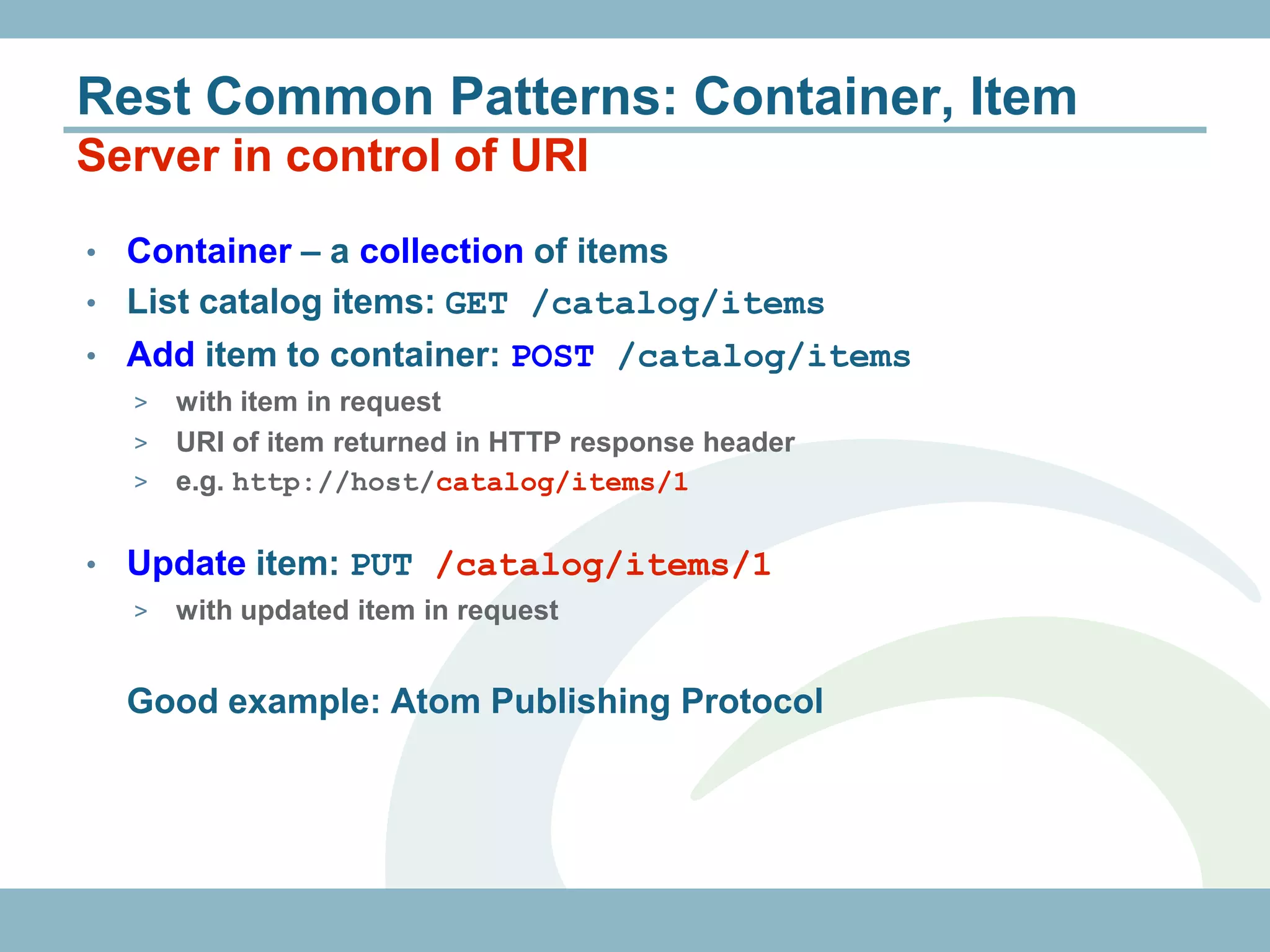
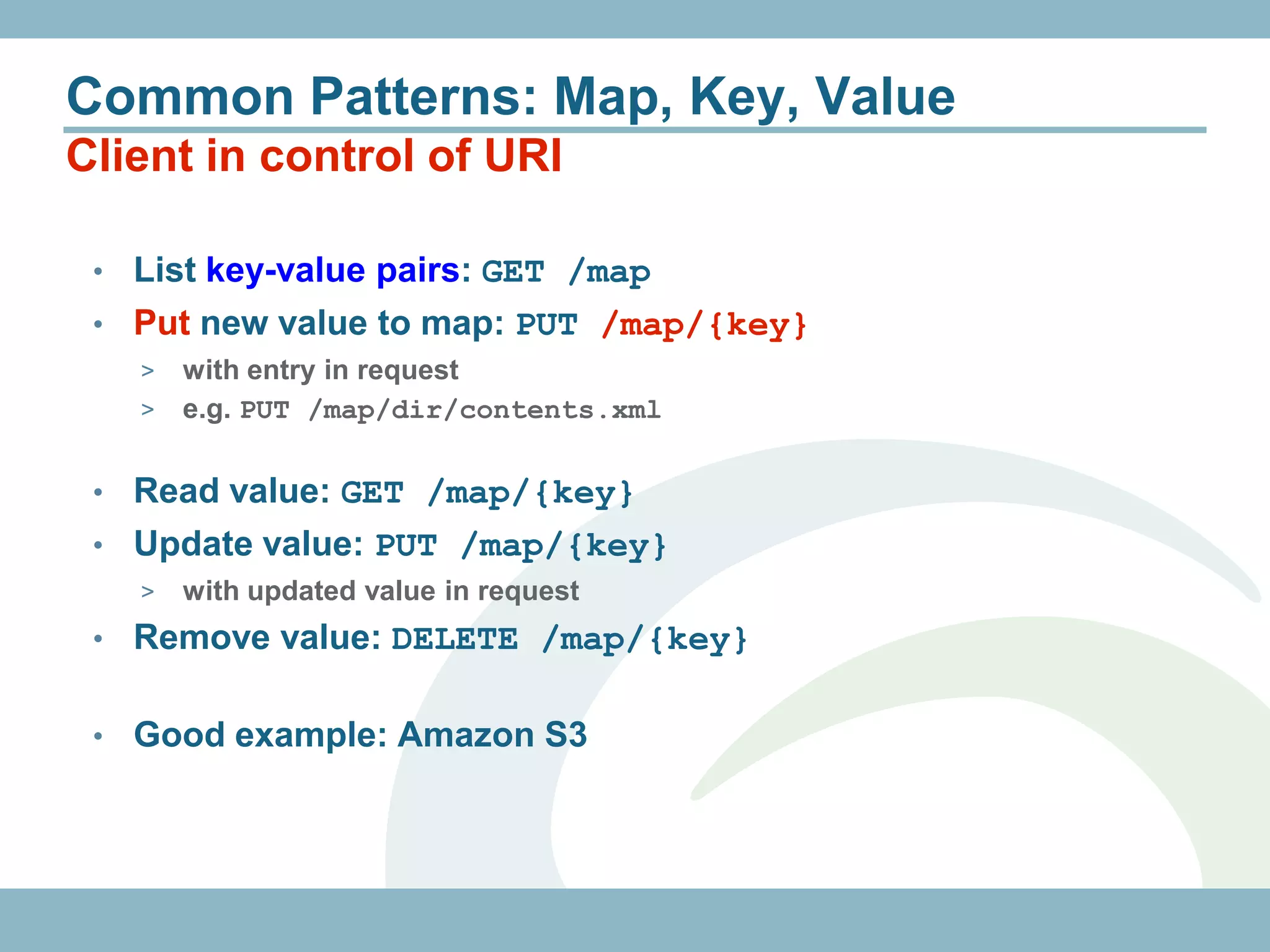
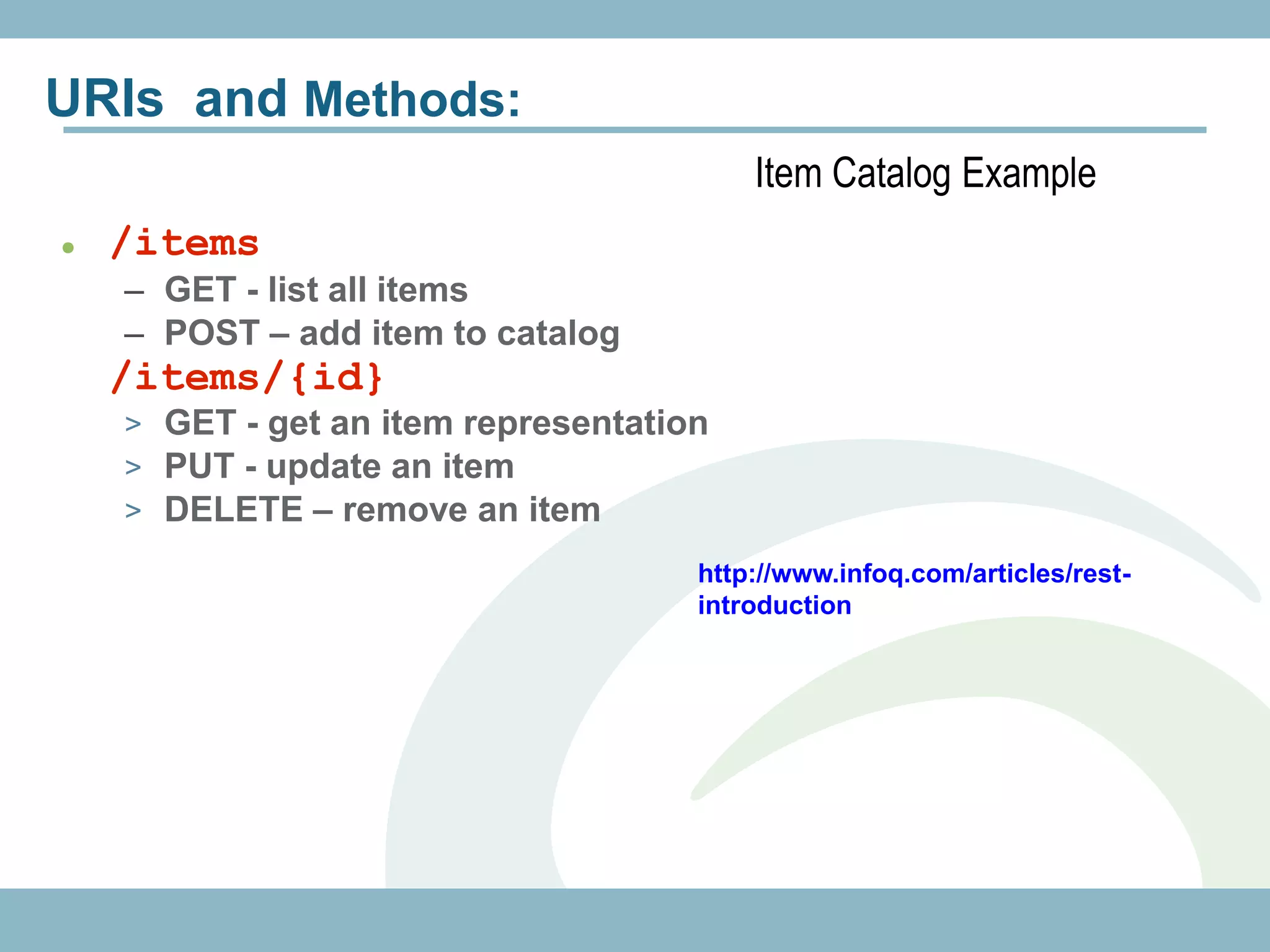
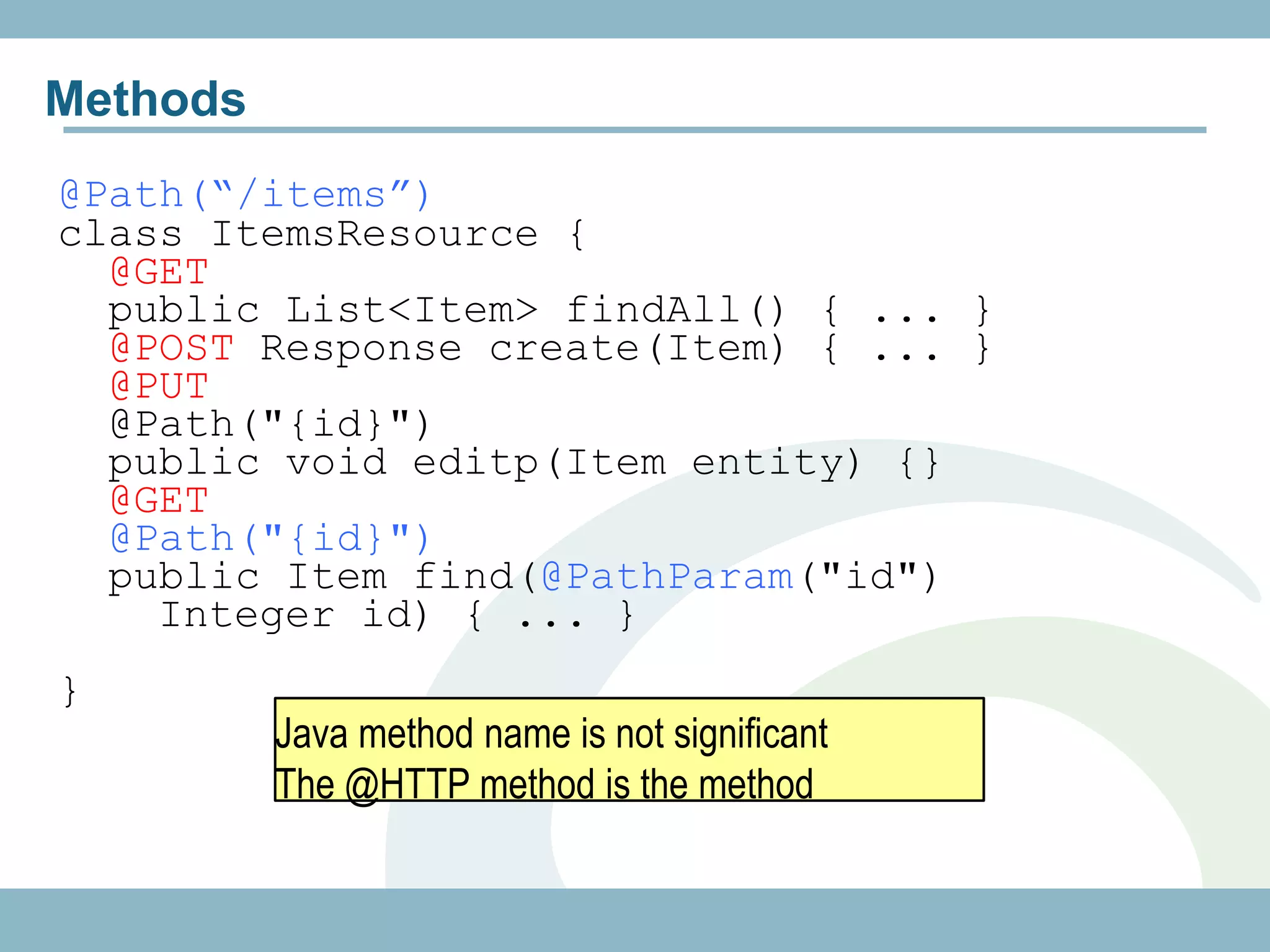
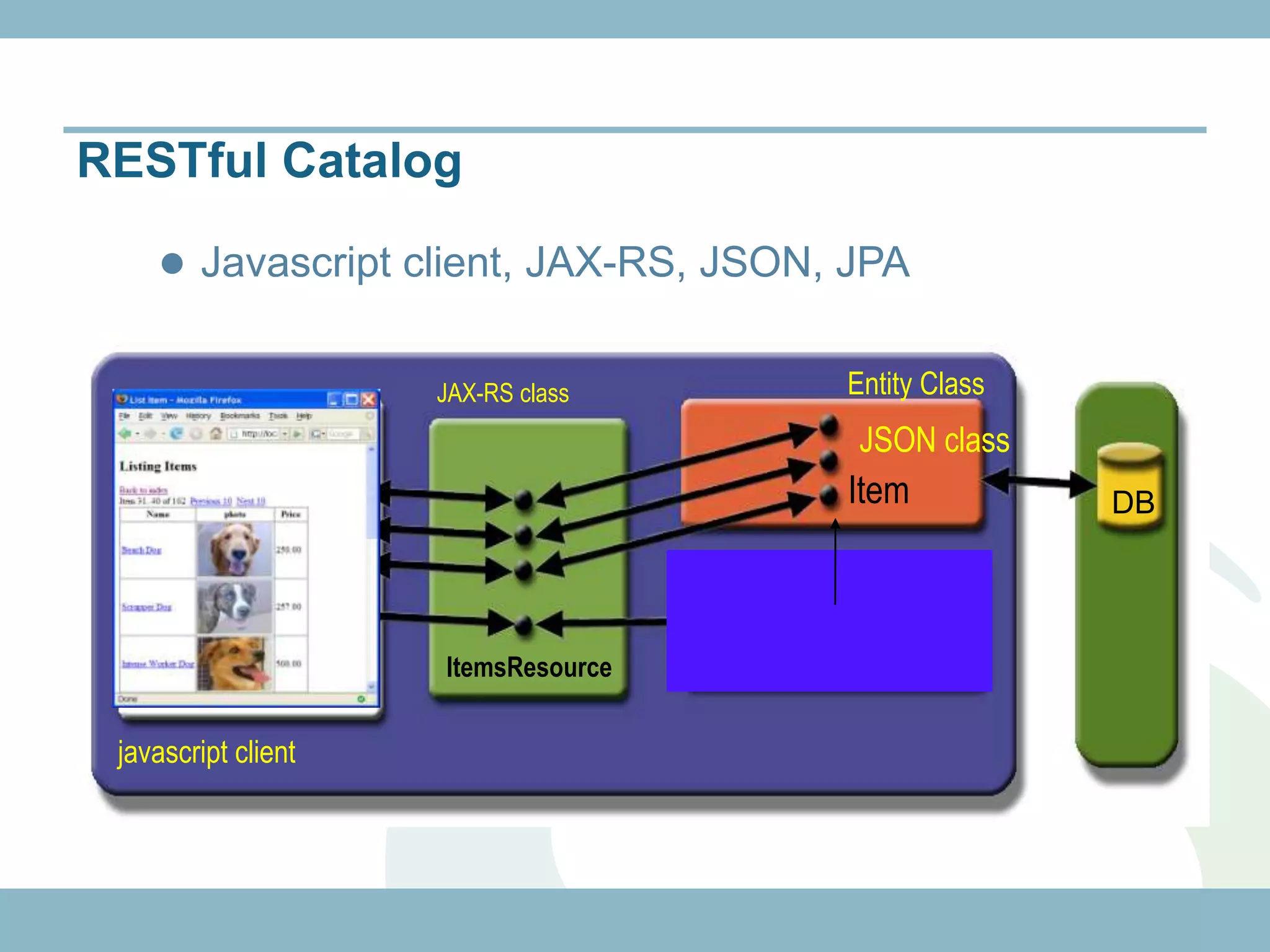
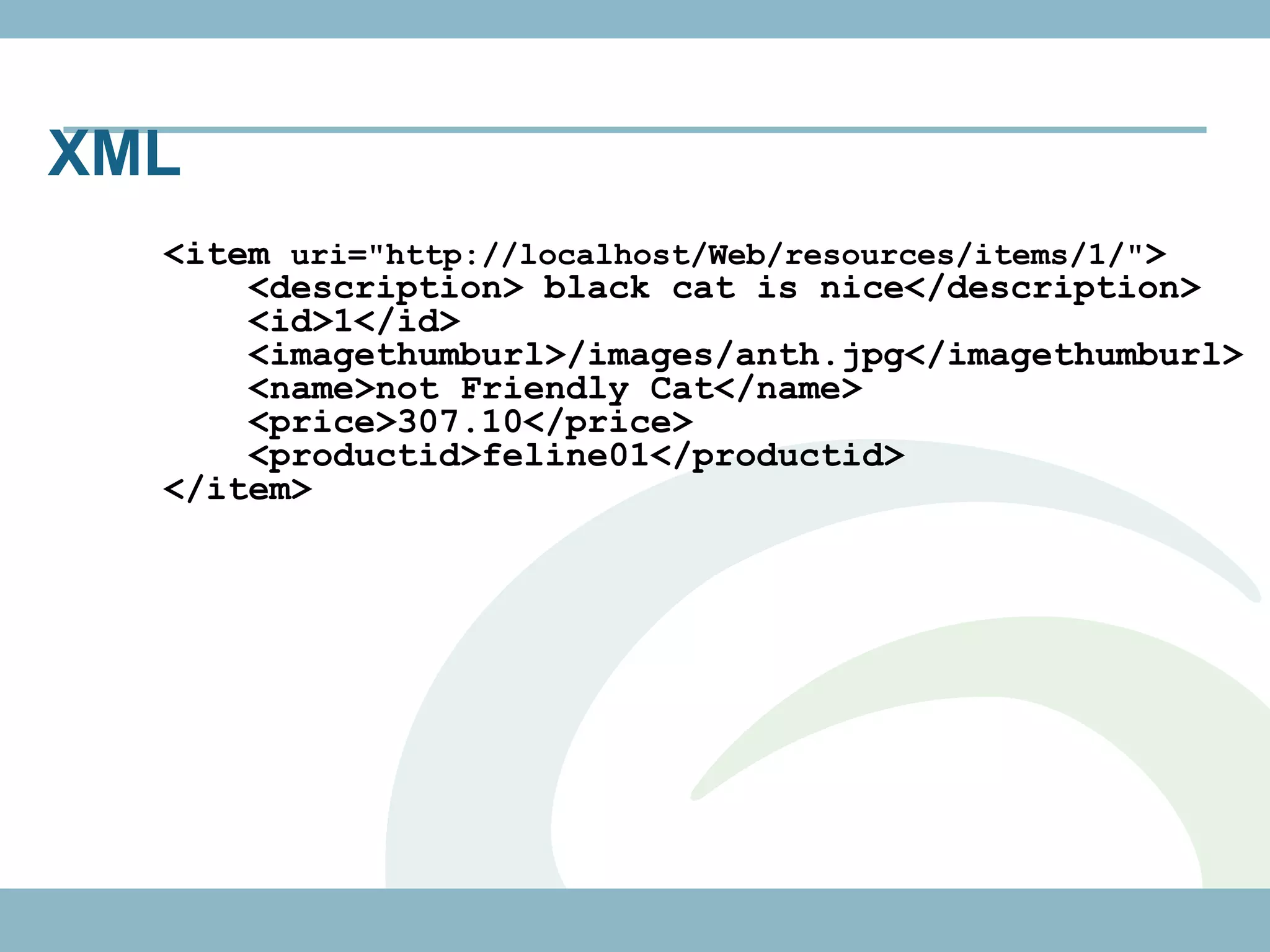
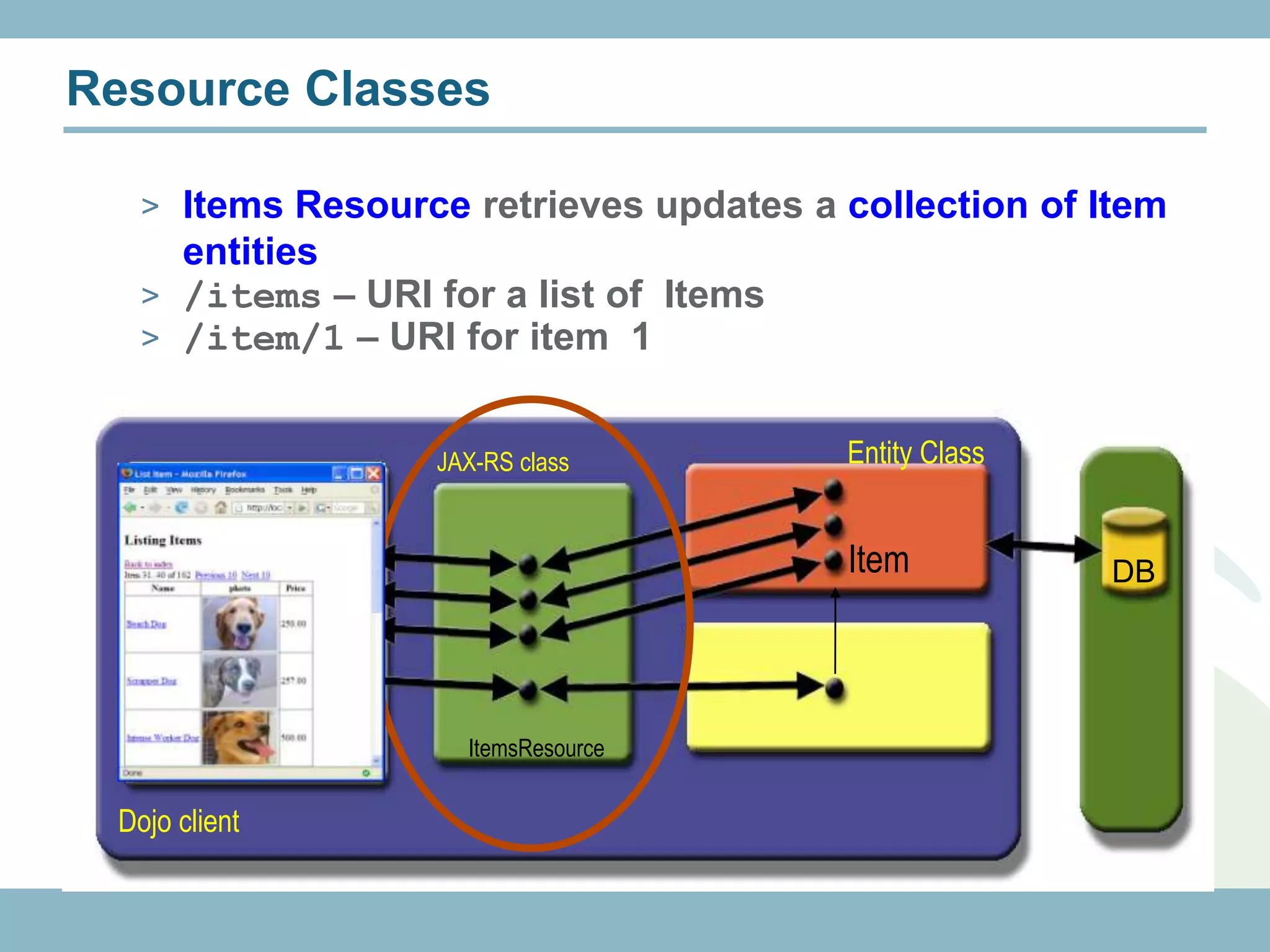
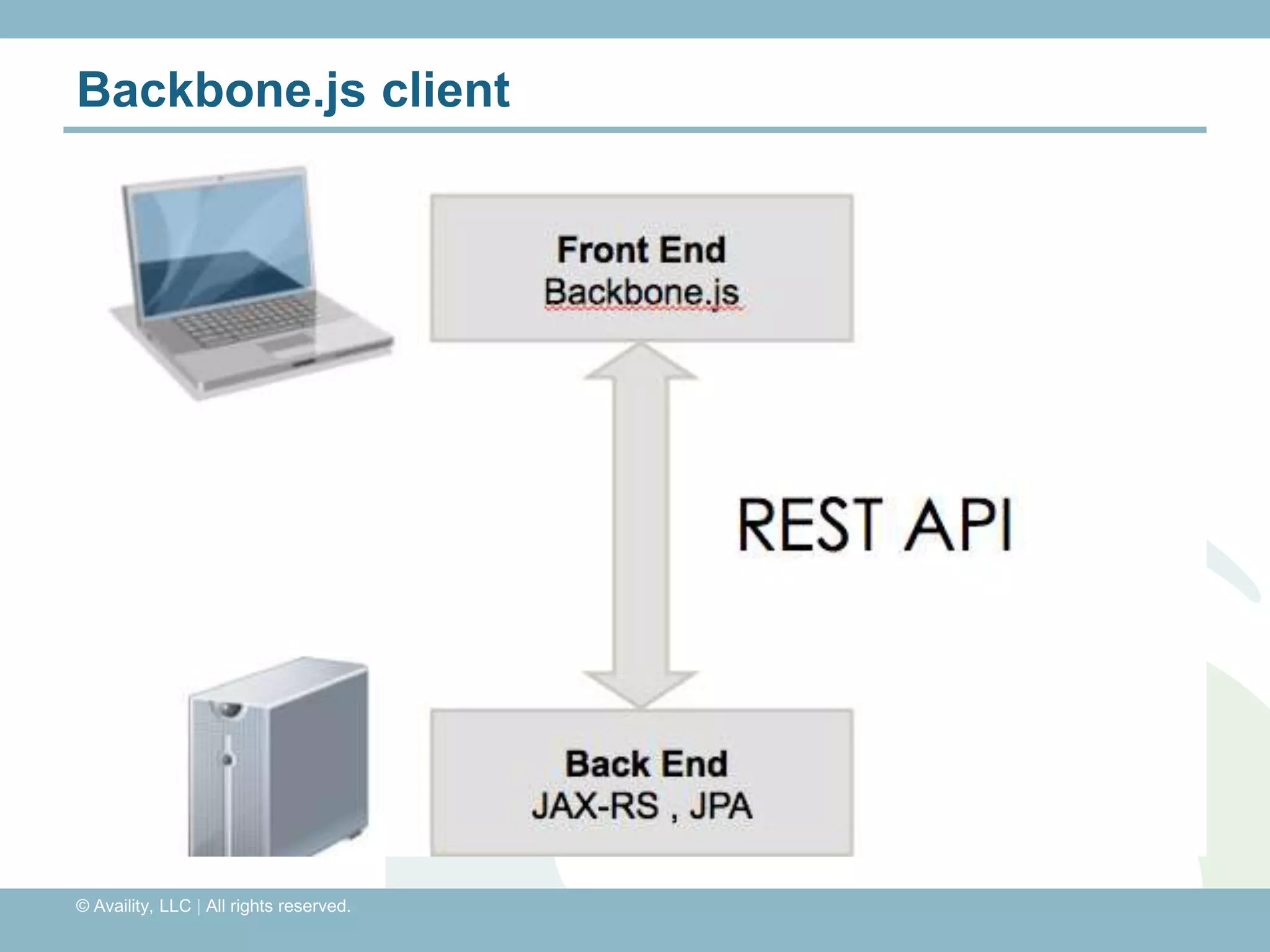
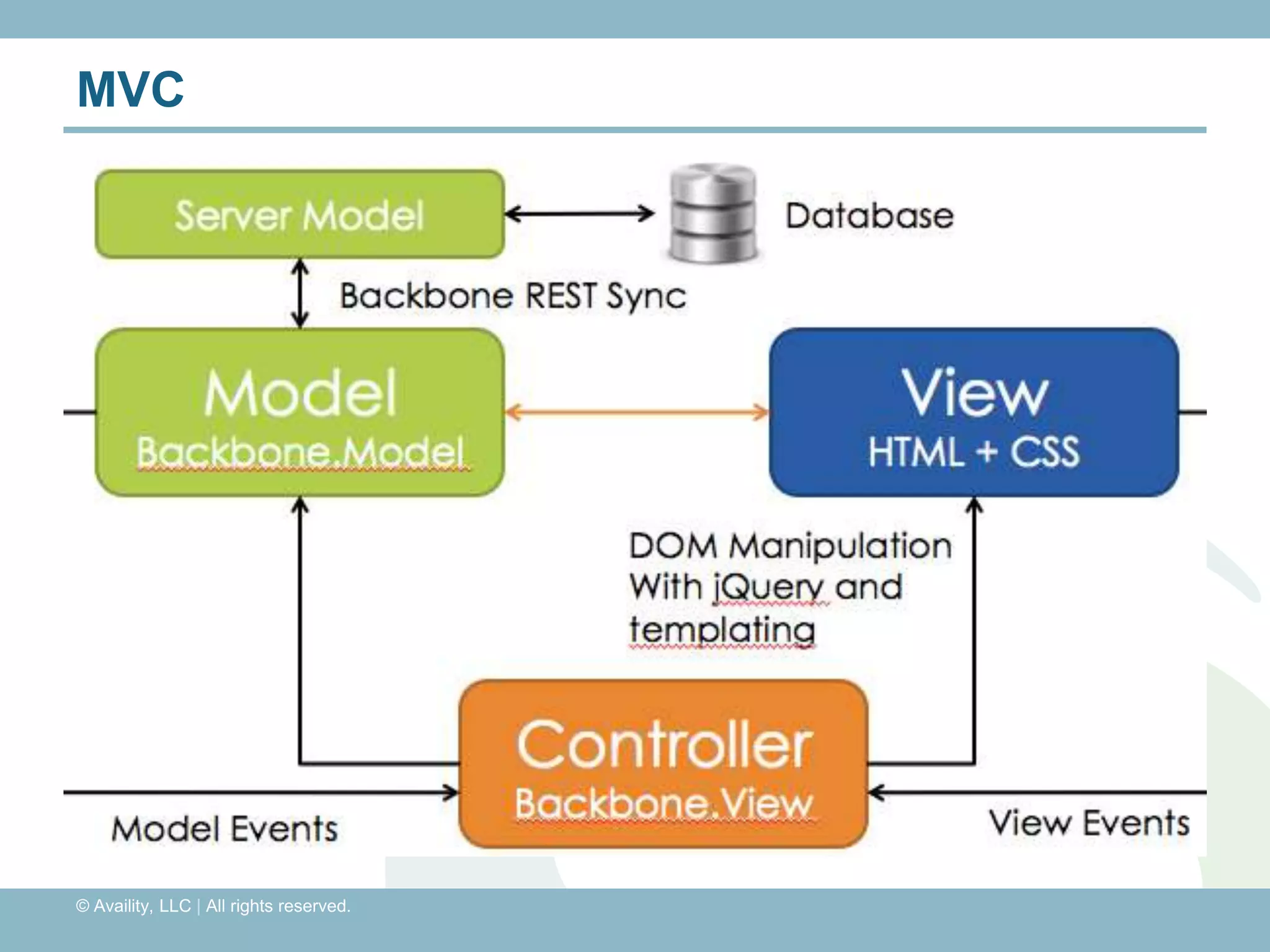
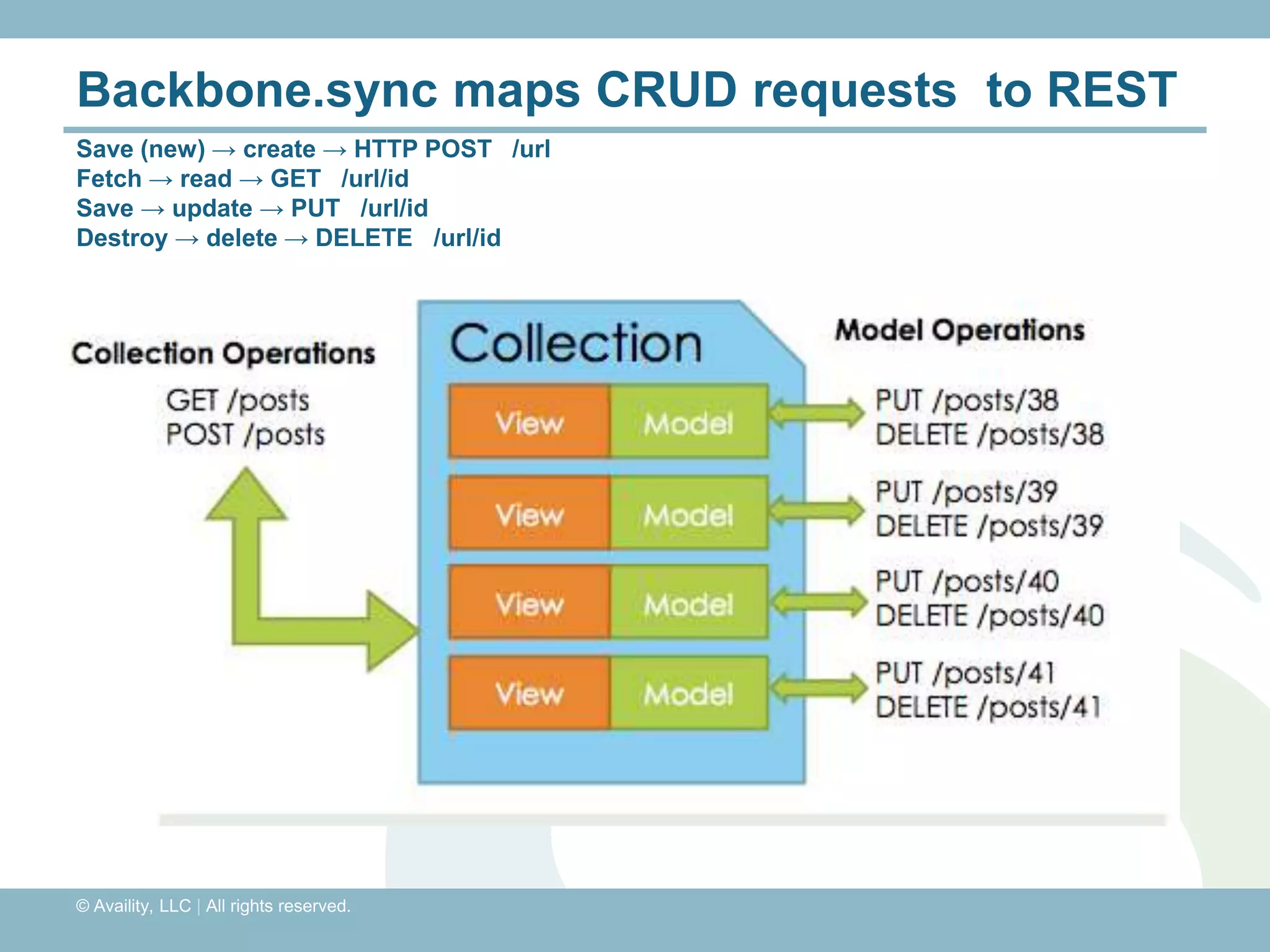
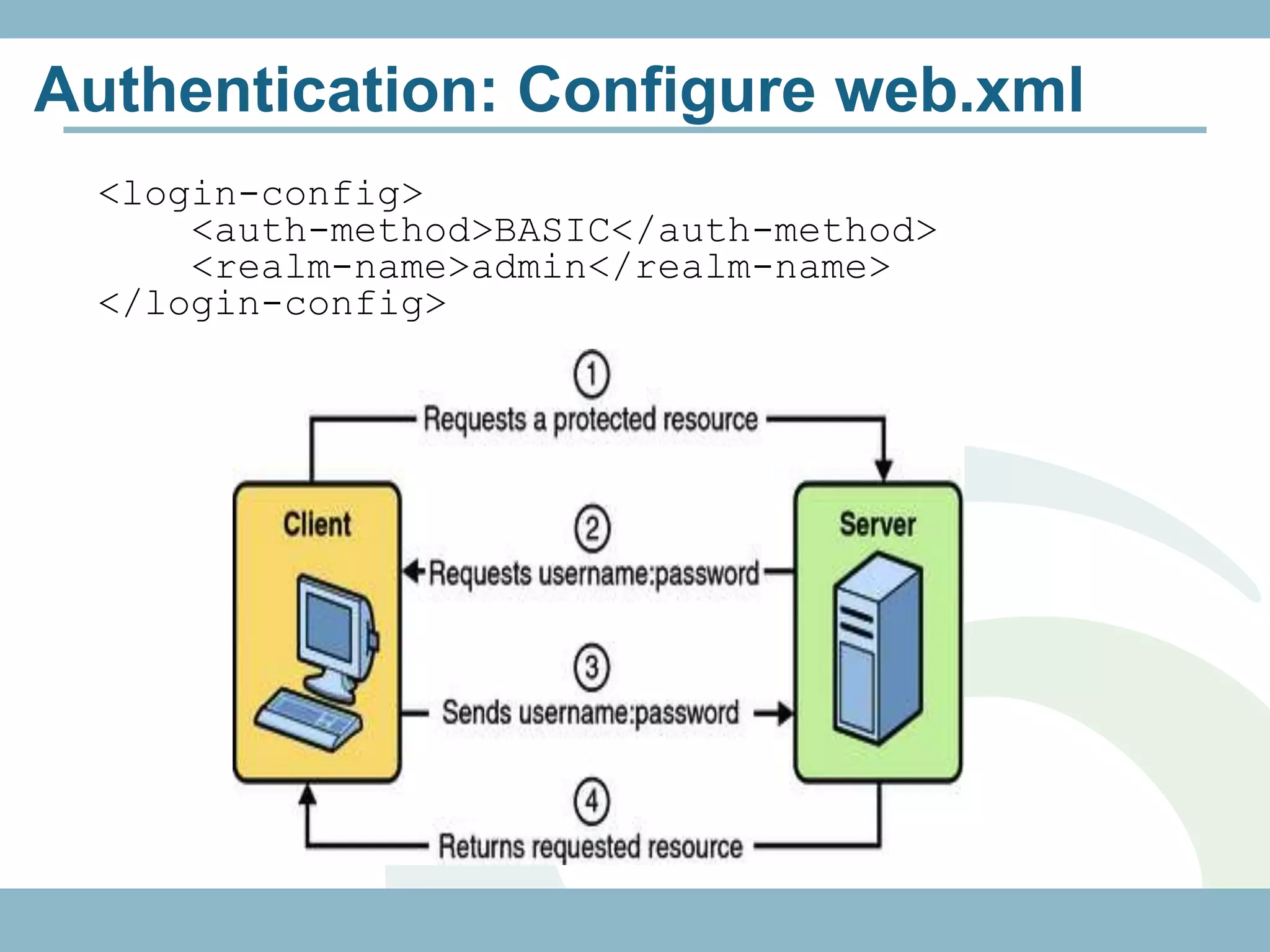
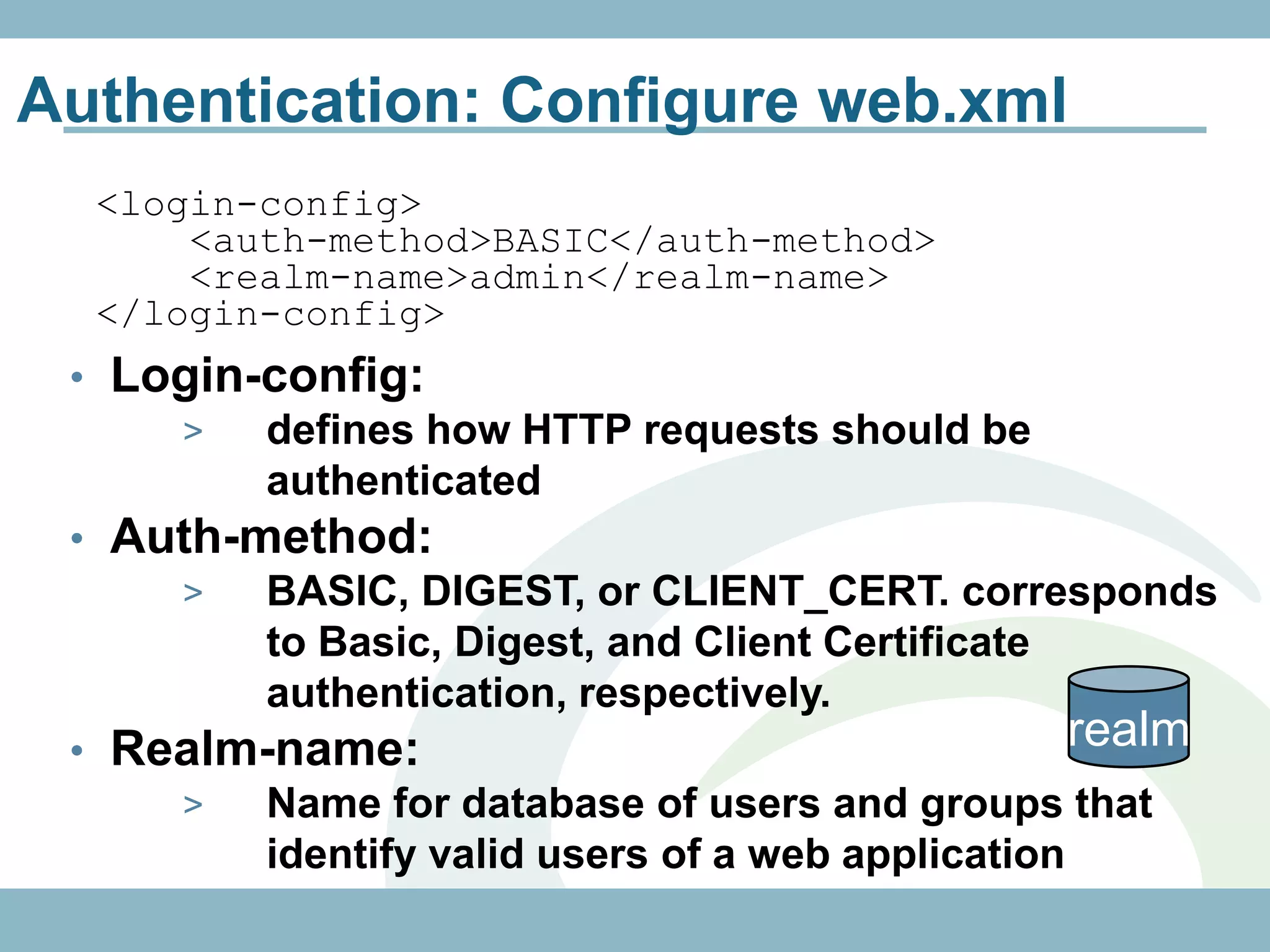
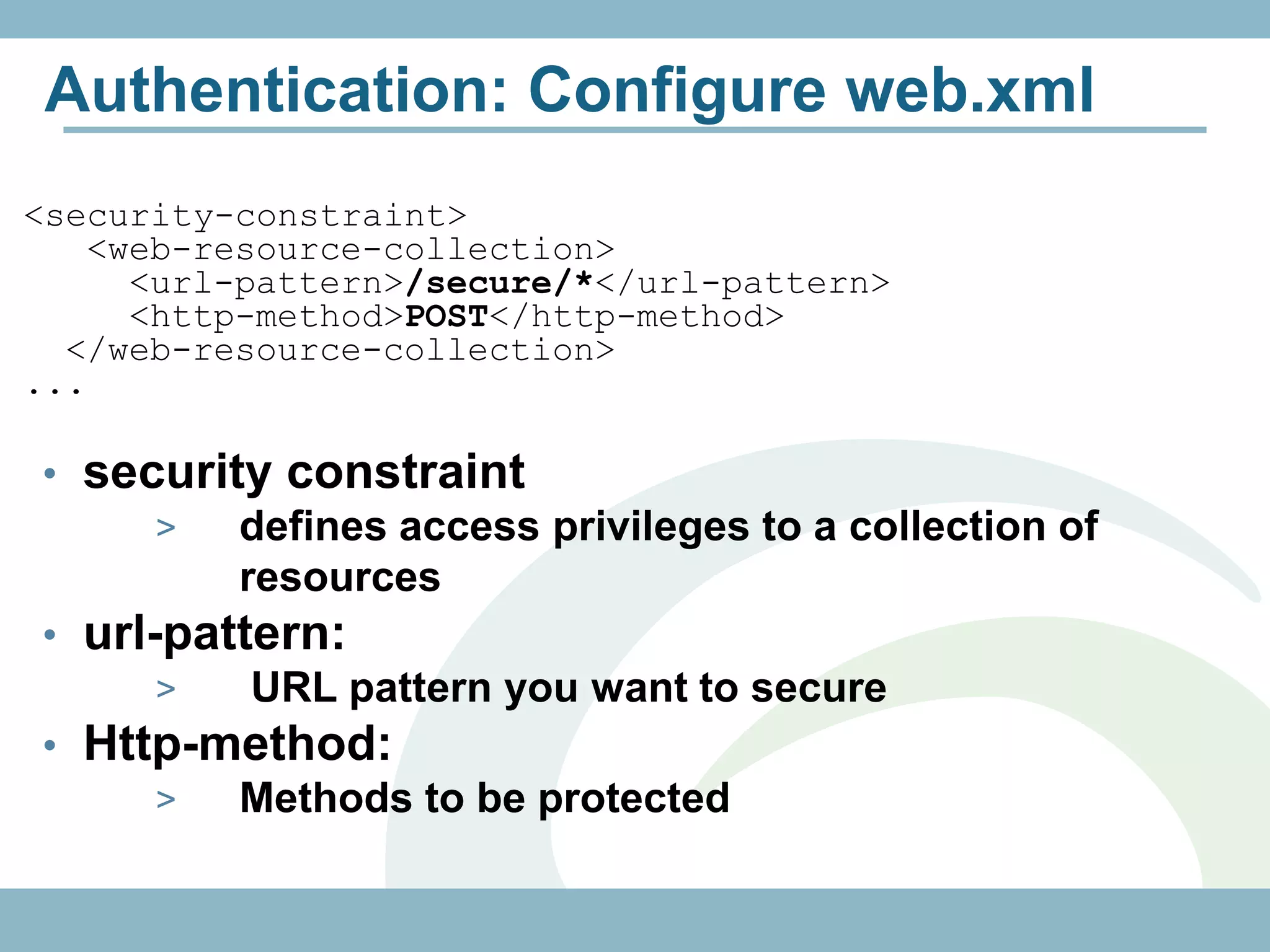
The document discusses REST with JAX-RS and security in Java EE 6, covering how to build a simple RESTful service using JAX-RS annotations to map resources and methods, support multiple representations, and link resources together, and how to secure the service by configuring authentication, authorization, and encryption in the web.xml deployment descriptor.



















![Authorization Annotations
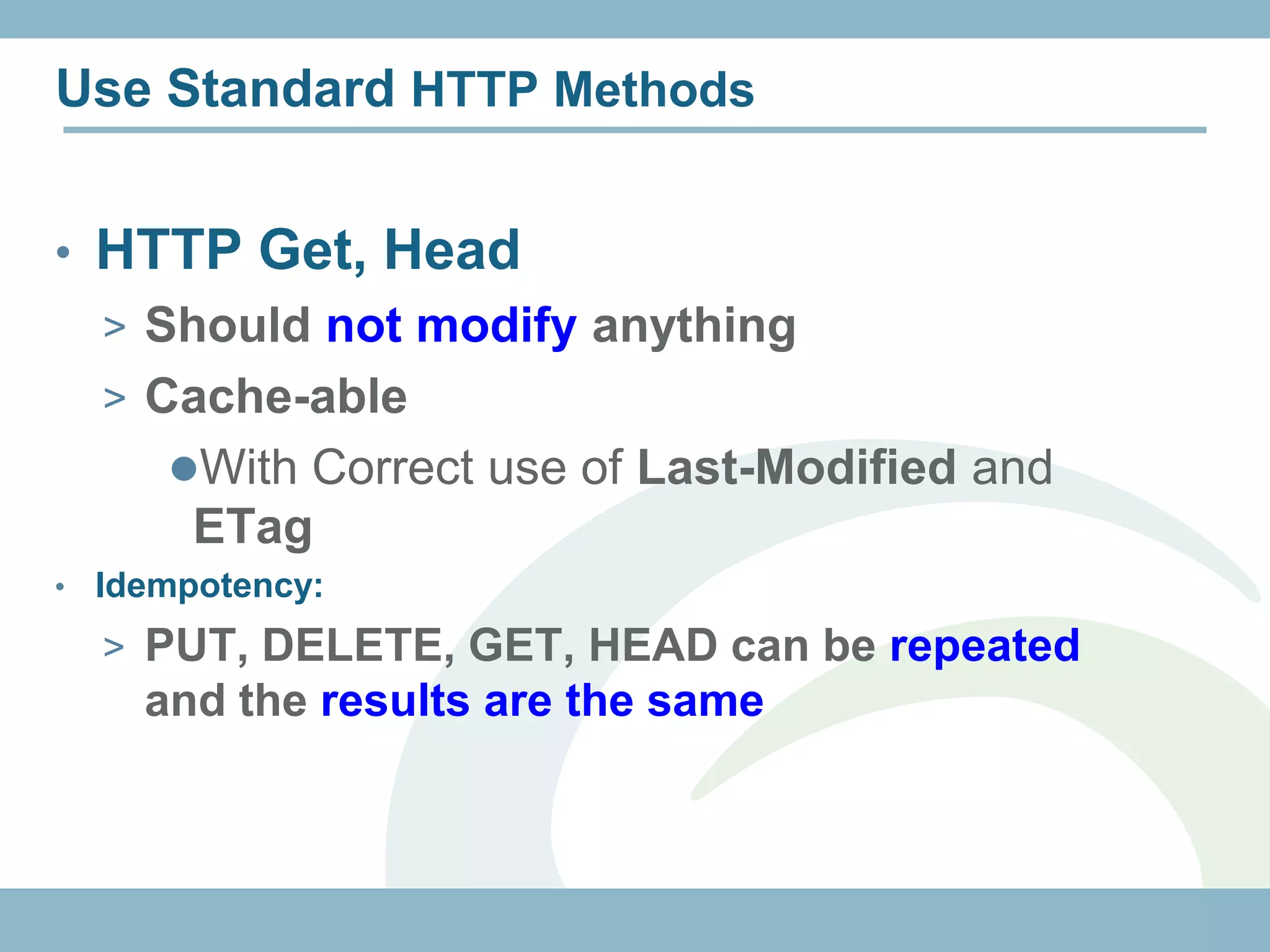
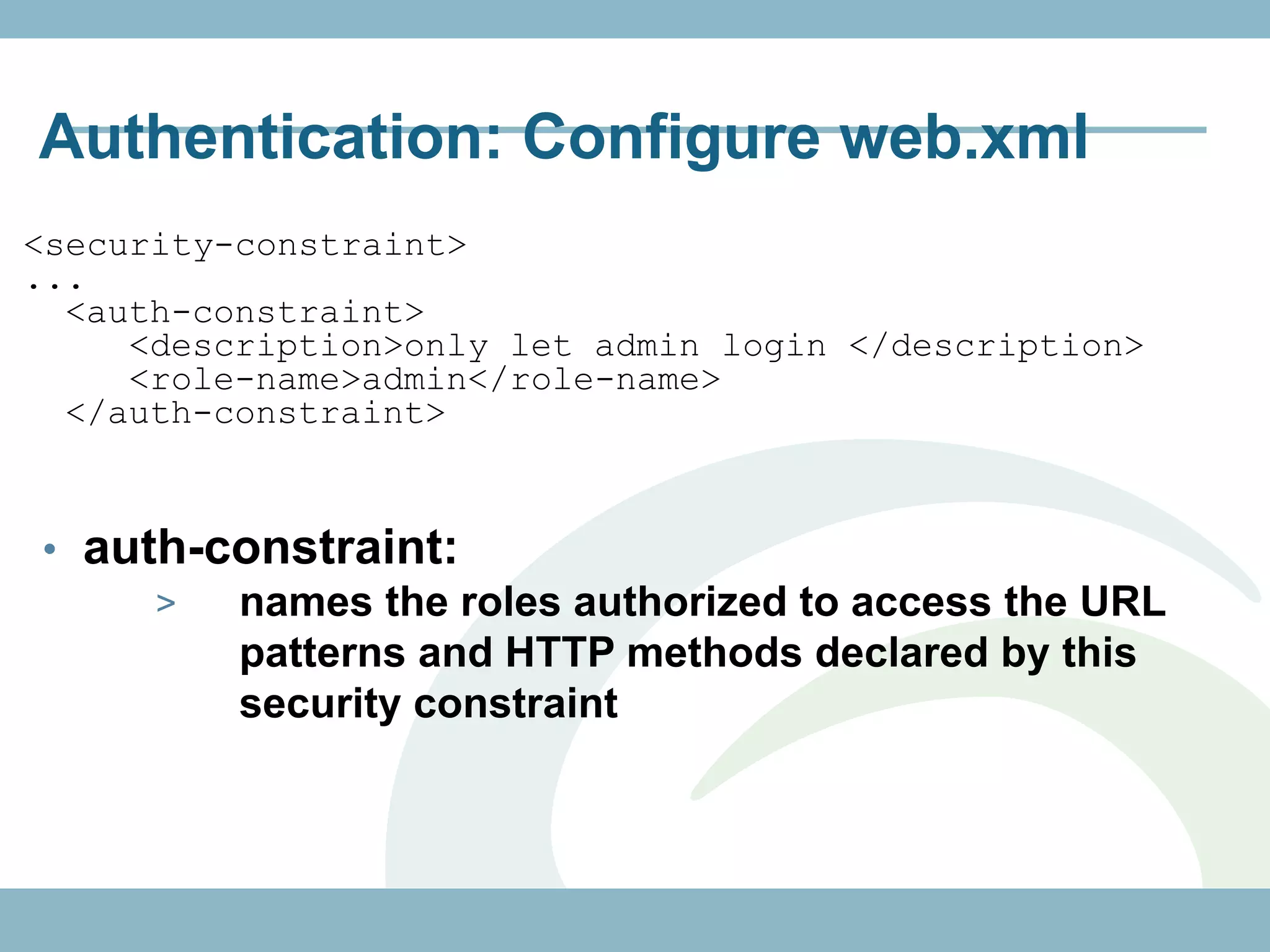
roles permitted to execute operation
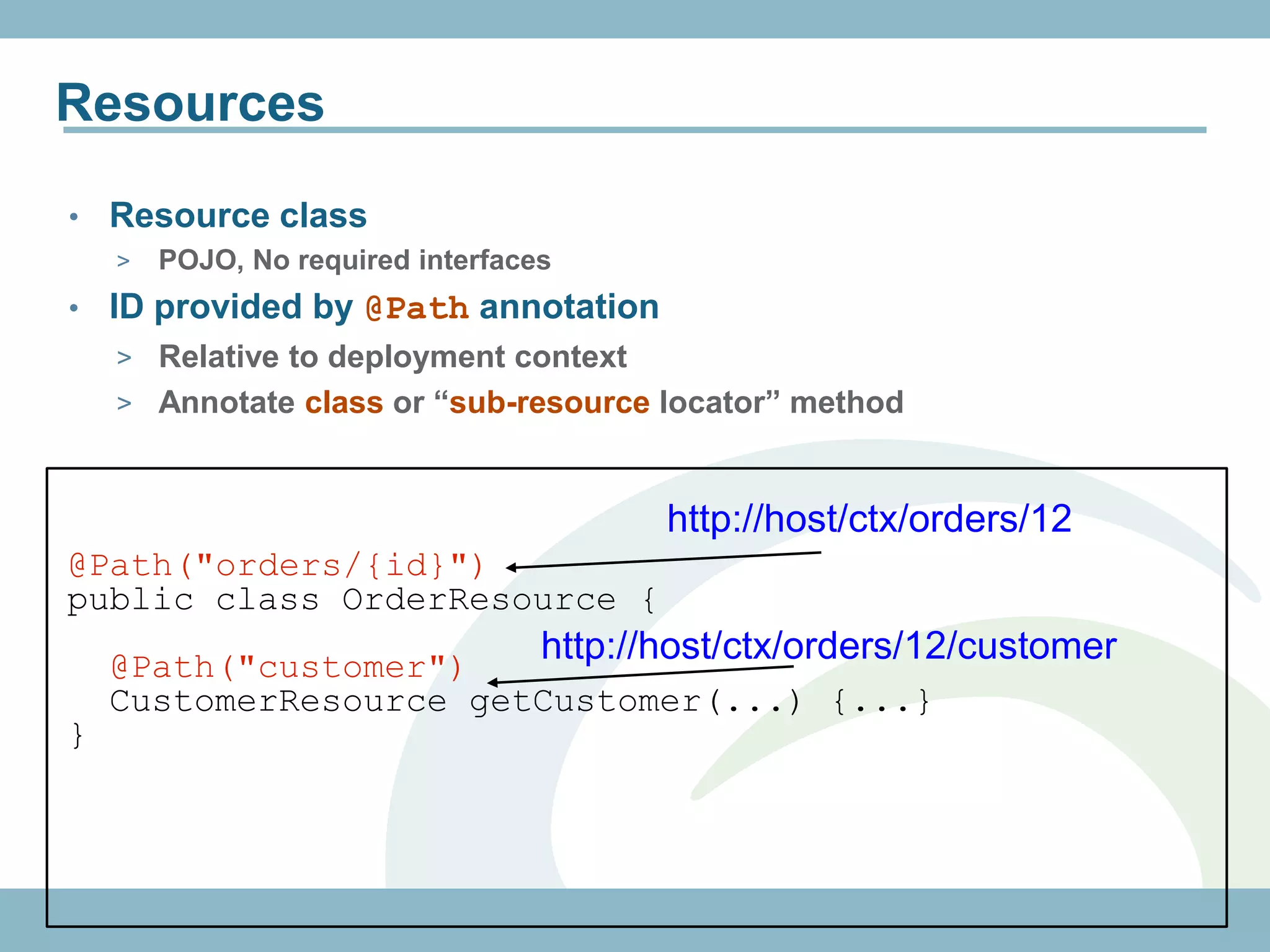
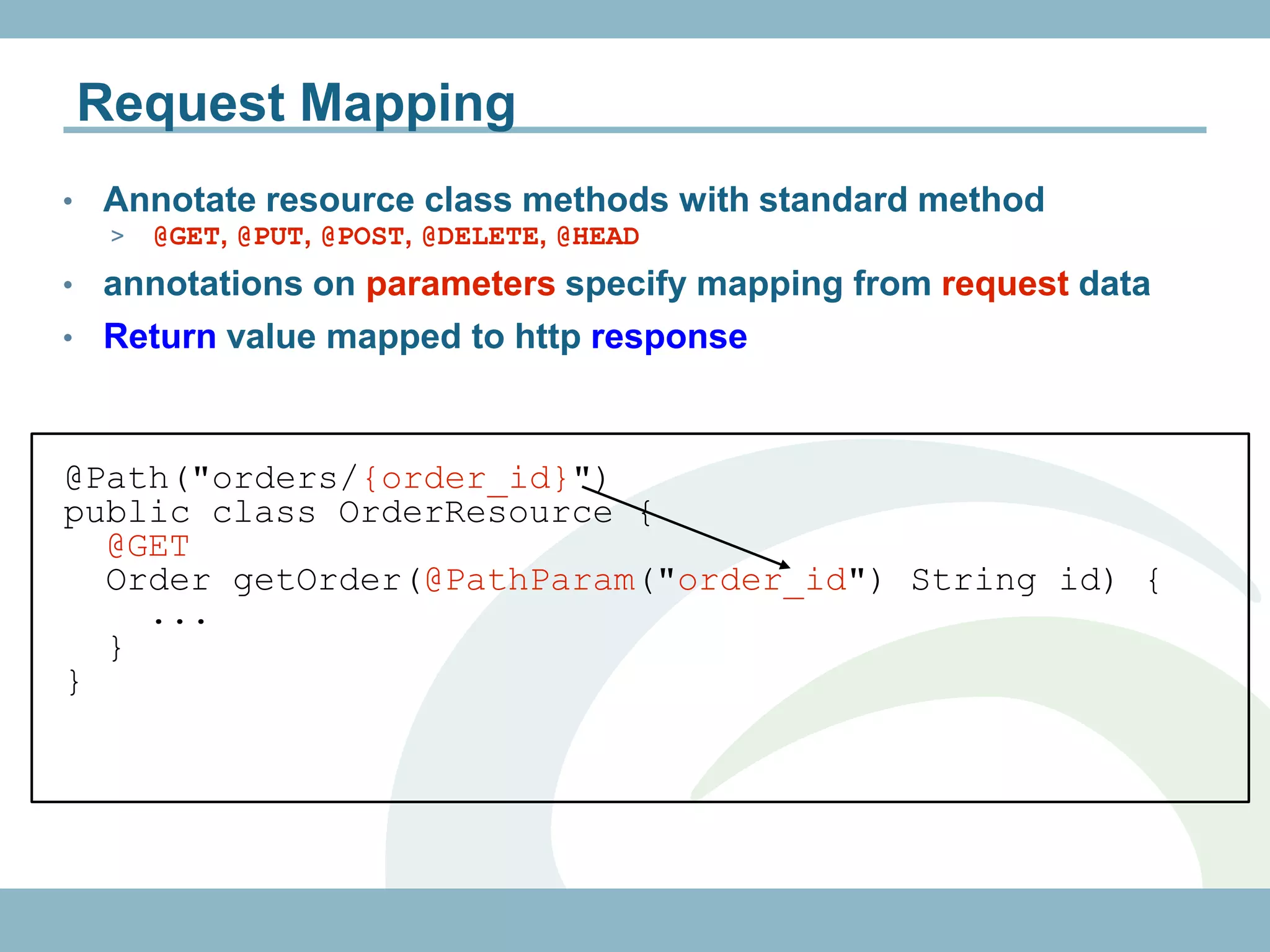
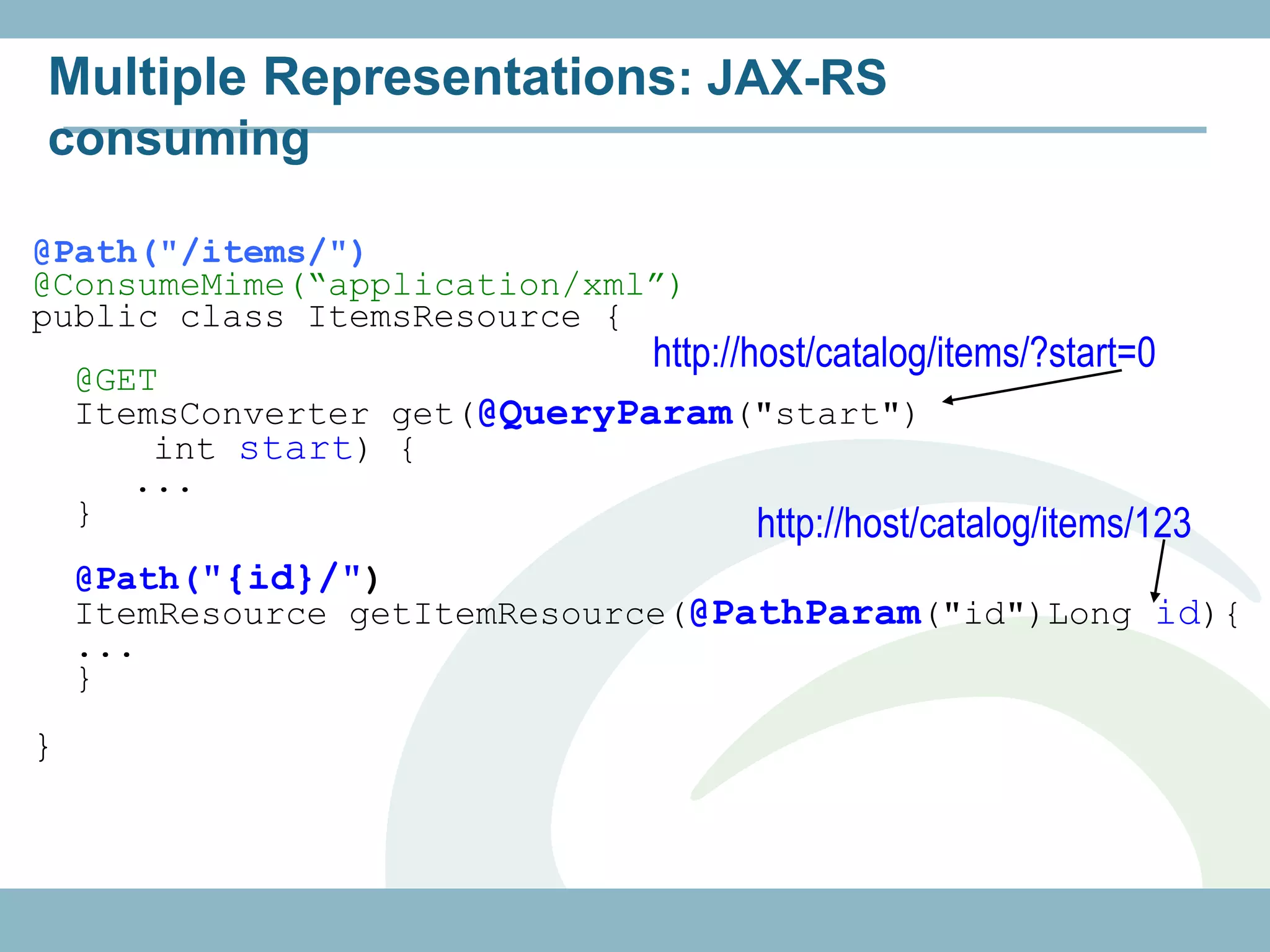
@Path("/customers")
@RolesAllowed({"ADMIN", "CUSTOMER"})
public class CustomerResource {
@GET
@Path("{id}")
@Produces("application/xml")
public Customer getCustomer(@PathParam("id")
int id) {...}
@RolesAllowed("ADMIN")
@POST
@Consumes("application/xml")
public void createCustomer(Customer cust) {...}
@PermitAll
@GET
@Produces("application/xml") authenticated user
any
public Customer[] getCustomers() {}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rest-121214142106-phpapp01/75/Rest-with-Java-EE-6-Security-Backbone-js-57-2048.jpg)
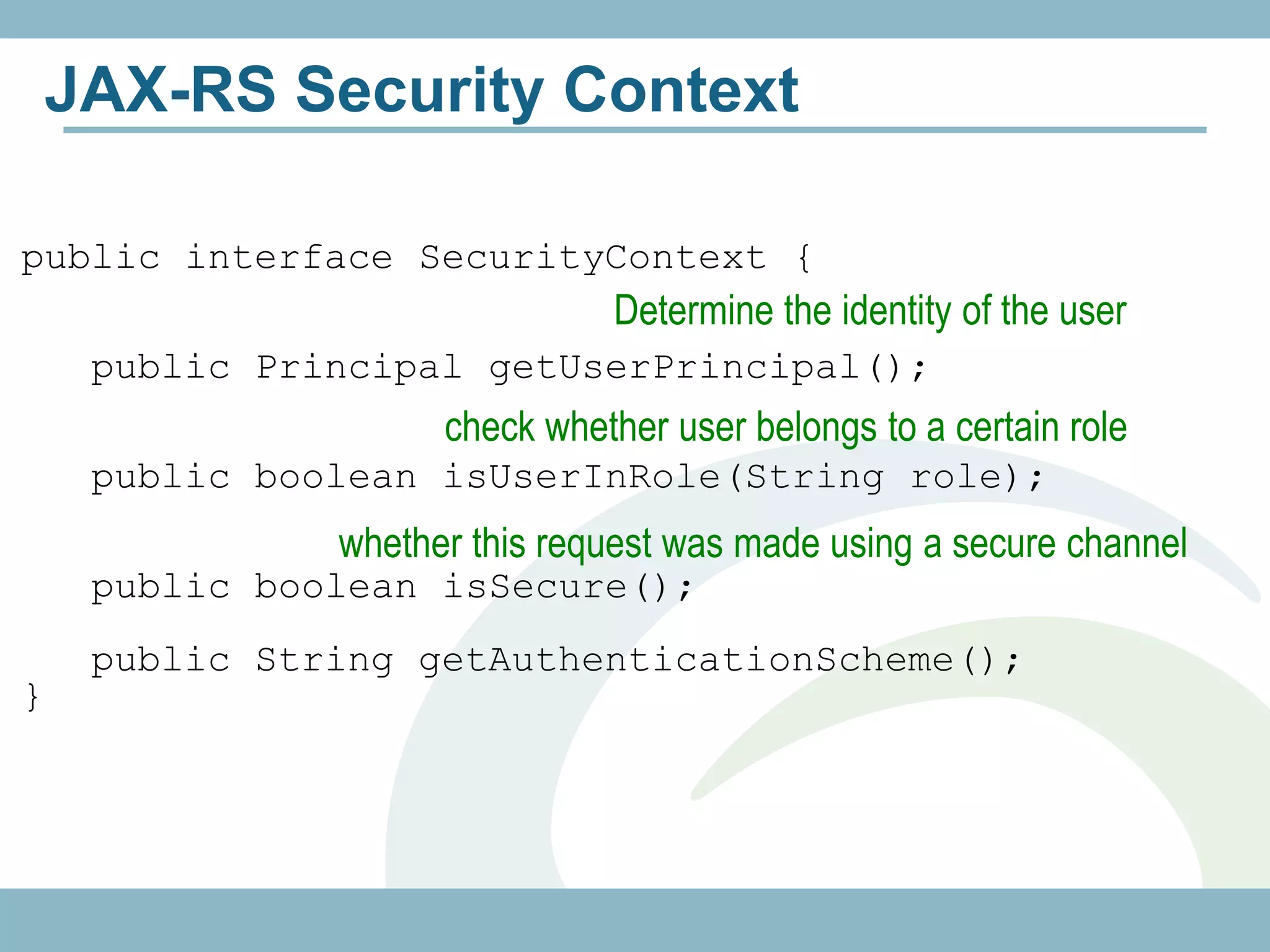
![JAX-RS Security Context
@Path("/customers") check whether user
public class CustomerService { belongs to a certain role
@GET
@Produces("application/xml")
public Customer[] getCustomers(@Context
SecurityContext sec) {
if (sec.isSecure() && !sec.isUserInRole("ADMIN")){
logger.log(sec.getUserPrincipal() +
" accessed customer database.");
}
...
}
}
Determine the identity of the user](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rest-121214142106-phpapp01/75/Rest-with-Java-EE-6-Security-Backbone-js-59-2048.jpg)