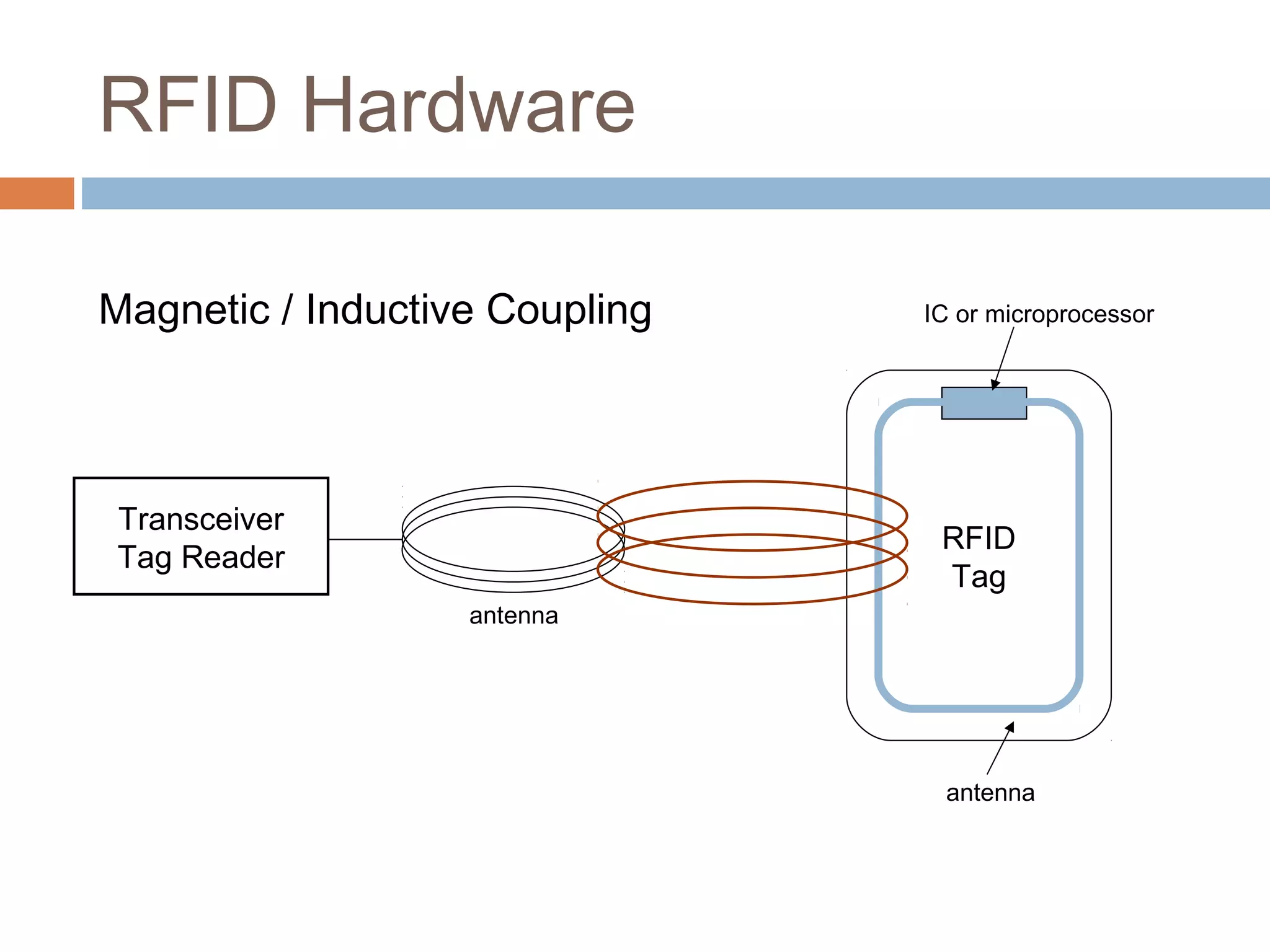
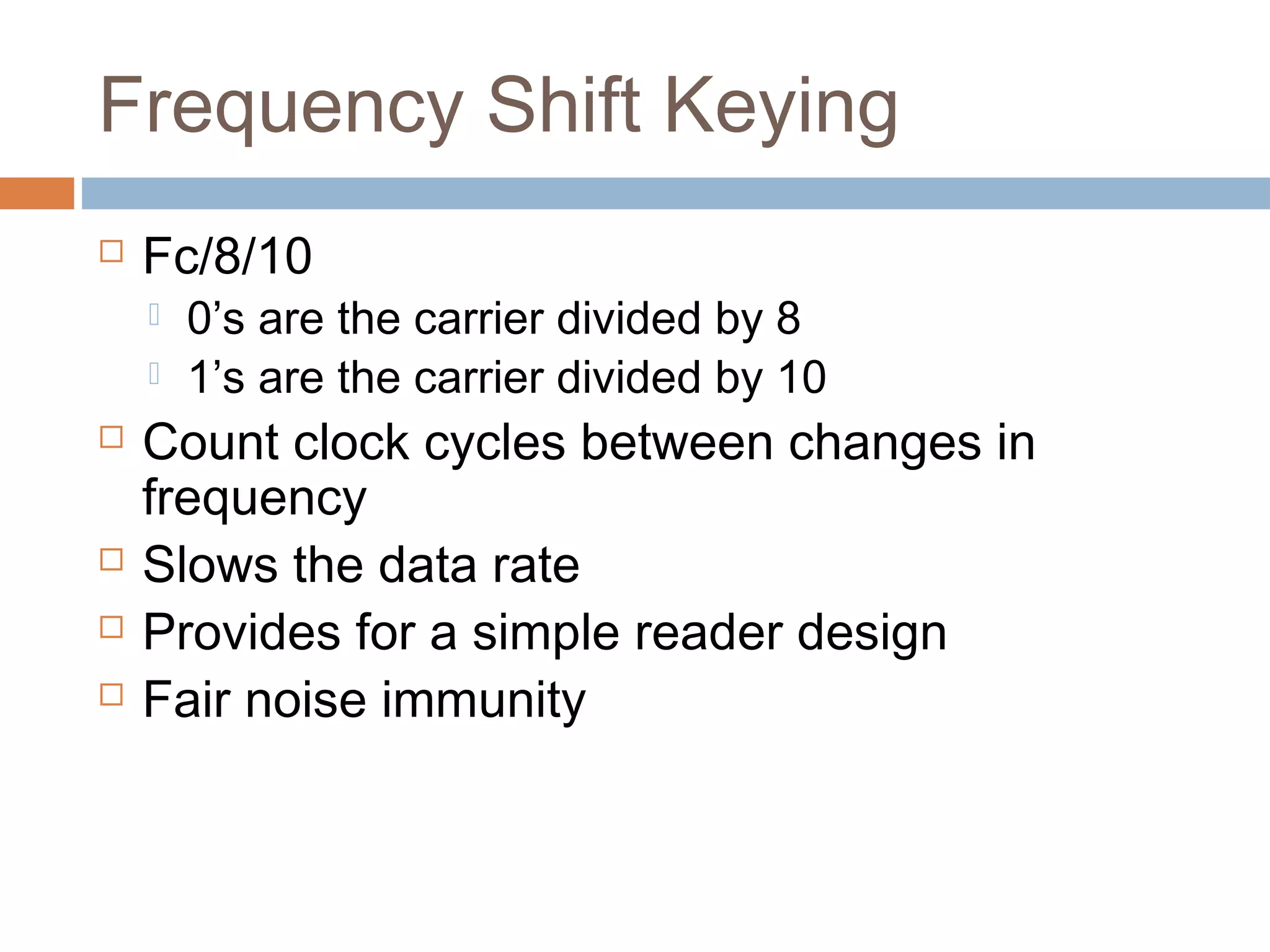
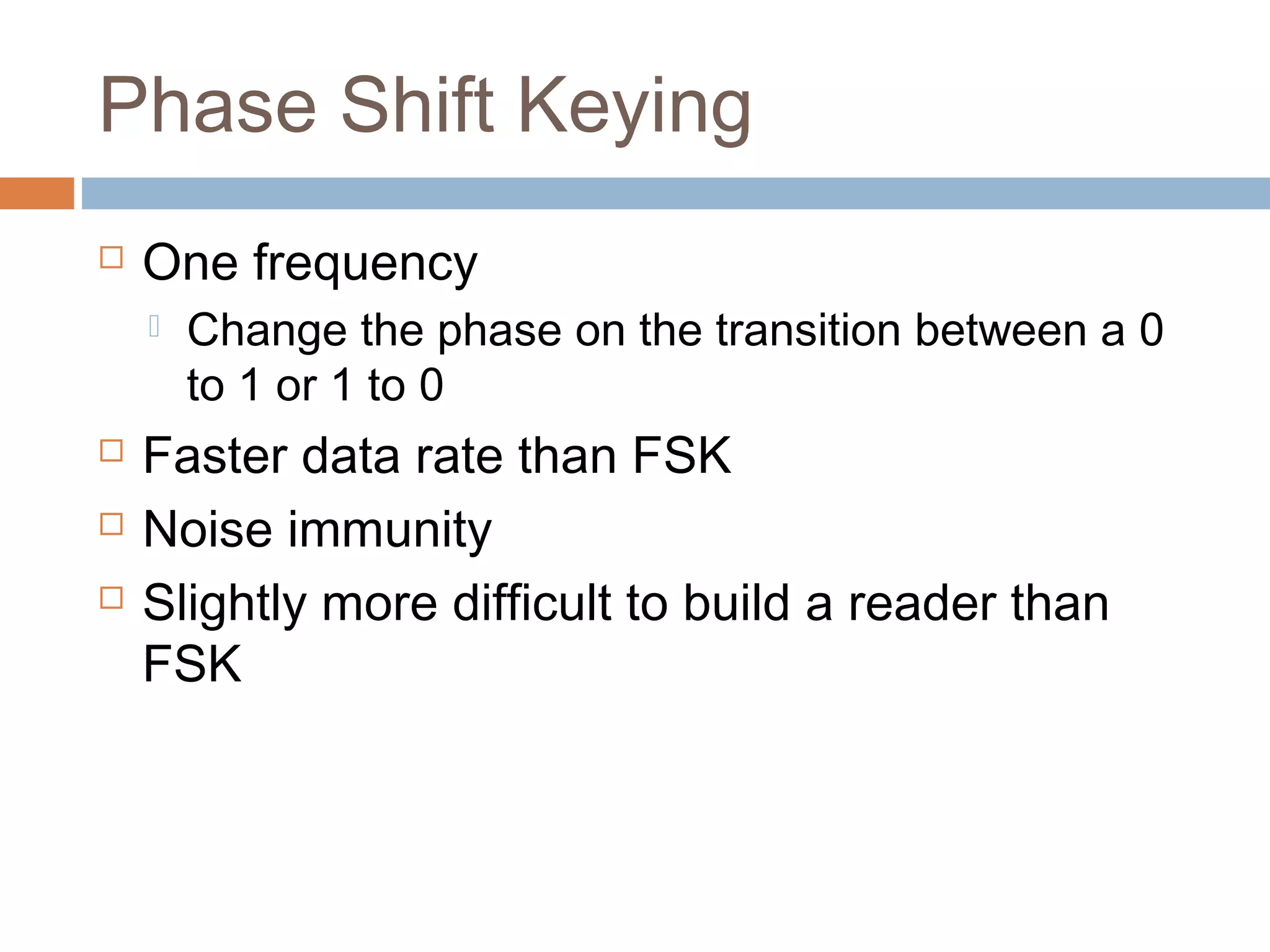
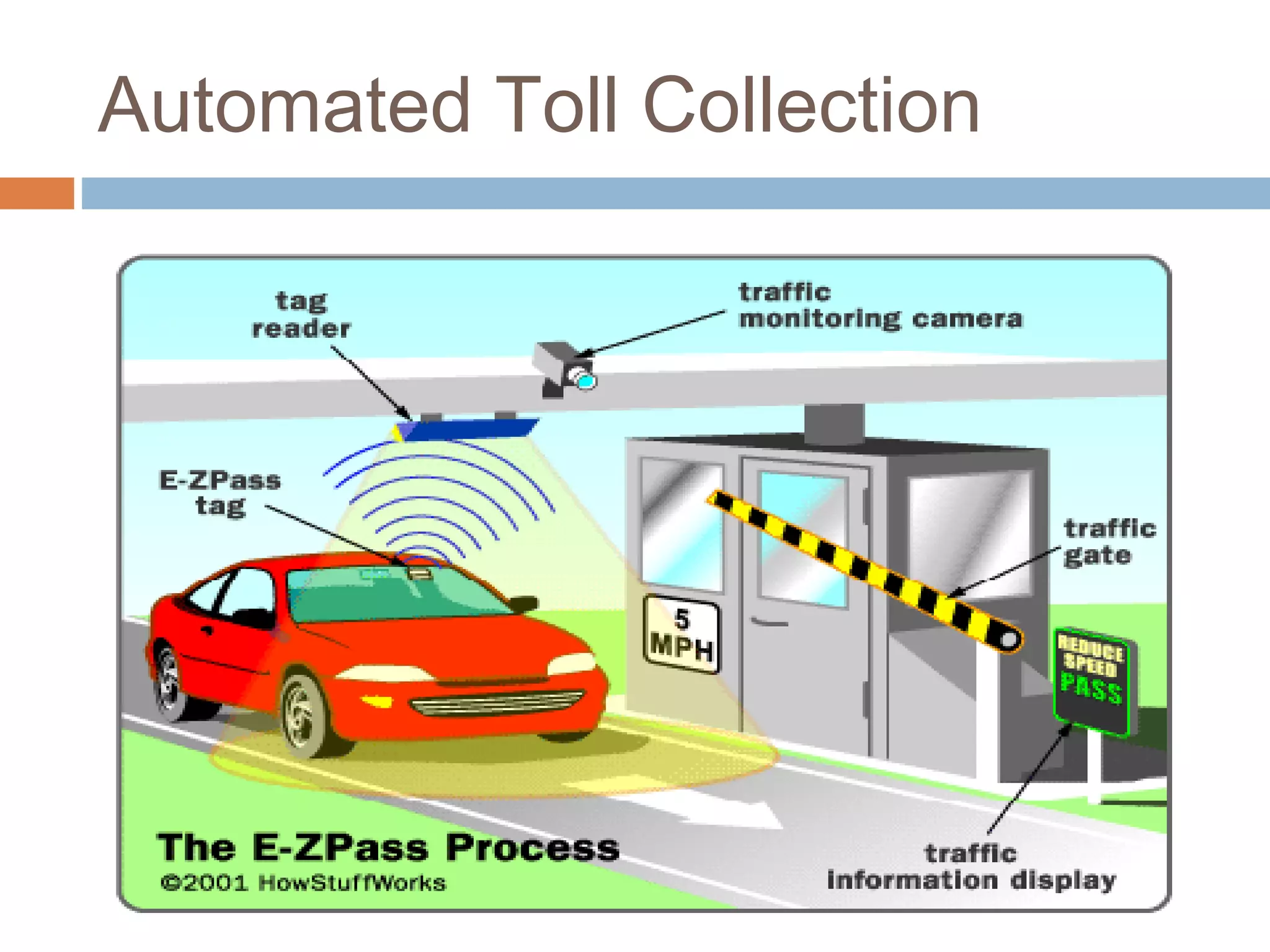
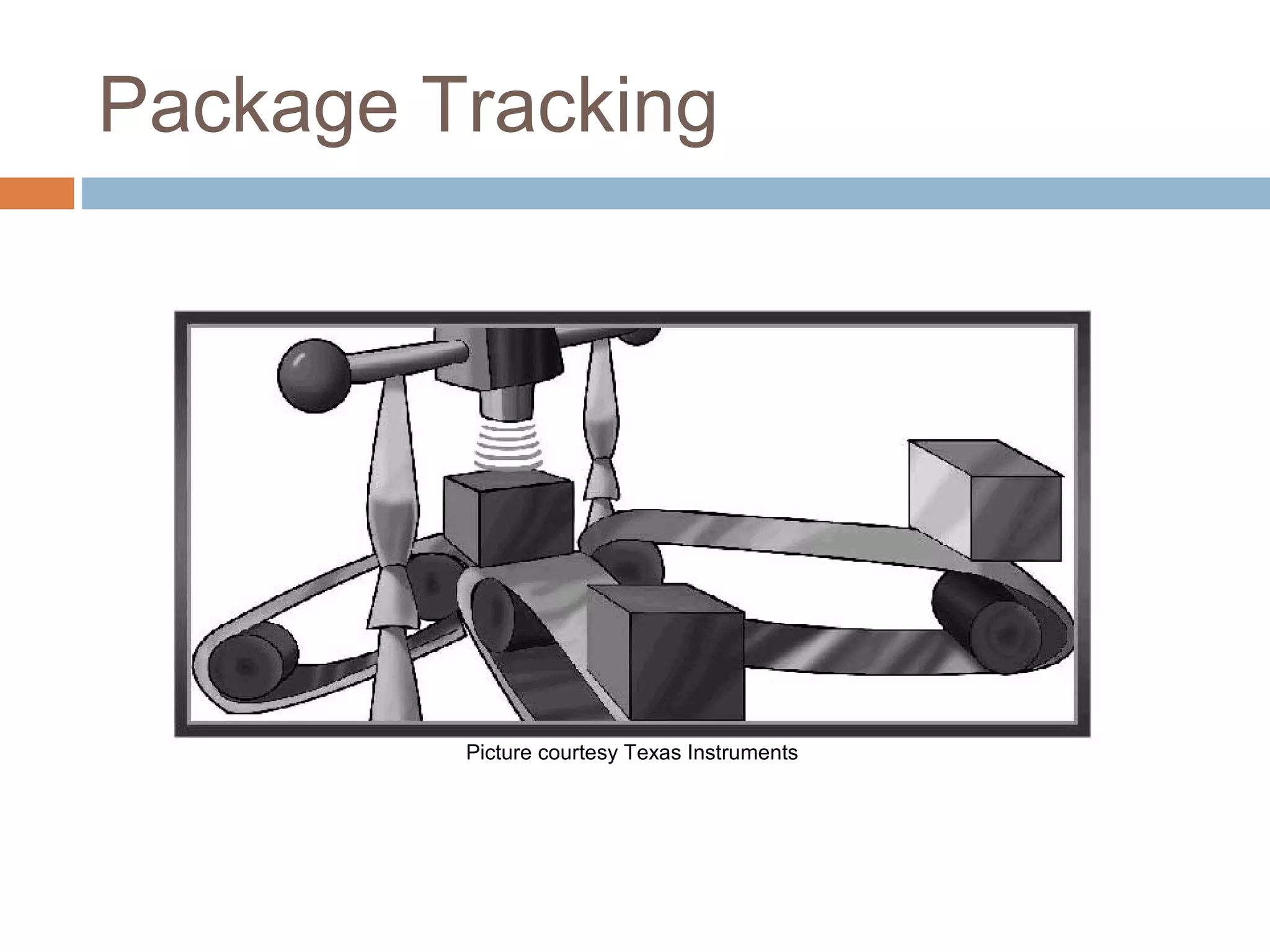
This document provides an overview of RFID (radio frequency identification) technology. It describes how RFID works using three main components: a transceiver or reader, an RFID tag, and an antenna. The document outlines the different types of RFID tags and how data is transferred. It also gives examples of current applications for RFID such as supply chain management, access control, and toll collection. Finally, it discusses some advantages and disadvantages of the technology.