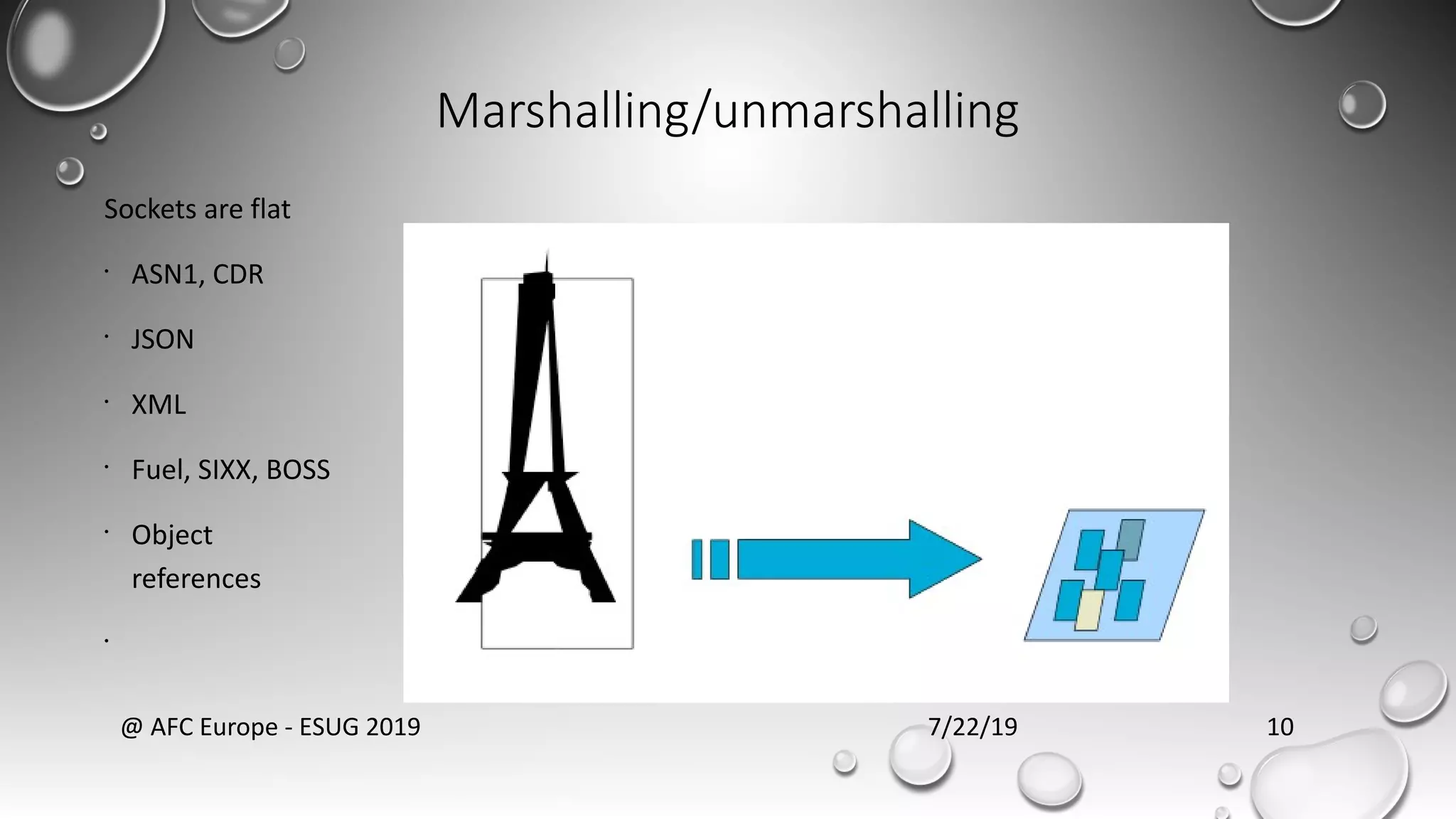
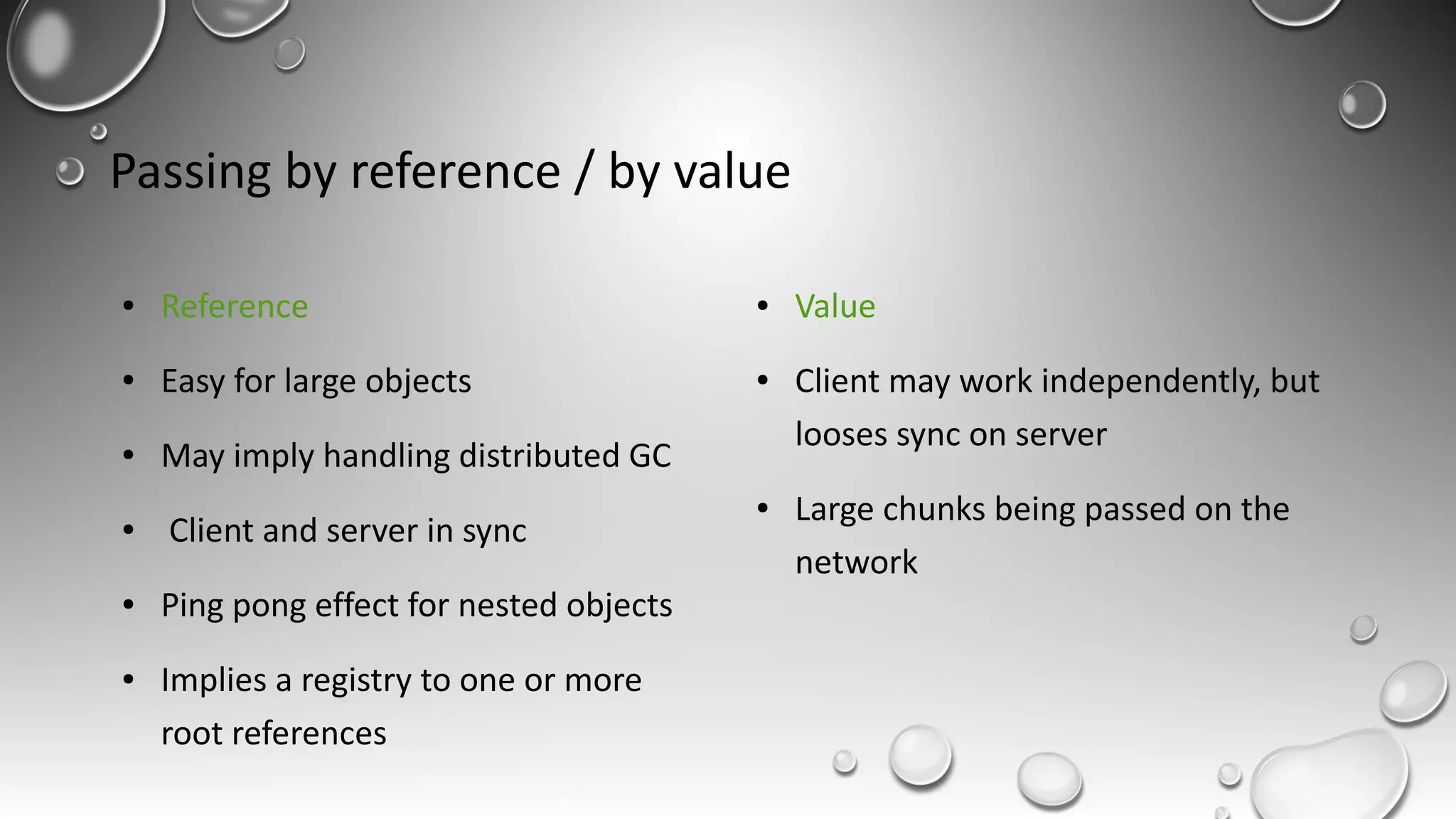
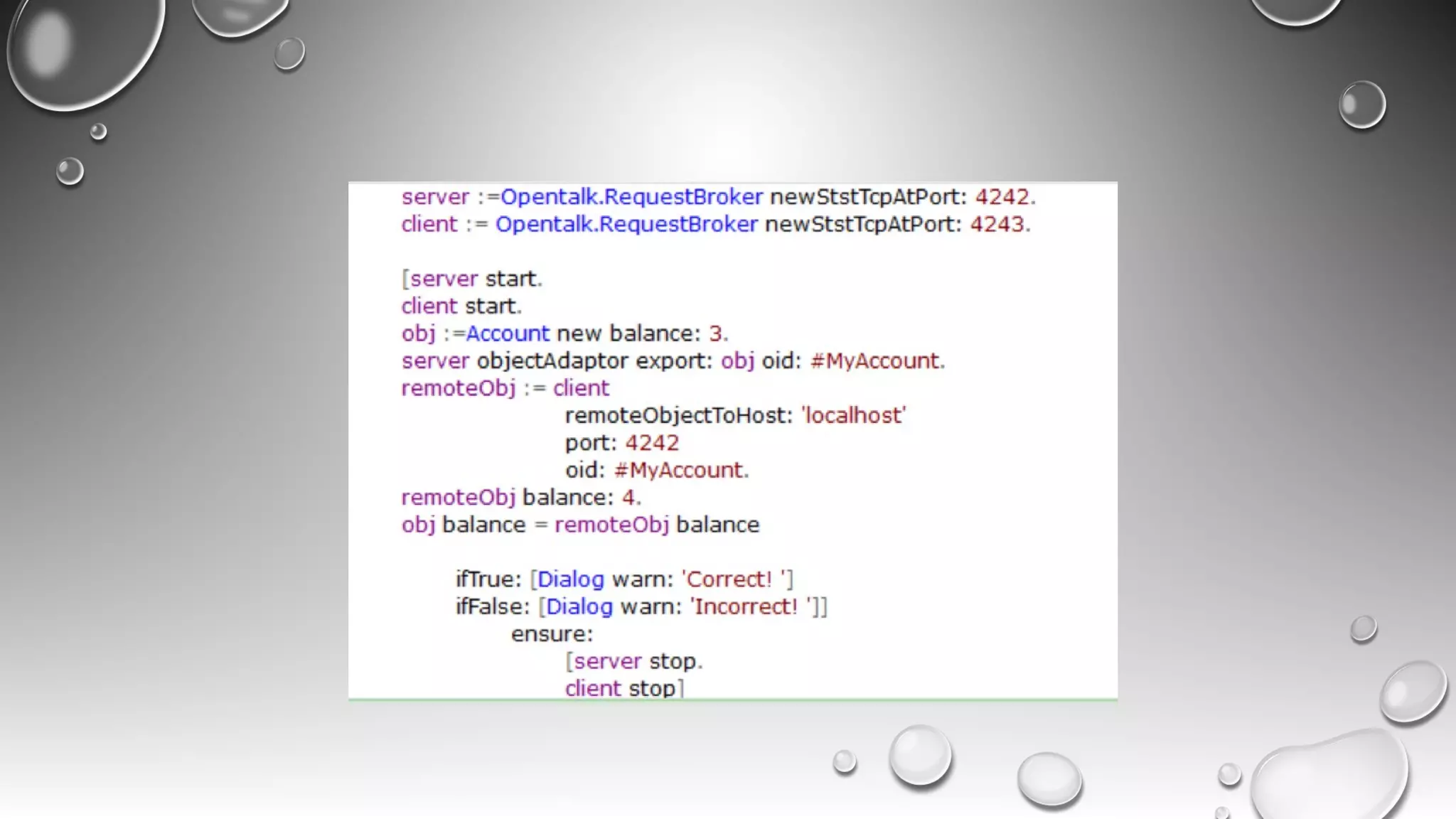
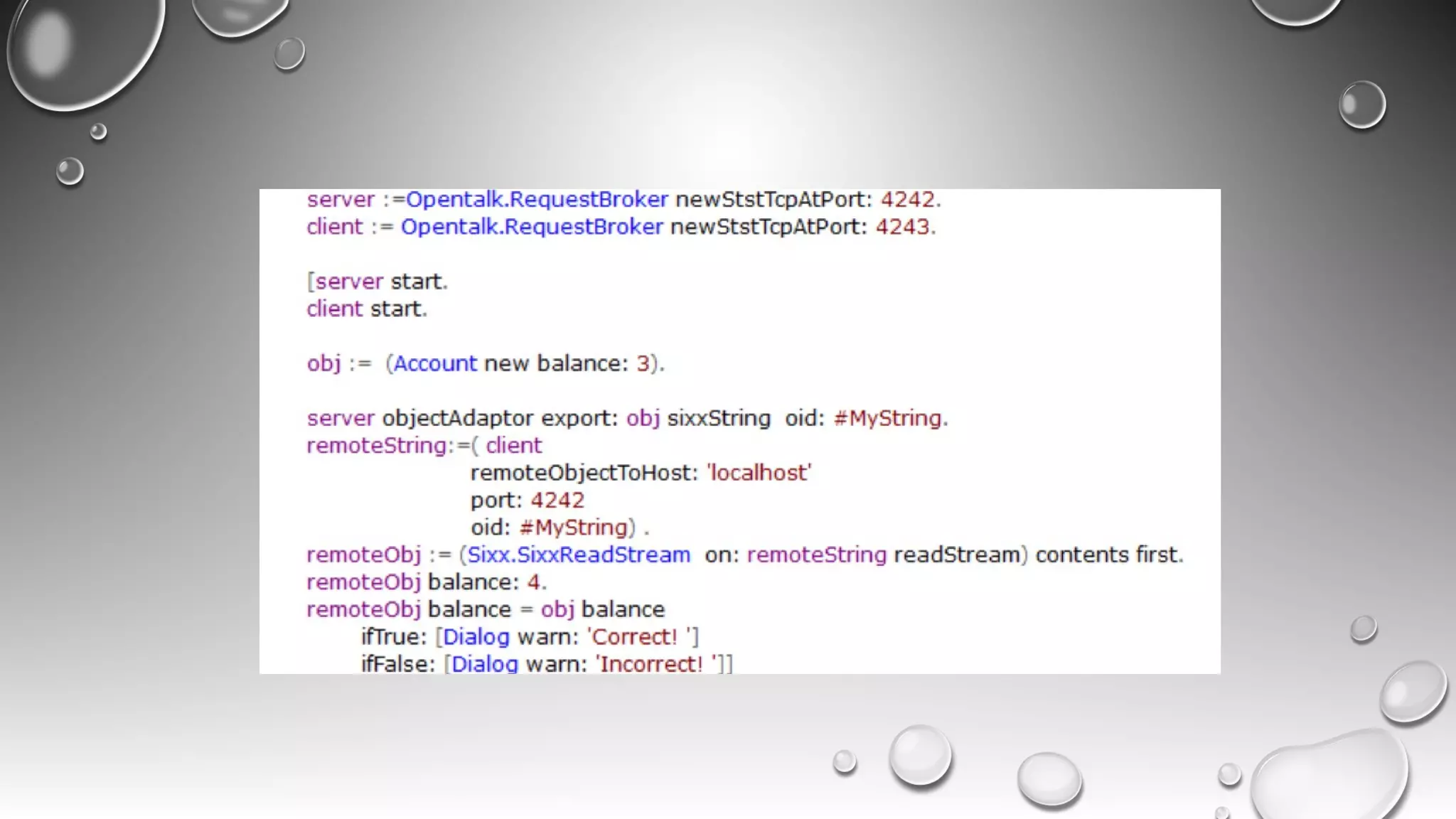
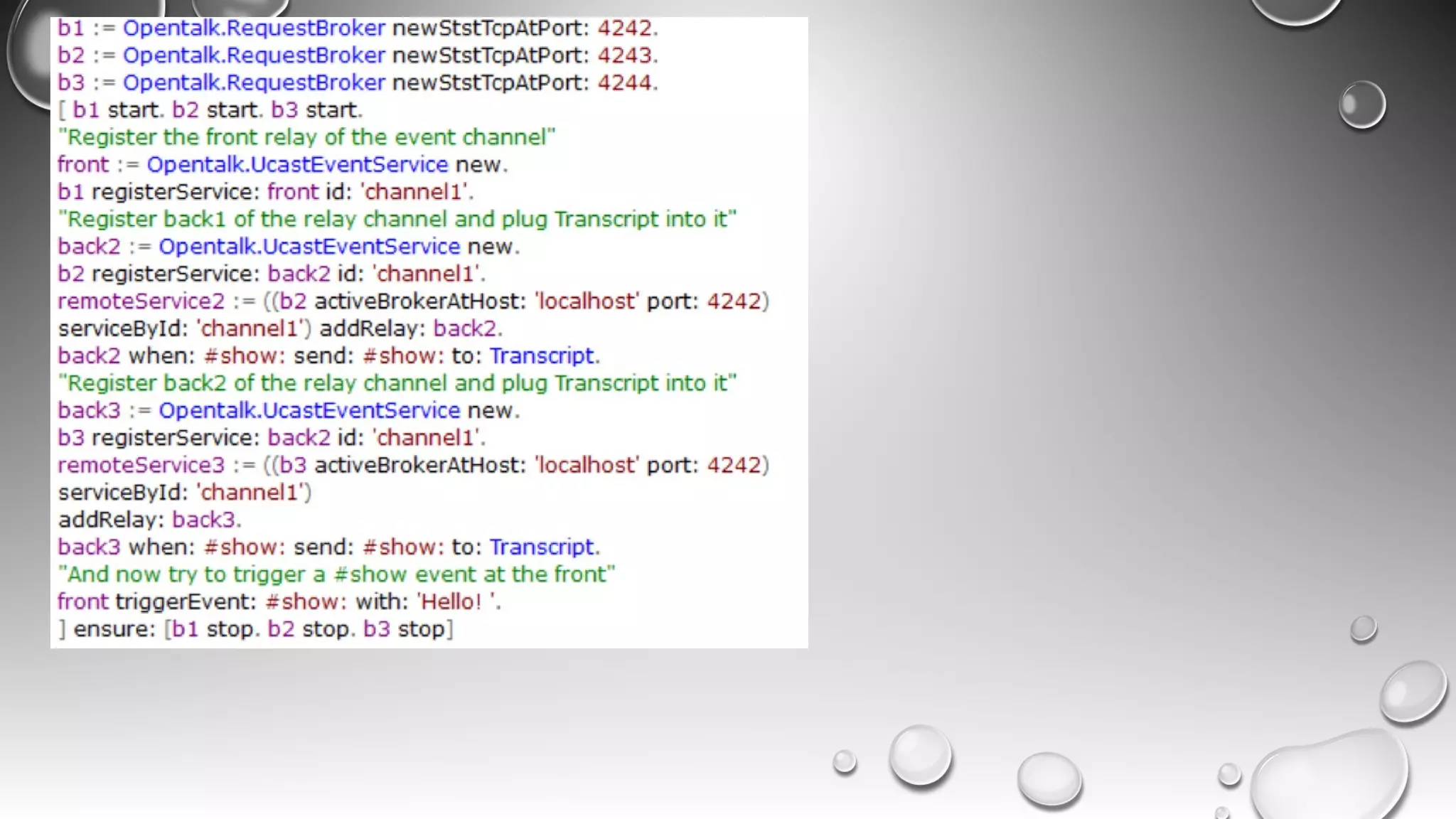
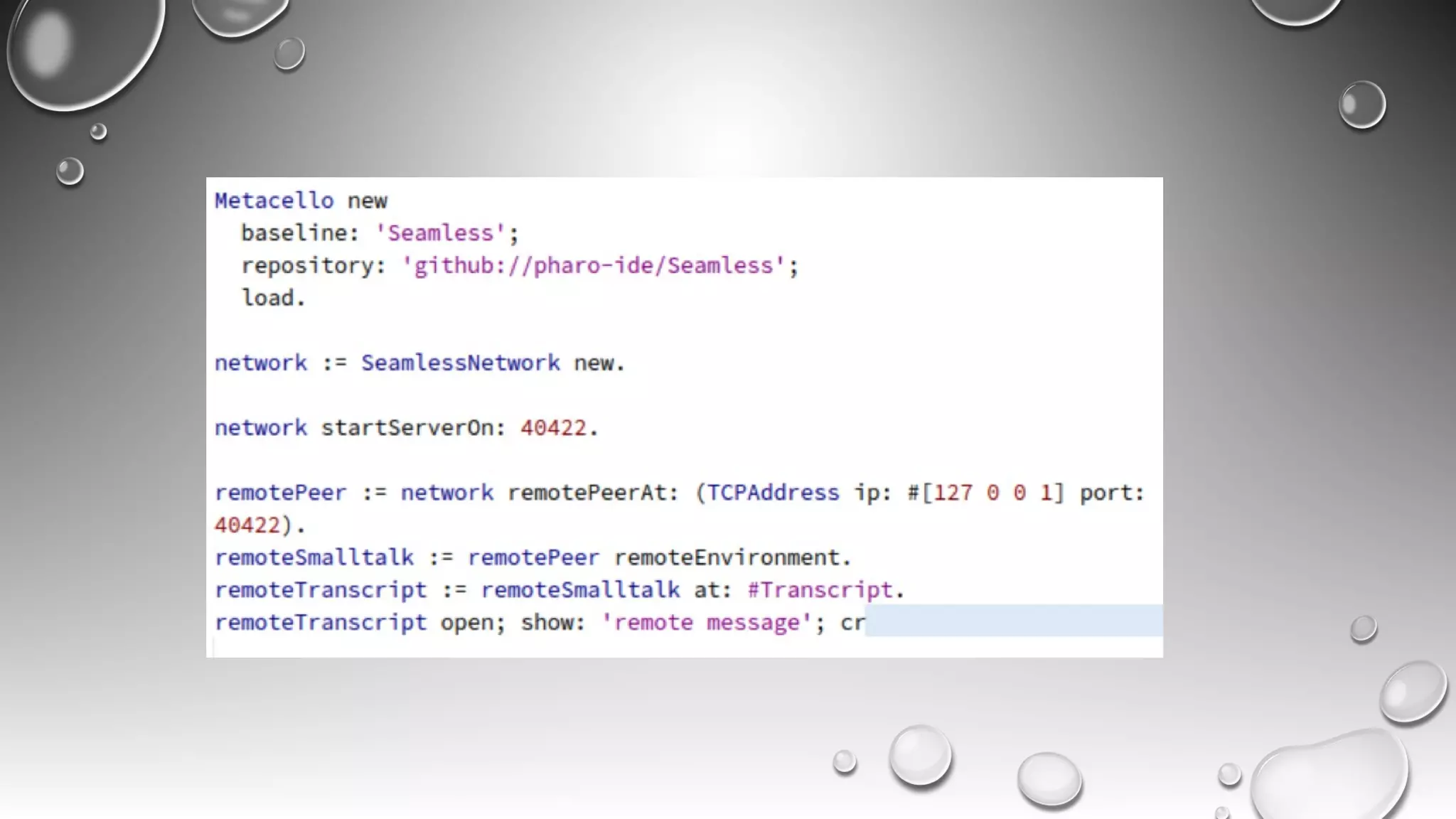
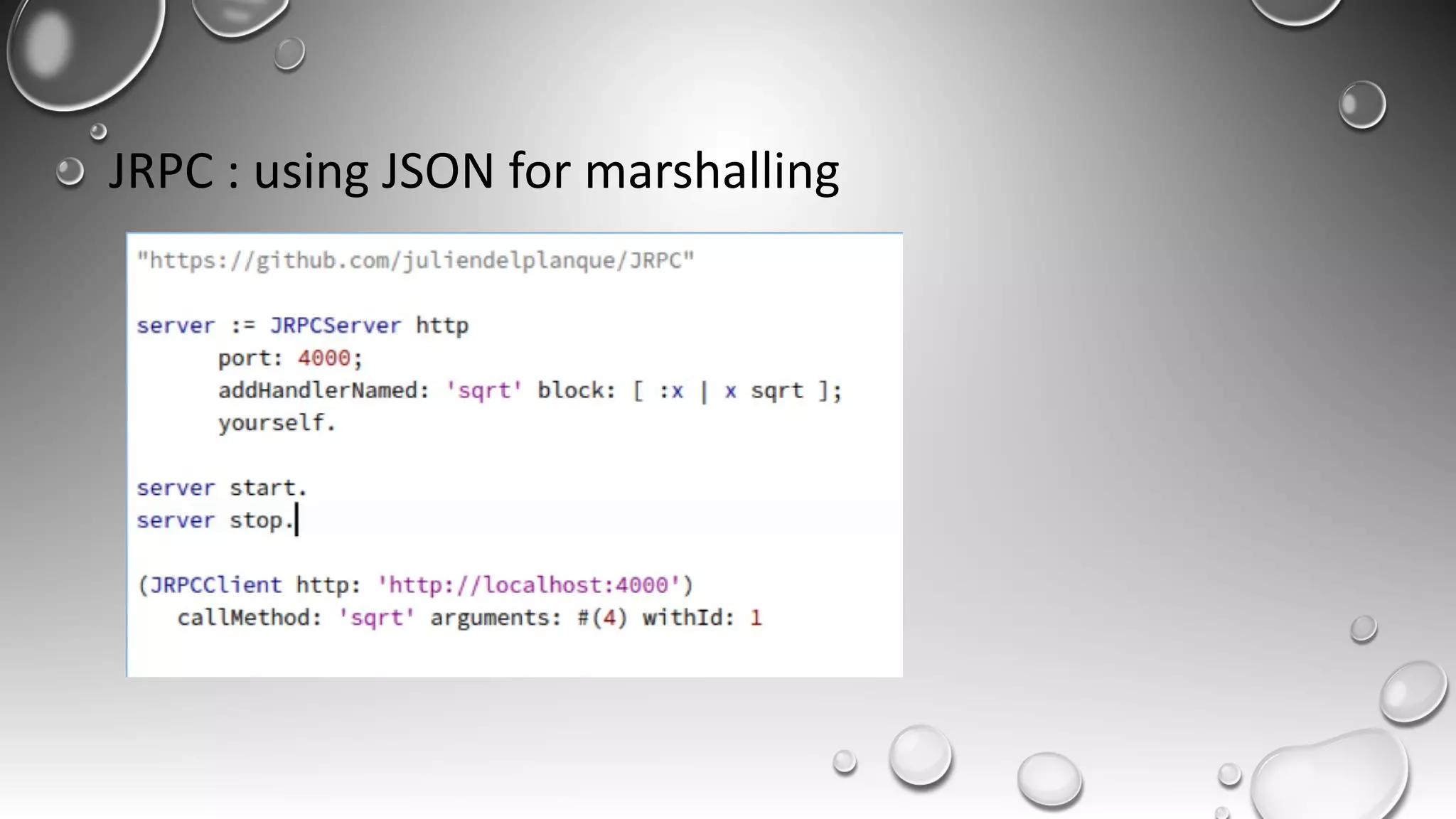
RPC allows calling methods on remote objects by marshalling parameters and unmarshalling return values. There are many challenges to RPC including unreliable networks, latency, security, and changing topologies. Smalltalk supports RPC through mechanisms like distributed events, value/reference passing, and marshaling objects to formats like JSON to enable communication across networks and between systems. Developing distributed systems requires strategies for handling issues like passing large objects efficiently and updating interfaces when remote objects change.
















![Web sockets
Wraps http request with handler
ZnServer default delegate: (ZnWebSocketDelegate handler:
[ :webSocket |
[ | message |
message := webSocket readMessage.
webSocket sendMessage: message ] repeat ]).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-rpc-191104144856/75/RPC-in-Smalltalk-24-2048.jpg)



![Different notification mechanisms
● Using notifySets to update the GUI
session1 addToNotifySet: leTournoi competition poules first.
session1 notificationAction: [:idSet | callbacks do: ….].
● Using Gem to gem signalling for workflow
session gemSignalAction:
[:aSession :aSignalNumber :aString |
self handleSignalFrom: aSession number: aSignalNumber string: aString].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-rpc-191104144856/75/RPC-in-Smalltalk-28-2048.jpg)
