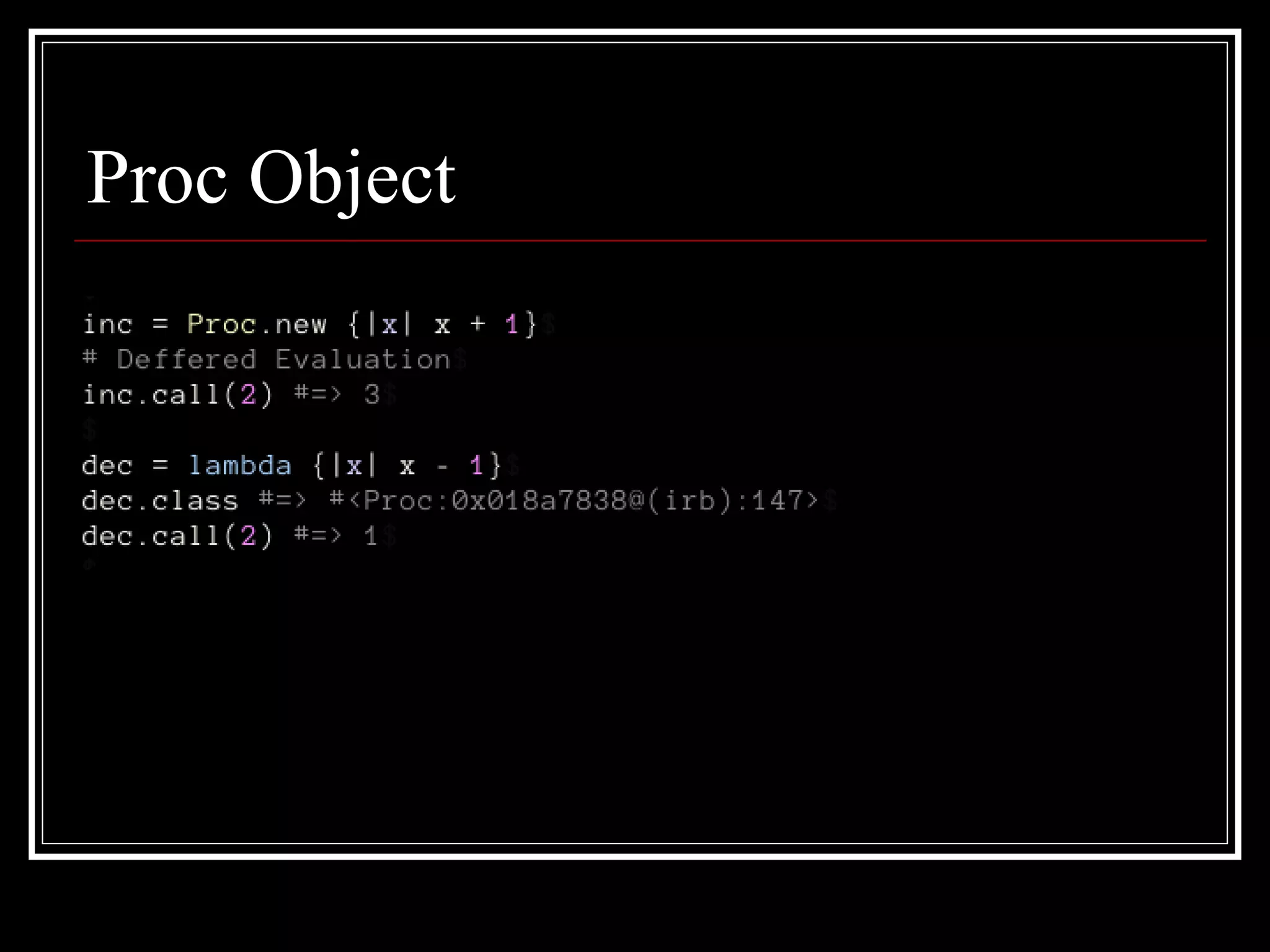
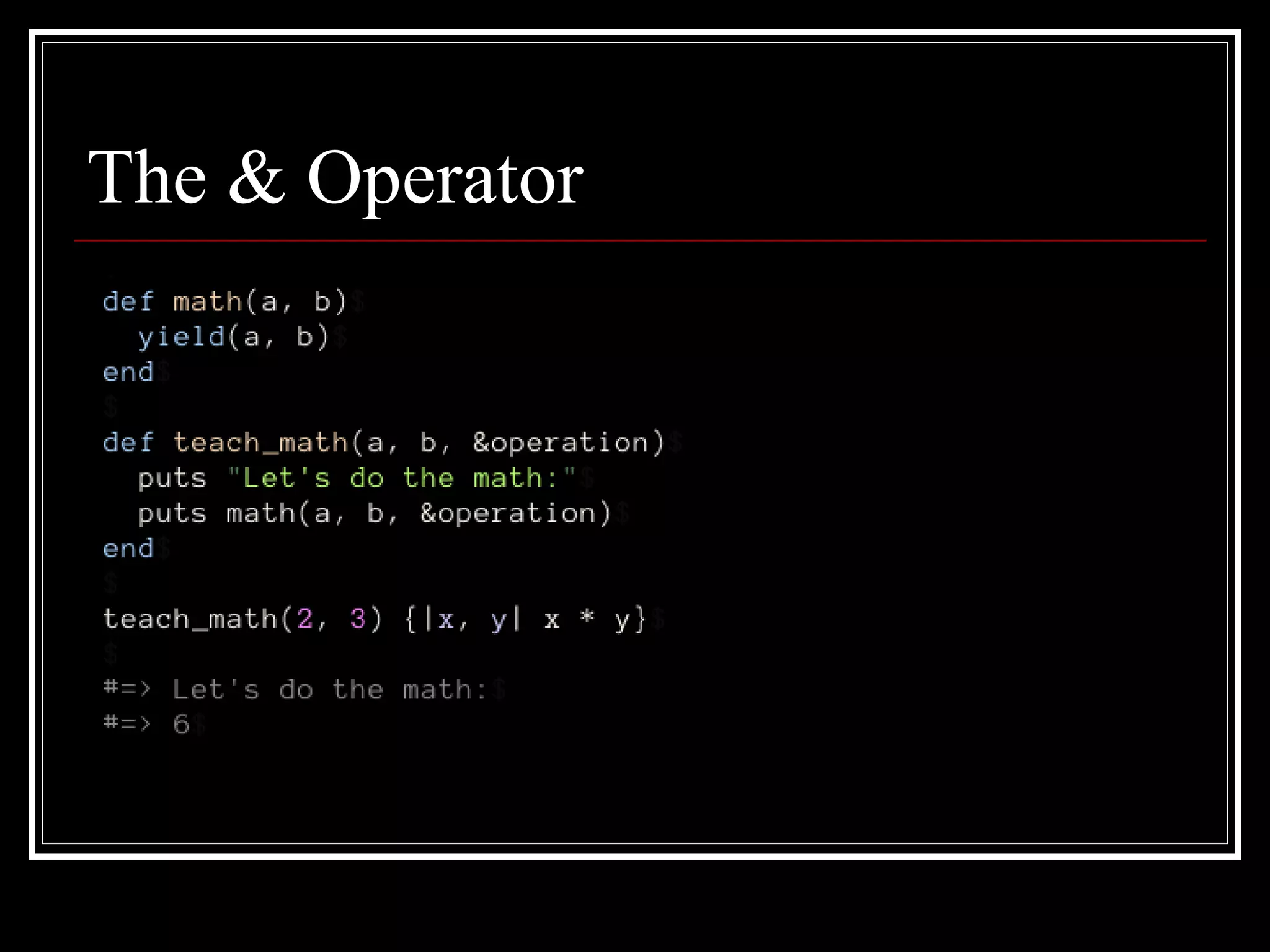
Ruby metaprogramming involves writing code that manipulates language constructs at runtime. Some key aspects of Ruby metaprogramming discussed in the document include:
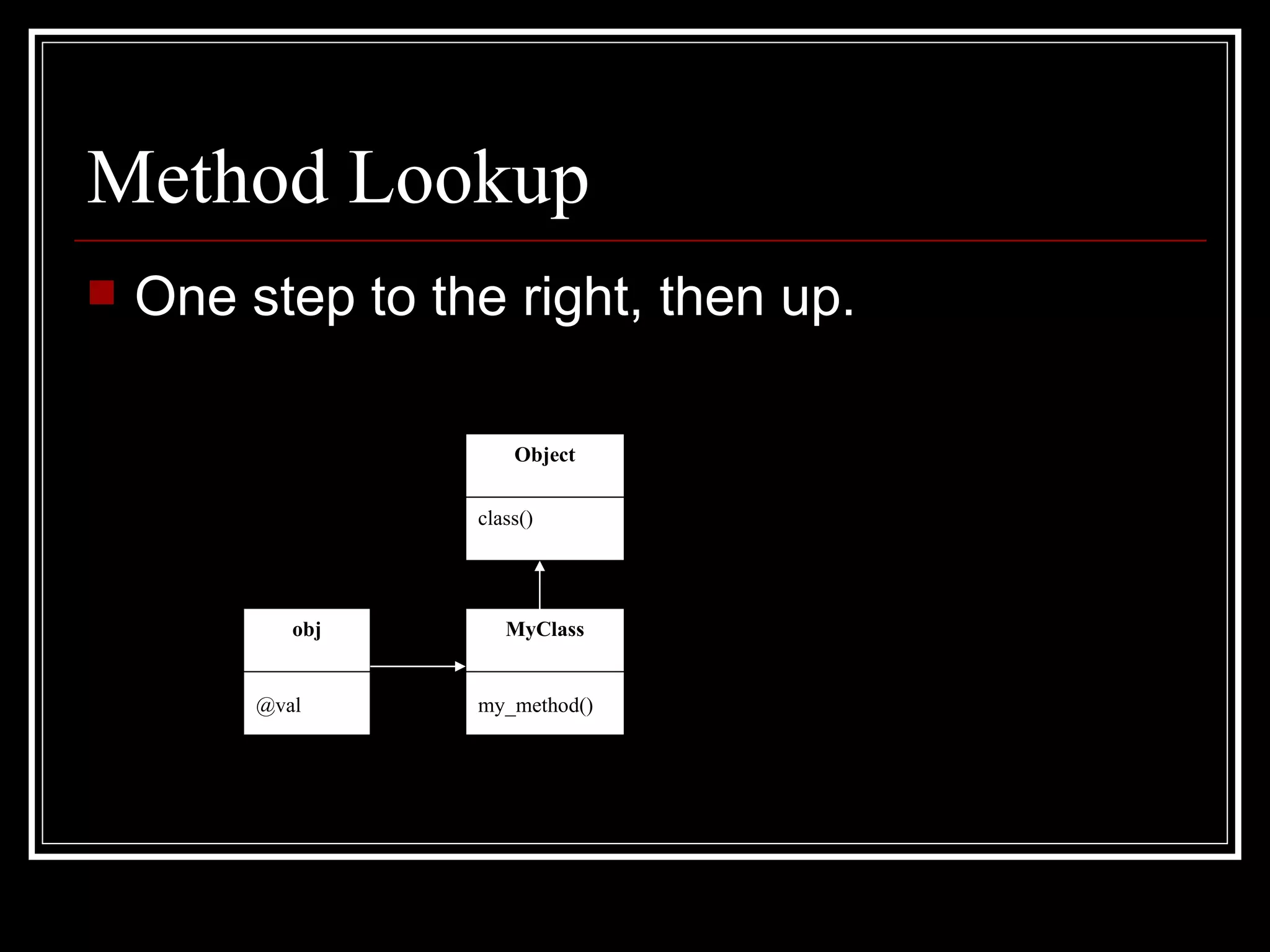
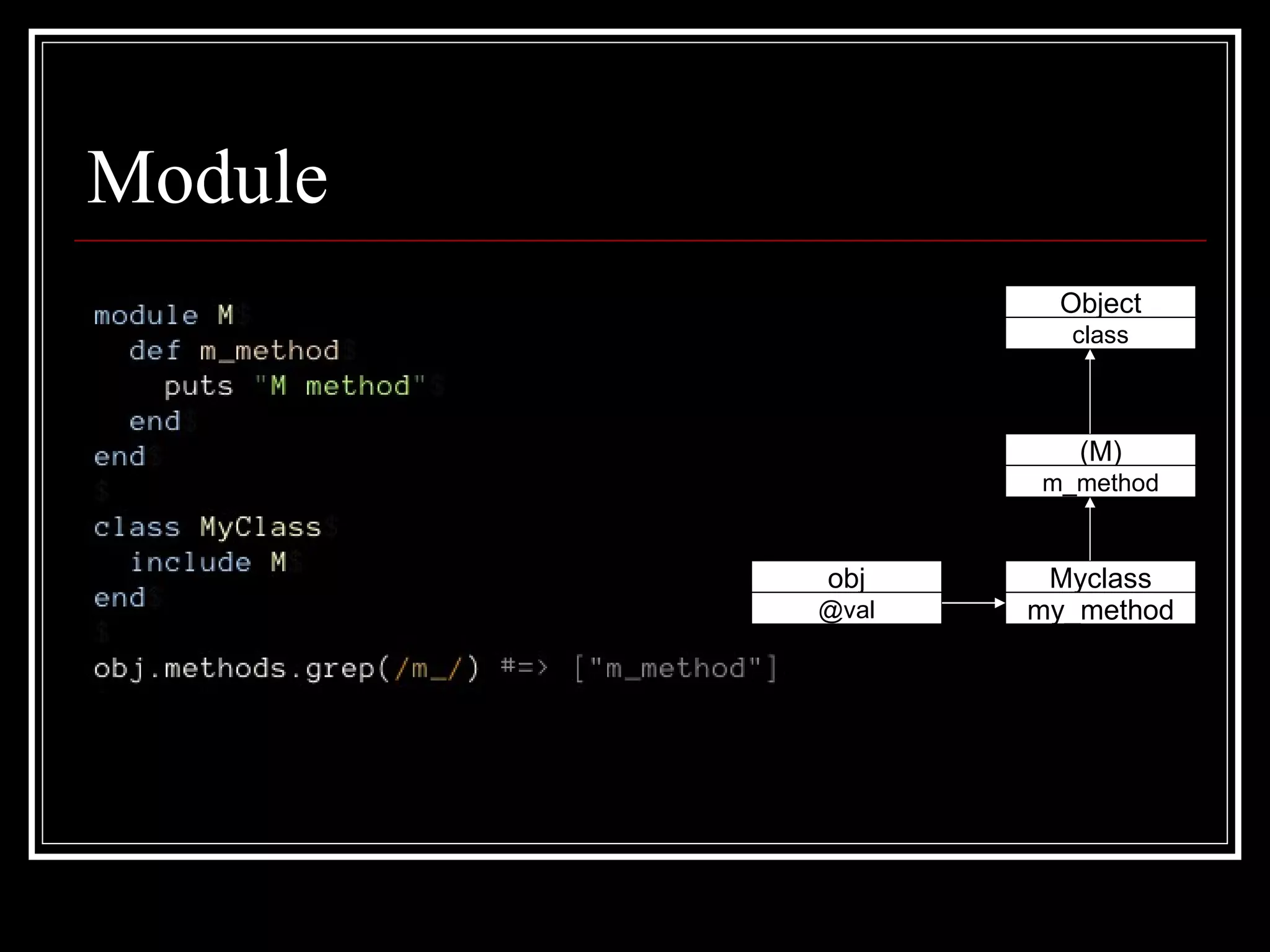
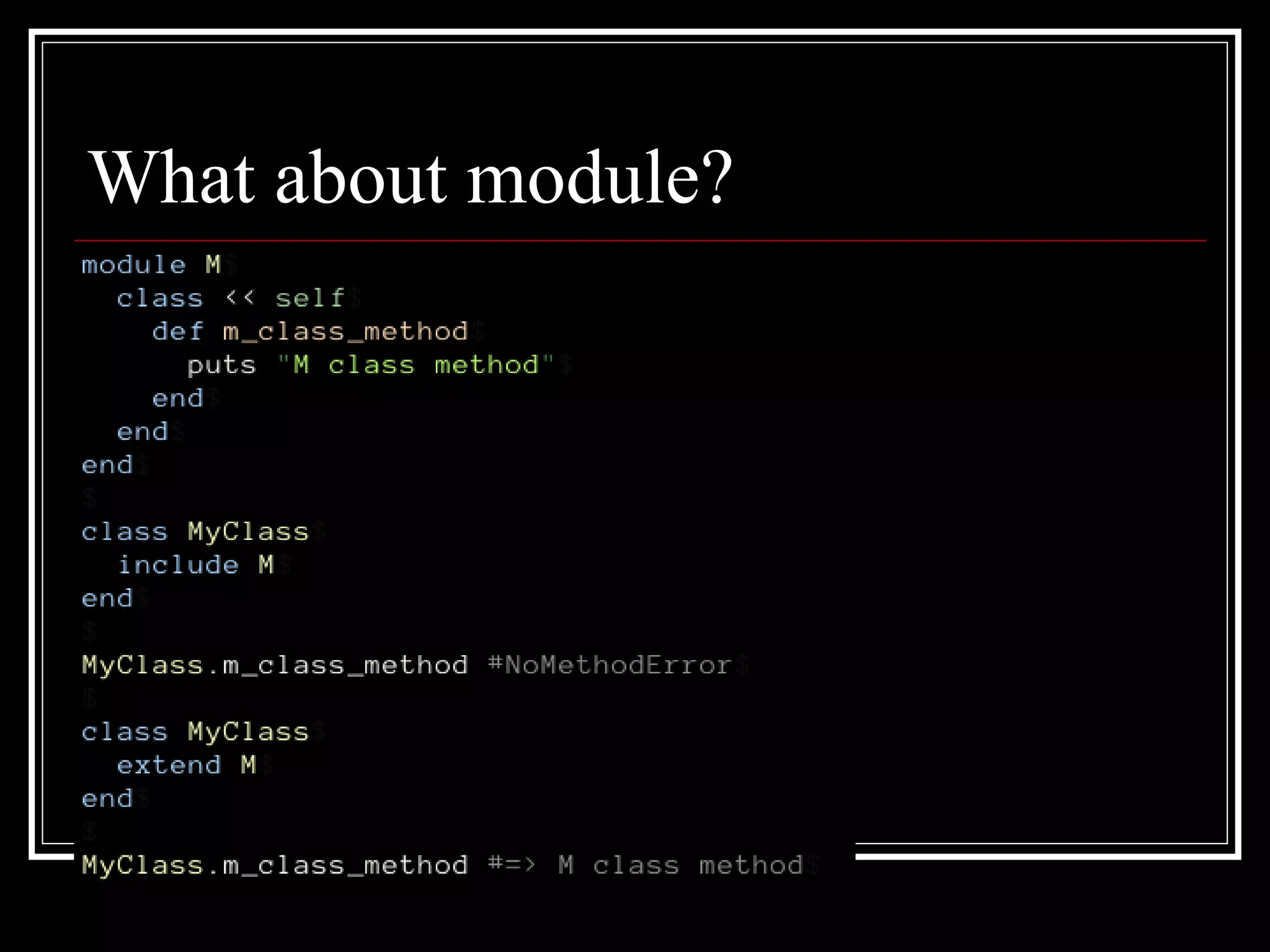
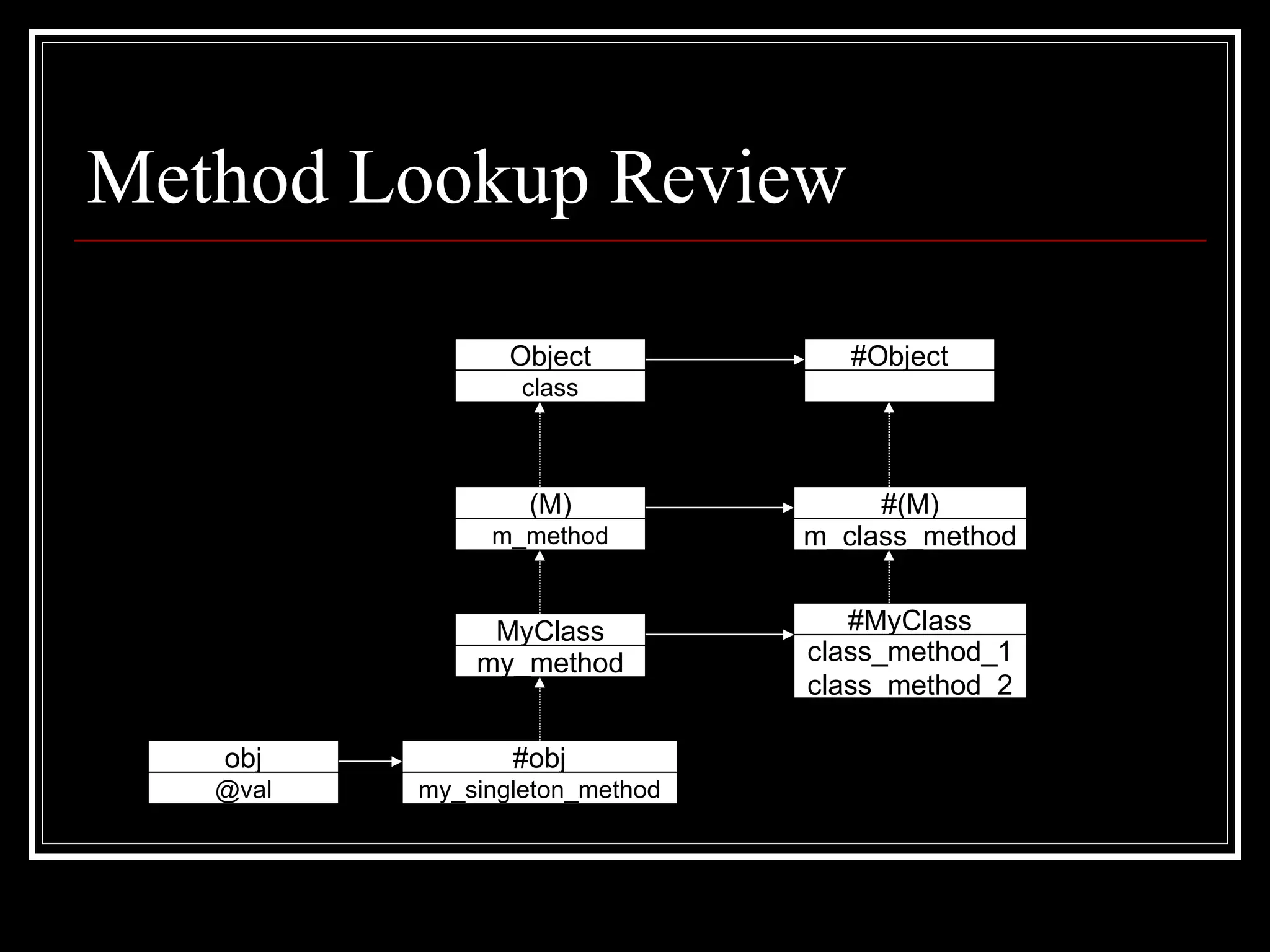
1. Objects, classes, and modules - Classes are objects and classes look up methods via objects and modules in their ancestors chain. Modules can be included to add methods.
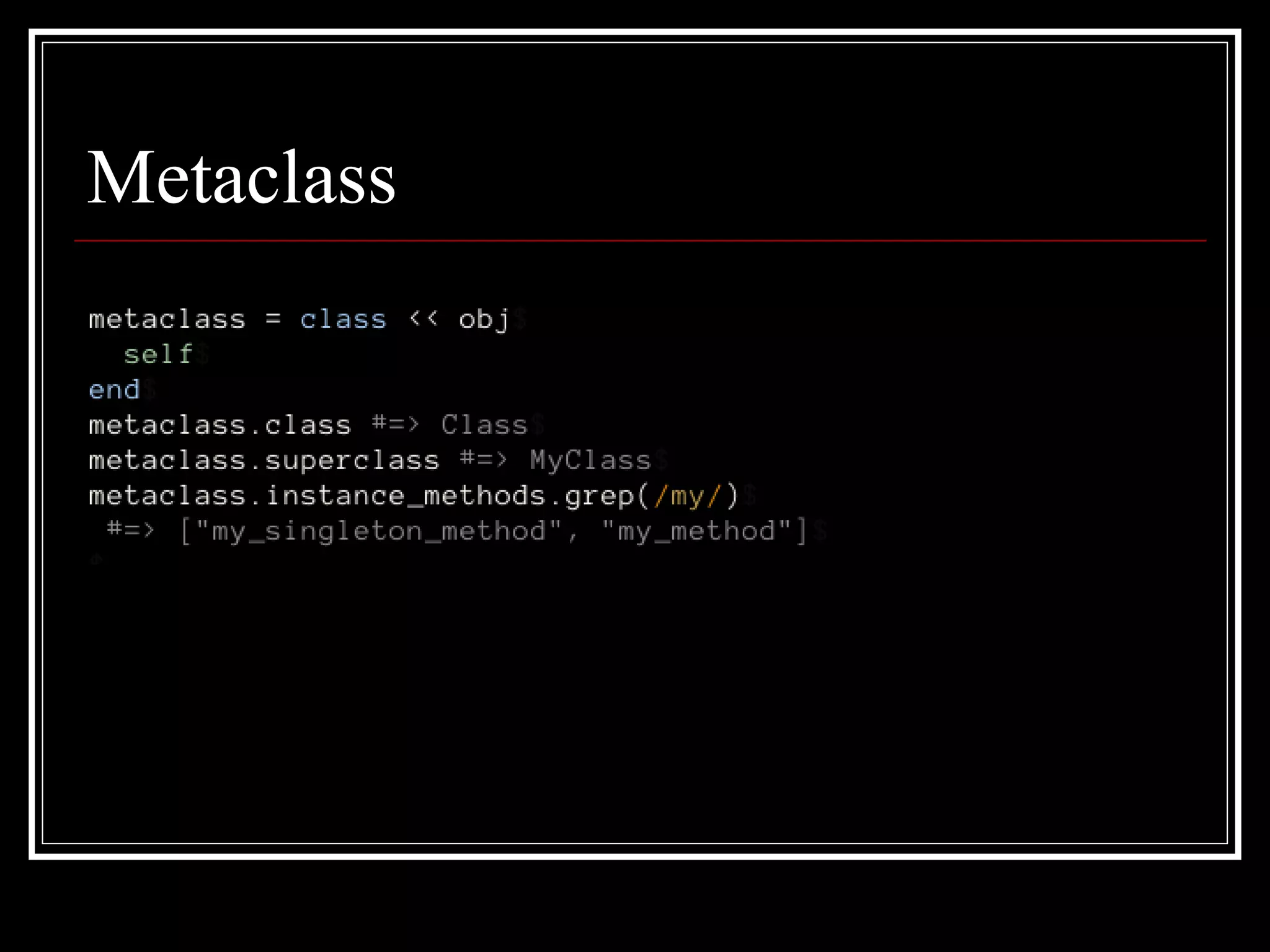
2. Singleton methods and metaclasses - Each object has a hidden metaclass that holds its singleton methods. Class methods are defined on the metaclass.
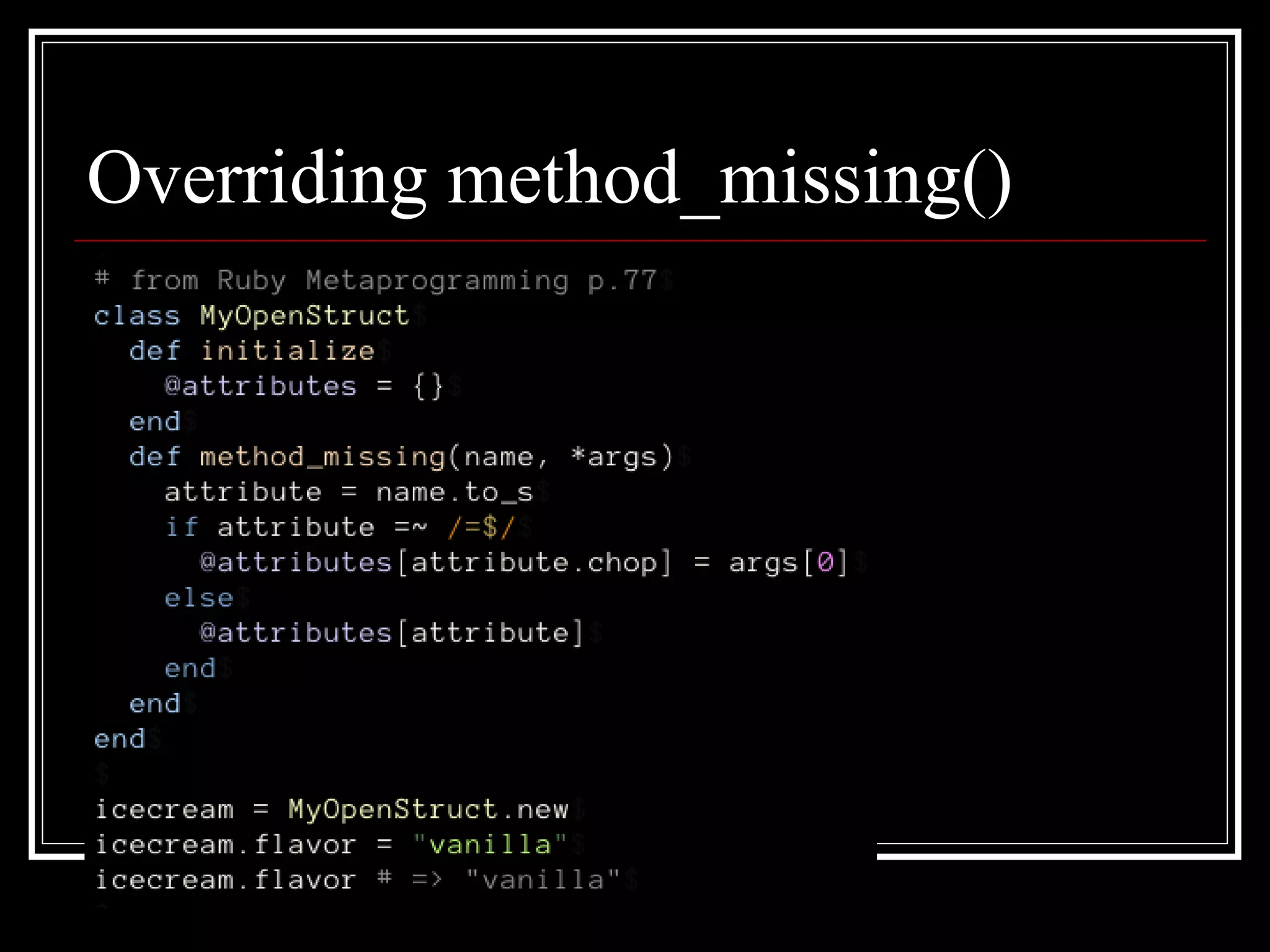
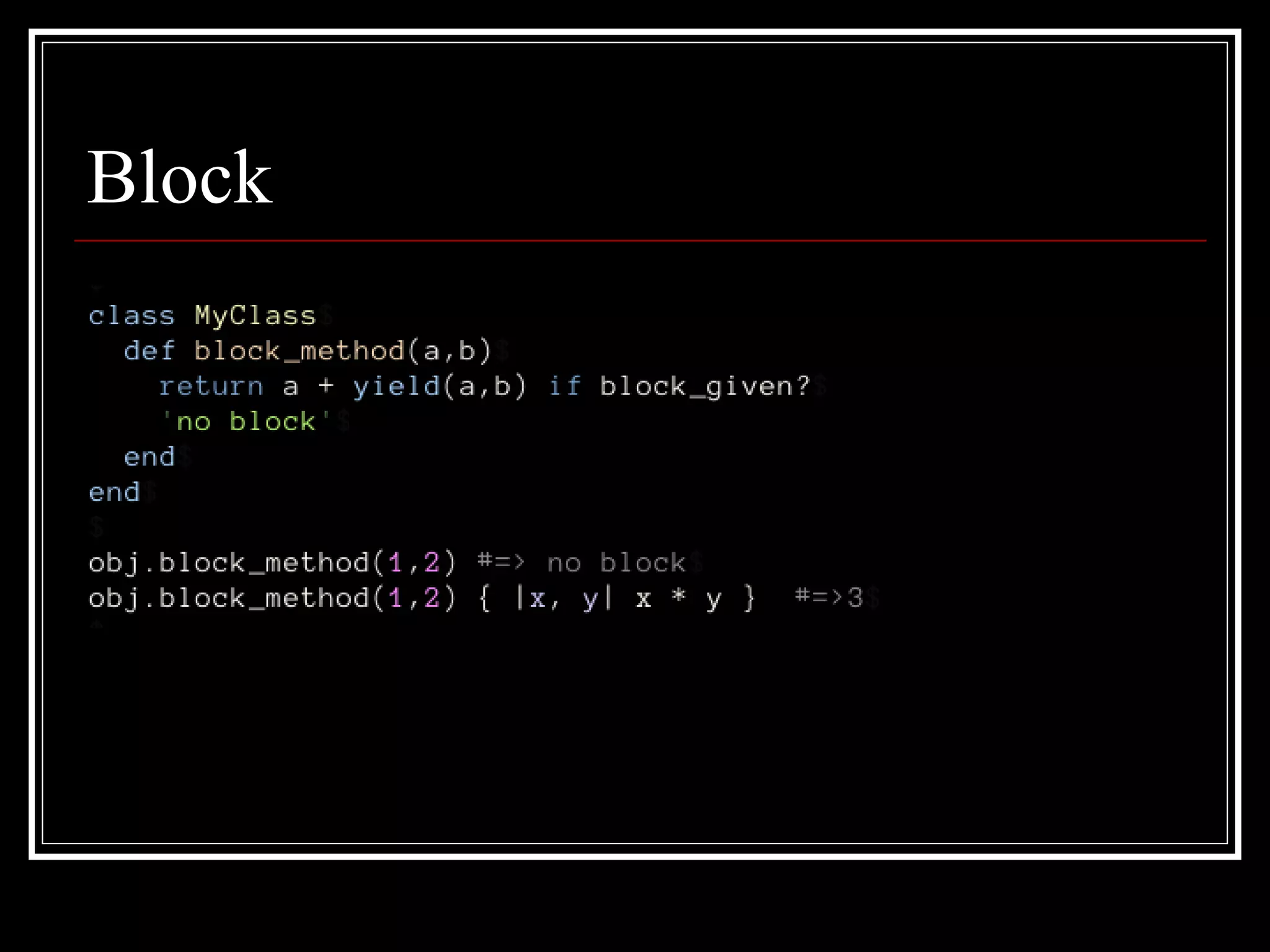
3. Dynamic method definition - Methods can be defined dynamically at runtime via open classes, modules, and metaclasses. Various eval methods also allow evaluating code to modify classes, modules, and objects.