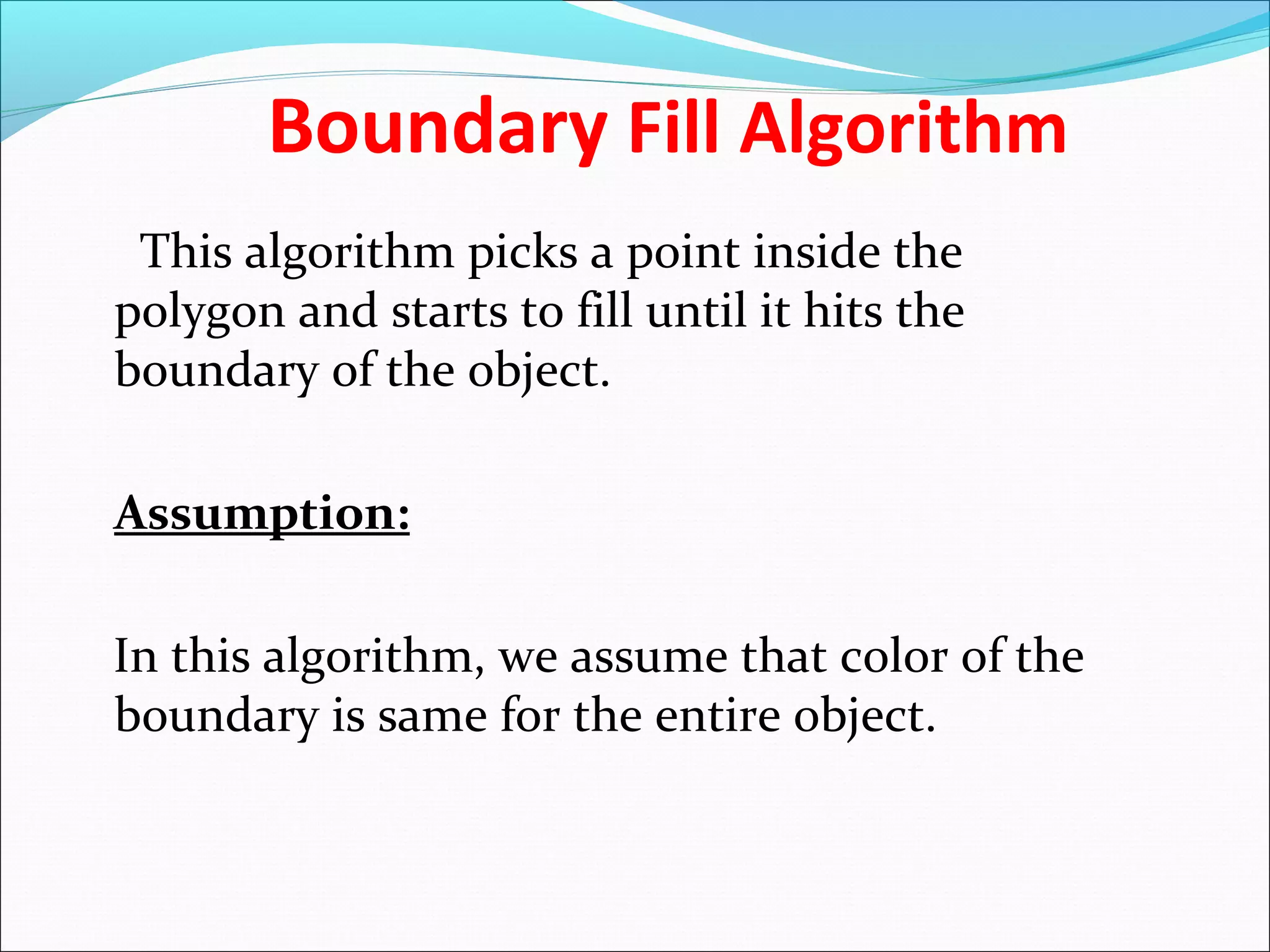
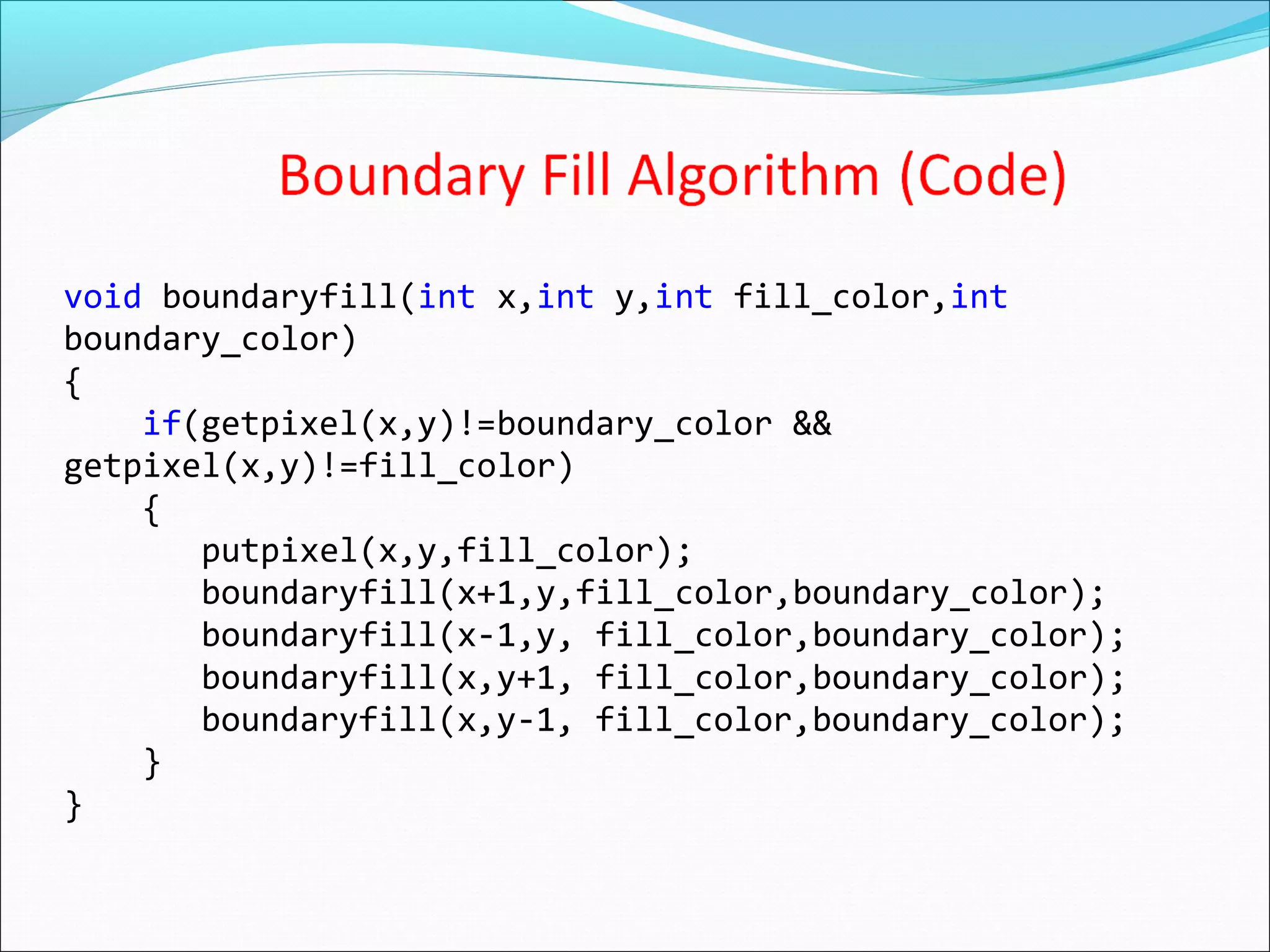
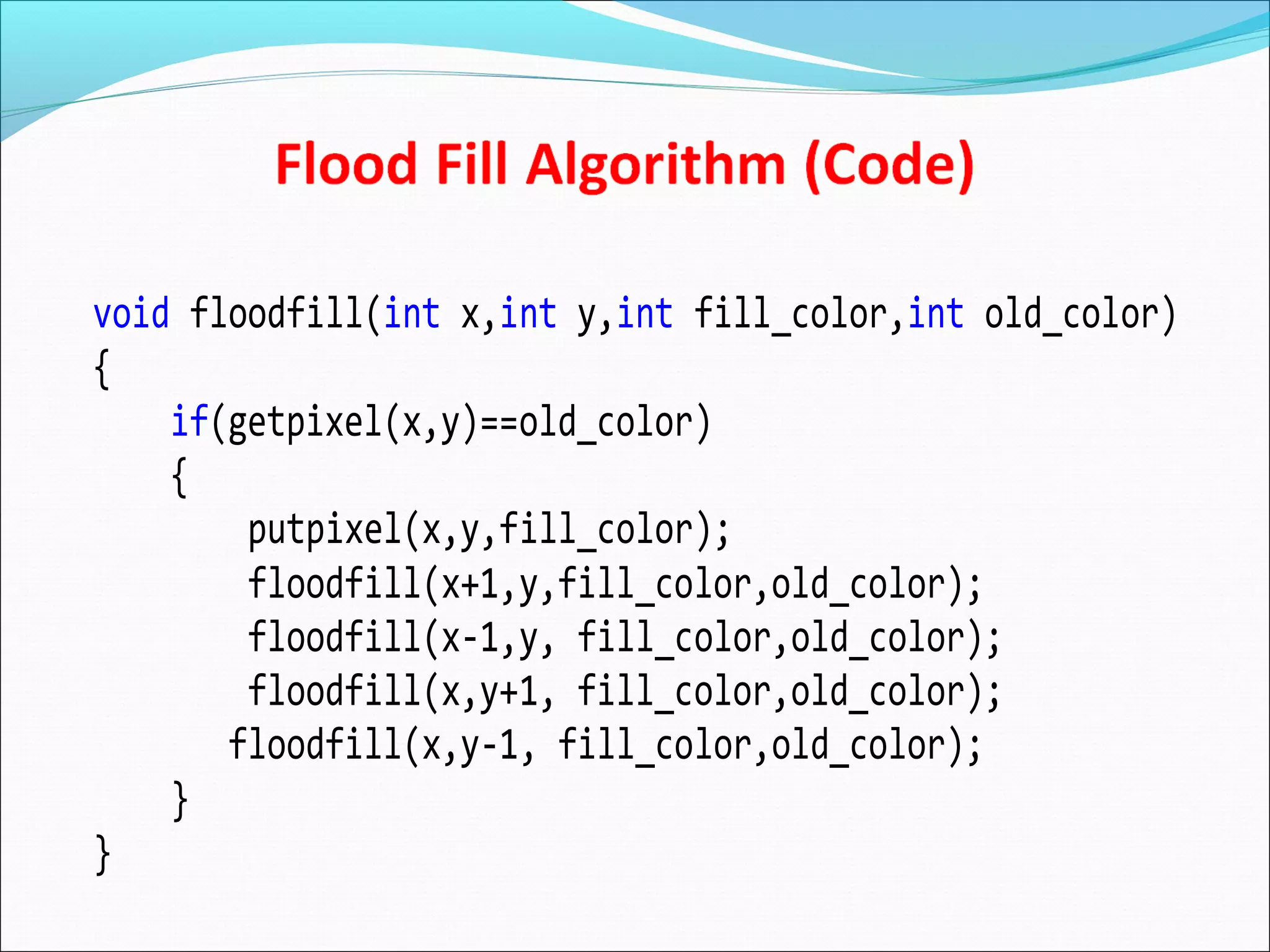
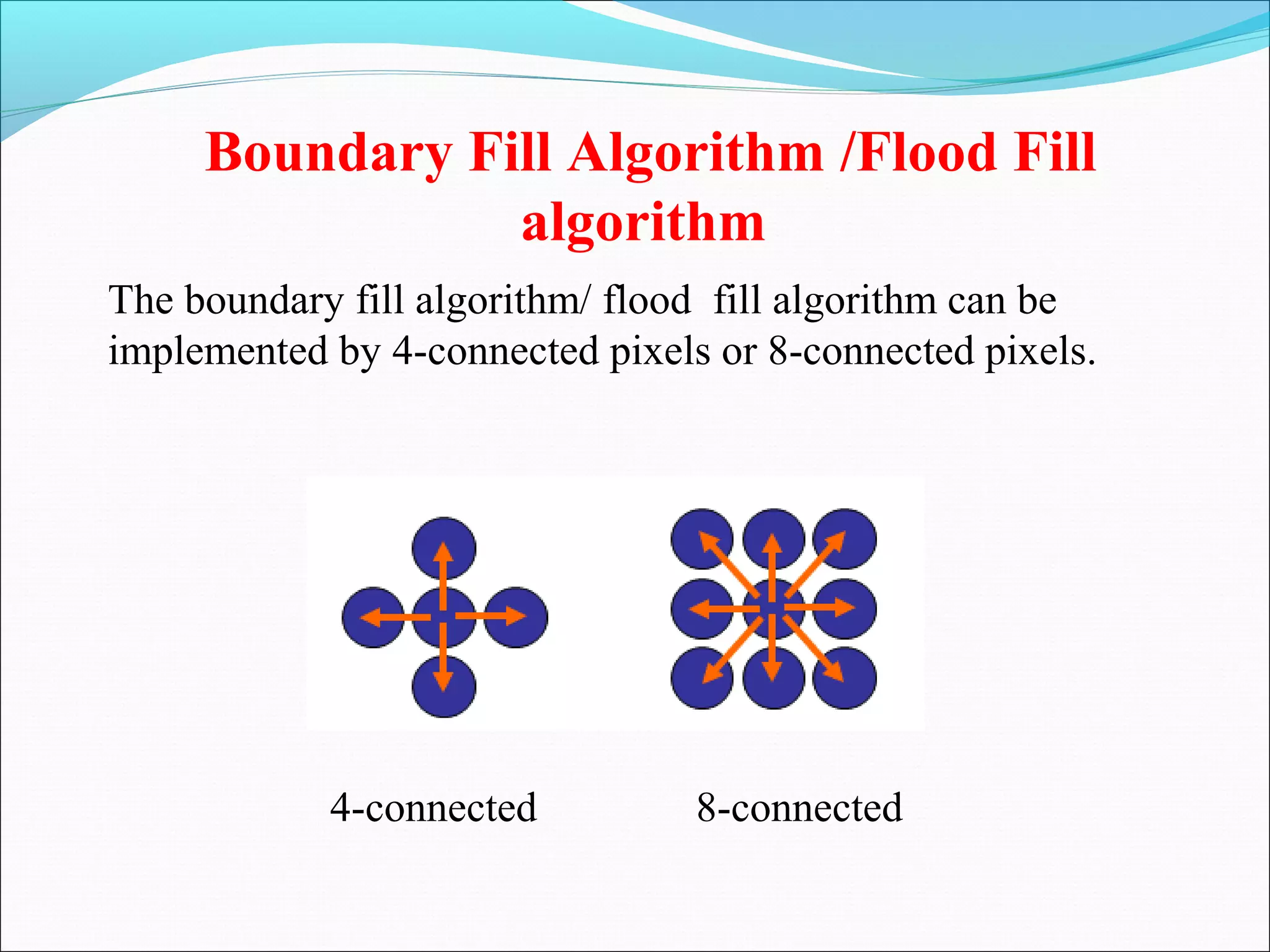
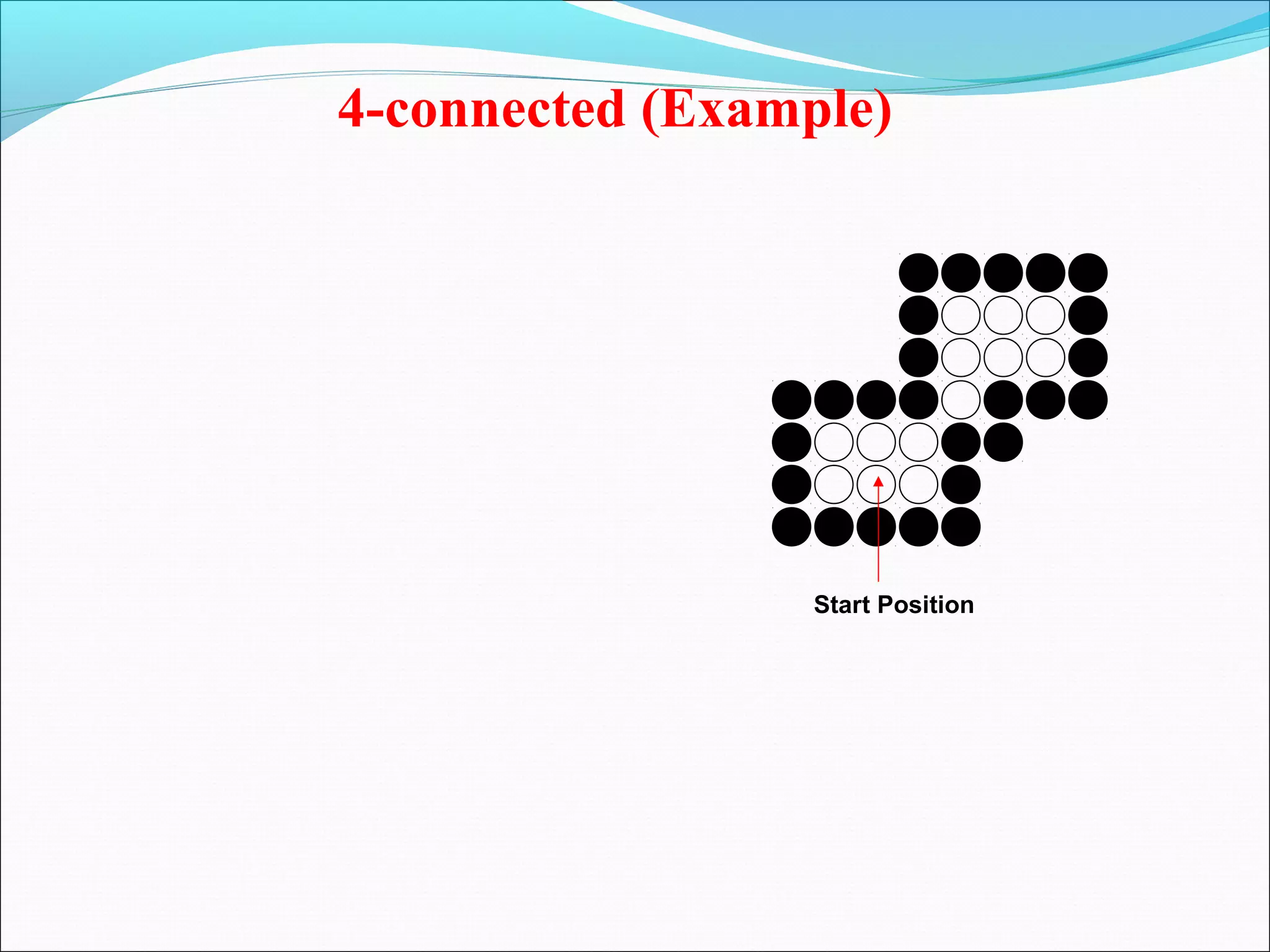
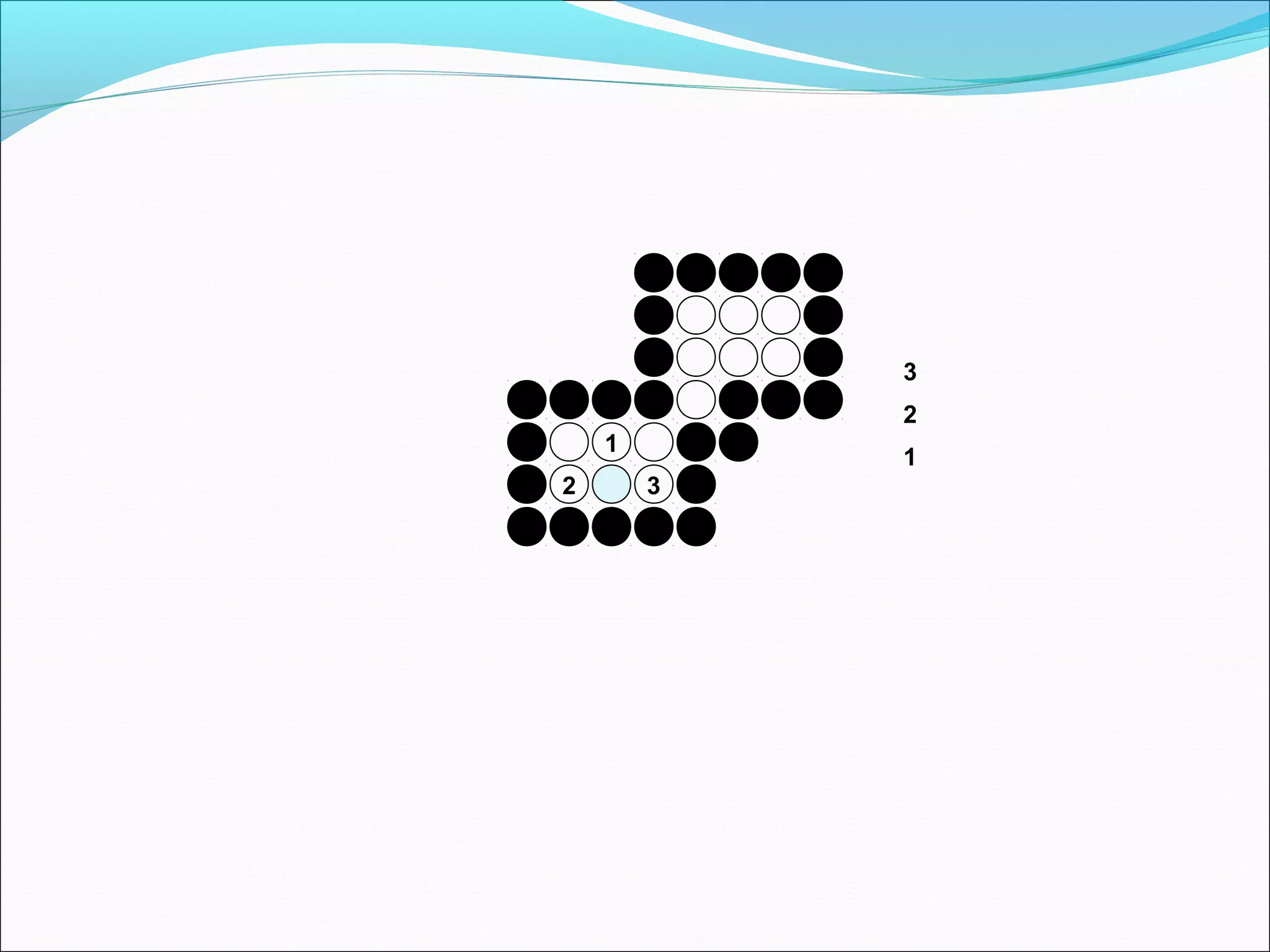
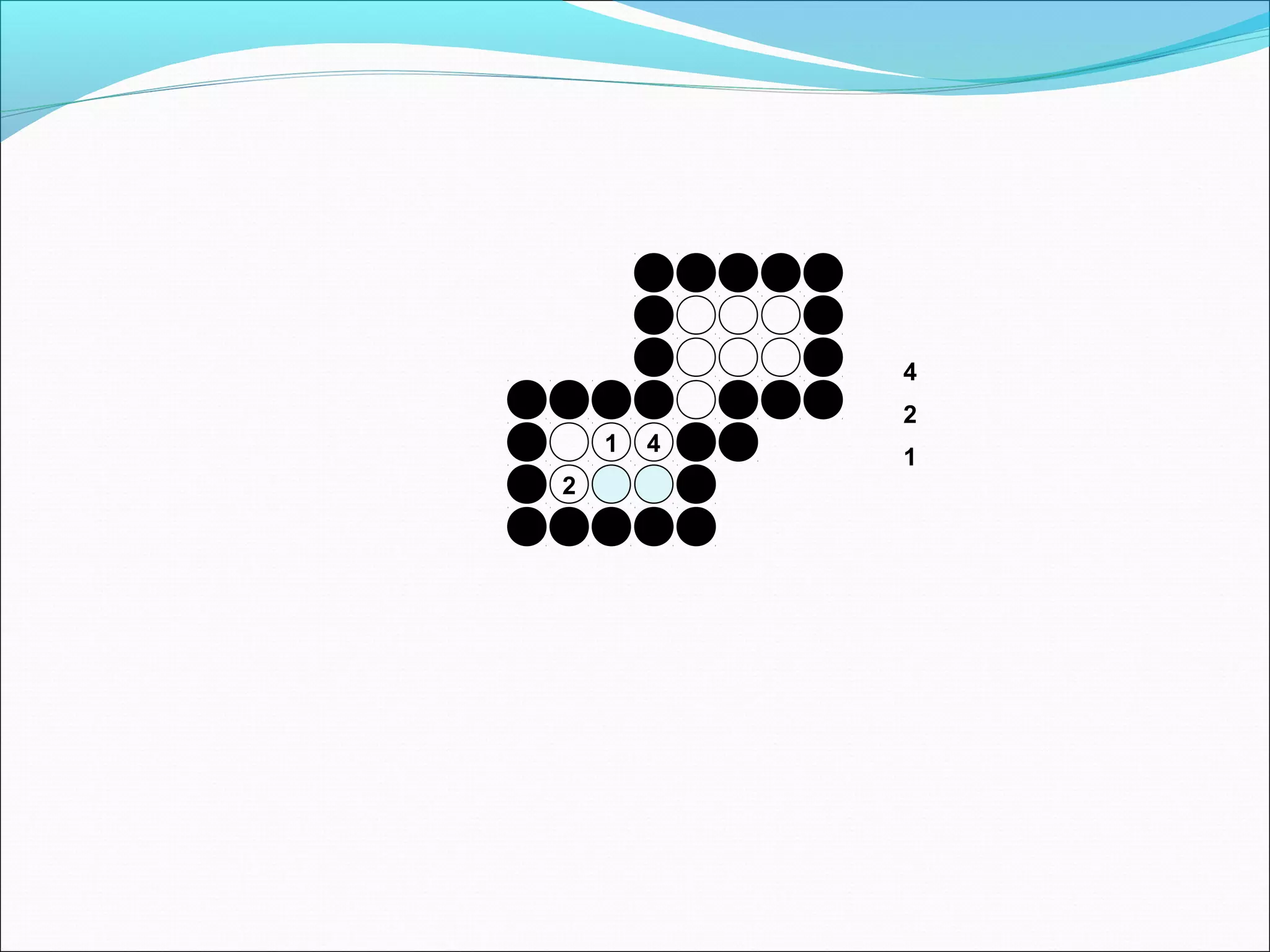
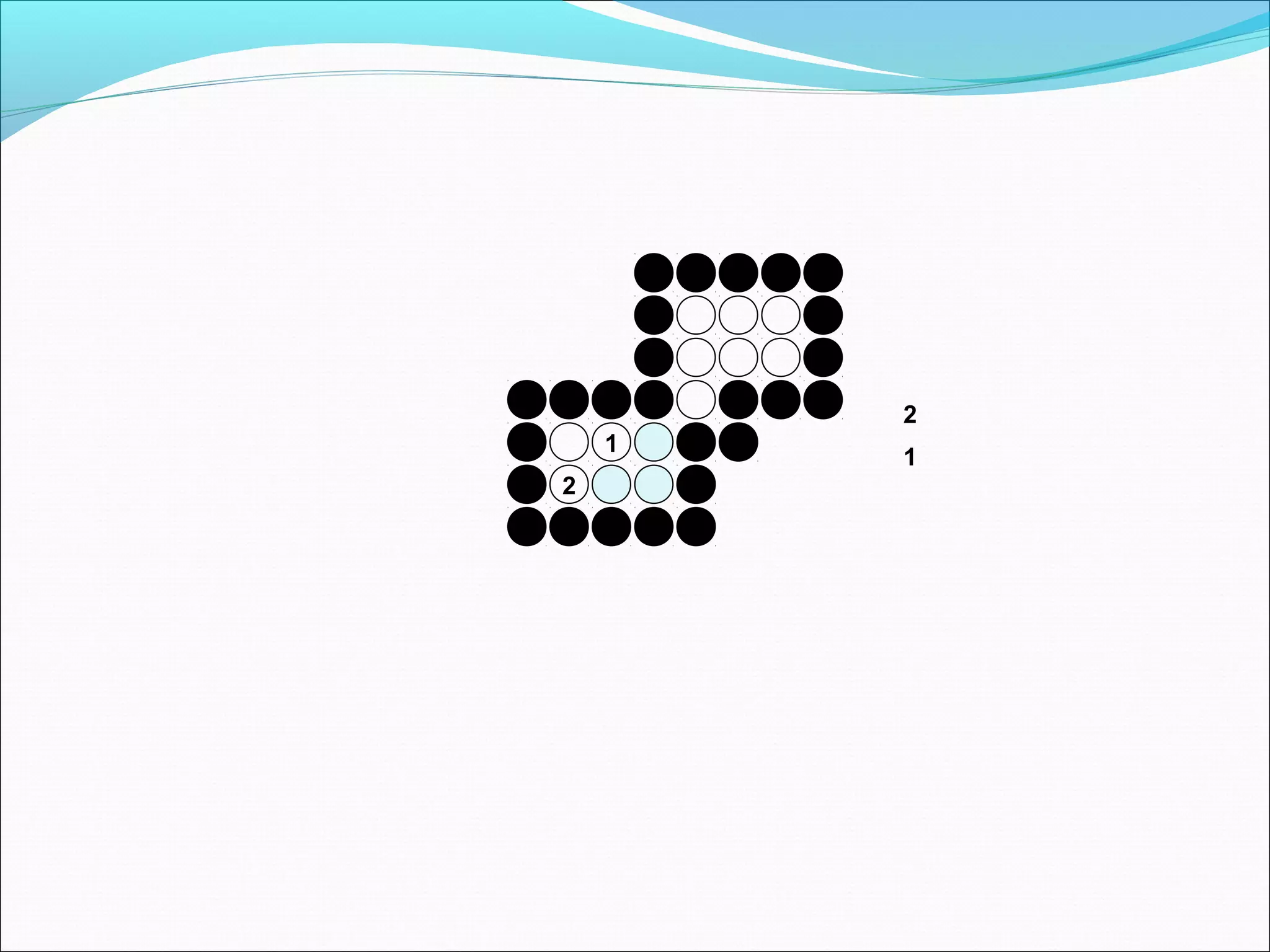
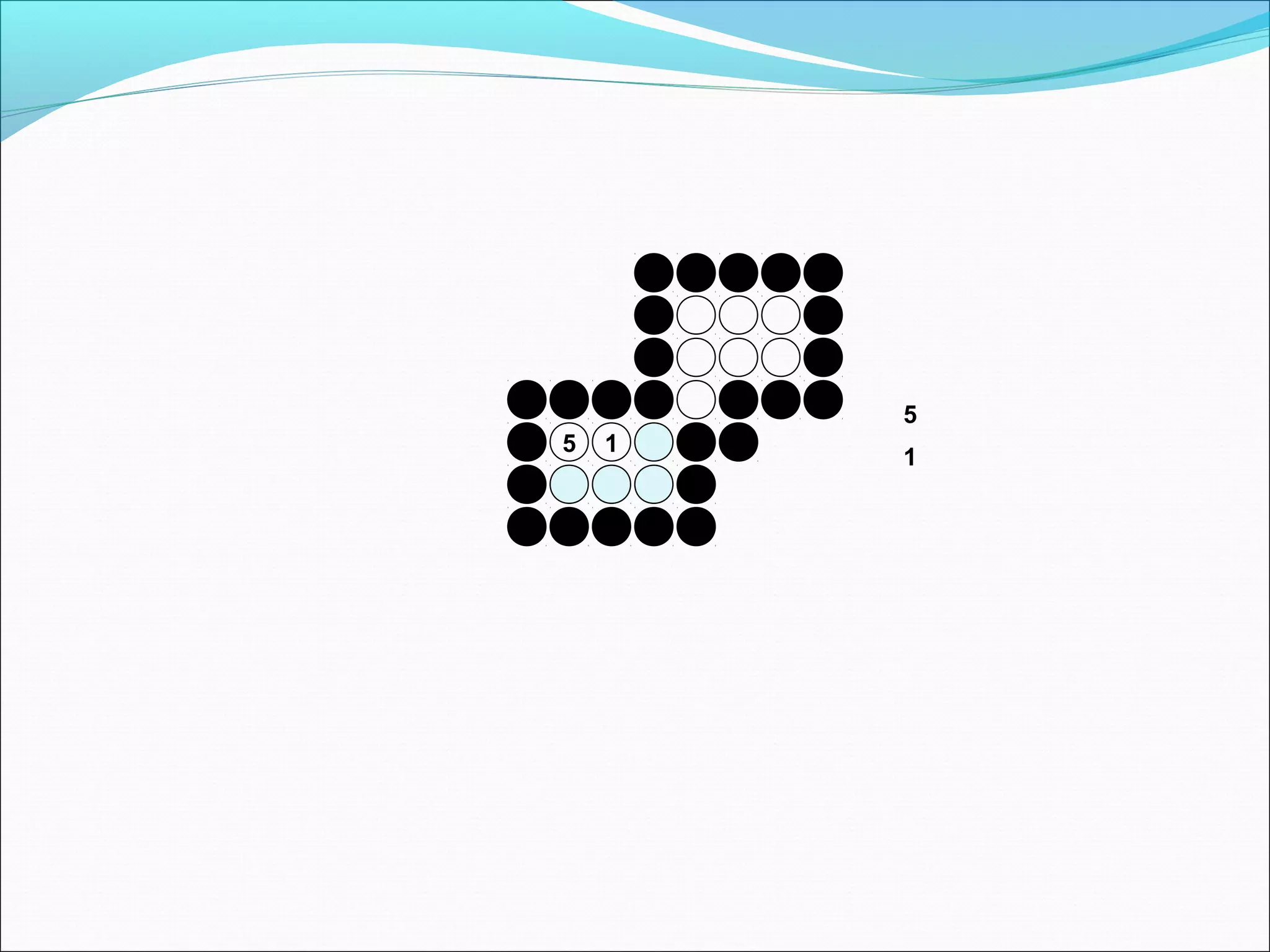
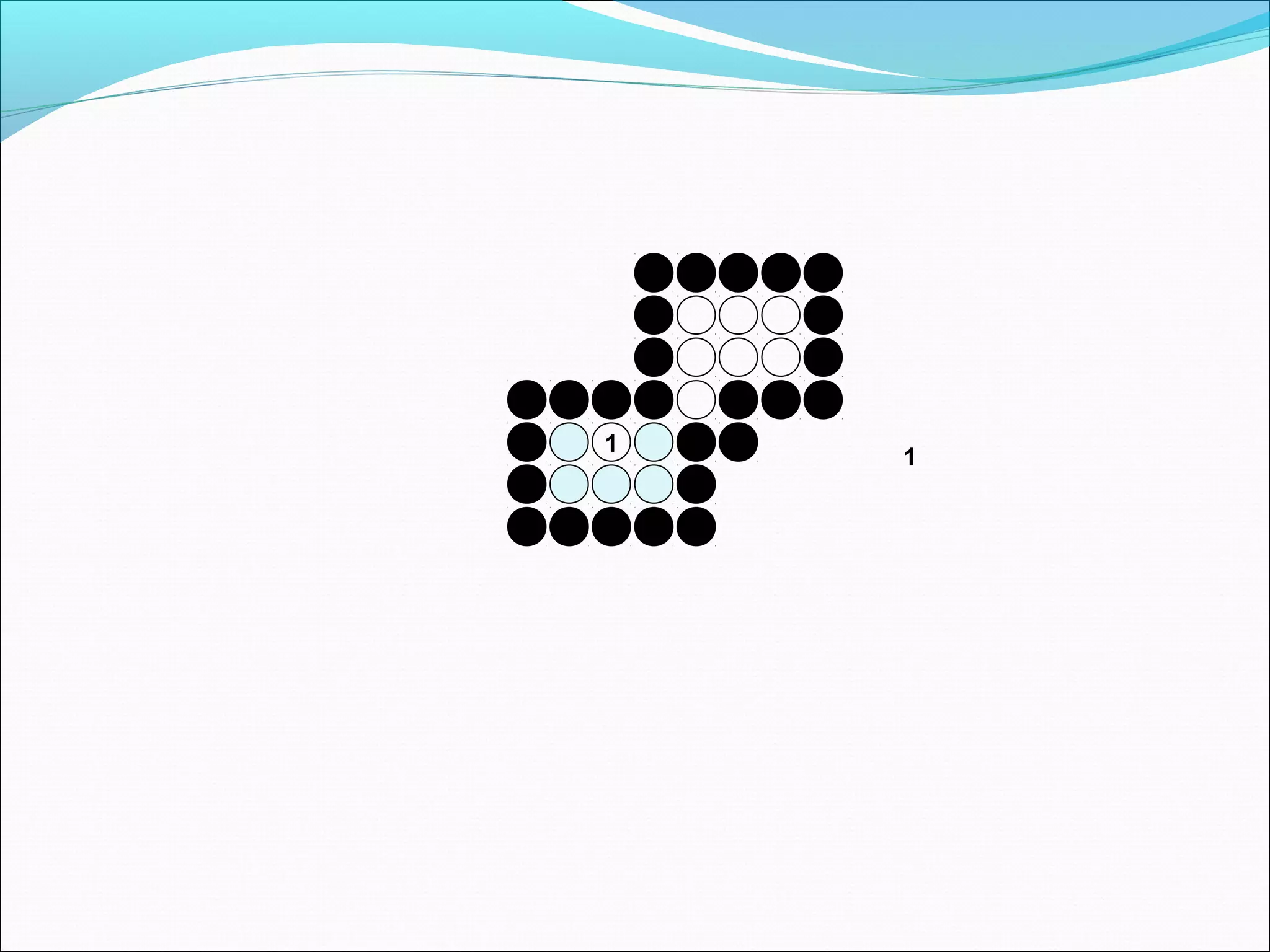
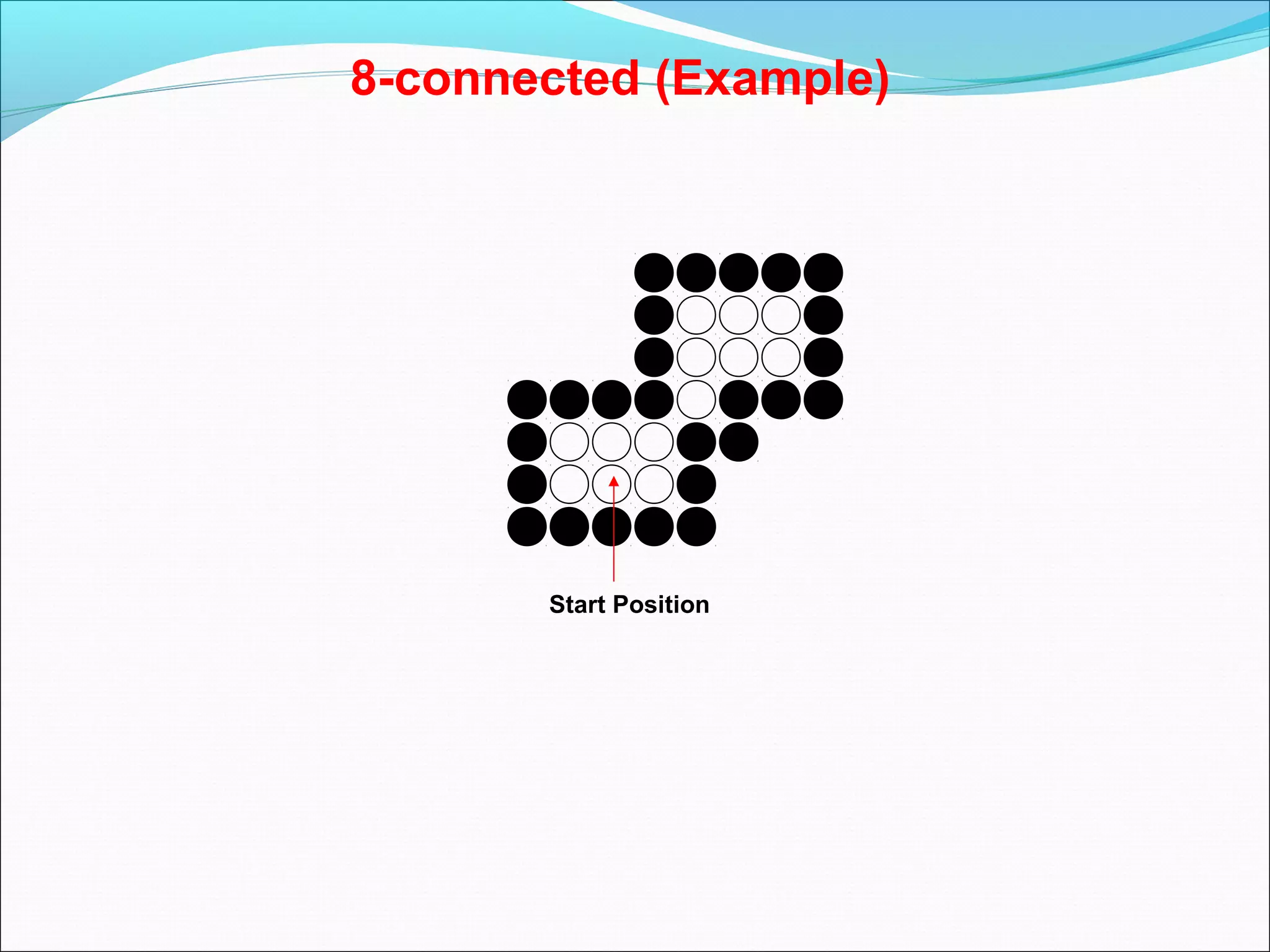
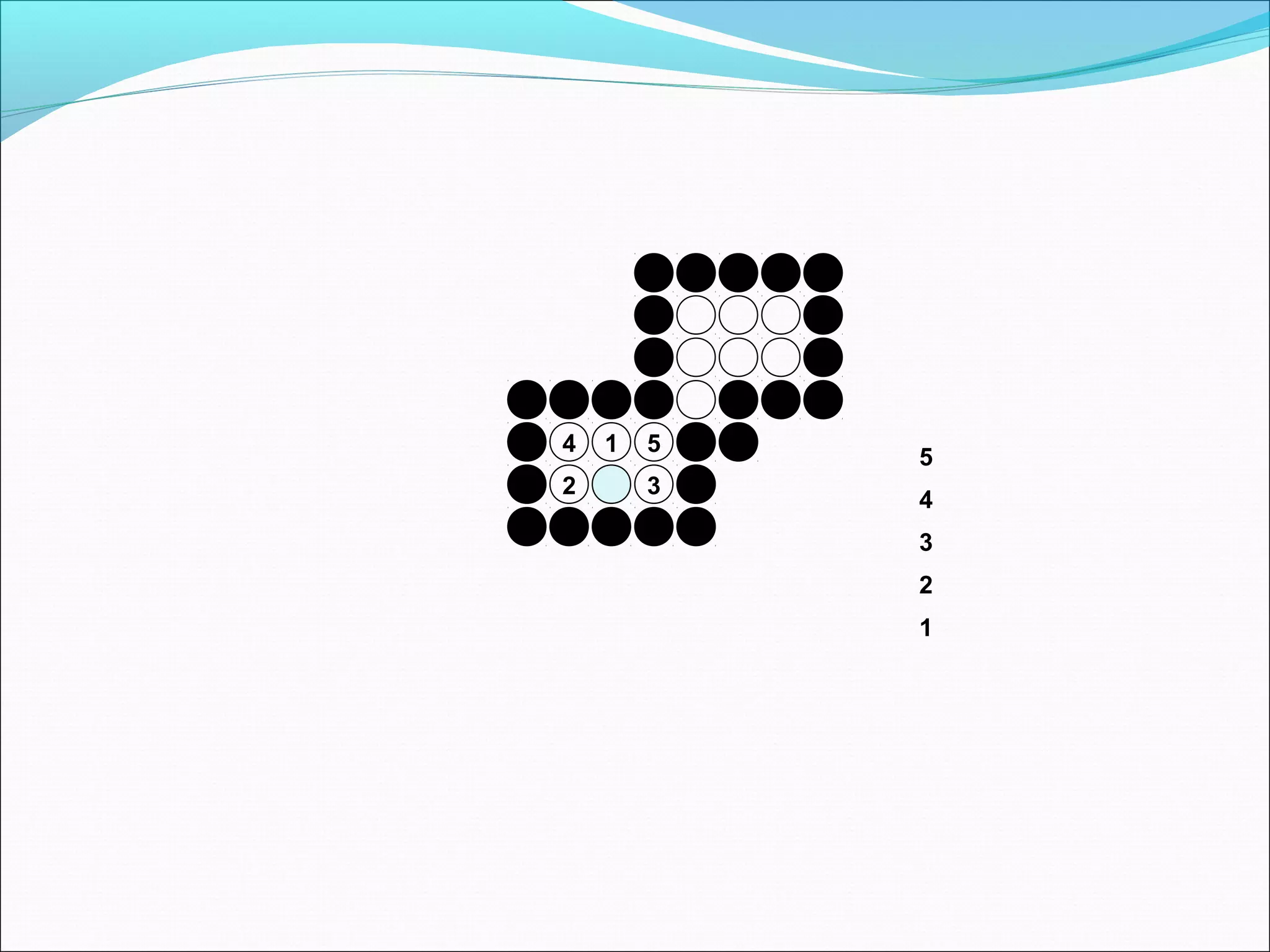
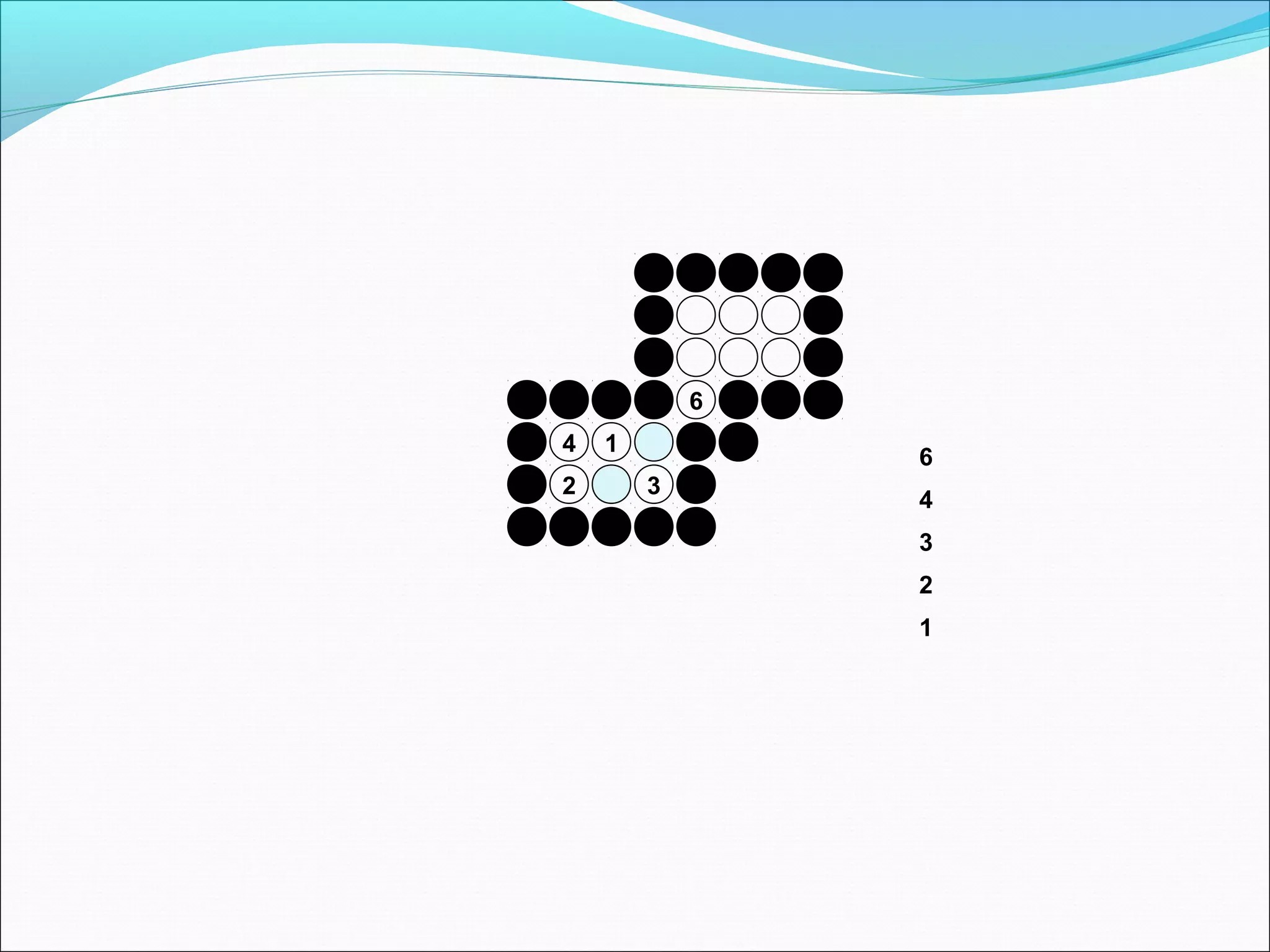
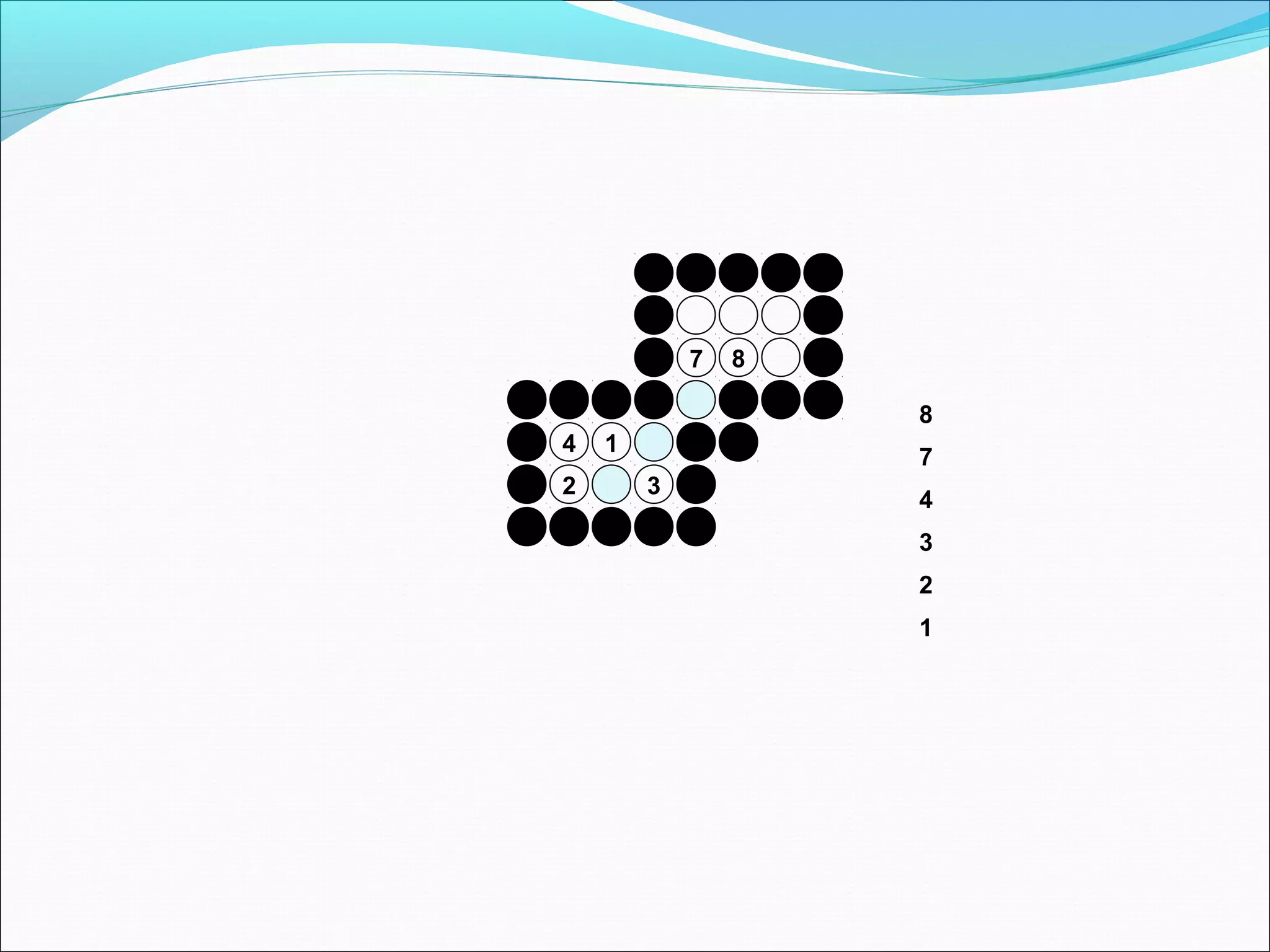
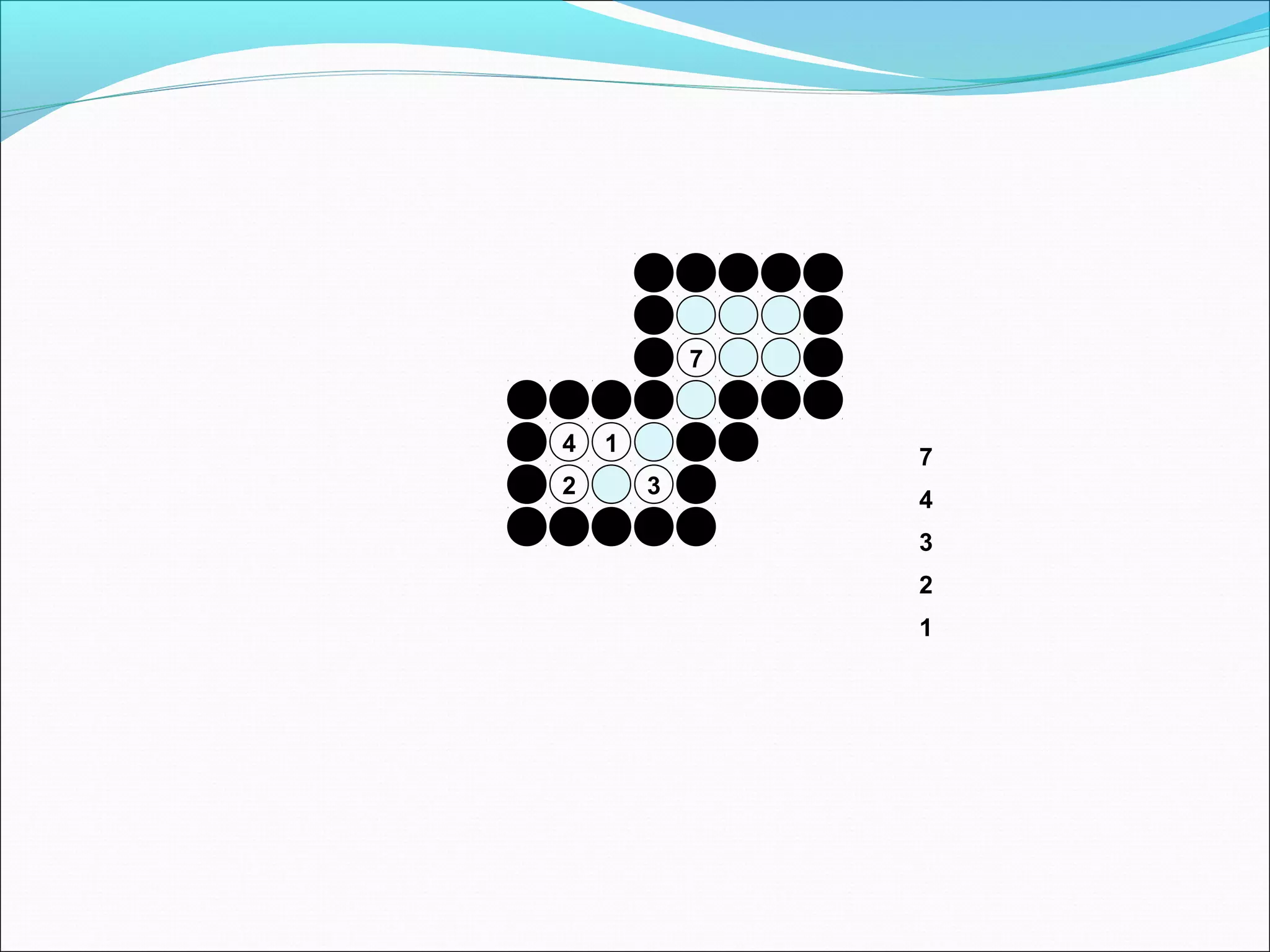
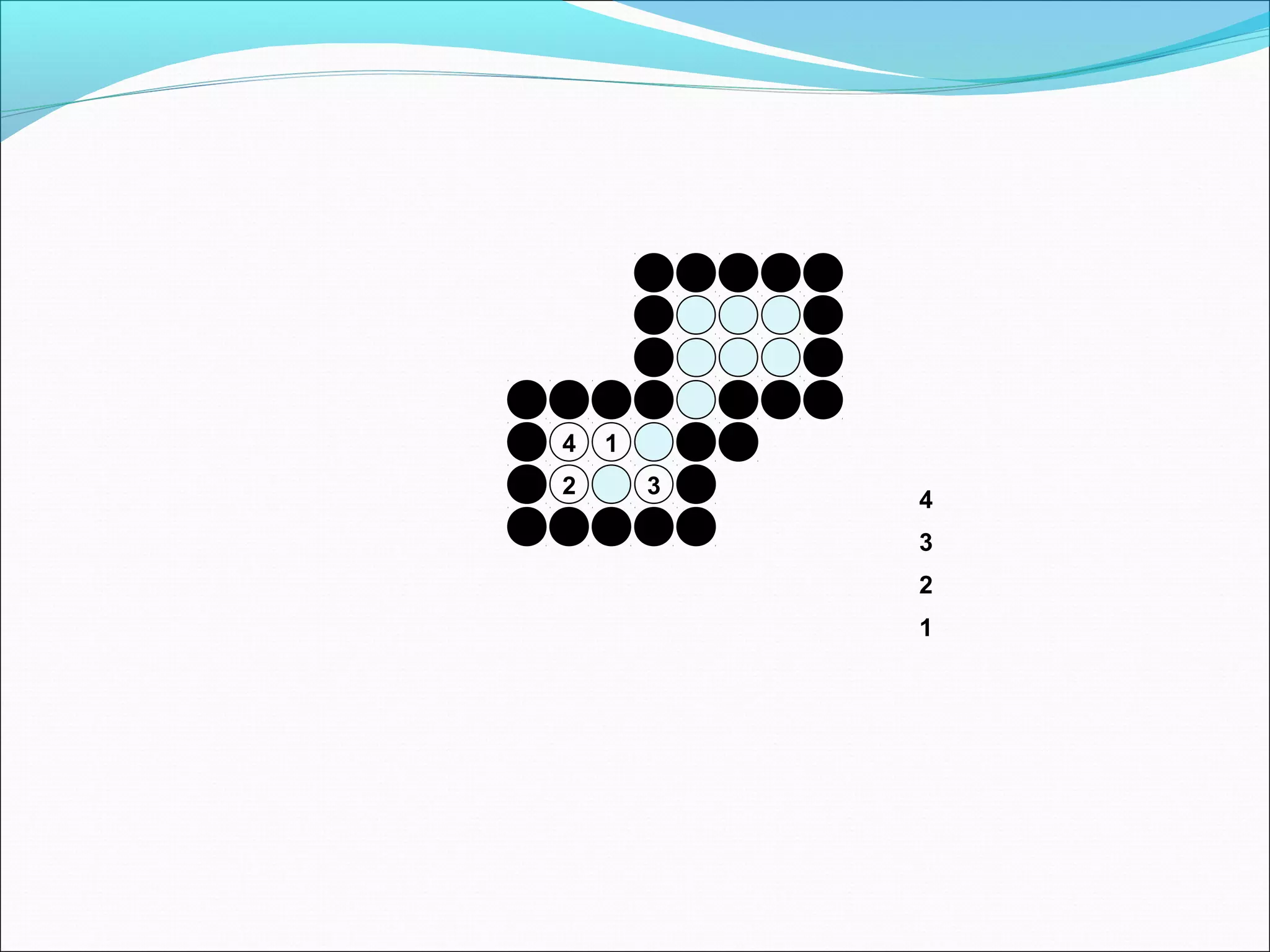
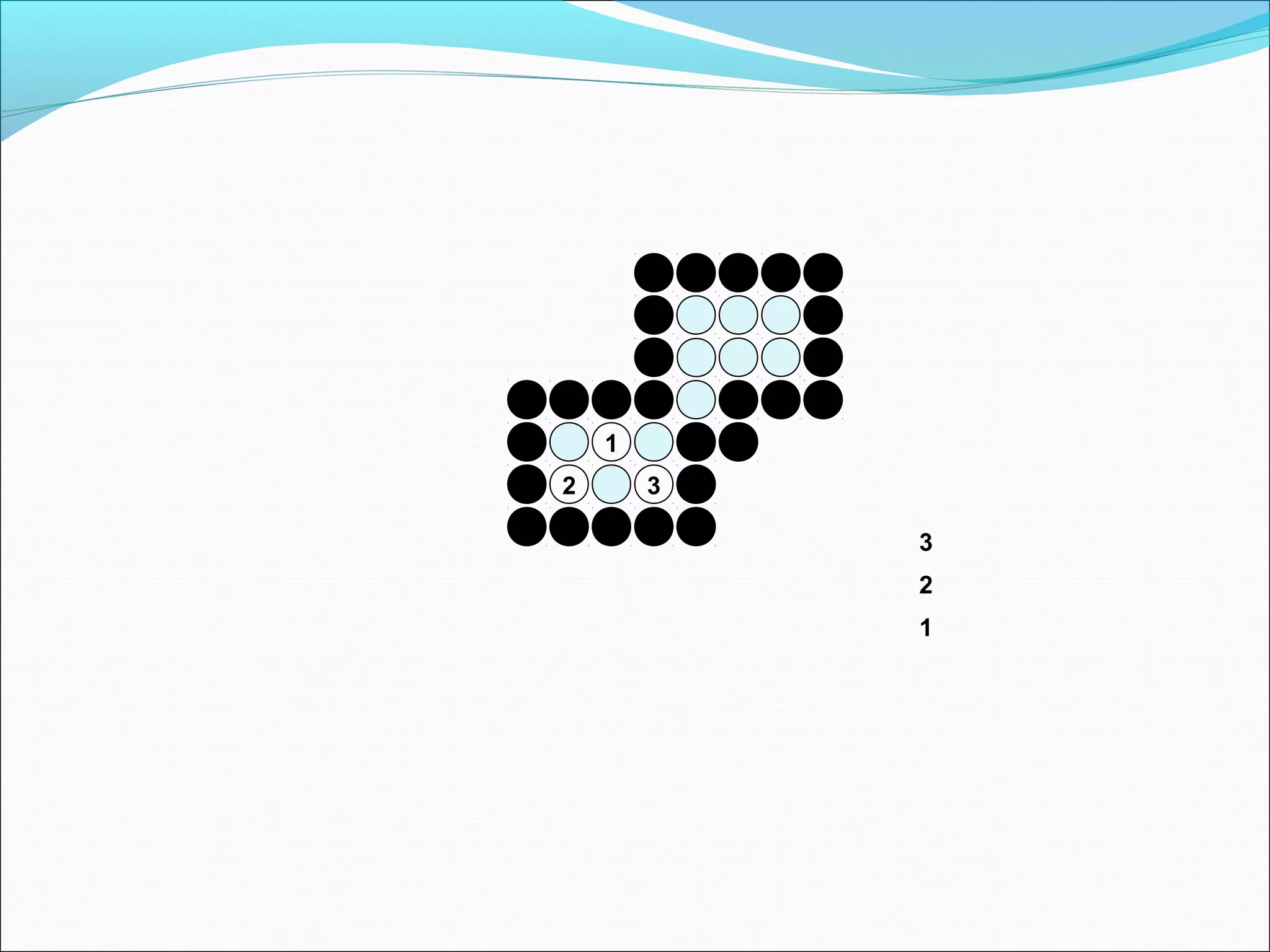
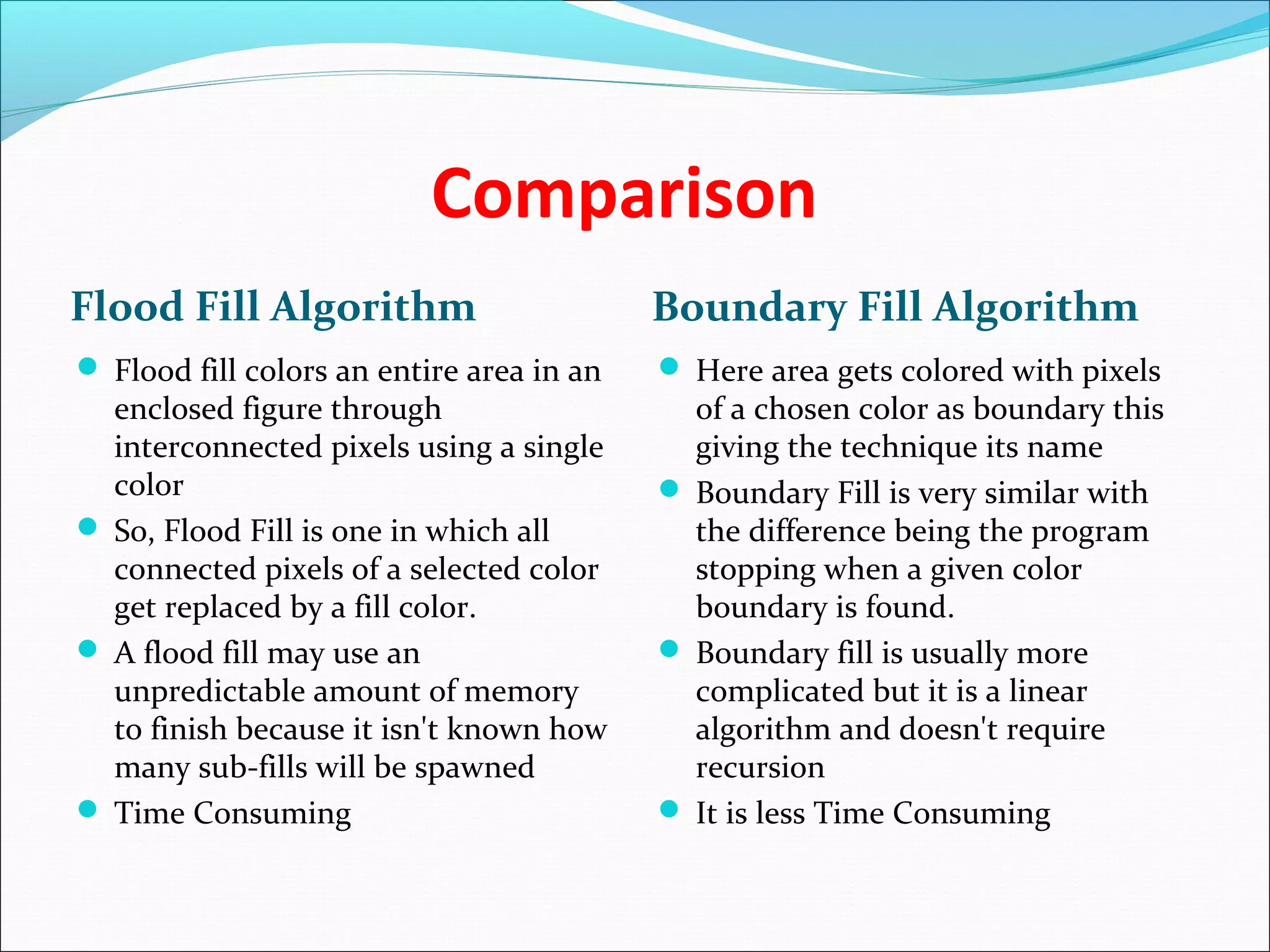
The document discusses two algorithms for filling polygons: boundary fill and flood fill. Boundary fill starts at a point inside the polygon and fills pixels until it reaches the boundary color. Flood fill replaces all pixels of a specified interior color with a fill color. Both can be implemented with 4-connected or 8-connected pixels. Flood fill colors the entire area but uses more memory, while boundary fill stops at the boundary and is more efficient.