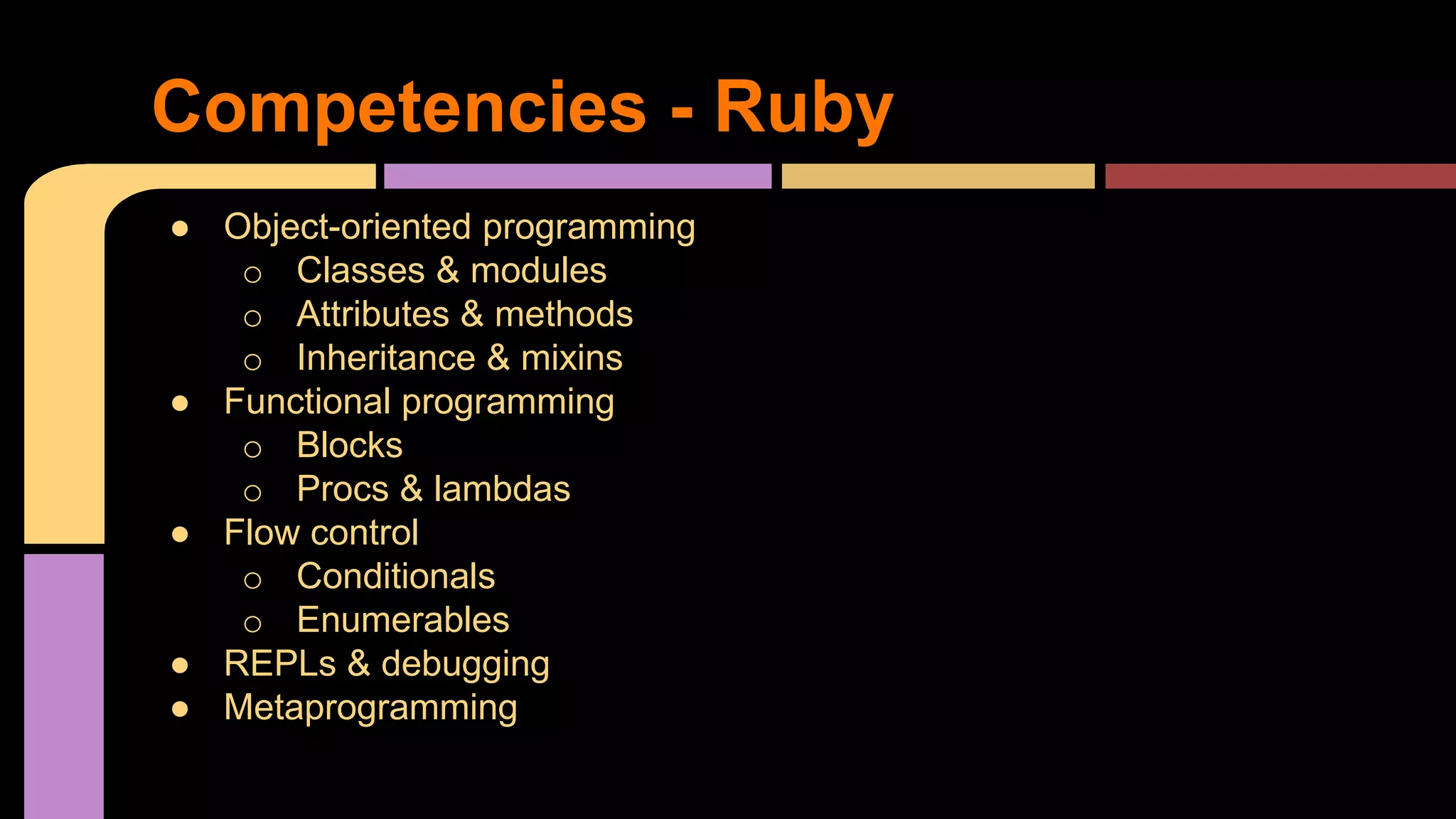
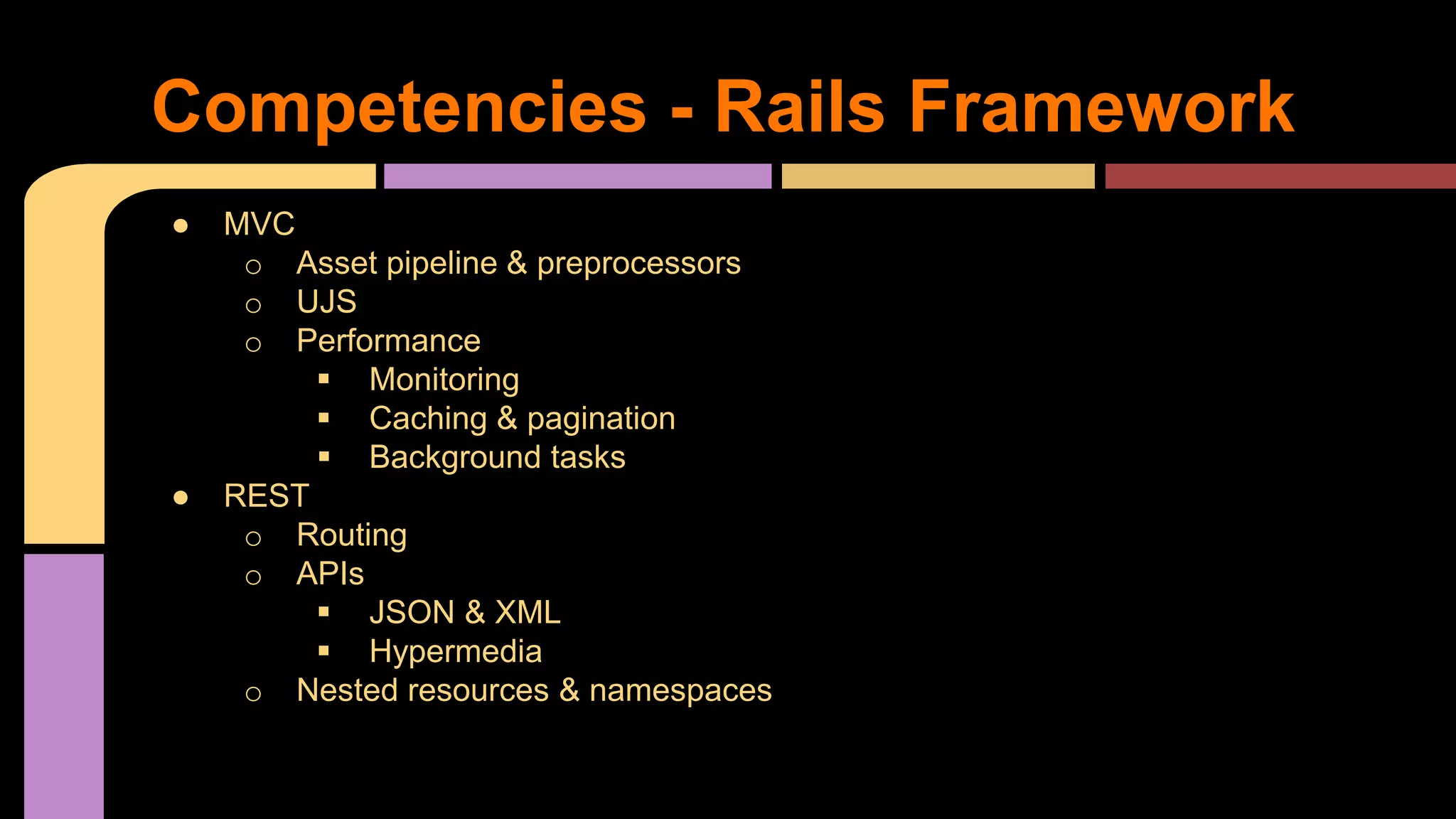
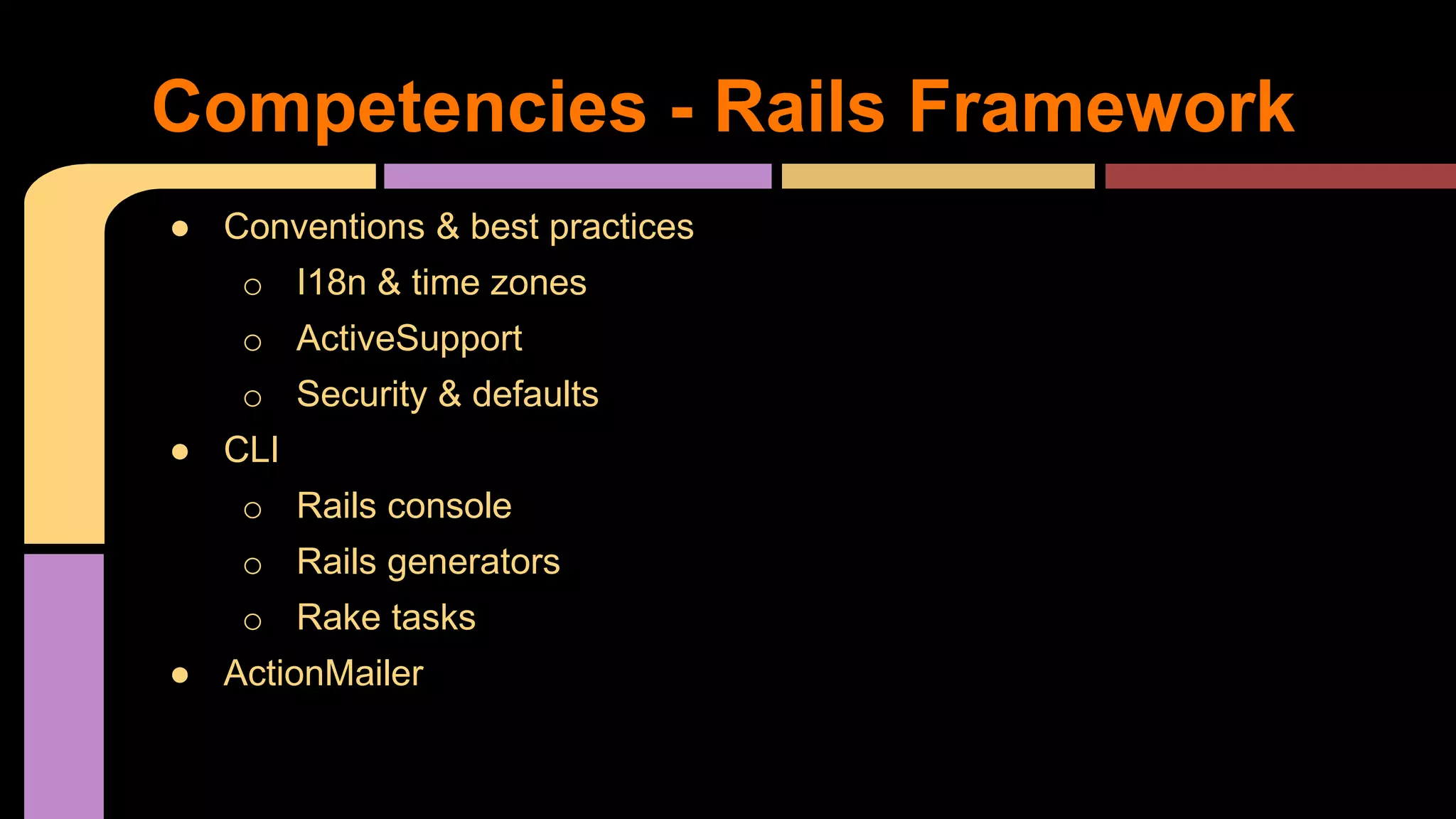
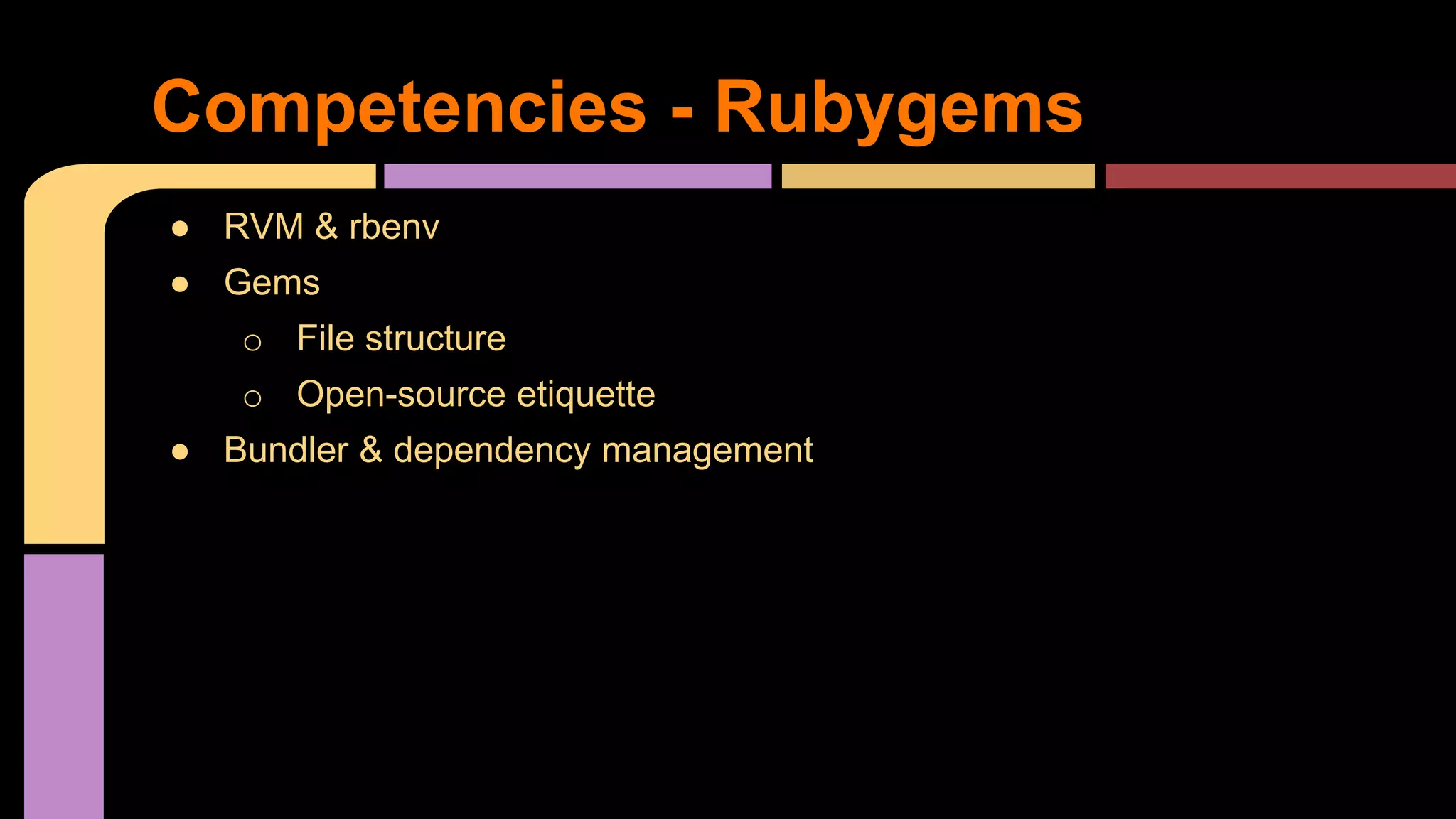
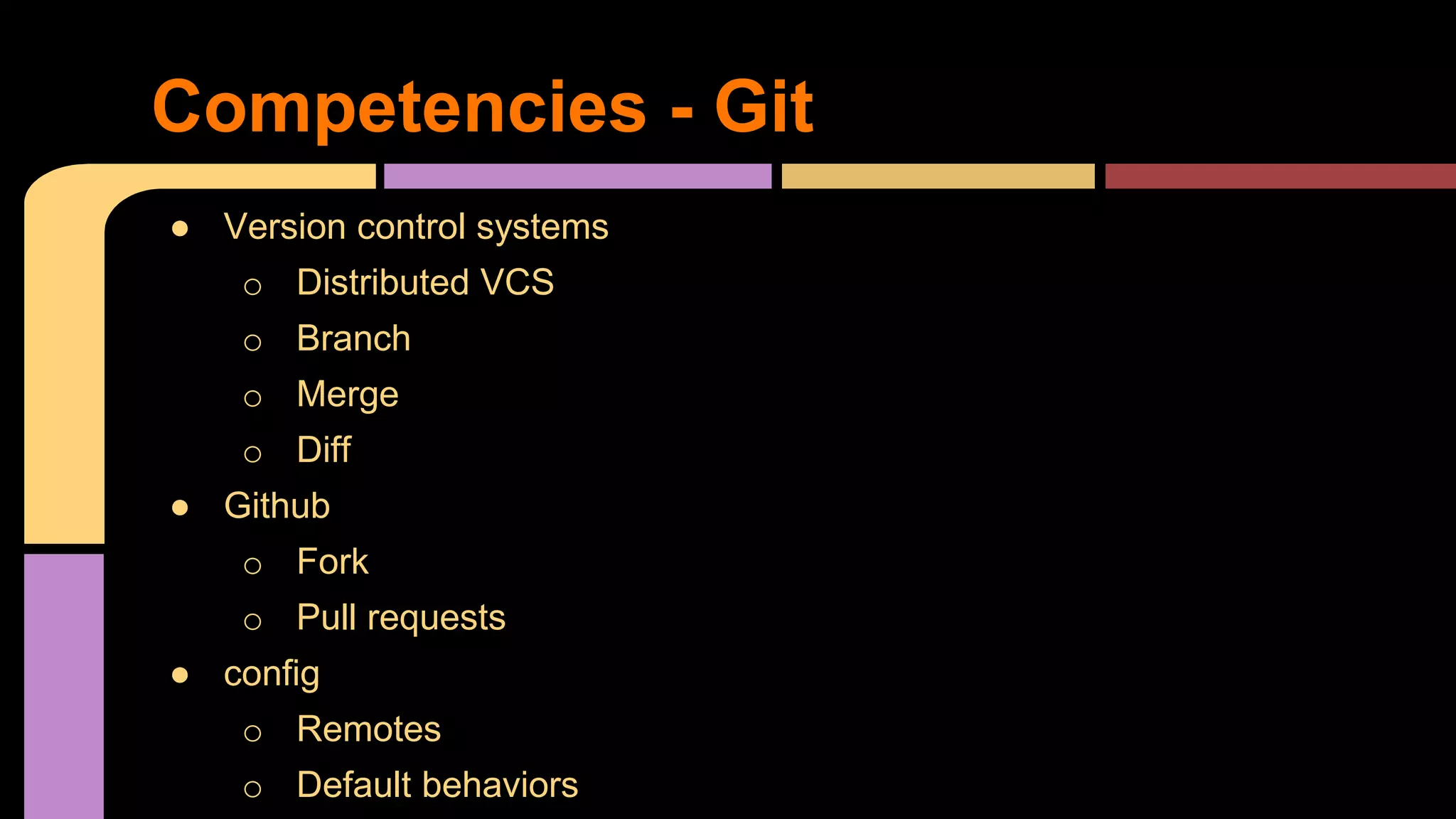
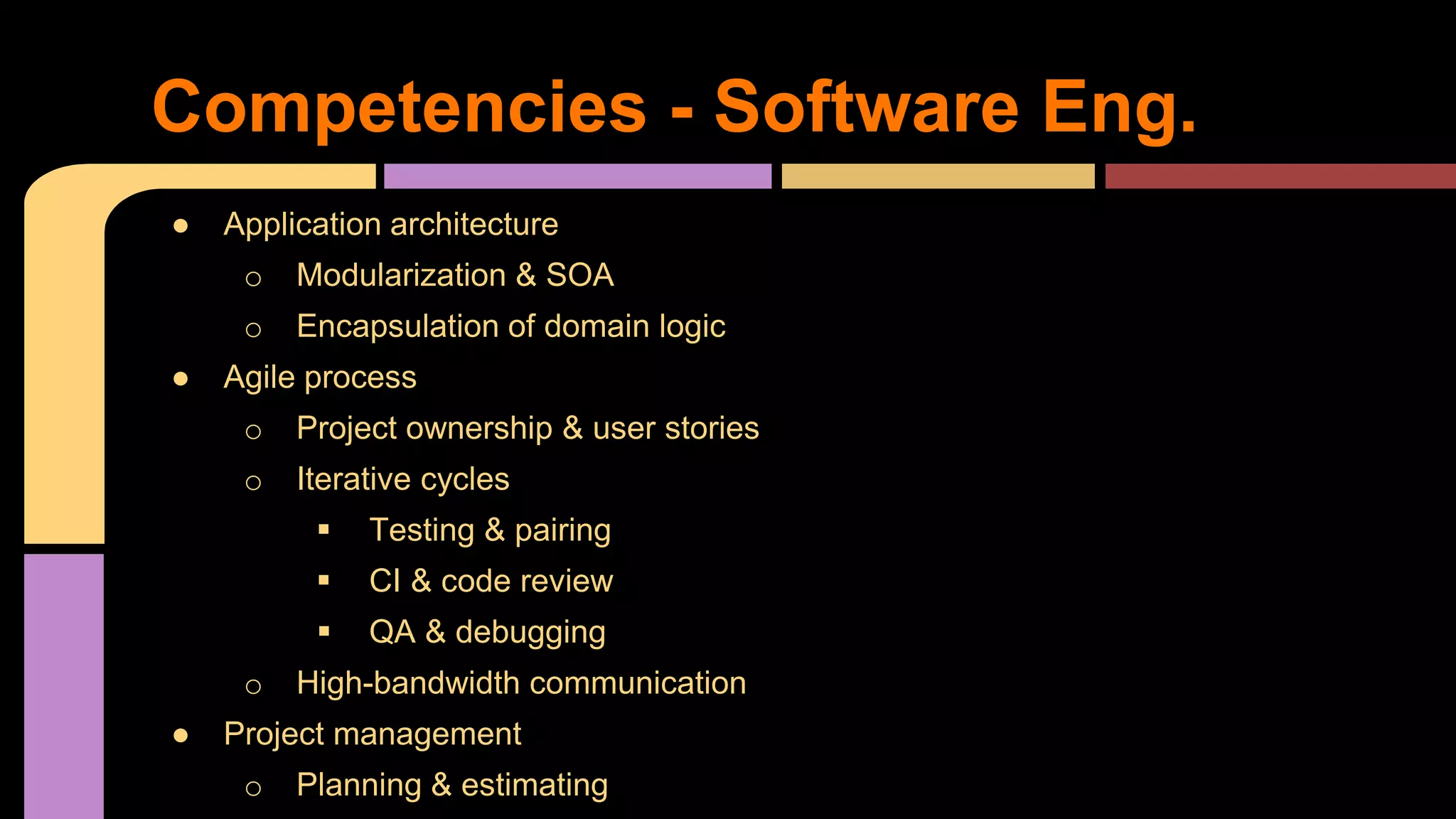
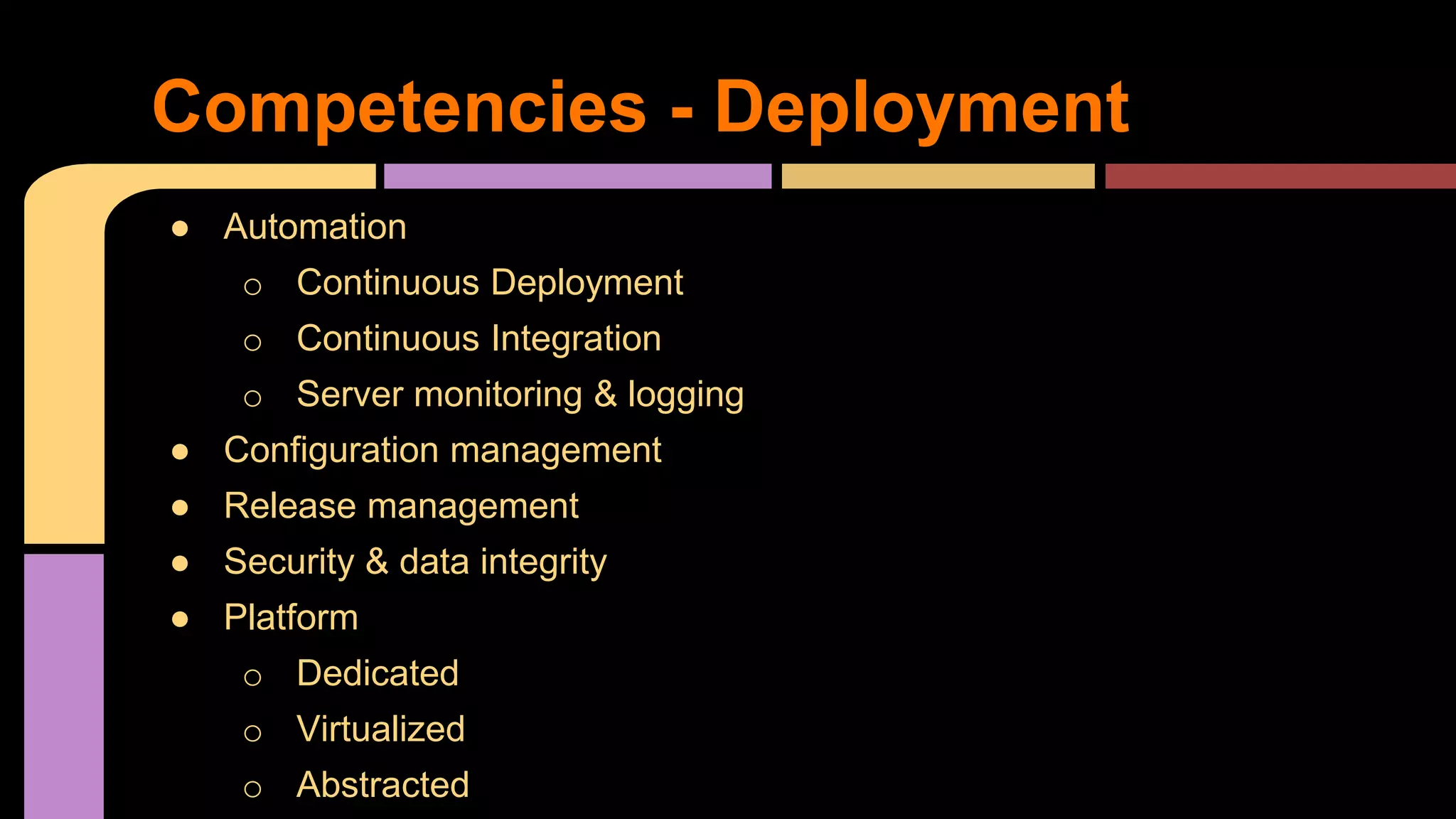
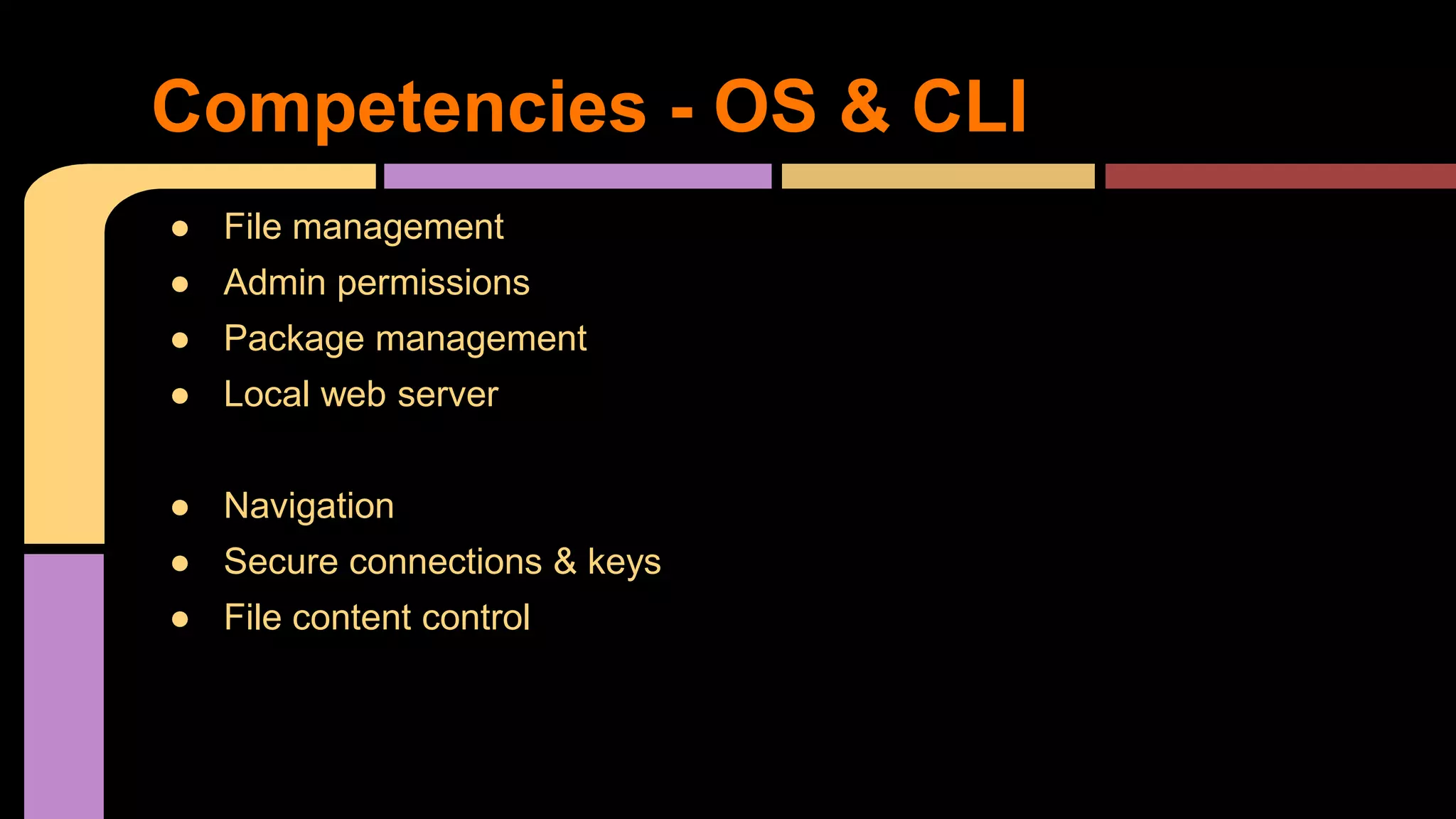
This document provides guidance on becoming a Rails developer beyond just learning the Rails framework. It discusses key competencies needed like understanding Ruby and object-oriented programming. It also recommends learning processes like mentoring, code reviews, and pair programming. Standard learning paths are outlined covering Ruby, Rails, SQL, testing, and more. Advice is given on freelancing, finding clients, and maintaining work-life balance.