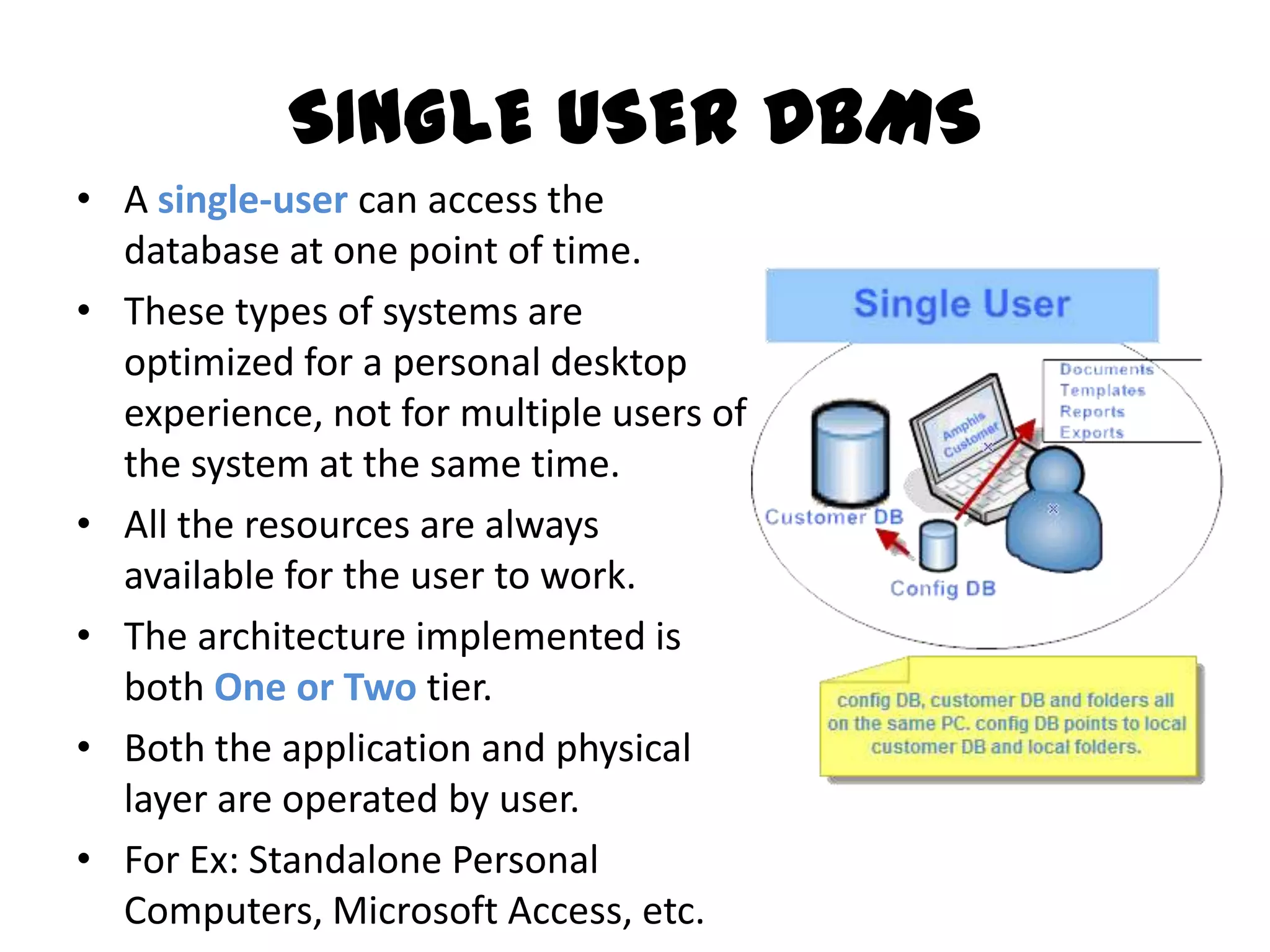
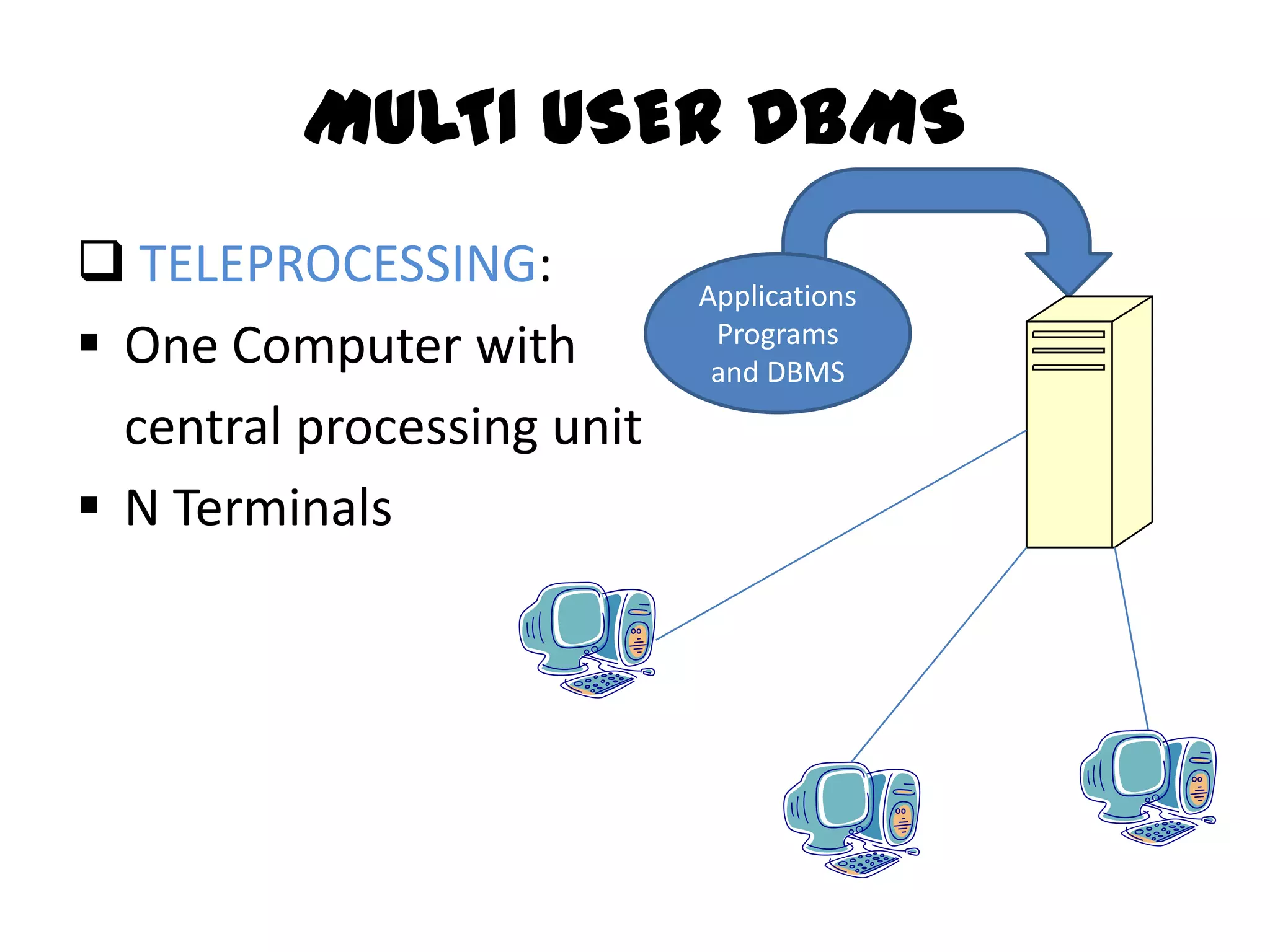
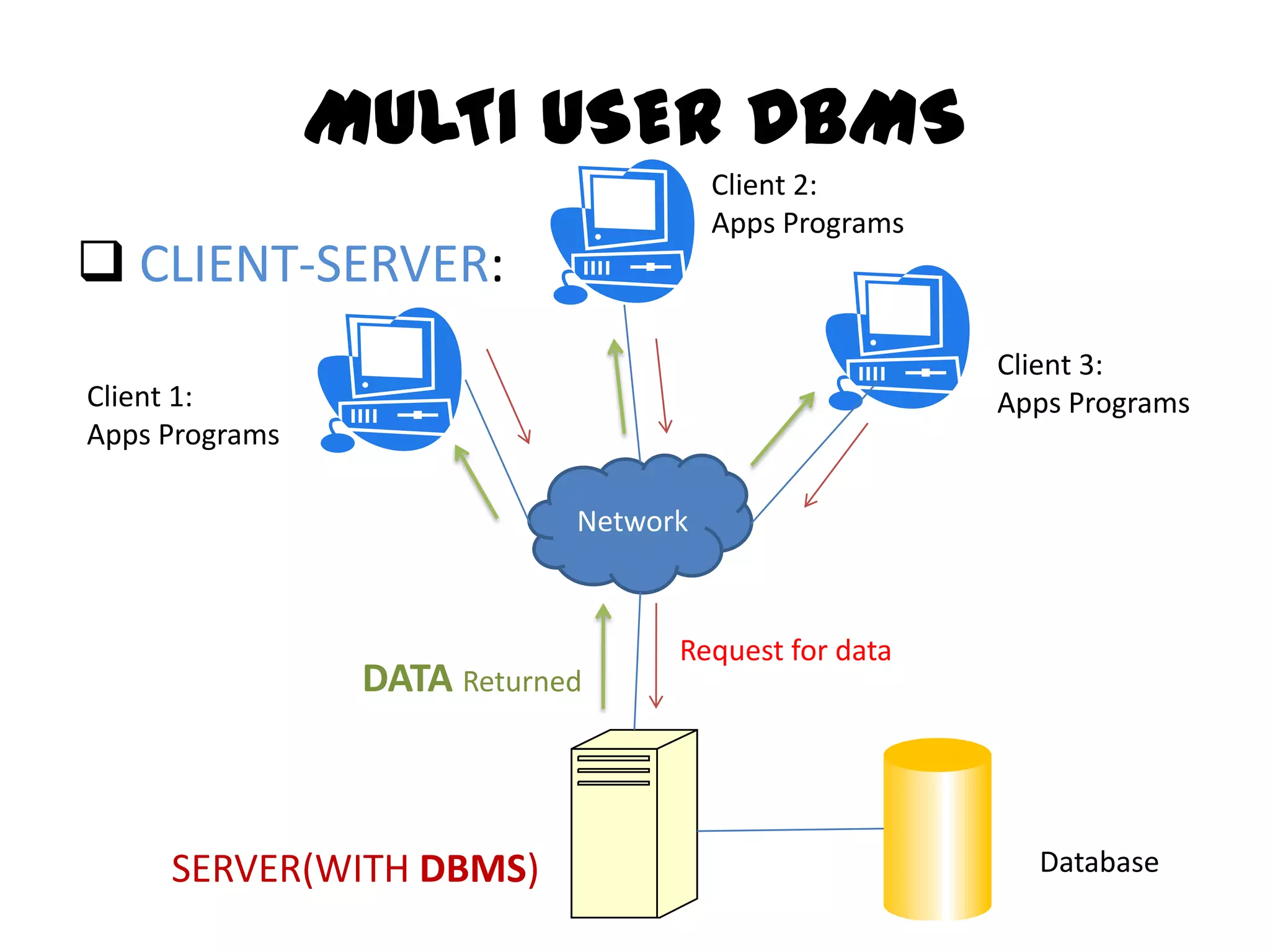
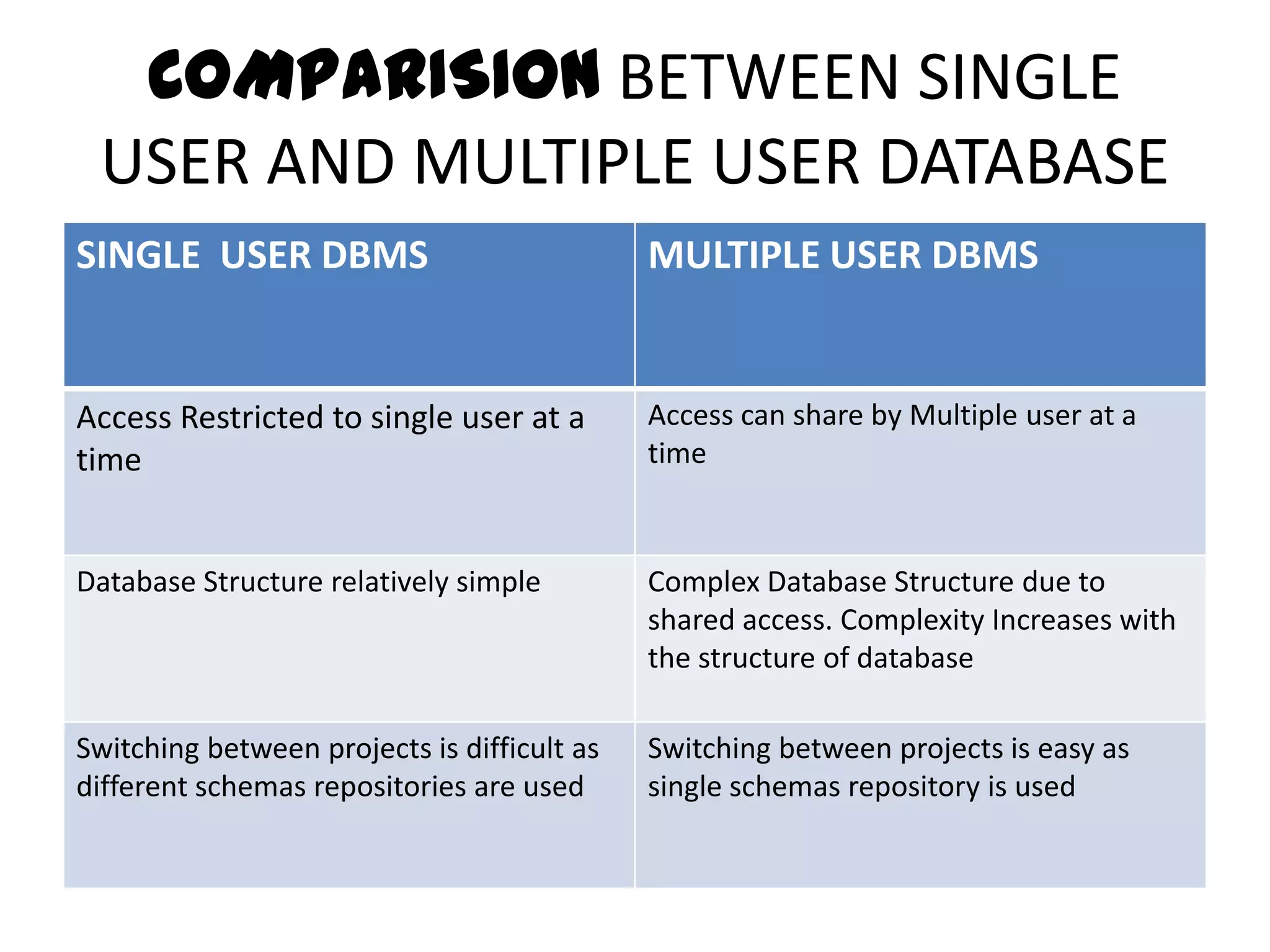
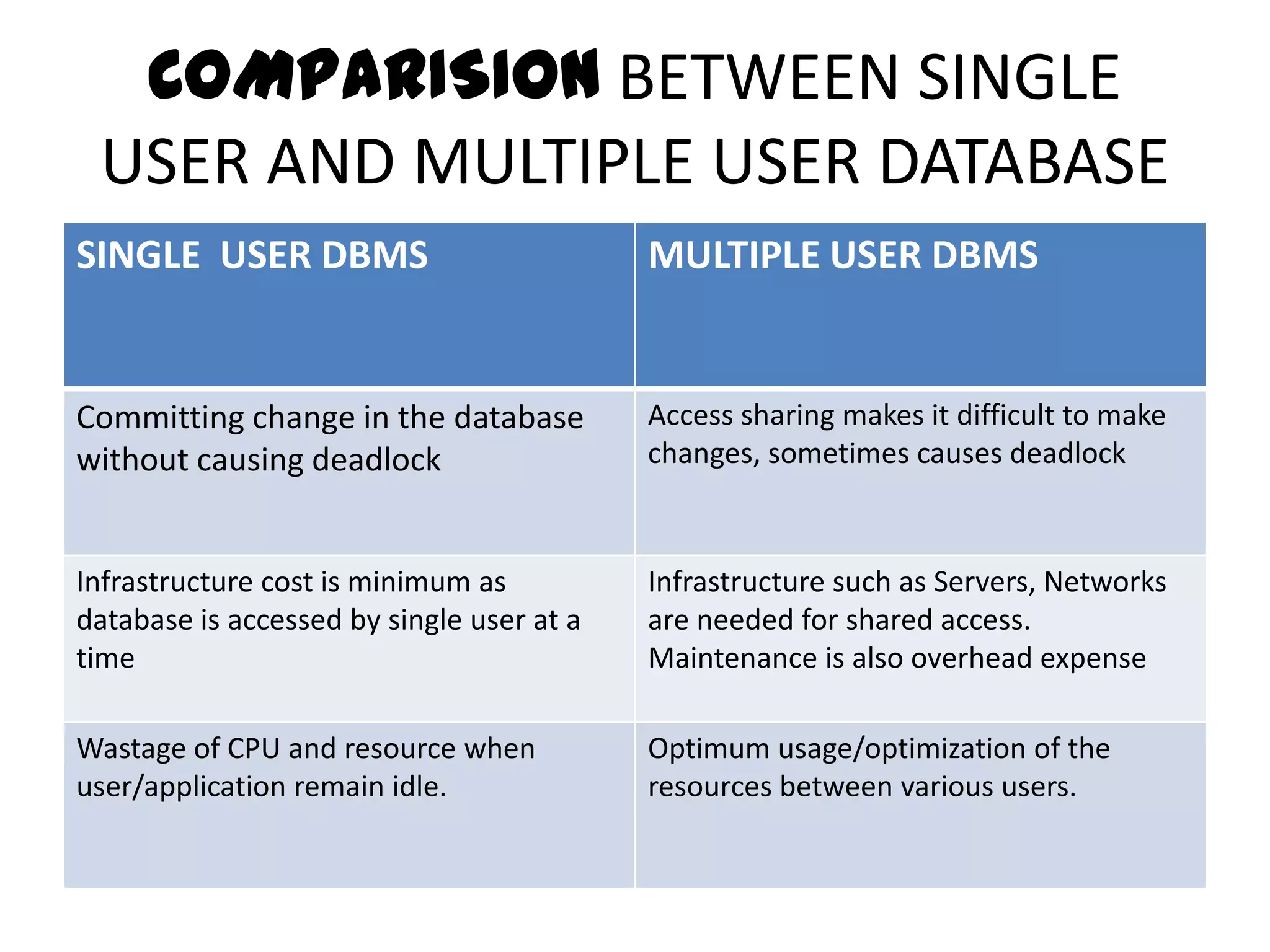
This document compares single-user and multi-user database management systems (DBMS). A single-user DBMS only allows one user to access the database at a time, while a multi-user DBMS allows simultaneous access from multiple users. Multi-user DBMSs require more complex structures and infrastructure like servers and networks to manage shared access, but allow for optimized resource usage and up-to-date information for all users. Key differences include access restrictions, database complexity, ease of switching projects, potential for deadlocks, and infrastructure costs.