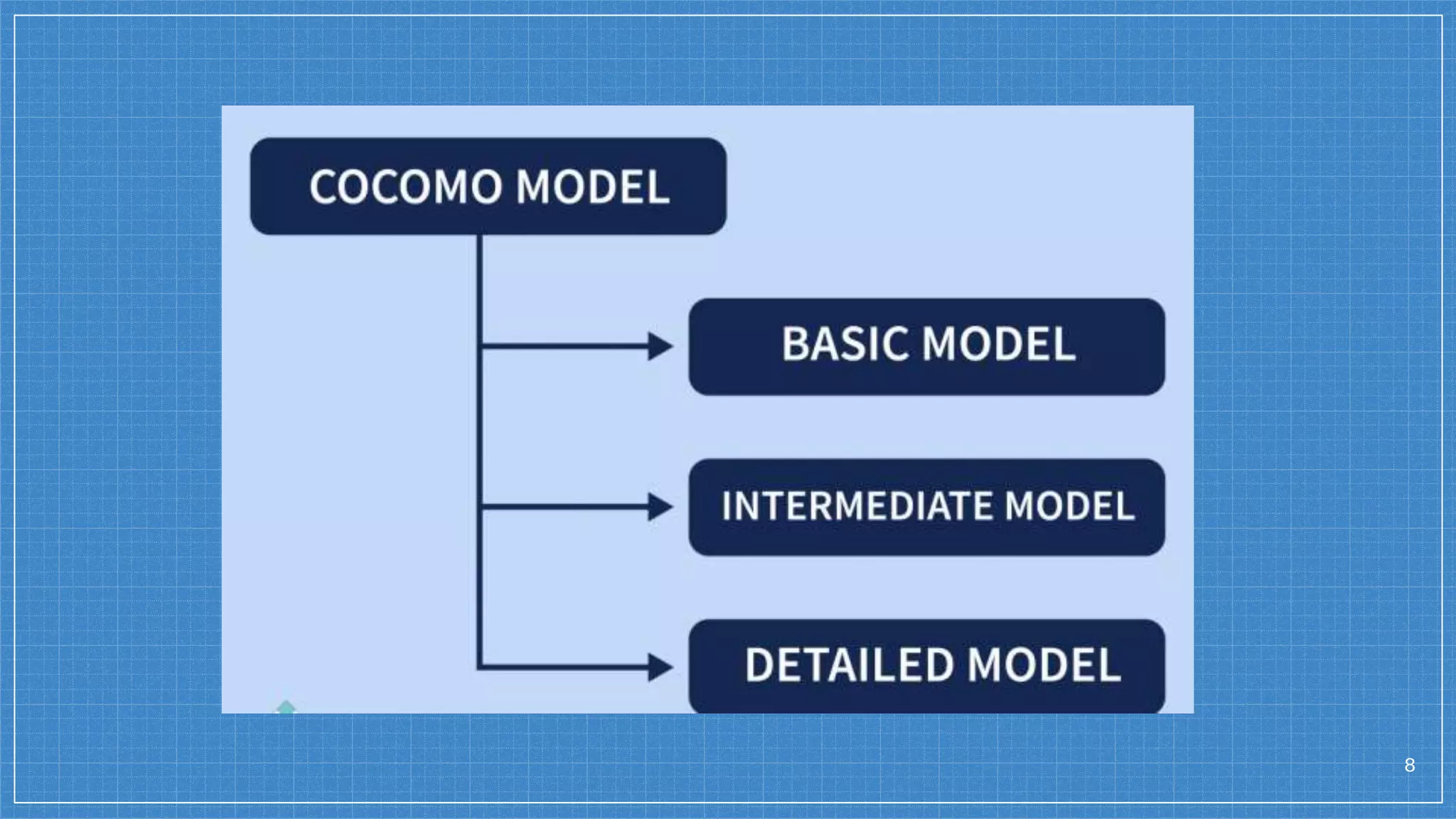
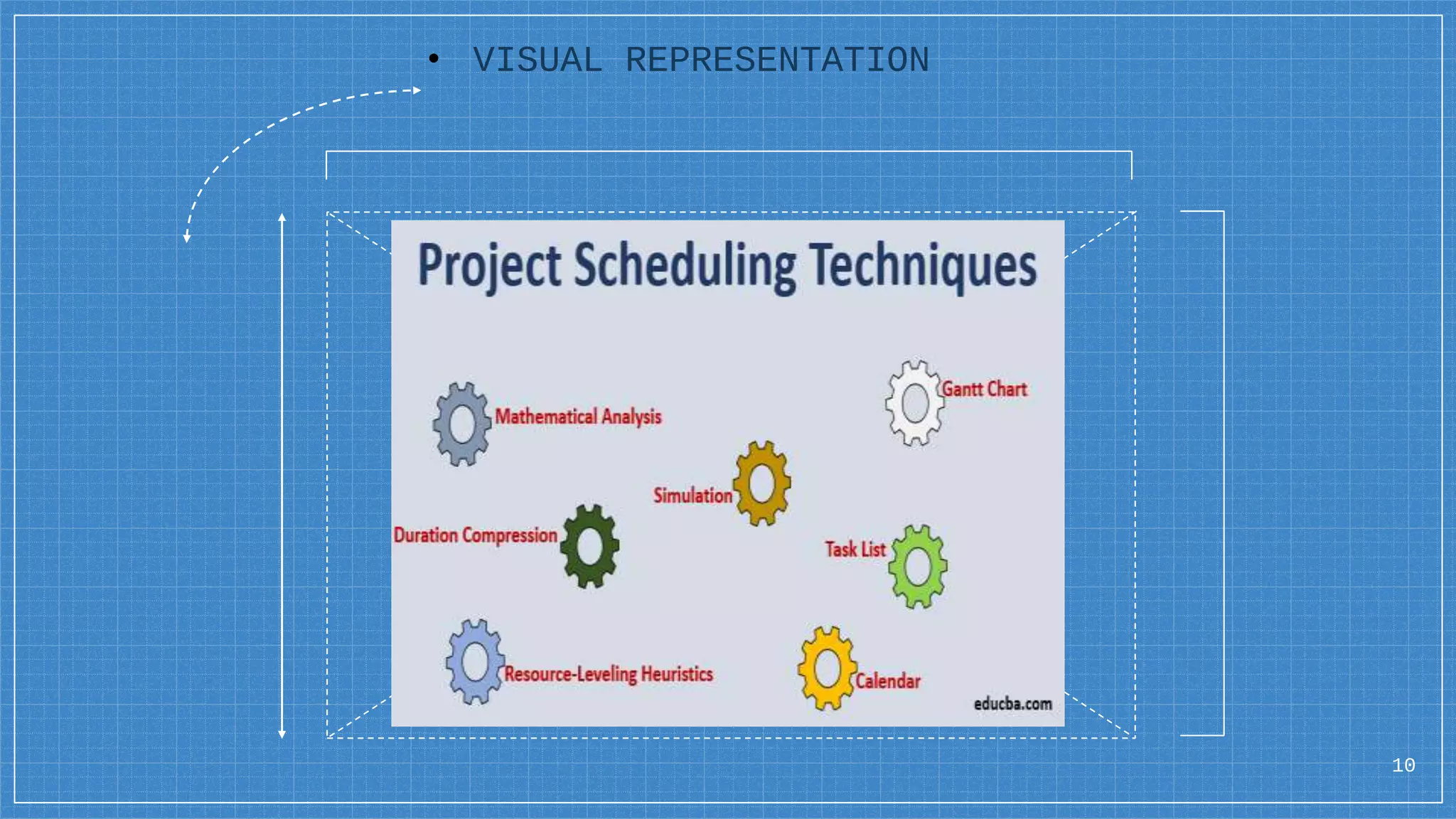
The document discusses software metrics, project management, and estimation techniques. It defines different types of metrics including product, process, and project metrics. It also discusses quality metrics, project management fundamentals involving people, product, process and project, and estimation techniques like function point analysis, lines of code estimation, and the COCOMO model. Project scheduling techniques like Gantt charts and critical path analysis are also covered. The conclusion emphasizes that metrics, project management, and estimation are essential for successful software development.