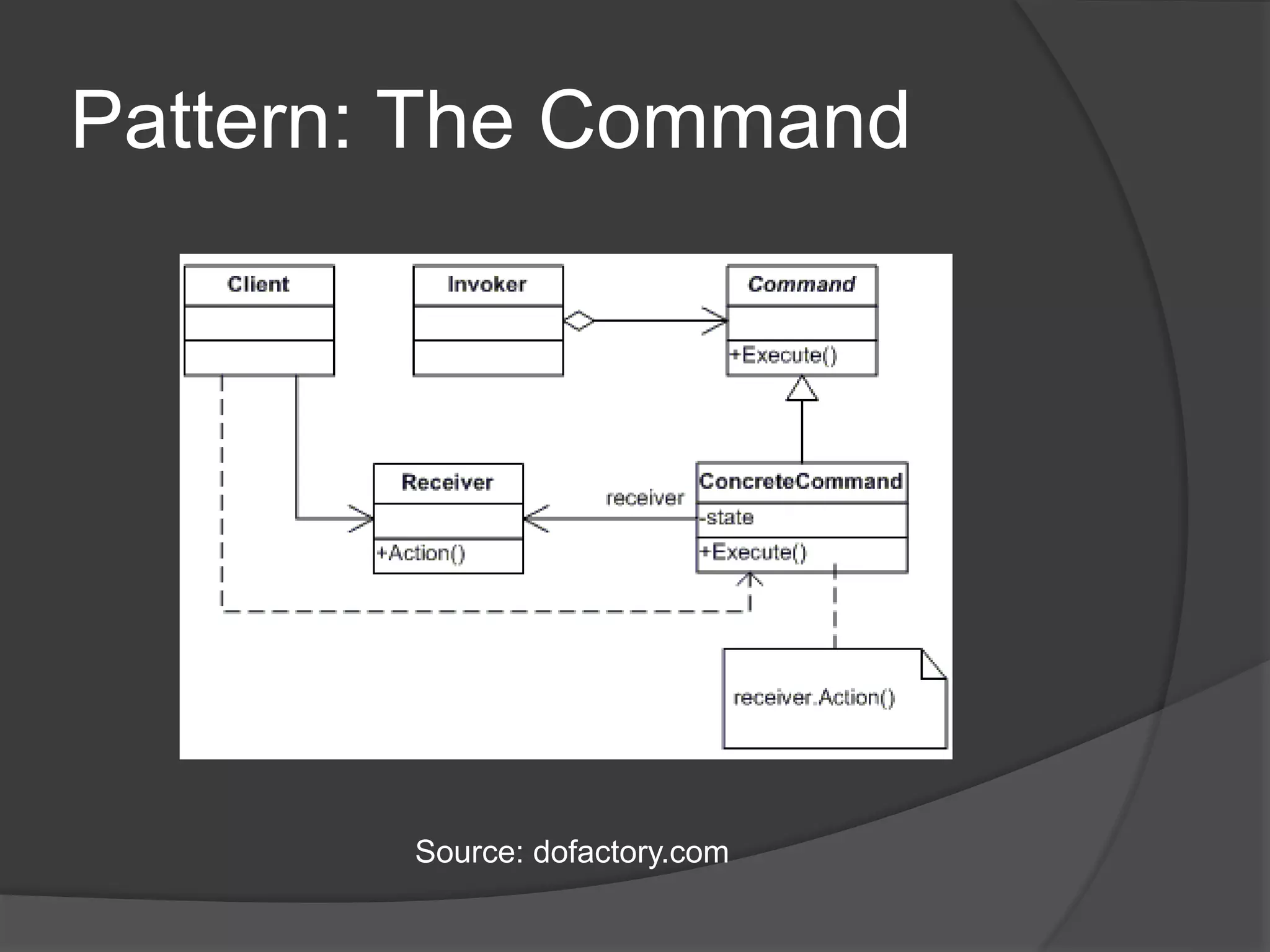
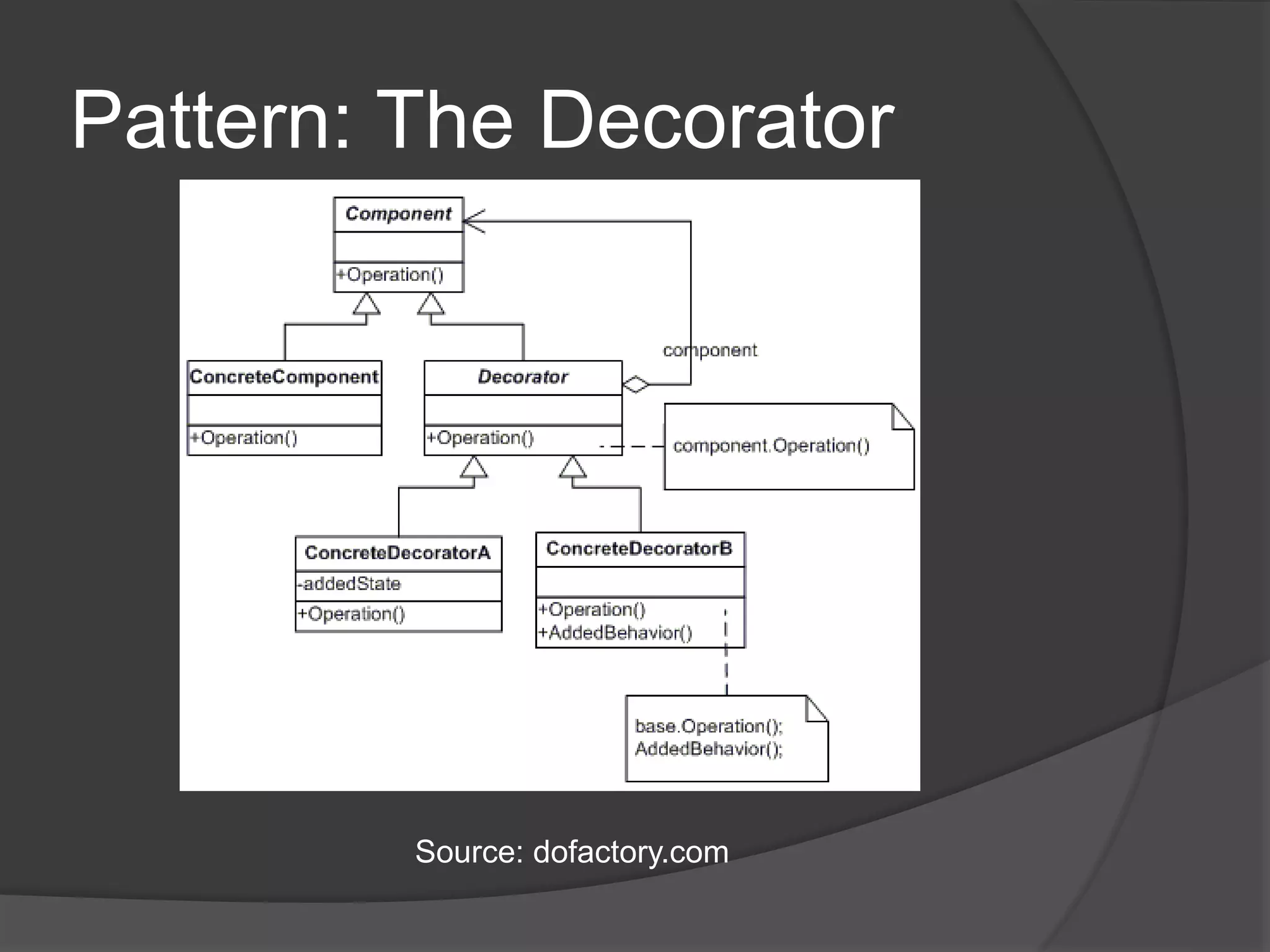
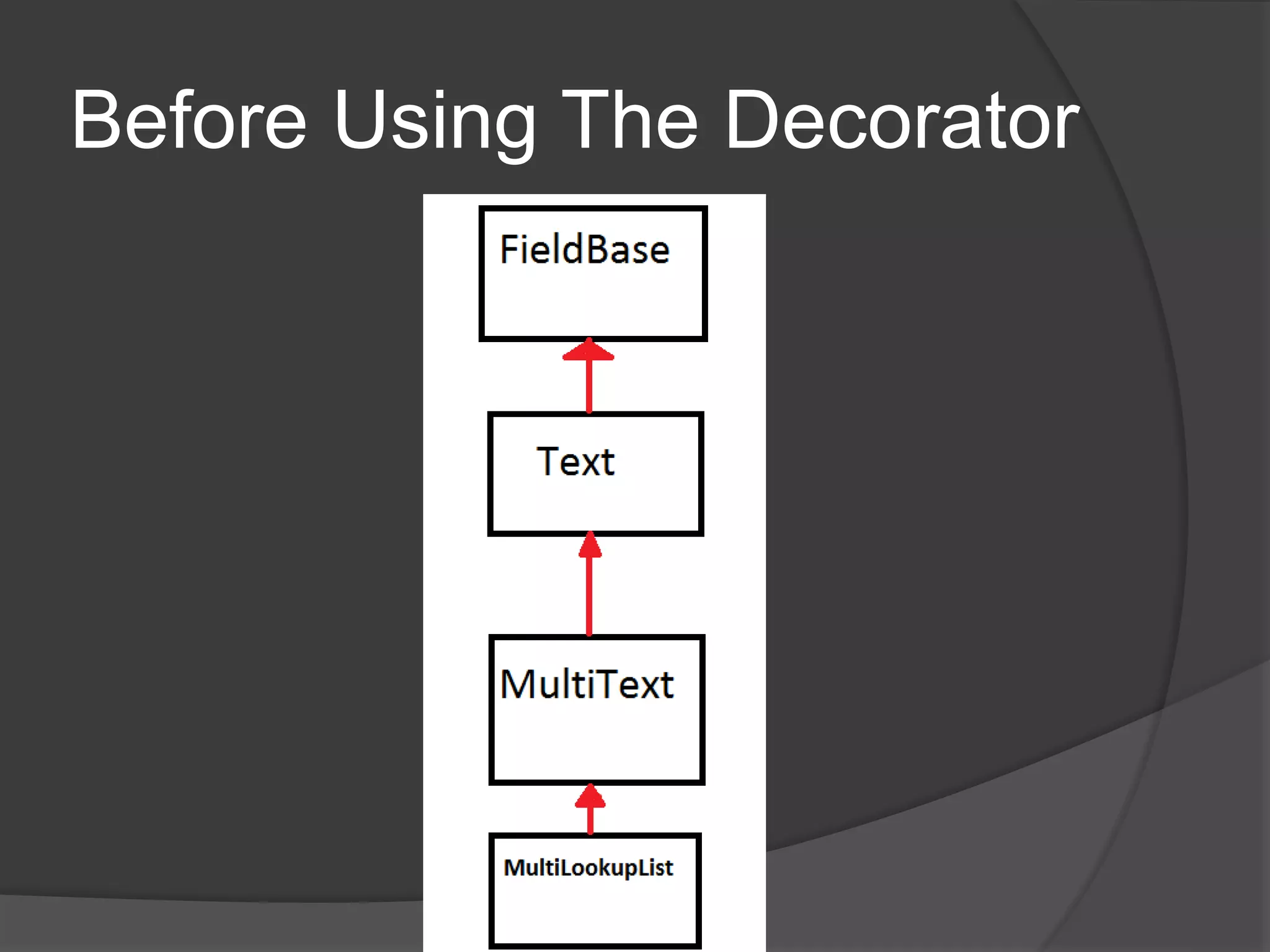
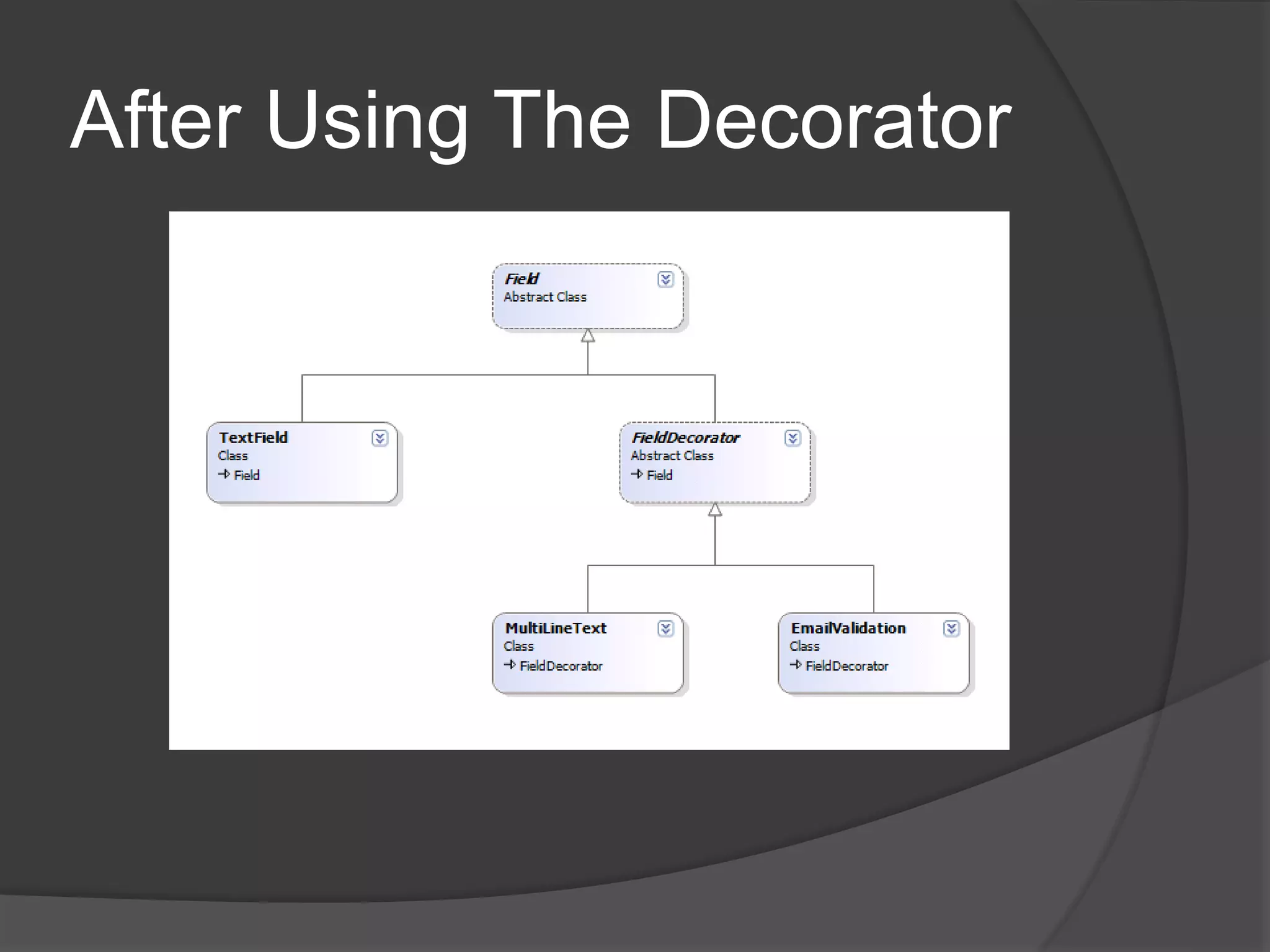
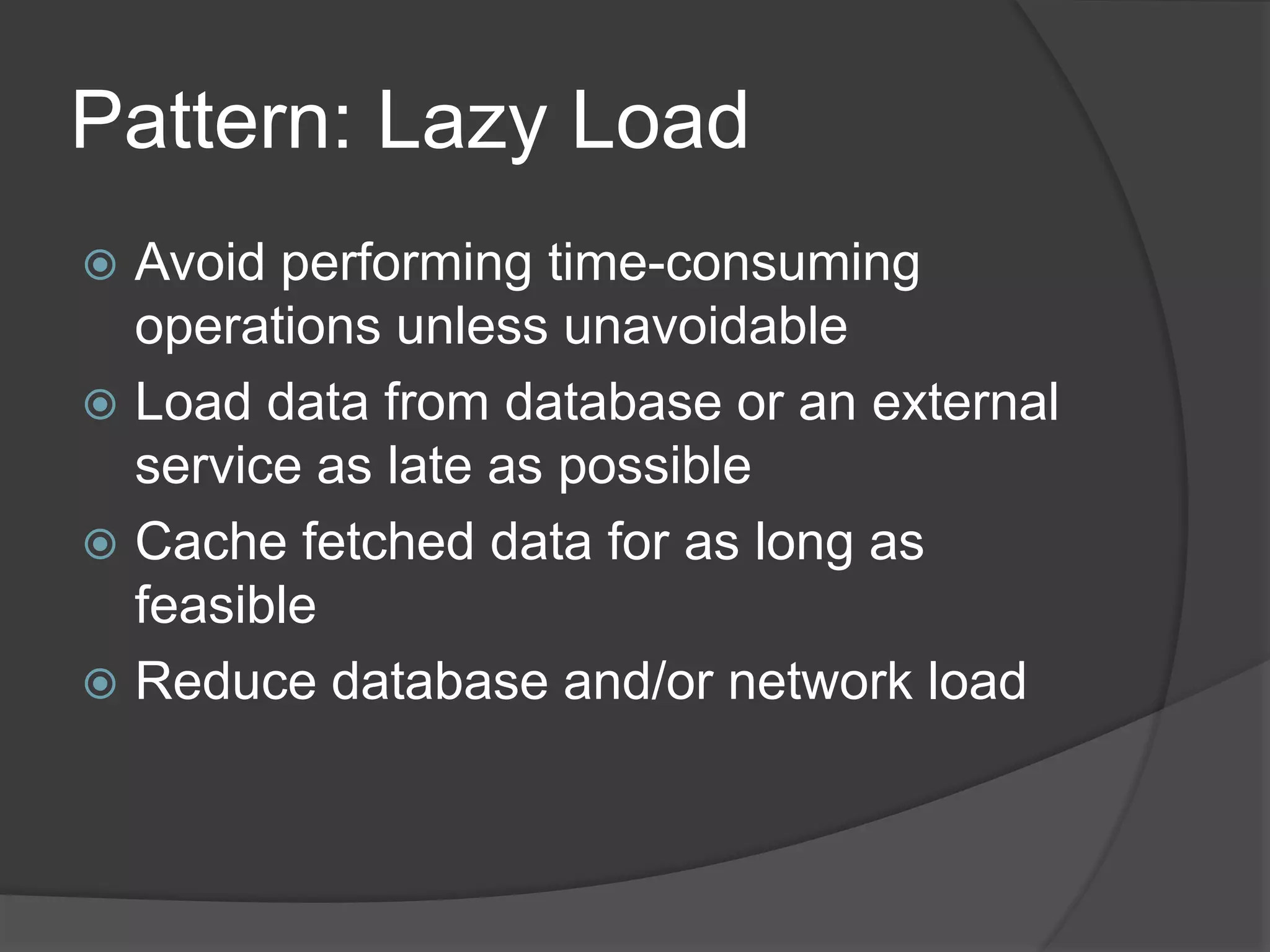
Design patterns are reusable code solutions to common programming problems. They create a common vocabulary that allows designers and developers to communicate effectively. Some key design patterns include the Command pattern, which encapsulates executing operations as objects, and the Decorator pattern, which allows adding new functionality to objects without modifying them. Using patterns like Lazy Load avoids unnecessary processing until needed.