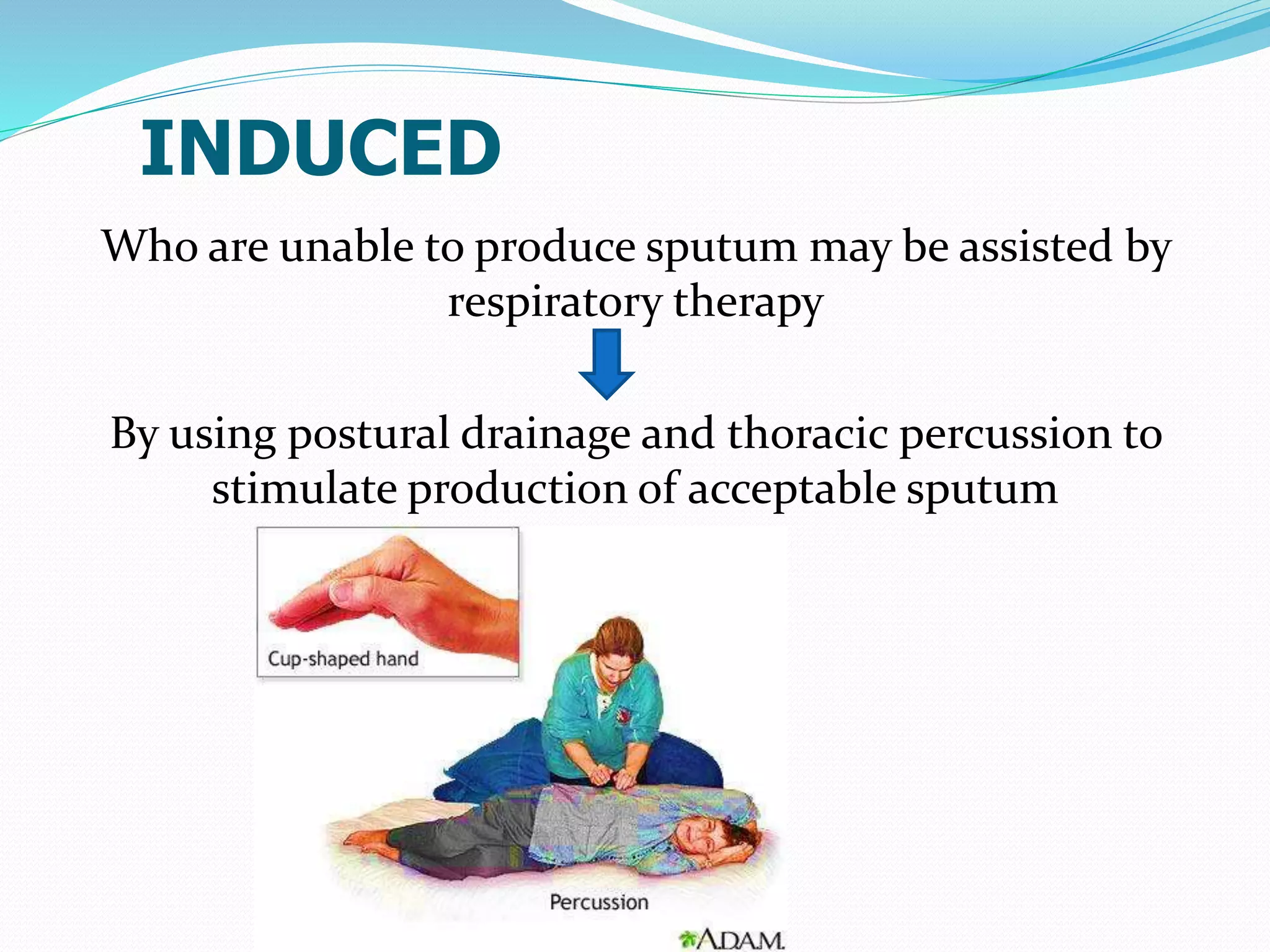
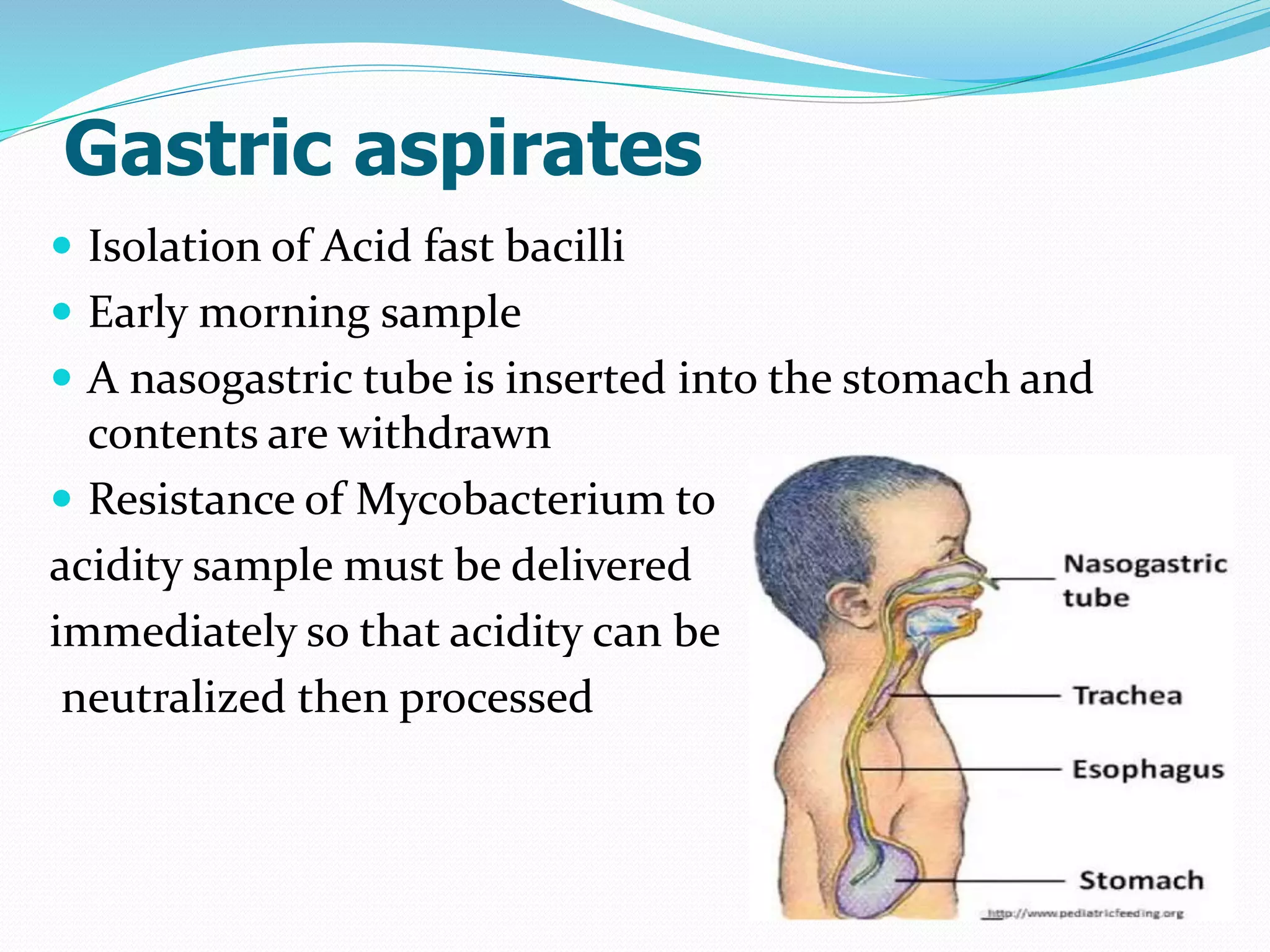
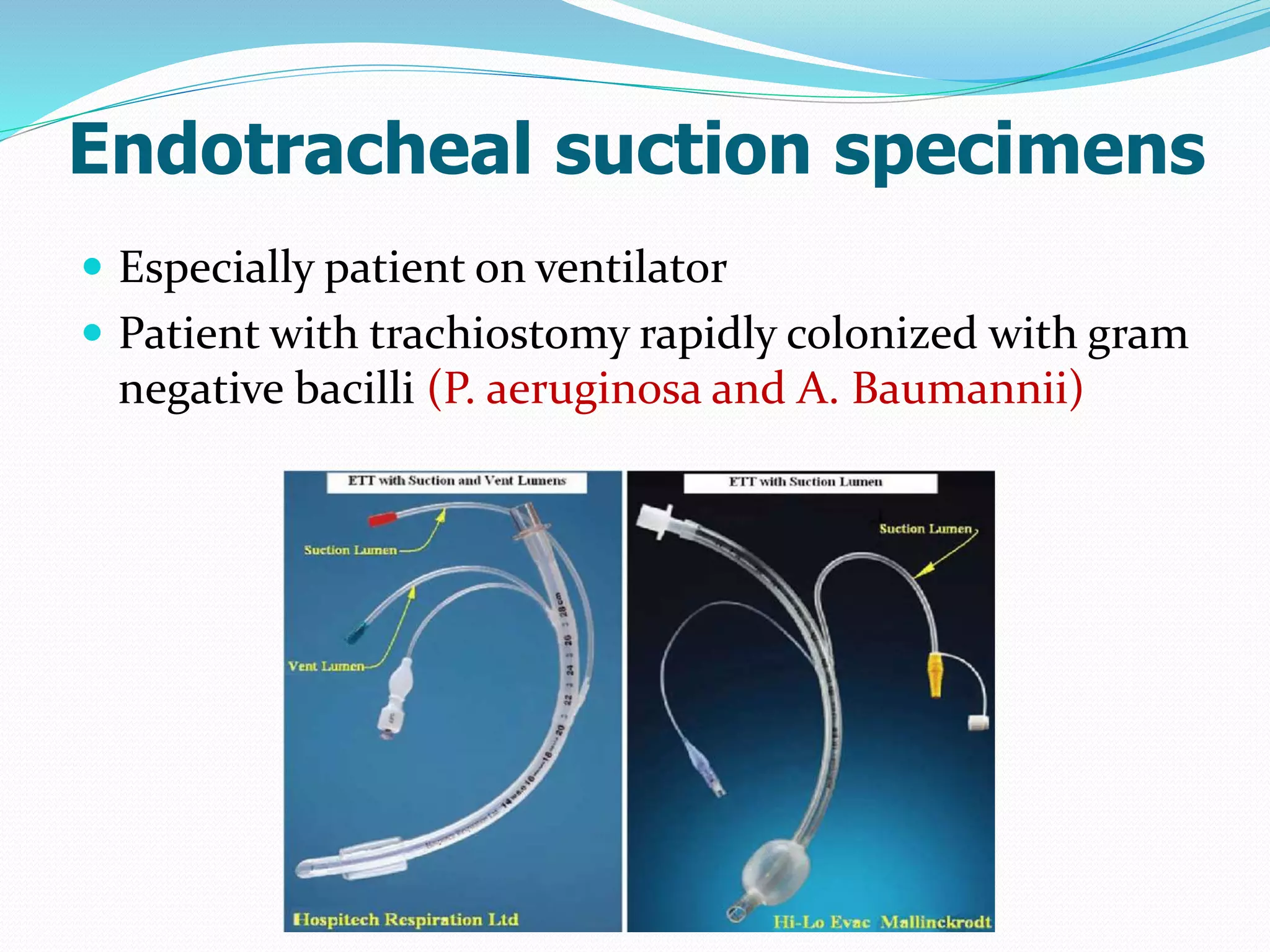
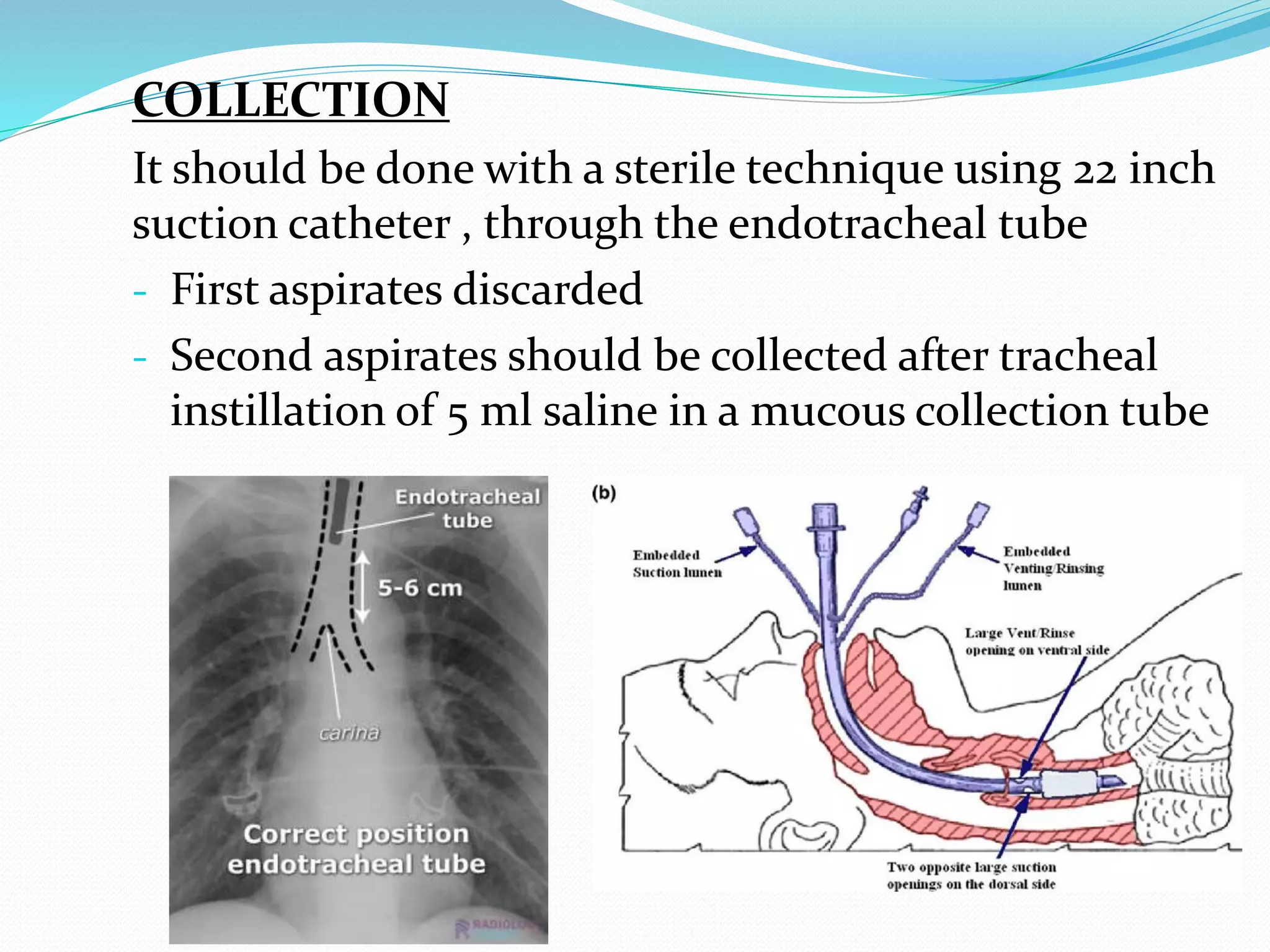
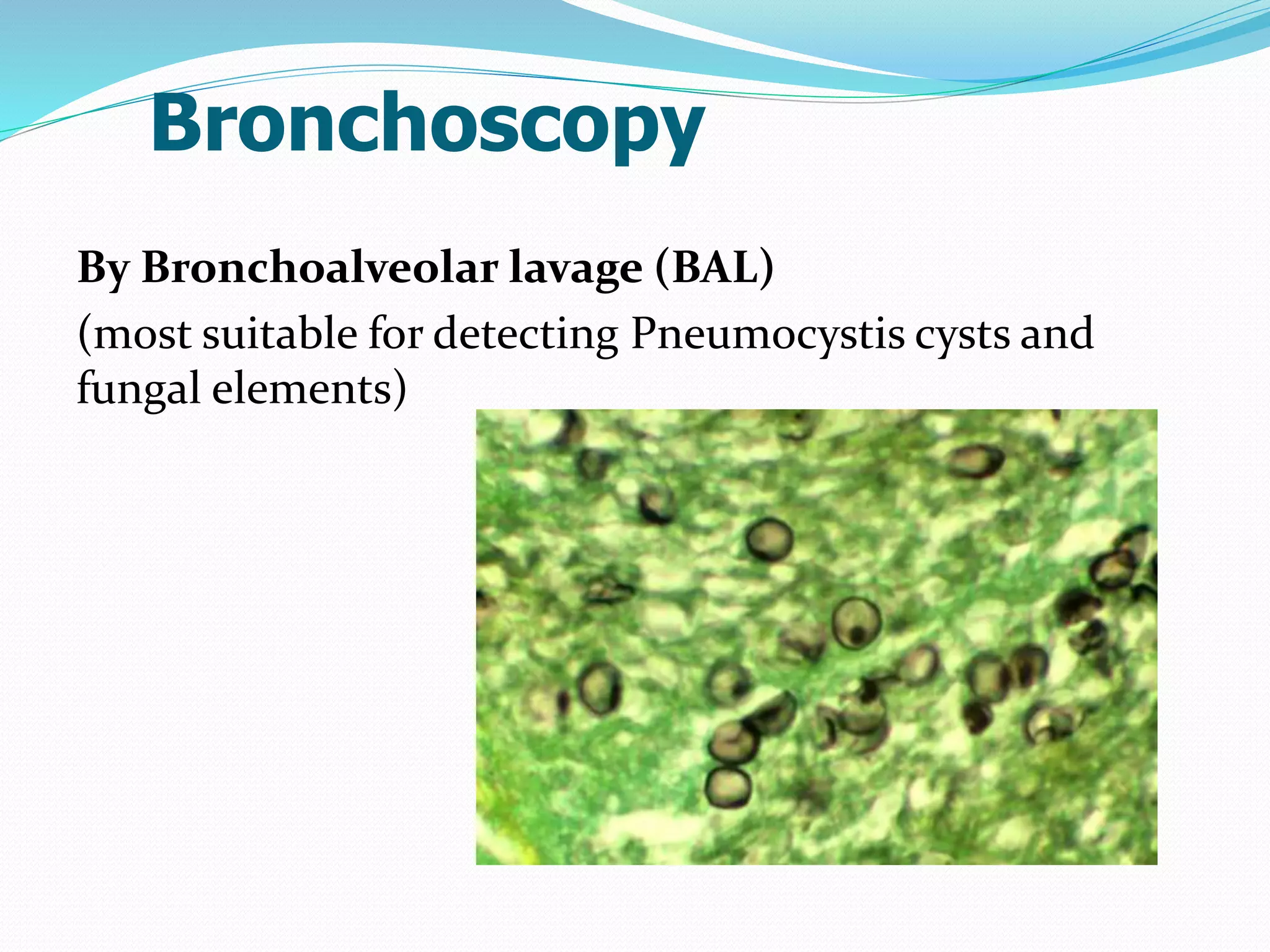
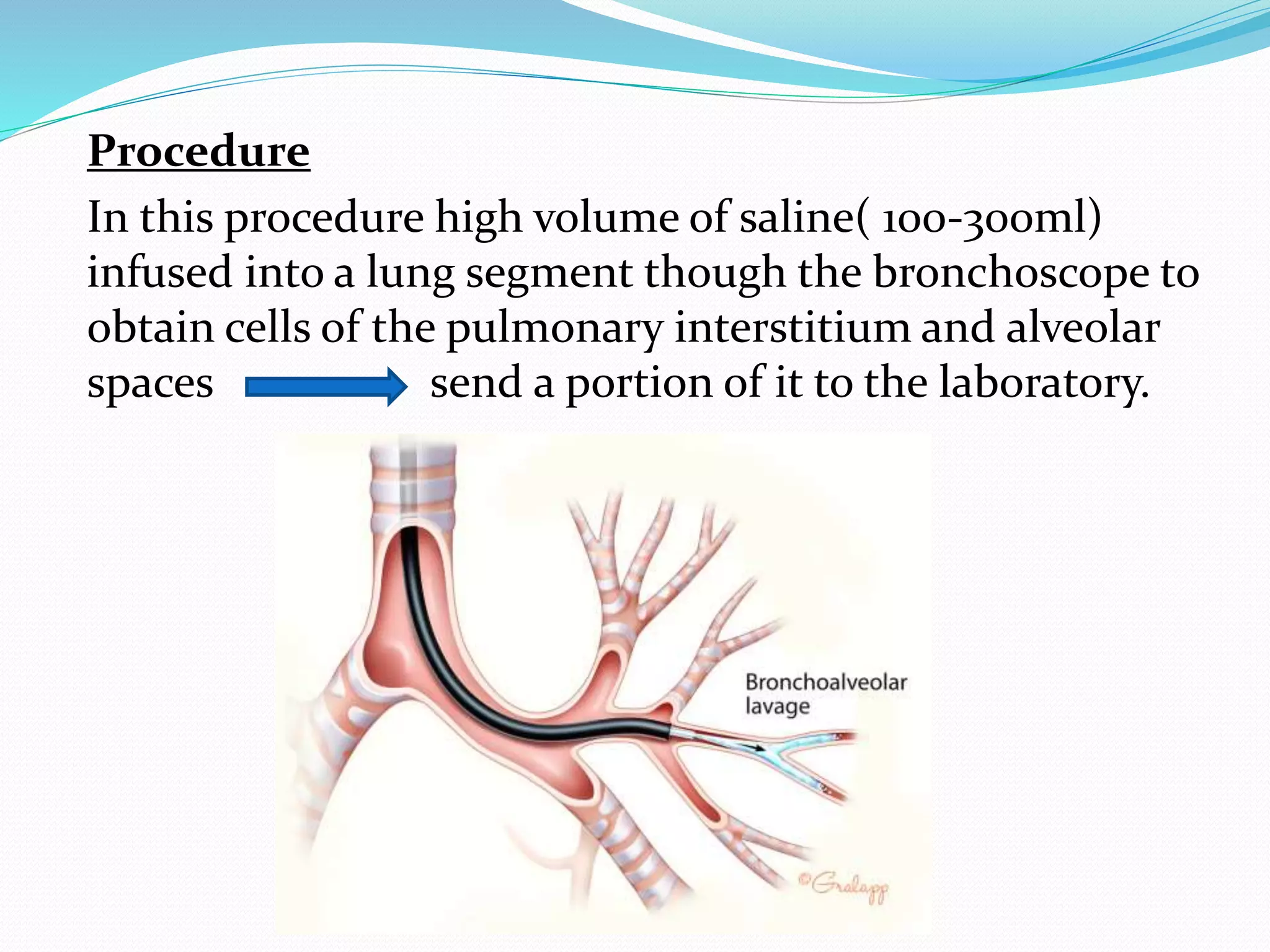
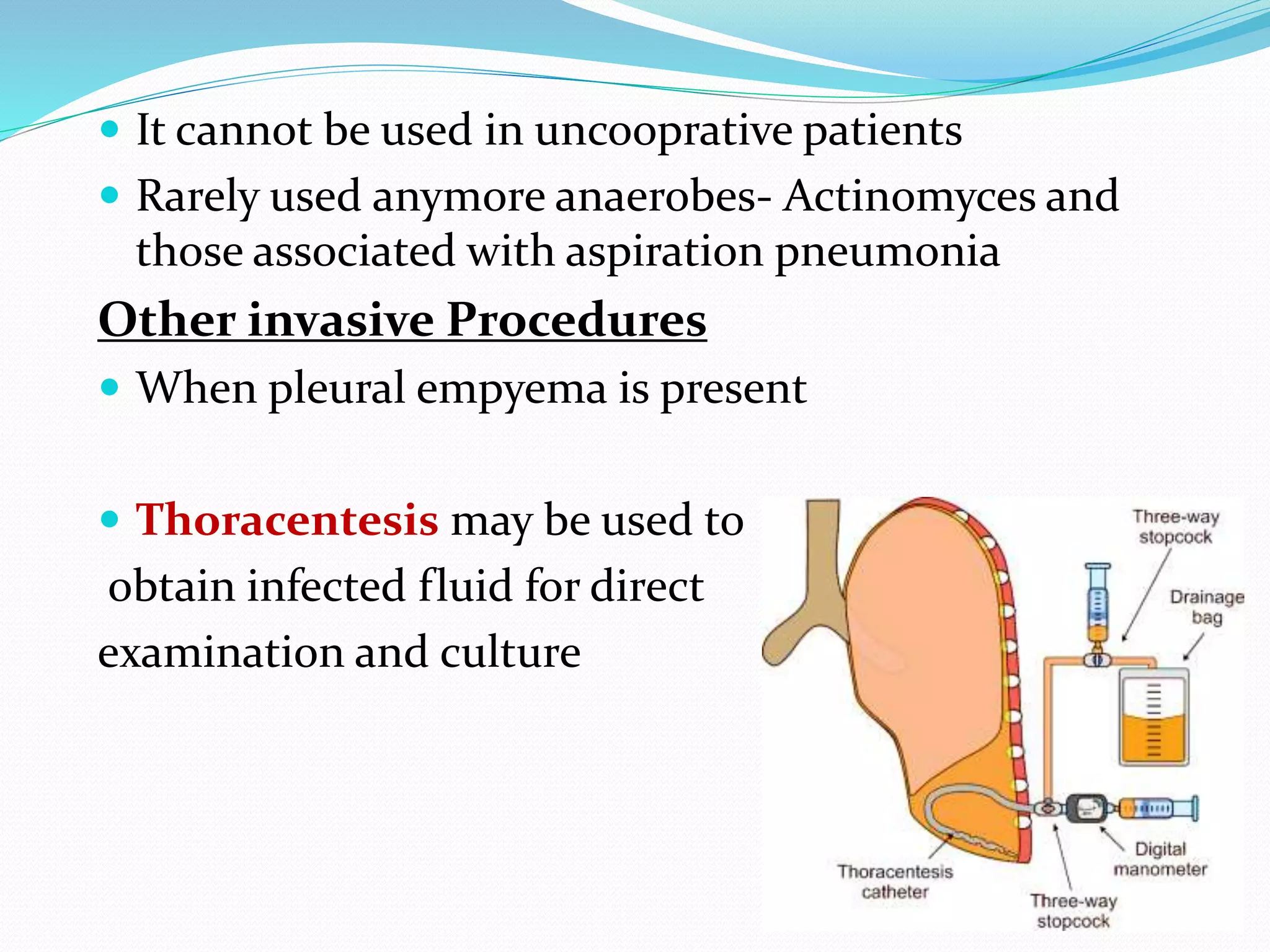
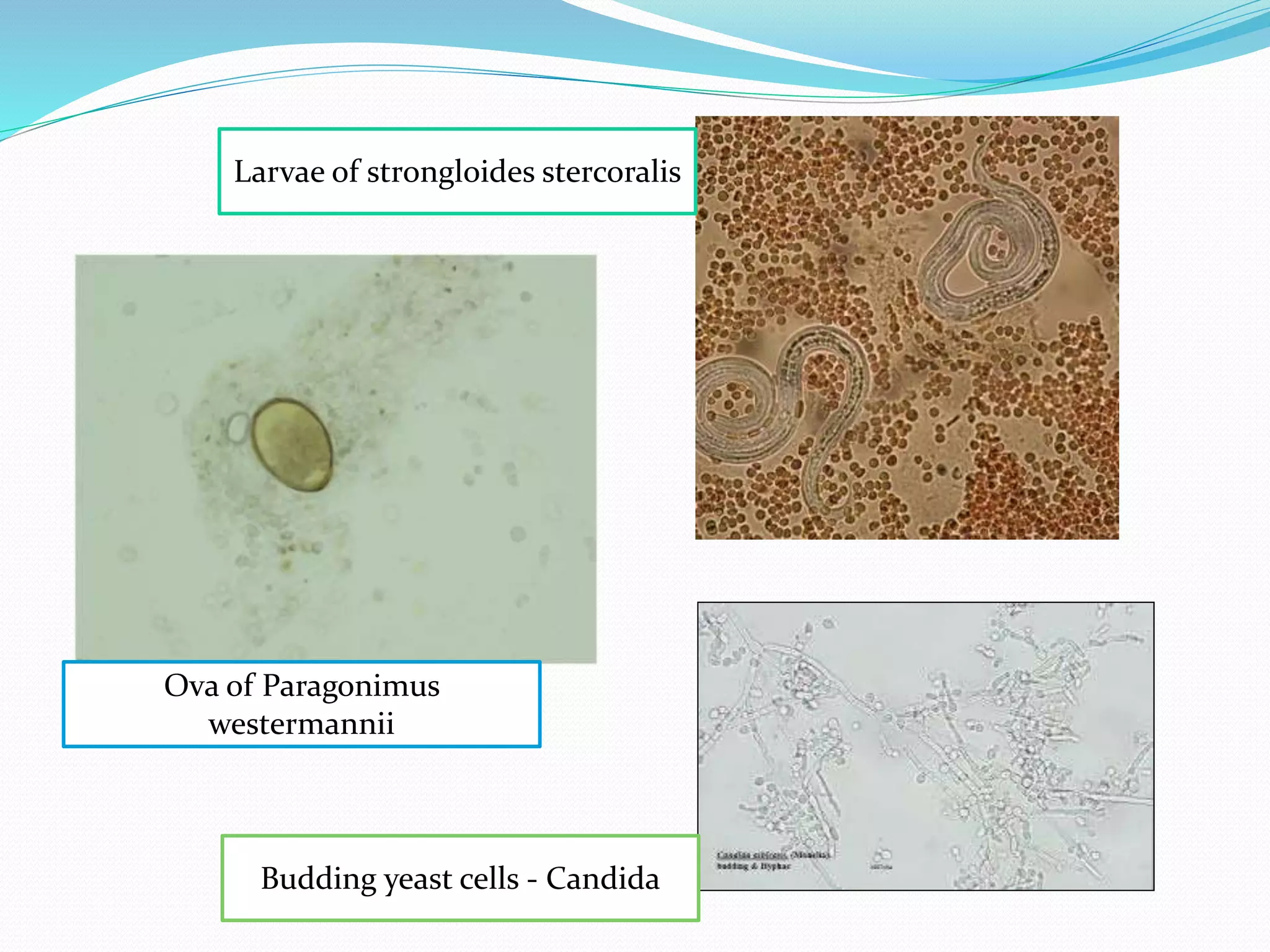
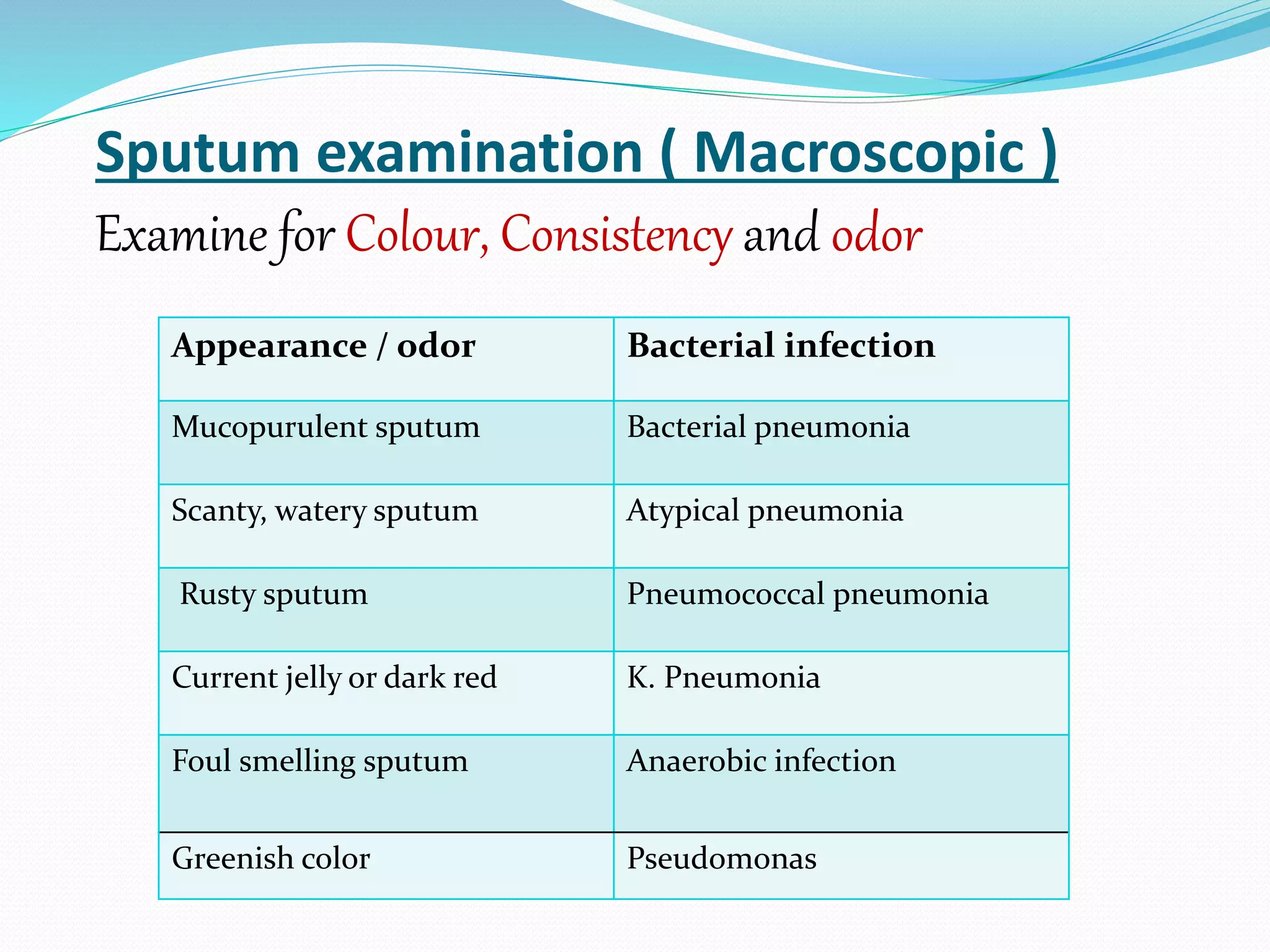
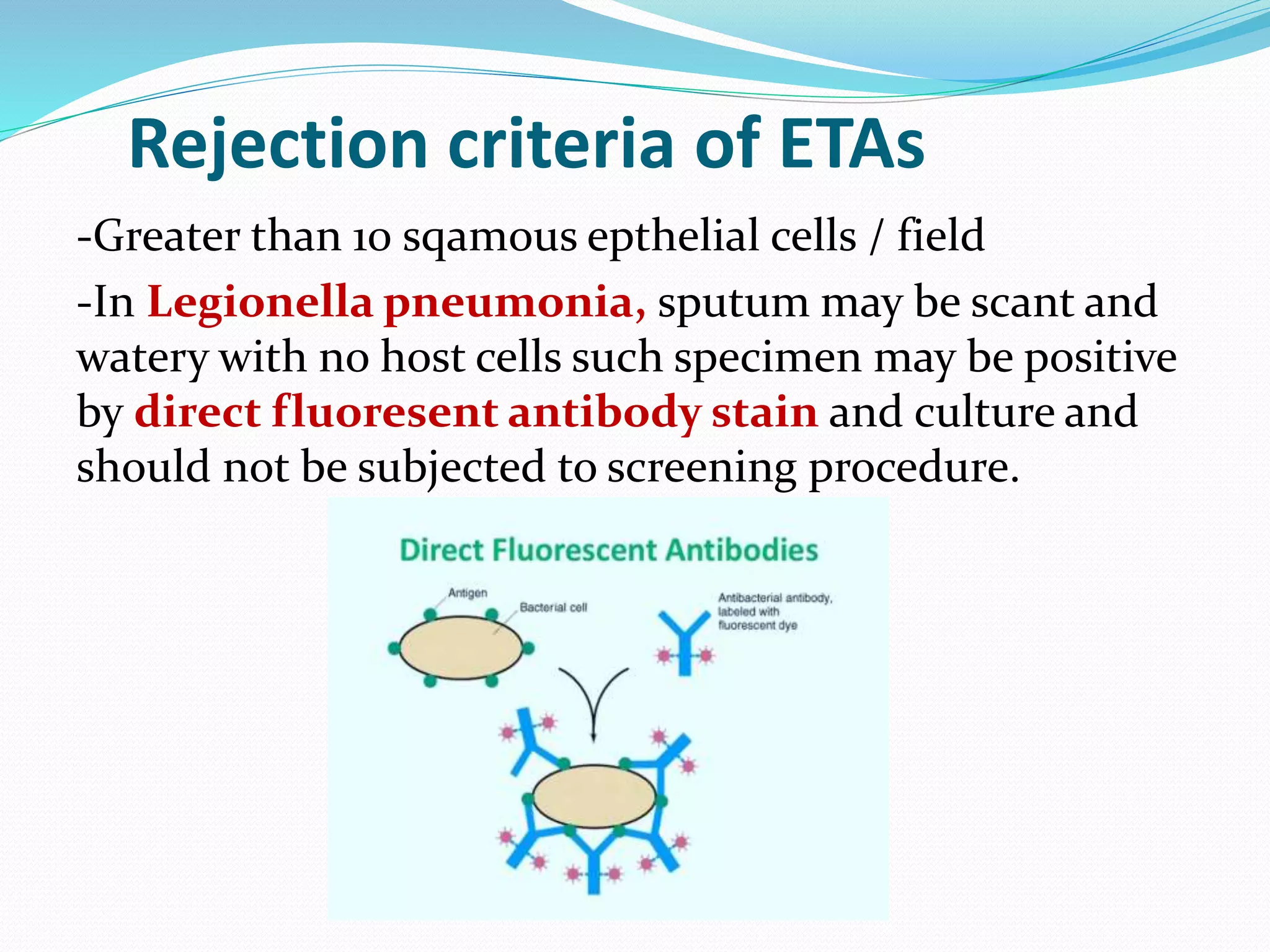
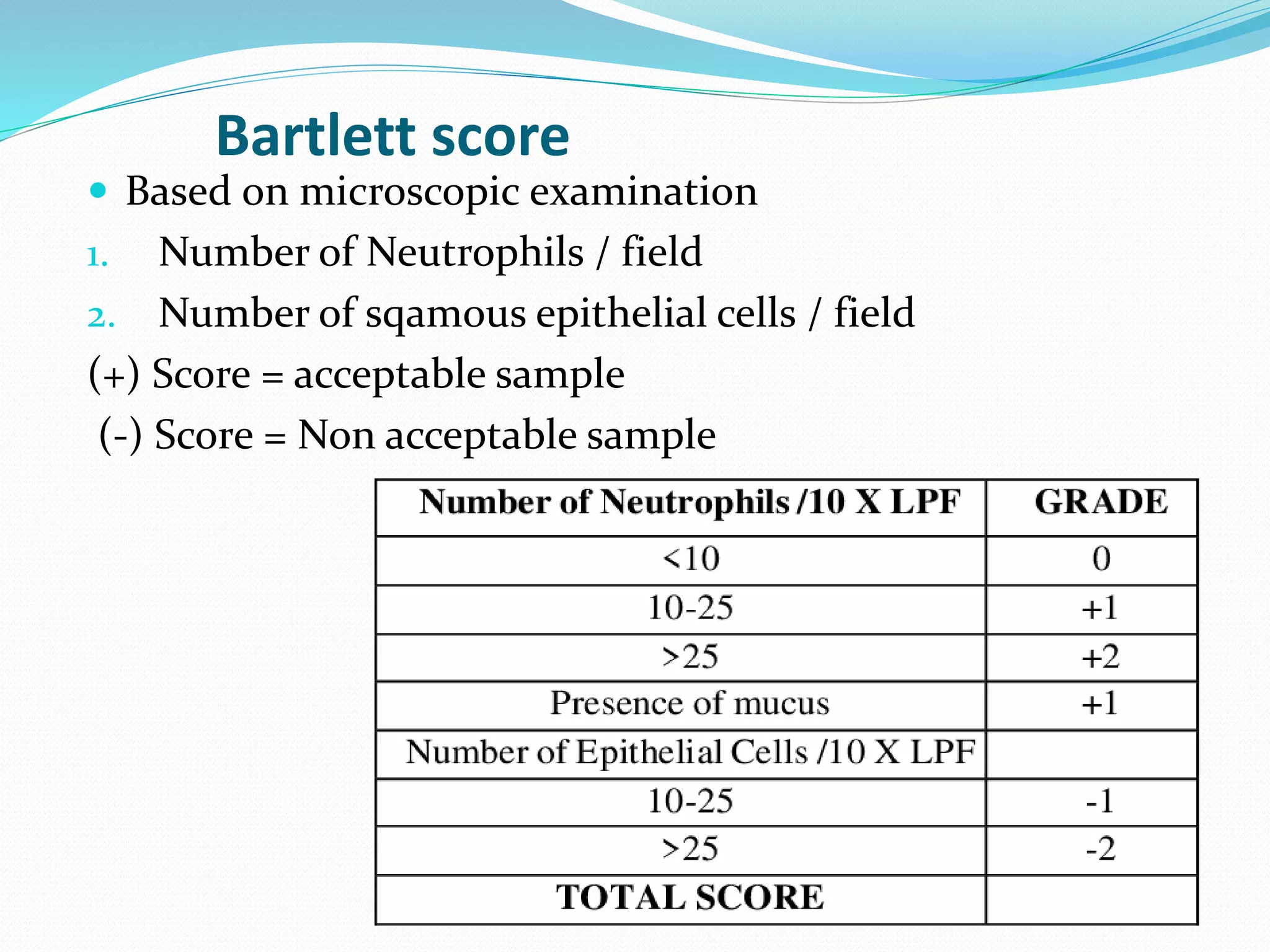
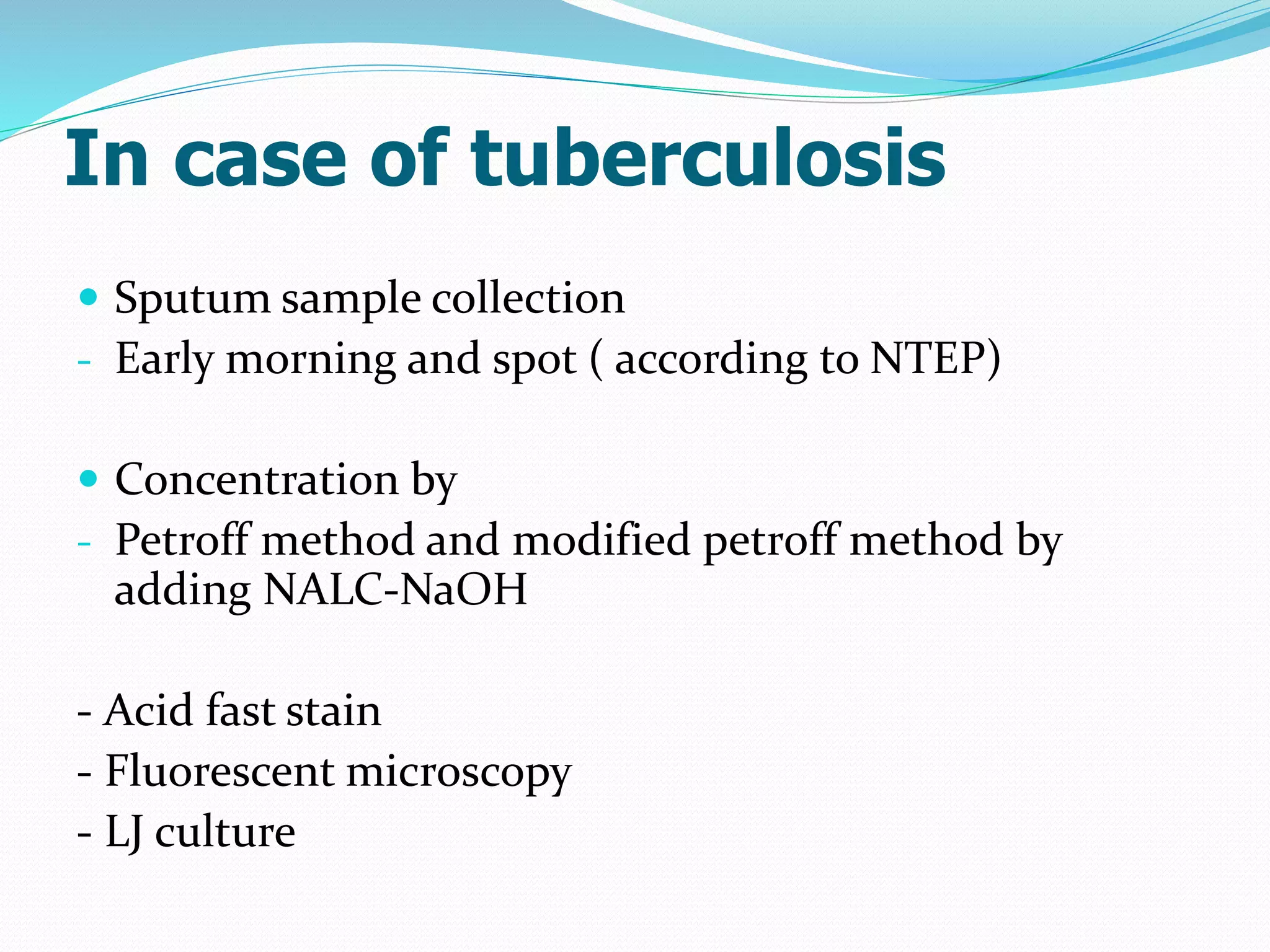
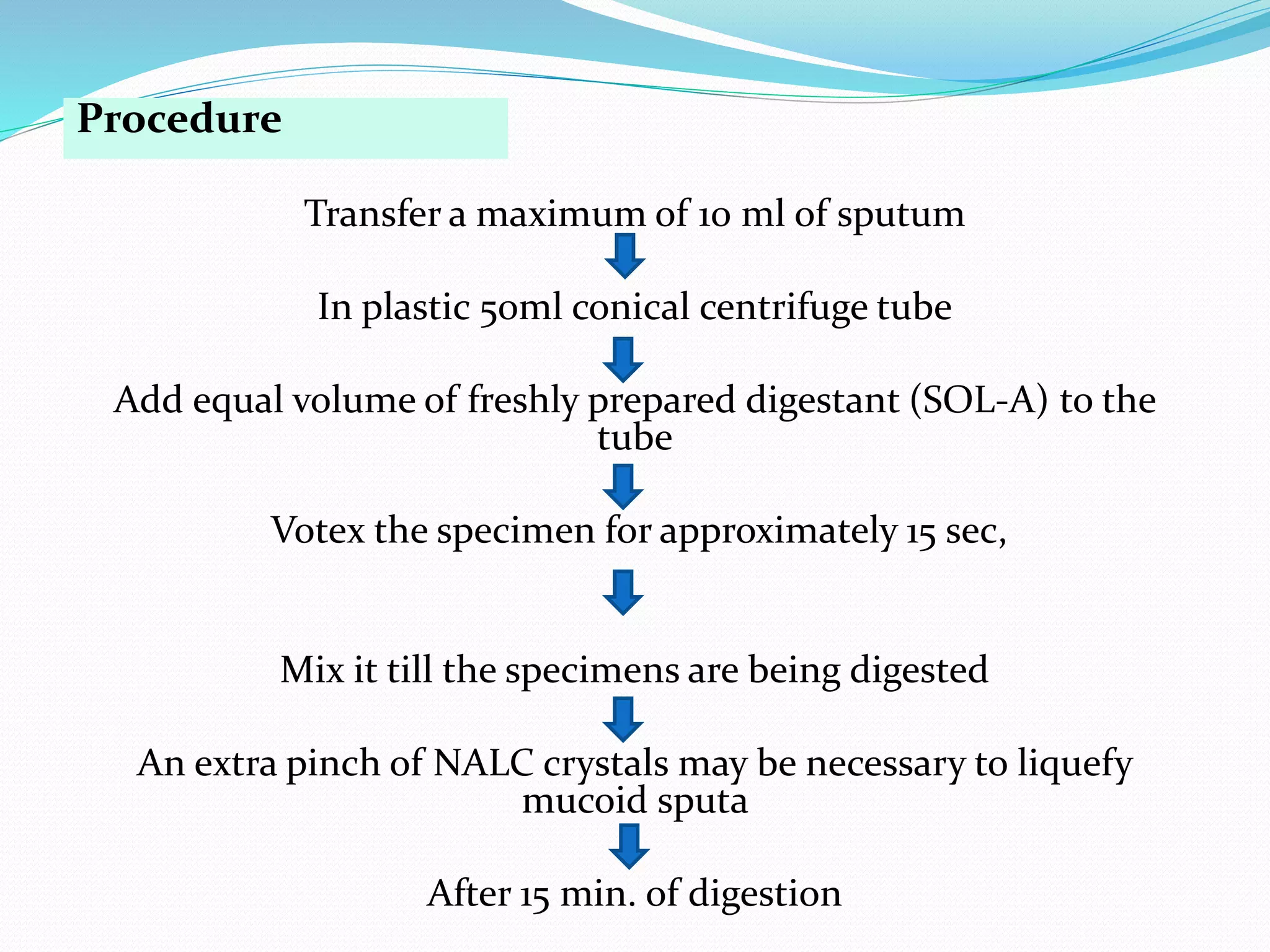
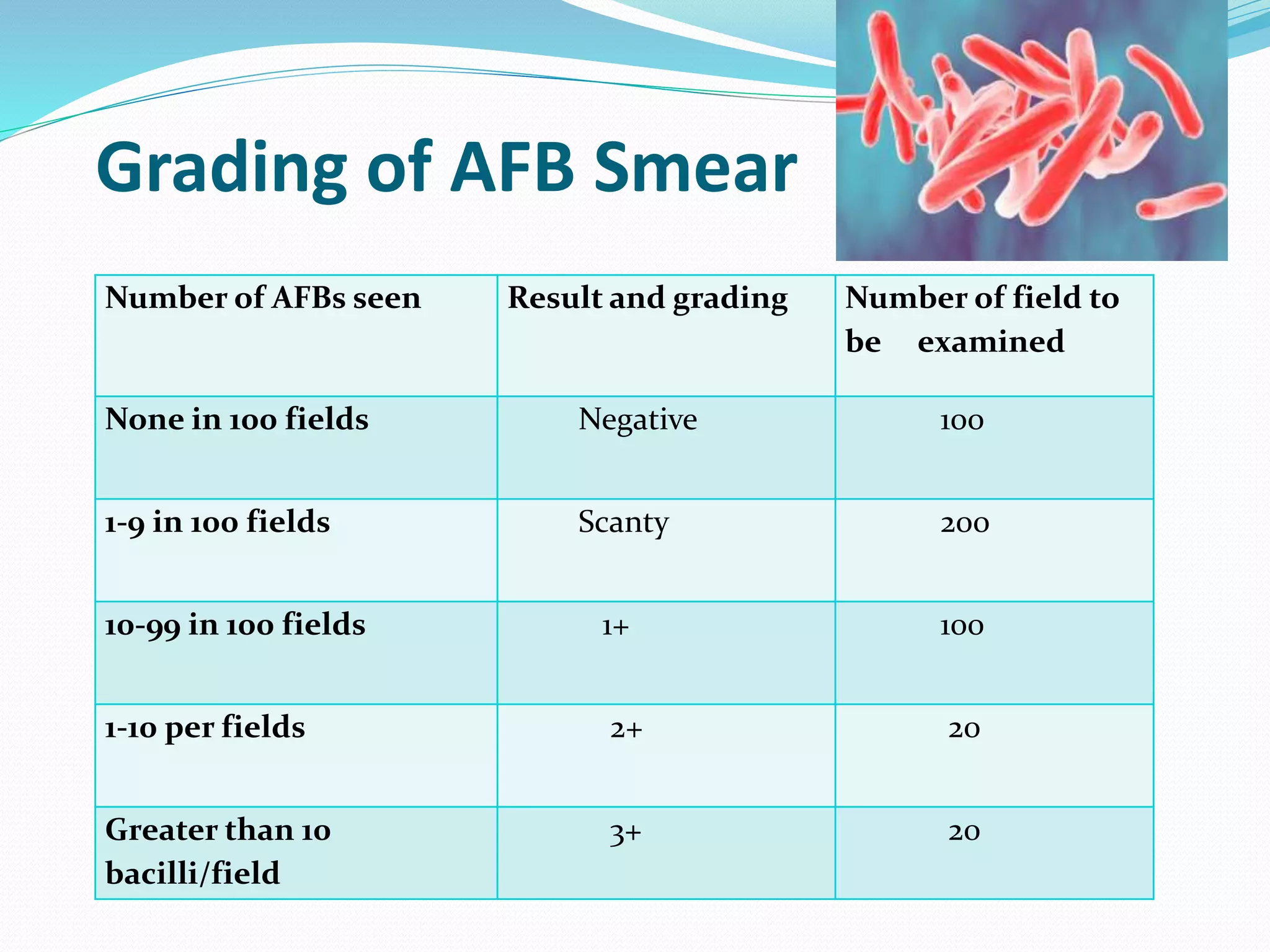
The document outlines various methods for sputum sample collection, including expectorated, induced, bronchoscopy, and transtracheal aspirates, emphasizing the importance of proper collection techniques and patient preparation. It also discusses the acceptability criteria for sputum specimens based on microscopic examination and various grading systems, alongside the processing methods for different types of sputum samples. Additionally, it details the preparation of solutions for digestion and the grading of acid-fast bacilli in cultures.