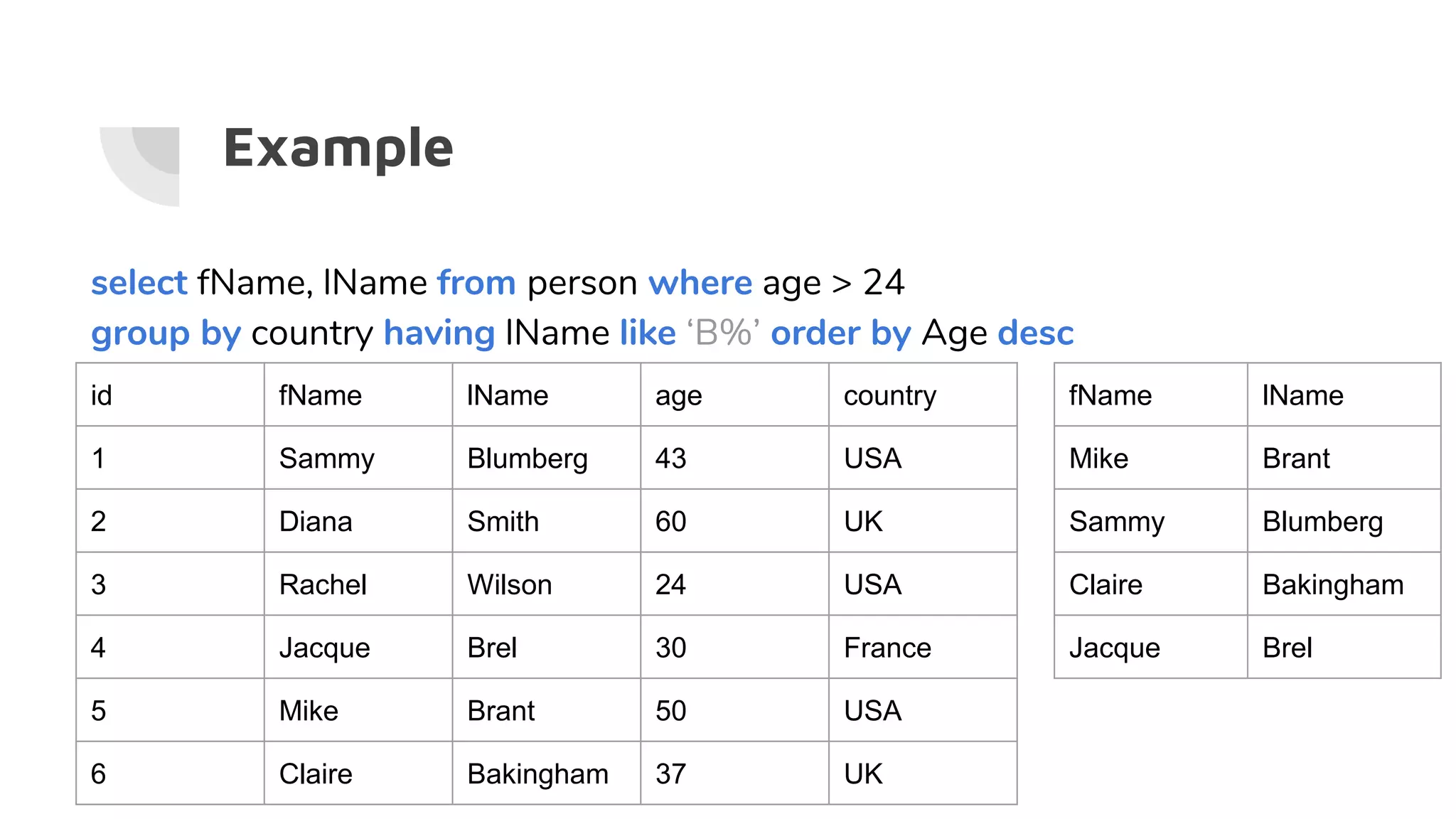
This document serves as a comprehensive guide to SQL and relational databases, covering key concepts such as database installation, basic SQL queries, data types, and table relationships. It includes step-by-step instructions for installing PostgreSQL, using pgAdmin, and performing CRUD operations, along with examples of queries and functions. Additionally, it explains advanced topics like joins, subqueries, and aggregate functions.








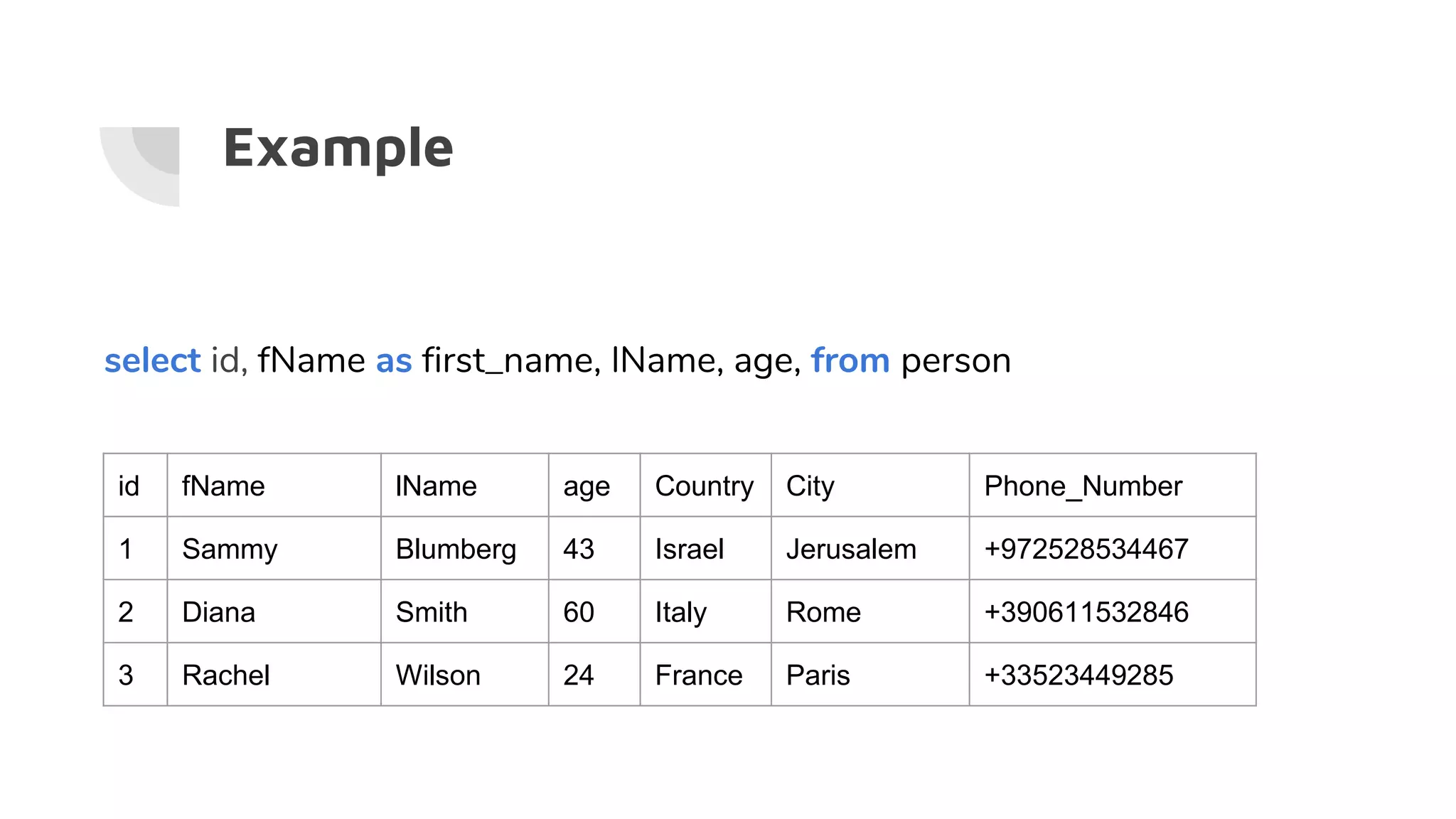
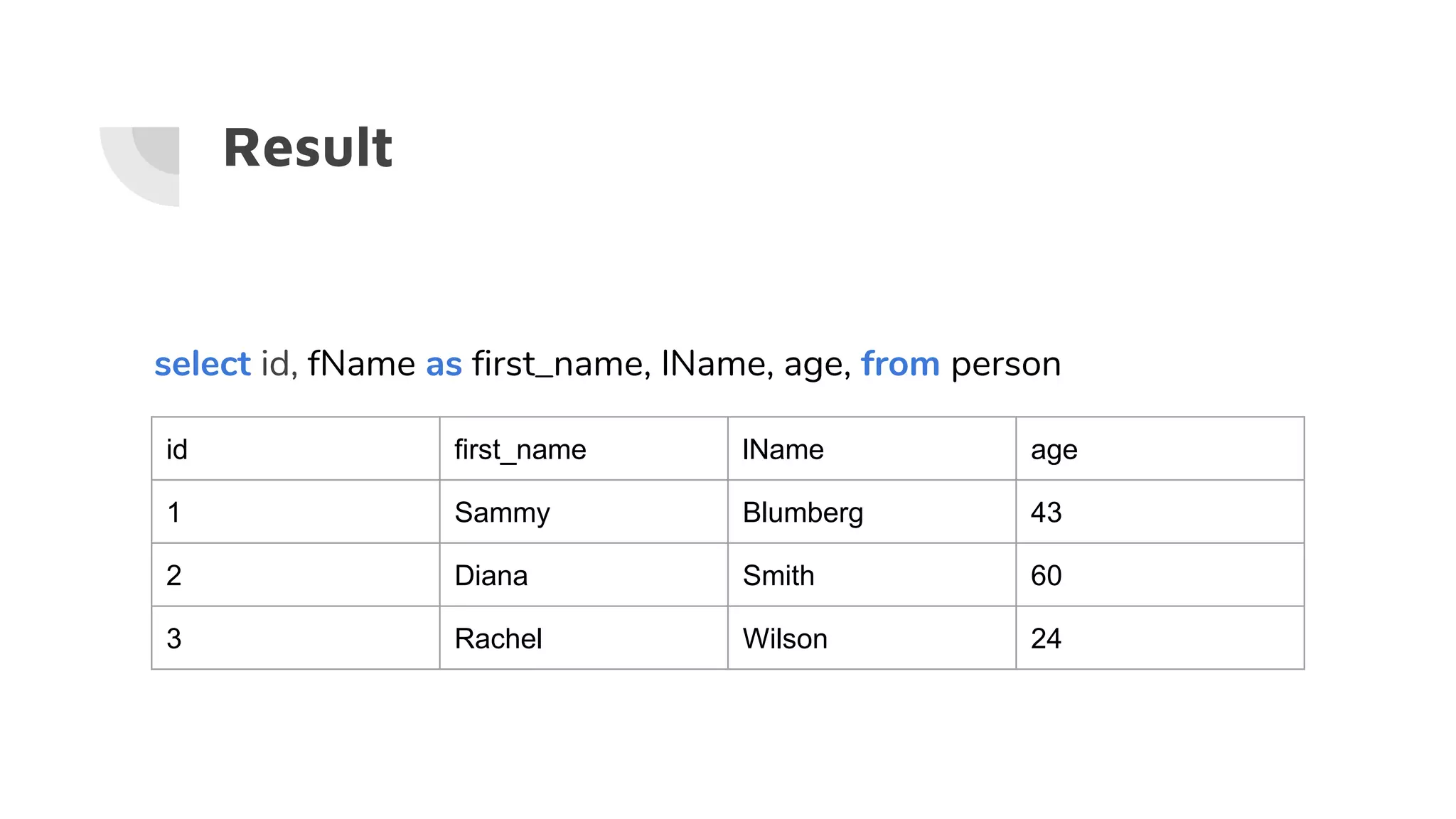

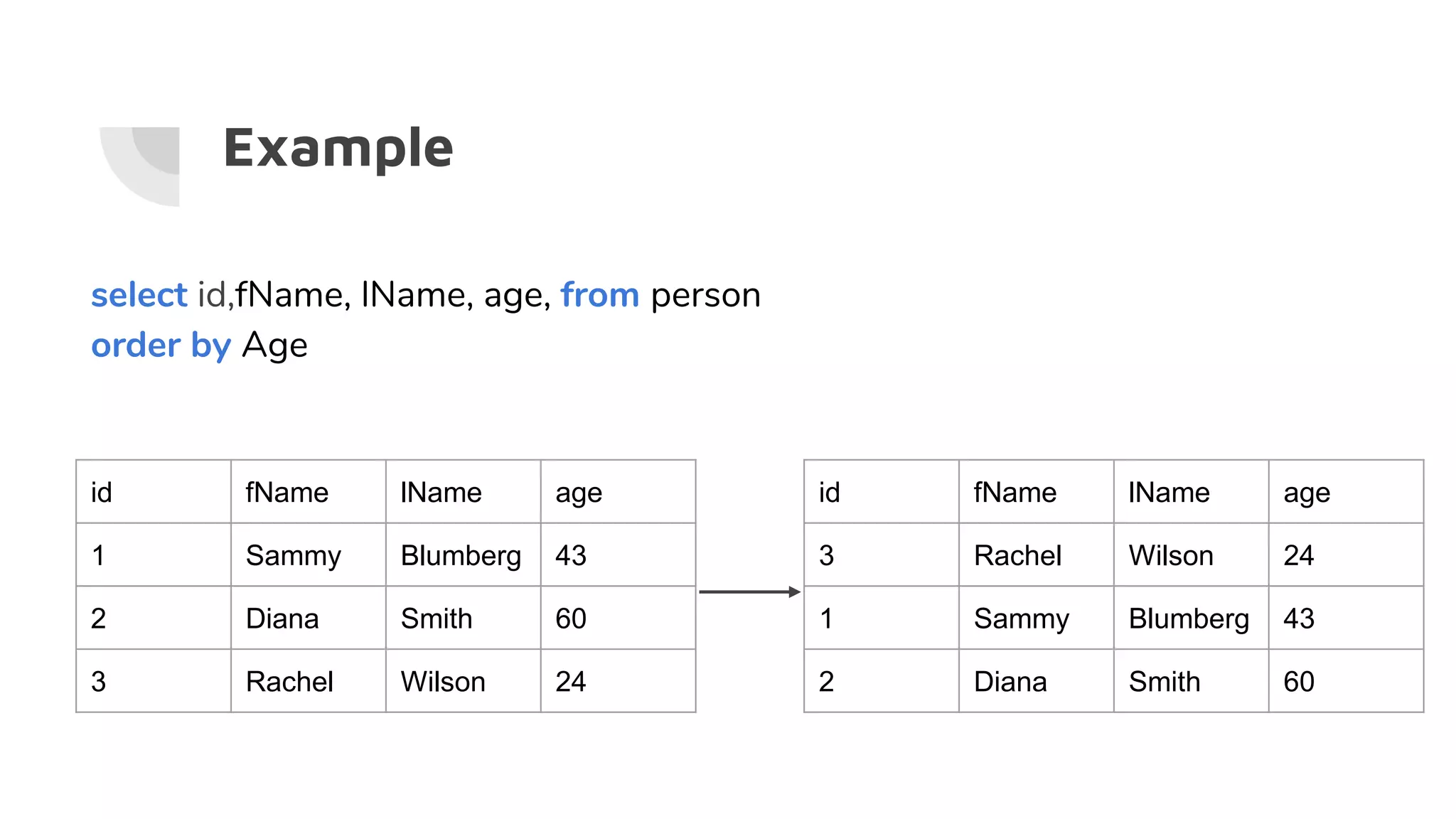


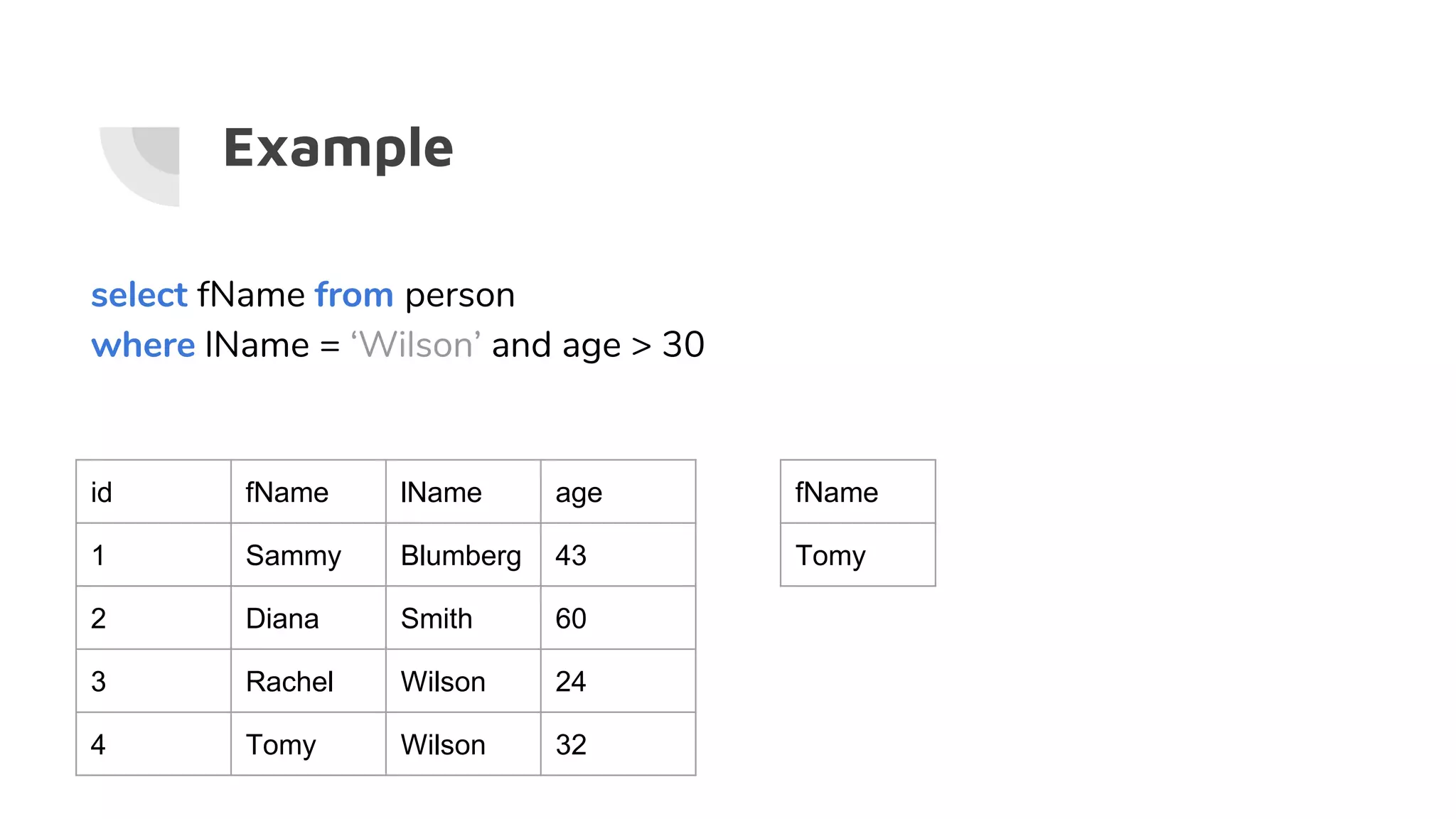
![Wildcards
● 'a%' - Finds any values that starts with "a"
● '%a' - Finds any values that ends with "a"
● '%or%’ - Finds any values that have "or" in any position
● '_r%' - Finds any values that have "r" in the second position
● 'a_%_%' - Finds any values that starts with "a" and are at least 3 characters in length
● 'a%o' - Finds any values that starts with "a" and ends with "o"
● [charlist] - Defines sets and ranges of characters to match
○ [abs]
○ [a-d]
● [^charlist] or [!charlist] - Defines sets and ranges of characters NOT to match
○ [!bef]
○ [!g-r]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql-gettingstarted-190207223847/75/SQL-with-PostgreSQL-Getting-Started-21-2048.jpg)

![Joining information
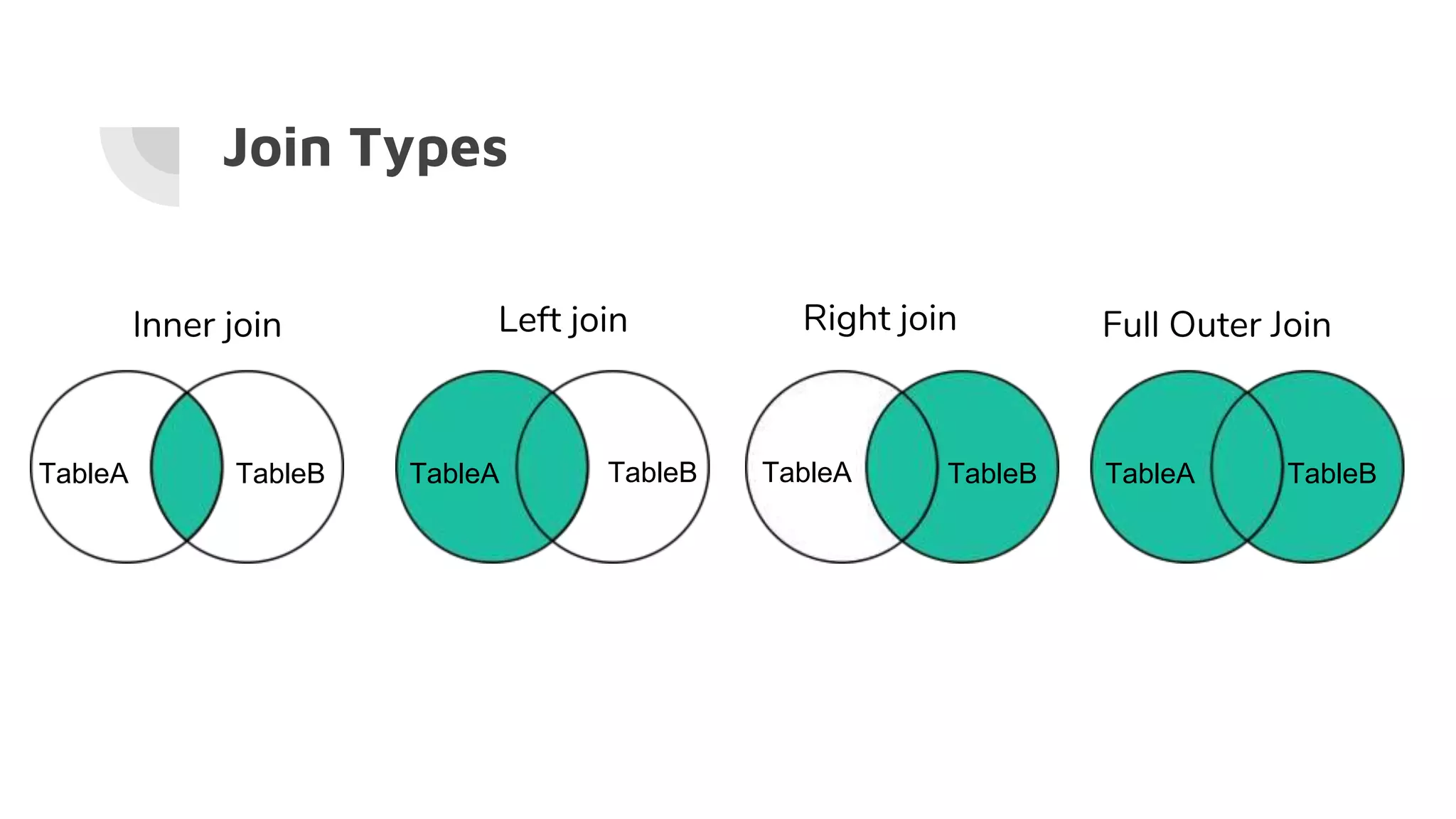
select t1.column1, t1.column2, t2.column1, t2.column2, t2.column3...
from t1 [A] (first table)
Join t2 [B] (second table) on t1.columnX = t2.columnX
● (Inner) join - Returns records that have matching values in both tables
● Left join - Return all records from the left table, and the matched records from
the right table
● Right join - Return all records from the right table, and the matched records
from the left table
● Full outer join - Return all records when there is a match in either left or right
table](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql-gettingstarted-190207223847/75/SQL-with-PostgreSQL-Getting-Started-25-2048.jpg)




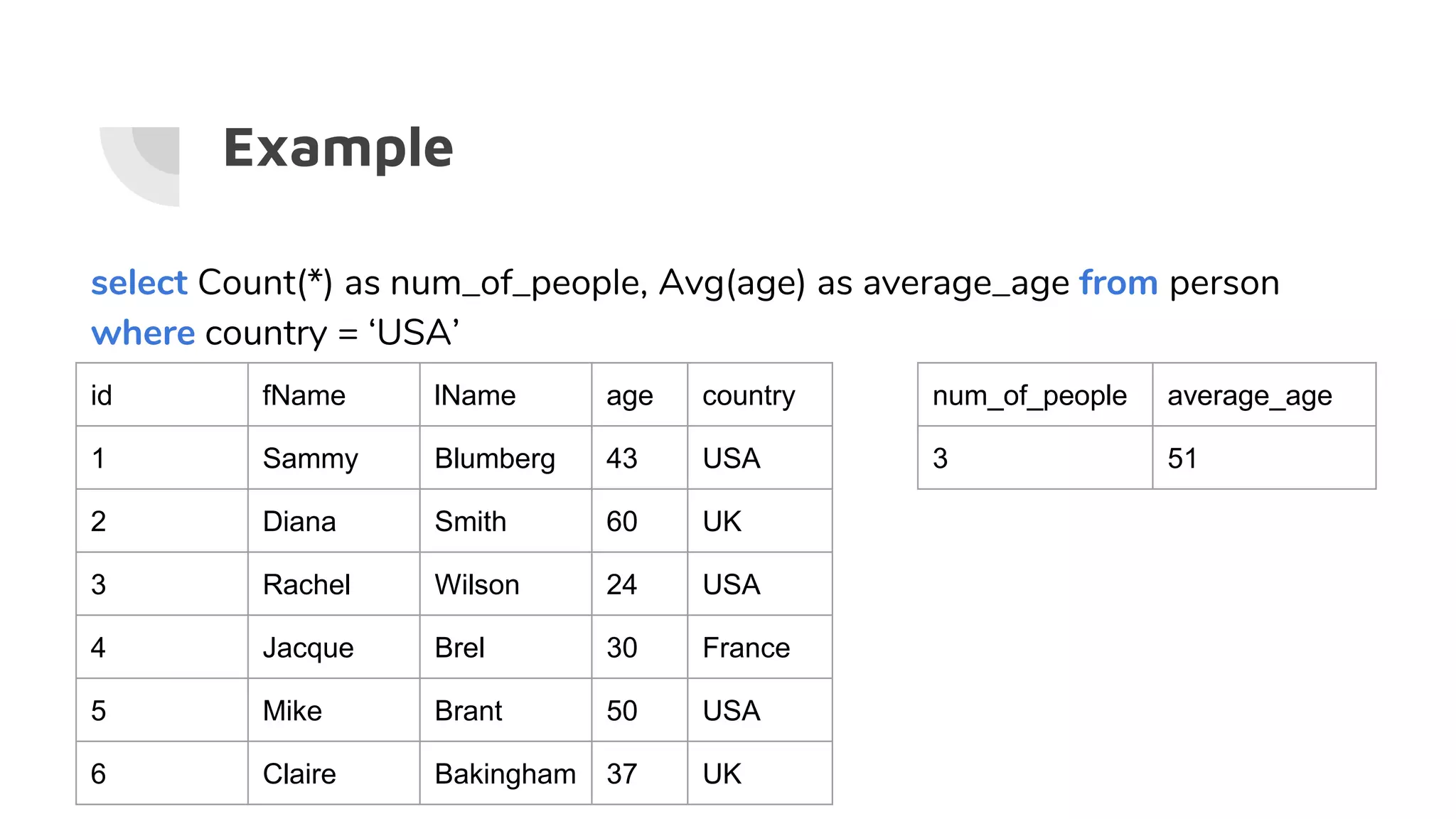
![Functions
Select [columns…], function(columnX), [columns…] from
tableName
● Count() - counts the number of rows that returned from the query.
Doesn’t count nulls
● Max() - gives the maximal value in a column
● Min() - gives the minimum value in a column
● Avg() - gives the average value of all values in a column
● Sum() - sums up all values in a column
● More...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql-gettingstarted-190207223847/75/SQL-with-PostgreSQL-Getting-Started-32-2048.jpg)