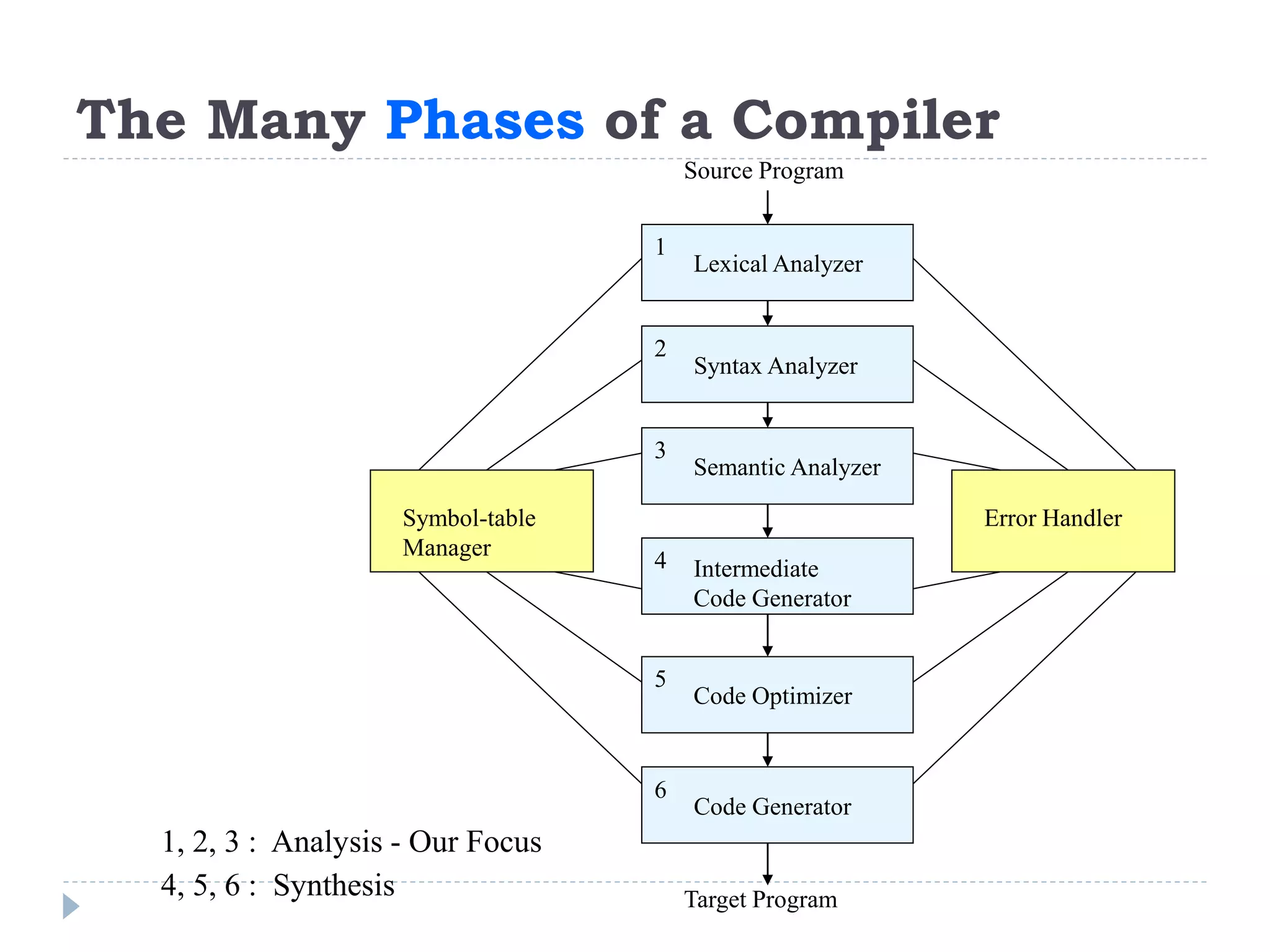
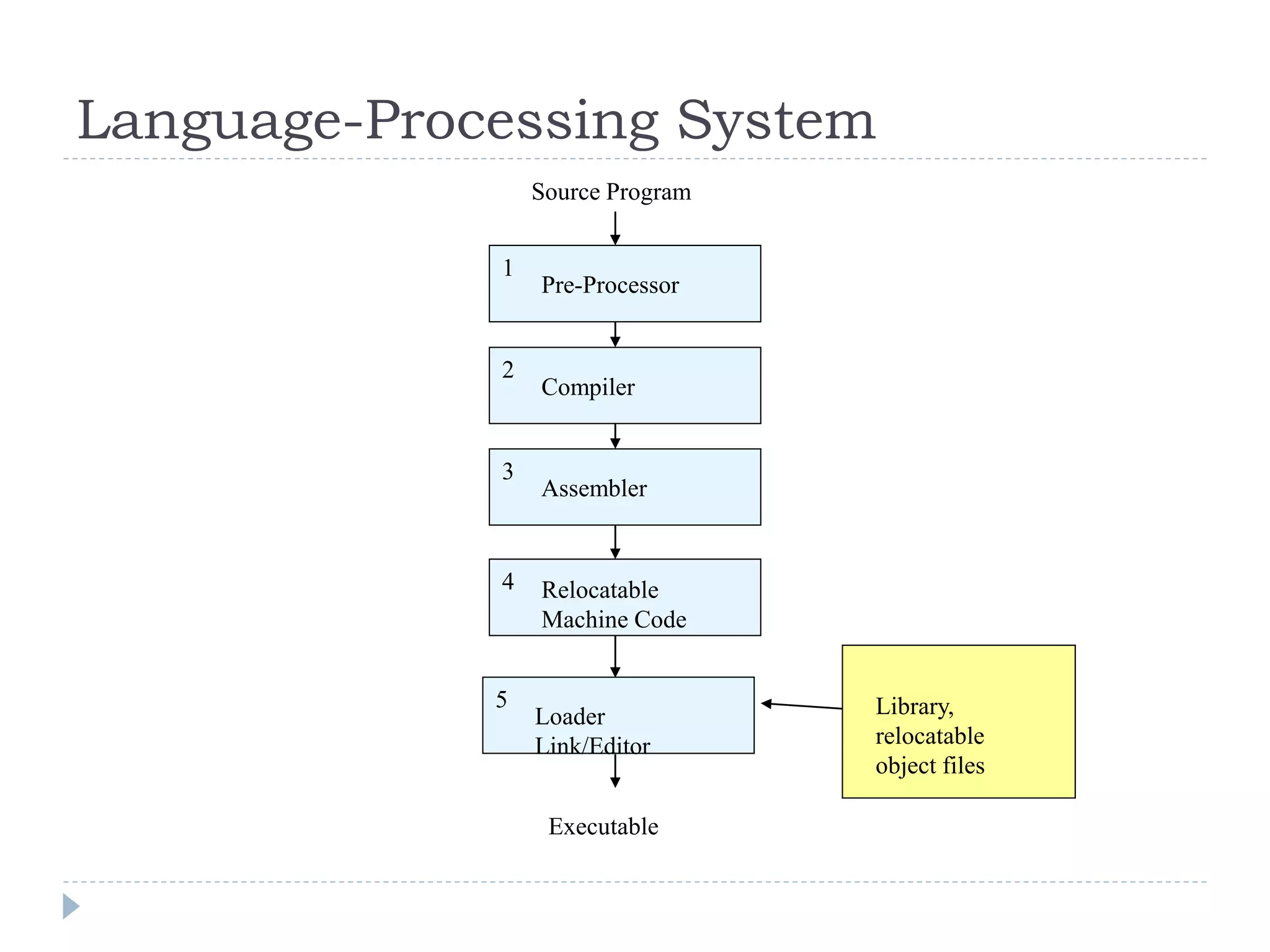
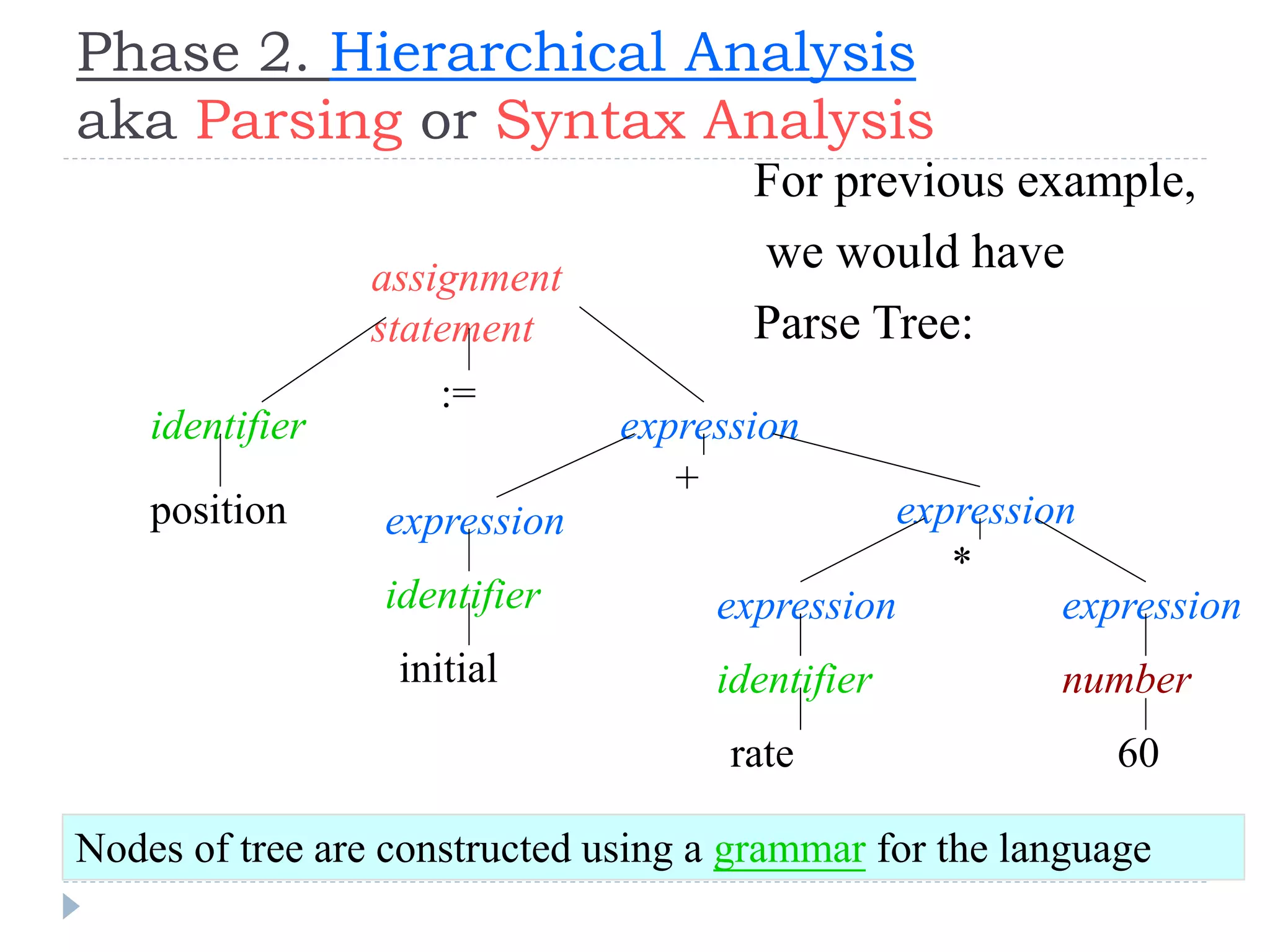
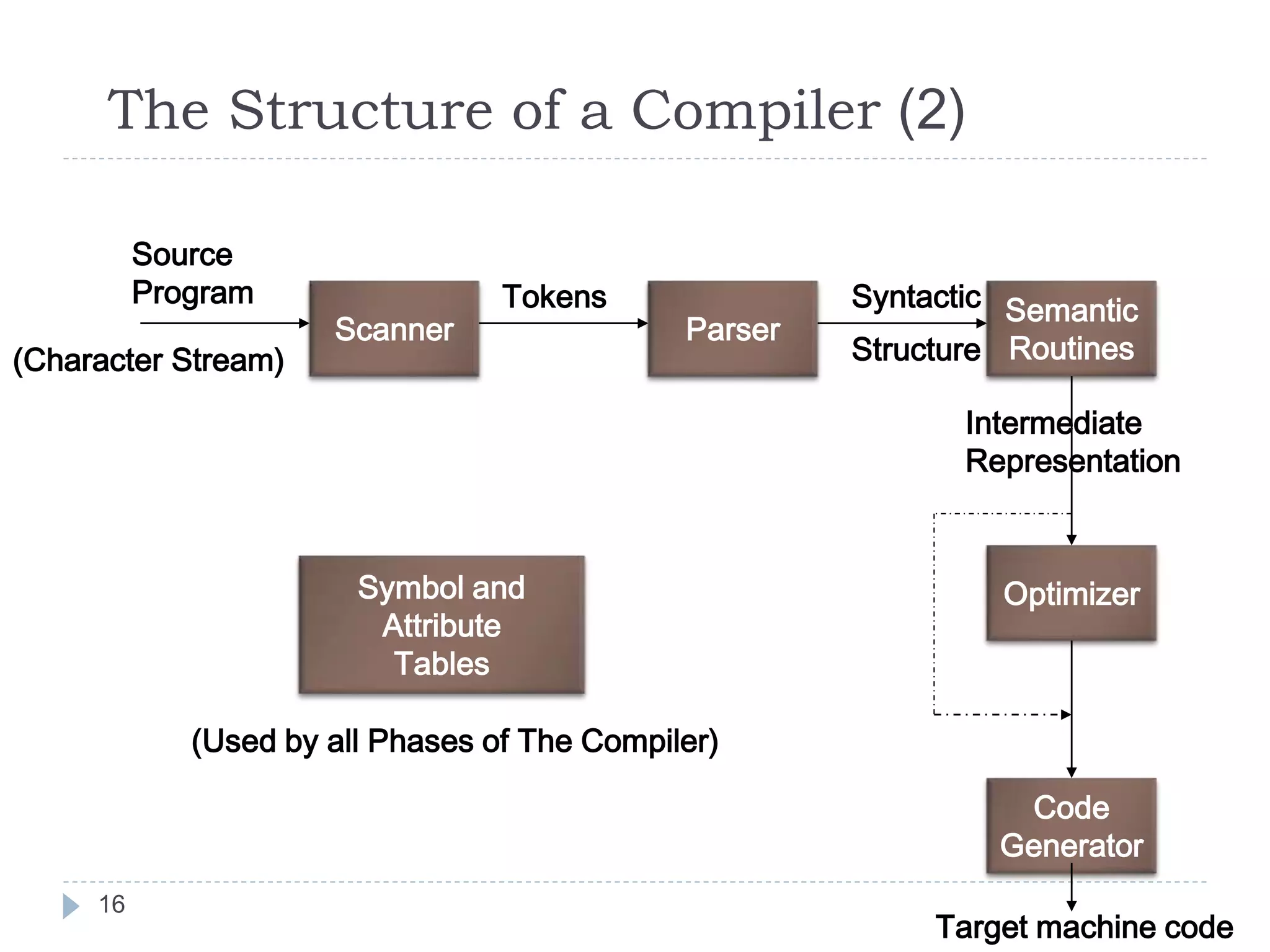
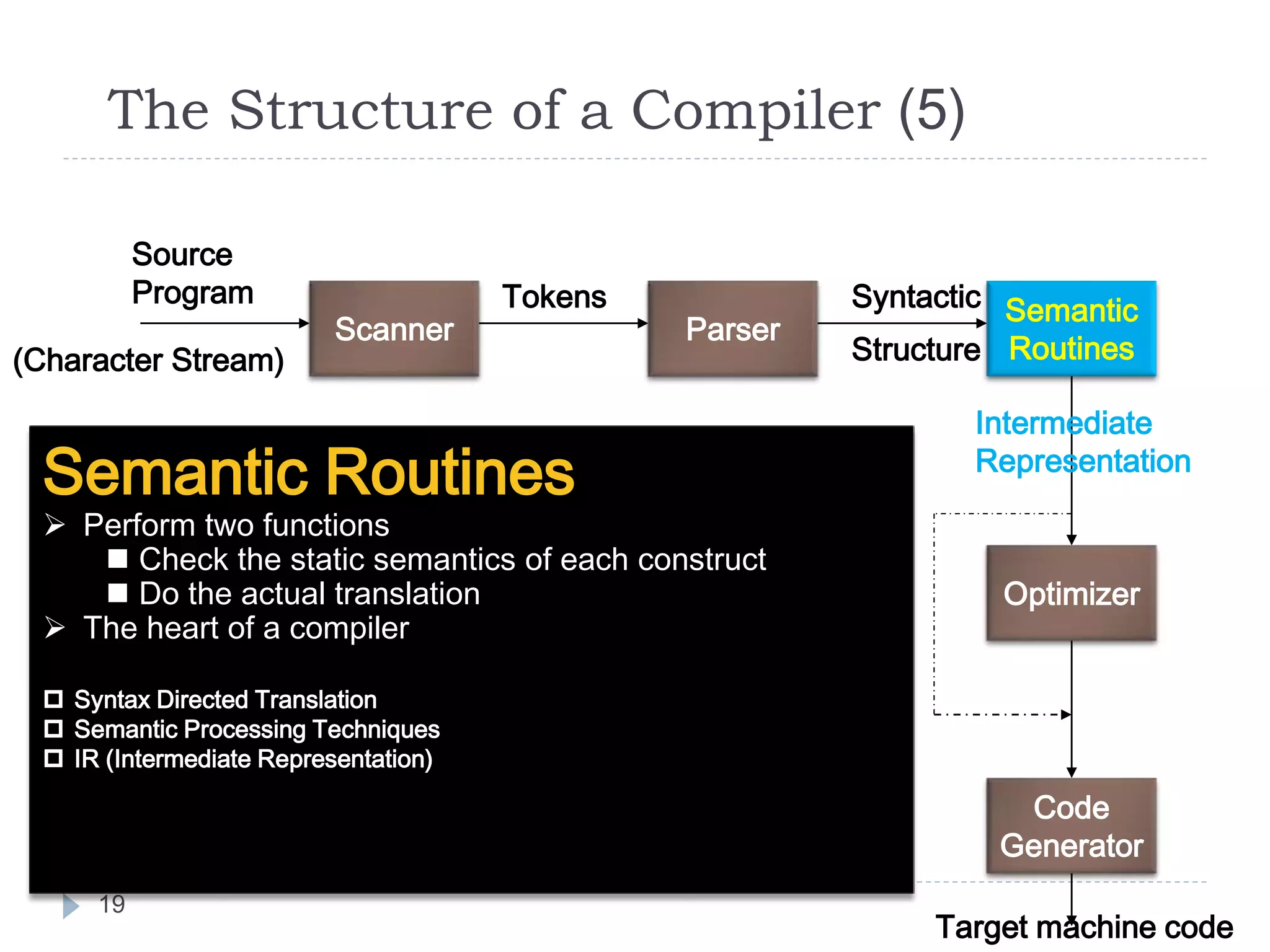
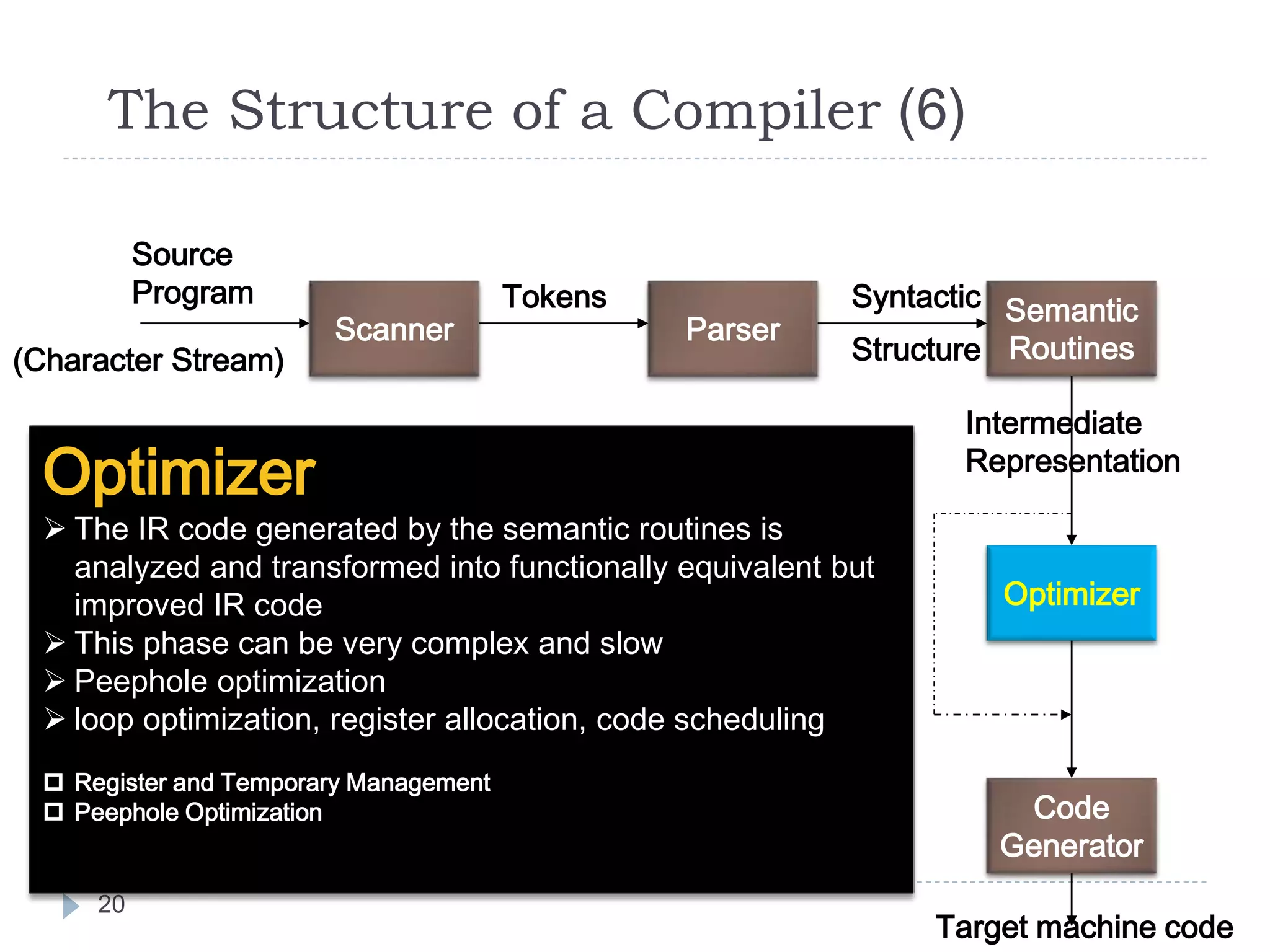
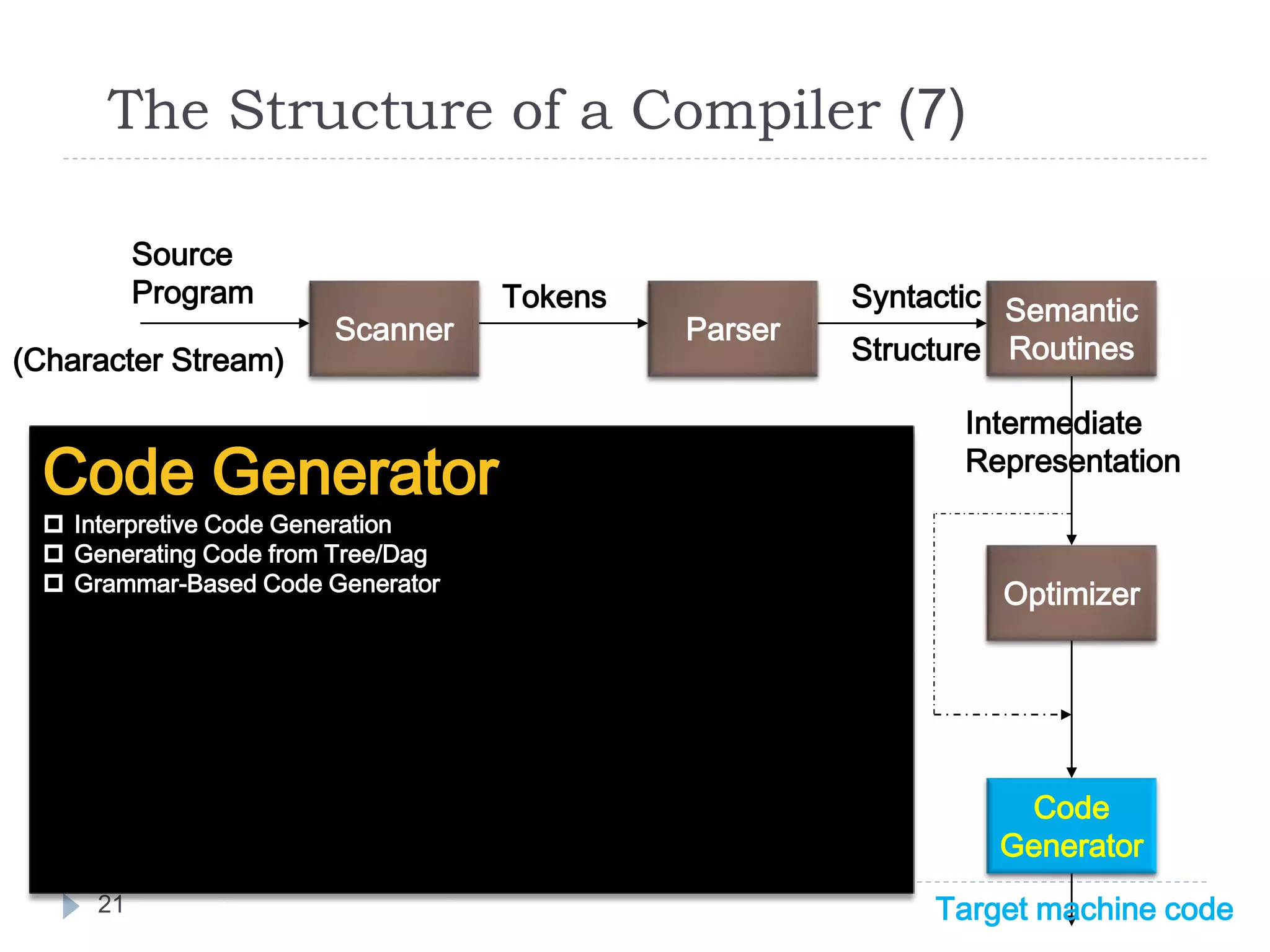
The document discusses the phases of a compiler in three sentences:
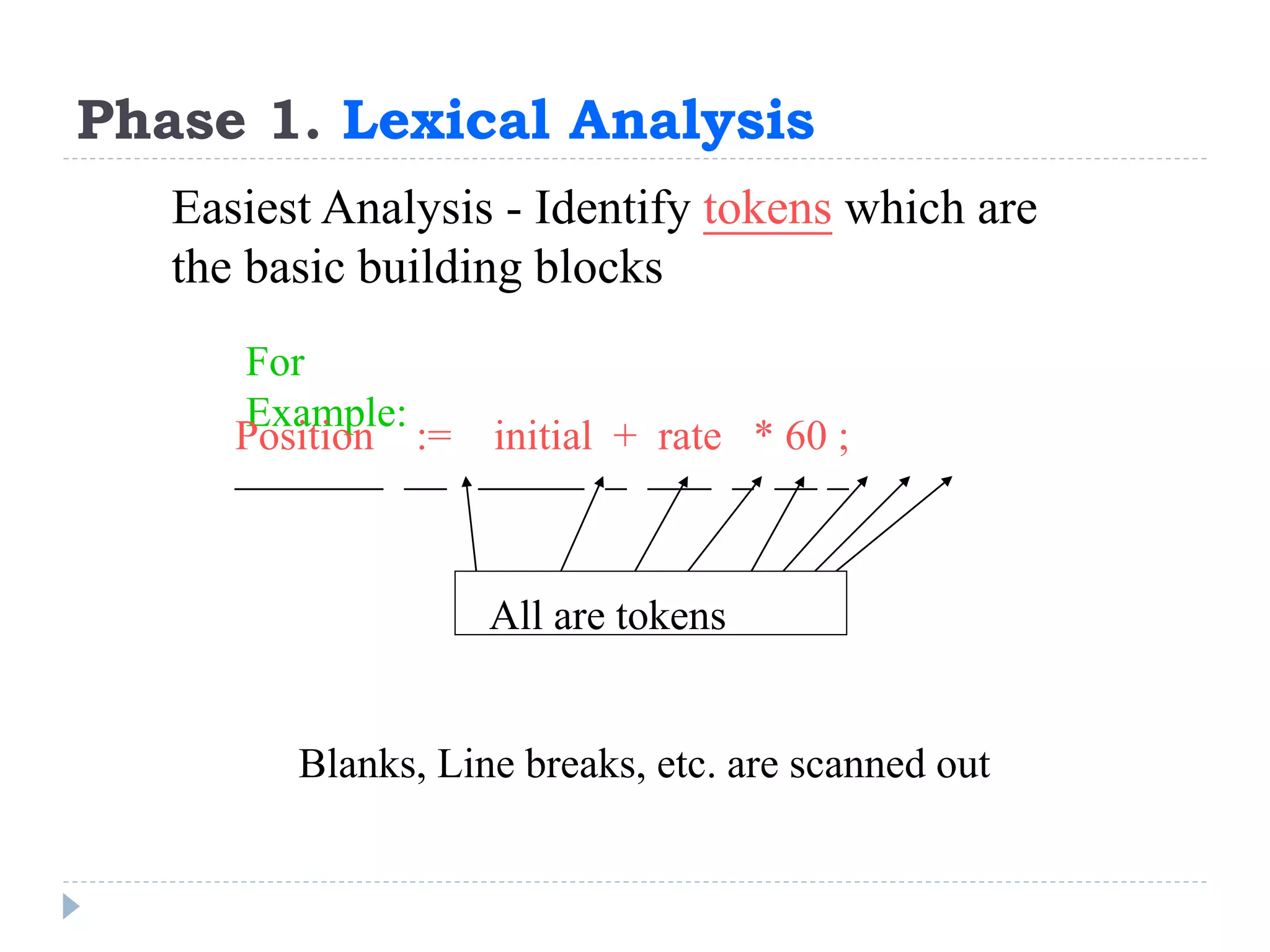
1) A compiler has analysis and synthesis phases, with analysis including lexical analysis to identify tokens, hierarchical/syntax analysis to group tokens into a parse tree, and semantic analysis to check correctness.
2) The synthesis phases generate intermediate code, optimize it, and finally generate target machine code.
3) Each phase supports the others through symbol tables, error handling, and intermediate representations that are passed between phases.






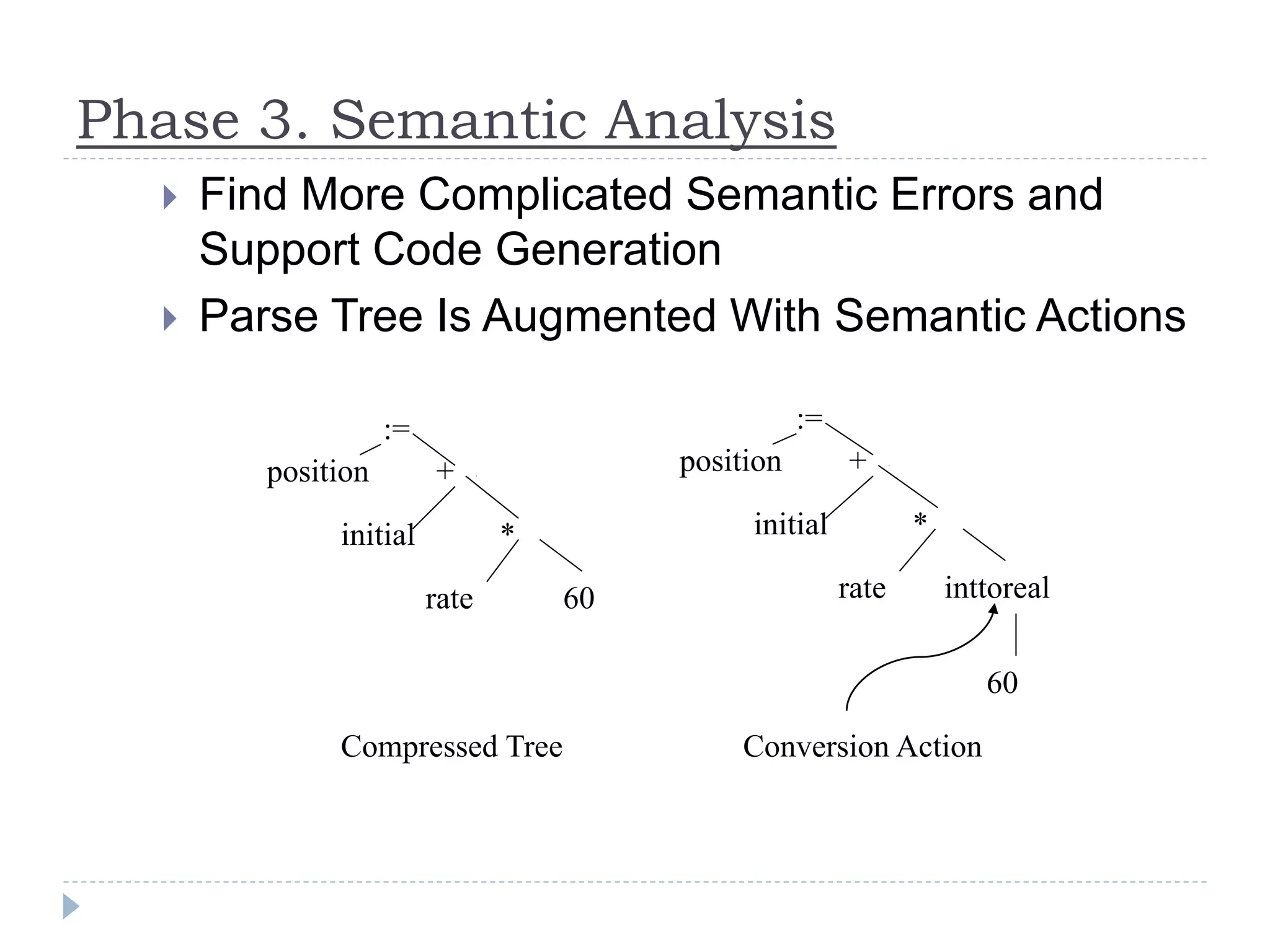
![Phase 3. Semantic Analysis
Most Important Activity in This Phase:
Type Checking - Legality of Operands
Many Different Situations:
Real := int + char ;
A[int] := A[real] + int ;
while char <> int do
…. Etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ssuilecture2-150915075030-lva1-app6891/75/Ss-ui-lecture-2-13-2048.jpg)


![The Structure of a Compiler (4)
18
Scanner Parser
Semantic
Routines
Code
Generator
Optimizer
Source
Program Tokens Syntactic
Structure
Symbol and
Attribute
Tables
(Used by all
Phases of
The Compiler)
Parser
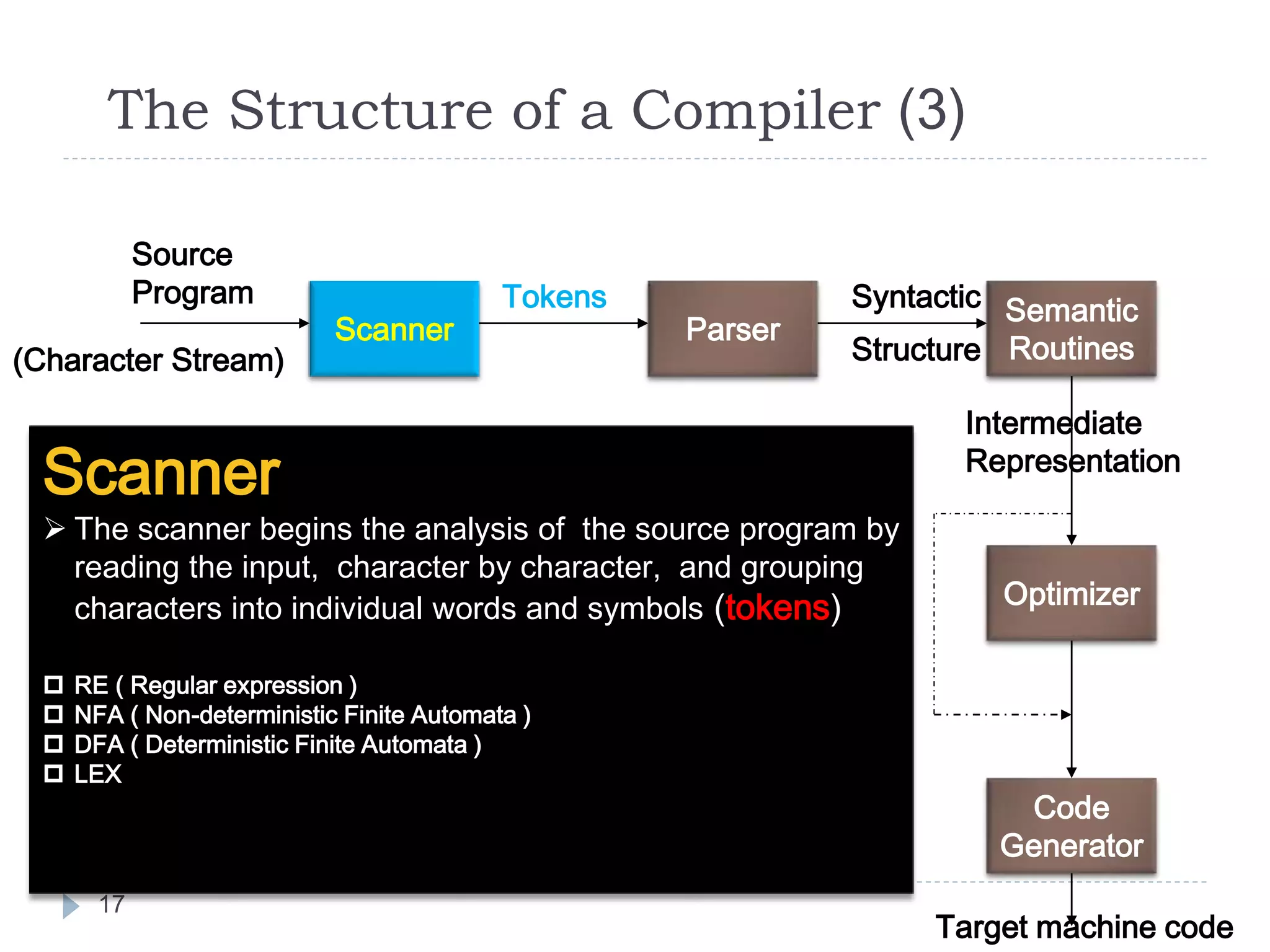
Given a formal syntax specification (typically as a context-
free grammar [CFG] ), the parse reads tokens and groups
them into units as specified by the productions of the CFG
being used.
As syntactic structure is recognized, the parser either calls
corresponding semantic routines directly or builds a syntax
tree.
CFG ( Context-Free Grammar )
BNF ( Backus-Naur Form )
GAA ( Grammar Analysis Algorithms )
LL, LR, SLR, LALR Parsers
YACC
(Character Stream)
Intermediate
Representation
Target machine code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ssuilecture2-150915075030-lva1-app6891/75/Ss-ui-lecture-2-18-2048.jpg)
![The Structure of a Compiler (8)
22
Scanner
[Lexical Analyzer]
Parser
[Syntax Analyzer]
Semantic Process
[Semantic analyzer]
Code Generator
[Intermediate Code Generator]
Code Optimizer
Tokens
Parse tree
Abstract Syntax Tree w/ Attributes
Non-optimized Intermediate Code
Optimized Intermediate Code
Code Optimizer
Target machine code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ssuilecture2-150915075030-lva1-app6891/75/Ss-ui-lecture-2-22-2048.jpg)


