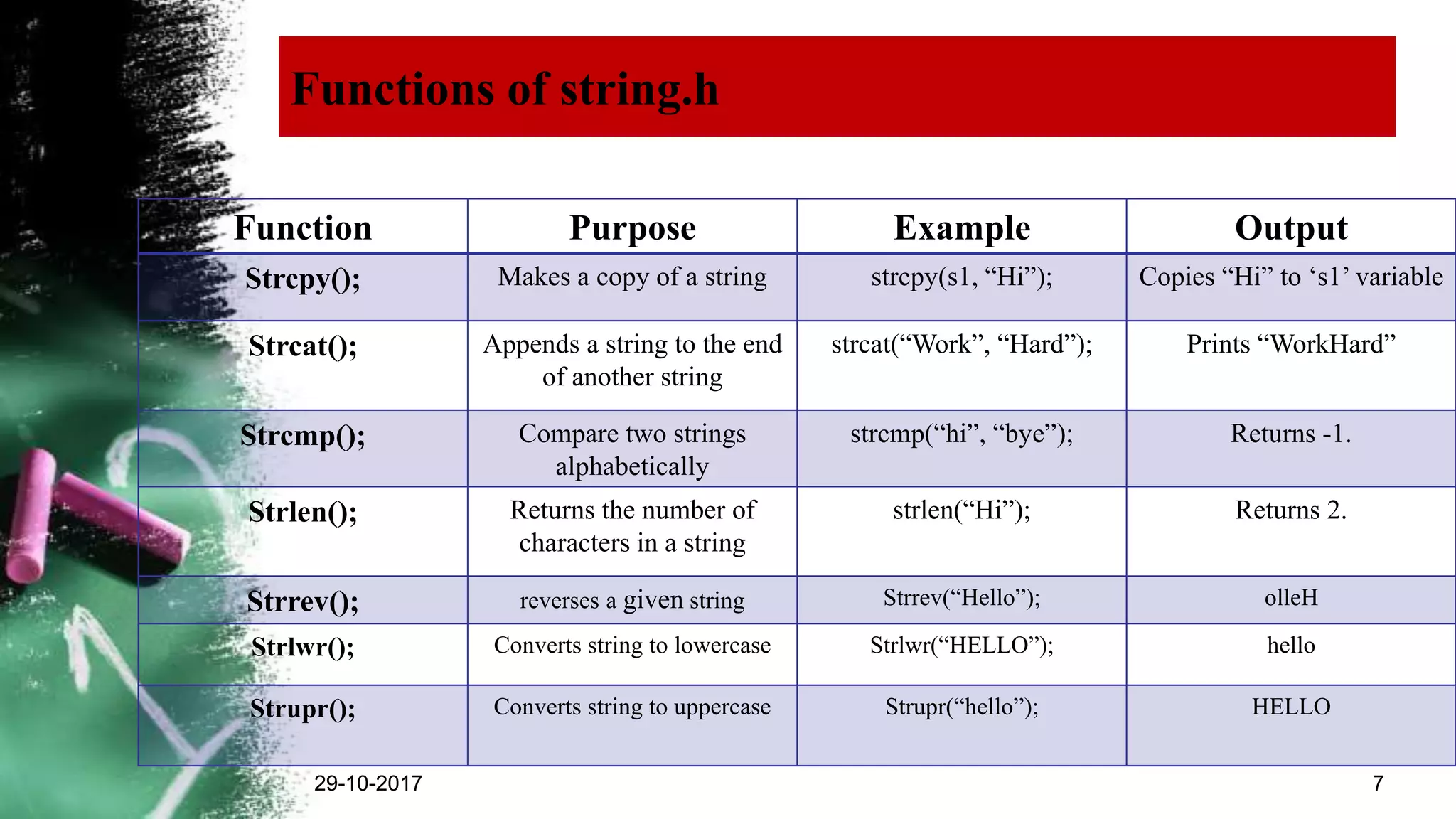
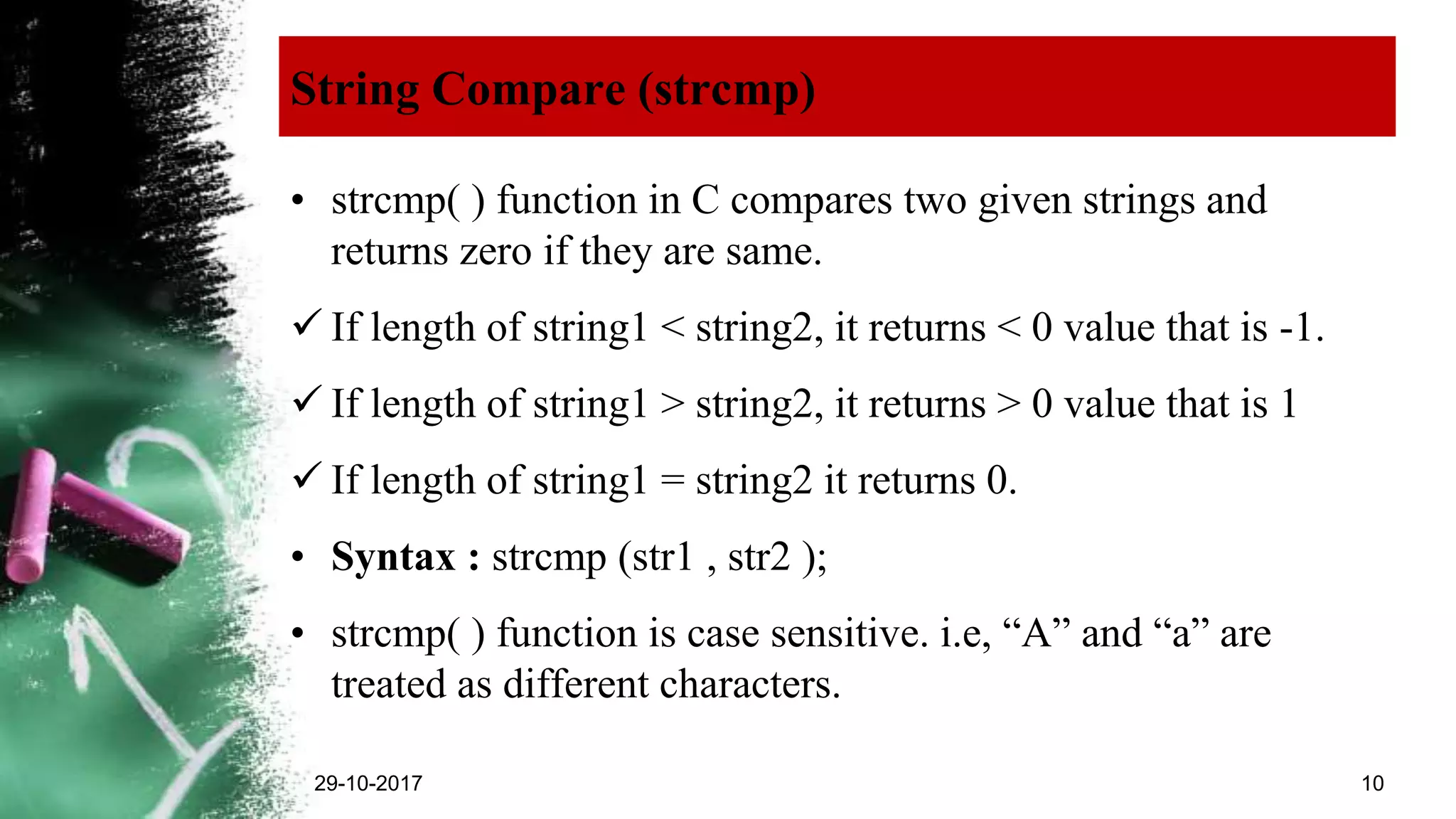
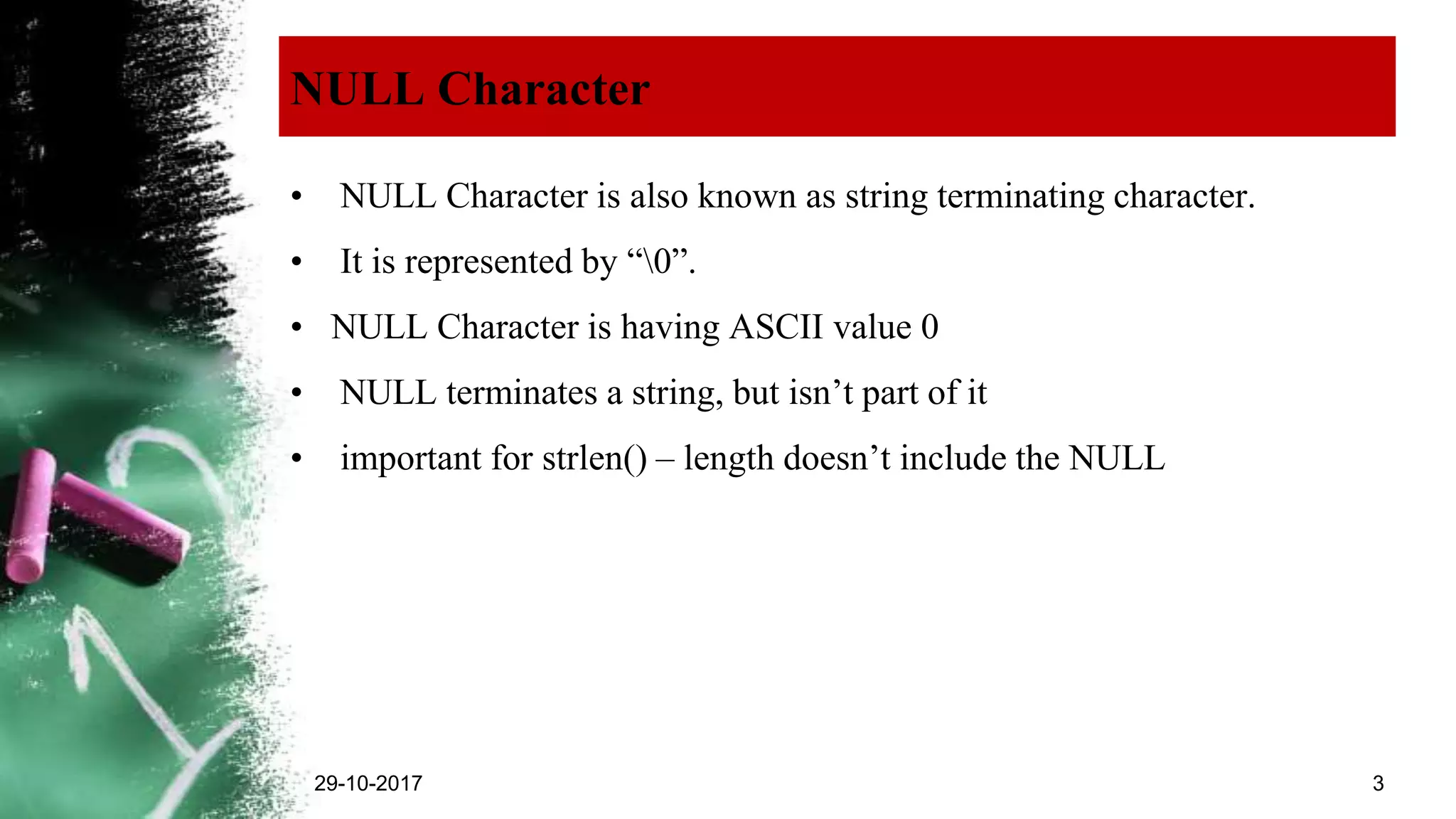
The document explains strings in C programming, defining them as collections of characters terminated by a null character (‘\0’). It outlines how to declare, initialize, and manipulate strings using functions from the string.h library, including strcpy(), strcat(), strcmp(), and strlen(). Additionally, it provides rules for declaring strings and example usages of various string functions.

![Strings
• A string is nothing but the collection of the individual array elements or
characters.
• String is enclosed within Double quotes.
• “programming" is a example of String.
• Each Character Occupy 1 byte of Memory.
• Size of “programming“ = 11 bytes
• String is always Terminated with NULL Character (‘0′).
char word[20] = “‘p’ , ‘r’ , ‘o’ , ‘g’ , ‘r’ , ‘a’ , ‘m’ , ‘m’ , ‘I’ , ‘n’ , ‘g’ ,
‘0’”
29-10-2017 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringincprogramming-171029034015/75/String-in-c-programming-2-2048.jpg)
![Declaration of a string
• Since we cannot declare string using String Data Type, instead of
which we use array of type “char” to create String.
• Syntax :
• char String_Variable_name [ SIZE ] ;
• Examples :
• char city[30];
• char name[20];
• char message[50];
29-10-2017 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringincprogramming-171029034015/75/String-in-c-programming-4-2048.jpg)
![Rules for declaring a string
• String / Character Array Variable name should be legal C Identifier.
• String Variable must have Size specified.
• char city[];
• Above Statement will cause compile time error.
• Do not use String as data type because String data type is included in
later languages such as C++ / Java. C does not support String data type
• When you are using string for other purpose than accepting and
printing data then you must include following header file in your code –
#include<string.h>
29-10-2017 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringincprogramming-171029034015/75/String-in-c-programming-5-2048.jpg)