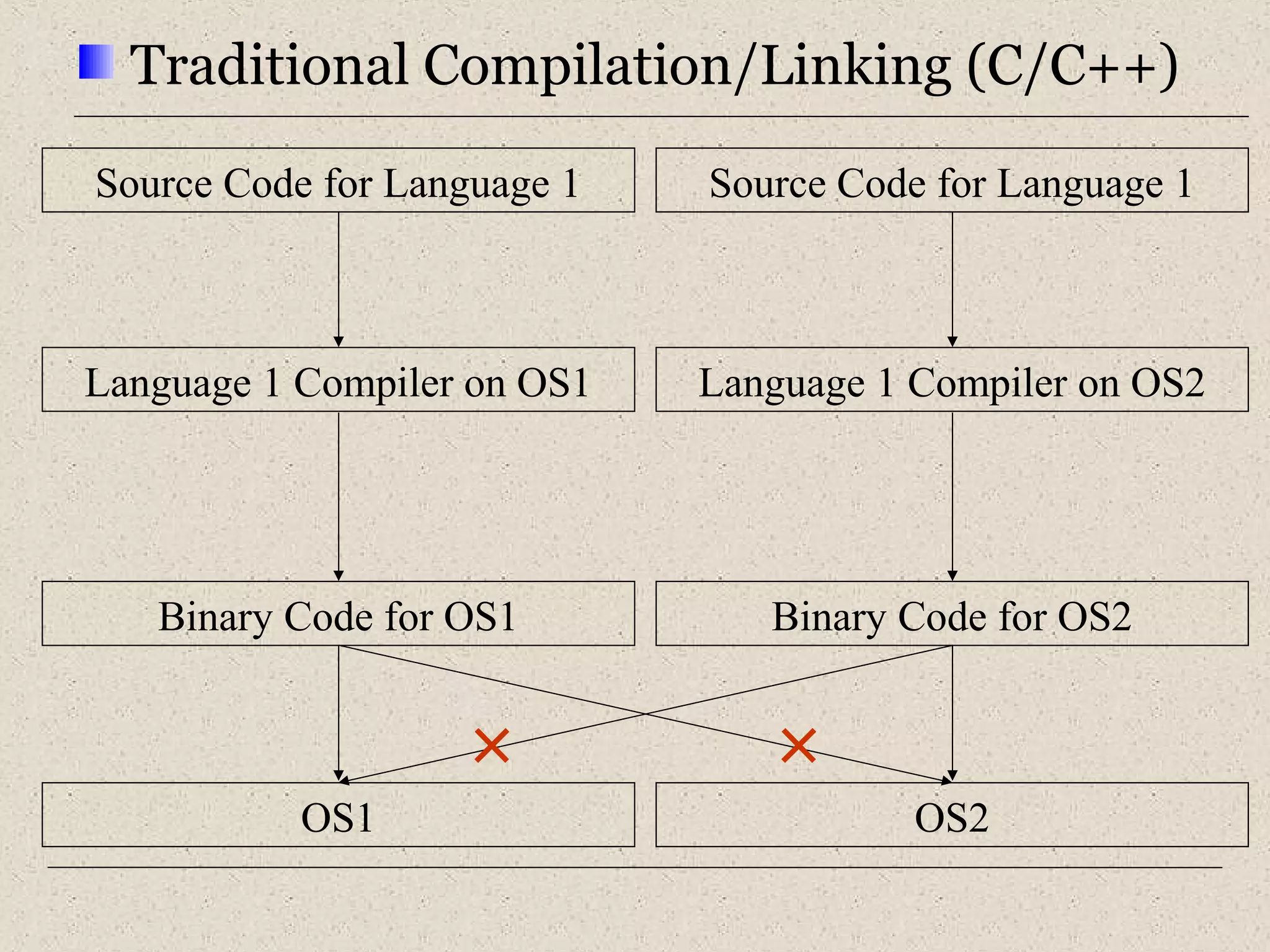
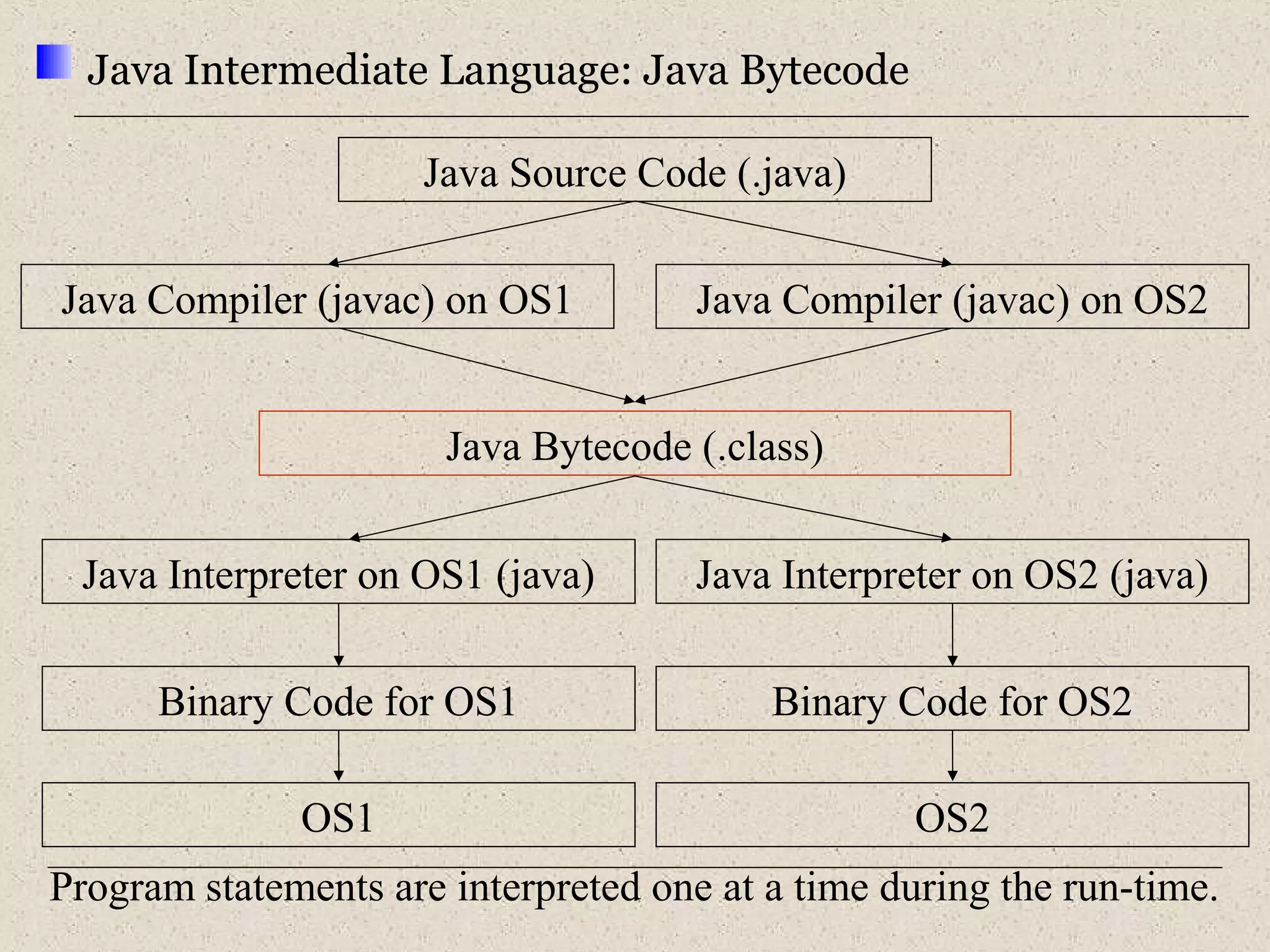
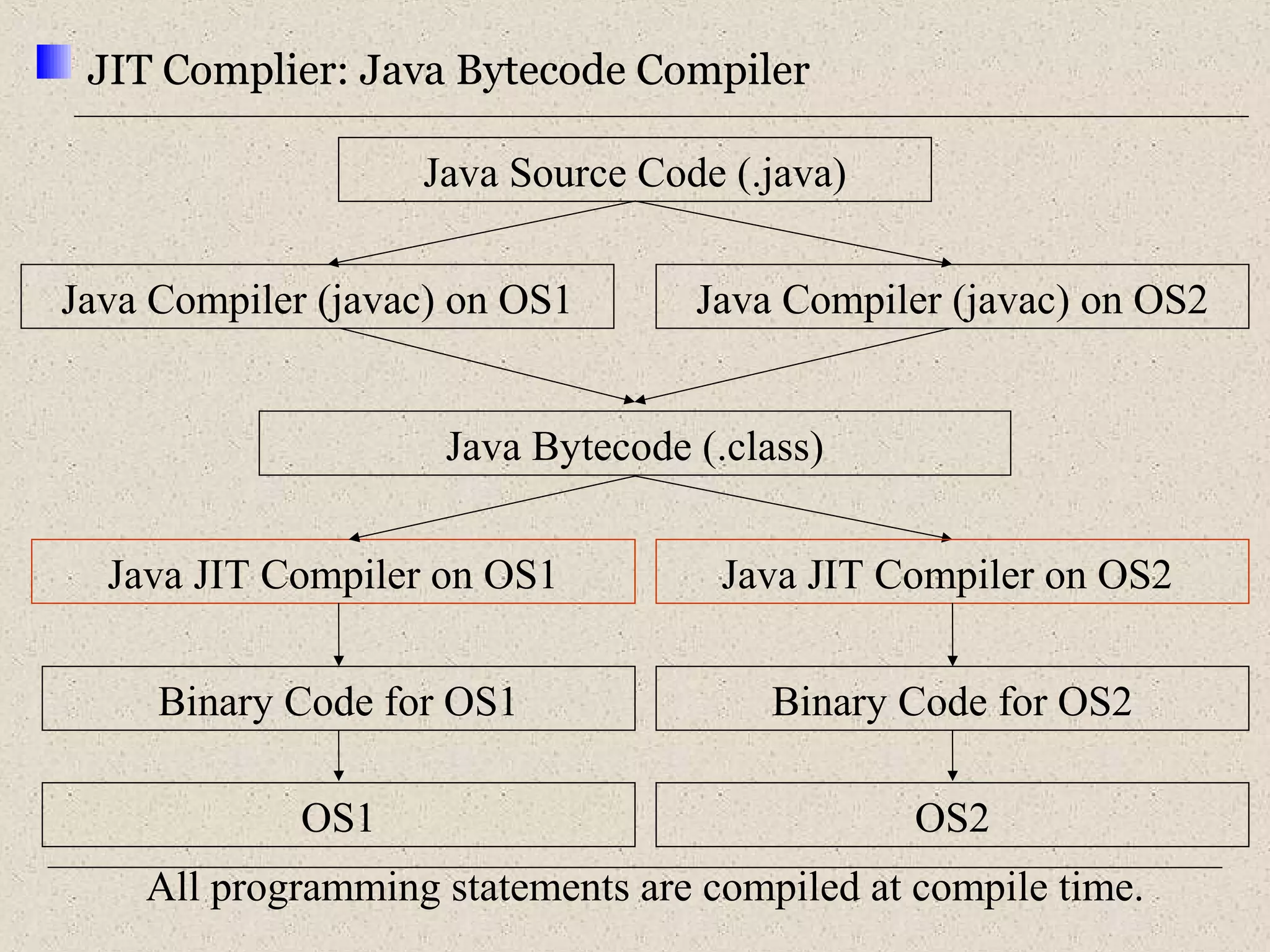
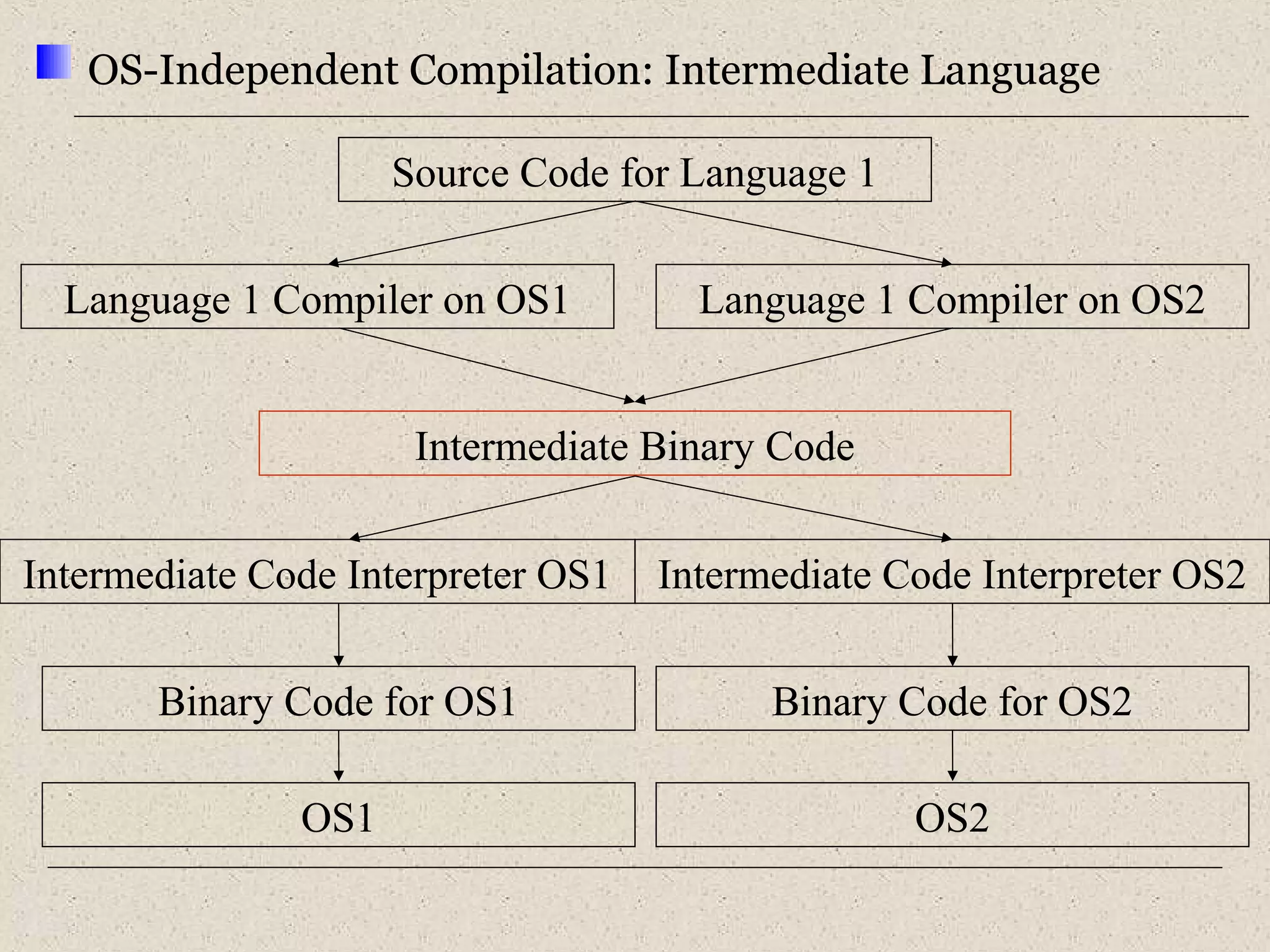
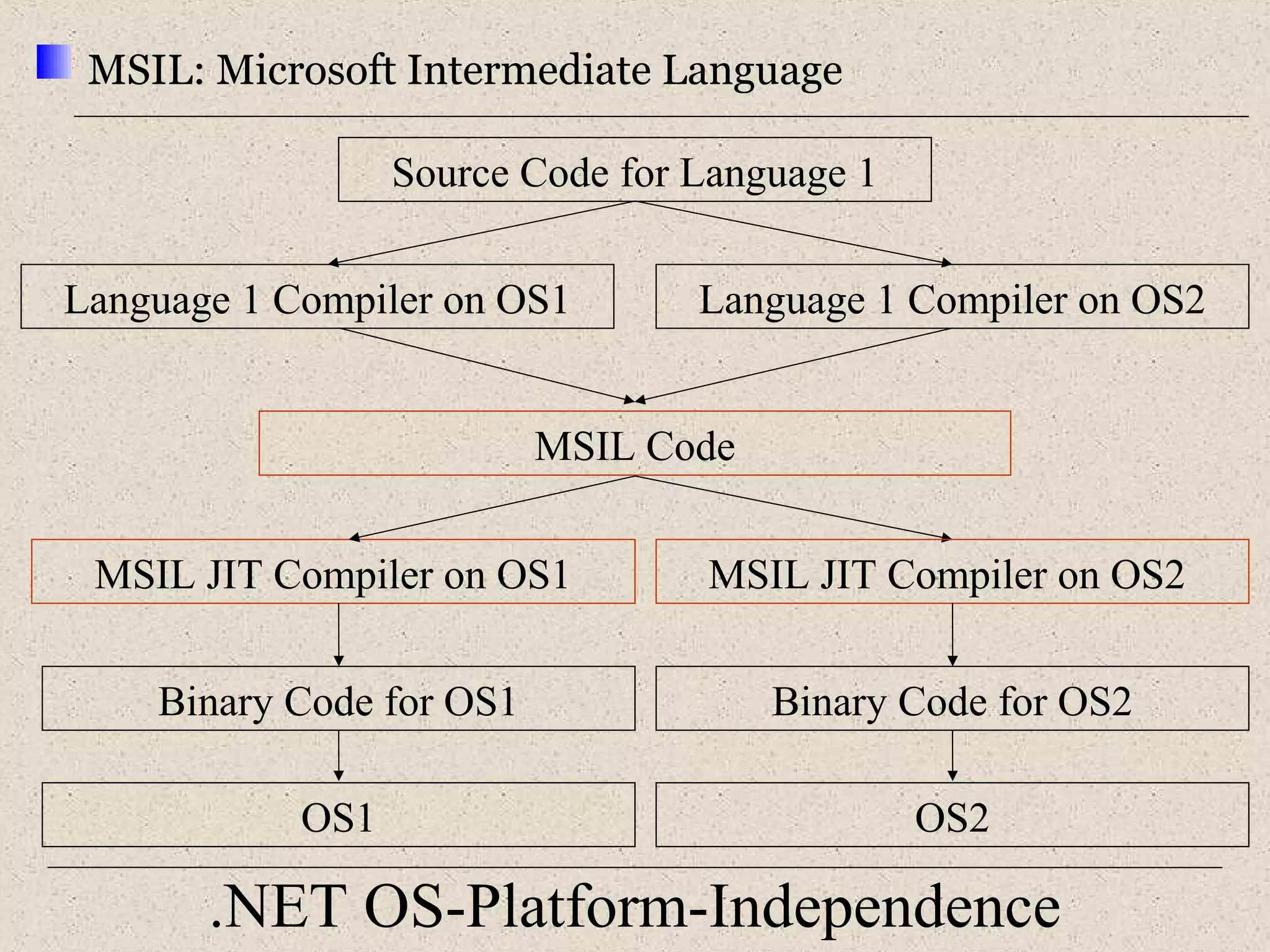
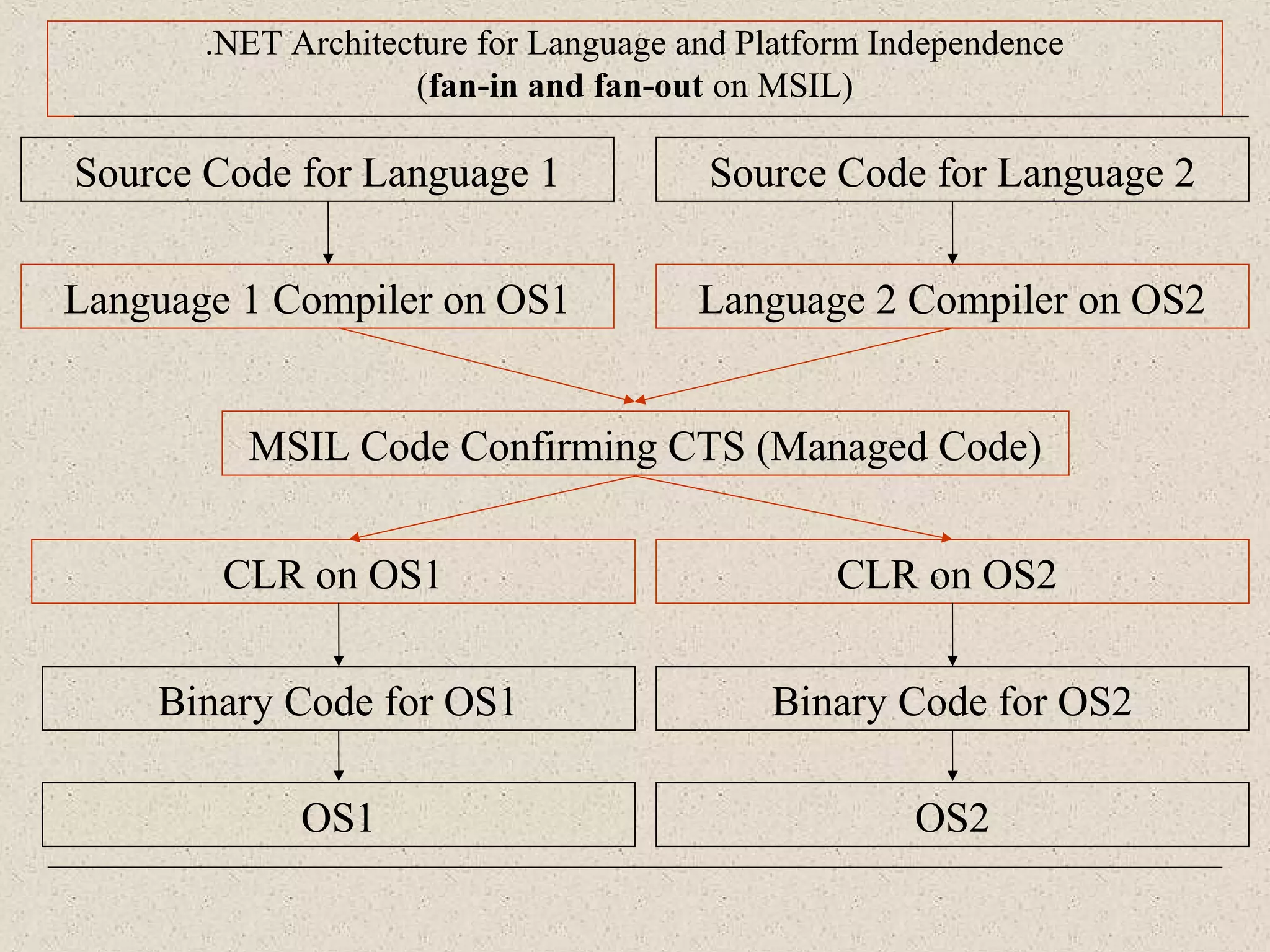
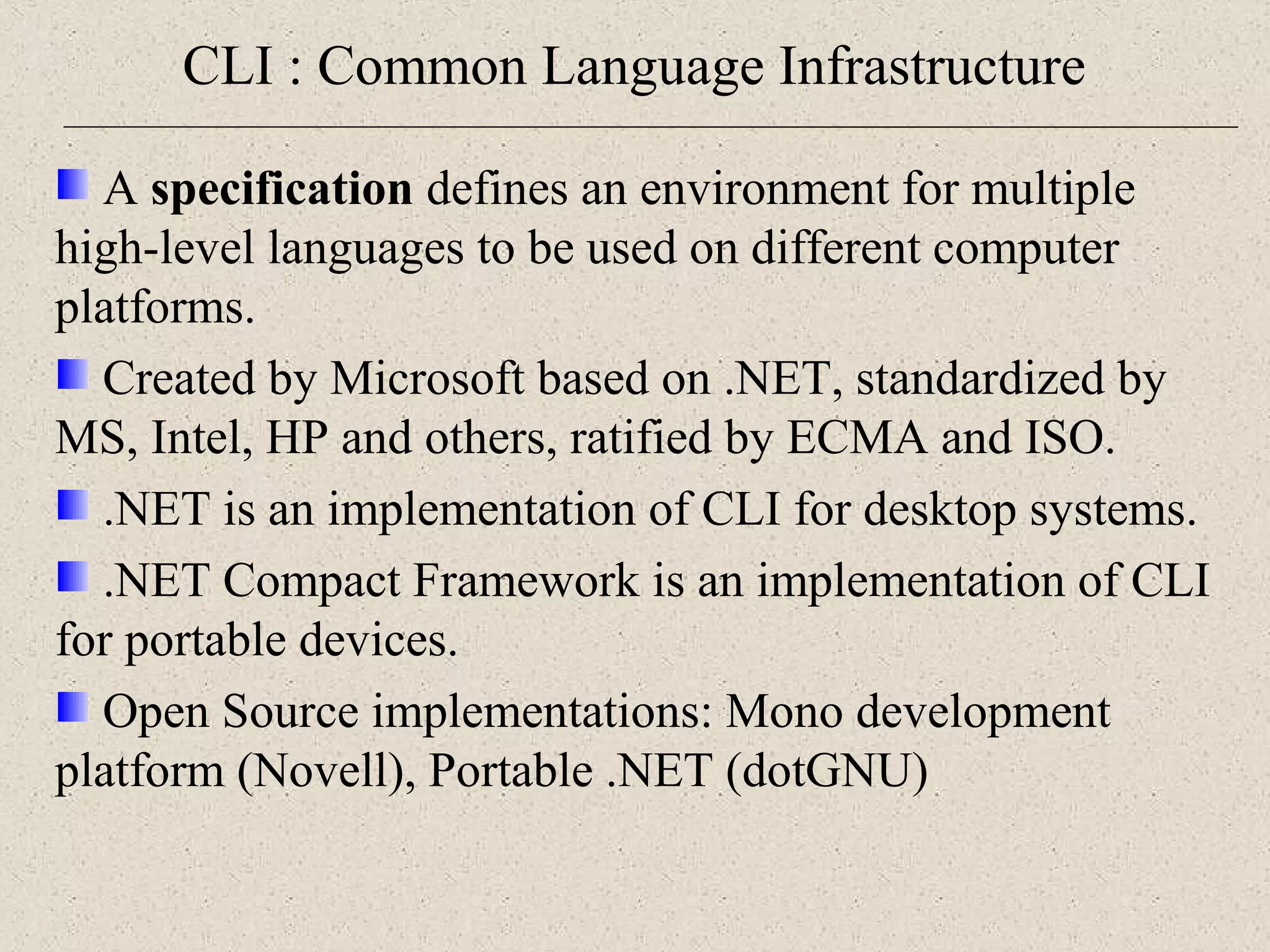
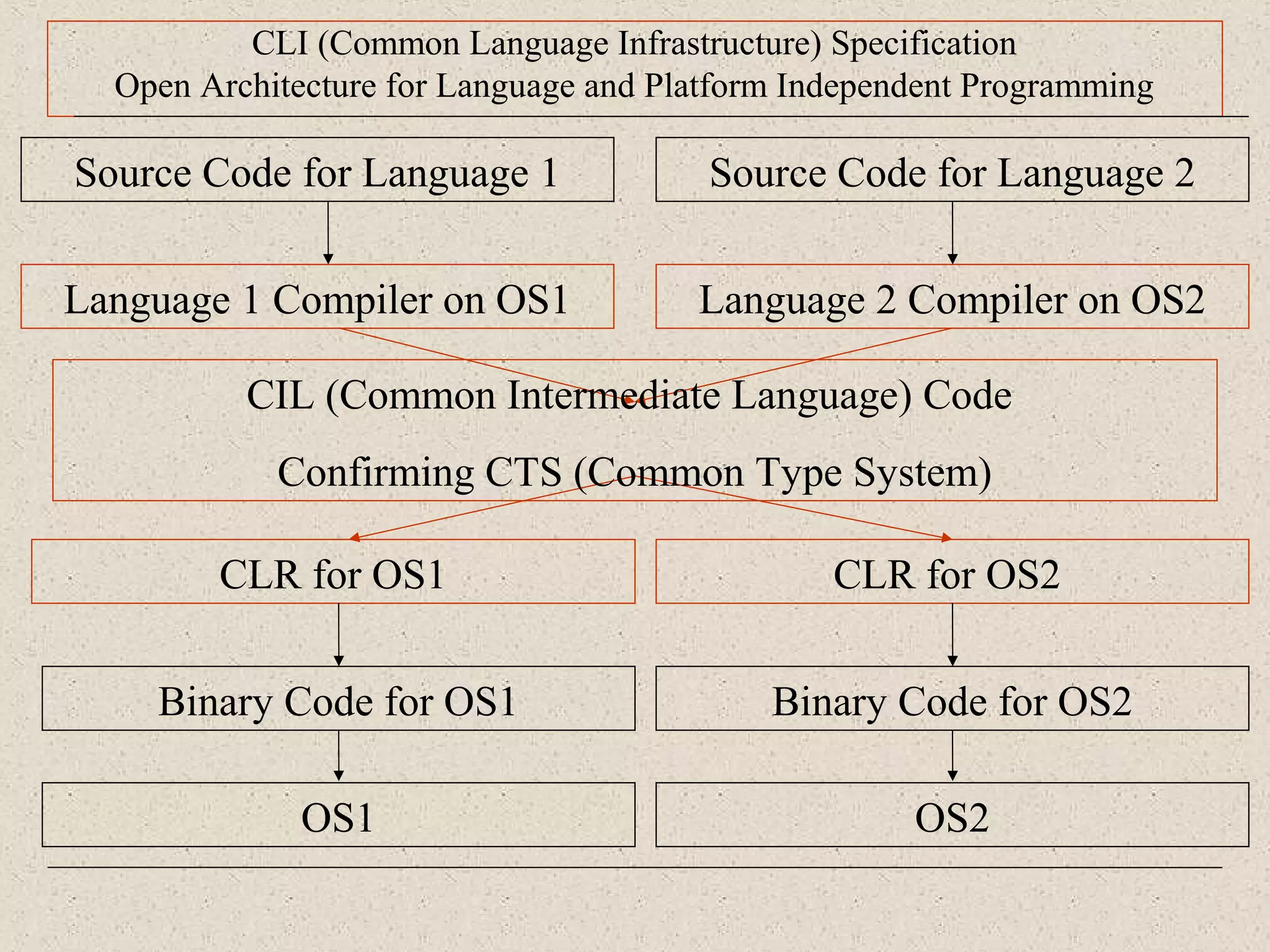
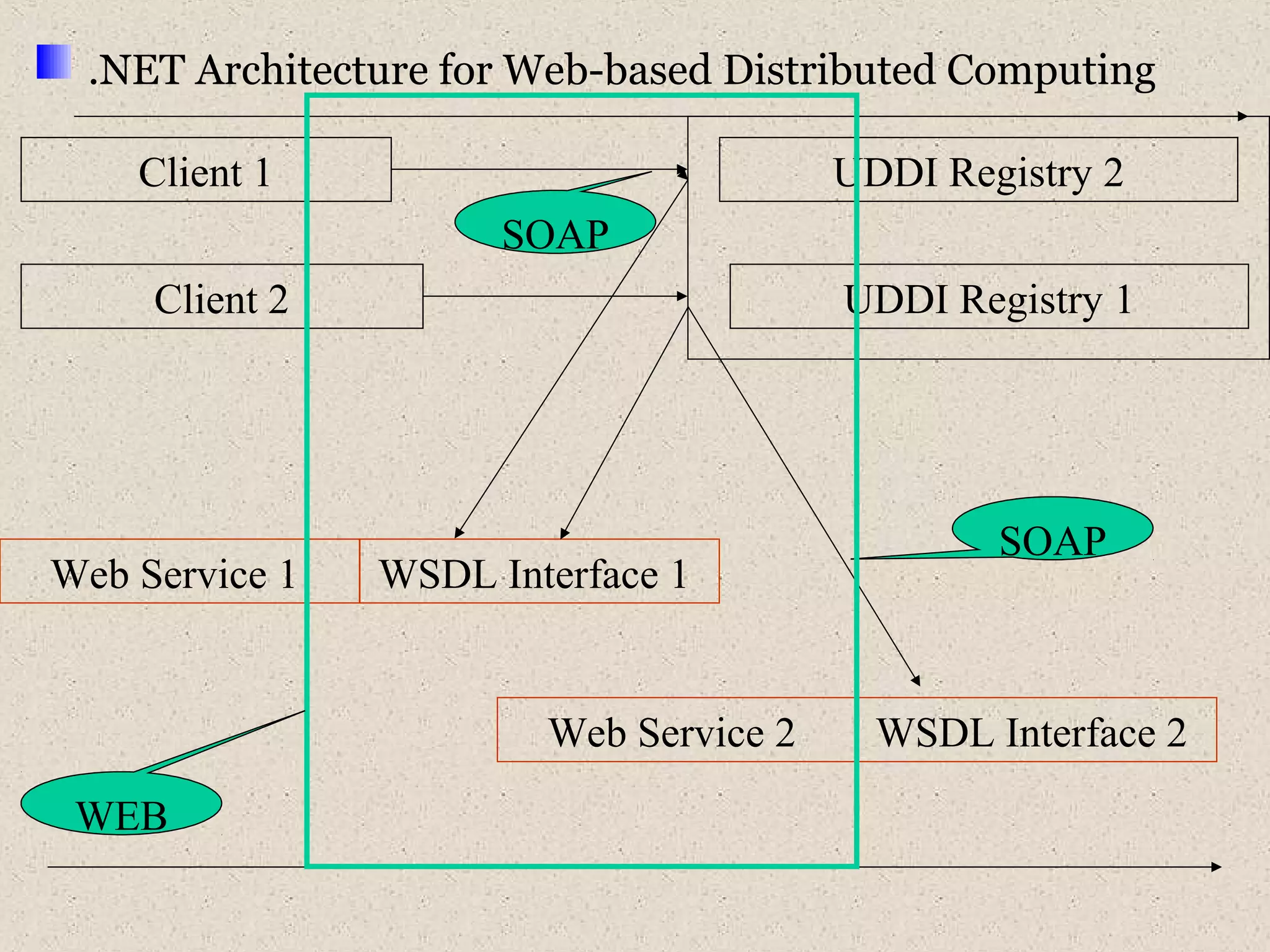
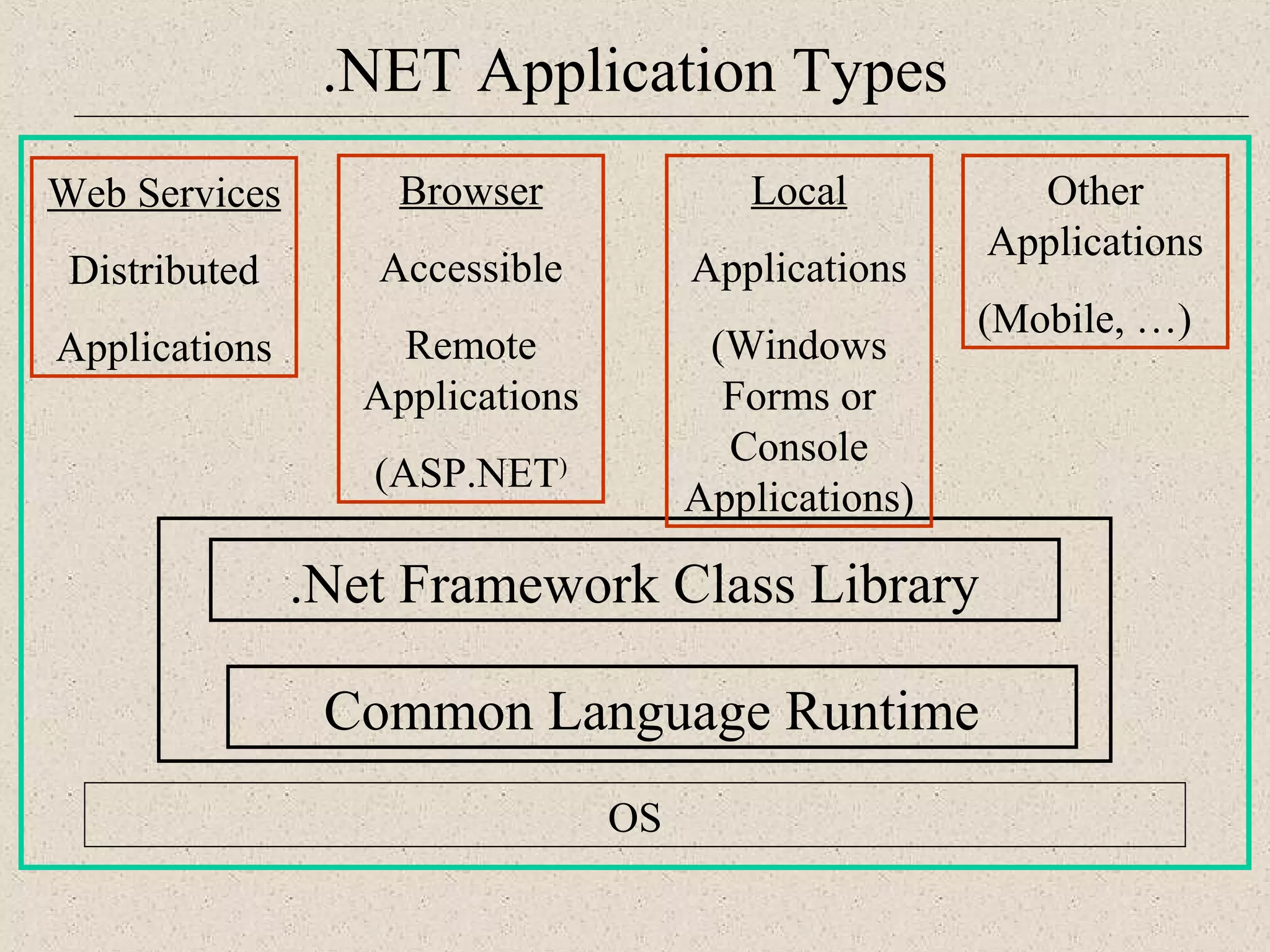
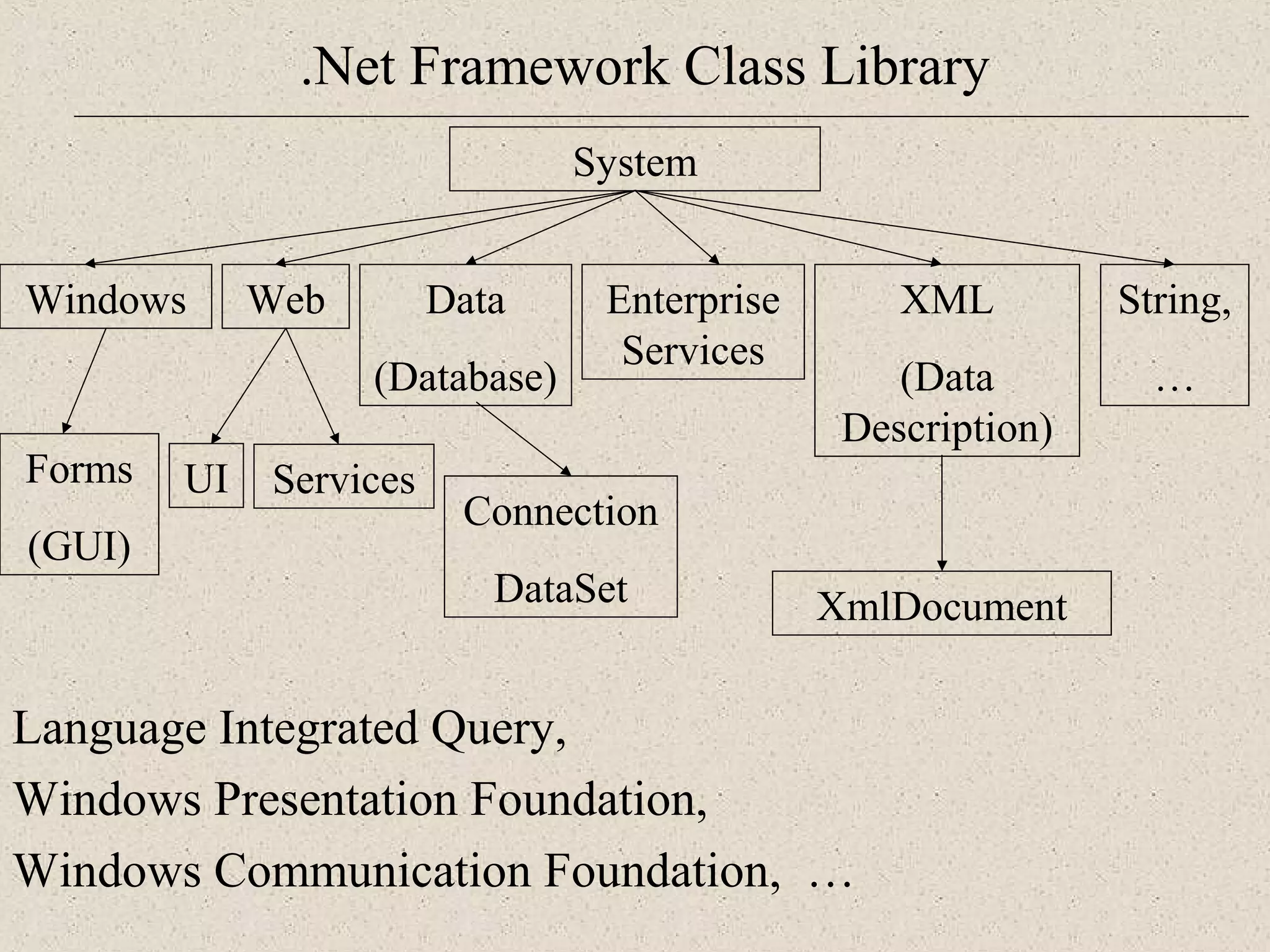
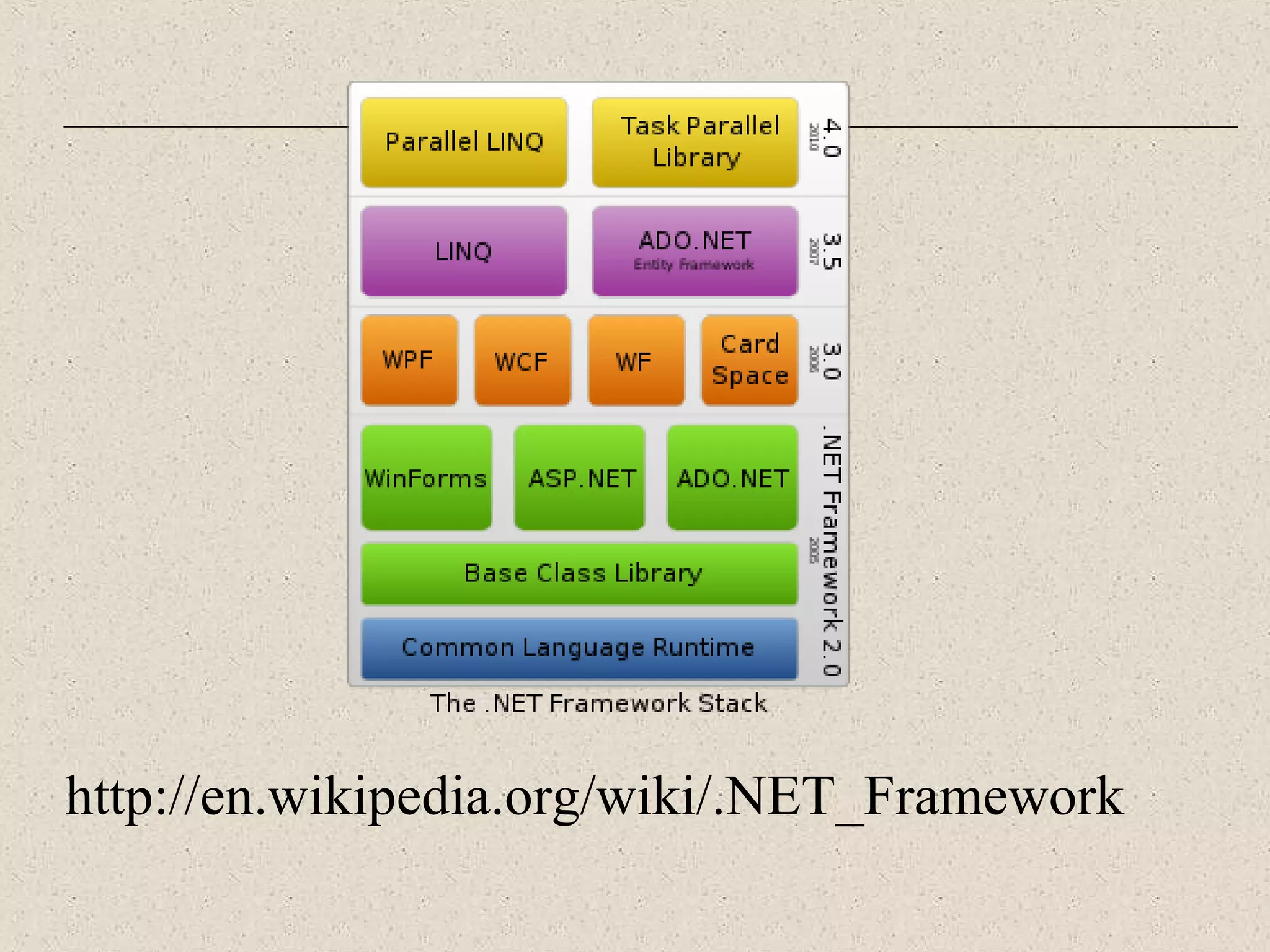
This document provides an introduction to ASP.NET by discussing key concepts such as the .NET framework, Common Language Runtime, and Common Type System which allow for language and platform independence. It also describes how ASP.NET enables web-enabled and distributed applications using technologies like XML, SOAP, and WSDL. The document outlines the architecture and components of the .NET framework including the common language runtime, class libraries, and support for different application types.