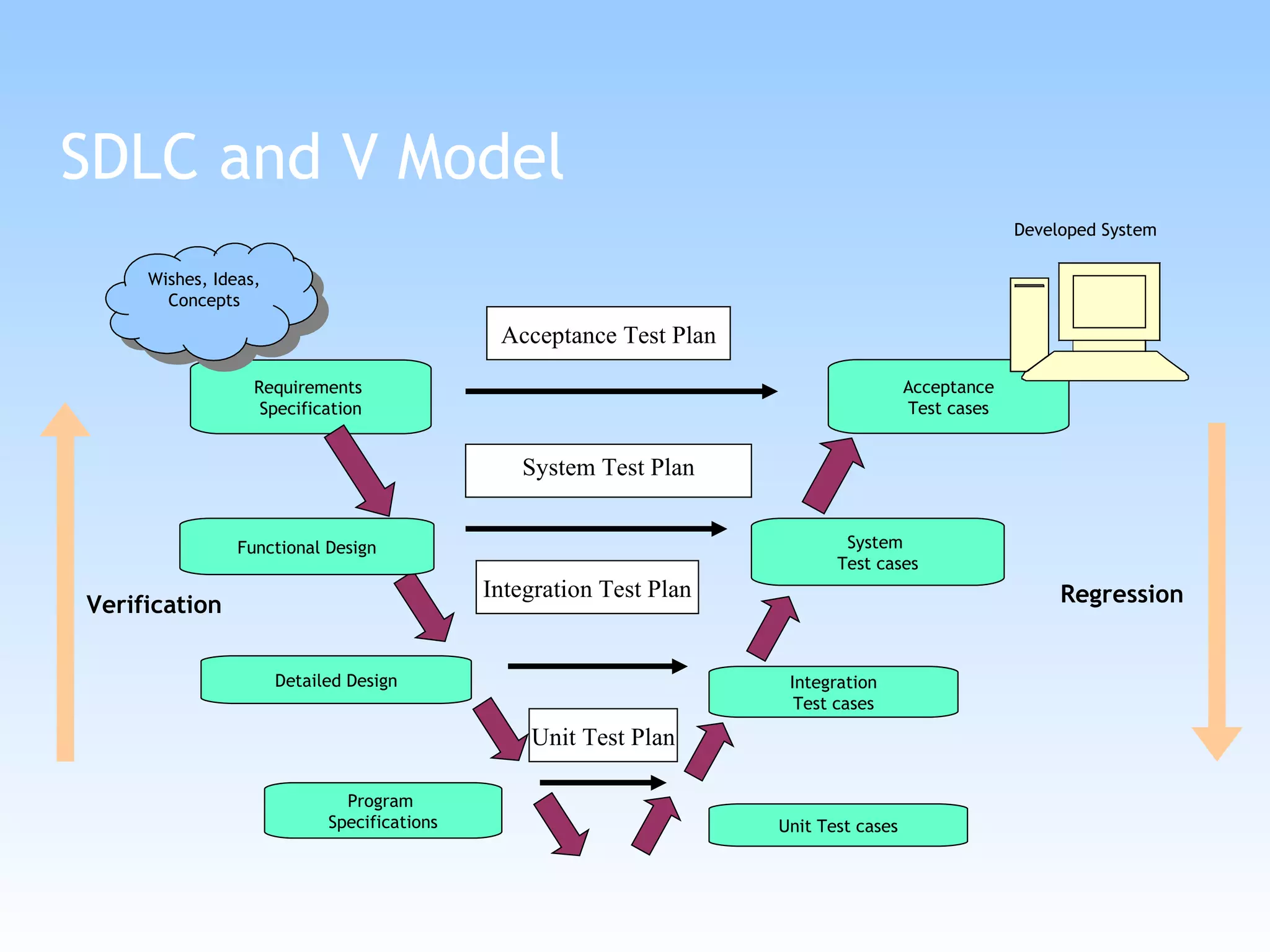
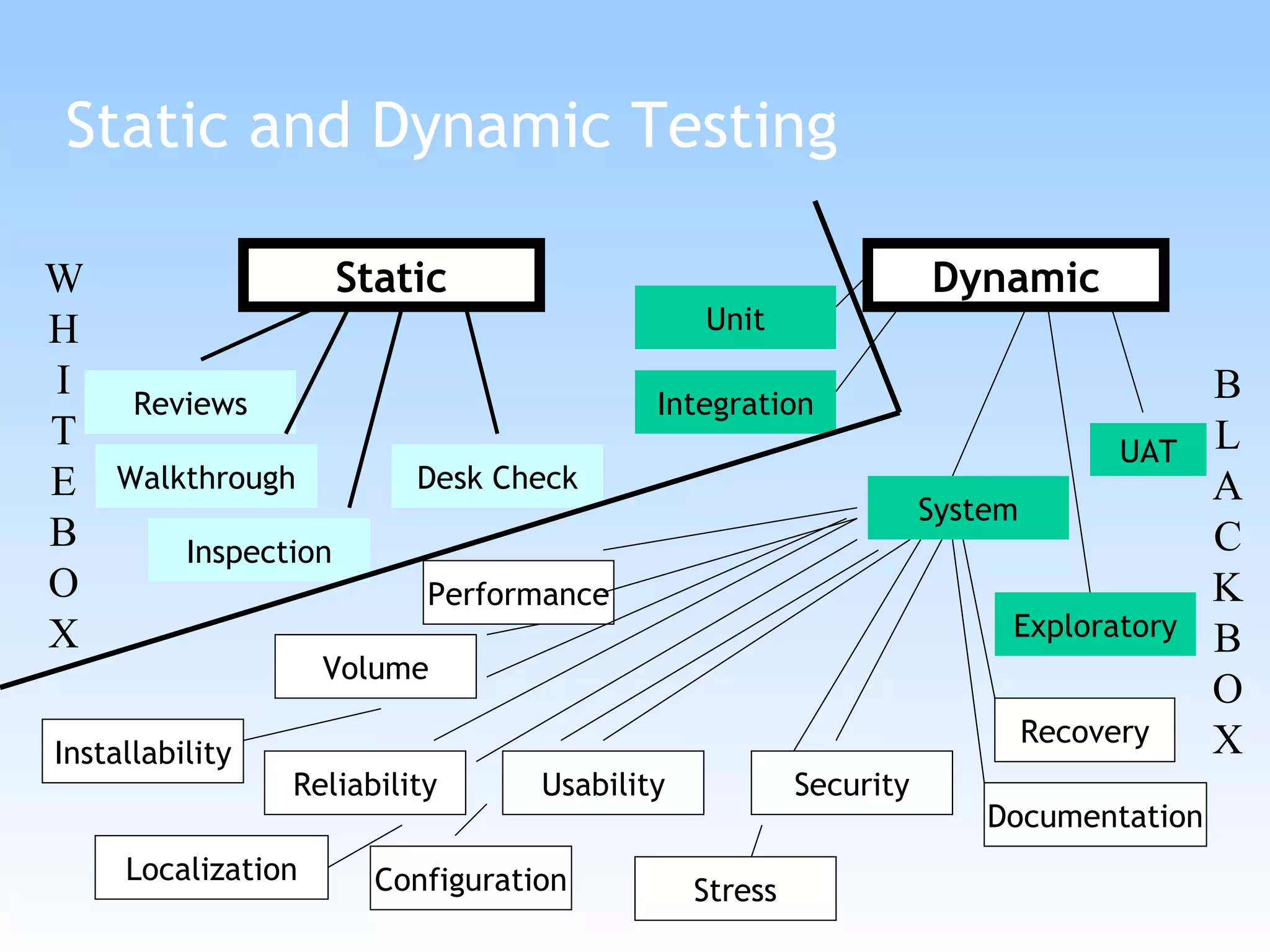
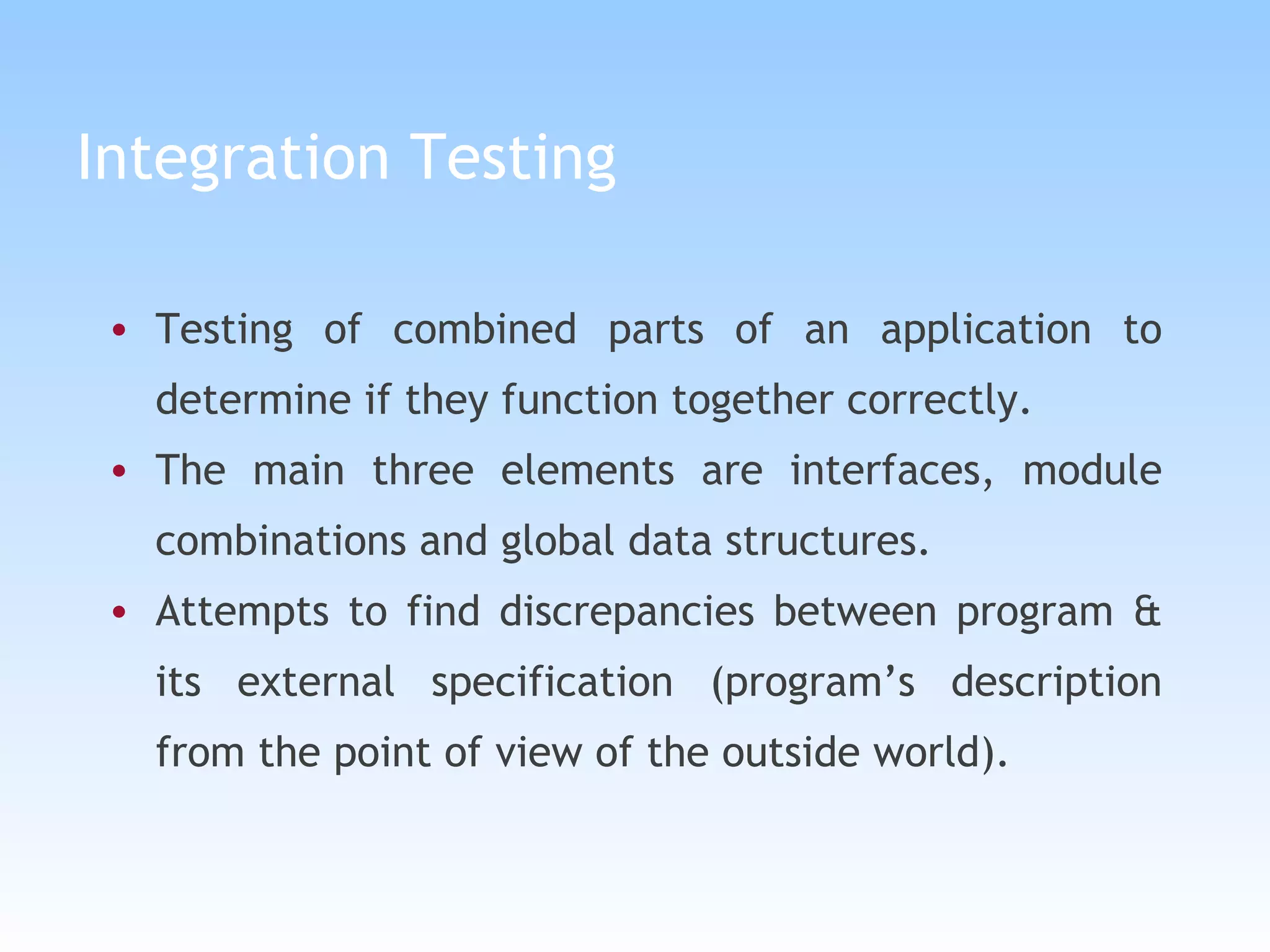
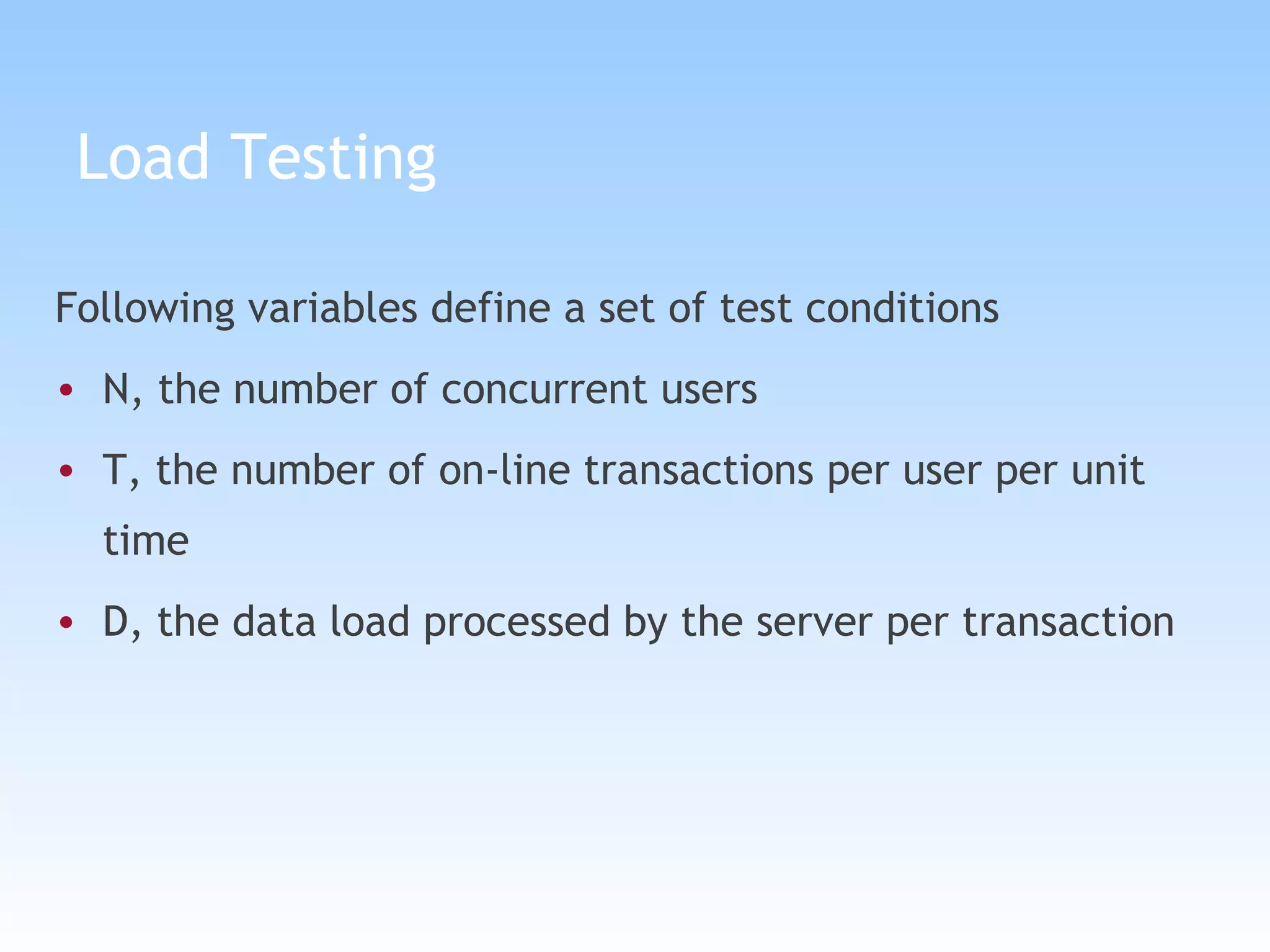
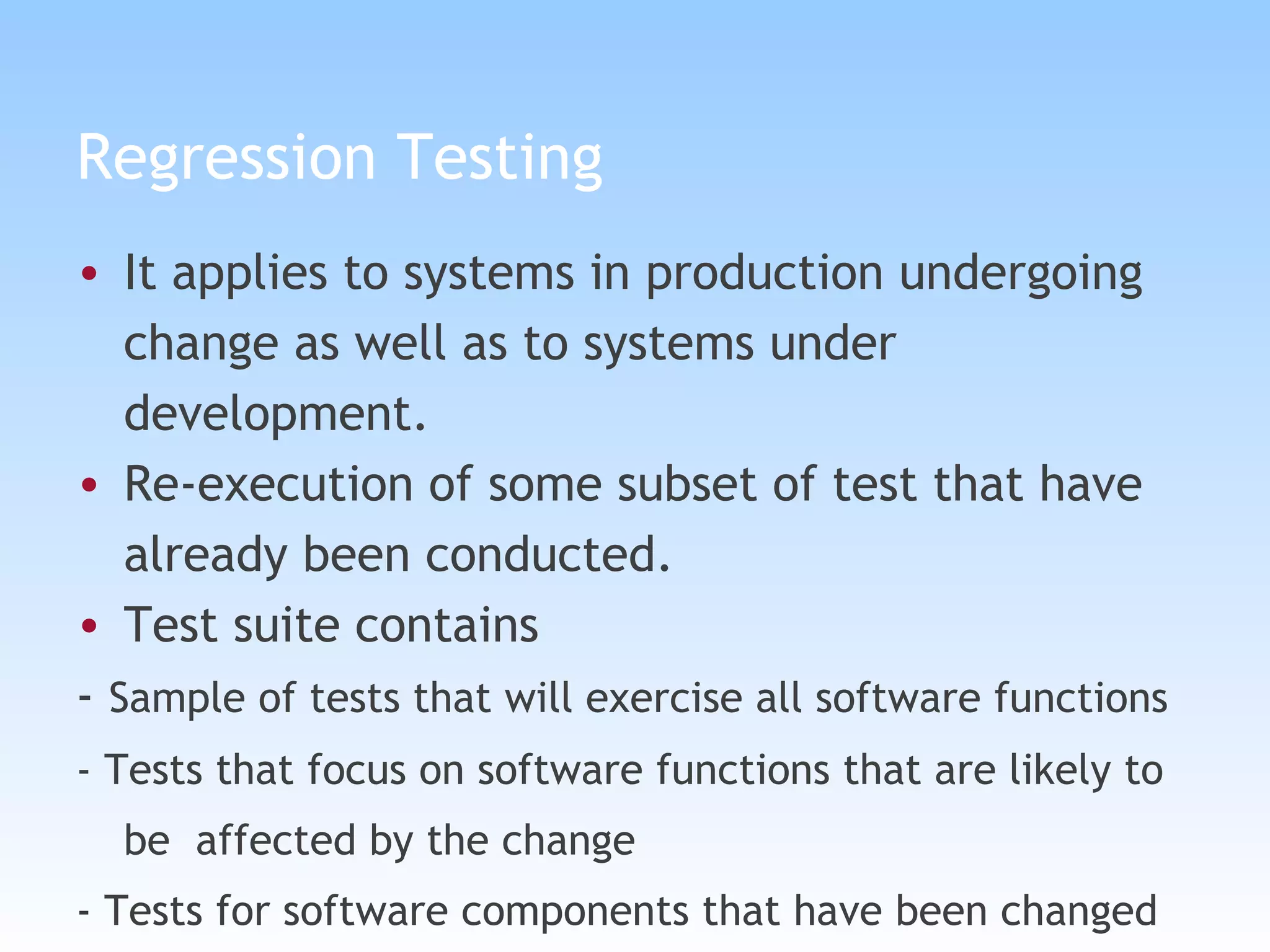
The document discusses different types of testing in the V-model, including static testing, dynamic testing, unit testing, integration testing, system testing, acceptance testing, and more. It provides details on each type of testing including what is tested, when it is performed, and the objectives.