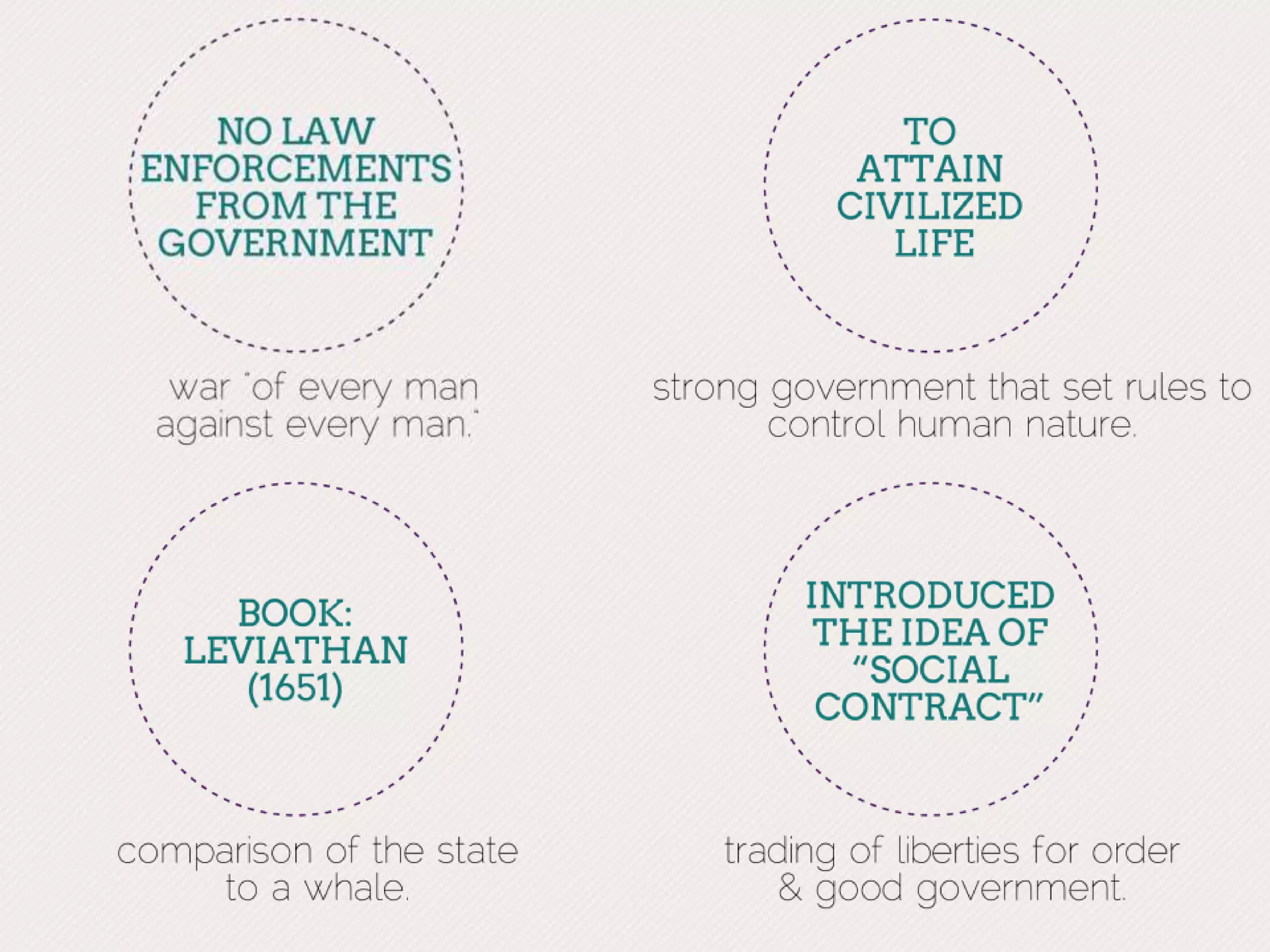
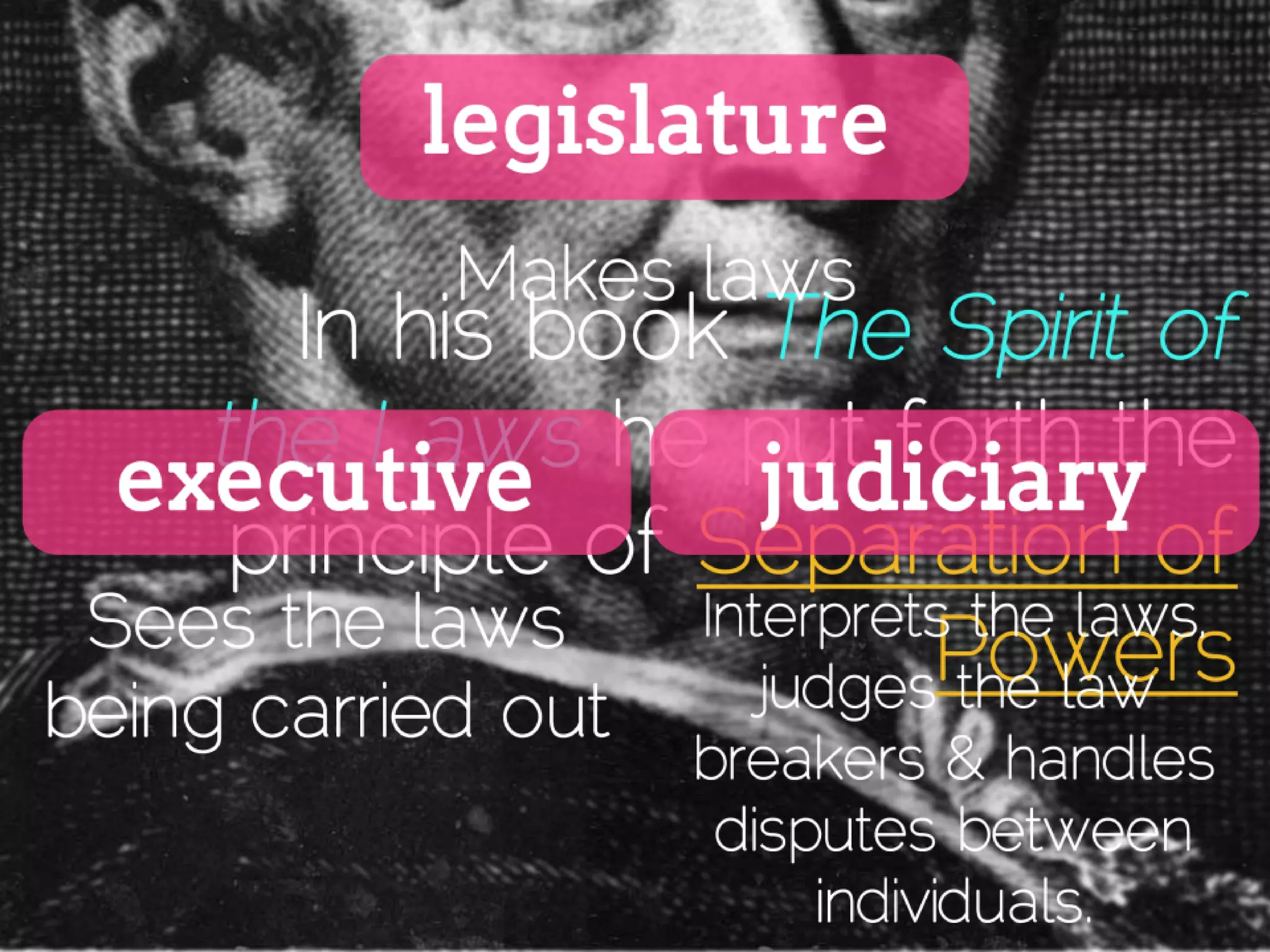
An English political theorist sought to create a science of politics and was influential in the politics of the Glorious Revolution in England. His most influential ideas were on government and natural rights. Later philosophers examined the questions he raised, influenced by Newton's discoveries and relating to his political ideas. The Enlightenment centered in France, where social critics and philosophers proposed reforms reacting against absolute monarchy and the divine right of kings. They also challenged nobility and clergy privileges and opposed censorship by church or government.