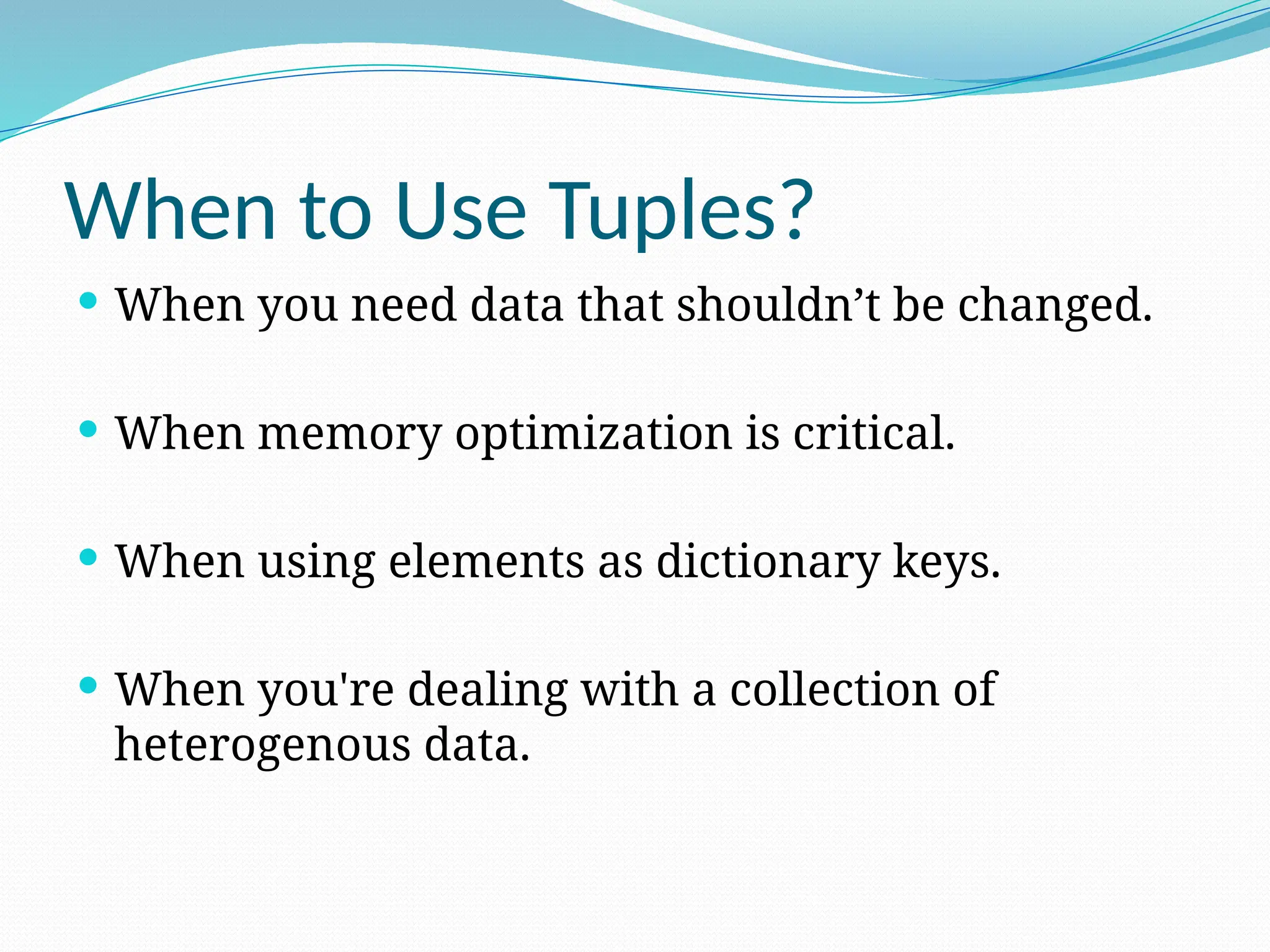
Tuples in Python are ordered and immutable collections, meaning their elements cannot be modified after creation. They are useful for maintaining data integrity, serving as dictionary keys, and representing fixed collections of related items. Tuples are memory efficient and facilitate faster operations compared to lists, making them ideal for read-only data needs.

![Immutability of Tuples
Key Property: Tuples are immutable.
You cannot modify, add, or remove elements after
creating a tuple.
Example: Attempting to modify a tuple:
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3)
my_tuple[0] = 5 # Error: TypeError: 'tuple' object
does not support item assignment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tuplesinpython2-241021143614-f707b904/75/Tuples-in-Python-2-Object-Oriented-Programming-pptx-2-2048.jpg)
![Nested Tuples
Tuples can contain other tuples (nested structure).
nested_tuple = (1, (2, 3), (4, 5, 6))
print(nested_tuple[1]) # Output: (2, 3)
print(nested_tuple[1][0]) # Output: 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tuplesinpython2-241021143614-f707b904/75/Tuples-in-Python-2-Object-Oriented-Programming-pptx-3-2048.jpg)