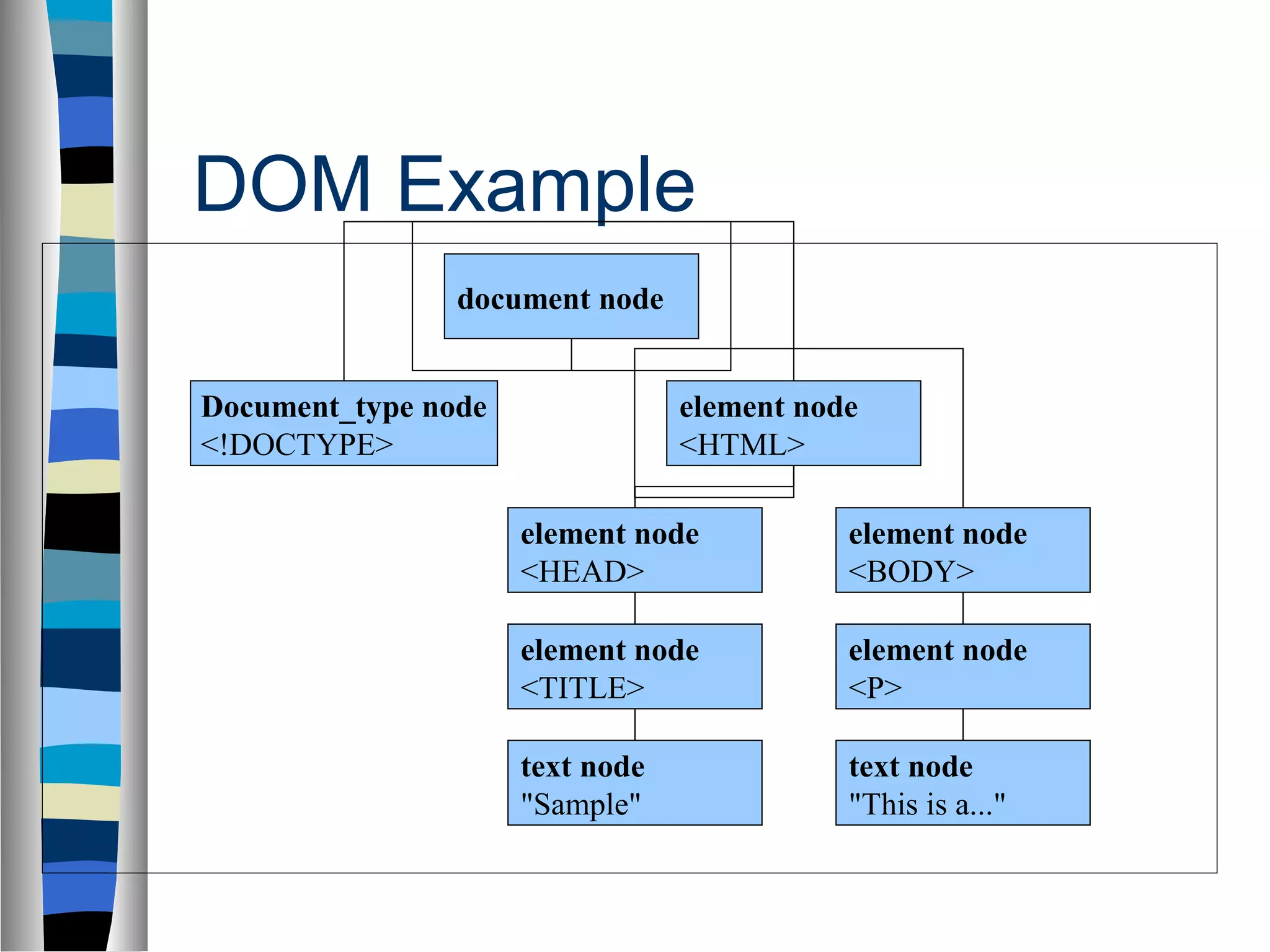
DHTML allows dynamic and interactive web pages through a combination of technologies including HTML, CSS, JavaScript and the DOM. It uses these components to manipulate page elements even after loading. The DOM represents the document as nodes that can be accessed and changed by scripts to alter the structure, style and content of the page. DHTML provides advantages like standardization and no plugins, but also has disadvantages like complex coding and limited browser support.