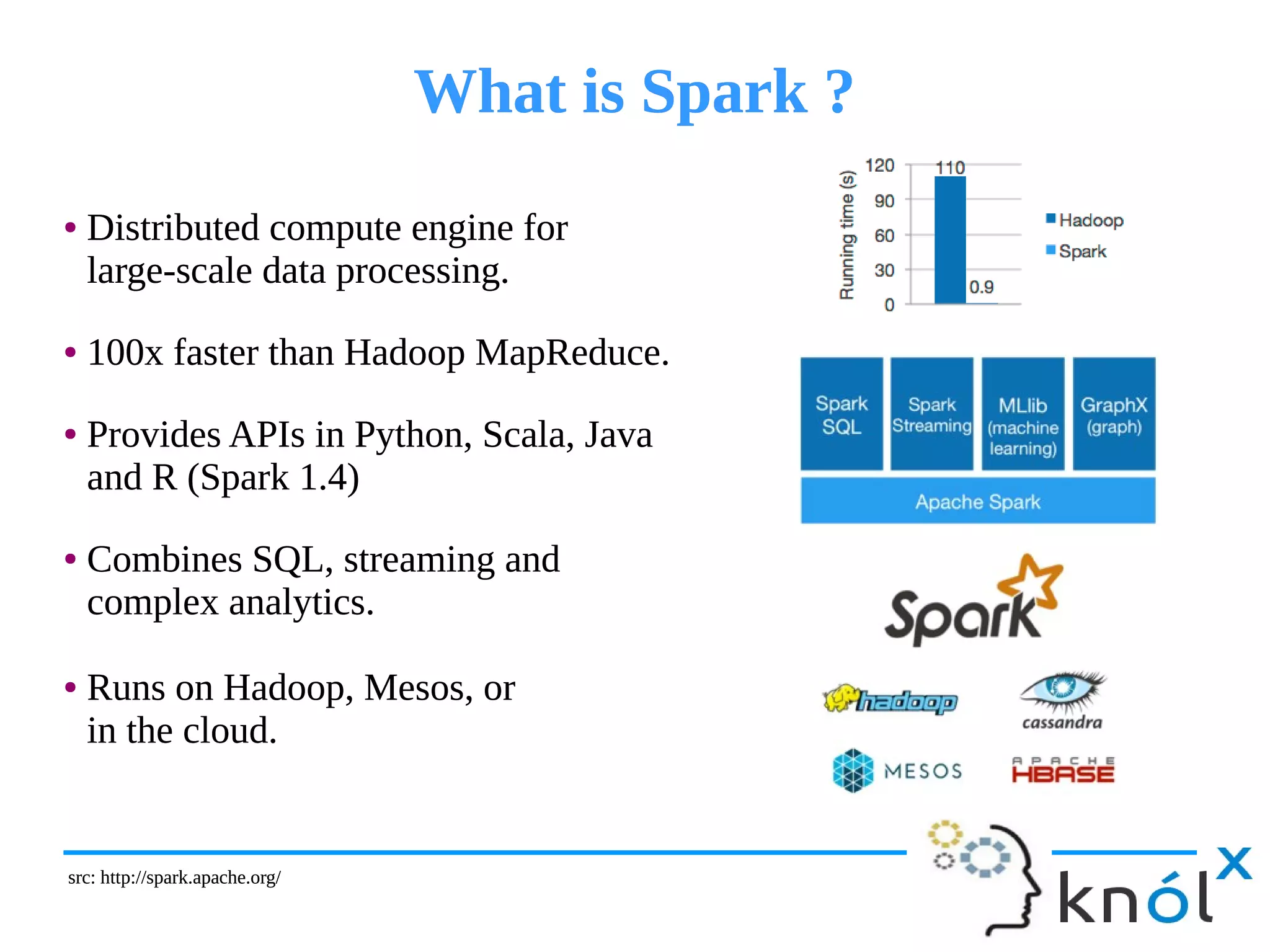
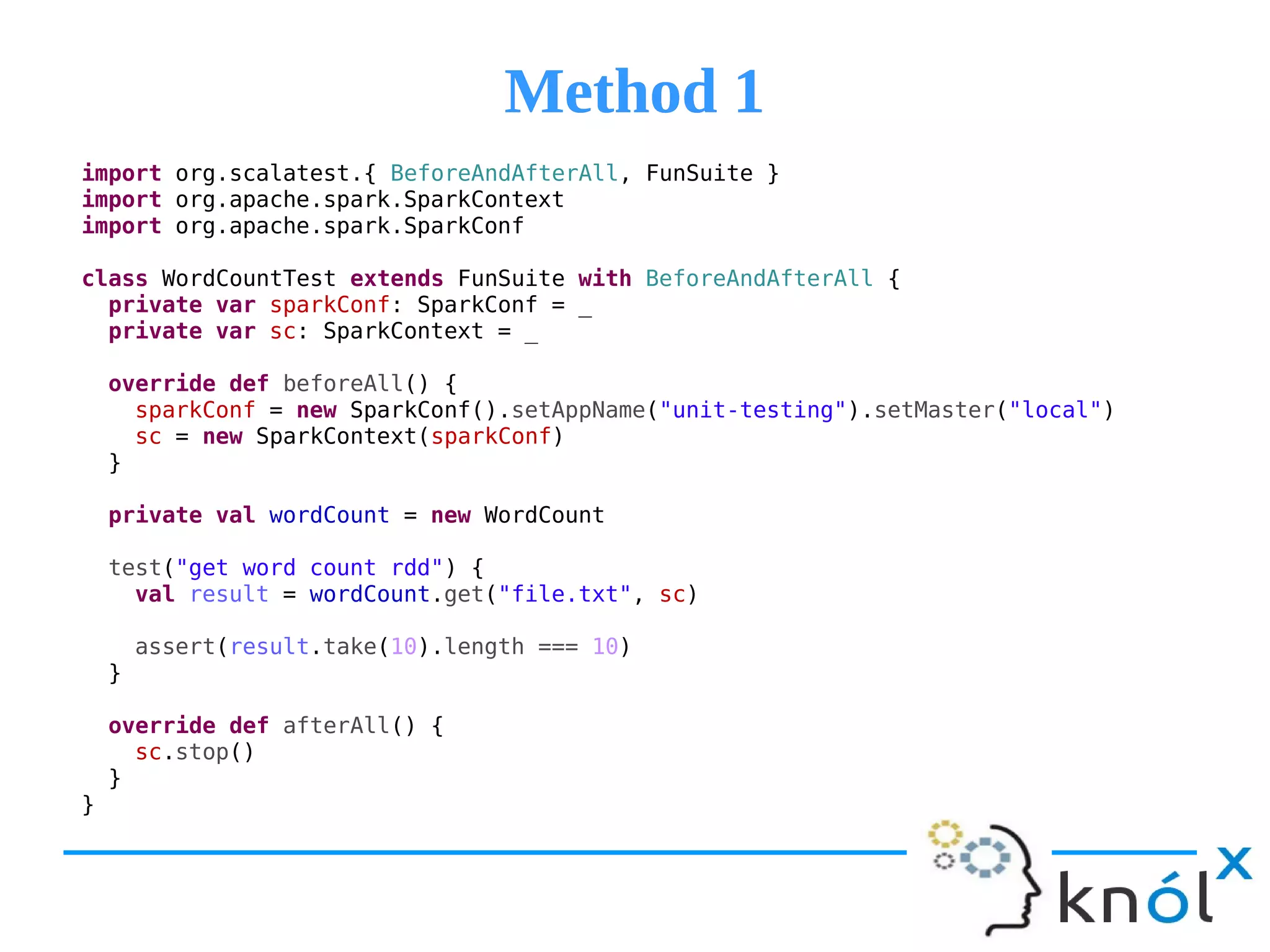
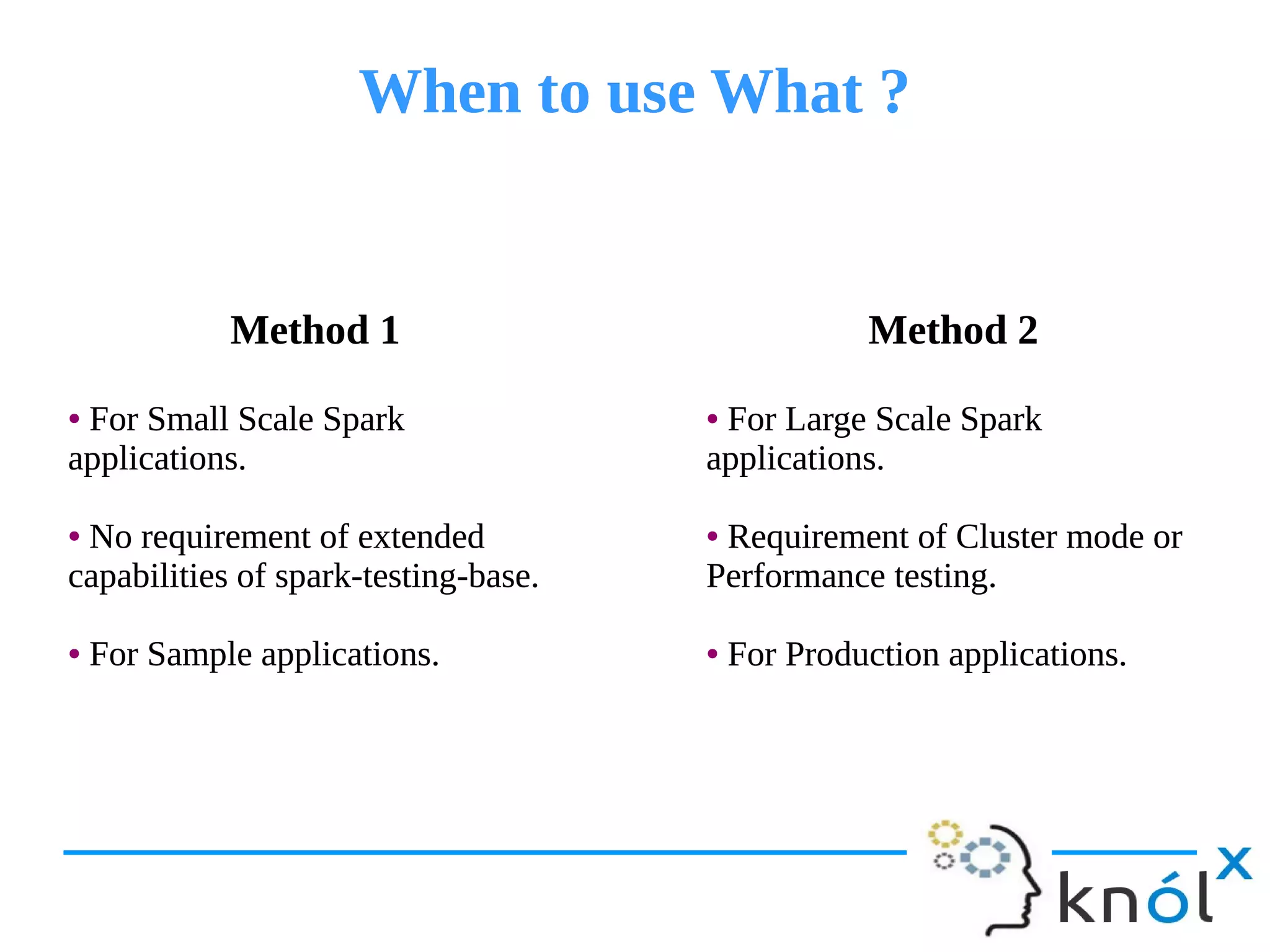
The document provides an overview of unit testing for Spark applications, detailing what Spark is and the importance of unit testing in software development. It discusses different methods for unit testing with Spark, comparing a more manual method with one using the 'spark-testing-base' library that streamlines the process. Key benefits of unit testing, such as early bug detection and easing integration, are also highlighted.





![Unit to TestUnit to Test
import org.apache.spark.SparkContext
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
class WordCount {
def get(url: String, sc: SparkContext): RDD[(String, Int)] = {
val lines = sc.textFile(url)
lines.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _)
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-testing-of-spark-applications-04-13-16-160418054355/75/Unit-testing-of-spark-applications-7-2048.jpg)



![Questions & Option[A]Questions & Option[A]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-testing-of-spark-applications-04-13-16-160418054355/75/Unit-testing-of-spark-applications-16-2048.jpg)

