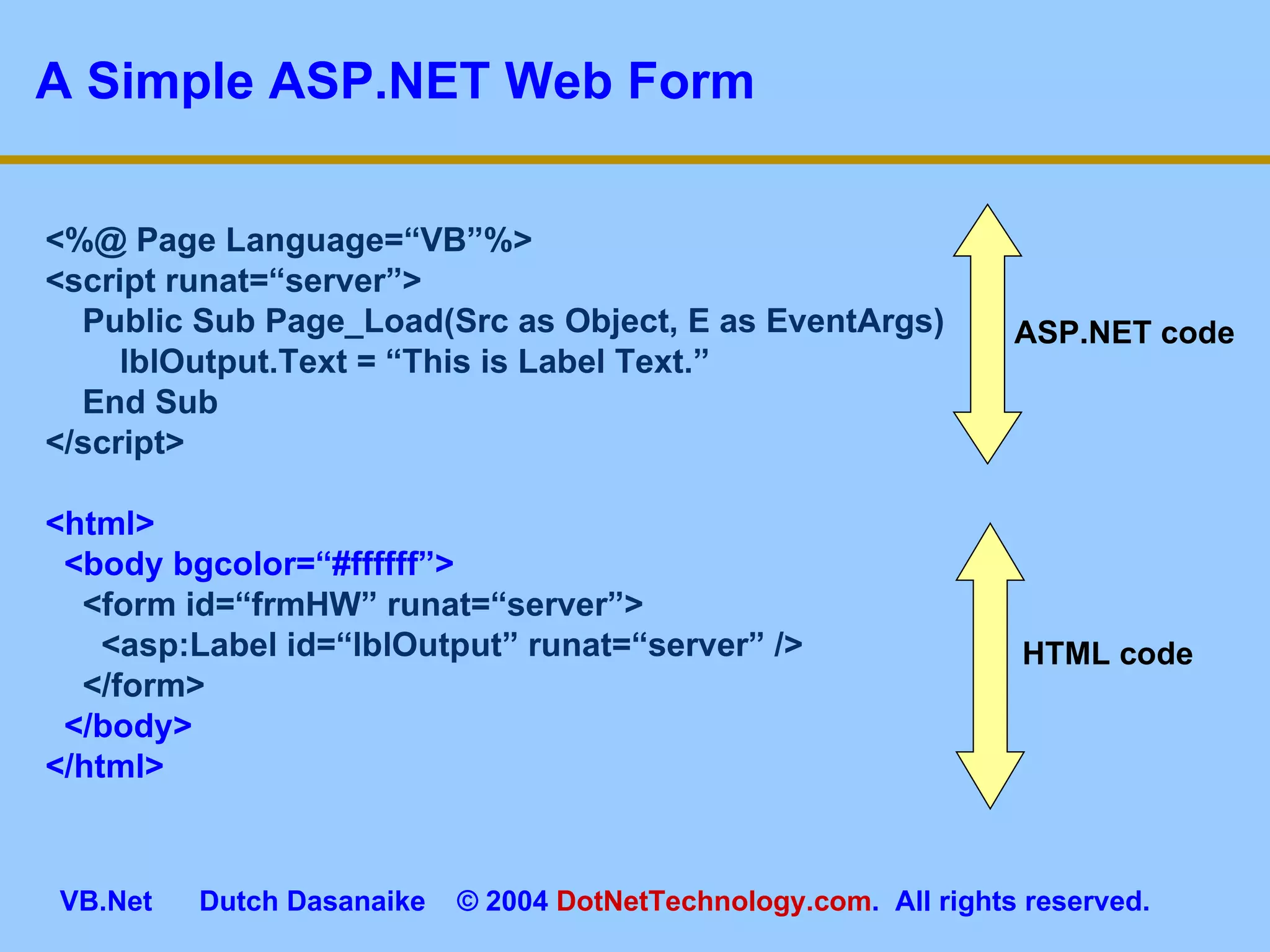
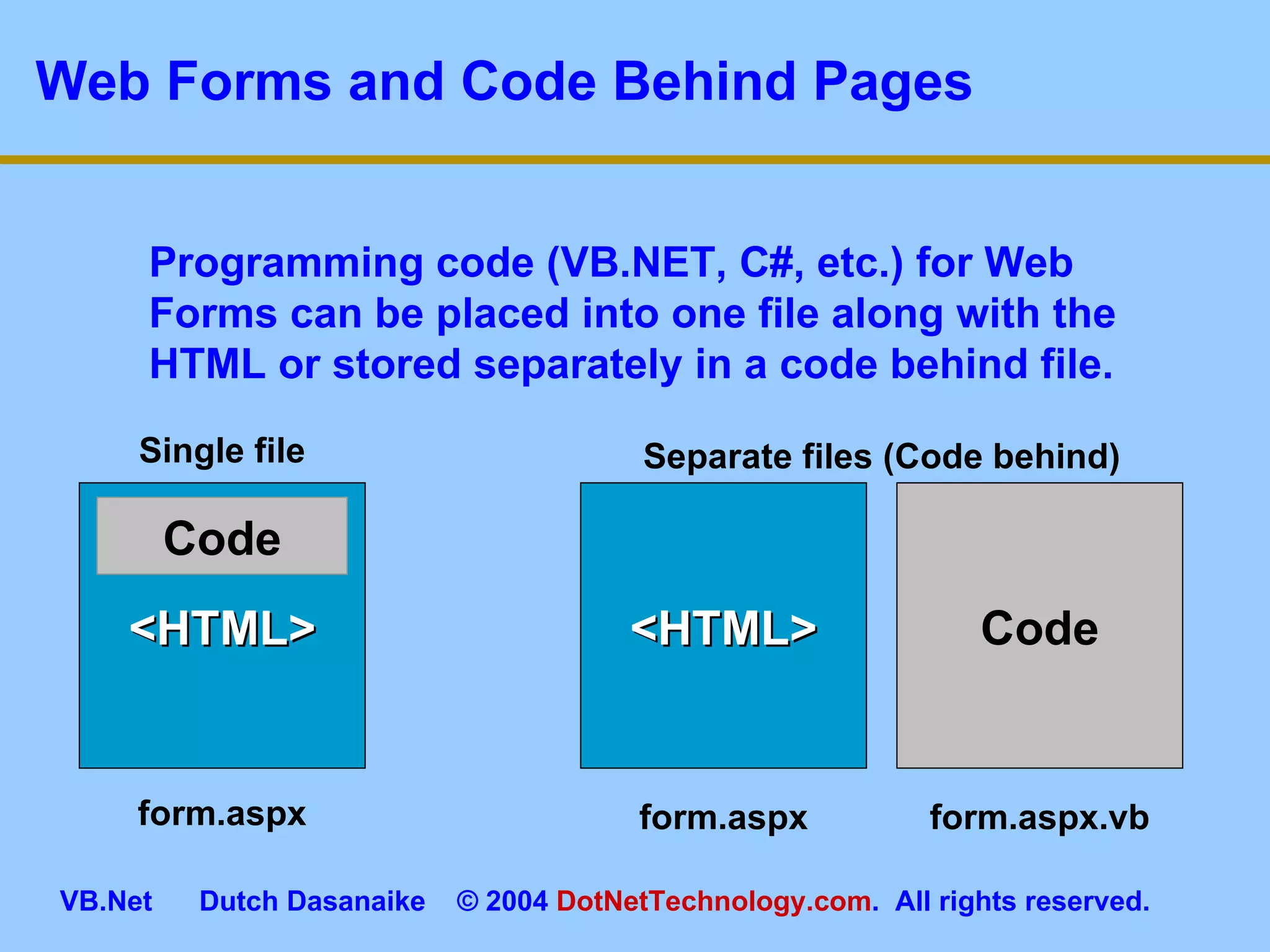
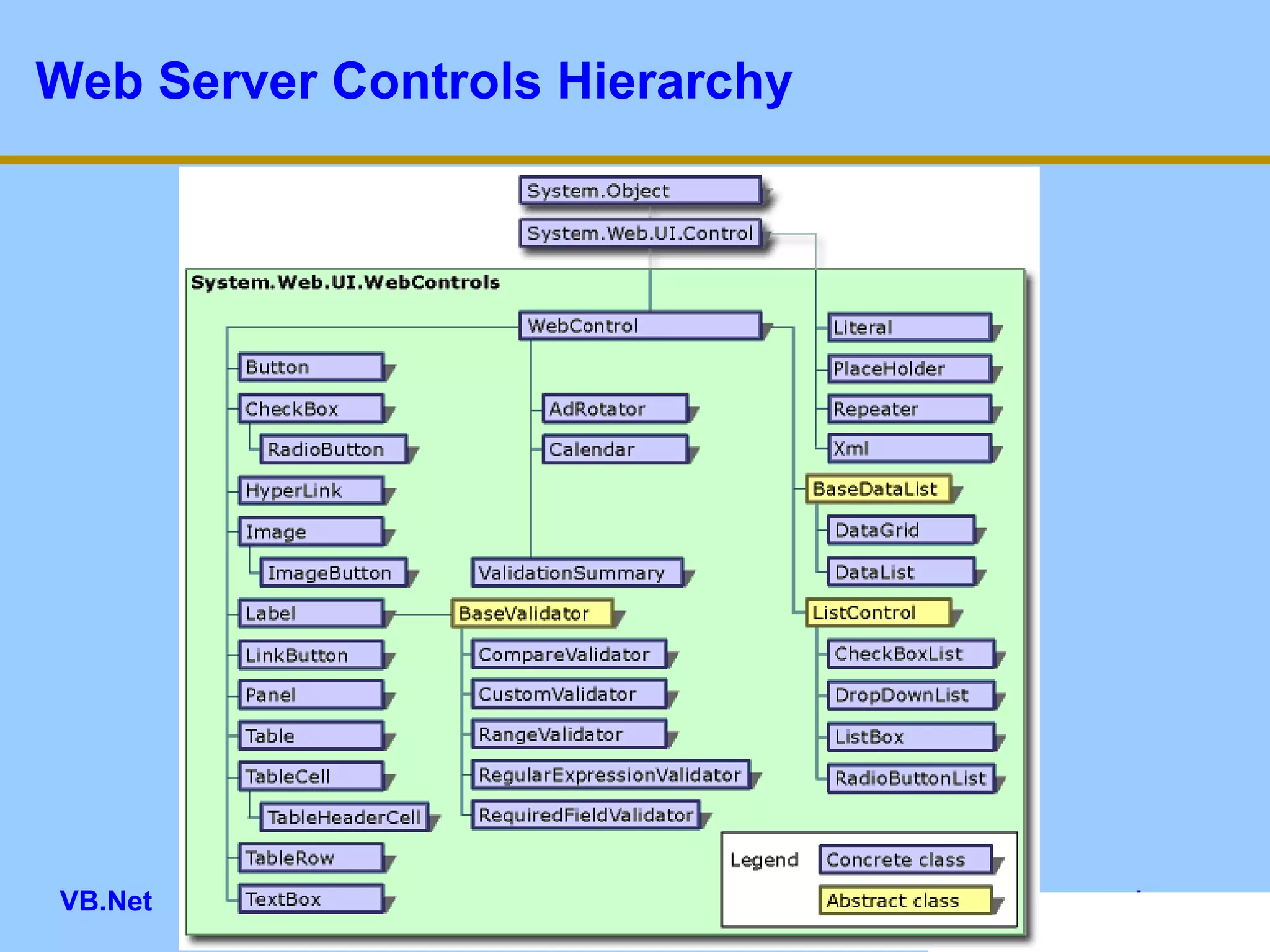
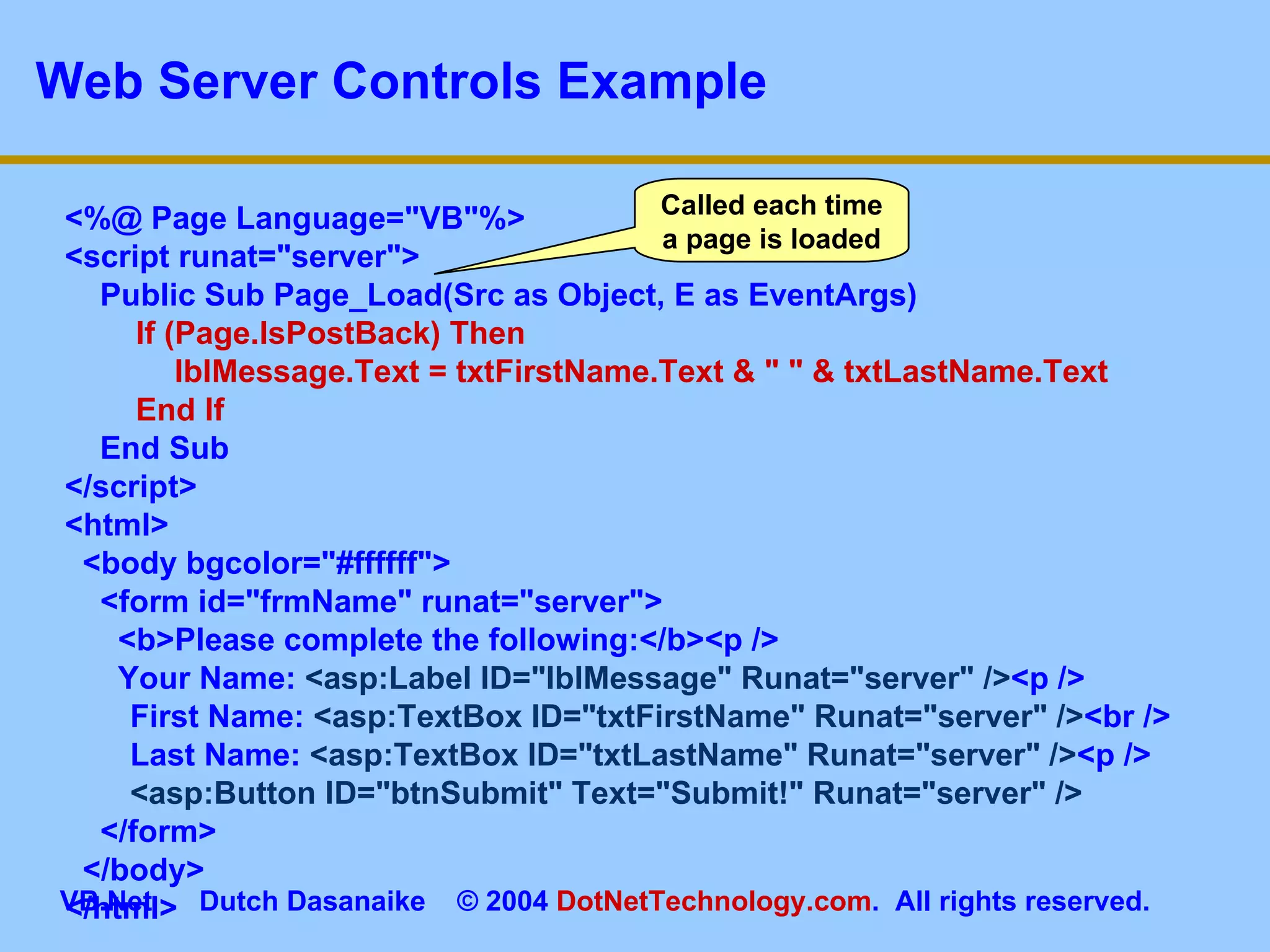
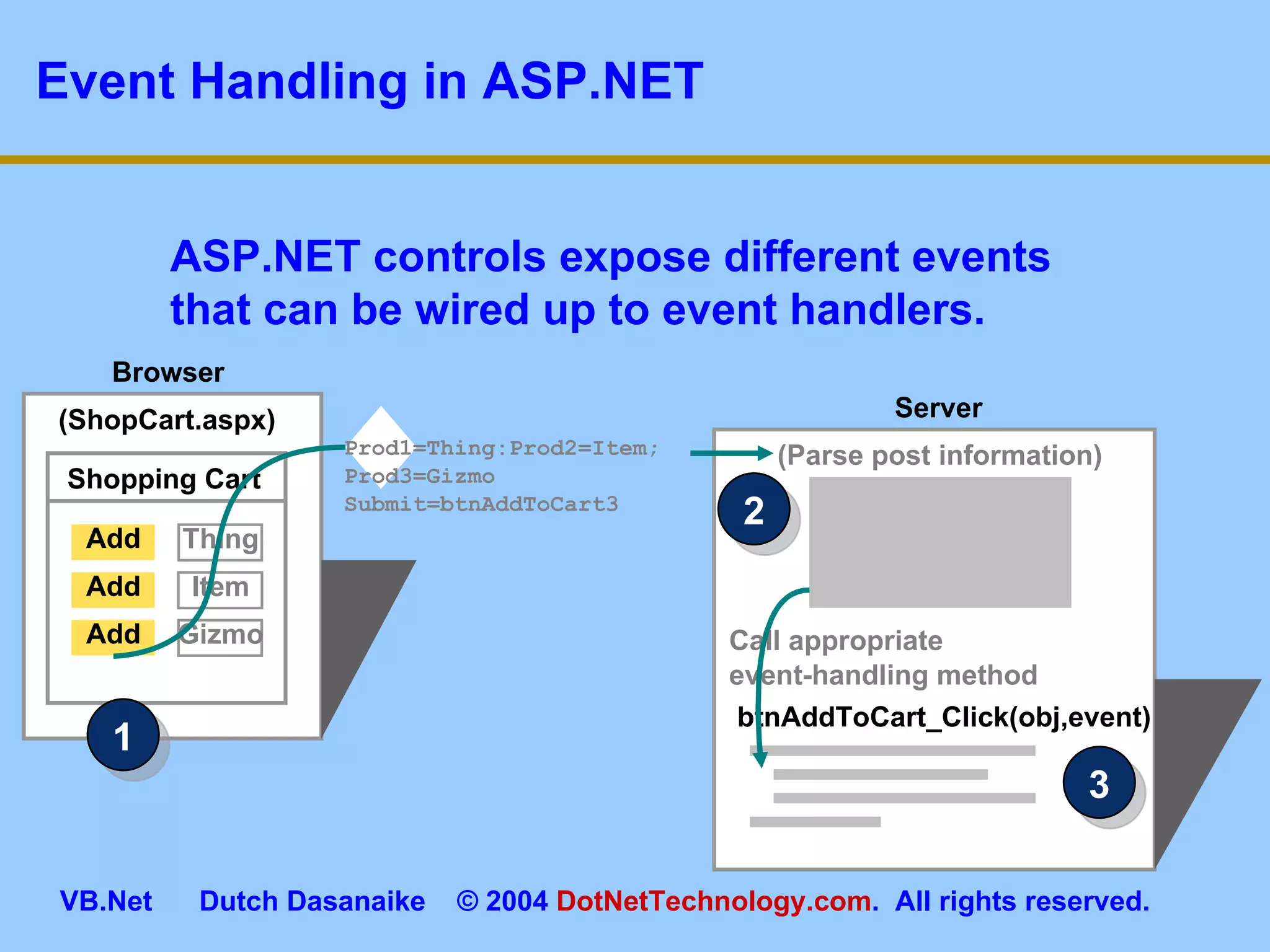
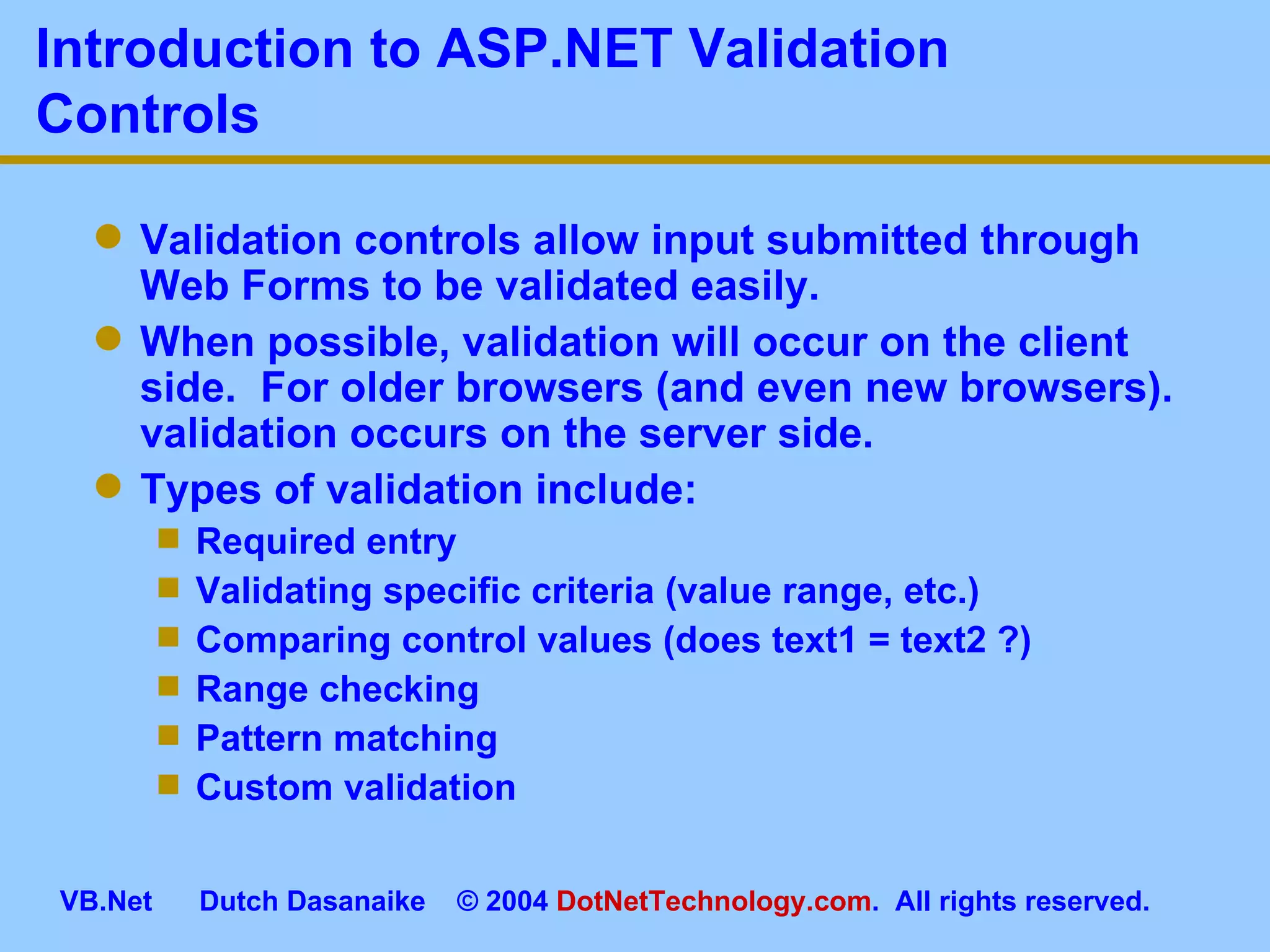
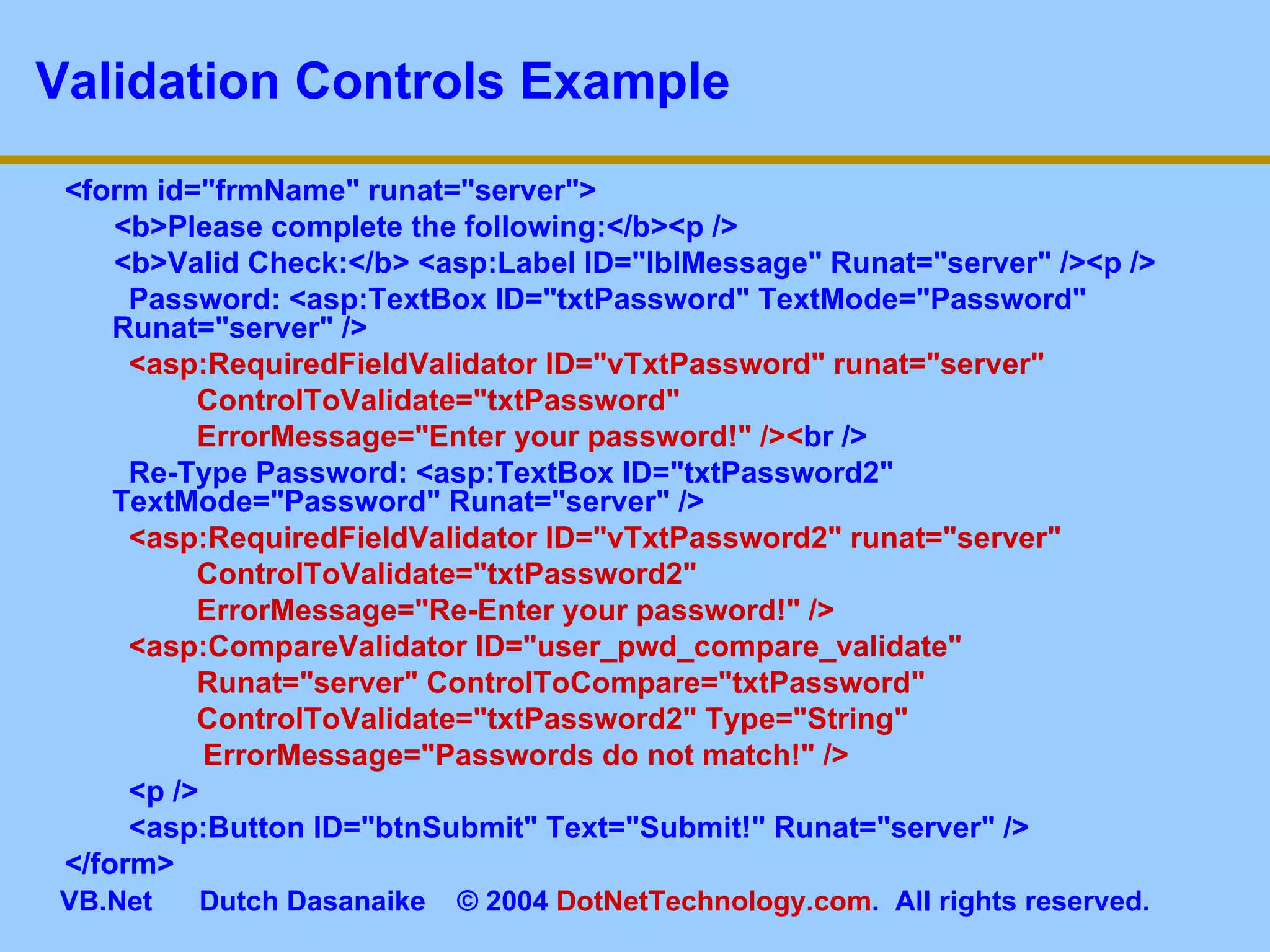
This document provides an overview of ASP.NET web forms and server controls. It discusses how to create a simple ASP.NET web form with code behind pages, introduces common server controls like labels and textboxes, and how to hook up event handling. It also covers using validation controls to validate user input on web forms.