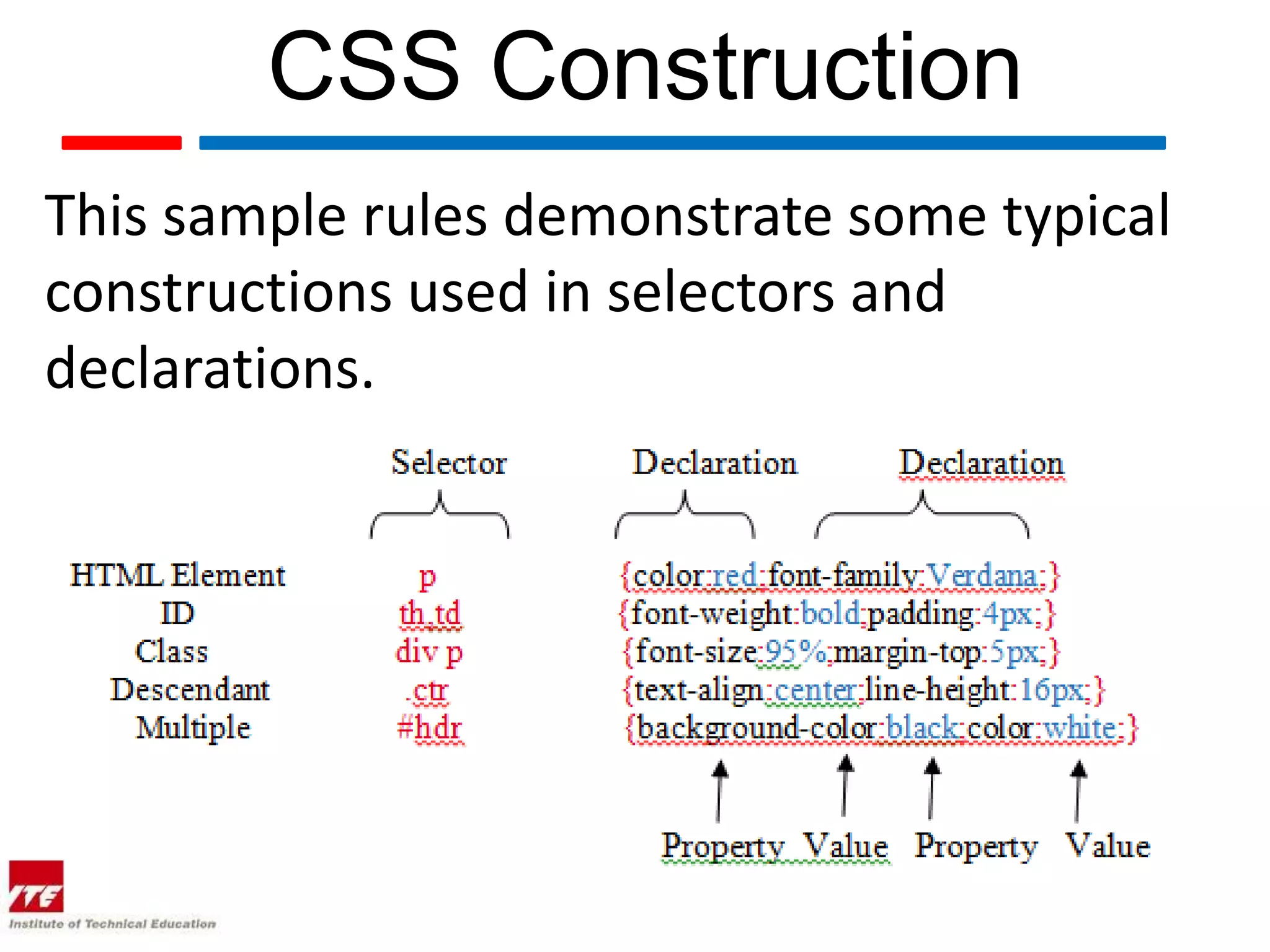
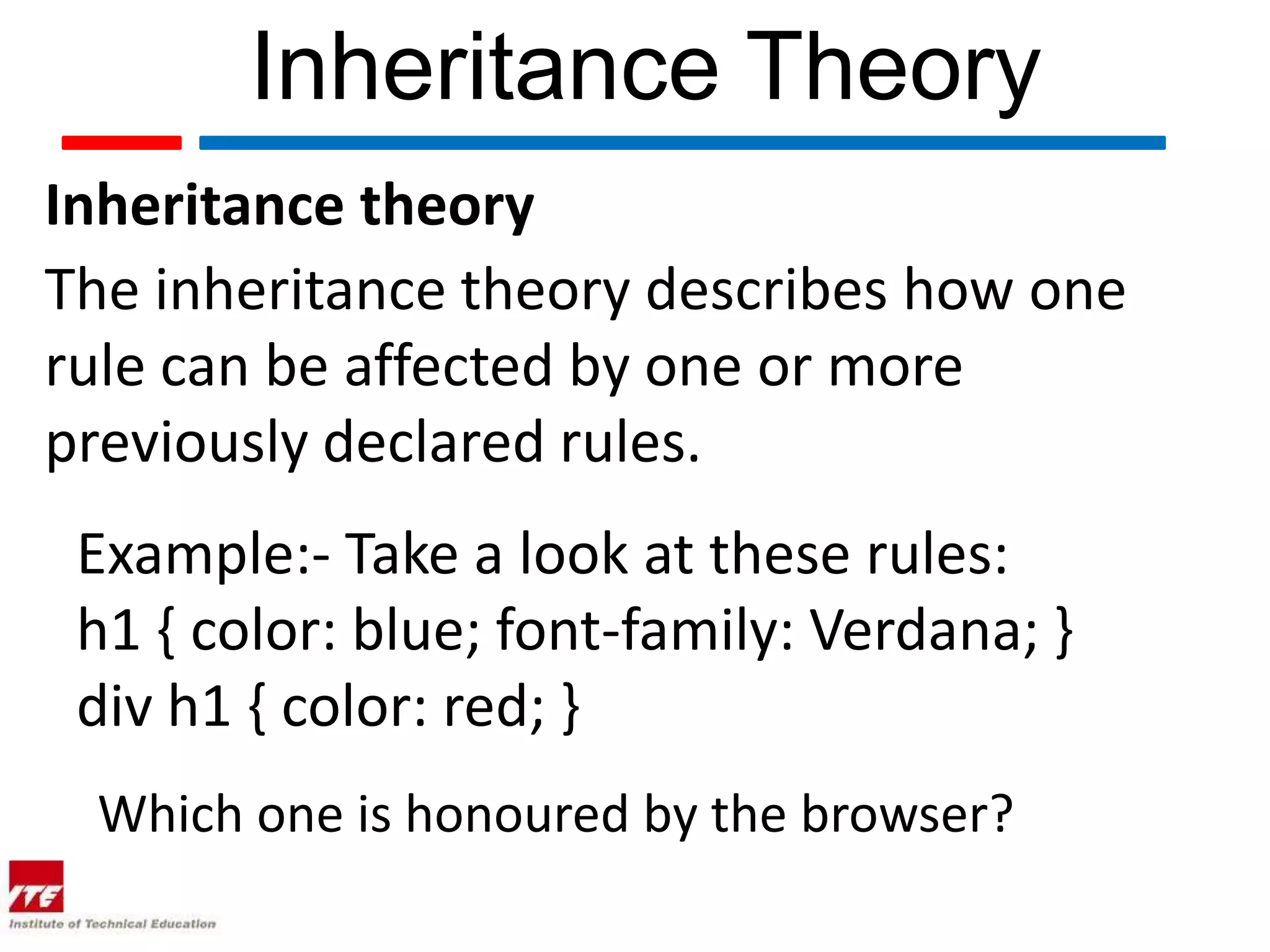
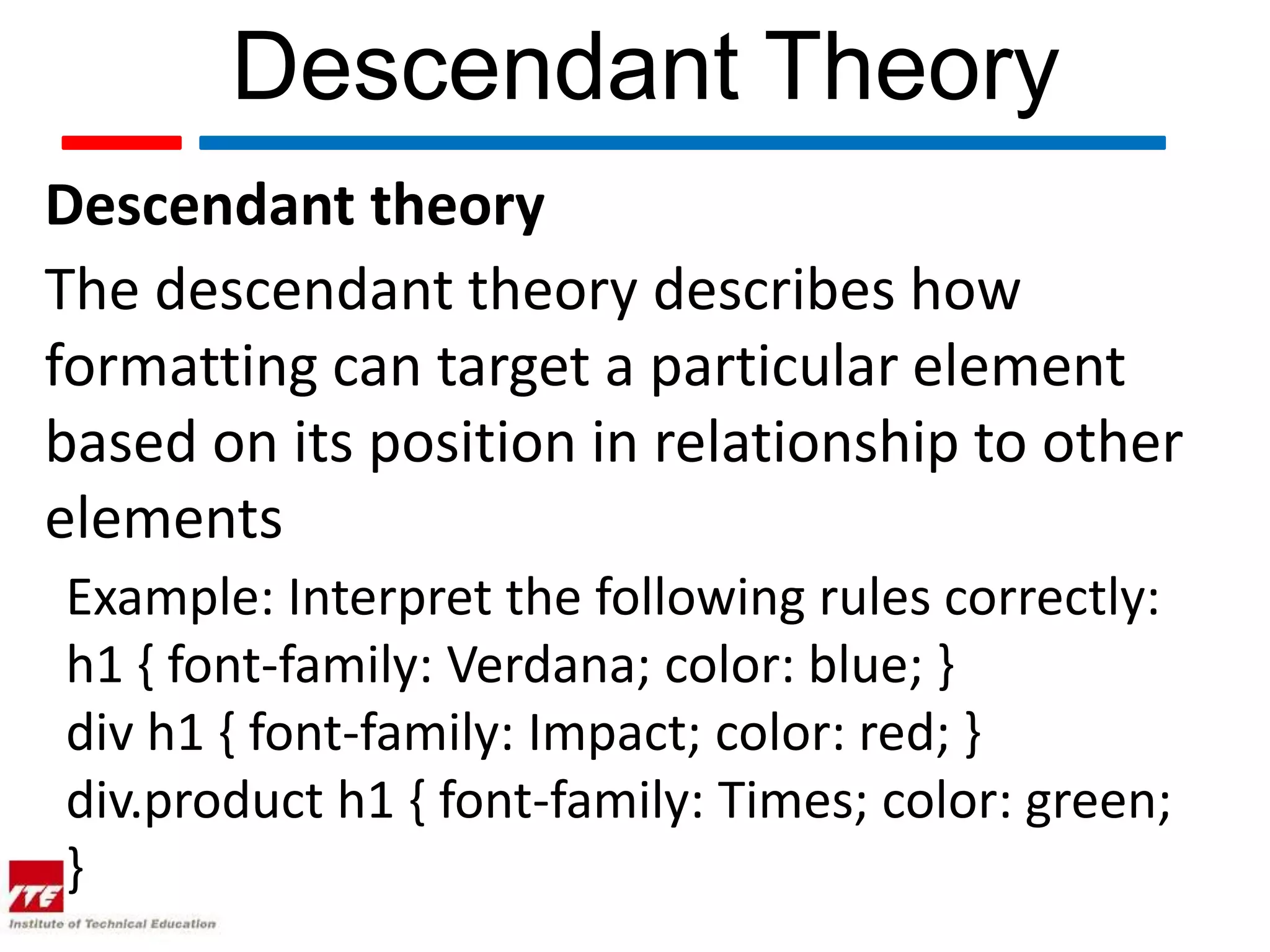
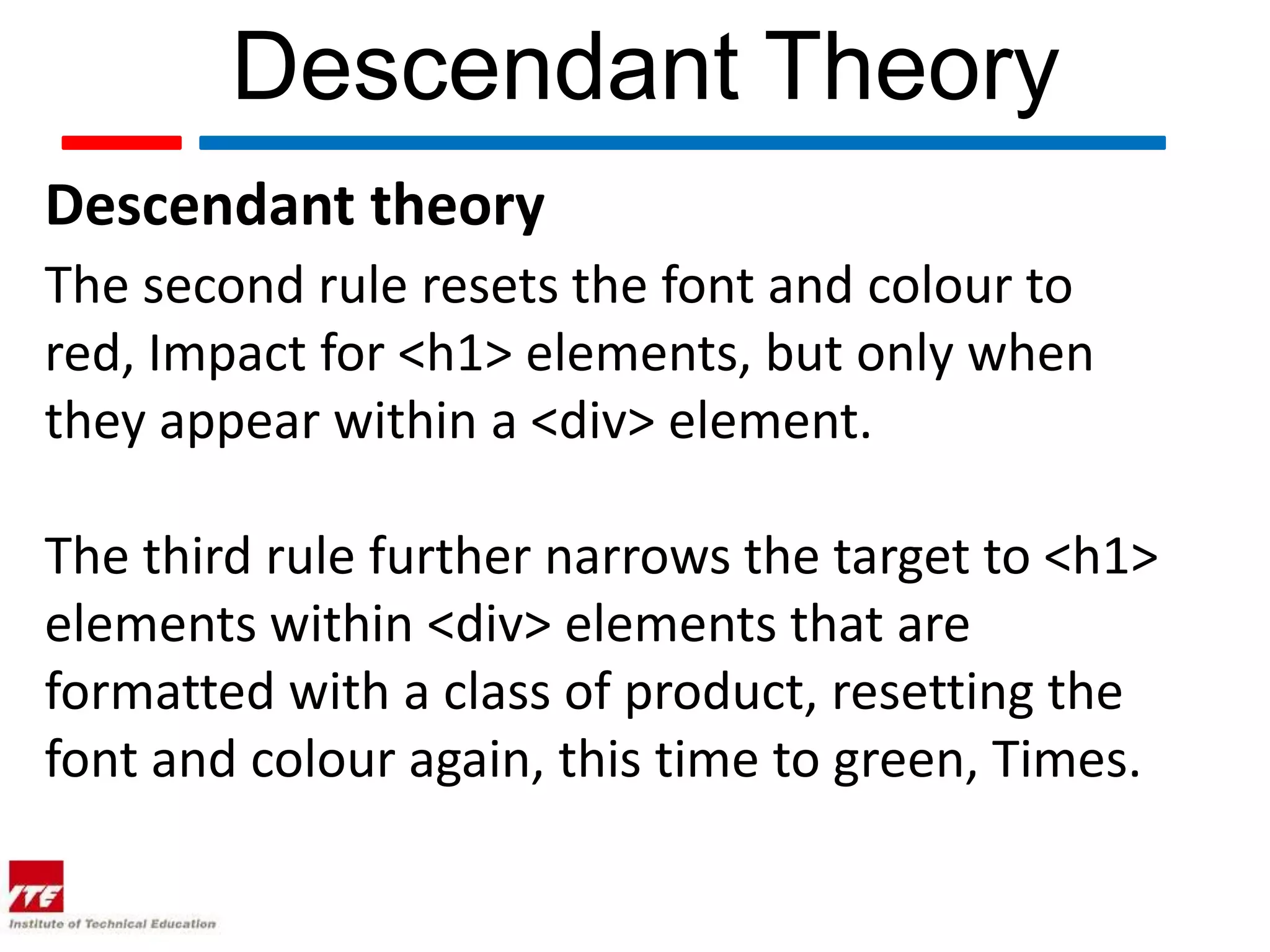
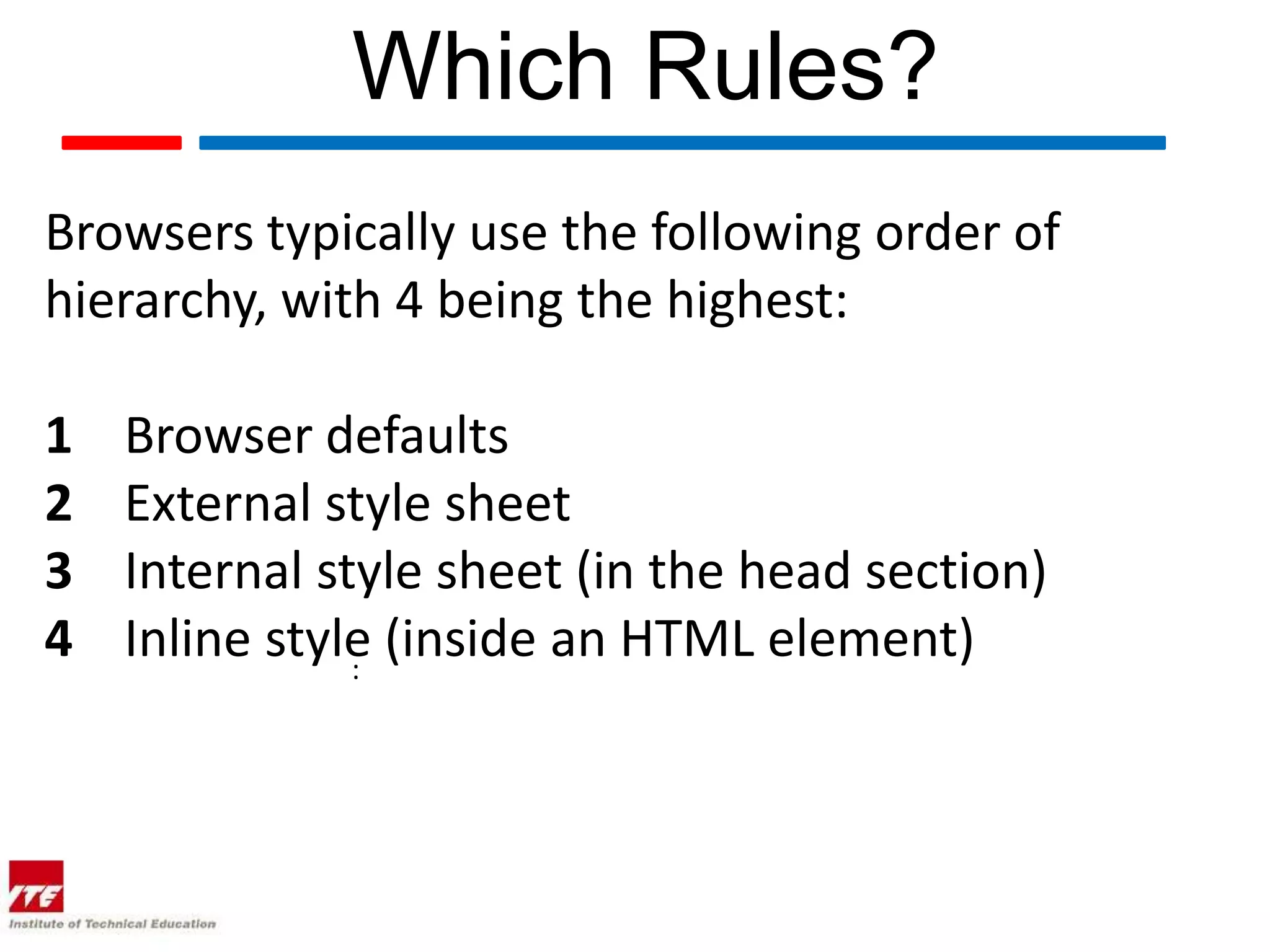
This document discusses four theories of Cascading Style Sheets (CSS):
1. Cascade theory describes how the order and placement of CSS rules affects styling.
2. Inheritance theory describes how rules can affect previously declared rules.
3. Descendant theory describes how rules can target elements based on their relationship to other elements.
4. Specificity theory describes how browsers determine which rules to apply when rules conflict based on an element's specificity weight.