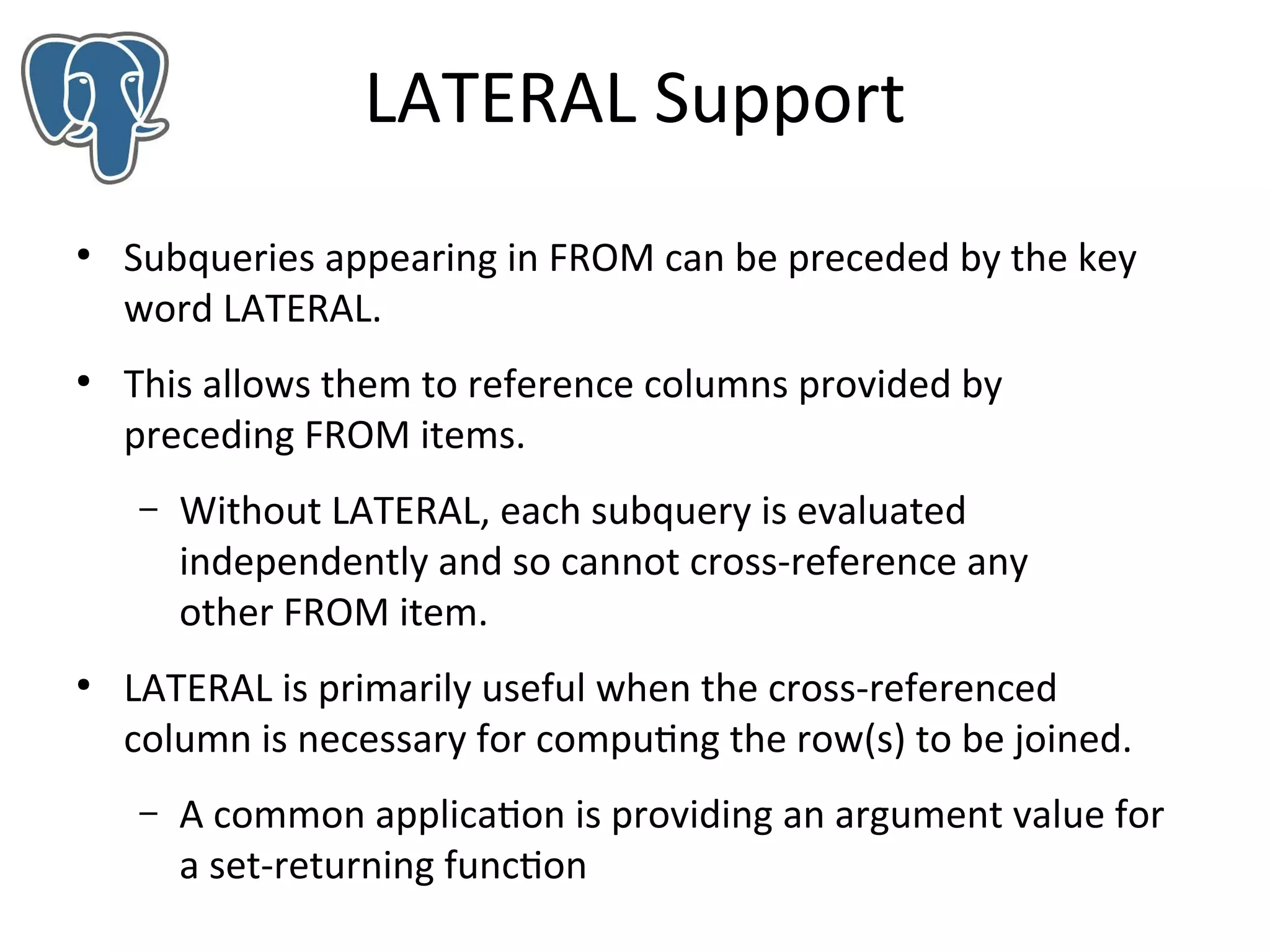
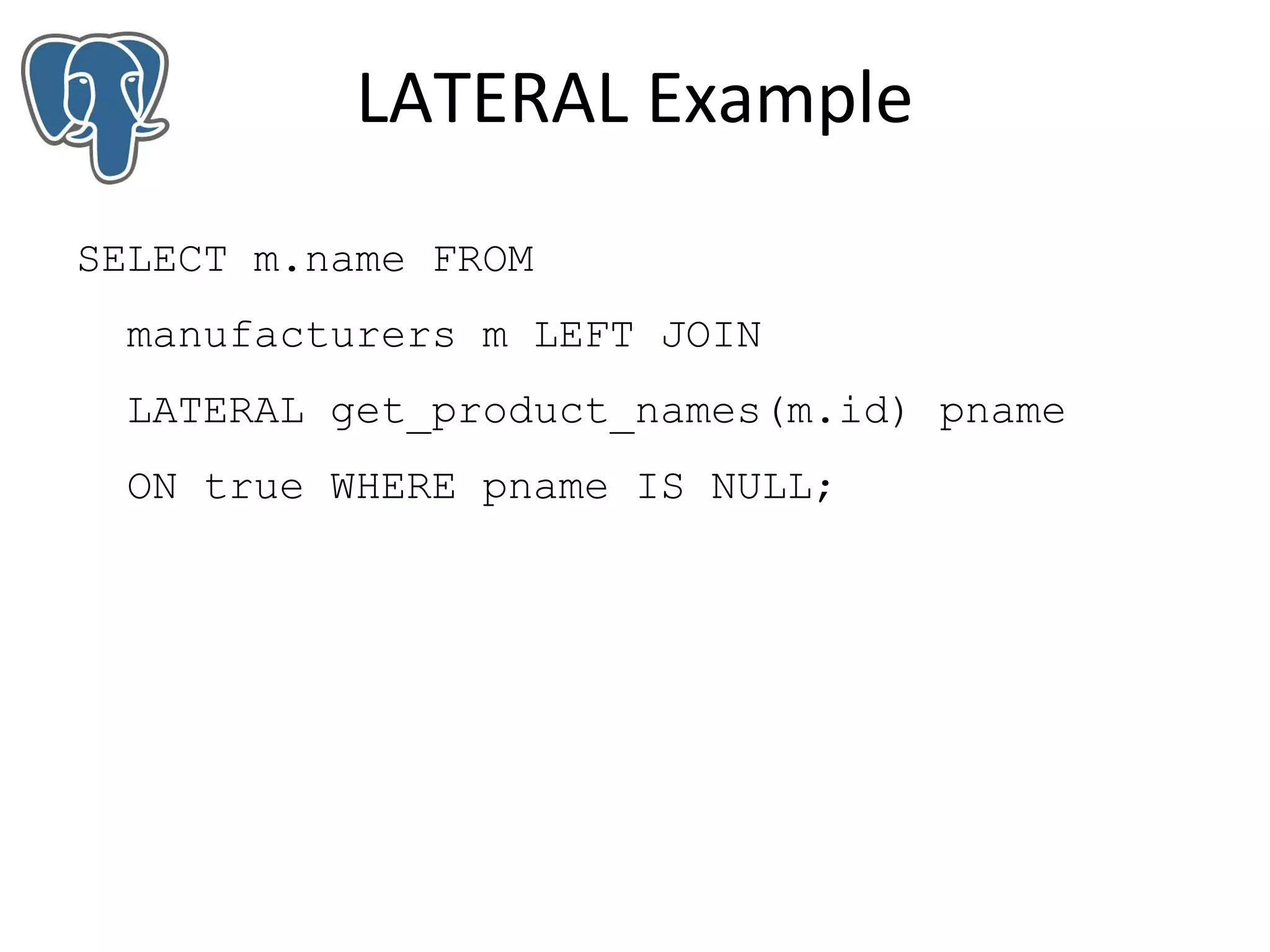
Pavan Deolasee gives an overview of new features in PostgreSQL 9.3. Key additions include support for auto updatable and materialized views, the LATERAL keyword for subqueries, range type enhancements, improved JSON support, foreign data wrappers allowing remote data access, parallel pg_dump for faster backups, event triggers for DDL monitoring, and streaming-only replication remastering. Many performance and management features are also introduced to make PostgreSQL more powerful and easier to administer.





![Materialized Views
●
●
Query is executed once and result is materialized on a stable
storage
Views must be refreshed manually
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
..
AS query [ WITH [ NO ] DATA ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatsnewinpostgresql93-131120010643-phpapp02/75/What-s-New-In-PostgreSQL-9-3-8-2048.jpg)