 TensorFlow 2 version
TensorFlow 2 version
|
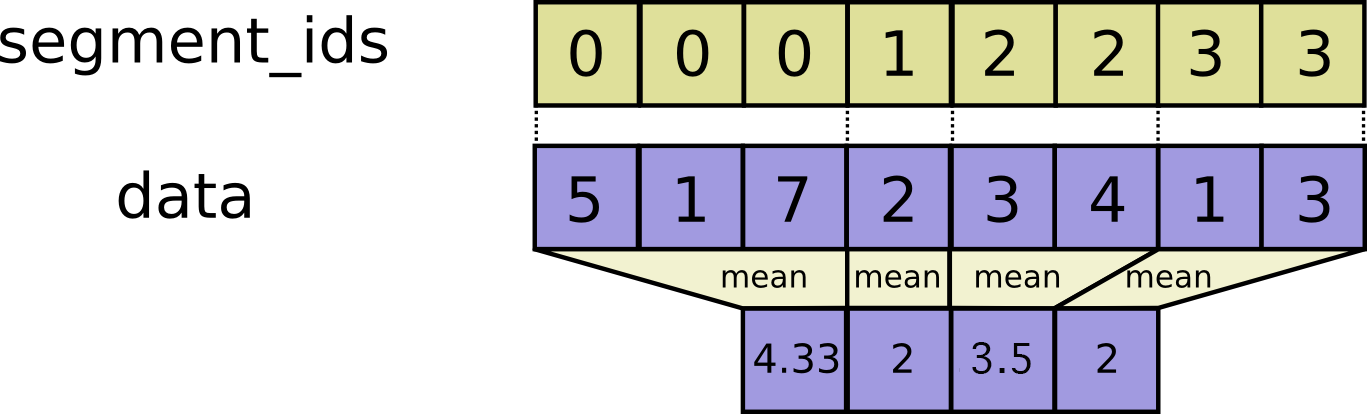
Computes the mean along segments of a tensor.
tf.math.segment_mean(
data, segment_ids, name=None
)
Read the section on segmentation for an explanation of segments.
Computes a tensor such that
\(output_i = \frac{\sum_j data_j}{N}\) where mean is
over j such that segment_ids[j] == i and N is the total number of
values summed.
If the mean is empty for a given segment ID i, output[i] = 0.
For example:
c = tf.constant([[1.0,2,3,4], [4, 3, 2, 1], [5,6,7,8]])
tf.segment_mean(c, tf.constant([0, 0, 1]))
# ==> [[2.5, 2.5, 2.5, 2.5],
# [5, 6, 7, 8]]
Args | |
|---|---|
data
|
A Tensor. Must be one of the following types: float32, float64, int32, uint8, int16, int8, complex64, int64, qint8, quint8, qint32, bfloat16, uint16, complex128, half, uint32, uint64.
|
segment_ids
|
A Tensor. Must be one of the following types: int32, int64.
A 1-D tensor whose size is equal to the size of data's
first dimension. Values should be sorted and can be repeated.
|
name
|
A name for the operation (optional). |
Returns | |
|---|---|
A Tensor. Has the same type as data.
|
